Abstract
Within the context of Finite-Time Thermodynamics (FTT) a simplified thermal power plant model (the so-called Novikov engine) is analyzed under economical criteria by means of the concepts of profit function and the costs involved in the performance of the power plant. In this study, two different heat transfer laws are used, the so called Newton’s law of cooling and the Dulong-Petit’s law of cooling. Two FTT optimization criteria for the performance analysis are used: the maximum power regime (MP) and the so-called ecological criterion. This last criterion leads the engine model towards a mode of performance that appreciably diminishes the engine’s wasted energy. In this work, it is shown that the energy-unit price produced under maximum power conditions is cheaper than that produced under maximum ecological (ME) conditions. This was accomplished by using a typical definition of profits function stemming from economics. The MP-regime produces considerably more wasted energy toward the environment, thus the MP energy-unit price is subsidized by nature. Due to this fact, an ecological tax is proposed, which could be a certain function of the price difference between the MP and ME modes of power production.
PACS:
05.70.Ln; 44.40+a89
1. Introduction
In a recent paper, Fischer and Hoffmann [1] showed that a simple endoreversible model (the so called Novikov engine) can reproduce the complex engine behavior of a quantitative dynamical simulation of an Otto engine including, but not limited to, effects from losses due to heat conduction, exhaust losses and frictional losses. Also Curto-Risso et al. [2] have published a FTT-model for an irreversible Otto cycle suitable to reproduce performance results of a real spark ignition heat engine. In these articles the spirit of Finite-Time Thermodynamics (FTT) is illustrated emphasizing the virtues and limitations of FTT methodology. However, the usefulness of FTT models is shown beyond any doubt. In fact, we can assert that the FTT spirit is concomitant with the spirit of a Carnotian thermodynamics in the sense of the search of certain kind of limits for thermodynamic variables and functionals. Within the context of Finite-Time Thermodynamics different economic analysis for thermodynamic cycles have been done. Salamon and Nitzan [3] viewed the operation of the endoreversible heat engine as a production process with work as its output. They carried out the economic optimization of the heat engine with the maximum profit rate as the objective function. The profit rate of the cycle was defined as
where and are the prices of exergy output rate and the exergy input rate, and and are the exergy output rate and the exergy input rate. This FTT economic analysis was termed as finite time exergoeconomic analysis [4,5,6,7,8] to distinguish it from the endoreversible analysis with pure thermodynamic objectives and the exergoeconomic analysis with long-run economic optimization. The effect of heat transfer laws were also investigated [9,10,11]. Another FTT economic analysis was proposed by De Vos [12]. In his 1995 paper, De Vos [12] made a thermoeconomic analysis of a model of power plant of the Novikov type [13] such as the one depicted in Figure 1. De Vos analyzed this endoreversible power plant with respect to economical exploitation, and he took the optimal exploitation point lying somewhere between the maximum-power point, that is, Curzon-Ahlborn (CA) efficiency and the maximum-efficiency point (Carnot efficiency), with an optimum efficiency such that,
where the subscripts and C mean maximum power and Carnot respectively. De Vos [12] found for the Novikov’s model that is given by
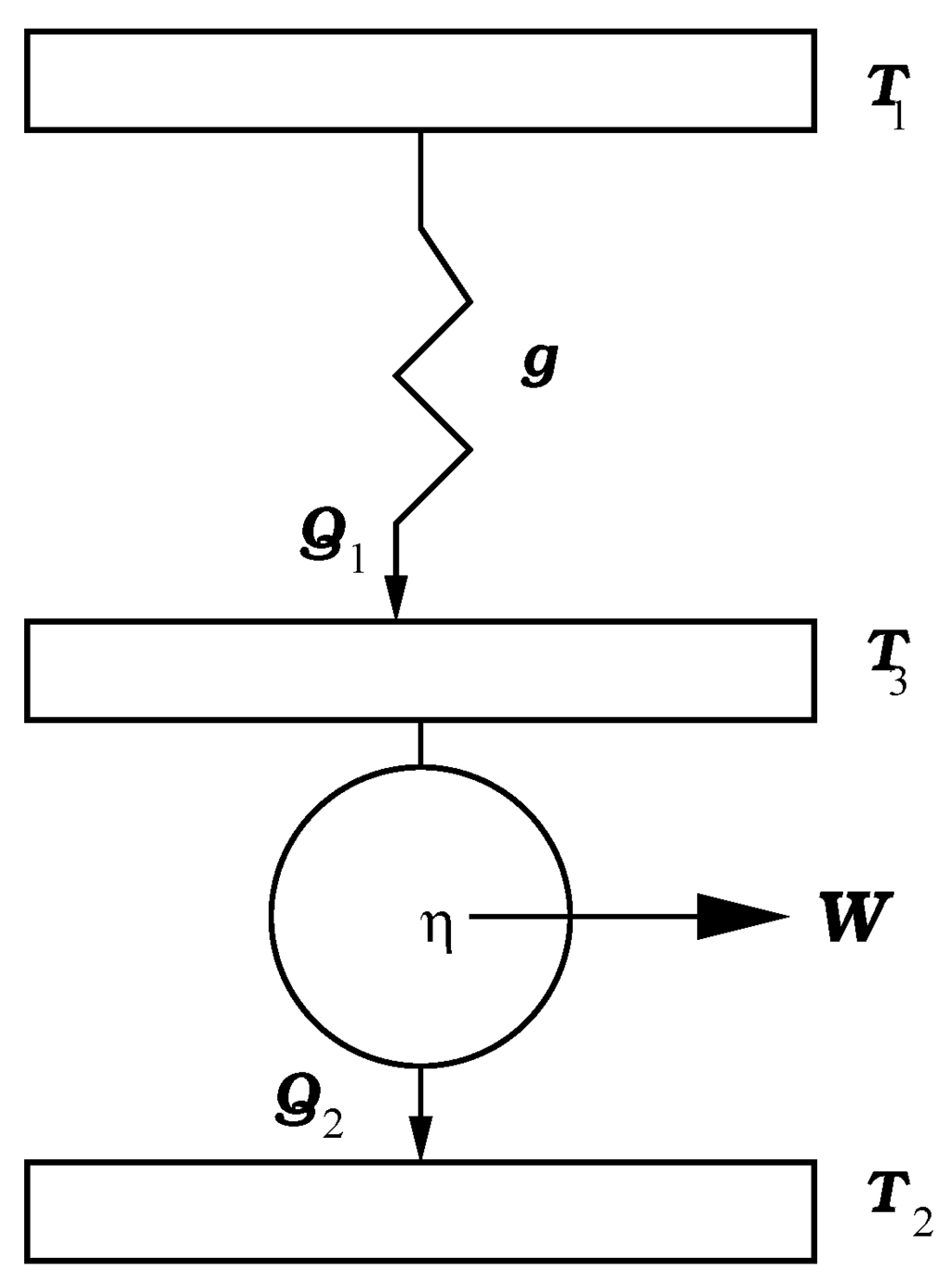
Figure 1.
Novikov’s model for a nuclear power plant.
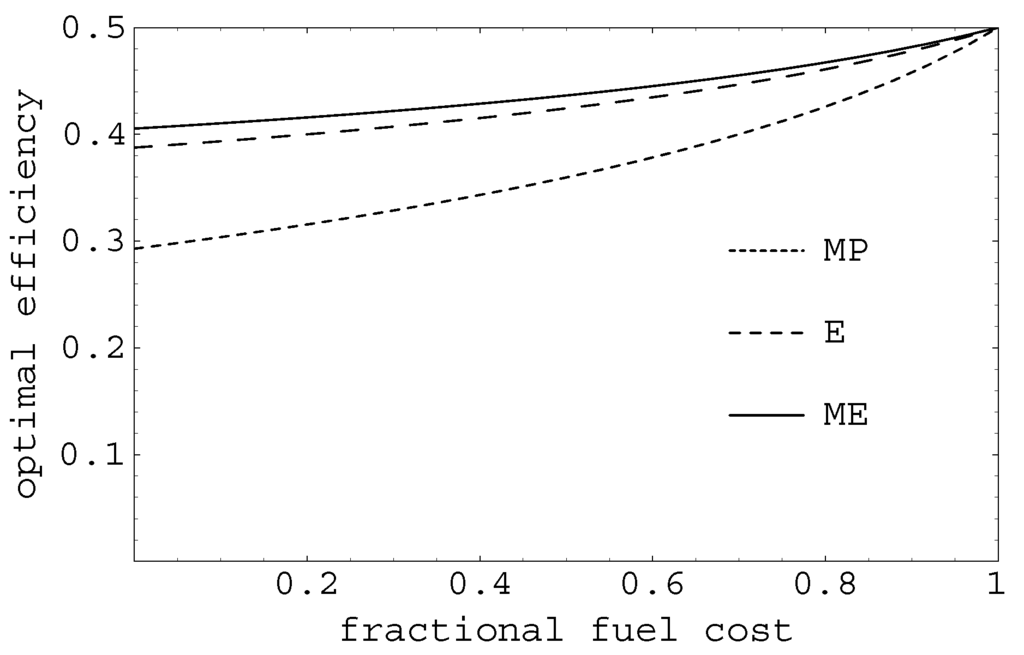
Figure 2.
Comparison between optimum efficiencies for both maximum power and maximum ecological regimes (the former E function and the modified ME) for .
where f is the fractional fuel cost, which is defined as the ratio of the cost of the fuel consumption and the running costs of the power plant; with and the temperatures of the hot and cold thermal reservoirs respectively (see Figure 1), the superscript N means Newtonian. Figure 2 shows how the De Vos optimal efficiency (Equation (3)) smoothly increases from the MP-efficiency, , corresponding to energy sources where the investment is the preponderant cost towards the Carnot value for , that is, for energy sources where the fuel is the predominant cost [12]. Equation (3) gives the optimal efficiency for a Novikov power plant working at maximum profit in terms of the fractional fuel cost f when the heat fluxes in Figure 1 are given by a linear Newtonian heat transfer law. Recently, Barranco-Jiménez and Angulo-Brown [14] also studied a Novikov engine following the thermoeconomical approach used by De Vos, but by means of the so-called modified ecological optimization criterion [15,16]. The ecological criterion combines the power output (high power output) and the entropy generation rate of the power plant (low entropy production), in terms of the maximization of the following expression[15],
where W is the plant’s power output, is the absolute temperature of the cold reservoir and σ is the total entropy production of the endoreversible power plant model. The so-called modified ecological optimization [16] consists in the maximization of the modified ecological function given by
where ϵ is a parameter depending on the heat transfer law [16]. The properties of E and have been discussed in several papers [17,18,19]. This criterion also leads to an efficiency between and and drastically reduces the entropy production of the engine [14]. These authors found that the optimal efficiency under the modified ecological regime, with a Newtonian heat transfer law is given by
Figure 2 also shows how smoothly varies with f (for a given τ) from the maximum ecological function point with () [15,20] until the Carnot point , in an analogous way to the De Vos-efficiency (see Figure 2). In this figure it is also shown a curve corresponding to the former ecological function given by Equation (4) [15]. The profit q in the De Vos approach [12] is defined as , with C being the running costs [12]. This function q is less for the curve in Figure 2 than for the one [14]. However, this loss of profits is concomitant with a better efficiency for a given f, and with an important reduction of wasted energy () to the environment compared with the MP-operation of the plant [14,21]. On the other hand, if the heat transfer law used in the Novikov’s model is of the nonlinear Dulong-Petit (DP) type, the economical optimal efficiencies for the MP and modified ME regimes are respectively [14,21]
These expressions have the same qualitative behavior as Equations (3) and (6) for the case of a Newtonian heat transfer law, that is, they smoothly vary from the point for to the Carnot point for [14,16]. Equation (8) also leads to a reduction of the profits q compared with the MP-regime (Equation (7)), but improving the efficiency and reducing the wasted energy. In a similar way to De Vos [12], Sahin and Kodal (SK) made a thermoeconomic analysis of a Curzon-Ahlborn engine [22]. They maximized a profit function defined by
where and are the annual investment and fuel consumption costs, respectively. Sahin and Kodal assumed that the plant’s size can be taken proportional to the total heat transfer area, instead of the maximum heat input previously considered by De Vos [12]. Thus, the yearly investment cost of the system can be given as
where and are the heat transfer areas of the heat exchangers in both the hot and the cold reservoirs and the proportionality coefficient for the investment cost is equal to the capital recovery factor times investment cost per unit heat transfer area. The annual fuel consumption cost is proportional to the heat rate input, that is
where the coefficient is equal to the annual operation hours times the price per unit heat input. SK also showed that the variation of the optimal thermal efficiency with respect to the fuel cost parameter in the interval under maximum power conditions satisfies the following inequality , that is the Carnot ( ) an the maximum power () efficiencies are the superior and inferior bounds of the optimum thermal efficiencies. The Sahin and Kodal economic criterion was applied to study the performance of endoreversible heat engine [22], refrigerator and heat pump [23], combined cycle refrigerator [24], combined cycle heat pump [25], as well as irreversible heat engine [26], irreversible refrigerator and heat pump [27], combined cycle refrigerator [28], combined cycle heat pump [29] and three-heat-reservoir absorption refrigerator and heat pump [30]. This method was also applied to the optimization of an endoreversible four-heat-reservoir absorption-refrigerator [31].
In the present paper, the mentioned properties of the ecological optimization are taken to propose a criterion for justifying ecological taxes. The paper is organized as follows: In Section 2 and Section 3, we present a thermo-economical analysis in terms of a profit function defined as the difference between the money earnings and the costs of the performance in the power plant, that is, with an economical profit different to that used by De Vos [12]. In Section 4, an ecological tax is proposed which depends on the difference between the ratio of prices of both the energy input and energy output under both the maximum power and maximum ecological regimes. Finally, in Section 5 the conclusions are presented.
2. Optimization of the Profit Function: Newtonian Heat Transfer Law Case
In the previous section a thermoeconomical point of view to analyze the optimum performance of an endoreversible power plant model (the Novikov model) was mentioned. In this section an economical approach based on a well known definition of the profit function more in the spirit of the economical disciplines is adopted [32,33].
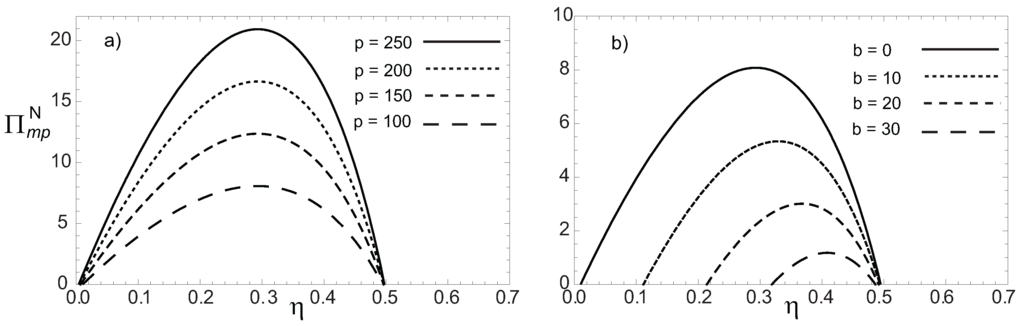
Figure 3.
Profits function in terms of the engine’s efficiency η with a Newton heat transfer law for a) and taking several values of p and b) and taking several values of b.
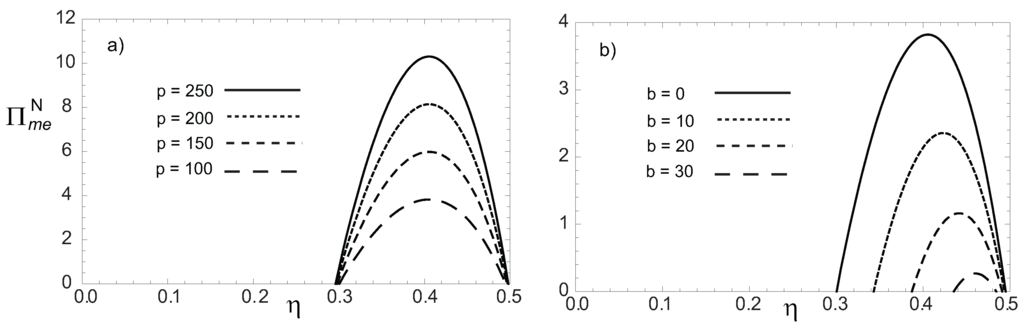
Figure 4.
Profits function in terms of the engine’s efficiency η with a Newton heat transfer law for a) and taking several values of p and b) and taking several values of b.
In an economic sense the profit is understood as the difference between the money influx minus the money outflux of the plant’s operation. Therefore, the benefit function Π is now given by the money earnings function I minus the money cost function C involved by the plant’s performance. If a perfect competition in the energy market is assumed, then the price of the energy unit (p) is given by the energy market [32,33]. Therefore, the revenue is obtained by the product of the price per watt of the power output by the total quantity of watts associated to the power plant output, that is, . Thus, the function Π is given by [32,33],
where C are the running costs of the plant operation, which are taken as in the De Vos approach [12], that is, they consist of two parts: (a) the cost of the investment, which is assumed proportional to the size of the plant, and (b) the cost of the fuel consumption, which is assumed as proportional to the quantity of heat (see Figure 1). De Vos assumed that is an appropriate measure for the plant size, then, the total costs can be expressed as:
where the proportionality constants a and b have units of and is the maximum heat that can be extracted from the heat reservoir without supplying work (see Figure 1), being g a thermal conductance [12]. Applying the first and the second laws of thermodynamics to the model of Figure 1 and considering that is given by a linear Newton heat transfer law, the function Π for a MP-regime is given by [34],
where is the efficiency of the Novikov engine. The modified ecological optimization [16] consists in the maximization of the so-called modified ecological function given by , with σ the universe entropy production and ϵ a parameter depending on the heat transfer law used in the model [16]. For the modified ecological regime, the profit function becomes [21,34]
In Equations (14) and (15), the expressions for the power output W, the modified ecological function and the function of the total costs C, corresponding to the endoreversible engine model presented in Figure 1 have been used. Equations (14) and (15), for the economic profit functions express how the maximum profit increases as the Watt’s price increases in the energy market (see Figure 3a and Figure 4a) while at the same time the functions Π diminishes with an increasing b, which is associated to the fuel price (see Figure 3b and Figure 4b). Besides, the maximum of Π is moved towards the Carnot’s point (maximum efficiency) as the fuel costs augment such as it is shown in Figure 3b and Figure 4b. Figure 4a also shows the profit loss when the system’s entropy production is considered through the definition of the modified ecological function. However, this profit loss represents a gain for the environment due to entropy production reductions associated to the ecological way of operation. From Equation (14), if is calculated, the optimum economical efficiency under maximum power conditions is found and solving for , one gets
from this expression,
is obtained, that is, a relationship between an optimal performance regime (the maximum power regime in this case), and the ratio of parameters linked to the prices of both the energy input and the energy output. On the other hand, Equation (3) gives the optimum efficiency of a Novikov model under maximum power conditions. By the substitution of Equation (3) into Equation (17), a relationship between the ratio and the fractional fuel cost f is obtained,
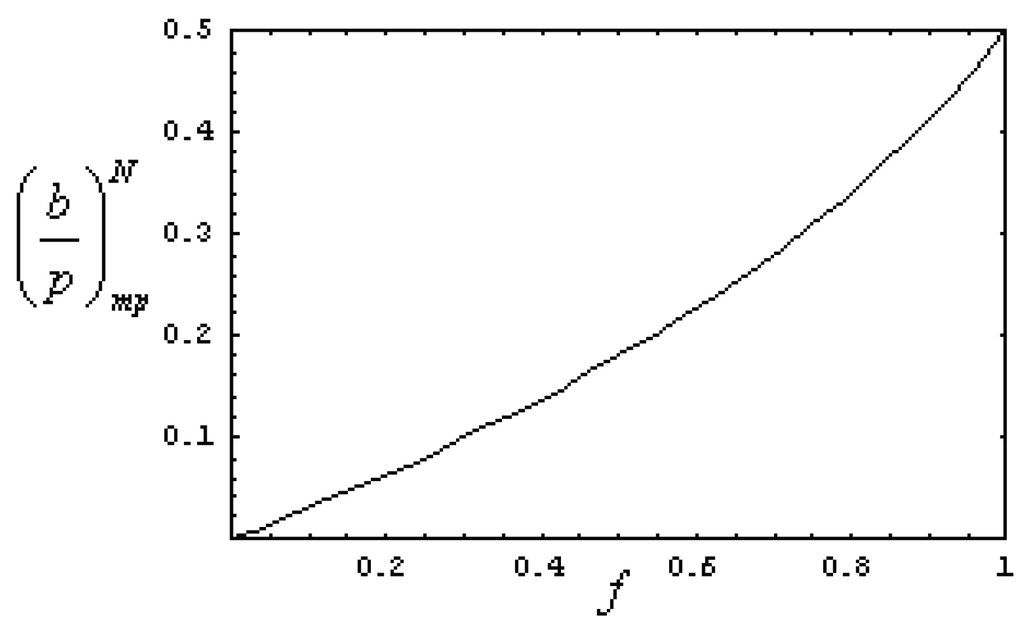
Figure 5.
Quotient between the price parameters versus fuel fractional cost under a Newton heat transfer law for .
In Figure 5, it can be seen how the ratio augments as the fractional fuel cost f augments. It can be observed in Figure 5, for , that the following inequality holds, which means that under optimum conditions, the price of power output is bigger than the parameter linked to the price of the energy input. Analogously, from Equation (15), if is calculated, the optimum economical efficiency under maximum ecological conditions is found, and by using Equation (6) the following relationship for the maximum modified ecological regime is obtained,
that is, a relationship between the parameters linked to the prices of both the energy output and energy input in terms of the fractional fuel cost. Analogously to Equation (18), the ratio augments as f augments, and for , the following inequality is also hold, which means that under the optimum ME conditions, the price of power output is also bigger than the parameter linked to the price of the energy input.
3. Optimization of the Profit Function: Dulong-Petit Heat Transfer Law Case
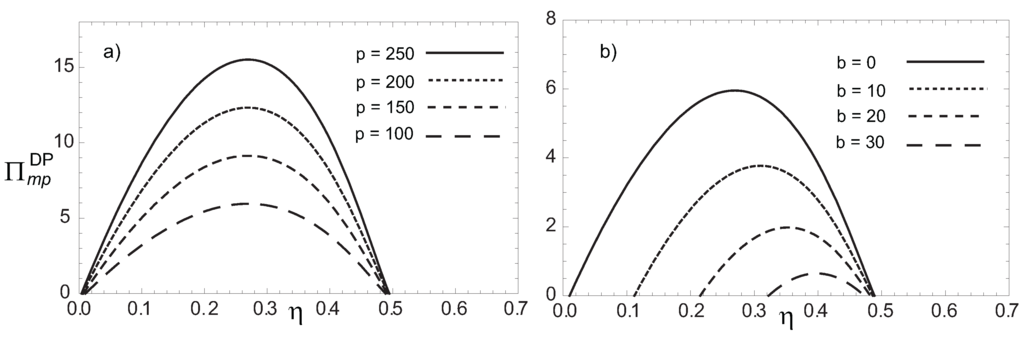
Figure 6.
Profit function in terms of the engine’s efficiency η under a DP heat transfer law for a) and taking several values of p and b) and taking several values of b.
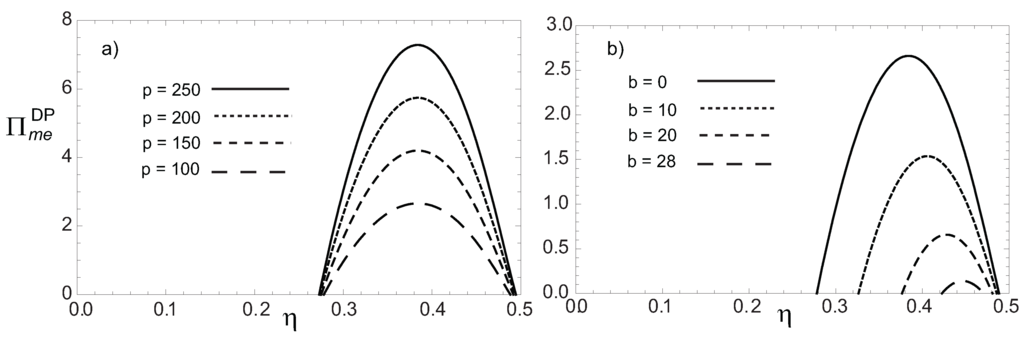
Figure 7.
Profit function in terms of the engine’s efficiency η under a DP heat transfer law for a) and taking several values of p and b) and taking several values of b.
It has been recognized in the literature [35,36,37] that a more realistic description of the heat exchange between the working substance and its reservoirs would include a term (Stefan-Boltzmann radiation). An attempt to describe combined conductive-convective and radiative cooling by a power-law relationship is given by the so-called Dulong-Petit law of cooling [35,36,37], which is
where is the rate of heat loss per unit area from a body at temperature T, α is a thermal conductance, is the temperature of the fluid surrounding the body, and n is an exponent with value between 1.1 and 1.6 [37]. Some authors have established that n = 5/4 based on studies made by Lorentz and Langmuir. As O’Sullivan [37] asserts in the original 1879 paper, Stefan took the results of Dulong and Petit (DP), along with experiments by Tyndall and pointed out that the DP model was in agreement with his law [37]. In the present section the DP law of cooling with n=5/4 is used. If in the Novikov model depicted in Figure 1, the irreversible heat fluxes are taken as given by a Dulong-Petit heat transfer law of the form [35,36,37]
for the profits function Π under MP-conditions [38],
is obtained. This expression has the same behavior that Equations (14) and (15), that is, Π increases when the Watt price augments (see Figure 6a). On the other hand, Π diminishes with the increments of parameter b associated to the fuel consumption cost, as it can be seen in Figure 6b. If the Novikov plant with a DP heat transfer law operates under the maximum ecological function criterion, the profit function Π becomes [21,38],
This function has the same qualitative behavior than Equation (21), as it can be seen in Figure 7a,b. Following the same procedure used in Section 2, by maximization of Equations (21) and (22) the derivatives and are calculated, and the optimal economical efficiencies are obtained. The ratio of price parameters of both the energy input and the energy output can also be obtained in terms of the optimal efficiencies, and by the appropriate substitution of the efficiencies given by Equations (7) and (8) for the MP and ME regimes, these ratios can be calculated in terms of the fractional fuel cost. In Figure 8, and versus fractional fuel cost are shown. It can be observed how the quotients have the same behavior that Equations (18) and (19), that is, they augment as f augments. For , it can also be observed in Figure 8 that the following inequality also holds, which means that under optimum conditions, the price of power output is also bigger than the parameter price of the energy input. However, in this case, the heat transfer law used in the Novikov model is of the Dulong-Petit type.
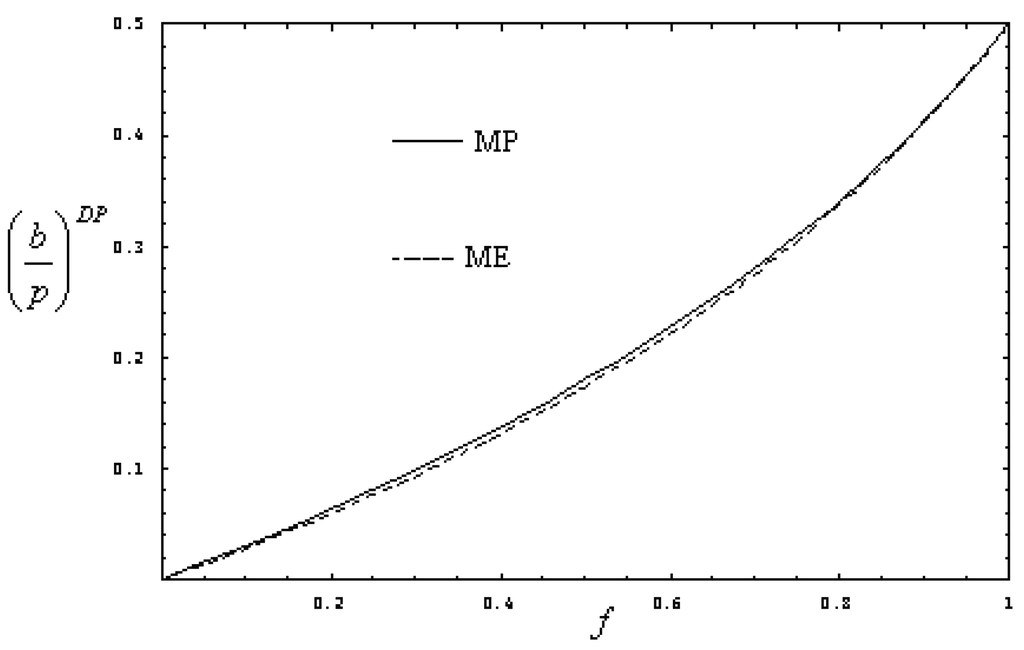
Figure 8.
Comparison between the ratio of price parameters under both the maximum power and maximum ecological regimes, for a DP heat transfer law with .
4. Proposal of an Ecological Lax
In the previous section the ratios of both price parameters of the energy input and the energy output were calculated in terms of the fractional fuel cost under both the maximum power and the maximum ecological regimes by means of a simplified model of the power plant (Novikov engine model). If in the Novikov model a Newtonian heat transfer law is considered, from Equations (18) and (19) the following quotient is obtained:
In Figure 9 the plot of ρ versus the fractional fuel cost for several values of τ is shown. It is observed that ρ is a decreasing function of f. For instance, for the case , when , and when , then ; that is, only in the limit where the relative cost is predominant, the price parameters of both cases are approximately the same, and the plant must work in the Carnot regime, (the maximum efficiency regime). For , in Figure 9 it can be seen that for all practical values of τ () [39], the following inequality holds:
In particular, when constant b (which has to do with the price of fuel consumption) is the same for both criteria, we get
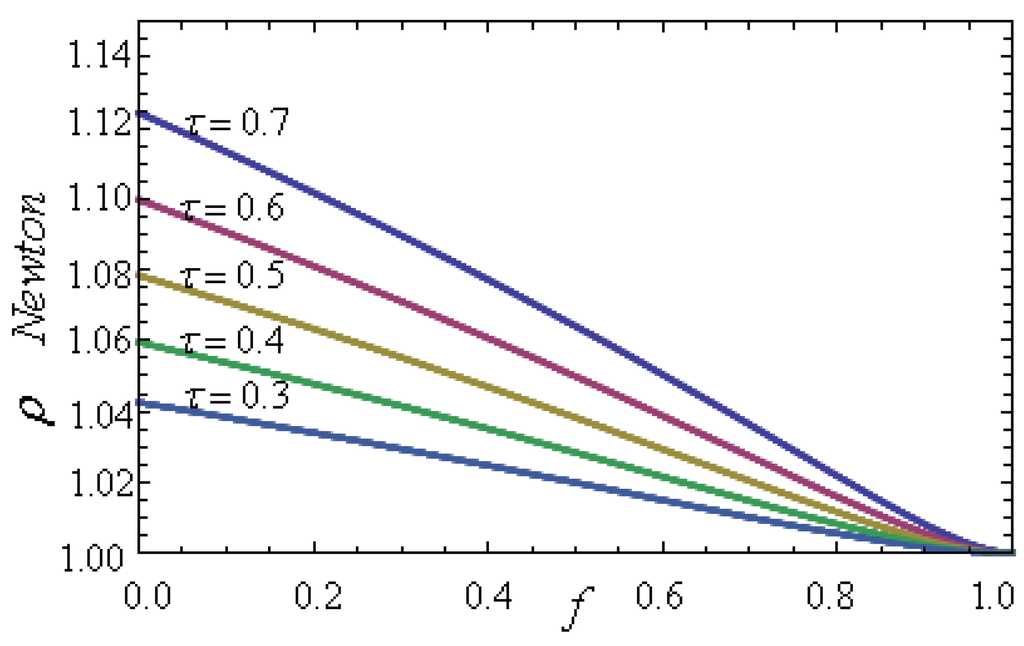
Figure 9.
Comparison between the quotients and for a Newton heat transfer law for several values of τ.
The previous expression means that the Watt price under ME conditions is bigger than the corresponding price under MP conditions. Analogously, when in the De Vos model a DP heat transfer law is considered, the inequality [21]
is obtained, and for the same value of b, it becomes,
which means again that the Watt price under ME conditions is also bigger than the price under MP conditions, but now considering a DP heat transfer law in the Novikov model. From Equations (25) and (27) it can be seen that the ecological price of a power unit is more expensive than the corresponding maximum power price. Thus, for the MP-regime, it can be concluded that the environment is subsidizing the MP-price of power unit. Thus, a possible ecological tax must be an increasing non-linear function of the following quantity
That is, a power plant operating under maximum power conditions must pay a larger ecological tax that one performing under ME conditions. If in Equation (28), Equations (18) and (19) are substituted, Λ in terms of f is obtained. In Figure 10 Λ against f for several values of τ is depicted. If the values of f are taken as in the De Vos article [12], that is, , then Λ is an increasing function of f and it augments for decreasing values of τ, within the interval of practical values of . On the other hand, if some data for τ and f stemming from actual power plants are taken, in Figure 10 it is found that at least three regions depending on τ and f values can be separated. For example, in the De Vos classification of fuel fractional costs, coal and natural gas correspond to , this kind of plants typically have τ’s in the interval [39] and therefore they fall in region A of Figure 10. If τ’s of uranium plants are considered, which are in the interval [20,39] and we take as given by De Vos [12], then, this kind of plants are within region B in Figure 10. Finally, the power plants based in renewable sources of energy have f’s in the vicinity of zero and [40] falling in region C of Figure 10. As particular cases, the following actual power plants data [39] corresponding to the dashed curves in Figure 10 are presented: (1) 1950 closed-cycle gas turbine in France ( and ); (2) West Thurrock (UK) 1962 conventional coal-fired steam plant ( and ); (3) CANDU (Canada) PHW nuclear reactor ( and ); (4) Larderello (Italy) geothermal steam plant ( and ). Therefore, in Figure 10, it can be seen that plants of type A must have bigger ecological taxes than plants of the type B and these must be charged with larger taxes than plants of type C.
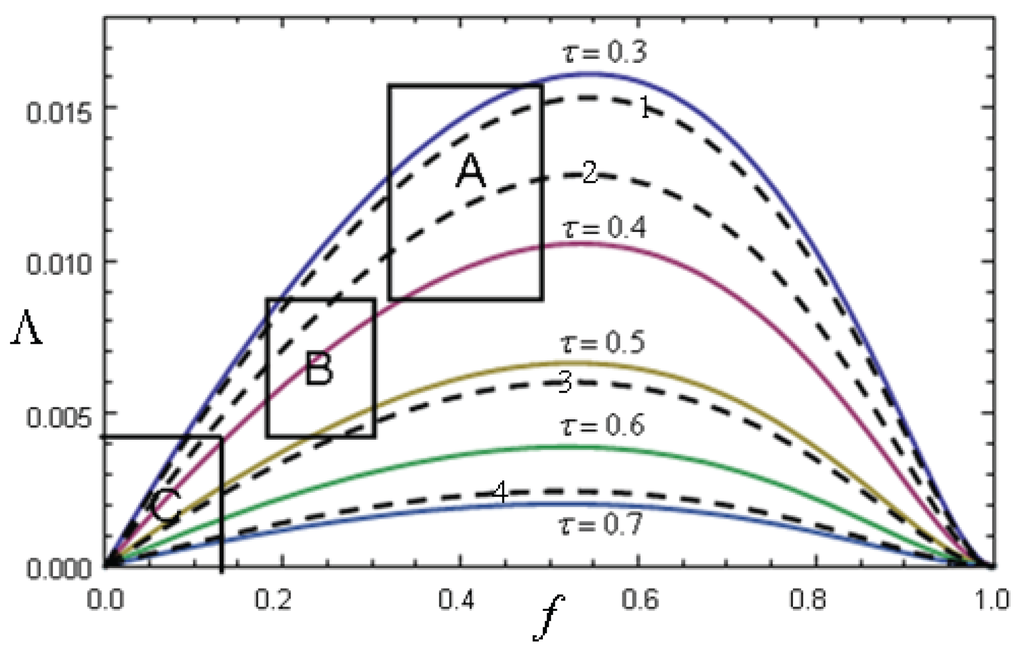
Figure 10.
Λ versus fractional fuel cost for several values of τ. Regions A corresponds to coal-gas power plants. Region B corresponds to nuclear power plants and region C to power plants based on renewable sources. The dashed curves 1, 2, 3 and 4, correspond to actual power plants (see end of Section 4).
5. Conclusions
In this work, by means of a simplified model of power plant (Novikov engine), it can be seen that the Watt price produced under MP conditions is cheaper than that produced under ME conditions. In this study, several fuel fractional costs were considered, since that corresponds to energy sources where the investment is the preponderant cost () until the fuel is the predominant cost (). However, for actual power plants, only the interval was considered. This was accomplished by using a typical definition of profit function stemming from economics. The MP-regime produces considerably more wasted energy toward the environment, thus the MP Watt price is subsidized by nature. Due to this fact an ecological tax is proposed, which could be a certain non-linear function of the price parameters difference between the MP and ME modes of power production. In Figure 10, it can be observed how one can identify at least three regions (A, B, C) corresponding to power plants based on several kinds of fuels. The present thermoeconomic analysis gives an approximated qualitative criterion to justify ecological taxes of power plants depending on their fuels expressed through the parameter f.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by COFAA and EDI-IPN-Mexico.
References and Notes
- Fisher, M.; Hoffmann, K.H. Can a quantitative simulation of an otto engine be accurately rendered by a simple novikov model with heat leak. J. Non-Equil. Thermodyn. 2004, 29, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto-Risso, P.L.; Medina, A.; Calvo-Hernández, A. Theoretical and simulated models for an irreversible otto cycle. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, P.; Nitzan, A. Finite time optimizations of a newton’s law carnot cycle. J. Chem. Phys. 1981, 74, 3546–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Chen, W. Finite time exergoeconomic performance bound and optimization criteria for two-heat-reservoir refrigerators. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1991, 36, 156–157. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. Maximum profit performance of an absorption refrigerator. Int. J. Energ. Environ. Econom. 1996, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. Finite-time exergoeconomic performance bound for a quantum stirling engine. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2000, 38, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. Maximum profit performance for generalized irreversible carnot engines. Appl. Energy 2004, 79, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. Maximum profit performance for a class of universal steady flow endoreversible heat engine cycles. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2007, 27, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, L.; Sun, F. Effect of heat transfer law on finite time exergoeconomic performance of heat engines. Energy Int. J. 1996, 21, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, L.; Sun, F. Effect of heat transfer law on finite time exergoeconomic performance of a carnot heat pump. Energ. Convers. Manage. 1998, 39, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, C.; Sun, F. Effect of heat transfer law on finite time exergoeconomic performance of a carnot refrigerator. Exergy Int. J. 2001, 1, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, A. Endoreversible thermoeconomics. Energ. Conv. Manage. 1995, 36, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, I.I. The efficiency of atomic power stations (a review). Atomimaya Energiya 1957, 3, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barranco-Jiménez, M.A.; Angulo-Brown, F. Thermoeconomic optimisation of novikov power plant model under maximum ecological conditions. J. Energy Inst. 2007, 80, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Brown, F. An ecological optimization criterion for finite-time heat engines. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 7465–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Brown, F.; Arias-Hernández, L.A. A replay to comments on a general property of endoreversible thermal engines. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 1520–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Brown, F.; Arias-Hernández, L.A.; Santillán, M. On some connections between first order irreversible thermodynamics and finite-time thermodynamics. Revista Mexicana de Física 2002, 48-S, 182–192. [Google Scholar]
- Barranco-Jiménez, M.A.; Sánchez-Salas, N. On thermodynamic optimisation of solar collector model under maximum ecological conditions. J. Energy Inst. 2008, 81, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barranco-Jiménez, M.A.; Sánchez-Salas, N.; Angulo-Brown, F. On the optimum operation conditions of an endoreversible heat engine with different heat transfer laws in the thermal couplings. Revista Mexicana de Física 2008, 54, 284–292. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco, S.; Rocco, J.M.; Medina, A.; White, J.A.; Calvo-Hernández, A. Optimization of heat engines including the saving of natural resources and the reduction of thermal pollution. J. Phys-D-Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barranco-Jiménez, M.A. Modelos endorreversibles para la conversión de energía solar en energía de viento y análisis termo-económico de plantas de potencia . PhD thesis, Autonomous University of the State of Mexico, Mexico City, México, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, B.; Kodal, A. Performance analysis of an endoreversible heat engines based on a new thermoeconomic optimization criterion. Energ. Convers. Manage. 2001, 42, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, B.; Kodal, A. Finite time thermoeconomic optimization for endoreversible refrigerators and heat pumps. Energ. Convers. Manage. 1999, 40, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, B.; Kodal, A. Thermoeconomic optimization of two-stage combined refrigeration systems: a finite time approach. Int. J. Refrig. 2002, 25, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodal, A.; Sahin, B.; Oktem, A.S. Performance analysis of two stage combined heat pump system based on thermoeconomic optimization criterion. Energ. Convers. Manage. 2000, 41, 1989–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodal, A.; Sahin, B. Finite tiem thermoeconomic optimization for ireversible heat engines. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2003, 42, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodal, A.; Sahin, B.; Yilmaz, T. Effects of internal irreversibility and heat leakage on the finite time thermoeconomic performance of refrigerators and heat pumps. Energ. Convers. Manage. 2000, 41, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, B.; Kodal, A.; Koyun, A. Optimal performance characteristics of a two-stage irreversible combined refrigeration system under maximum cooling load per unit total cost conditions. Energ. Convers. Manage. 2001, 42, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodal, A.; Sahin, B.; Erdil, A. Performance analysis of a two-stage irreversible heat pump under maximum heating load per unit total cost conditions. Int. J. Exergy 2002, 2, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodal, A.; Sahin, B.; Ekmekci, I.; Yilmaz, T. Thermoeconomic optimization for irreversible absorption refrigerators and heat pumps. Energ. Convers. Manage. 2003, 44, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Wu, C. Thermoeconomic optimization of an endoreversible four-heat-reservoir absorption-refrigerator. Appl. Energy 2005, 81, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreps, D.M. A Course in Microeconomic Theory; Princeton University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Tirole, J. The Theory of Industrial Organization; MIT Press Cambridge Mass: London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Barranco-Jiménez, M.A.; Angulo-Brown, F. Thermoeconomical optimization of an endoreversible power plant model. Revista Mexicana de Física 2005, 51, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Gutowicz-Krusin, D.; Procaccia, J.; Ross, J. On the efficiency of rate processes: Power and efficiency of heat engines. J. Chem. Phys. 1978, 69, 3898–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, F.; Chen, W. Influence of heat transfer law on the performance of a carnot engine. Chin. J. Engng. Thermophys. 1990, 11, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, C.T. Newton’s law of cooling - a critical assessment. Amer. J. Phys. 1990, 58, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barranco-Jiménez, M.A.; Angulo-Brown, F. Proceedings of 17th Conference on Efficiency, Costs, Optimization, Simulation and Environmental Impact of Energy Systems (ECOS 2004), Guanajuato, México, 7–9 July 2004; Instituto Mexicano del Petróleo: Distrito Federal, México, 2004; pp. 351–357.
- Bejan, A. Advanced Engineering Thermodynamics; Addison Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- de Vos, A. Endoreversible Thermodynamics of Solar Energy Conversion; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).