Abstract
With recent technological advancements, advanced communication technology, sensors and distributed generation (DG), it is an undeniable fact that modern power systems are flooded with massive amounts of data. These vast amount of generated data are difficult to interpret and comprehend, and are slow to sort through and explain. With ever increasing renewable power generation, grid operators should gain insights on identifying the vulnerabilities, behaviour and interactions of various power system components and anticipate challenges to enhance power system resiliency. Visualisation offers a means to reveal patterns, trends and connections in data that speed up and present information to a power system operator in a way that can be well understood topographically and provide an ability to accommodate increasing DG resources. Hence, this paper presents a comprehensive literature review of several visualisation techniques that can be embedded for improving operational efficiency and resiliency in modern power grids embedded with distributed and renewable energy resources.
1. Introduction
Countries all around the world are aiming to tackle climate change by actively participating in achieving net zero target by mid of this century. The mitigation of climate change leads to fewer storms, floods, droughts and other extreme weather events caused by rising temperatures. In order to meet the global climate goals under the Paris Agreement, several countries have set up a number of targets that reflect the government’s commitment to accelerating action and working together with other global partners to overcome the climate crisis and to limit global temperature rise to 1.5 °C. One of the promising technologies used to reduce the net zero target is the replacement of fossil fuels with clean, renewable and dependable energy supported by battery storage. Given this need, many policies have been enacted in transitioning to a clean energy future [1,2].
With the rapid adoption of renewable energy in the modern grid, emissions are expected to decline the most from 2020 to 2035. Renewables are the cheapest form of new generation and supported by federal, state and territory policies in Australia. Australia is projected to lower emission trends by increasing the national renewable energy target. It is envisaged that the proportion of renewable energy will increase to 82% of electricity generated in Australia’s electricity grids by 2030 through rewiring the nation. Rewiring the nation will support grid transformation and accelerate new transmission projects, increasing the availability of lower-cost renewable generation and storage [3,4].
To attain net zero targets and harvest the benefits of DG technologies, numerous challenges need to be addressed. Two primary challenges at the forefront of this are the integration of DG into the network to maximise its benefits and the management and analysis of the substantial amounts of data generated by DG installations. Firstly, the integration of DG poses several obstacles, such as disruption in grid stability due to intermittent and decentralised characteristics of DG [5], concerns pertaining to power quality [6], grid planning [7,8], capacity management [9], voltage fluctuations [10], fault current [11], grid operation and control [12,13]. As a result, ensuring the grid’s ability to withstand, adapt and recover from these challenges is crucial.
Secondly, with a growing number of DG units in the system, the technological advancements associated with the DG, such as smart grid, communication philosophy and sensors are gaining significant momentum. This massive amount of data is collected and generated in centralised units through various sources such as phasor measurement units (PMU), supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA), smart meters (SM), meteorological information systems (MIS), geographical information systems (GIS), simulation and user inputs, social media, traffic updates, remote terminal units (RTUs), programmable thermostats and many more [14]. The sheer volume of data collected from these diverse sources can unveil concealed patterns and offer valuable insights. Nevertheless, interpreting and presenting the information in a manner that is understandable to the power system operators is a major concern.
Overcoming these challenges necessitates the implementation of a visualisation technique that can expedite the process, present the information effectively and uncover the hidden patterns within the network. Addressing these challenges through visualisation techniques improves monitoring the decision-making of grid operators to improve their ability to anticipate, respond and recover from grid disturbances, which results in creating a resilient power grid.
This paper aims to review existing visualisation methods applied in power systems and explore various visualisation techniques that can be embedded for improving the resiliency of modern power grids integrated with distributed and renewable energy sources. By leveraging these visualisations, the power industry can overcome barriers, transition towards a clean and sustainable energy future and promote solutions that are cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
The remainder of this paper is organised as follows: Section 2 provides current trends in power system visualisation techniques. Section 3 presents novel visualisation methods for future grids. Section 4 highlights big data and data analytics in power system visualisation. Section 5 explores a comprehensive overview and comparison of visualisation techniques applicable to enhancing the power system’s resiliency. Section 6 presents the simulation and results. Finally, Section 7 includes a concluding remark, summarising the key findings and implications.
2. Power System Visualisation Techniques: Current Trends
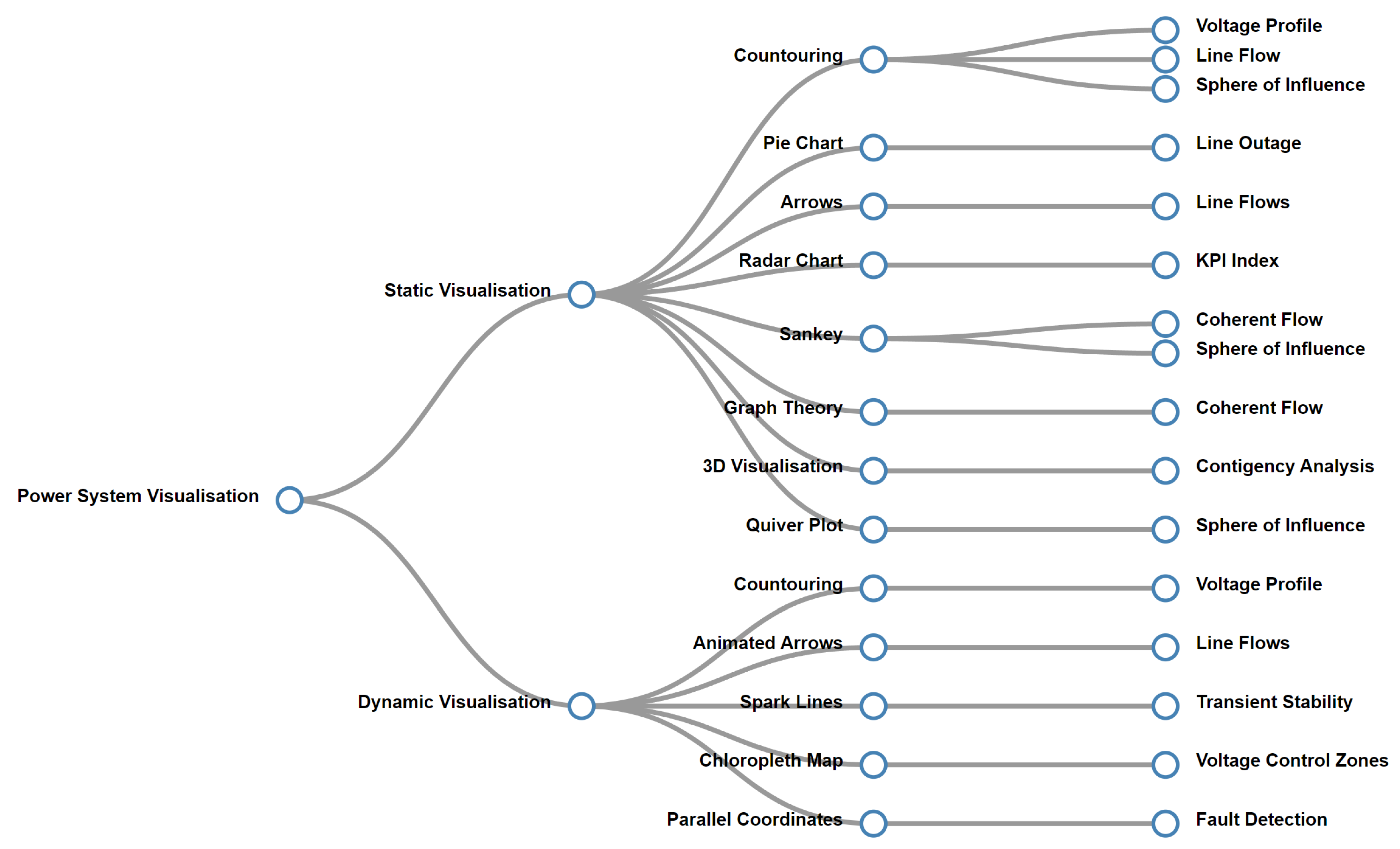
This section aims to examine the current trends in power system visualisation, specifically in terms of both static and dynamic visualisation approaches. Figure 1 provides a brief overview of power system visualisation highlighting various techniques and applications in this field.
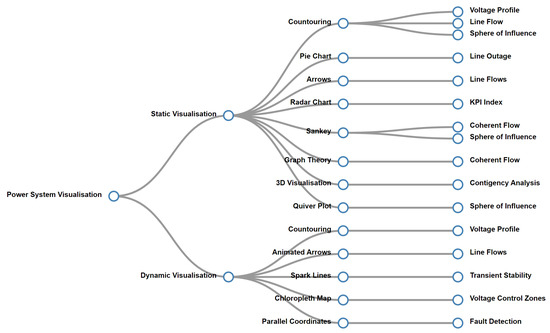
Figure 1.
Literature map on power system visualisation.
2.1. Static Visualisation Techniques in Power Systems
Static visualisation techniques in power systems refer to visualisation that does not change over time and provides a snapshot of system information. This section explores some commonly used static visualisation techniques in the existing power system literature. In [15], the authors propose a novel visualisation technique using quiver and reflection principles to determine the sphere of influence of DG in the network using line current flows. Real and imaginary parts of current are extracted and projected as quivers in a line section. The proportion of real and imaginary parts of a current vector can be seen simultaneously by mapping the line current information as a quiver. The sphere of influence of each source can be examined through quiver attributes such as magnitude, direction and location, which allows the network to be segmented into zones depending on the sphere of influence of different generating sources.
The proposed concept by [16,17] introduces a novel approach for analysing the sphere of influence of single and multiple DG units using critical line current analysis and Sankey visualisation. Unlike traditional methods that require complex calculations and predefined cluster numbers, this approach simplifies the partitioning of the network. By considering both real and reactive power, the Sankey visualisation mentioned in the literature provides a holistic view of real and reactive power flows, identifying sources that serve the node and exploring node-to-node flows.
Sankey diagrams also depict bulk power transactions for operators’ situational awareness. A novel flow-oriented visualisation approach using the Sankey diagram was proposed in [18] to depict power flow dispositions within power grids. The authors claimed that the suggested visualisation technique simplifies the process of tracking patterns of heavy flow in the grid. Identifying such heavy coherent flow and associated congestion bottlenecks is crucial to determine serious operational vulnerabilities like cascading outages, load-shedding and frequency problems. In the diagram, the lines are oriented so that all power flows move from the top to the bottom, with the thickness of each line indicating the magnitude of the active power flow. This enables the quick identification of key bulk power exchanges during a specific generation dispatch snapshot.
The research in [19] uses the connectivity-oriented visualisation or structural-oriented visualisation approach to visualise the electrical grid. The author demonstrated that power system diagrams can be visualised as connectivity-oriented diagrams, which explicitly show inter-node electrical distances that help in the rapid identification of electrically connected buses. By explicitly illustrating inter-node electrical distances, the proposed approach enhances the understanding of system vulnerabilities and facilitates effective decision-making for grid planning, operation and resiliency enhancement.
The authors of [20,21] propose a directed acyclic graph to model the instantaneous state of power grids, determining sets of branches that form heavily loaded and potentially vulnerable flow gates within the grid. One of the advantages of directed acyclic graphs is that they allow the identification of coherent power flows along a set of branches that partition the network into two islands. The available flow-oriented visualisation techniques presented in the literature mainly focus on detecting and visualising the coherent flow gates within the grids. To achieve this, power grids are modelled as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs), where the direction of power flow on the lines determines the directionality of the graph’s edges.
In [22], the author uses a radar chart to visualise six situational awareness key performance indicators (KPIs) for the operational security of power systems with a high penetration of renewable energy sources (RES). These KPIs includes reserve capacity abundance, ramp resource abundance, COI frequency deviation, interface power flow margin, synthesised voltage stability, and angle stability margin. The real-time situational awareness results of power systems are obtained by the decision tree method, and the situational awareness results at the specific time are displayed by the radar chart method for monitoring the operation states. The author claims the proposed KPI-based situational awareness method is able to accurately monitor the real-time state of power systems with a high proportion of RES and can guide power dispatchers in making effective decisions.
The author introduces the use of interactive 3D visualisation [23,24] to present operational and economic data in power systems. Reactive power data are depicted as cylinders placed on a single line diagram. This innovative approach enhances the interpretation of large volumes of multivariate data by allowing users to interact with the visualisation, gaining insights and finding patterns. The inclusion of cylinders representing reactive power improves the understanding of power distribution and highlights areas requiring attention. Overall, the application of interactive 3D visualisation provides a valuable information for researchers and decision-makers, improving data analysis and facilitating informed decision-making in power system operations.
The introduction of a third dimension to represent additional data was proposed in [24,25]. The general idea is to enhance the display of 3D physical data by using a representation similar to common 3D surface plots but substituting the surface layer for a grid view of the system. Using this approach, voltage magnitude and power flow in the associated grid elements can be viewed clearly.
Geographic data views (GDV) were proposed in the literature [26,27] to visualise a relevant subset of the network by embedding power network parameters with the geographic information. The author claims these methods are effective when the task switches from monitoring to corrective control or analysis, which requires all the information needed in a particular scenario for effective decision-making. A key advantage of GDV is they can be used to visualise various power system field values with the ability to use different display attributes such as location, size, colour, rotation, and shape to simultaneously show different fields.
Traditionally, the most common representation of voltage magnitudes on one-lines has been a digital numeric display of the voltage next to the bus. While this representation is certainly accurate, the user has difficulty in perceiving patterns in the voltages with a greater number of buses. An initial replacement of numerical displays is an analogue-type display next to each bus. As an example, for bus voltage magnitudes, approaches based on placing a “thermometer” next to each bus have been used. Though the thermometer-based representation was definitely an enhancement over the digital displays when looking at hundreds of buses, it is still not easy to analyse vast amounts of information and to see patterns [28,29].
Contour visualisation is a technique that displays multivariate data in a two-dimensional plane using a colour-coded contour map. In power system visualisation, contour visualisation can be used to analyse the behaviour of variables such as voltage, current, power, and frequency over a geographical region or a power network. In [23,30,31,32], the voltage levels of a power network are displayed as a contour map over a geographical area using a colour-coded contour map. In this map, each point on the map is assigned a colour based on its voltage level. This type of visualisation isolates areas of the network that experience high or low voltage levels and identifies potential voltage violations.
Similarly, a frequency contour map that displays the frequency levels of a power network over a geographical area using a colour-coded contour map is proposed in [33]. The same as voltag level, each point on the map is assigned a colour based on its frequency level that shows the areas of the network experiencing high or low frequency levels and frequency stability issues.
In [34], the impact of DG and its sphere of influence on the network are visualised through contour plots. The author extracts a sensitivity matrix in terms of active power and visualised electrical distance by superimposing contours in the medium voltage power system network.
A line flow is displayed as a contour in [35] to display the power flow of a network over a geographical area using a colour-coded contour map. In this map, each line on the map is assigned a colour based on its power flow level. This type of visualisation defines flow congestion or overloading issues through high- or low-power flow levels.
In [23,32,35], the pie chart is embedded in the power network to display the line flow distribution factor to quickly indicate the location of overloads/outages in a transmission network. The percent fill of each pie chart represents the percentage loading on the line. The numeric text and colour shadings are superimposed to indicate the exact percentage and highlight the devices that are above some threshold percentage. These pie charts quickly provide an overview of the system loading for displays with fewer lines. However, for larger networks, pie charts are cluttered, and there is insufficient space to show each individual pie chart. Extending the technique to larger cases requires decreasing the size of the "normal" pie charts so that they become essentially invisible.
2.2. Dynamic Visualisation Techniques in Power Systems
Dynamic visualisation techniques in power systems encompass the utilisation of visual representations that exhibit changes and variations over time. These techniques play a crucial role in comprehending the dynamic behaviour of the power system and analysing the impact of various factors on its performance. Several studies in the power system literature have focused on incorporating time and generation variations into their visualisations to provide a more in depth understanding of system dynamics.
In [36], the utilisation of time-sequence animations for visualisation is discussed, drawing a parallel with weather radar sequences. However, a notable drawback of this approach is that it necessitates time to observe the display, making it unable to provide instantaneous results. Moreover, such plots are unable to convey geographically distributed information effectively.
In [26], an alternative approach is proposed to integrate small strip charts onto existing one-lines adjacent to the relevant areas of interest. One advantage of this approach is that the strip charts are displayed within the appropriate geographic context, offering a better understanding of the data. However, a limitation of this method is that displaying strip charts for all fields would necessitate reducing their size significantly. To address this challenge, the authors introduce a visualisation technique that utilises spark lines overlaid on geographic representations to display transient stability data. This proposed technique aims to overcome the limitations of the strip charts by providing a compact yet informative visualisation of the data within their geographical context.
In [37], researchers introduced wide-area frequency visualisation methods using animated event replays. These methods utilise data obtained from frequency disturbance recorders (FDRs) in a wide area frequency monitoring network (FNET) system. The collected data are presented in the form of coloured contours for each time step and played back as a movie. These visualisations represent frequency behaviour over time, enabling analysts to observe and analyse the frequency disturbances in a more intuitive and detailed manner. The use of animated event replays enhances the understanding of the system’s response to events and facilitates the identification of patterns or anomalies in the frequency data.
In [23,38], the authors introduce a dynamic visualisation technique for representing current flows in a power grid using animated arrows. These arrows are overlaid onto the lines of the grid and animated to depict the direction and magnitude of the current flow. The aim of this approach is to provide users with a quick and comprehensive understanding of the actual flows happening within the system. By observing the animated arrows, users can easily familiarise themselves with the flow patterns and detect any unusual or outlier conditions. Additionally, the size and colour of the arrows can be utilised to visually emphasise the severity of certain issues or problems. This innovative visualisation method enhances situational awareness and enables users to gain deeper insights into the operational state of the power grid.
Andrews curves [39] display relationships among multivariate data. Unlike traditional plots with orthogonal axes, this method employs a Cartesian plot where all the dimensions are spread out horizontally. The x-axis represents the dimensions, while the y-axis represents the data for each dimension. Each data vector is depicted as a connected line spanning the entire width of the plot. To ensure comparability, the data are typically normalised due to varying ranges. Though this chart identifies the weak areas prone to stability issues and detects the patterns and relationships within the data, it is not possible to locate the origin of the signals within the geographic footprint of the system.
In [40], the author partitioned the power system into several zones and determined voltage control through probabilistic assessment and visualised using a choropleth map. A Choropleth map is a visualisation that uses colour shading to represent data values within predefined voltage control regions. These maps divide the power system into predefined voltage control regions and use colour gradients or shading to indicate the probability levels of voltage violations within each region. The colour intensity or hue on the map represents the likelihood of voltage issues, with darker or more saturated colours indicating higher probabilities.
3. Novel Visualisation Methods for Future Grids
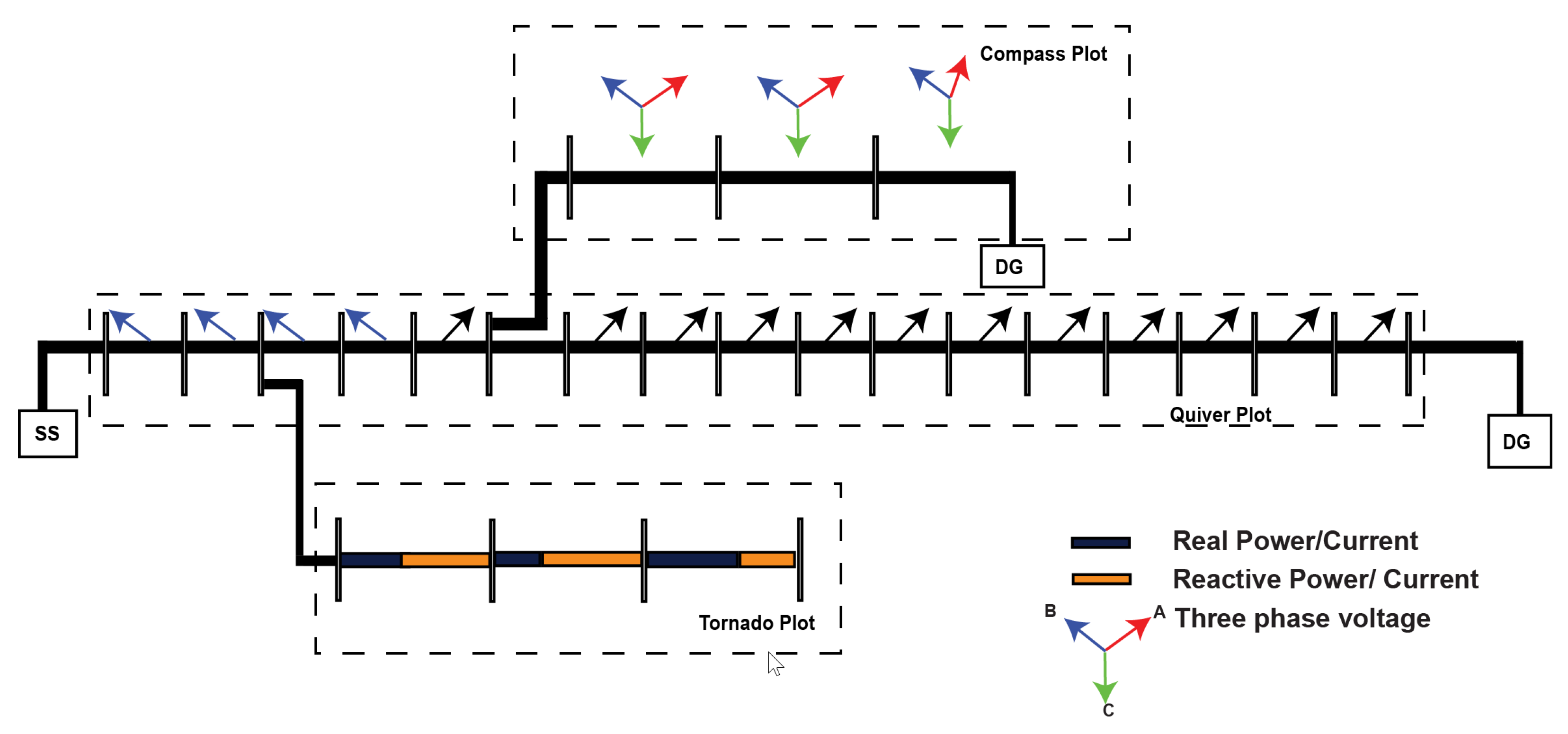
This section provides an overview of potential visualisations that can be integrated into the power network to facilitate power system resiliency and the management of multiple DG sources. These visualisation techniques aim to support operators in monitoring and controlling the power system effectively. Some of the visualisation techniques that can be embedded in the power network are included below, and the conceptual model of the proposed visualisation is illustrated by means of the a sample distribution system depicted in Figure 2.
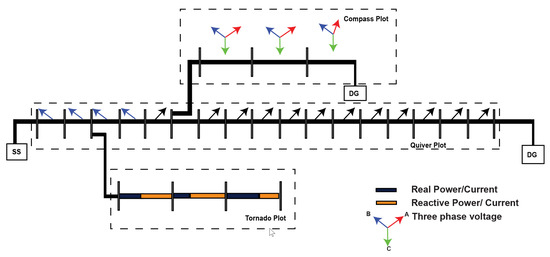
Figure 2.
Novel visualisation technique conceptual model.
3.1. Matrix Plot
A matrix plot is a data visualisation technique that can be used to display large volumes of data in a compact and informative way [41]. The matrix plot can be displayed as a rectangular grid of coloured squares. The rows and columns of the grid represent the nodes in the power system, and the colour of each square represents the value of the real or reactive power at that node. The rows represent the flow of source to line sections from the grid, and the column represents the flow of the source to the line section from DG. By creating this matrix plot, operators can quickly identify areas of the power system where there are imbalances between real and reactive power and where the DG is contributing more or less than the grid. This assists operators in taking corrective actions to maintain a stable and reliable power system.
3.2. Tornado Plot
A tornado plot is a type of bar chart which is placed back to back to represent the two categories simultaneously [42]. This can be used to compare the impacts of different factors or interventions on real and reactive powers or currents in an electrical power system. The tornado plot presents which line sections have the largest and smallest impacts on real and reactive powers and which factors may be driving those impacts. To illustrate, Figure 2 incorporated tornado plots in one section of the lateral in the sample distribution system. As can be seen, the contribution of real and reactive currents is clearly visible, and in the event of a disruption, the line section which deems immediate attention and its source of disruption can be identified.
3.3. Compass Plot
A compass plot is a graphical representation of the three-phase voltage phasors in a power system [43,44]. The compass plot can be used to visualise the magnitude and phase angle of the three-phase voltage phasors relative to a reference axis. By creating a compass plot for three-phase voltage, operators can quickly detect any imbalances or phase shifts in the voltage phasors, which can be indicative of power quality issues or other problems in the power system. The compass plot can be used to diagnose these issues and take corrective actions to ensure a stable and reliable power supply. Figure 2 shows the compass plot in one lateral of the sample distribution system. As can be observed, the compass plot shows the phase change in line current. Hence, corrective measures can be applied in those line sections to ensure the reliability of the system.
3.4. Polar Histogram
A polar histogram is a graphical representation of the frequency distribution of a variable in polar coordinates [45,46]. It can be used to visualise the frequency distribution of various parameters in a power system, such as voltage and current magnitudes, power factor, and harmonic contents. This polar histogram chart, when mapped in the network with the details of real and imaginary current components, shows the probabilistic approach to determine the sphere of influence of DG in the network.
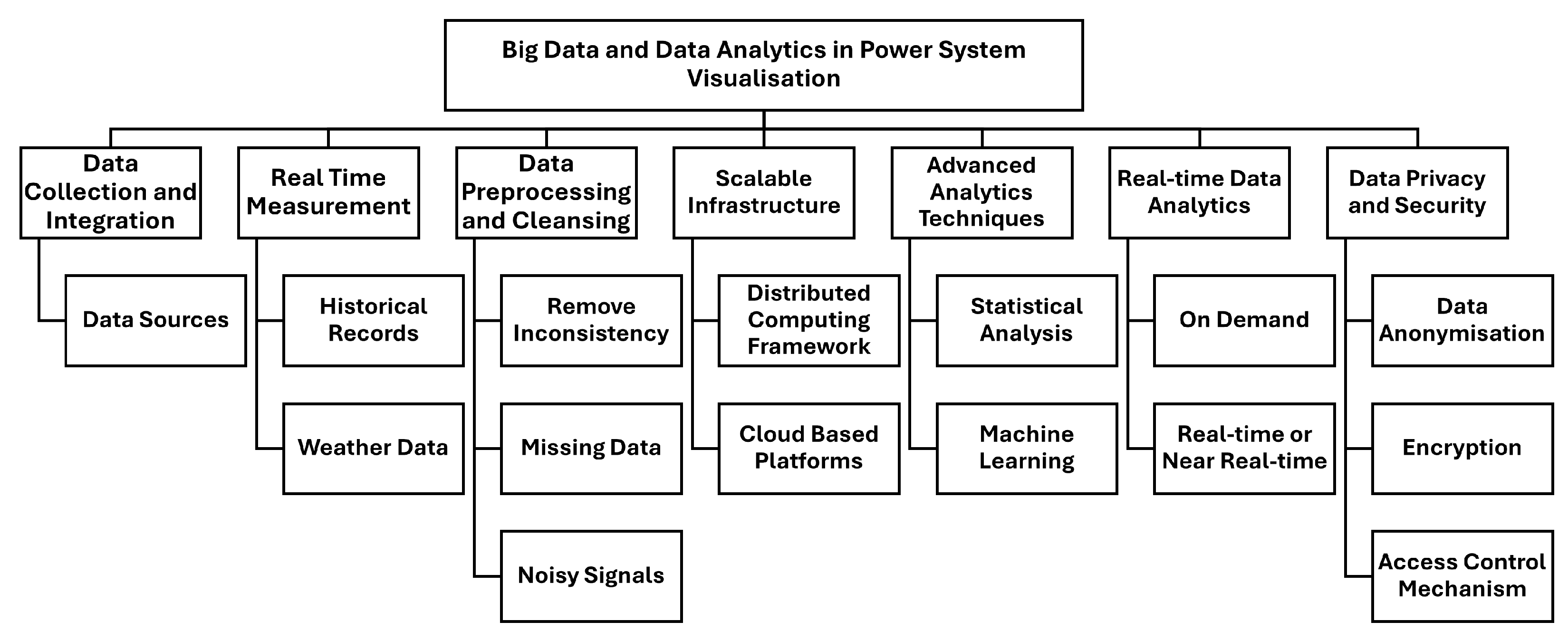
4. Big Data and Data Analytics in Power System Visualisation
Understanding the concept of big data is essential in interpreting its impact on power systems. This section delves into the pivotal role of big data and data analytics in visualising power systems with main focus on different stages such as data collection and integration, data preprocessing and cleansing, scalable infrastructure, advanced analytics techniques, real-time data analytics and data privacy and security, as shown in Figure 3.
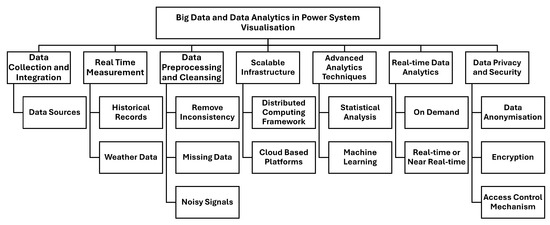
Figure 3.
Big data and power system visualisation.
4.1. Data Pipeline and Scalability
Big data are characterised by their volume, velocity, variety and veracity [14,47]. In the context of power systems, these characteristics are raised from the availability of data from diverse data sources, including sensors, SMs, SCADA systems, real time measurement and other monitoring devices [48]. These collected big data contain noise, outliers and redundant information, which can impact the quality of the results. Therefore, data preprocessing and cleansing techniques are mandatory to eliminate inconsistencies, interpret missing data and smooth out noisy signals which makes the data reliable and accurate for numerical analysis [49]. Moreover, as the volume of data is immense, it is difficult to process and analyse data in real time. Hence, scalable infrastructure such as distributed computing and cloud-based platforms are required to handle the computational demands of big data analytics. These high-performance computing resources and parallel processing techniques enable efficient data processing to receive timely insights and make decisions [50].
4.2. Real-Time and Advanced Data Analytics Techniques
Real-time data analytics refers to processing and analysing data streams on-demand and in real-time or near real-time [51]. Advanced data analytics techniques such as statistical analysis, machine learning and predictive modelling are needed to discover valuable insights from big data [52]. These techniques identify data correlations, patterns and anomalies, thereby building predictive models and decision support systems. Through the use of advanced analytics techniques, power systems can go beyond descriptive analysis and provide predictive and prescriptive capabilities, aiding system design for resiliency planning. Hence, integrating visualisation to the real-time data complements network operators to monitor system conditions, uncover emerging issues and take appropriate actions that foster strategic planning and enhance situational awareness. In addition, visualisation tools should adhere to privacy regulations and standards while providing secure access to authorised users to protect data privacy and integrity [53].
Overall, big data and data analytics provide detailed insights into power system operations. However, the sheer magnitude and intricacy of these data can be overwhelming without the utilisation of effective visualisation techniques. Consequently, visualisation plays a vital role in delivering the benefits of big data, leading to improved resiliency planning, operational monitoring and proficient response strategies during intervals of disturbances in the network.
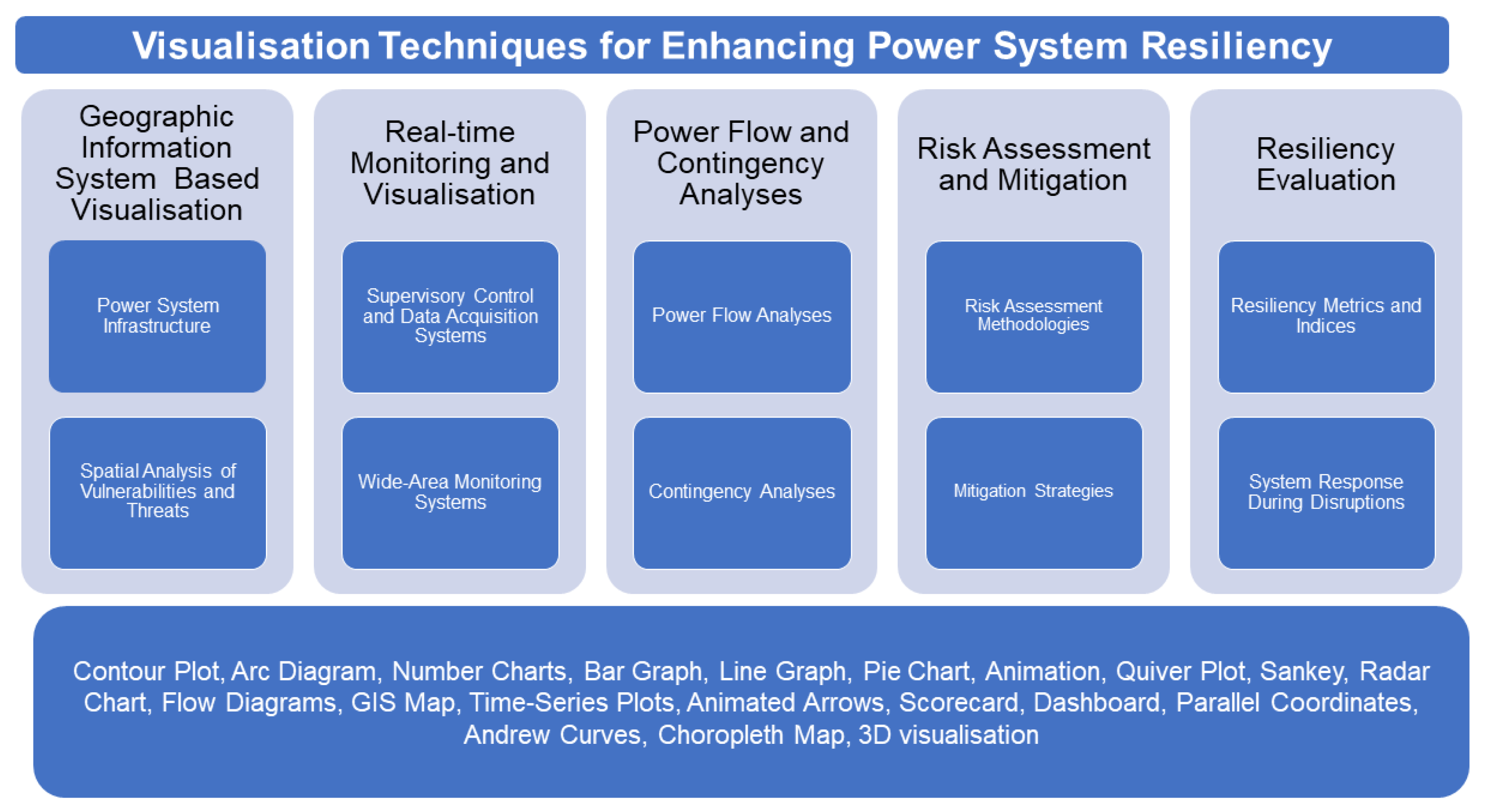
5. Visualisation for Enhancing Power System Resiliency
This section discusses various visualisation techniques that have been effective in bolstering power system resiliency and their specific applications, as shown in Figure 4. In resilience-driven power systems, deciphering data through visuals provides significant benefits, including real-time monitoring, dynamic resilience assessment, targeted resilience optimisation, decision support, user-friendliness and the development of a standardised resilience metric. The consequent improvement in understanding, managing and enhancing the resilience of power systems ensures reliable and robust power system operations.
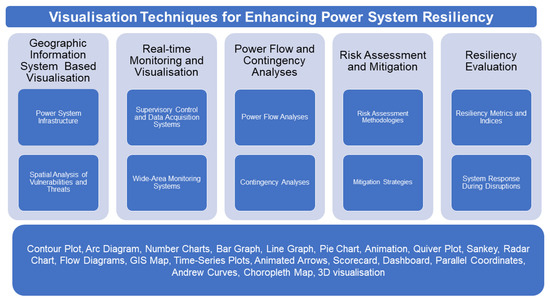
Figure 4.
Visualisation techniques for enhancing power system resiliency.
5.1. Geographical Information System-Based Visualisation
GIS is a powerful tool for visualising power system infrastructure and analysing spatial data. It provides an overview of the physical layout and geographical distribution of the power system in a map-based interface. It assists operators and decision-makers in understanding spatial relationships between different components and pinpointing critical assets. Visualising data through GIS-based technology helps in the spatial analysis of power system vulnerabilities and threats. By overlaying data on hazard maps, such as flood zones, earthquake-prone regions or wildfire risks, operators can spot high-risk areas and adopt mitigation measures. For instance, it aids in determining optimal locations for backup generation capacity or discerning areas prone to extended power outages during severe weather events. By visualising the spatial relationships between infrastructure, vulnerabilities and threats, decision-makers can develop targeted strategies to elevate power system resilience.
5.2. Real-Time Monitoring and Visualisation
Real-time monitoring gives operators a dynamic view of the power system, assisting them with monitoring and analysing system conditions instantly. Data relating to voltage, current, frequency and other operational parameters are collected in real time by SCADA, wide area measurement systems (WAMS) and PMUs. The presentation of these data using Andrews curves, strip charts, sparklines, contouring and dashboards provides an overview of the power system’s dynamic behaviour. Thus, operators are able to detect anomalies, diagnose system disturbances and take prompt actions to mitigate unforeseeable events, enhancing the resilience of the power system.
5.3. Visualisation of Power Flow and Contingency Analyses
Power flow and contingency analysis are important studies conducted to assess the reliability and performance of power systems. The representation of power flow and contingency analysis results simplify complex data, aid decision-making and provide insight into power system behaviour and contingencies. Visualisation techniques such as quiver plot, animation, Sankey diagrams, pie charts and contouring intutively represent voltage deviations, line loadings, power transfers and system stability margins. These visualisations highlight the power flows in the network and analyse the impacts of contingencies on system performance. Thereby, assisting operators to spot critical contingencies, assess the system’s vulnerability and develop appropriate mitigation strategies is important to enhance resiliency.
5.4. Visualisation of Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Risk assessment and mitigation are integral components of power system resiliency planning. Visualisation techniques play a crucial role in representing risk assessment methodologies and adopting mitigation strategies. By visualising network wide resilience risk, operators and planners can effectively communicate resiliency plans to stakeholders, enhance transparency and foster collaboration among different entities involved in power system operation and planning. Through GIS representation, heat maps and charts, the likelihood of various risks, such as natural disasters, equipment failures, cyber-attacks or extreme weather events are monitored. These visuals aid engineers in analysing the spatial distribution of risks, locating hotspots and prioritising mitigation efforts in high-risk areas.
5.5. Visualisation of Resiliency Evaluation
Resiliency evaluation is a process of assessing the overall resilience of a power system and measuring its ability to withstand and recover from disruptions. Visualisation techniques are essential for representing resiliency metrics and indices. Visualisation techniques such as radar charts, dashboards or scorecards represent the values and trends of metrics such as system average interruption duration index (SAIDI), system average interruption frequency index (SAIFI), customer average interruption duration index (CAIDI), customer minutes interrupted (CMI) [54] and resiliency indices in a visually intuitive manner. Also, the visualisation such as time-series plots, animations, maps and GIS-based representation can also be utilised to illustrate the system’s dynamic response during different crisis stages, provide a spatial understanding of the system’s performance and locate regional variations in resiliency levels. This allows operators and decision-makers to monitor the system’s performance over time, compare different regions or components and ascertain areas of improvement.
5.6. Comparison of Visualisation Techniques in Power System
This section presents a comparative Table 1 highlighting different visualisation techniques in the context of power system resilience, along with their applications. These techniques can be categorised based on their relevance to different aspects of power system resiliency, such as situational awareness, contingency planning, mitigation strategies, resilience evaluation, risk management and disruption events. Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the appropriate choice depends on the specific requirements and objectives of the analysis or visualisation task in the context of power system resiliency. By selecting appropriate techniques, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into power system resilience and make informed decisions to enhance the reliability and adaptability of power systems.

Table 1.
Comparison of Visualisation Techniques used in Power System Resiliency Studies.
6. Simulation and Results Depicting the Applicability of Selected Visualisation Techniques
This section demonstrates the application of four main types of visualisation techniques to enhance power system resiliency. These visualisation techniques aim to support operators in monitoring and controlling the power system effectively by determining the sphere of influence of DG. By determining the sphere of influence of DG, the resiliency of the grid can be improved significantly by strategically positioning the DG units to support critical loads during outages, improve grid performance instantly after blackouts and enhance grid visibility under extreme events. The proposed visualisation methods for determining the sphere of influence of DG are tested using the 33 bus distribution system. The system topology load data and line data for the base configuration are given in [56]. The total real and reactive power demands are 3.715 MW and 2.30 Mvar, respectively. The active and reactive power losses for the base configuration are 0.11 MW and 0.08 Mvar, respectively. The network voltage is maintained between 0.95 p.u. and 1.05 p.u. The percentage level of DG connected to the network is calculated as follows:
where is the active power injection by DG, is the reactive power injection by DG, is the total real power demand in the system and is the total reactive power demand in the system.
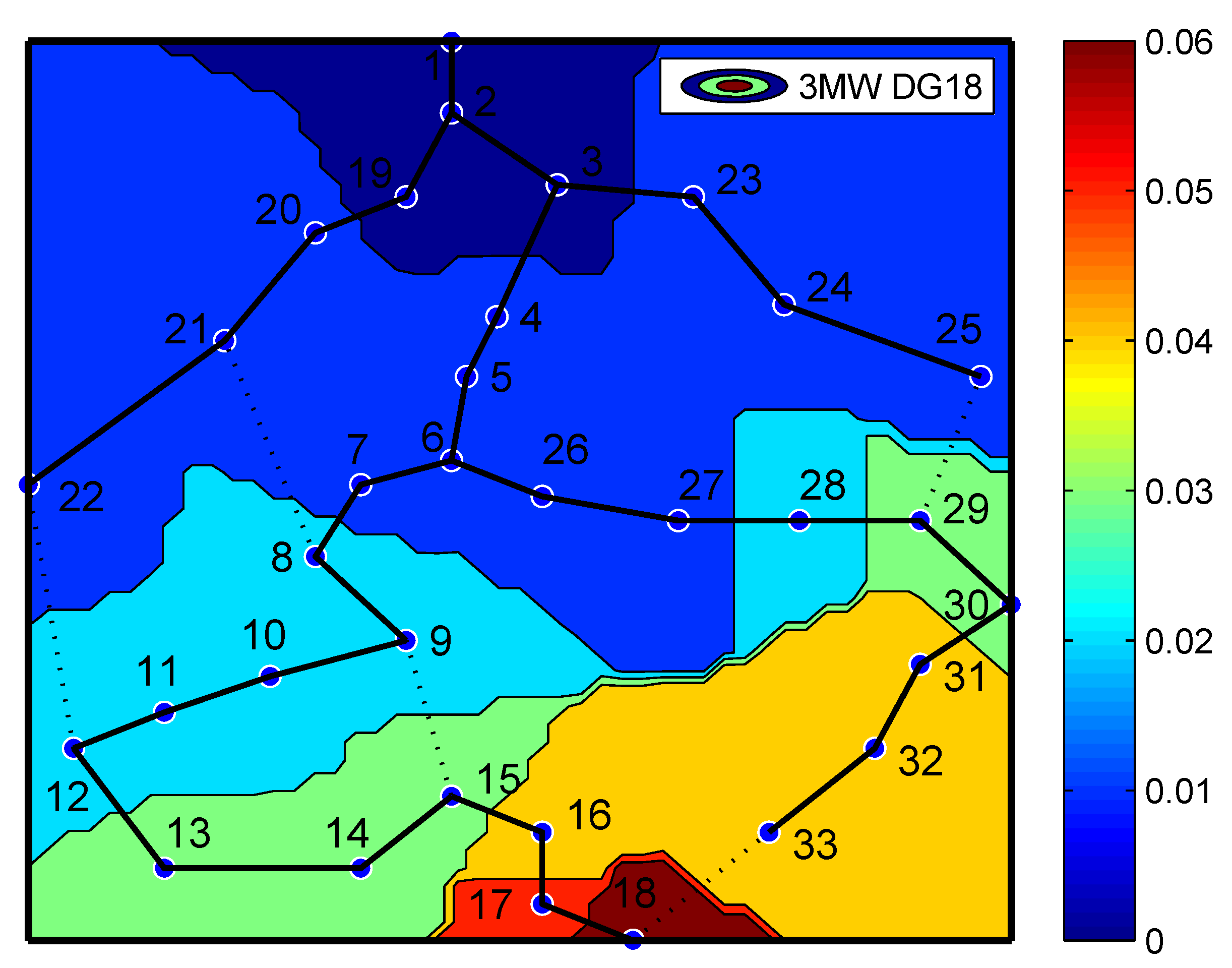
6.1. Contour Plot
Contour plot is a type of visualisation that helps in visualising the pattern of voltage levels in distribution network through colour code. In this case study, it is assumed DG is supplying 3 MW of real power and is connected at bus 18. The voltage levels at different buses are analysed and visualised through the contour plot. The proposed contour plot combines voltage information with the overview of entire topological 33 bus system. As seen from the Figure 5, the buses are grouped based on their voltage levels with similar colour patterns and voltage violation, i.e., bus voltages within +/−5% are encountered at bus 17 and 18 due to placement of DG at bus 18. Through this type of visualisation mitigation strategy, the optimal placement and allocation of DG can be identified to enhance the resiliency of the system.
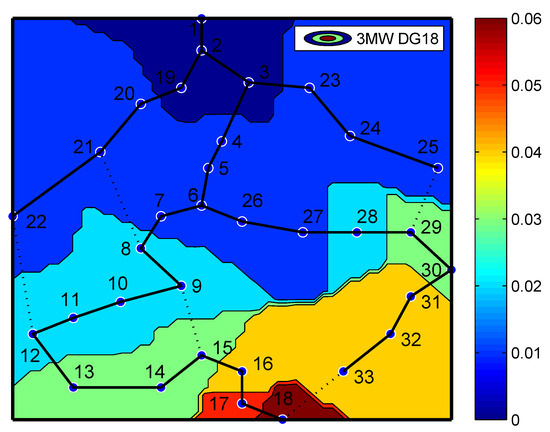
Figure 5.
Contour plot.
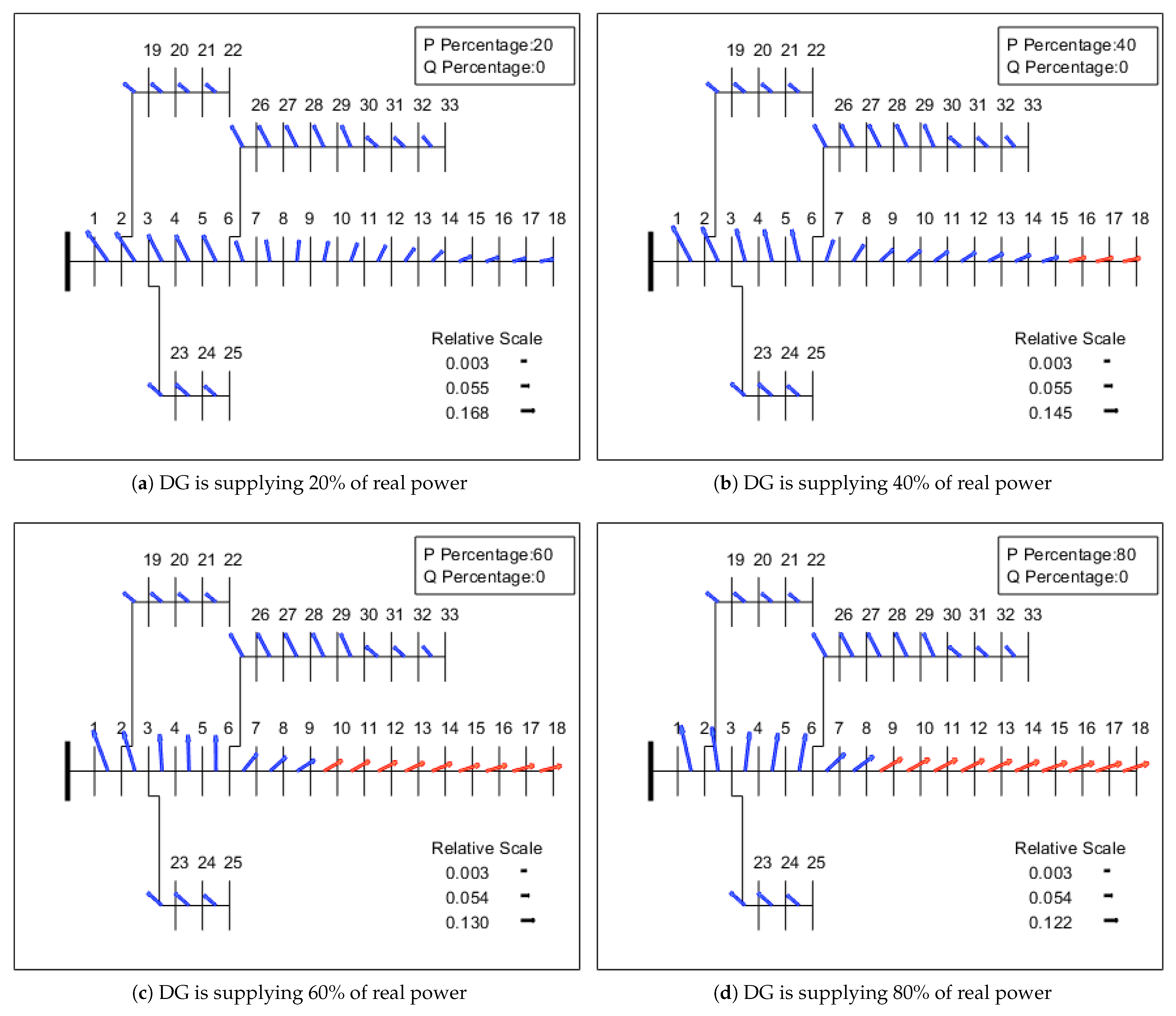
6.2. Quiver Plot
A quiver plot is a type of vector graph that illustrates the magnitude and direction attributes. These plots are widely used in flow visualisation and represent the weather and wind data. When line current data are projected as a quiver, the proportion of the real and imaginary parts of a current vector can be seen at the same time. Analysing the quiver properties such as magnitude, direction and location, the sphere of influence of respective sources can be identified. This section examines the visual way to determine the DG influence with varying sizing. Simulations are carried out by increasing the DG size at bus 18 from 20% to 100% of load and the quiver placement patterns are analysed and voltage violation are highlighted in red. When DG is supplying the real power of total load, the real current flows from DG and reactive current flows from the substation. So, the quiver is located in first quadrant.
As illustrated in Figure 6, when DG is supplying 20% of real power, the current reversal occurs until Section 8 of the line and there is no voltage violation in the network. Though there is a current reversal, DG supports the network by increasing the voltage level. However, when DG penetration is increased from 20% to 40% and 60% of total load, the sphere of influence of DG connected at bus 18 can be seen until bus 6 and exceeds the voltage threshold limit. For 40% of the load, the voltage violations are seen at buses 16, 17 and 18 and a greater number of buses, from 10 to 18, deal with voltage violation for 60% of the load. In the case where DG is supplying 80% of the load, the impact of DG is increased further until Section 3 of the line and voltage violation can be seen from buses 9 to 18.
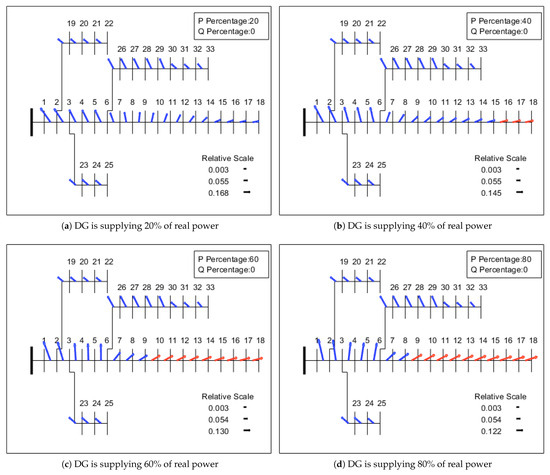
Figure 6.
Sphere of influence of DG supplying real power.
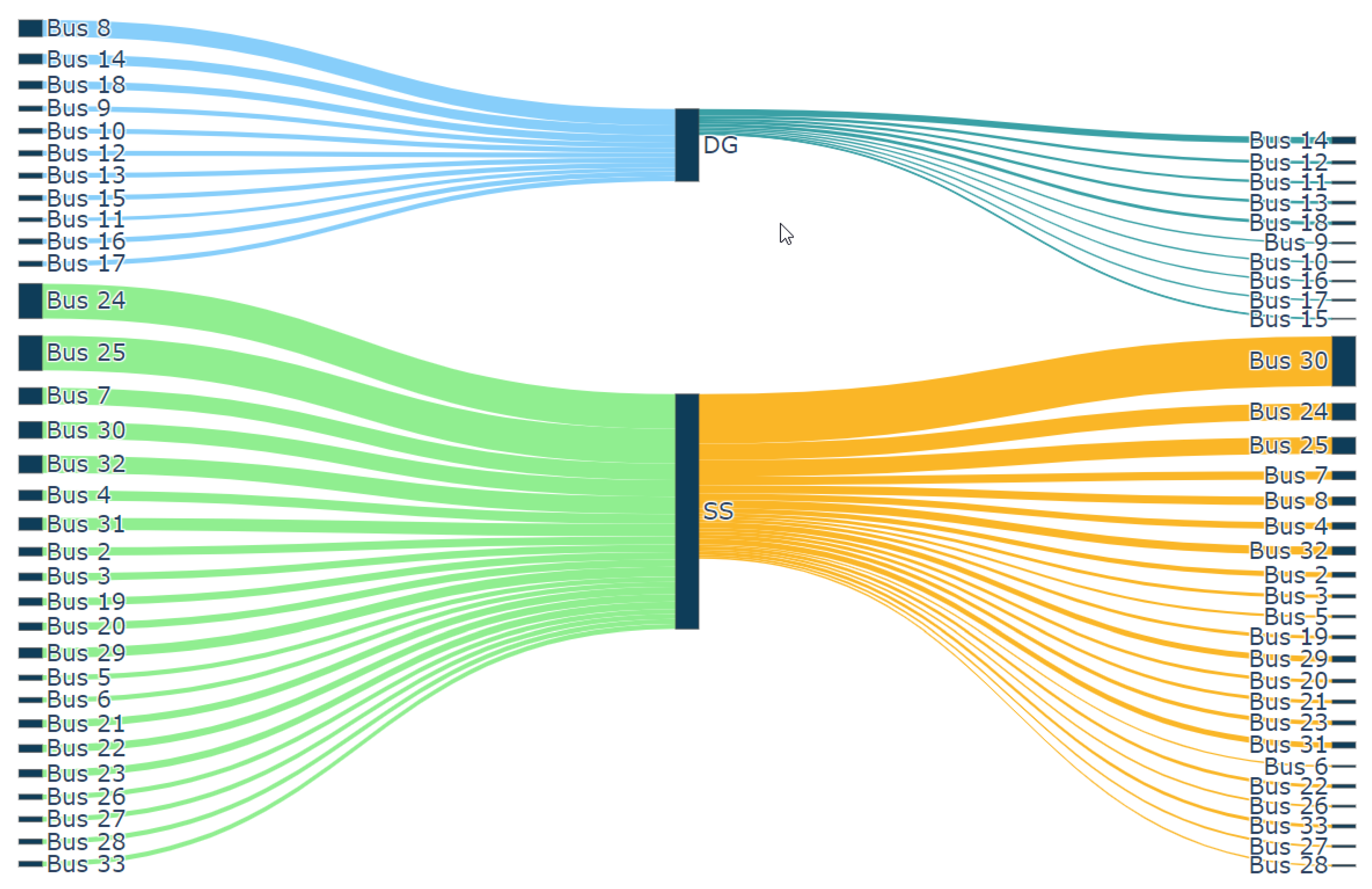
6.3. Sankey Chart
A Sankey chart is a type of visualisation that helps to visualise the flow of power from source to node. By analysing the flow of power from source to node, the impact of DG on the buses in the close vicinity and bus served by grid or respective DG can be determined. Further, network partitioning insights can be viewed intuitively and quickly through this visualisation approach.
In this case study, the simulation was carried out by connecting DG at bus 18 with DG supplying both 20% of real and reactive powers. As shown in Figure 7, the bus draws real and reactive powers from the grid and DG, respectively. As DG is connected to bus 18, an additional current flows from DG into the network, serving the real and reactive load demands from buses 9 to 18. In bus 8, DG serves real power demand while grid serves reactive power. All other buses from 1 to 7, and the three laterals of 19 to 22, 23 to 25 and 26 to 33, are served by the source. The width of the link from source and DG to respective buses depicts the real and reactive power drawn by the buses. The colour of the link shows the different zones of the DG and grid sphere. Through this Sankey visualisation, the sphere of influence of DG can be visualised intuitively.
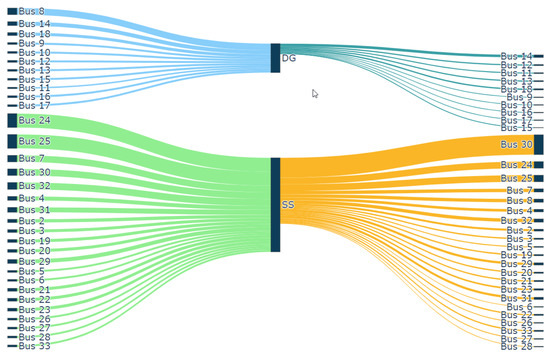
Figure 7.
Sankey diagram.
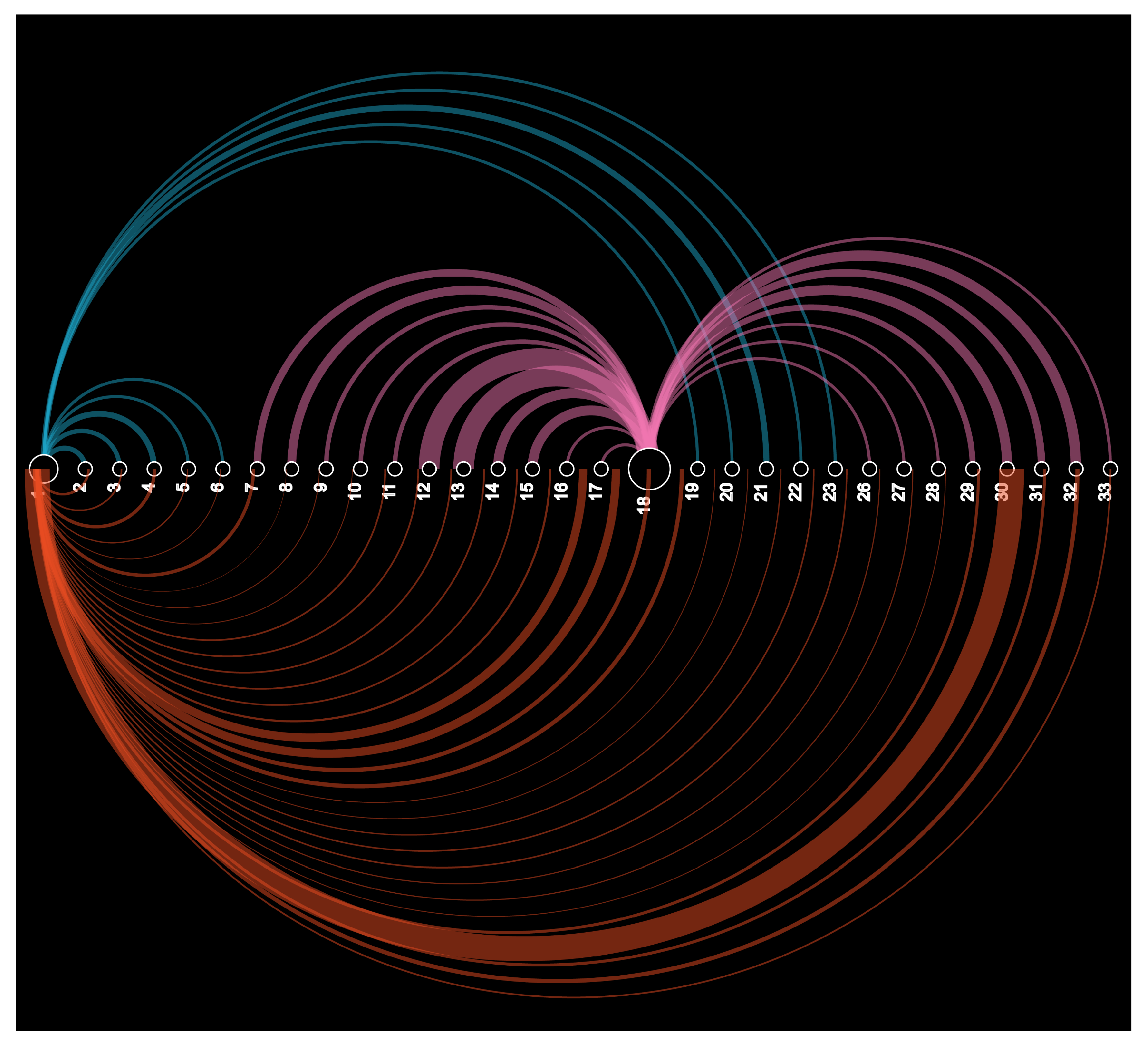
6.4. Arc Diagram
An arc diagram is a data visualisation technique that is commonly used to display network data [55]. It is particularly useful for visualising the connections between nodes in a network, as well as the flow of data or other quantities between nodes. In the context of power networks, an arc diagram can be used to visualise the flow of power between various nodes in the network, with colors representing different zones. By creating an arc diagram for a power network, operators can gain insight into the flow of power through the network, identify bottlenecks and other issues that could impact system stability, and plan system expansions or upgrades to improve the network’s efficiency and reliability. The results shown in Figure 8 portray the illustration of the sphere of influence of the DG in the 33 bus distribution systems connected at bus 18. As DG supplies 50% of the real power, the contribution of DG in the respective nodes from buses 7 to 18 and laterals 26 to 33 is clearly visible in the diagram. All other buses are served by the grid. Since the DG supplies only real power, all buses are served by the grid for the reactive power demand. This diagram can be incorporated with a geographical information system to address the necessary action required in the event of congestion and determine the critical node that needs immediate attention and the source of issues.
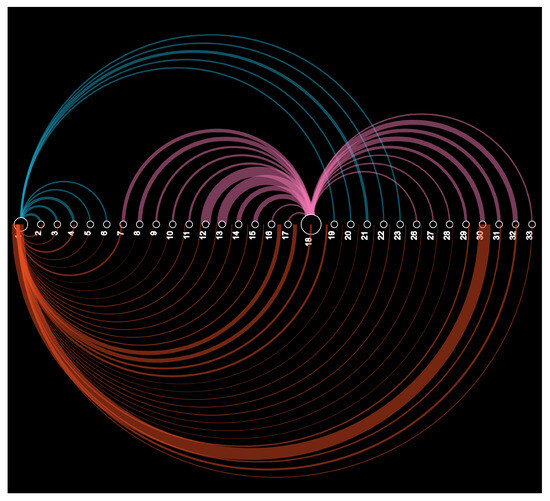
Figure 8.
Arc diagram when DG supplying 50% real power at bus 18.
6.5. Comparative Analyses of the Proposed Methods
This section presents comparative analyses of the three methods of power flow, sensitivity analyses and visualisation methods based on computational effort, output type, advantage and disadvantage, as depicted in Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparative analyses of the traditional analytical methods with the proposed methods.
7. Conclusions
Power system visualisation techniques have become increasingly important in recent years due to the growing complexity of power systems and the need for real-time data to maintain the reliability and stability of the grid. A systematic literature review of this topic reveals that there are a variety of visualisation techniques that can be used for different purposes, such as monitoring and control, energy management and power system protection.
The literature and simulation results suggest that visualisation can be effective in improving power system reliability, reducing the risk of blackouts and enabling the more efficient use of distributed energy resources. However, there are still challenges to overcome, such as the need for standardised visualisation techniques, the rendering of different visuals into existing power system operations and the need for more effective training and education for operators.
Overall, this paper highlights the potential benefits of using visualisation in power systems and the need for further research to develop more effective and efficient techniques that can be integrated seamlessly into power system operations to assess modern grids.
Author Contributions
Y.N.A.R.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review & Editing, Visualisation; A.P.A.: Conceptualization, Validation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision, Project Administration; K.M.: Conceptualization, Validation, Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision, Project Administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Charani Shandiz, S.; Rismanchi, B.; Foliente, G. Energy master planning for net-zero emission communities: State of the art and research challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110600. [Google Scholar]
- Rogelj, J.; Shindell, D.; Jiang, K.; Fifita, S.; Forster, P.; Ginzburg, V.; Handa, C.; Kheshgi, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Kriegler, E.; et al. Mitigation pathways compatible with 1.5 °C in the context of sustainable development. In Global Warming of 1.5 °C; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rogelj, J.; Shindell, D.; Jiang, K.; Fifita, S.; Forster, P.; Ginzburg, V.; Handa, C.; Kheshgi, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Kriegler, E.; et al. Net Zero Plan Stage 1: 2020–2030; NSW Government: Sydney, Australia, 2020.
- Bouckaert, S.; Pales, A.F.; McGlade, C.; Remme, U.; Wanner, B.; Varro, L.; D’Ambrosio, D.; Spencer, T.; Abergel, T.; Arsalane, Y.; et al. Net Zero by 2050 A Roadmap for the Global Energy Sector; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.B.; Islam, M.R.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Sutanto, D.; Agalgaonkar, A.P. Advancement of fuel cells and electrolyzers technologies and their applications to renewable-rich power grids. J. Energy Storage 2023, 62, 106842. [Google Scholar]
- Kharrazi, A.; Sreeram, V.; Mishra, Y. Assessment techniques of the impact of grid-tied rooftop photovoltaic generation on the power quality of low voltage distribution network—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 120, 109643. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Shafiullah, G.; Das, C.K.; Wong, K.W. A systematic review of optimal planning and deployment of distributed generation and energy storage systems in power networks. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 105937. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, K.; Agalgaonkar, A.P.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Perera, S. Distribution System Planning With Incorporating DG Reactive Capability and System Uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2012, 3, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, L.F.; Dent, C.J.; Harrison, G.P. Distribution network capacity assessment: Variable DG and active networks. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2009, 25, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Afandi, I.; Ciufo, P.; Agalgaonkar, A.; Perera, S. A holistic approach for integrated volt/var control in MV and LV networks. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 165, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Uzair, M.; Li, L.; Eskandari, M.; Hossain, J.; Zhu, J.G. Challenges, advances and future trends in AC microgrid protection: With a focus on intelligent learning methods. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 178, 113228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, L.; Meng, K.; Dong, Z.Y.; Muttaqi, K.; Du, W. Autonomous control strategy for microgrid operating modes smooth transition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 142159–142172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.A.; Majid, M.S.; Rezaee Jordehi, A.; Chin Kim, G.; Hassan, M.Y.; Fadhl, S.O. Operation and control strategies of integrated distributed energy resources: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, T.; Bompard, E.F. Big data analytics in smart grids: A review. Energy Inform. 2018, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigar, Y.; Agalgaonkar, A.P.; Muttaqi, K.M. Visualisation of spheres of influence of distributed generation through critical line flow analysis. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 34, 101046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigar, Y.; Agalgaonkar, A.P.; Muttaqi, K.M. Identification of Sphere of Influence of single and multiple DG Units through Visualisation in Distribution Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Global Conference on Computing, Power and Communication Technologies (GlobConPT), New Delhi, India, 23–25 September 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nigar, Y.; Agalgaonkar, A.P.; Muttaqi, K.M. Identification of Sphere of Influence of Single and Multiple DG Units in Distribution Networks: A Visualisation Approach Involving Sankey Diagrams and Geospatial Mapping. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 5362–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiranvand, A.; Cuffe, P. Sankey Network Diagrams to Depict Bulk Power Transactions for Operator Situational Awareness. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Madrid PowerTech, Madrid, Spain, 28 June–2 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cuffe, P.; Keane, A. Visualizing the electrical structure of power systems. IEEE Syst. J. 2015, 11, 1810–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiranvand, A.; Cuffe, P. A topological sorting approach to identify coherent cut-sets within power grids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 35, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.J.; Beiranvand, A.; Cuffe, P. Clustering nodes in a directed acyclic graph by identifying corridors of coherent flow. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th IEEE International Energy Conference (ENERGYCon), Gammarth, Tunisia, 28 September–1 October 2020; pp. 604–609. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, S.; Qiu, W.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, D.; Qian, M.; Yang, L. KPI-based Real-time Situational Awareness for Power Systems with a High Proportion of Renewable Energy Sources. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 8, 1060–1073. [Google Scholar]
- Overbye, T.J.; Weber, J.D. Visualization of power system data. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 7 January 2000; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Overbye, T.J. Visualizations for power system contingency analysis data. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2004, 19, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, F. Three-dimensional visualization and animation for power systems analysis. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2009, 79, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbye, T.J.; Rantanen, E.M.; Judd, S. Electric power control center visualization using geographic data views. In Proceedings of the 2007 iREP Symposium-Bulk Power System Dynamics and Control-VII. Revitalizing Operational Reliability, Charleston, SC, USA, 19–24 August 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Overbye, T.J.; Wert, J.; Birchfield, A.; Weber, J.D. Wide-area electric grid visualization using pseudo-geographic mosaic displays. In Proceedings of the 2019 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Wichita, KS, USA, 13–15 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Thiyagarajah, A.; Carlson, B.; Bann, J.; Mirheydar, M.; Mokhtari, S. Seeing results in a full graphics environment. IEEE Comput. Appl. Power 1993, 6, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, H.; Christie, R.D. Visualizing voltage profiles for large scale power systems. IEEE Comput. Appl. Power 1997, 10, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbye, T.J.; Weber, J.D. Visualizing the electric grid. IEEE Spectr. 2001, 38, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, J.D.; Overbye, T.J. Voltage contours for power system visualization. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2000, 15, 404–409. [Google Scholar]
- Overbye, T.J.; Wiegmann, D.A.; Rich, A.M.; Sun, Y. Human factors aspects of power system voltage contour visualizations. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2003, 18, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Hirsch, P.; Lee, S. Wide area frequency visualization using smart client technology. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, Tampa, FL, USA, 24–28 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nigar, Y.; Agalgaonkar, A.P.; Ciufo, P. Impact of variable solar PV generation on MV distribution systems. In Proceedings of the 2014 Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference (AUPEC), Perth, WA, Australia, 28 September–1 October 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Overbye, T.J.; Weber, J.D. Visualization of large scale power systems. In Proceedings of the EPSOM’98, Zurich, Switzerland, 23–25 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Klump, R.; Dooley, G.; Wu, W. Displaying aggregate data, interrelated quantities, and data trends in electric power systems. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, 6–9 January 2003; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Ye, Y.; Markham, P.; Bank, J.; Dong, J.; Yuan, Z.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Y. Visualization of wide area measurement information from the FNET system. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Detroit, MI, USA, 24–28 July 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Overbye, T.J.; Weber, J. Smart grid wide-area transmission system visualization. Engineering 2015, 1, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Overbye, T.J. Feature extraction and visualization of power system transient stability results. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 29, 966–973. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Alimisis, V.; Milanović, J.V.; Taylor, P.C. Probabilistic assessment of voltage control zones and visualization using choropleth map. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Manchester PowerTech, Manchester, UK, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Guo, F.; Ma, Y.; Chen, W. A survey of network anomaly visualization. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2017, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschenbach, T.G. Spiderplots versus tornado diagrams for sensitivity analysis. Interfaces 1992, 22, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Rueda, J.; Colome, D. Probabilistic performance indexes for small signal stability enhancement in weak wind-hydro-thermal power systems. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2009, 3, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guan, M.; Huang, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Savić, D. Visualisation of the combinatorial effects within evolutionary algorithms: The compass plot. J. Hydroinformatics 2021, 23, 517–528. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, Y.F.; Towsey, M.; Roe, P. Revealing the ecological content of long-duration audio-recordings of the environment through clustering and visualisation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigar, Y.; Agalgaonkar, A.P.; Muttaqi, K.M. Unveiling the Dynamic Influence Zones of Distributed Generation Units Using a Visualisation Approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Energy Technologies for Future Grids (ETFG), Wollongong, Australia, 3–6 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Daki, H.; El Hannani, A.; Aqqal, A.; Haidine, A.; Dahbi, A. Big Data management in smart grid: Concepts, requirements and implementation. J. Big Data 2017, 4, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Diamantoulakis, P.D.; Kapinas, V.M.; Karagiannidis, G.K. Big Data Analytics for Dynamic Energy Management in Smart Grids. Big Data Res. 2015, 2, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S.; Wu, C. Data quality of electricity consumption data in a smart grid environment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 75, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, C.; He, X.; Shuai, Z.; Jiang, F. Big data issues in smart grid—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, W.; Saunders, C.; Gao, F.; Yu, Y. Real-time complex event processing and analytics for smart grid. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 61, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milić, S.D.; Đurović, Ž.; Stojanović, M.D. Data science and machine learning in the IIoT concepts of power plants. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 145, 108711. [Google Scholar]
- Ponnusamy, V.K.; Kasinathan, P.; Madurai Elavarasan, R.; Ramanathan, V.; Anandan, R.K.; Subramaniam, U.; Ghosh, A.; Hossain, E. A Comprehensive Review on Sustainable Aspects of Big Data Analytics for the Smart Grid. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega Penagos, C.A.; Diaz, J.L.; Rodriguez-Martinez, O.F.; Andrade, F.; Luna, A.C. Metrics and Strategies Used in Power Grid Resilience. Energies 2023, 17, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, T.; Duval, E. A visual survey of arc diagrams. In Proceedings of the IEEE Visualization, Atlanta, GA, USA, 13–18 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hossam-Eldin, A.A.; Abdelaziz, A.R.; Fard, A.E.I.A. A simulated annealing-based automation of distribution systems. In Proceedings of the 45th International Universities Power Engineering Conference UPEC2010, Cardiff, UK, 31 August–3 September 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).