Abstract
Earth–Air Heat Exchange (EAHE) systems are an eco-friendly and energy-efficient technology as pre-heating or pre-cooling systems in civil buildings. Technically, the performance of the EAHE system is influenced by properties associated with the technology. In this paper, the focus is placed on the properties covered by the published literature to understand how they impact the efficiency of these systems. The review scrutinizes the implication of pipe properties such as the material type (steel, Polyvinyl Chloride [PVC], concrete, or high-density polyethylene), diameter and length, and depth in the context of modern building design and energy conservation. Other properties considered in this work are air velocity and the bonding of pipes with the soil. The EAHE systems’ performance is not significantly influenced by the pipe material, unlike the pipe length and diameter. It is reported that longer pipes enhance the cooling output in the EAHE system. The pipe length positively correlates with the in-pipe air temperature. An increment in the pipe diameter led to a drop in the in-pipe air temperature. An indicative report states that an increasing air flow velocity can lead to thermal losses from pipes to their surrounding soil. The addition of sand below and above the pipe enhances the thermal conductivity, just as an increase in the moisture content of the soil will contribute. There are attempts to use additives, construction waste, graphite, and fly ash as a backfill material, but with opposing economic feasibility. Construction waste could help the EAHE system to improve by 80%. A combination of graphite and fly ash as a backfill material is cost-effective. Research on the pipe material type and standards development are limited. Overall, the pipe material type and length to adopt for an EAHE system are based on the funds’ availability for the construction.
1. Introduction and Background Analysis
Passive systems are valued due to their ability to minimize energy usage for cooling and heating in buildings. They can achieve interior thermal comfort using natural energy resources. The growing need for energy-efficient and sustainable building solutions has given significant attention to Earth–Air Heat Exchangers (EAHE). The system has been identified as a feasible option for conventional cooling and heating systems. Potentially, it can help reduce heat consumption when coupled with traditional air conditioning systems. This technology is a green and energy-efficient way to heat or cool indoor environments based on geothermal energy. An Earth-to-Air Heat Exchanger could be efficiently integrated into Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems for significant energy savings [1]. EAHE systems provide a cost-effective solution that reduces the energy consumption of typical air conditioning appliances. Generally, it exploits the stable sub-surface temperature.
1.1. Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy (GE) is the natural heat associated with the Earth. It drives geological activity on a global scale. GE is both renewable and sustainable. It has many applications including district heating, the space cooling and heating of buildings, power generation, etc. It has significant potential to meet countries’ energy demands [2]. GE is a measure of how the surface temperature of the Earth increases with depth. According to Cadelano et al. [3], geothermal systems can improve HVAC energy efficiency and renewable energy use in museums without compromising indoor conditions. The ground temperature at relatively shallow depths can already reach a level that is greater than the atmospheric temperature in winter and lower in summer. Beyond a depth of 10 m, this temperature remains relatively constant throughout the year. The most common way to classify geothermal resources is by geothermal fluid’s enthalpy. It transfers heat from deeply embedded hot rocks to the surface of the ground [4]. Using this classification, Trota et al. [5] assessed the feasibility of geothermal power at two sites in Portugal. They confirmed both the low- and high-enthalpy geothermal resources. The heat capacity of the Earth for air conditioning buildings is more effective in regions with large temperature variations, either daily (like in desert environments) or seasonally (like in temperate climates) [6].
1.2. Recent Applications of Geothermal Systems
There have been efforts to generate energy-efficient and ecologically friendly geothermal solutions. First, an Italian project entitled GEOGRID was developed to create novel methods and structures for the sustainable use of GE throughout enthalpy sources that are low, moderate, and high [7]. The outcomes of the GEOGRID initiative have resulted in an extension of research towards international applications. It was to provide cooling to Emirates through the utilization of GE of low enthalpy [8]. Second, Battaglia et al. presented a framework for measuring GE communities on a worldwide scale [9]. In their study, a network of four-pipe district cooling and heating was installed and linked to a plant of an Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC). This application uses GE from the Solfatara region, to offer residential facilities such as hot water and direct heating in the cold season. The establishment of geothermal plants, like other forms of energy facilities, may have a considerable economic influence on regional or local economies. Both economic and environmental development strategists will be interested in the scales of these consequences. GE is relatively easy to utilize and available. Pishkariahmadabad et al. [10] worked on an economic–thermal analysis of a ground heat pump used domestically for geothermal technologies’ economic aspects by using different working fluids. The study deduced that decreasing the cycle evaporator pressure will lower the cost for generating a unit of energy. Another economic and energetic investigation conducted by D’Agostino et al. [11] compared the Air-to-Air and Earth-to-Air heat exchangers’ performance as HVAC systems for office buildings in Italy. They analyzed the lowered payback durations of both systems and offered clues into their financial sustainability. Additionally, a techno-economic study was undertaken to analyze the energy capacity extracted from the geothermal fluid. They emphasized assessing the system’s energy and ecological effectiveness within the context of renewable energy societies [9].
1.3. Energy Consumption in Buildings
Buildings are the world’s greatest energy consumer and account for over one-third of the total power consumption. They are equally a crucial source of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions [12]. Significant energy and carbon reductions in the building or housing sector are a difficult but attainable policy aim. In Europe, buildings account for about 40% of the total national primary energy consumption. A significant portion of the residential building stock is distinguished by outdated technical and thermal design elements. In effect, lowering the usage of energy in buildings would result in significant energy savings. Natural gas, coal, and crude oil are among the non-renewable energy sources used worldwide. Annually, natural gas constitutes over 50% of the energy that buildings consume. Therefore, the savings to be realized by an increase in the energy performance within buildings will have a major impact on natural gas imports [13]. The discussion above contributes to the justification of increased global concern and interest for energy-efficient buildings.
Traditional systems for cooling and heating rely largely on fossil fuels. This dependency results in substantial environmental implications, despite the high energy costs. The environmental challenges include continued the global temperature rise, the worsening of greenhouse and urban heat island impacts, the deterioration of interior air quality, and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions [14]. A potential solution to ameliorate the challenges is to develop and use renewable energy-based technologies centered on geothermal, wind, solar, and biomass resources [15,16]. GE has been in use for several decades, especially beyond the global crisis for crude oil in 1973 [17]. Regarding heating/cooling, many passive approaches are employed such as wind towers, Trombe/solar walls, solar chimneys, cross-ventilation, phase change materials (PCM), evaporating cooling, heat insulation, etc., [18]. The ground-coupled systems can be effectively used for both purposes (cooling in summer and heating in winter) and depict the operation of some passive heating/cooling systems. Among the many promising solutions, the Earth-to-Air Heat Eexchanger (EAHE) has become an alternative for enhancing buildings’ energy efficiency.
1.4. Geothermal Role in EAHE
Geothermal energy has a unique advantage. The temperature of the soil at a specified depth, where an EAHE can be installed, remains relatively stable throughout the year [19]. The soil temperature changes both daily and seasonally, mainly influenced by sun radiation and an atmospheric temperature. During daylight, the ground surfaces absorb energy from the sun, causing the temperature to rise. Some of this thermal power is re-emitted into the air through evaporation and convection, while the remainder is transferred to the subsurface. Due to the temporal delay of temperatures between the subsoil and ground surface, there is temperature stability in the subsoil year-round [20]. The fluctuations in the ground temperature are not as significant as the seasonal fluctuations in the external air temperature. Moreover, to mitigate these fluctuations, which can affect the operation of geothermal systems, there are regulatory strategies that focus on HVAC systems, rather than being specific to these systems. Furthermore, the ground temperature within deeper depths roughly equals the air’s yearly mean temperature. Winter temperatures are higher than those at the surface of the Earth, but summer temperatures are lower than those at the surface [21]. This accounts for the soil’s double function as a source and heat sink even though it functions both as a cooling and heating medium [22].
1.5. EAHE Systems’ Component and Operation
The EAHE origins date back to ancient civilizations that recognized the Earth’s thermal properties and used them for several purposes [23]. In the building sector, EAHE systems are widely used in both residential and commercial properties. They are used for ventilation [24], agricultural climate control, process cooling [25], and space heating and cooling [26]. An EAHE system utilizes below-ground soil for a heat exchange using air as the transfer medium. In the cold season, it releases heat into the subsoil, while in the hot season, it extracts heat from the subsoil, taking advantage of the Earth’s stable subsurface temperature [27]. An EAHE system consists of a subterranean duct and a ventilation shaft with a filter system that regulates the air temperature. A fan directs the heated or cooled air into the room. By conditioning the incoming air, EAHE systems help decrease the load on traditional HVAC systems, Figure 1. They also enhance the indoor air quality by supplying fresh and filtered air. EAHE systems are generally categorized into two types: (1) open-loop systems [28], where fresh outdoor air is either precooled or preheated by passing through pipelines hidden underground, and (2) closed-loop systems [29], where air from within the building flows through pipes buried underground and circulates between the interior and the subsurface.
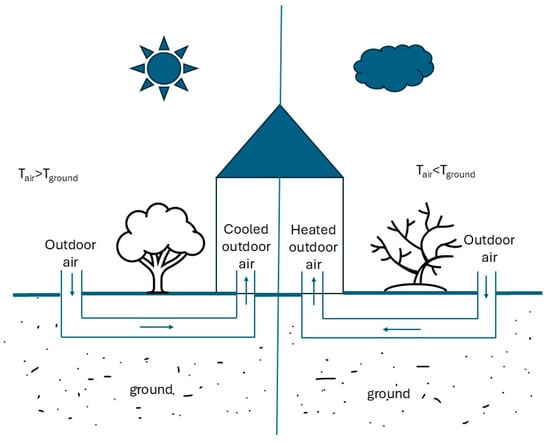
Figure 1.
EAHA system for pre-cooling and pre-heating the outdoor air in summer and in winter season.
1.6. Application and Benefits of EAHE
There are research studies on the integration of the EAHE system with civil buildings and with greenhouses. Chel and Tiwari [30] implemented an EAHE system inside an earthen home. The author found that in winter, the indoor air temperature was 5–15 °C more than the temperature of the ambient air. The integration of the EAHE system also resulted in a yearly energy saving estimate of 5375 kWh. Rodrigues et al. [31] found that integrating an EAHE system with PCM reduced room temperature instability by 47%. Deglin et al. [32] highlighted the importance of factors such as the soil type, air speed, and pipe parameters. These characteristics significantly affected the efficiency of the heat exchange between the soil and the air in motion within the pipes. In Taiwan, Hsu et al. [33] analyzed a monitoring study of an EAHE system which has seven underground pipes for the long term with a length of 50 m and a diameter of 0.24 m in a restaurant building. The results demonstrated that the technique achieved a yearly coefficient of performance (COP) of 27.
Boutera et al. [34] examined the effectiveness of an EAHE to improve indoor conditions for industrial-scale poultry farms, alongside the assessment of its energy-economic advantages. Li et al. [35] applied an evolutionary algorithm to optimize different parameter sets for EAHE-integrated buildings combined with thermoelectric and photovoltaic technologies. The outcomes indicated that the combinations of the improved technology parameters were suitable for the cases. Additionally, for the Algerian semi-arid climate, Belloufi et al. [36] investigated the EAHE’s behavior functioning in the cooling mode under transient situations. The system featured a single horizontal coil, 53 m in length and with a surface area of 85 m2. Their findings indicated that the EAHE was able to achieve an air temperature difference of nearly 10 °C, dropping the temperature of the air to 30 °C. Maerefat and Haghighi [37] explored passive cooling for buildings by combining an Earth-to-Air Heat Exchanger with solar chimneys during hot seasons. Aslan et al. [38] conducted a one-year monitoring of a geothermal district heating system in Turkey. The authors reported that the energy efficiency ranged from 36% to 57%, while the exergy efficiency varied between 41% and 56%, depending on the operating conditions. Soni et al. [39] observed that in Bhopal, India, the ground temperature stayed stable at around 30 °C beyond 2.6 m.
Ahmed et al. [40] set up 20 horizontal pipes (7.5 m long and 0.7 m deep) over an 8 × 2 m area to compare conventional and heat exchanger-ventilated systems. The maximum difference in temperature was 2 °C once the temperature outside was above 34.1 °C. Ozgener [41,42] evaluated the exergoeconomic and exergetic efficiency of the subterranean air tube system used for cooling and heating the greenhouse. Qi et al. [43] introduced an indicator (η) that combines the heat transfer efficiency and pressure drop to assess the overall performance of a multi-pipe EAHE in enhancing the greenhouse thermal environment. Florides and Kalogirou [44] reviewed ground heat exchanger systems, covering various types, models, and applications. They discussed different system configurations and calculation methods. Gan [45] studied how atmospheric conditions and heat exchanger–environment interactions influence the system’s efficiency. In [46] and [47], the authors used TRNSYS to analyze a hybrid system with a solar chimney, an EAHE, and fan, showing it could lower indoor temperatures by 8–9 °C below ambient, especially at sunset.
1.7. General Analysis of the Geothermal Energy Systems
There are many technologies that exploit geothermal energy. In fact, it can be used for Ground Source Heat Pump (GSHP) and Earth–Air Heat Exchanger (EAHE) systems. These systems use shallow-soil geothermal energy as a heat source and heat sink for winter and summer air conditioning, respectively. The system is also known as a ground-source heat exchanger (GSHP) or ground-coupled heat exchanger (GCHE) when air runs into underground ducts for both cooling and heating. The foundation pathways engaged with air conditioning from geothermal energy are (i) the GSHP system and (ii) the EAHE system for supplying interior thermal comfort. When compared to the air temperature, some scientists discovered that over a depth of 3.1 m, the ground keeps a temperature which is steady, known as the undisturbed temperature of soil [48]. The EAHE system relies on air as the working fluid, which permits the circulation via tunnels dug at a level of roughly 2.2–3.1 m [49]. Otherwise, the GSHP system utilizes liquid (water/anti-freezing liquid/refrigerants) as the dynamic medium [50]. Generally, EAHE pipes are often put horizontally at a depth of 2–5 m, whereas GSHP pipes are typically erected vertically at a depth of 20–200 m [51,52]. However, there are lower-depth GSHP technologies, utilizing a parallel duct arrangement at a depth of between 1.9 and 5.1 m from the soil. A pipe with a vertical arrangement can also be employed for EAHE systems with depths greater than 4 m. Therefore, the size of the available land area and the installation expenses determine the preference [53,54]. In this paper, the focus will be on the EAHX and its proprieties. This present study is an attempt to highlight updated knowledge regarding the performance of the EAHE system.
2. Methodology
This review article dives into scientific databases on the EAHE from 1981 to the present, covering journal publishers such as Springer, Scopus, Web of Science, etc. Additional literature was taken from books, theses, and conference proceedings. The searches were carried out using related keywords or phrases to the topic. They included earth–air heat exchangers, earth tube air heat exchangers, earth pipe air heat exchangers, buried pipe systems, ground-to-air heat exchangers, and underground air tunnels.
Presented in the earlier chapter is the overview of the EAHE system as a sustainable green technology. This work continues in the next chapters to cover the individual properties with potential influence on the performance of EAHE. It outlines subsections on pipes’ description and their impact, the system’s air velocity, bonding of installed pipes, and soil with backfilling materials. This review concludes with a summary of key points from the literature cited and a provision of perspective.
3. Pipes in Earth-to-Air Heat Exchange Systems
The pipe acts as a medium for heat exchange, linking the passing fluid (e.g., antifreeze or water) within the pipe and the backfill or surrounding soil. Its substance may possess thermal conductivity that is high for improving the efficiency of transferring the heat in both directions. Additionally, to be durable, easy to install, robust, adaptable, and cost-effective, the pipe should be versatile and flexible as well as able to withstand wear, damage, and leaks [55]. The geometric configuration and thermal properties of the pipe are crucial factors that significantly impact the behavior of an EAHE system. A properly functioning EAHE system takes several factors into account. These include the pipe material, length, diameter, spacing, number, soil type, burial depth, and air flow rate. There are no compressors, burners, or chemicals required for the EAHE system. The system just uses blowers to circulate the air, it is a feasible and economical option for replacing conventional air-conditioning systems. Heat is transferred between the air and soil by the pipes within the Earth–Air Heat Exchange systems. Generally, pipes are constructed of materials that have high thermal conductivity, are resistant to corrosion, and are durable. Typical components for Earth–Air Heat Exchanger pipes are PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), Ductile Iron, and HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) [56]. Geothermal systems operate most efficiently while the circuit’s pipes are placed in the ground, having significant thermal conduction and excellent heat transfer properties. Thus, it is essential to choose a geographical location that has favorable condition characteristics, like sandstone, wet, or sandy soil to ensure the best system efficiency [57]. The local climate, the conditions of the soil, and the availability of resources all influence the choice of material.
3.1. Impact of Pipe Properties on EAHE Technology
The geometrical characteristics include the pipe spacing and arrangement type (helical, vertical, horizontal, and spiral), the type of material, the pipe diameter, and the length. These are fundamental parameters that influence the output of the EAHE system. The next subsections have a short view of these parameters.
3.1.1. Pipe Material Type
Regarding EAHE pipes, several materials such as rough-cast iron, aluminum, polyethylene, plastic, and concrete may be useful [58,59]. The material of the gas duct in several technologies such as a thermoelectric converter unit influences energy saving [60]. Many studies have evaluated the influence of internal and external pipe parameters on the performance of EAHEs during the summer and winter seasons. However, the impact of the pipe material was explored less thoroughly than the other parameters [61]. Rosa et al. [62] studied the effects of the pipe spacing, pipe diameter, and air velocity. They discovered that the key criteria influencing the EAHE performance are the pipe diameter and the air velocity. Furthermore, the distance between the two pipes may be lowered to 0.5 m. Bansal et al. [63] investigated the heating capacity and assessed the potential of cooling and heating for two EAHEs made from mainly steel and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) materials. The authors concluded that the material of pipes possessed no influence of the EAHE system efficiency. Serageldin et al. [64] evaluated the thermal performance of an EAHE system developed and installed to offer heat and cooling for Egyptian premises. It studied how various operation parameters and designs, such as the airflow velocity, distance between pipes, length of pipe, duct material, and diameter of the pipe influence the performance of the system. The findings indicate that several of these characteristics have a discernible effect on the temperature of the air. When the diameter of a pipe rises, the temperature of the air drops. For instance, as the pipe diameter increases from 50.8 mm to 76.2 mm, the air temperature output drops from 20 °C to 18.6 °C. In addition, if the pipe length increases, so does the outlet air temperature. A pipe length increment from 5 m to 7.1 m causes a rise in temperature from 19.6 °C to near 20 °C. When the pipe spacing is increased (20–50 cm), the exit air temperature barely changes (19.6 °C to 19.7 °C). Rosa et al. [65] investigated the impact of various design characteristics, including the material of the pipe. They observed that the pipe had no meaningful effect after upgrading from PVC to steel. Therefore, according to the literature, the pipe material does not affect the EAHE performance, making cost-effective options like PVC a suitable choice for EAHE systems [66].
3.1.2. Effect of Pipe Length and Diameter
The initial investment of an EAHE system can be significant owing to the need for longer pipes and greater excavation costs. The expenditure of digging the trench accounts for around 25–30% of the entire cost of installing an EAHE system [66,67]. To maximize the economic sustainability of an EAHE system, the trench and pipe lengths must be reduced. The pipe length needed for the construction of any EAHE system may greatly decrease with enhancing the heat conductivity of the soil surrounding the pipe [66]. The thermal conductivity of the soil near a pipe could be enhanced with the use of soil that has better thermal conductivity (not natural soil) as the material for backfilling (BFM) or by raising the moisture content of the soil. Bansal et al. [68] conducted a thermal performance analysis for various EAHE pipe lengths in India. Their study also considered the influence of soil thermal conductivity and the time duration of continuous EAHE operation. The pipe diameter also has a significant impact on the thermal efficiency of eco-friendly technology [47]. A study on system behavior was conducted by Agrawal et al. [67] using pipe sizes of 50 mm, 75 mm, and 100 mm. They discovered that after 6 h of continuous operation, a reduction in the temperature of the air with a length of 30 m was 13 °C, 11.4 °C, and 8.6 °C for GAHE with soil that was dry; 13.2 °C, 12.2 °C, and 11 °C for GAHE with soil that was wet (a moisture content of 5% [MC]); and 13.4 °C, 12.7 °C, and 11 °C for soil with 20.2% MC with pipes with a 50, 75, and 100 mm diameter, respectively. The outcomes demonstrate that increasing the pipe diameter reduces the decrease in the temperature of the air, achieved with a length of 30 m. This may be attributed to the fact that increasing the diameter of the pipe increases the distance between the soil layer and the center of the pipe. An extended pipe length enhances the cooling efficiency by increasing the duration of air contact with the pipe’s surface, allowing for a greater heat exchange, as observed in EAHE systems [69].
3.1.3. Pipe Depth
Knowledge of the distribution of the subsoil temperature and its fluctuation with depth is essential in constructing the EAHE system. The mechanical qualities and layout of the soil, as well as the cover of the soil surface, all have an impact on the dispersion of soil temperatures [44]. An increment in depth narrows the variation in the ground temperature. The ground level temperature changes according to daily time (seasonal and diurnal). The stable temperature of the ground is typically determined for a 1.9 to 4.1 m depth. However, in certain locations, it may be greater than 4.1 m. A prediction of the soil thermal property is feasible at various depths by adopting Equation (1) [70] and the temperature of the soil surface at any latitude by Equation (2) [71]:
where Tm is the mean annual ground surface temperature (K); As is the surface temperature amplitude (K); z is the depth (m); α is the soil thermal diffusivity (m2/h); t is time referring to the beginning of the year (days); and t0 is the phase constant.
where
in which the soil thermal conductivity is is the ground surface temperature, and is the temperature of the air above the ground surface. The latent heat flow of ground surface evaporation is , is the soil surface’s convective heat transfer coefficient, and S is the Earth’s surface’s incoming solar radiation. The absorptivity at the ground surface is and represents the Earth’s surface’s emittance, whereas is dependent on the effective sky temperature, soil radiative characteristics, and the relative humidity of the air above and below the ground. is the wind speed above the surface of the Earth and F(u) is determined by the wind velocity, is the saturation vapor pressure on the ground’s surface, while is the vapor pressure on the surface above it.
The burial depth needs to be adequate to achieve a zone of a relatively steady temperature while reducing digging costs [72]. With regards to this, there have been studies targeted at finding the optimal buried depth of the pipe. Mihalakakou et al. [73] investigated the pipe depth effect on the performance in a cooling mode using depths of 1 m, 2.1 m, and 3.2 m. It was determined that a pipe at a depth of 3 m provided the best cooling. Kaushal [28] found that increasing the burial depth beyond 3.5 m results in only marginal performance improvements. However, the ideal depth depends on the specific location and site conditions. A piece of research work run by Ahmed et al. [74] evaluated the thermal performance of the horizontal earth pipe cooling system (HEPC) at pipe depths of 0.6 m, 2 m, 4 m, and 8 m and found that the cooling effect is increased at an 8 m pipe depth. Wu et al. [20] analyzed the thermal performance of an EATHE system by comparing two burial depths (3.2 m and 1.6 m). They found that during summer cooling, the outlet air temperature ranged from 25 °C to 30 °C at a depth of 3.2 m and 27 °C to 31 °C at a depth of 1.6 m. Depth variations are influenced by factors such as local ground temperature profiles, soil properties, and climate conditions. Ref. [75] identified 1 m as the optimal depth in Malaysia, whereas Khan et al. [76] recommended 4.5 m for Lahore, Pakistan.
4. Effect of Air Velocity
The reduction in the total temperature variation between in-flow and out-flow air indicates that the air velocity within a pipe underground affects the operation of the EAHE technology [77]. The capacity to cool/heat and the system’s performance are mostly determined by the airflow rate [78,79]. The impact of a varied airflow velocity was studied using four different levels: 2, 5, 8, and 10 m/s [67]. This study found that as the airflow velocity rises, there are thermal losses from the pipes to the surrounding soil, altering the temperature noticeably. An increased soil moisture content, on the other hand, mitigates the negative effects of the increased velocity of the airflow. Heat transmitted to the surrounding ground layer is sustained by the moisture. Overall, this causes an improvement in the energy efficiency. Another study indicated that during summer cooling, the highest air temperature decrease was with an air velocity of 2.1 m/s and the maximum hourly cooling was with 5.2 m/s [80]. Similarly, Wu et al. [20] reported a rise in temperature for the out-flow air and conductivity as the velocity of air increased (starting with near to 0.9 until 4.2 m/s, caused by a higher flow rate of mass). There is around a 2-fold increase in the coefficient convective thermal transfer when the air velocity goes up from 2 m/s to 5 m/s, whereas the period of the remaining air in touch with the soil is reduced by a factor close to 2.4. Dubey et al. [81] found that the temperature of the air lowered from 9 to 4.2 °C, while the coefficient of performance (COP) dropped from 6 to 3.7 when the air speed increased from 4 to 12 m/s. Taking different stream speeds for cooling operation (2.5, 2, 1.5, 1, and 0.5 m/s), Niu et al. [82] discovered that the air temperature drop rate was greatest for the lower velocity, which gives a longer interaction time between the pipe and air. Abdelkrim et al. [83] used the number of Reynolds to evaluate the efficiency of an EAHE system and concluded that the air residence time within the pipe decreases as the Reynolds number increases, raising the out-flow air temperature in the case of the cooling operation. A numerical parametric investigation was conducted by Ahmed et al. [74], using four different air speeds to evaluate the air velocity effect on the thermal behavior of the pipe–Earth technic during the cooling operation. An air flow of about 1.4 m/s was the best option for the summer performance based on their report.
5. Bonding of Soil with Pipes
The practice of bonding soil with pipes, also known as a soil–pipe interaction, is a crucial part of geotechnical and civil engineering. It entails connecting subterranean pipes to the surrounding soil, assuring the stability and integrity of the buried infrastructure [84]. This bonding procedure is critical in avoiding pipe movement or damage, especially during water supply, sewage, and utility applications. The soil–pipe interaction is influenced by various factors, including the type of soil, pipe material, and installation techniques. A strong bond between the pipes and the ground ensures an efficient energy exchange. The pipes should have firm contact with the soil to avoid heat losses through debonding. Gaps left around the pipe increase the resistance of heat and impedes a thermal transmission from below ground to the installed pipe. Heat conduction between pipes and soil can be improved by embedding pipes in materials whose properties facilitate the conduction of heat. It is possible to enhance thermal contact by adding a layer of sand below the pipes and above them [85].
A significant portion of EAHE efficiency is centered around the type of soil surrounding the pipe and the compaction procedure. Heat is transferred more effectively from soil with higher moisture levels due to their greater thermal conductivity. Backfilling the pipes properly eliminates air gaps [86], which can act as insulators and hinder a heat transfer [87]. The material used for backfilling (sand and/or gravel) occupies the gap left after pipe installation below ground. It can consist of natural soil, or a blend of additional materials designed to enhance the thermal connection between the EAHE and the surrounding soil [88].
Some studies have investigated how the backfill material influences the performance of green energy technology [89,90]. The authors emphasize the impact of incorporating additives like graphite, cement, slag, and steel fibers into backfill materials to enhance their thermal and mechanical properties. However, as noted in [91], the high cost of materials such as graphite and large quantities of steel fibers makes their use in backfill applications economically unfeasible. Additionally, research nowadays is about the utilization of backfill materials issued from solid industrial waste. The idea is to improve thermal effectiveness for the EAHE while lowering the installation costs. A research study addressed the viability of reusing manufacturing and construction waste products [92]. The findings demonstrated that metallic waste products as the backfill had a greater thermal performance, almost 80%, compared to sand as the backfill. The observed improvement indicates a beneficial compromise among the lifecycle cost (LCC) and thermal efficiency. A combination of graphite and fly ash (FA) waste was used as a backfill material to increase the heat transfer. The same study mentioned that it is a cost-effective alternative to traditional backfill options [93]. Głuchowski investigated the possibility of obtaining backfill materials from FA, recycled concrete aggregate (RCA), and its combination [94]. It was found that the mixture of FA + RCA confirmed the thermal conductivity that was high with a negligible error. This contributes to decreasing the system’s resistivity and led to cost saving over the lifecycle of the system.
Jahanbin [95] found that the use of increased heat conductivity materials as the backfill could raise the temperature at the surface of a system and reduce the heat resistance. Enhancing the backfill material’s heat conductivity helps to reduce the temperature gradient between the pipe and the surrounding soil, thereby improving the efficiency of the heat exchange process [96]. Ma et al. [97] collected hydrological, geological, and geothermal data using a heat response test designed for the field with a temperature sensor built on distributed optical fibers. They created a numerical model to assess the heat transfer efficiency of underground pipes throughout the heating season. The research investigates how varied ground conditions impact the thermal conductivity and heat exchange efficiency.
Liu et al. [98] introduced the concept of ‘functional backfill’ and categorized it into three types: the cold load/storage function backfill, heat storage and release function backfill, and cavity-building function backfill. These classifications illustrate several roles that backfill materials may play in improving the durability and thermal performance of the system. Smith and Perry [99] evaluated the backfill material effect on an efficiency heat transfer. The findings suggested that enhancing the conductivity of heat for the backfill material improves transferring heat. Debonding in the EAHE can occur for a variety of causes, including nearby components’ thermal incompatibility, soil shrinkage, and poor grout application. Philippacopoulos and Berndt [100] studied the impacts of soil and pipe debonding. They found 66% of heat reduction attributed to 360° debonding at grout and pipe contact. Table 1 shows the main key findings of the literature review.

Table 1.
Summary of the key findings.
6. Conclusions and Future Directions for Research
This review paper focused on EAHE properties that have the potential to influence the system’s performance. Evidently, the type of material constituting the pipe, and pipe characteristics such as the diameter, length, and burial depth have individual influences. Other influencing properties include the system’s air velocity and the bonding of installed pipes and soil with a backfilling material like graphite, sand, and fly ash. The extensive evaluation of previous studies has underscored the intricate interplay between these factors and their influence on the energy efficiency and environmental sustainability of EAHE systems. The key findings of this review are as follows:
- The local climate, especially temperature extremes, impacts the EAHE system’s efficiency. In colder regions, EAHEs may preheat the inflowing air, while in warmer climates, they may pre-cool it. The temperature variation for the soil and inflowing air determines the efficiency of pre-cooling or pre-heating.
- The efficiency of EAHE systems varies with seasons. They tend to be more effective during extreme weather conditions (winter and summer) when the temperature differential between the external air and the subsurface is larger.
- Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) or PVC, are commonly used. The choice of material should consider factors like the durability, corrosion resistance, and thermal properties.
- The heat exchange capacity is influenced by the diameter and length of the pipes in the system. Larger pipes (more than 30 cm diameter) with lengths between (80 m and 120 m) can exchange more heat, but they may occupy more space and incur higher installation costs.
- The cooling and heating capacity of an EAHE system enhances as the pipe depth increases, until a specific point (about 3 m), beyond which no significant output occurs.
- The difference in temperature for the air entering and exiting the pipe increases per its length. However, it reaches a length (about 100 m) where no further effects are observed.
- The potential of the EAHE system to heat or cool a facility goes up by reducing the pipe diameter (less than 20 cm) at a given airflow rate.
It is acknowledged that there are some potential barriers that need to be considered in the specific design of the EAHE system. Key among the barriers are high initial costs, site suitability and geological conditions, and regulatory and permitting issues. But government incentives, site assessments, and the understanding of local regulations may overcome these issues. Looking into the future, avenues for further research on EAHE systems are possible. One such area of exploration will be the integration of this technology into common heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning systems in civil buildings or greenhouses, to evaluate whether it is possible to eliminate the need for an air-handling unit or to avoid a heating or cooling coil maintaining indoor thermal comfort conditions. Additionally, to enhance public acceptance and for the widespread adoption of EAHE systems, it will be essential to develop standardized design guidelines. The document could take a holistic approach to pipe the selection and system configuration. Furthermore, practical aspirations into real-world applications need to be gathered through in-depth assessments of the system performance and durability over time.
Achieving a more sustainable and energy-efficient built environment will ultimately require interdisciplinary collaboration between geothermal engineering, materials science, and sustainable building design. Research in these areas will contribute to an increasingly greener and more energy-efficient future, as well as innovations in the EAHE system’s design and implementation. Per this review paper, more research is needed to contribute toward the following issues: to test the suitability of other pipe materials; establishing the percentage contribution of each property to the performance of the EAHE; developing guidelines and standards for designing the EAHE system for a peculiar environment (Mediterranean, arid, Saharian, temperate…); and to consider a combination of EAHE systems with other renewable energy systems to form an efficient hybrid system.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- D’Agostino, D.; Marino, C.; Minichiello, F. The use of Earth-to-Air and Air-to-Air Exchangers for Different Italian Climates. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2016, 34, s287–s294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, M. Performance analysis of clean energy using geothermal earth to air heat exchanger (GEAHE) in Lower Himalayan Region—Case study scenario. Energy Build. 2021, 248, 111166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadelano, G.; Cicolin, F.; Emmi, G.; Mezzasalma, G.; Poletto, D.; Galgaro, A.; Bernardi, A. Improving the energy efficiency, limiting costs and reducing CO2 emissions of a museum using geothermal energy and energy management policies. Energies 2019, 12, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, M.H.; Fanelli, M. What is GEOTHERMAL ENERGY? In Renewable Energy; Sørensen, B., Ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trota, A.; Ferreira, P.; Gomes, L.; Cabral, J.; Kallberg, P. Power production estimates from geothermal resources by means of small-size compact climeon heat power converters: Case studies from Portugal (Sete cidades, Azores and Longroiva spa, mainland). Energies 2019, 12, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, M.K.; Tiwari, G.N. Modeling and parametric studies for thermal performance of an earth to air heat exchanger integrated with a greenhouse. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GEOGRID PROJECT. Available online: www.geogrid.it (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Italian-Lead Research Project to Demonstrate Use of Low Enthalpy Geothermal in Emirates. Available online: https://www.thinkgeoenergy.com/italian-lead-research-project-to-demonstrate-use-of-low-enthalpy-geothermal-in-emirates/ (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Battaglia, V.; Ceglia, F.; Laudiero, D.M.; Maione, A.; Marrasso, E.; Vanoli, L. Empowering Energy Communities through Geothermal Systems. Energies 2024, 17, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishkariahmadabad, M.; Ayed, H.; Xia, W.F.; Aryanfar, Y.; Almutlaq, A.M.; Bouallegue, B. Thermo-economic analysis of working fluids for a ground source heat pump for domestic uses. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 27, 101330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, D.; Marino, C.; Minichiello, F. Earth-to-Air Versus Air-to-Air Heat Exchangers: A Numerical Study on the Energetic, Economic, and Environmental Performances for Italian Office Buildings. Heat Transf. Eng. 2020, 41, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency. Transition to Sustainable Buildings: Strategies and Opportunities to 2050. Available online: https://globalabc.org/resources/publications/transition-sustainable-buildings-strategies-and-opportunities-2050 (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- Építésügyi Minőségellenőrző és Innovációs. National Building Energy Performance Strategy. 2015. Available online: https://energy.ec.europa.eu/document/download/9eee3d91-28a7-4cac-8a86-d3b0e2946020_en?filename=2014_article4_hungary_en%20translation.pdf (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Karytsas, S.; Theodoropoulou, H. Public awareness and willingness to adopt ground source heat pumps for domestic heating and cooling. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Jian, Y.; Arıcı, M.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Q. Thermal environment evaluation of plastic greenhouses in southern China and optimization by phase change materials. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorjian, S.; Calise, F.; Kant, K.; Ahamed, S.; Copertaro, B.; Najafi, G.; Zhang, X.; Aghaei, M.; Shamshiri, R.R. A review on opportunities for implementation of solar energy technologies in agricultural greenhouses. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 285, 124807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacovides, C.P.; Mihalakakou, G.; Santamouris, M.; Lewis, J.O. On the ground temperature profile for passive cooling applications in buildings. Sol. Energy 1996, 57, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, K.K.; Misra, R.; Agrawal, G.D.; Bhardwaj, M.; Jamuwa, D.K. The state of art on the applications, technology integration, and latest research trends of earth-air-heat exchanger system. Geothermics 2019, 82, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshlak, H. Earth-Air Heat Exchangers: A Comprehensive Review. 2025. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202501.1370/v1 (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, D. Modelling and evaluation of cooling capacity of earth–air–pipe systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojic, M.; Trifunovic, N.; Papadakis, G.; Kyritsis, S. Numerical simulation, technical and economic evaluation of air-to-earth heat exchanger coupled to a building. Energy 1997, 22, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, A.; Masselli, C. The optimization of the thermal performances of an earth to air heat exchanger for an air conditioning system: A numerical study. Energies 2020, 13, 6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisoniya, T.S.; Kumar, A.; Baredar, P. Experimental and analytical studies of earth–air heat exchanger (EAHE) systems in India: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 19, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, F.; Gang, W. Utilization of earth-to-air heat exchanger to pre-cool/heat ventilation air and its annual energy performance evaluation: A case study. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Tao, Y.; Shi, L.; Tu, J.; Wang, Y. A review of ventilation and cooling systems for large-scale pig farms. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 89, 104372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, D.; Esposito, F.; Greco, A.; Masselli, C.; Minichiello, F. Parametric analysis on an earth-to-air heat exchanger employed in an air conditioning system. Energies 2020, 13, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, D.G.L.; Nagendra, S.M.S.; Maiya, M.P. Passive alternatives to mechanical air conditioning of building: Areview. Build. Environ. 2013, 66, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, M. Geothermal cooling/heating using ground heat exchanger for various experimental and analytical studies: Comprehensive review. Energy Build. 2017, 139, 634–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Sawhney, R.L.; Lazarus, I.J.; Kishore, V.V.N. Recent advancements in earth air tunnel heat exchanger (EATHE) system for indoor thermal comfort application. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2162–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chel, A.; Tiwari, G.N. Performance evaluation and life cycle cost analysis of earth to air heat exchanger integrated with adobe building for New Delhi composite climate. Energy Build. 2009, 41, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.T.; Gillott, M. A novel low-carbon space conditioning system incorporating phase-change materials and earth-air heat exchangers. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2013, 10, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deglin, D.; Van Caenegem, L.; Dehon, P. Subsoil heat exchangers for the air conditioning of livestock buildings. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1999, 73, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Huang, P.C.; De Liang, J.; Chiang, Y.C.; Chen, S.L. The in-situ experiment of earth-air heat exchanger for a cafeteria building in subtropical monsoon climate. Renew. Energy 2020, 157, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutera, Y.; Boultif, N.; Moummi, N.; Arıcı, M.; Saleh, M.S.; Rouag, A.; Kethiri, M.A.; Beldjani, C. Evaluation of the earth-air heat exchanger’s performance in improving the indoor conditions of an industrial poultry house using computational fluid dynamics verified with field tests. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 434, 140218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Shahsavar, A.; Al-Rashed, A.A.A.A.; Kalbasi, R.; Afrand, M.; Talebizadehsardari, P. Multi-objective energy and exergy optimization of different configurations of hybrid earth-air heat exchanger and building integrated photovoltaic/thermal system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 195, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloufi, Y.; Brima, A.; Zerouali, S.; Atmani, R.; Aissaoui, F.; Rouag, A.; Moummi, N. Numerical and experimental investigation on the transient behavior of an earth air heat exchanger in continuous operation mode. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2017, 35, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maerefat, M.; Haghighi, A.P. Passive cooling of buildings by using integrated earth to air heat exchanger and solar chimney. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 2316–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.; Yüksel, B.; Akyol, T. Effects of different operating conditions of Gonen geothermal district heating system on its annual performance. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 79, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.K.; Pandey, M.; Bartaria, V.N. Energy metrics of a hybrid earth air heat exchanger system for summer cooling requirements. Energy Build. 2016, 129, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Khan, M.M.K.; Amanullah, M.T.O.; Rasul, M.G.; Hassan, N.M.S. Thermal performance of building-integrated horizontal earth-air heat exchanger in a subtropical hot humid climate. Geothermics 2022, 99, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgener, L.; Ozgener, O. Energetic performance test of an underground air tunnel system for greenhouse heating. Energy 2010, 35, 4079–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgener, O.; Ozgener, L. Determining the optimal design of a closed loop earth to air heat exchanger for greenhouse heating by using exergoeconomics. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, C.; Li, S.; Song, B.; Li, A. Optimizing the thermal environment of greenhouse with multi-pipe earth-to-air heat exchanger system using the Taguchi method. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 242, 122469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florides, G.; Kalogirou, S. Ground heat exchangers—A review of systems, models and applications. Renew. Energy 2007, 32, 2461–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, G. Dynamic interactions between the ground heat exchanger and environments in earth-air tunnel ventilation of buildings. Energy Build. 2014, 85, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serageldin, A.A.; Abdeen, A.; Ahmed, M.M.S.; Radwan, A.; Shmroukh, A.N.; Ookawara, S. Solar chimney combined with earth to-air heat exchanger for passive cooling of residential buildings in hot areas. Sol. Energy 2020, 206, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, K.K.; Misra, R.; Agrawal, G.D.; Bhardwaj, M.; Jamuwa, D.K. Effect of different design aspects of pipe for earth air tunnel heat exchanger system: A state of art. Int. J. Green Energy 2019, 16, 598–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoloi, N.; Sharma, A.; Nautiyal, H.; Goel, V. An intense review on the latest advancements of Earth Air Heat Exchangers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahare, S.; Harinarayana, T. Energy Efficient Air Conditioning System Using Geothermal Cooling-Solar Heating in Gujarat, India. J. Power Energy Eng. 2016, 4, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, S.; Tirumalachetty, H.; Athikesavan, M.M. A comprehensive review on experimental, numerical and optimization analysis of EAHE and GSHP systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 67559–67603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascione, F.; Bellia, L.; Minichiello, F. Earth-to-air heat exchangers for Italian climates. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.B.M.; Schmid, A.L. Cooling and heating potential of underground soil according to depth and soil surface treatment in the Brazilian climatic regions. Energy Build. 2015, 90, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamovsky, D.; Neuberger, P.; Adamovsky, R. Changes in energy and temperature in the ground mass with horizontal heat exchangers—The energy source for heat pumps. Energy Build. 2015, 92, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, G.H.; Lee, S.R.; Yoon, S.; Kim, M.J. Optimum design of horizontal ground-coupled heat pump systems using spiral-coil-loop heat exchangers. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhein, K.; Kobus, C.J.; Zohdy, M. Control of Heat Transfer in a Vertical Ground Heat Exchanger for a Geothermal Heat Pump System. Energies 2022, 15, 5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisoniya, T.S. Design of earth–air heat exchanger system. Geotherm. Energy 2015, 3, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhein, K.; Kobus, C.J.; Zohdy, M.; Annekaa, A.M.; Alhawsawi, E.Y.; Salheen, S.A. Heat Transfer Performance Factors in a Vertical Ground Heat Exchanger for a Geothermal Heat Pump System. Energies 2024, 17, 5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M.; Mihalakakou, G.; Balaras, C.A.; Lewis, J.O.; Vallindras, M.; Argiriou, A. Energy conservation in greenhouses with buried pipes. Energy 1996, 21, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Asati, A.K.; Kumar, R. Temperature Difference findings from Earth Air Heat Exchanger System in Hot-Dry Climate. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratiev, V.V.; Sysoev, I.A.; Kolosov, A.D.; Galishnikova, V.V.; Gladkikh, V.A.; Karlina, A.I.; Karlina, Y.I. Development and Testing of the Thermoelectric Thermal Energy Conversion Device in the Conditions of Existing Aluminum Production. Materials 2022, 15, 8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhri, N.; Menni, Y.; Chamkha, A.; Salmi, M.; Ameur, H. Earth to Air Heat Exchanger and Its Applications in Arid Regions—An Updated Review. Ital. J. Eng. Sci. 2020, 64, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, N.; Soares, N.; Costa, J.J.; Santos, P.; Gervásio, H. Assessment of an earth-air heat exchanger (EAHE) system for residential buildings in warm-summer Mediterranean climate. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 38, 100649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.; Misra, R.; Agrawal, G.D.; Mathur, J. Performance analysis of earth–pipe–air heat exchanger for winter heating. Energy Build. 2009, 41, 1151–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serageldin, A.A.; Abdelrahman, A.K.; Ookawara, S. Earth-Air Heat Exchanger thermal performance in Egyptian conditions: Experimental results, mathematical model, and Computational Fluid Dynamics simulation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 122, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, N.; Santos, P.; Costa, J.J.; Gervásio, H. Modelling and performance analysis of an earth-to-air heat exchanger in a pilot installation. J. Build. Phys. 2018, 42, 259–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, K.K.; Agrawal, G.D.; Misra, R.; Bhardwaj, M.; Jamuwa, D.K. A review on effect of geometrical, flow and soil properties on the performance of Earth air tunnel heat exchanger. Energy Build. 2018, 176, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, K.K.; Misra, R.; Agrawal, G.D. To study the effect of different parameters on the thermal performance of ground-air heat exchanger system: In situ measurement. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 2070–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.; Misra, R.; Agarwal, G.D.; Mathur, J. Transient effect of soil thermal conductivity and duration of operation on performance of Earth Air Tunnel Heat Exchanger. Appl. Energy 2013, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rocha Camba, E.; Petrakopoulou, F. Earth-cooling air tunnels for thermal power plants: Initial design by CFD modelling. Energies 2020, 13, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalakakou, G.; Santamouris, M.; Asimakopoulos, D.; Tselepidaki, I. Parametric prediction of the buried pipes cooling potential for passive cooling applications. Sol. Energy 1995, 55, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalakakou, G.; Santamouris, M.; Lewis, J.O.; Asimakopoulos, D.N. On the application of the energy balance equation to predict ground temperature profiles. Sol. Energy 1997, 60, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshlak, H. A Review of Earth-Air Heat Exchangers: From Fundamental Principles to Hybrid Systems with Renewable Energy Integration. Energies 2025, 18, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalakakou, G.; Santamouris, M.; Asimakopoulos, D.; Papanikolaou, N. Impact of ground cover on the efficiencies of earth-to-air heat exchangers. Appl. Energy 1994, 48, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Amanullah, M.T.O.; Khan, M.M.K.; Rasul, M.G.; Hassan, N.M.S. Parametric study on thermal performance of horizontal earth pipe cooling system in summer. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 114, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanusi, A.N.Z.; Shao, L.; Ibrahim, N. Passive ground cooling system for low energy buildings in Malaysia (hot and humid climates). Renew. Energy 2013, 49, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Shabbir, K.; Khan, M.M.; Siddiqui, F.A.; Taseer, M.Y.R.; Imtiaz, S. Earth-Tube System to Control Indoor Thermal Environment in Residential Buildings. Tech. J. Univ. Eng. Technol. 2020, 25, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kabashnikov, V.P.; Danilevskii, L.N.; Nekrasov, V.P.; Vityaz, I.P. Analytical and numerical investigation of the characteristics of a soil heat exchanger for ventilation systems. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transf. 2002, 45, 2407–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalakakou, G.; Lewis, J.O.; Santamouris, M. The influence of different ground covers on the heating potential of earth-to-air heat exchangers. Renew. Energy 1996, 7, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhammou, M.; Draoui, B. Parametric study on thermal performance of earth-to-air heat exchanger used for cooling of buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, V.; Misra, R.; Agrawal, G.D.; Mathur, J. Performance analysis of earth–pipe–air heat exchanger for summer cooling. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Student, M.T.; Deptt, M. Earth Air Heat Exchanger in Parallel Connection. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2013, 1, 2463–2467. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F.; Yu, Y.; Yu, D.; Li, H. Heat and mass transfer performance analysis and cooling capacity prediction of earth to air heat exchanger. Appl. Energy 2015, 137, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehli, A.; Hasni, A.; Tamali, M. The Potential of Earth-air Heat Exchangers for Low Energy Cooling of Buildings in South Algeria. Energy Procedia 2012, 18, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Sawicki, A. Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2001, 54, B103–B104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M. Use of Earth to Air Heat Exchanger for Cooling; International Energy Agency, Energy Conservation in Buildings and Community Systems Programme: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Salhein, K.; Kobus, C.J.; Zohdy, M. Heat Transfer Control Mechanism in a Vertical Ground Heat Exchanger: A Novel Approach. Fundam. Res. Appl. Phys. Sci. 2023, 5, 59–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Resources Canada, Earth to Air Thermal Exchanger (EATEX): Design Principles and Concept Design Tool. 2021. Available online: https://publications.gc.ca/site/eng/9.903329/publication.html (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Choi, W.; Ooka, R. Effect of natural convection on thermal response test conducted in saturated porous formation: Comparison of gravel-backfilled and cement-grouted borehole heat exchangers. Renew. Energy 2016, 96, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Liu, G.; Zhan, T.; Yao, Y.; Ni, L. Performance study of cement-based grouts based on testing and thermal conductivity modeling for ground-source heat pumps. Energy Build 2022, 272, 112351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, M.L. Strength and permeability of steel fibre reinforced grouts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 768–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Muñoz, P.; Indacoechea-Vega, I.; Zamora-Barraza, D.; Castro-Fresno, D. Experimental analysis of enhanced cement-sand-based geothermal grouting materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 185, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ameen, Y.; Ianakiev, A.; Evans, R. Recycling construction and industrial landfill waste material for backfill in horizontal ground heat exchanger systems. Energy 2018, 151, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, G.; Chen, A. Investigation of the Long-Term Performance of Waste Backfill Materials of High Thermal Conductivity in Vertical Ground Heat Exchangers. Buildings 2024, 14, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głuchowski, A. Optimizing Backfill Materials for Ground Heat Exchangers: A Study on Recycled Concrete Aggregate and Fly Ash for Enhanced Thermal Conductivity. Materials 2024, 17, 5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanbin, A. Thermal performance of the vertical ground heat exchanger with a novel elliptical single U-tube. Geothermics 2020, 86, 101804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, S.E.; Schincariol, R.A. Effect of thermal-hydrogeological and borehole heat exchanger properties on performance and impact of vertical closed-loop geothermal heat pump systems. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, F.; Yan, E.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Deng, H.; Gao, X.; Kang, J.; Shi, H.; et al. Analysis of the Heat Transfer Performance of a Buried Pipe in the Heating Season Based on Field Testing. Energies 2024, 17, 5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Jie, X. Basic theories and applied exploration of functional backfill in mines. Meitan Xuebao/J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.D.; Perry, R.L. Borehole grouting: Field studies and thermal performance testing. ASHRAE Trans. 1999, 105, 451. [Google Scholar]
- Philippacopoulos, A.J.; Berndt, M.L. Influence of debonding in ground heat exchangers used with geothermal heat pumps. Geothermics 2001, 30, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).