Abstract
Power network codes necessitate that any renewable source aligns with LVRT rules and assists in voltage restoration during voltage dips. This paper focuses on increasing the low-voltage ride through capability of a doubly fed induction generator-based wind turbine. Three different controllers are discussed in this article. The first is based on robust super-twisting sliding mode control, which is a recent robust control technique. The second uses a new metaheuristic optimizer called the Arctic Puffin optimizer (APO), and the third relies on the traditional PI controller. The grid-side converter sustains the potential of the DC converter link and the regulation of both the active and reactive power supplied to the power grid via three controllers. The rotor-side converter regulates the generator’s electromagnetic torque via two controllers. Doubly fed induction generator control is a challenging task as the two converters have five controllers, and it is vital to specify the ideal parameters for each controller. In the case of super-twisting sliding mode control, the APO is utilized to obtain the sliding surfaces needed for the five controllers. Moreover, the APO is exploited to obtain the optimal constants of the suggested PI regulators. The simulation results prove the excellent performance of both super-twisting- and APO-based controllers, with better performance demonstrated with super-twisting sliding mode control, which demonstrates excellent transient performance with the least overshoot among the three controllers. The super-twisting-based controller has a distinct feature, as it has good performance with parameter variations.
1. Introduction
The doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) is considered the best generator utilized with wind turbines (WTs) [1], as its solid-state converter has 30% of the generator rating [2]. However, because the power system is susceptible to unforeseen events, the operation of DFIGs could be significantly impacted [3]. Given that the DFIG is a complex plant with numerous nonlinearities [4], it is a real challenge to operate and control the DFIG under unexpected contingencies [5], regardless of where the contingencies occur in the power system, even if they are far away from the DFIG [6]. If a high-capacity WT is unexpectedly halted, the continuity of the electrical system may be impacted [7]. So, specific laws or requirements regarding the addition of any sustainable energy sources to the grid have been dedicated to grid codes [8,9]. Based on these requirements, DFIGs should stay in operation during contingencies that may produce voltage fluctuations [10]. Meanwhile, the generator must provide the adequate reactive power needed by the grid to restore the normal power system operation [11]. The previously mentioned procedure is titled the low-voltage ride through (LVRT) capability and is clarified by Figure 1, which shows the voltage–time relation during and after voltage variations [12,13,14]. According to Figure 1, power grid codes require each generator to align with the LVRT rules and to assist in voltage restoration.
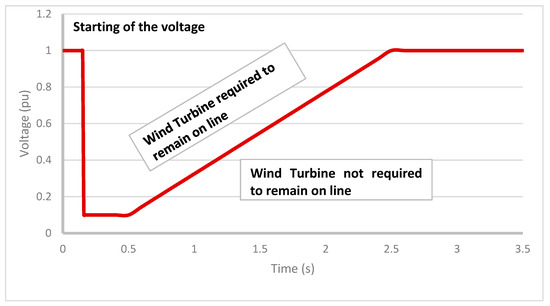
Figure 1.
LVRT grid code requirements.
Due to the inductive nature of a DFIG, during a high voltage dip (VD) in power systems, the VD causes the stator of the DFIG to have a DC transient current component. The value of this current depends on the instance of the VD. This transient current sets up a DC transient flux that is stationary with the stator of the DFIG. This transient flux cuts the rotor conductors and produces an emf in the rotor conductors, whose value depends on flux and the speed difference between the stationary transient field and the rotor windings [15]. The value of the resulting induced voltage in the rotor windings could be large enough to disturb the DC link voltage and initiate the protection circuit, causing the tripping of the DFIG. This action should be avoided; moreover, the DFIG has to deliver enough reactive power to the system to re-establish the voltage [16,17,18].
The LVRT problem has been investigated in the literature, and numerous LVRT techniques have been proposed. These techniques can be divided into three different categories. The first one is based on using solid-state converters, such as an SVC [19], STATCOM [20], bridge circuit [21], DC-chopper circuit [22,23], unified power quality conditioner [24], and DVR [25]. These power electronics devices will add complexity to the system regarding its coordination and control. The second category uses solid-state converters equipped with storage systems. A crowbar circuit provided with an SS was used in [26] to enhance the LVRT ability, and a DVR with super-magnetic energy storage was used in Ref. [27]. A crowbar circuit cannot only force the DFIG to inject the needed reactive into the system. An SS with a DVR is used in [28] to restore the voltage to its nominal value. All the previous methods will add a new component to the system, which will increase costs. The third category employs advanced control methods to improve the LVRT, such as vector control methods [29,30], pitch angle control [31], predictive control [32,33], and sliding mode control [34]. These advanced control methods are preferred as they do not add any devices to the system.
Different parameters can affect the LVRT problem; for example, Rafiee [35] showed that regulating the transient voltage could improve LVRT [36]. Herzog [37] pointed out that the rotor speed is vital to LVRT as it disturbs the slip of the generator; consequently, it could disturb the generator performance through voltage variations [38]. A more detailed review of different LVRT techniques is discussed in [39,40].
To support the power grid to restore voltage during voltage dips, a robust super-twisting sliding mode controller (STSMC) is suggested to boost the LVRT capability of a DFIG in order. This control technique is more suitable for nonlinear systems and highly robust against external disturbances, model uncertainties, and parameter variations, making it suitable for systems like DFIGs in wind turbines [41]. Unlike traditional sliding mode control, the super-twisting technique effectively reduces the chattering phenomenon, which is a common disadvantage with standard sliding mode controllers. The following is a summary of the main contributions:
- Enhancing the LVRT capacity of the DFIG-based WT by using STSMC and without inserting any external device.
- The Arctic Puffin optimizer (APO) is used to calculate the optimal sliding surface required for super-twisting control.
- The APO is also used to find the best parameters for a PI controller compared to the proposed controller.
- The suggested controllers are implemented entirely in the Simulink/MATLAB environment version 2024b.
The article is organized as follows: A brief review of the various techniques employed to improve the LVRT capability is discussed in Section 1. The complete mathematical model of DFIG in a synchronously rotating reference frame is covered in Section 2. The robust sliding mode control, the super-twisting technique, and the control law are covered in Section 3. A synopsis of the Arctic Puffin optimizer is outlined in Section 4. The proposed system and all its components are shown in Section 5. The assessment and computer modeling results of the suggested system for the three regulators are analyzed and discussed in Section 6. The conclusion is summarized in Section 7.
2. The Mathematical Model of DFIG
The space vector model of the DFIG expressed in reference frame (RefF) revolving at synchronous speed is provided by the following formulas:
where , are the space phasors of the stator voltage (STV) and rotor voltage (ROV), respectively, in volts.
, and represent the stator and rotor parts of the d- and q-axis voltage, respectively, represented by and .
, are the space phasors of stator and rotor currents, respectively, in Amperes.
, and represent the stator and rotor parts of the d- and q-axis current, respectively, in Amperes, expressed as and , are the stator flux (STFL) and rotor flux (ROFL) linkage space phasors, respectively, in Wb.
and are the components of the d- and q-axis flux linkage, respectively, expressed by and .
Rs and Rr stand for the stator and rotor windings resistance, respectively, in Ω.
is the synchronous velocity of the RefF in rad/s.
represents the rotor’s angular speed in rad/s.
p is the operator of differentiation ().
The voltage terms and in Equations (1) and (2) are the induced motional voltages in the stator and rotor due to the speed difference between the revolving RefF and both the stator and rotor. All of the rotor’s parameters and variables are referred to the stator. The difference in speed between the rotor and the revolving RefF is called the slip and is calculated as
The phase angle θ is essential to transform from stationary frame to the RefF and is calculated as
is the phase angle at the start.
where is the rotor position phase angle, and is the difference between the stator voltage.
The dq-axis RefF moves at speed , which is associated with the angle θ by
The flux linkages could be divided into dq-components as
The equation of motion links the generator torque to the mechanical torque is given as
may be expressed as
where is the rotor moment inertia in kg.m2, the number of pole pairs is designated by P, and is the rotor mechanical velocity.
The system of Equations (1)–(11) describes the d-q generator model in a RefF moving at speed ωs. The last equation, Equation (11), is decisive in voltage control. Anyone may orient the STV, STFL, or ROFL in the same direction as the d-axis. For instance, by adjusting the STFL phasor in the d-axis direction, and , and the previous process is called STFL-oriented control. A similar explanation applies if the ROFL is oriented to d-axis; then, and , and this is called the ROFL orientation. Since the STV is effortlessly assessable, it is better to orient the STV in the d-axis direction. Furthermore, in typical generator conditions, the stator resistance voltage drop is very small and may be deserted. Then, under these assumptions, Equation (1) becomes
This is the straight forward and simple relation between STV and STFL. In this article, STFL-oriented control is selected, and the machine model has the following form:
The WT is held working at this maximum power point (MPPT) by controlling the DFIG torque, Te, in a way to track the MPPT. When the wind speed changes to another speed, the operating point changes to a new operating point; consequently, Tt changes. The mechanical input power of the wind turbine can be calculated as [15]
where is the air density, R is the rotor blade radius, Vω is the wind speed, Cp is the power coefficient of the turbine, which is a function of the pitch angle, β is the pitch angle, and λ is the tip speed ratio. The tip speed ratio is expressed as .
Cp depicts the efficiency of the power extracted by the WT. Cp is the ratio of the extracted power to wind power and can be represented by numerous functions. The following equation is usually used [15]:
The WT system may be expressed by a two-mass model given as [40]
where JT, JG are the inertia of the WT rotor and the generator in kgm2, TT and Te are the WT and generator torque in Nm, DT and DG are the damping coefficients of the WT and generator, respectively, Kθ and Bθ are the stiffness and damping of the drive train, is the efficiency of the drive train, Ng is the gear ratio, and θt is the shaft torsion angle.
3. Sliding Mode Control
SMC is a nonlinear control approach that was first introduced by Utkin [42] and received noticeable attention in numerous research articles. SMC has many great features, such as robustness, insensitivity to parameter variations [43], more accurate responses, and good transient performance, and it is easy to implement [44]. Since SMC is easy to implement and simple to construct, it has attracted attention in numerous fields. SMC is easy to be tailored to accomplish specific performance requirements [45]. There are two steps to implement SMC [46]: the first is referred as the “reaching phase” [47], and the other is called the sliding phase [48].
3.1. Super-Twisting
SMC has many versions, such as first- and higher-order SMC. One of the higher-order forms of SMC is super-twisting (STW). STW reduces the chattering problem accompanied with first-order sliding mode control. In addition, it has superior performance features and is simple to put into practice. The principal problem that could be found in SMC is the issue with chattering resulting from the fast-switching action of SMC [49]. SMC is achieved in two steps: the first is the orientation of the regulated variables to a specific surface, namely, a sliding surface, and the other is to maintain the system state on this surface and then slide in the direction of the ultimate solution [44].
3.2. The Control Law
SMC has many versions; in this article, STSMC is selected to reach the sliding surface. STSMC has the following rule [50]:
The equation of the sliding surface has the form [51]:
The success of the control algorithm rests on the proper value of the parameters b and c. The Arctic Puffin optimizer (APO) will be used in this article to calculate the values of b and c.
4. Arctic Puffin Optimizer
APO is a new optimization technique presented by Wang [52] in 2024. It simulates the fishing procedure of the Arctic Puffin (AP), which is a little bird with gorgeously colored plumage. An AP weighs 400 g and is about 26 cm in length. AP hunts fish and zooplankton in the North Atlantic and North Sea, where they reside. They are skilled at flying at around 90 km/h [53]. When fishing, APs use their feet as a rudder and extend their wings halfway, turning them into blades that propel them through the water. They can swim quickly, descend to significant depths, and stay underwater for up to 60 s. There are two stages in the APO algorithm: the exploration phase and the exploitation phase [52]. The APO process is shown in Figure 2.
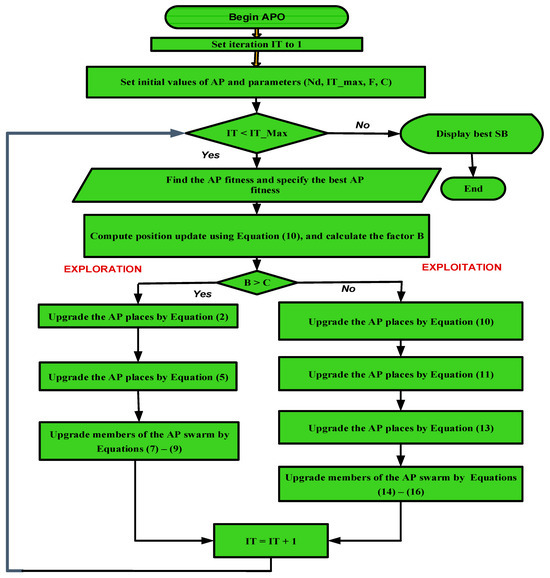
Figure 2.
The APO flowchart.
An objective function is required in order to determine the ideal controller parameters, which are around ten constants existing in five controllers. Although there are numerous criterions to be used in the objective function, in this article, the time integral of the sum of square errors is used, and it is stated as
5. The Studied System
Enhancing the DFIG’s LVRT capability is the main target of this article. In order to protect the rotor circuit and avoid a voltage spike during the transient period caused by a voltage dip, the first step is to temporarily integrate a crowbar (CB) circuit into it [2]. The second stage comprises regulating both the rotor-side converter (RSC) and grid-side converter (GRS) to insert the necessary reactive power required by the grid to restore the voltage [1]. Figure 3a,b illustrate the entire system with the controllers.
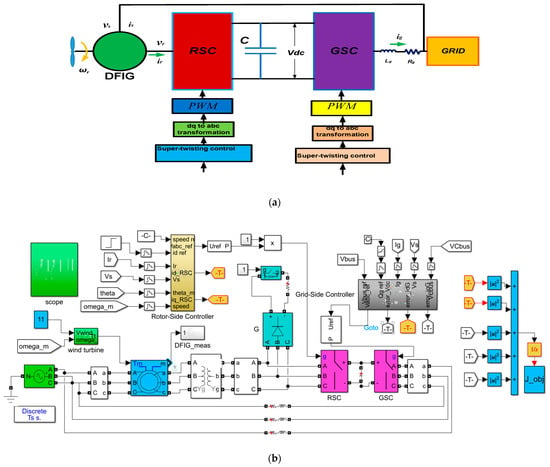
Figure 3.
The proposed scheme block diagram: (a) simplified block diagram of the proposed scheme; (b) detailed scheme.
5.1. RSC Controller
The proposed RSC regulator utilized for controlling the dq current components is given in Figure 4, in which Park transformation is utilized to transform variables from the abc frame to the revolving dq frame with the help of the STFL angle. The voltage control of the DFIG is achieved in a synchronously revolving dq frame, where the d-axis is oriented to the STFL space vector. As a result of this orientation, the d-component of the rotor current is proportional to the stator reactive power, while the q-component of the rotor current is proportional to the torque [15]. So, the d-component of the rotor current will be used to inject reactive power when the system needs it.
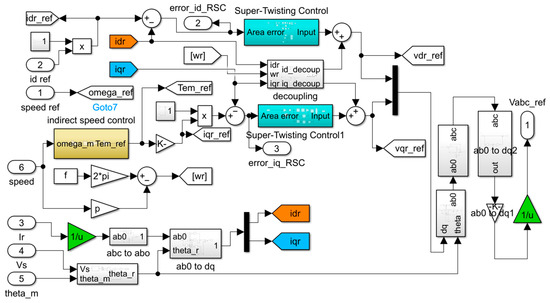
Figure 4.
The suggested controllers of the RSC.
5.2. GSC Controller
The GSC also uses vector control technique, and its main target is to deliver the generated power to the grid through the rotor circuit and to preserve the DC link voltage at the specified value. Since SMC uses a high switching frequency, which is not suitable for capacitor operation, a PI controller will be used to control the DC link voltage, while the remaining controllers in the GSC will use super-twisting SMC. The Simulink scheme of the GSC regulator is shown in Figure 5.
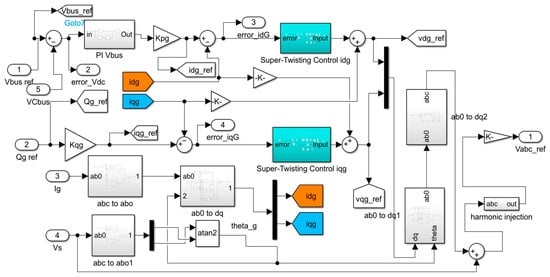
Figure 5.
The suggested controllers of the GSC.
5.3. The Crowbar Circuit
Figure 3 shows a crowbar (CB) circuit that involves a resistor connected with a 3-phase diode rectifier that is controlled by a controllable switch. The main rule of the CB is to protect the rotor circuit from the transient voltage rise at the instant of a fault occurring. The CB circuit will work by turning on the controllable switch once the rotor current or ROV exceeds the specified limits.
5.4. Wind Turbine Control
The main controller task is to keep the system working at the MPPT. When the turbine is working at the maximum power point, then , , and . The WT torque at the MPPT is
where
6. Simulation Results
Simulink\MATLAB is used to simulate the system depicted in Figure 3; all data concerning the WT and the DFIG are shown in Appendix A [15]. The generator started from rest until it attained its rated speed. The contingency is represented by a symmetrical three-phase voltage reduction of 90%, and the stator voltage is reduced to 10% of the rated value. The contingency lasted for a duration of 0.15 s. The restoration of the stator voltage occurred in 0.1 s as a gradual increase in the stator voltage, as indicated in Figure 6.
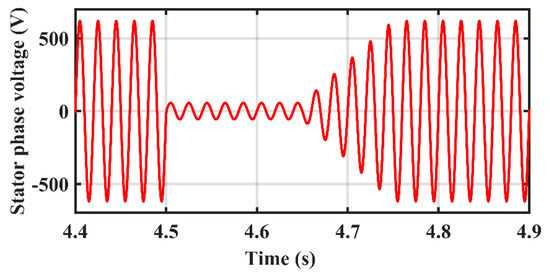
Figure 6.
The 90% symmetrical three-phase voltage dip in the SV.
For comparison’s sake, three different controllers will be considered here. The first is the conventional PI controller; its parameter values are obtained from Ref. [15]. The second controller is based on the APO described in Section 5, while the third controller is based on STW, as described in Section 4. The values of different controllers’ parameters are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Parameters of the different controllers.
To protect the rotor circuit during the contingency event, a CB is inserted for a duration of 0.1 s. The CB current is shown in Figure 7 for the three controllers. The conventional PI controller has the worst response as it has an overshoot 250% higher than the other controllers. The STW controller has the best performance, while the APO has an analogous response to the STW controller.
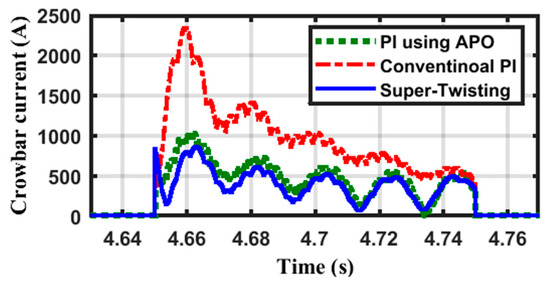
Figure 7.
The shape of the CB current with time during the VD.
The STFL is illustrated in Figure 8, and its steady-state value is nearly 2 pu. This value drops too much due to the reduction in the SV. Comparing the three curves, the conventional PI has the worst performance, while the STW controller has the best performance, and it reaches its prefault value before the other controllers. The APO has a response close to the STW controller. Figure 9 shows the ROFL variation during and after the contingency. Both the PI controllers have large oscillations, while the STW controller has minimal oscillations.
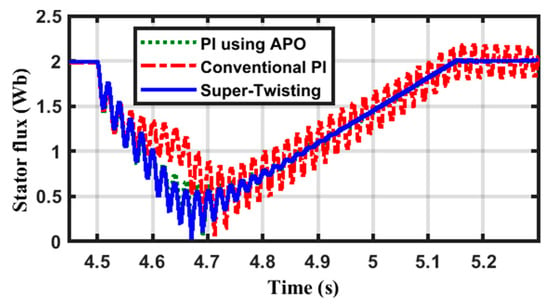
Figure 8.
The shape of the STFL variation during the VD.
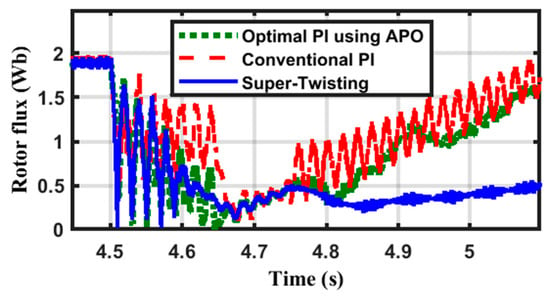
Figure 9.
The ROFL variation’s form during the VD.
Figure 10 displays the generator torque. The figure illustrates how the contingency event has a significant impact on the torque. Although the conventional PI controller has the maximum overshoot, all controllers were able to return the torque to its nominal value.
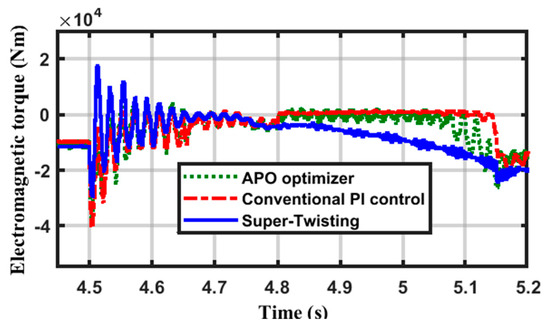
Figure 10.
The change in DFIG electromagnetic torque over time.
Figure 11 shows the rotor speed. The figure shows an increase in the velocity of the rotor during the contingency event as a result of a decrease in the electromagnetic torque. According to that figure, the STW controller has the lowest overshoot (18.5%), while the conventional PI has the highest overshoot (34.4%). The conventional PI controller responds the slowest, whereas the STW controller responds the fastest. The rated speed was successfully restored by all controllers.
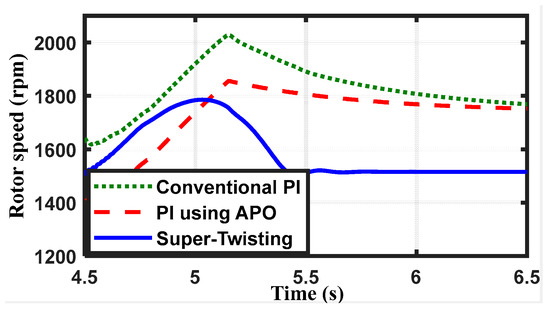
Figure 11.
The speed of the rotor in rpm.
The rotor current is shown in Figure 12. It is necessary to mention two significant points regarding Figure 12. The first is that during the contingency occurrence, the rotor current rises. Second, the rotor current frequency value raises, and it has a value that is proportional to the rotor speed, but it is not equal to the slip frequency as in normal operation. The conventional PI controller has the greatest overshoot, whereas the STW has the least. All of the controls were successful in bringing the current back to its steady value.
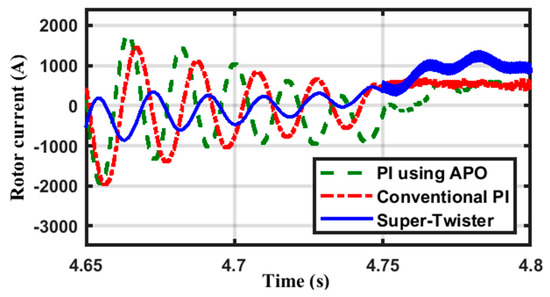
Figure 12.
The rotor current changes over time.
In Figure 13, the ROV is indicated. As seen in Figure 13, the ROV has two components: a transient component and a sinusoidal component. The conventional PI controller has the greatest overshoot, whereas the STW has the least. After the contingency, the CB circuit is removed, and the ROV is restored to its prefault value.
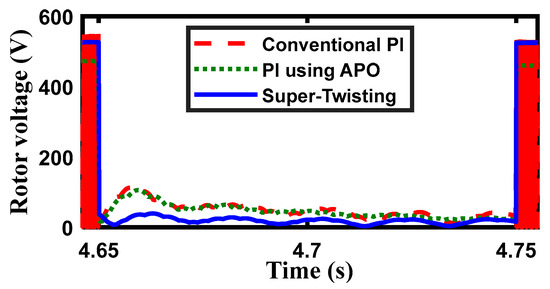
Figure 13.
The ROV changes over time.
The stator current shown in Figure 14 shows a significant, abrupt fluctuation as a result of the contingency. The conventional PI controller has the most variations, whereas the STW controller has the least.
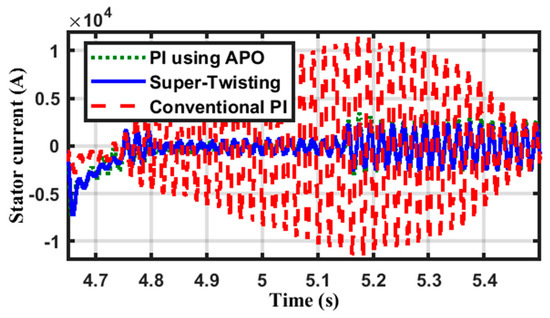
Figure 14.
The stator current changes over time.
The DC link voltage is depicted in Figure 15, which also reveals that the DC link voltage returns to its steady-state value even though it was affected by the contingency event. The maximum overshoot in case of the conventional PI is nearly 100%, whereas it is 38% in case of the STW controller.
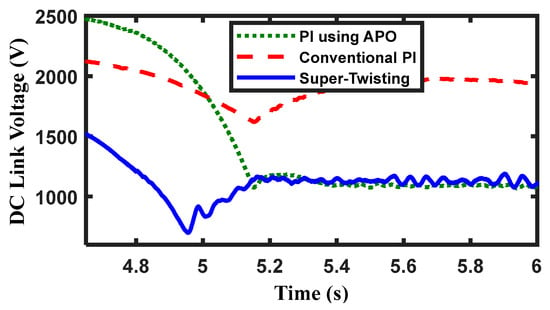
Figure 15.
The DC link voltage changes over time.
Two parameters, the rotor resistance and the mutual inductance, are raised by 25% in order to evaluate the APO and STW controllers’ performance in the event of parameter variation. Figure 16 shows the torque of the DFIG in the case of STW. As seen, the torque in a steady state is nearly the same for both cases, while the transient torque is slightly affected by the variation in parameters, demonstrating that the STW is insensitive to parameter variation. For the APO case, Figure 17 shows the machine torque, which is affected by the parameter variation, where the steady-state values of the torque (before 4.5 s) are changed by a noticeable value (around 37%), while the transient performance slightly varied.
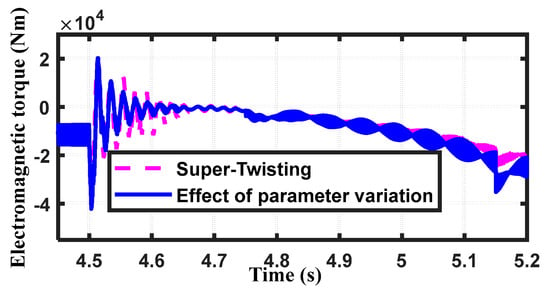
Figure 16.
The electromagnetic torque in the case of parameter variations with STW.
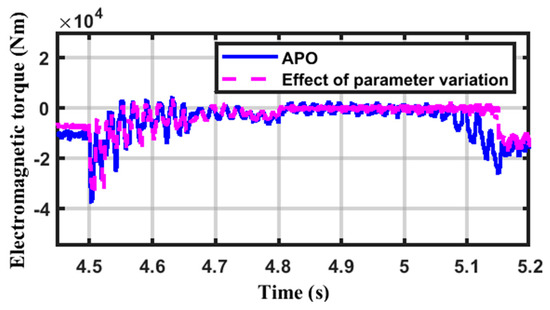
Figure 17.
The electromagnetic torque in the case of parameter variations with the APO.
7. Conclusions
Power grid codes dictate that any renewable source must follow LVRT rules to help the power grid and assist during voltage fluctuations. Since DFIGs have high LVRT capability, they are preferred for WTs. With appropriate control of the DFIG-based WT, the DFIG can help the system restore the voltage during any contingencies. Three distinct controllers are proposed in this article to enhance the LVRT capability of the DFIG. To achieve this task, three controllers are suggested: the first controller is based on a traditional PI controller, the second is based on robust super-twisting SMC, and the last one is based on an APO. The DFIG is controlled such that it injects the needed reactive power to the power system to assist the grid in restoring the voltage. From the perspective of transient response, the STW-based controller performs the best among the three controllers, while the conventional PI controller performs the worst. One unique characteristic of the STW controller is that, unlike the other controllers, it is inherently insensitive to changes in system parameters.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K.A.; Formal analysis, A.K.A. and M.A.E.-H.; Investigation, A.K.A. and M.A.E.-H.; Methodology, A.K.A.; Supervision, M.A.E.-H.; Validation, A.K.A. and M.A.E.-H.; Visualization, A.K.A. and M.A.E.-H.; Writing–original draft, A.K.A.; Writing–review and editing, M.A.E.-H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DFIG | Doubly fed induction generator |
| STSMC | Super-twisting sliding mode control |
| APO | Arctic Puffin optimizer |
| WTs | Wind turbines |
| LVRT | Low-voltage ride through |
| VD | Voltage dip |
| RefF | Reference frame |
| STV | Stator voltage |
| ROV | Rotor voltage |
| STFL | Stator flux |
| ROFL | Rotor flux |
| MPPT | Maximum power point |
| STW | Super-twisting |
| RSC | Rotor-side converter |
| GRS | Grid-side converter |
| CB | Crowbar |
Appendix A

Table A1.
The DFIG-based WT data.
Table A1.
The DFIG-based WT data.
| Turbine Data | ||
| Parameter | Magnitude | Units |
| Axle inertia at low speed values | 800.0 | Kg.m2 |
| Axle friction at low speed values | 0.10 | Nm.s/rad |
| Stiffness factor | 12500.0 | Nm/rad |
| Damping factor | 1300.0 | Nm.s/rad |
| Axle inertia at high speed values | 90.0 | Kg.m2 |
| Axle friction at high speed values | 0.10 | Nm.s/rad |
| Data of the Generator | ||
| Parameter | Magnitude | Units |
| The nameplate-rated active power | 2.00 | MW. |
| The nameplate-rated torque | 12732.0 | Nm. |
| Rated voltage of the stator windings | 690.0 | Volts |
| Rated speed | 1500.0 | rpm. |
| Speed range | 900.0–2000.0 | rpm. |
| Pole pairs | 2.0 | |
| Mutual inductance, | 2.50 | mH. |
| Leakage inductance of the rotor, | 87.0 | μH. |
| Leakage inductance of the Stator, | 87.0 | μH. |
| Rotor resistance, | 0.0260 | Ω. |
| Stator resistance, | 0.0290 | Ω. |
| Stator/rotor turns ratio | 1/3 | |
| Maximum slip | 1/3 | |
References
- Badawi, A.; Soliman, M.; Elzein, I.M.; Alqaisi, W. Optimizing Low-Voltage Ride-Through in DFIG Wind Turbines via QPQC-Based Predictive Control for Grid Compliance. Int. J. Robot. Control Syst. 2025, 5, 86–104. [Google Scholar]
- Loulijat, A.; Hilali, A.; Makhad, M.; Chojaa, H.; Ababssi, N.; Mossa, M.A. Low-voltage ride-through capability of DFIG-based WECS improved by nonlinear backstepping controller synthesized in novel power state model. E-Prime-Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2025, 11, 100864. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, A.; Ullah, S.; Rahman, T.U.; Sami, I.; Rahman, A.U.; Alghamdi, B.; Pan, J. Enhanced wind energy conversion system performance using fast smooth second-order sliding mode control with neuro-fuzzy estimation and variable-gain robust exact output differentiator. Appl. Energy 2025, 377, 124364. [Google Scholar]
- Fouad, A.; Kotb, H.; AboRas, K.M.; ElRefaie, H.B.; Alqarni, M.; Baqasah, A.M.; Yakout, A.H. Enhancing grid-connected DFIG’s LVRT capability using dandelion optimizer based the hybrid fractional-order PI and PI controlled STATCOM. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 120181–120197. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Gao, B.; Cao, Z. Low-voltage ride-through strategy for offshore wind turbines based on current relaxation region. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 223, 109704. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, M.A.; El-Hay, E.A.; Elkholy, M.M. An overview and case study of recent low voltage ride through methods for wind energy conversion system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 183, 113521. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, M.G.; Alvarez, J.M.G. Technical and Regulatory Exigencies for Grid Connection of Wind Generation. In Wind Farm; Gastón, O.S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Erlich, I.; Bachmann, U. Grid code requirements concerning connection and operation of wind turbines in Germany. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting 2005, San Francisco, CA, USA, 16 June 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Moheb, A.M.; El-Hay, E.A.; El-Fergany, A.A. Comprehensive review on fault ride-through requirements of renewable hybrid microgrids. Energies 2022, 15, 6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yameen, M.Z.; Lu, Z.; Rao, M.A.A.; Mohammad, A.; Nasimullah; Younis, W. Improvement of LVRT capability of grid-connected wind-based microgrid using a hybrid GOA-PSO-tuned STATCOM for adherence to grid standards. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2024, 18, 3218–3238. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Shukla, A.; Abusara, M. DFIG Driven Wind Turbine with Grid Supporting Battery Storage System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 72, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar]
- Code, D.G. Grid Code. 2005. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/495816846/Grid-Code-2005-1 (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Joshi, J.; Swami, A.K.; Jately, V.; Azzopardi, B. A Comprehensive Review of Control Strategies to Overcome Challenges During LVRT in PV Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 121804–121834. [Google Scholar]
- Moheb, A.M.; El-Hay, E.A.; El-Fergany, A.A. Consolidation of LVFRT capabilities of microgrids using energy storage devices. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 22294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, G.; Lopez, J.; Rodriguez, M.; Marroyo, L.; Iwanski, G. Doubly Fed Induction Machine: Modeling and Control for Wind Energy Generation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gomis-Bellmunt, O.; Junyent-Ferre, A.; Sumper, A.; Bergas-Jane, J. Ride-Through Control of a Doubly Fed Induction Generator Under Unbalanced Voltage Sags. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Milimonfared, J.; Fathi, S.H. A review of low-voltage ride-through enhancement methods for permanent magnet synchronous generator based wind turbines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsili, M.; Papathanassiou, S. A review of grid code technical requirements for wind farms. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2009, 3, 308–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, H.; Kazemi-Rahbar, M.H. Enhancing voltage stability and LVRT capability of a wind-integrated power system using a fuzzy-based SVC. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 22, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalin Kumar Samal, R.T.; Karad, S. STATCOM with Fuzzy-PI Controller for Low Voltage-Ride through Enhancement of DFIG based Wind Farm. Int. J. Emerg. Trends Eng. Res. 2021, 9, 518–523. [Google Scholar]
- Lella, K.; Mohan, N.R. Application of Bridge Type Fault Current Limiter for Fault Ride-Through Capability Enhancement of Dfig Based Variable Speed Wind Turbines. J. Electr. Eng. 2017, 17, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Alaboudy, A.H.K.; Mahmoud, H.A.; Elbaset, A.A.; Abdelsattar, M. Technical Assessment of the Key LVRT Techniques for Grid-Connected DFIG Wind Turbines. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 15223–15239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S.; Asghar, R.; Mehmood, F.; Saleem, H.; Azeem, B.; Ullah, Z. Evaluating a Hybrid Circuit Topology for Fault-Ride through in DFIG-Based Wind Turbines. Sensors 2022, 22, 9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshiram, T.; Kumari, S.L. Power Quality Enhancement and Low Voltage Ride Through Capability in Hybrid Grid Interconnected System by Using D-Fact Devices. In Emerging Technologies for Computing, Communication and Smart Cities; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanein, W.S.; Ahmed, M.M.; Abed el-Raouf, M.O.; Ashmawy, M.G.; Mosaad, M.I. Performance improvement of off-grid hybrid renewable energy system using dynamic voltage restorer. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 1567–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endale, S.M.; Tuka, M.B. Fault Ride through Capability Analysis of Wind Turbine with Doubly Fed Induction Generator. Preprints 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.H. Compensation of distribution system voltage sag by DVR and D-STATCOM. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Porto Power Tech Proceedings (Cat. No.01EX502), Porto, Portugal, 10–13 September 2001; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 1, p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Vilathgamuwa, D.M.; Gajanayake, C.J.; Loh, P.C.; Li, Y.W. Voltage Sag Compensation with Z-Source Inverter Based Dynamic Voltage Restorer. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2006 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Forty-First IAS Annual Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 October 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 2242–2248. [Google Scholar]
- Gayathri, K.; Jeevananthan, S. Refined vector control structure and indirect MPPT for grid connected DFIG-based wind energy conversion system, and appraisal on matrix converter interface. Int. J. Model. Identif. Control 2024, 44, 255–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moumani, Y.; Laafou, A.J.; Ait Madi, A.; Boutssaid, R. An improved dual vector control for a doubly fed induction generator based wind turbine during asymmetrical voltage dips. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2024, 13, 3757–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thet, A.K.; Saitoh, H. Pitch control for improving the low-voltage ride-through of wind farm. In Proceedings of the 2009 Transmission & Distribution Conference & Exposition: Asia and Pacific, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 26–30 October 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Qin, L.; Sun, C.; Li, H. Model Predictive Control on Transient Flux Linkage and Reactive Power Compensation of Doubly Fed Induction Wind Generator. Int. J. Energy Res. 2024, 2024, 6648691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achar, A.; Djeriri, Y.; Benbouhenni, H.; Bouddou, R.; Elbarbary, Z.M.S. Modified Vector-Controlled DFIG Wind Energy System Using Robust Model Predictive Rotor Current Control. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 50, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, R.; Moger, T. Improving the DC-Link Voltage of DFIG Driven Wind System Using Modified Sliding Mode Control. Distrib. Gener. Altern. Energy J. 2023, 38, 715–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, Z.; Heydari, R.; Rafiee, M.; Aghamohammadi, M.R.; Blaabjerg, F. Enhancement of the LVRT capability for DFIG-based wind farms based on short-circuit capacity. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 3237–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yang, P.; Xu, L.; Xu, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. Cause, Classification of Voltage Sag, and Voltage Sag Emulators and Applications: A Comprehensive Overview. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 1922–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, F.; Röder, J.; Frehn, A.; Ruhe, N.; De Doncker, R.W. Influences on the LVRT behavior of DFIG wind turbine systems. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffarzadeh, H.; Mehrizi-Sani, A. Review of Control Techniques for Wind Energy Systems. Energies 2020, 13, 6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Liu, W. Low-Voltage Ride-Through Techniques in DFIG-Based Wind Turbines: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahela, O.P.; Gupta, N.; Khosravy, M.; Patel, N. Comprehensive Overview of Low Voltage Ride Through Methods of Grid Integrated Wind Generator. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 99299–99326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurumurthy, G.; Das, D.K. Terminal sliding mode disturbance observer based adaptive super twisting sliding mode controller design for a class of nonlinear systems. Eur. J. Control 2021, 57, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.; Lee, H. Chattering Problem in Sliding Mode Control Systems. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Variable Structure Systems, Alghero, Sardinia, 5–7 June 2006; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 346–350. [Google Scholar]
- Gambhire, S.J.; Kishore, D.R.; Londhe, P.S.; Pawar, S.N. Review of sliding mode based control techniques for control system applications. Int. J. Dyn. Control 2021, 9, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurcugil, H.; Biricik, S.; Bayhan, S.; Zhang, Z. Sliding Mode Control: Overview of Its Applications in Power Converters. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2021, 15, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.S.T.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Nguyen, D.Q.; Vo, H.H.; Tran, T.C.; Brandstetter, P. PMSM Drive with Sliding Mode Direct Torque Control. In AETA 2022—Recent Advances in Electrical Engineering and Related Sciences: Theory and Application; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Wei, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Li, H. Convergence rate sliding mode control of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on expanded sliding mode observer. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2024, 71, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehan, A.; Boiko, I.; Zweiri, Y. Chaotic Chattering in Sliding Mode Control Systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2024, 69, 7925–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Pathak, P.K. A State-of-the-Art Review on Recent Load Frequency Control Architectures of Various Power System Configurations. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2024, 52, 722–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.S.; Orlov, Y.V. Vadim I. Utkin and sliding mode control. J. Frankl. Inst. 2023, 360, 12892–12921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, A.K.; Shaheen, A.M.; El-Fergany, A.A.; Alqahtani, M.H. Sliding mode control based dynamic voltage restorer for voltage sag compensation. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 102936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, A.K.; El-Hameed, M.A. Application of Robust Super Twisting to Load Frequency Control of a Two-Area System Comprising Renewable Energy Resources. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Tian, W.C.; Xu, D.M.; Zang, H.F. Arctic puffin optimization: A bio-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for solving engineering design optimization. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2024, 195, 103694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, K.K.; Burnham, J.L.; Johnson, J.A.; Huffman, A. Migratory movements of Atlantic puffins Fratercula arctica naumanni from high Arctic Greenland. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).