Research on the Fire Risk of Photovoltaic DC Fault Arcs Based on Multiphysical Field Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Photovoltaic DC SAF Detection Test Standard Analysis
2.1. Basic Requirements of the Test
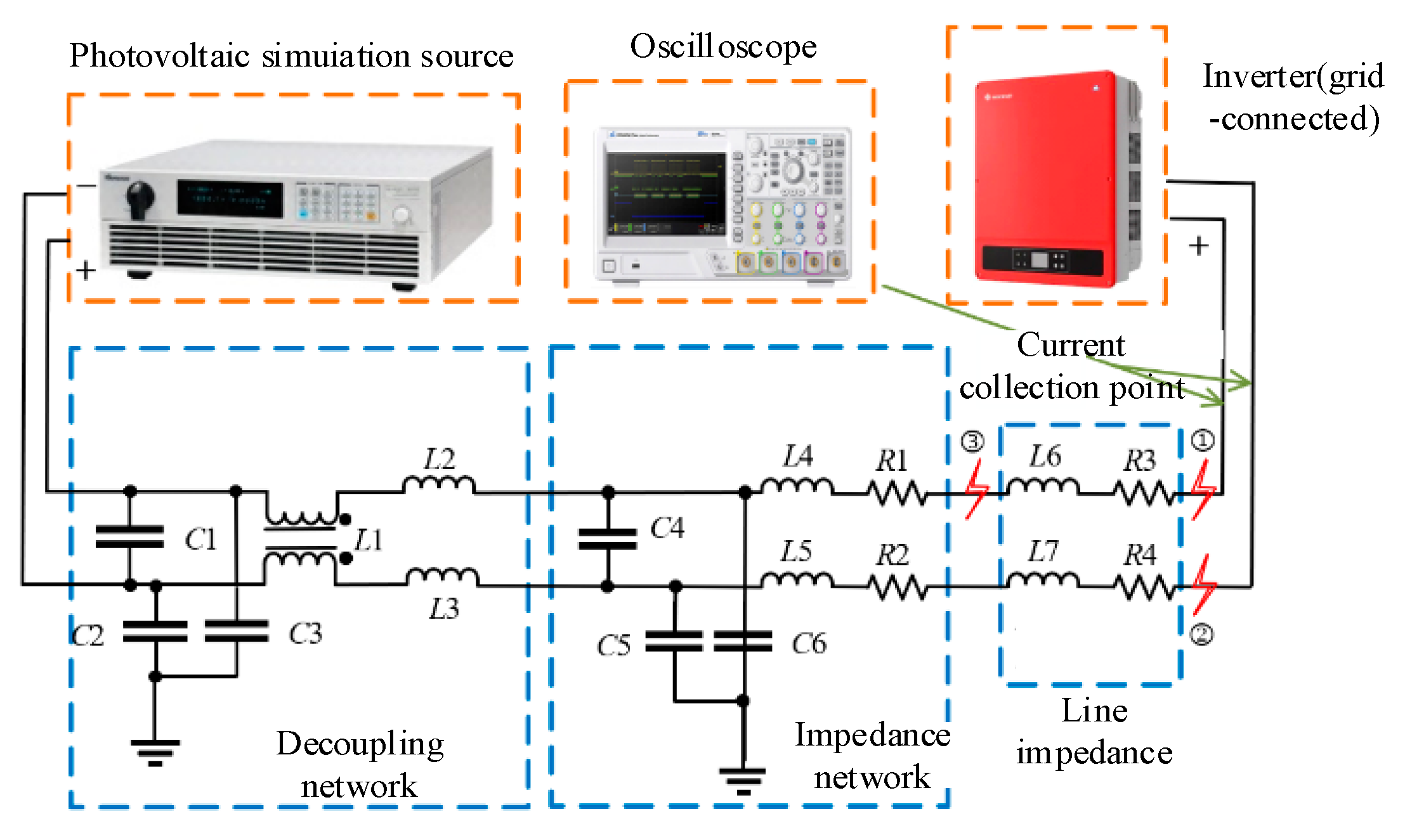
2.2. Analysis of Photovoltaic DC SAF Detection Test Scheme
3. Characteristic Analysis and Model Construction of DC Fault Arc
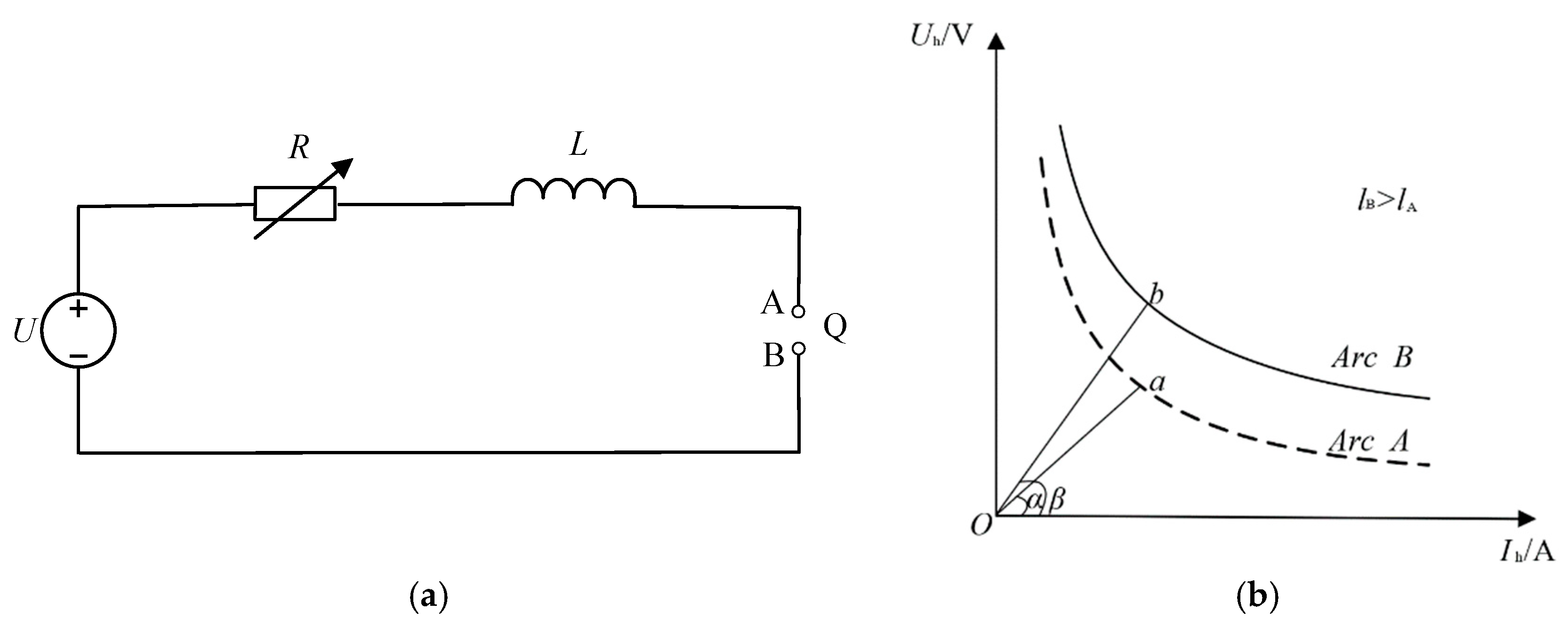
3.1. Characteristic Analysis
3.2. Arc Simulation Model Control Equation
- (1)
- The arcing stage is not considered;
- (2)
- The burning of the two electrodes by the arc and the sheath in the near-polar region is ignored;
- (3)
- The arc is treated as an incompressible fluid;
- (4)
- The arc is axisymmetric, and the flow of the arc fluid is laminar in the case of free arcing;
- (5)
- The arc’s thermodynamic properties vary with temperature, including density, thermal conductivity, constant pressure heat capacity, and viscosity coefficient.
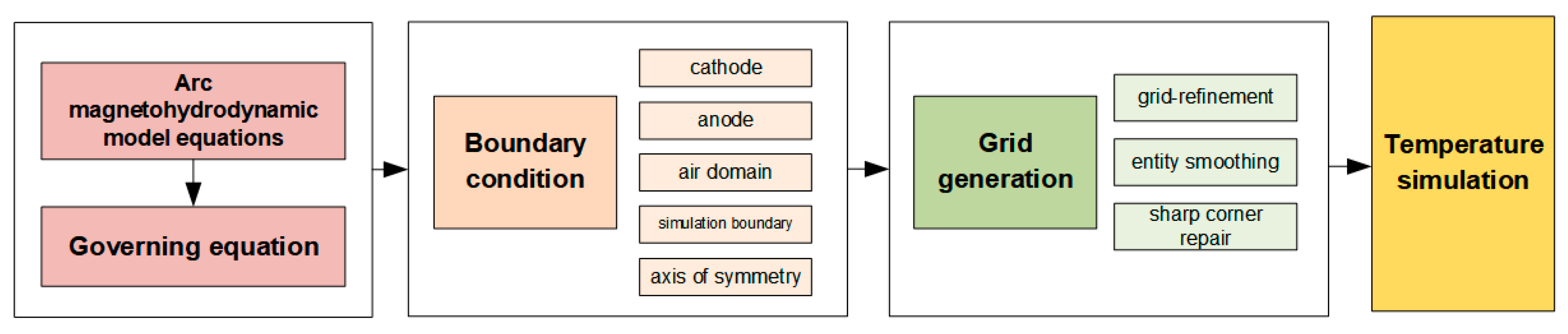
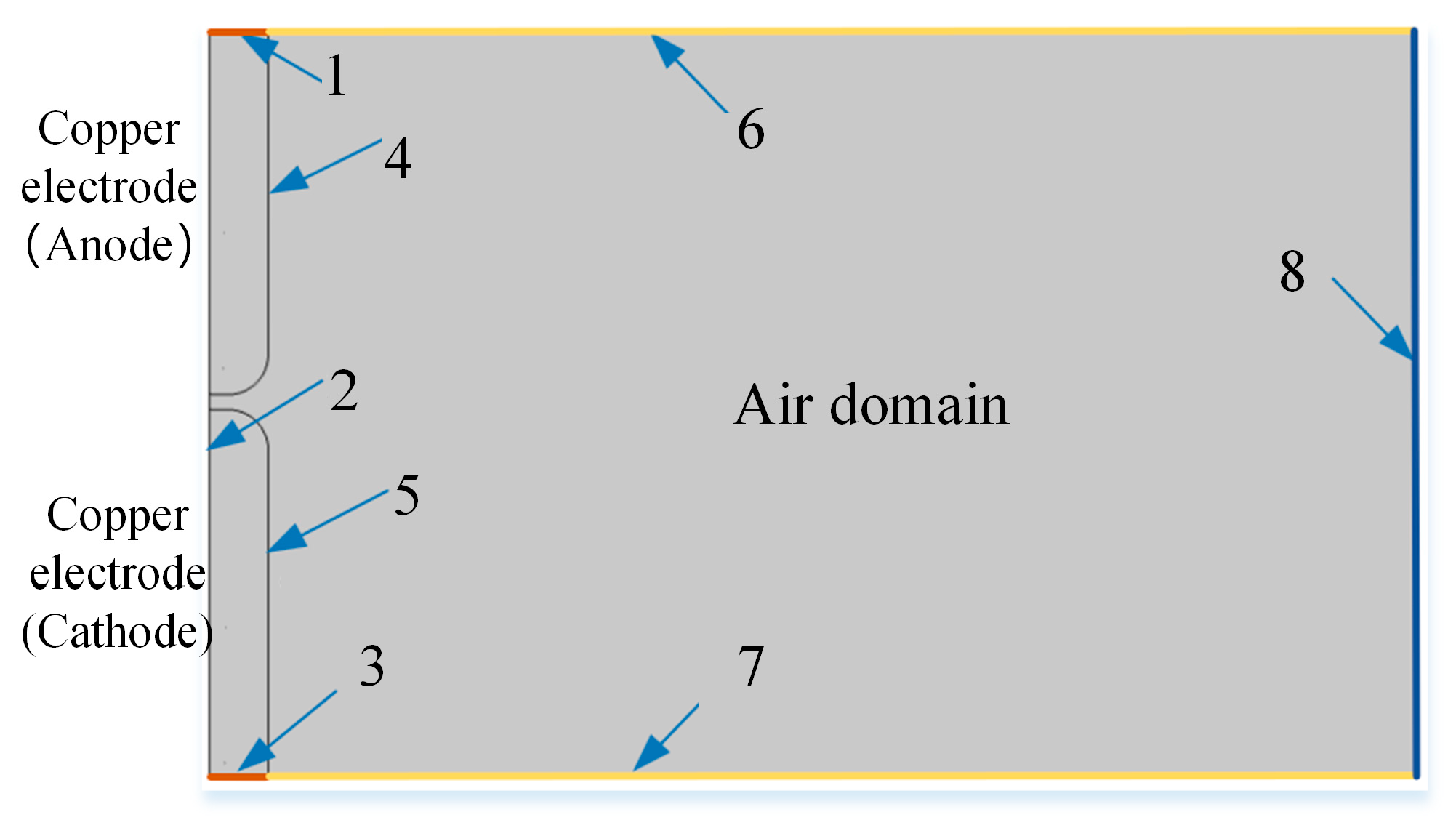
3.3. Fault Arc Boundary Conditions and Mesh Generation
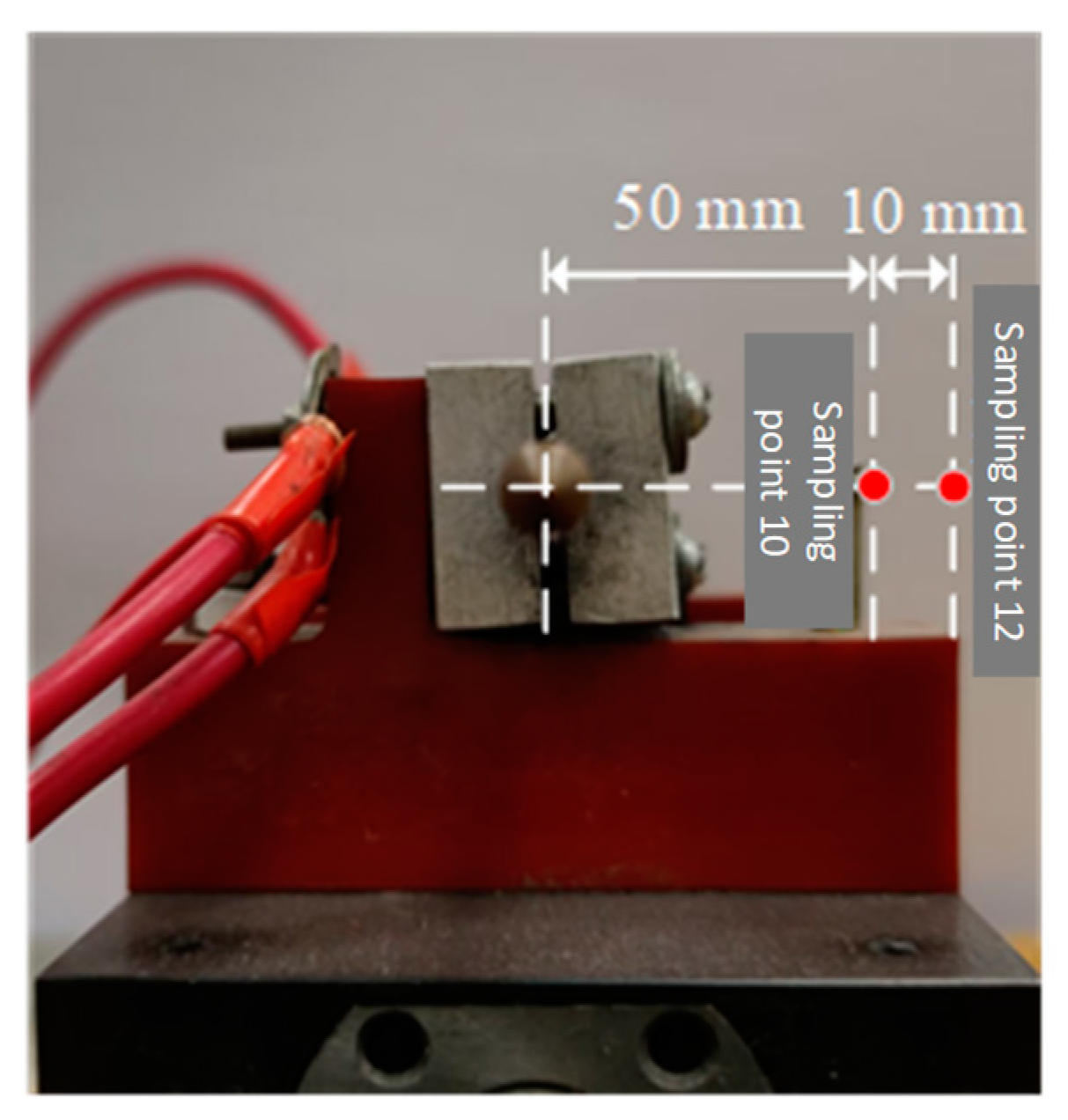
4. Experimental Verification and Fire Risk Analysis
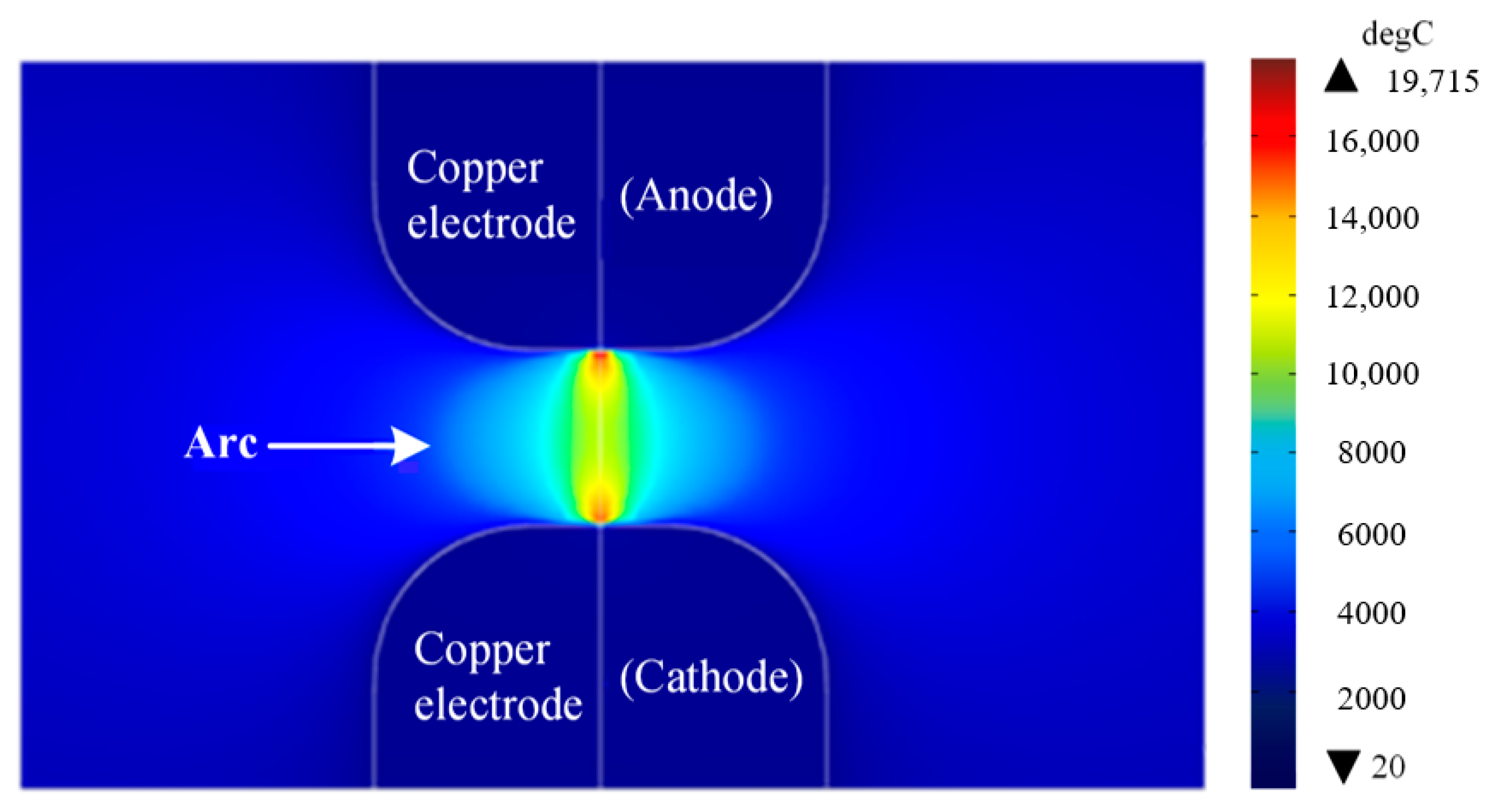
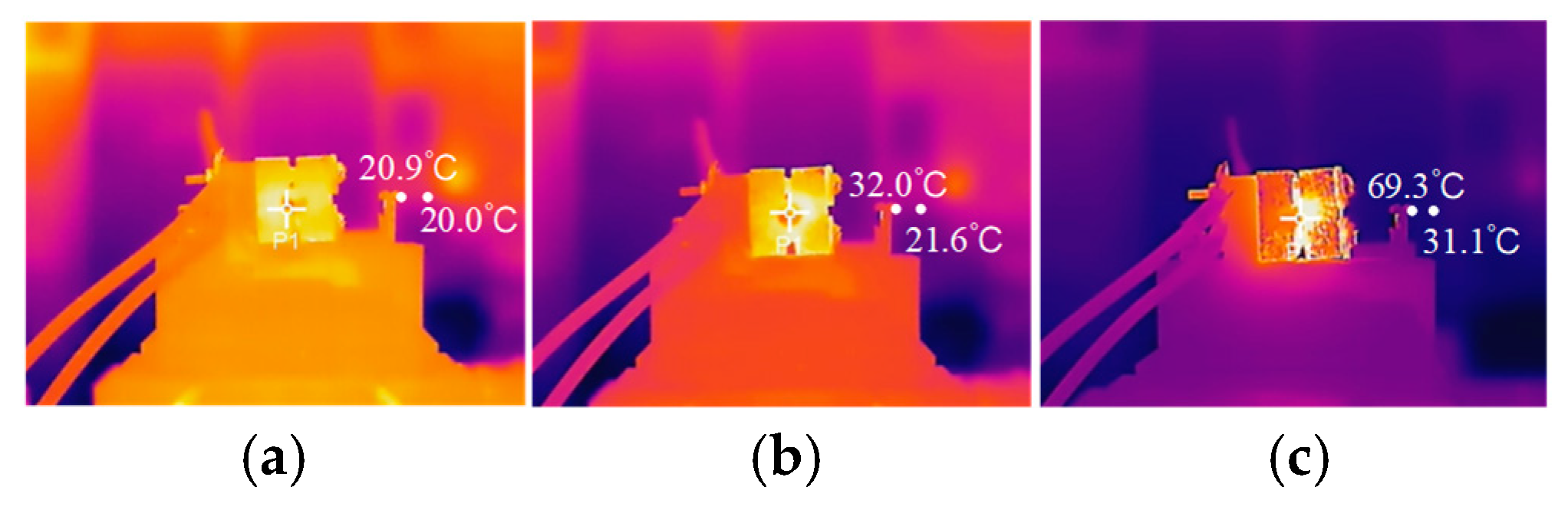
4.1. Arc Gap Temperature Change Rule
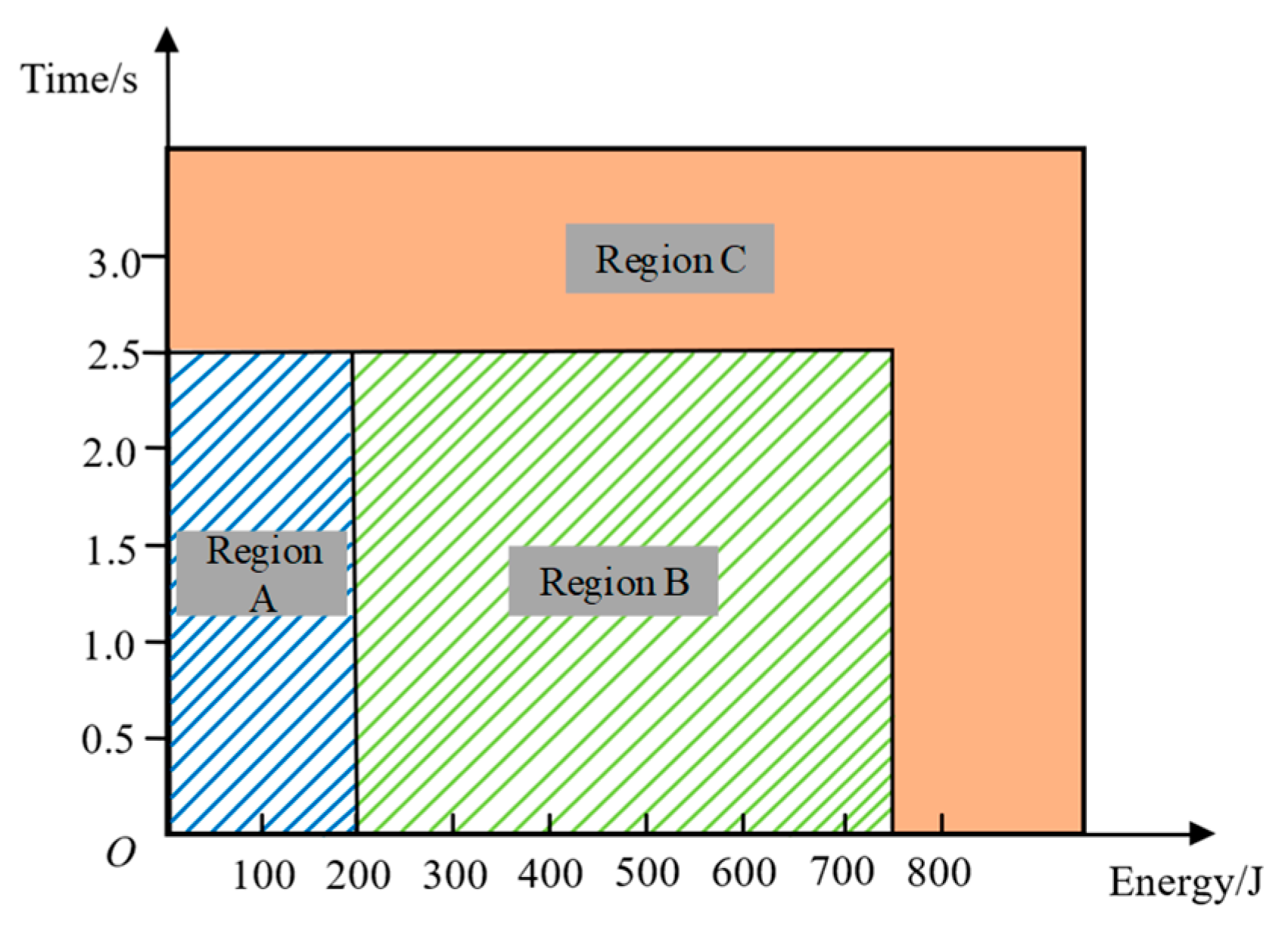
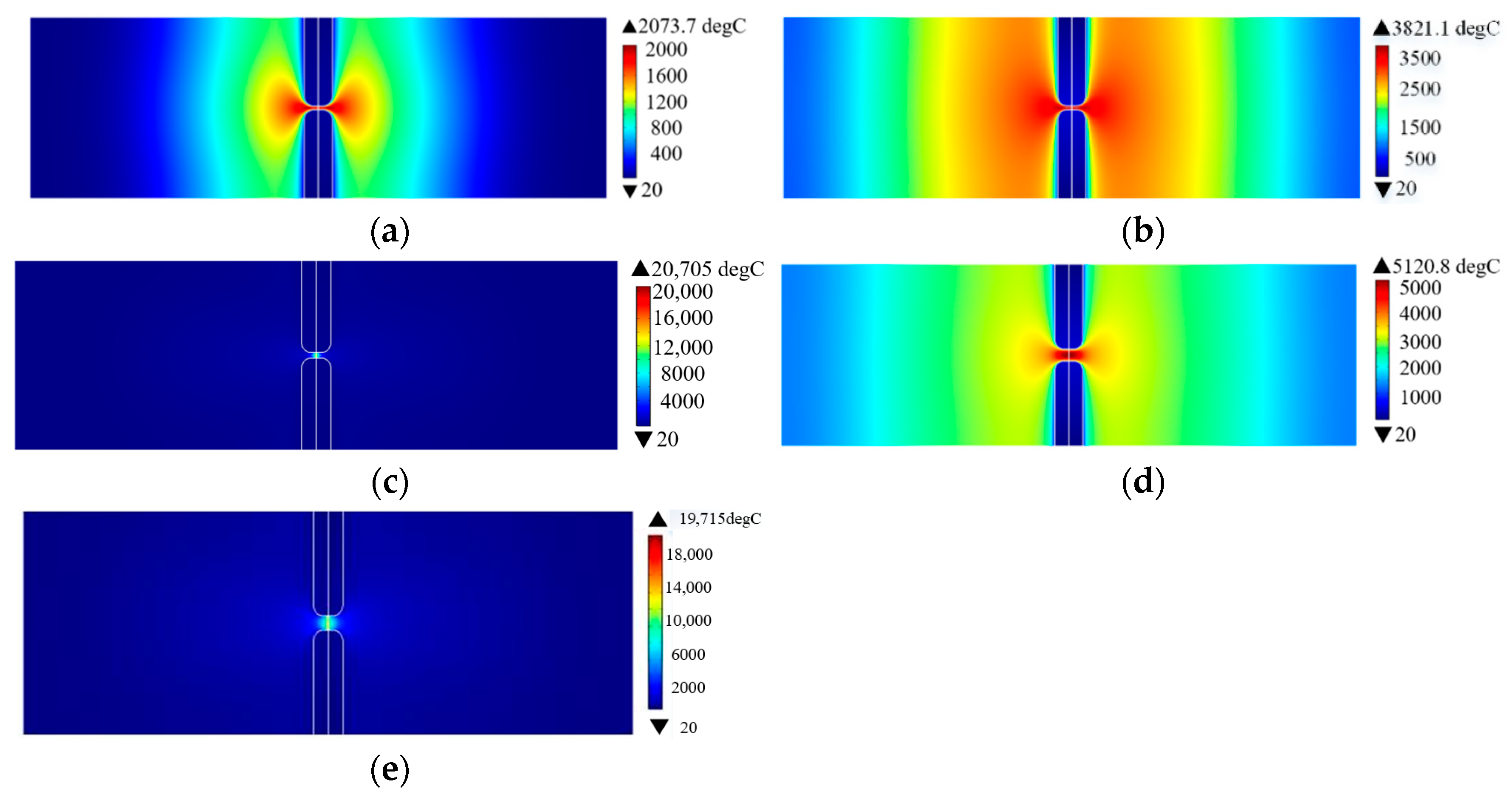
4.2. Risk Analysis
4.3. Risk Validation
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K. A review of research on photovoltaic DC arc fault detection methods. Electr. Appl. Energy Effic. Manag. Technol. 2018, 561, 1–6+37. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Wu, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, F. Comparative study of DC arc fault detection methods in photovoltaic systems. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2020, 41, 204–214. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, N.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. An Arc Fault Detection Method Based on Current Amplitude Spectrum and Sparse Representation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 3785–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.; Fu, G.; Han, B.; Wang, W.; Liu, C. Series Arc Fault Detection Based on Dual Filtering Feature Selection and Improved Hierarchical Clustering Sensitive Component Selection. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 6050–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Samet, H.; Ghanbari, T. Series Arc Fault Detection in Photovoltaic Systems Based on Signal to Noise Ratio Characteristics Using Cross-Correlation Function. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 16, 3198–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, G.; Zhou, X.; Yang, W. Arc characteristics test when disconnecting DC inductive load under longitudinal and transverse magnetic fields. Trans. Chin. Soc. Electrotech. Eng. 2011, 26, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. Simulation Study on the Influence of Multiple Physical Factors on Arc and Electrical Erosion of DC Contactor. Bachelor’s Thesis, Shenyang University of Technology, Shenyang, China, 2020; pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y. Arc Characteristics and Simulation Research in DC Vacuum Circuit Breaker Under Transverse Magnetic Field. Bachelor’s Thesis, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin, China, 2017; pp. 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Yao, L.; Qi, J.; Tian, S.; Zhang, X.; Pan, M.; Wu, X. Extraction of Fault Characteristic Frequency Band of Photovoltaic DC Series Arc Based on Wavelet Packet Transform and Tsallis Entropy. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th Asia Energy and Electrical Engineering Symposium (AEEES), Chengdu, China, 23–26 March 2023; pp. 551–558. [Google Scholar]
- Blažič, A.; Škrjanc, I.; Logar, V. Arc Quality Index Based on Three-Phase Cassie–Mayr Electric Arc Model of Electric Arc Furnace. Metals 2024, 14, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, E.; Niayesh, K. DC Current Interruption Based on Vacuum Arc Impacted by Ultra-Fast Transverse Magnetic Field. Energies 2020, 13, 4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadidian, J. A Compact Design for High Voltage Direct Current Circuit Breaker. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2009, 37, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Niu, C.; Wu, Y.; Rong, M.; Yang, F.; Sun, H. Arc Plasma Simulation Method in DC Relay with Contact Opening Process. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on Electric Power Equipment-Switching Technology (ICEPE-ST), Kitakyushu, Japan, 13–16 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, B.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Wu, H.; Peng, X.; Dai, J.; Chen, R. Magneto-hydrodynamic simulation study of direct current multi-contact circuit breaker for equalizing breaking arc. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2023, 25, 025506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, S.; Lv, Y.; Hu, D.; Liu, Y.; Feng, B.; Hou, S.; Fu, M. Simulation Study on Steady-State Heat Transfer characteristics of DC Arc Fault. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2021, 36, 2697–2709. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wen, J.X.; Zhou, F.; Ye, X. A Review for Solar Panel Fire Accident Prevention in Large-Scale PV Applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132466–132480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, W. Modelling and calculation method of minimum safety distance for photovoltaic fire extinguishing under energized conditions. Sol. Energy 2025, 288, 113300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Reda, I.; Aram, M.; Qi, D.; Wang, L.L.; Fellouah, H. Wind-driven smoke dispersion in rooftop photovoltaic fires: An experimental investigation with helium smoke. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 83, 108467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgijevic, N.L.; Jankovic, M.V.; Srdic, S.; Radakovic, Z. The Detection of Series Arc Fault in Photovoltaic Systems Based on the Arc Current Entropy. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5917–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Zheng, H. Review of anti-interference technology for DC arc fault detection in photovoltaic systems. J. Electr. Eng. 2019, 14, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kavi, M.; Mishra, Y.; Vilathgamuwa, M. DC Arc Fault Detection For Grid-Connected Large-Scale Photovoltaic Systems. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2020, 10, 1489–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammon, T.; Lee, W.J.; Zhang, Z.; Johnson, B.C. A Review of Commonly Used DC Arc Models. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, K.; Qi, Y.; Tu, R. Numerical investigations of AC arcs thermal characteristics in the short gap of copper-cored wires. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Hu, S.; Gao, Z. Research progress in numerical simulation of plasma arc. Ordnance Mater. Sci. Eng. 2007, 30, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bauchire, J.M.; Gonzalez, J.J.; Gleizes, A. Modeling of a DC Plasma Torch in Laminar and Turbulent Flow. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 1997, 17, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthaeus, W.H.; Brown, M.R. Nearly incompressible magnetohydrodynamics at low Mach number. Phys. Fluids 1988, 31, 3634–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Hu, S.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, L. Numerical simulation of plasma arc welding arc. J. Weld. 2006, 27, 51–54+115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y. MHD Model Simulation and Experimental Study of Low Current DC Air Arc. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2020; pp. 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, K.; Ma, S.; Wang, W.; Du, P.; Xu, Z. Research on low voltage series arc discharge detection and fault protection simulation based on wavelet analysis and Cassie model. Electr. Appl. Energy Effic. Manag. Technol. 2019, 48–52+67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Gao, Y. Simulation analysis of fast transient overvoltage in GIS under Mayr arc model. Electr. Appl. Energy Effic. Manag. Technol. 2024, 28–32+38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, S. Modeling and simulation of single-phase grounding arc in distribution network based on Mayr-Cassie. Electr. Eng. 2020, 519, 48–51. [Google Scholar]



| Installation Site | Applicable Circuit |
|---|---|
| Integrated in the inverter | (1) Concentrated power inverter, a series of photovoltaic modules. (2) Concentrated power inverter, two strings of photovoltaic modules. (3) The micro-inverter inverts a series of photovoltaic modules. (4) The micro-inverter inverts two series of photovoltaic modules, respectively. |
| Installed in the junction box | Circuit with confluence box |
| Free standing | (1) Concentrated power inverter, a series of photovoltaic modules. (2) Concentrated power inverter, two strings of photovoltaic modules. (3) Circuit with confluence box. |
| In DC-DC rectifier system | (1) Rectifiers rectify a series of photovoltaic modules. (2) The rectifier rectified two series of photovoltaic modules, respectively. |
| Test | Minimum | Impp | Vmpp | Voc | Rtot | Gap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | (A) | (A) | (V) | (V) | (Ω) | (mm) |
| 1 | 2.5 | 3 | 312 | 480 | 56 | 0.8 |
| 2 | 7 | 8 | 318 | 490 | 21 | 0.8 |
| 3 | 14 | 16 | 318 | 490 | 11 | 1.1 |
| 4 | 7 | 8.5 | 607 | 810 | 24 | 2.5 |
| Component | Value | Component | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 20 µF | L1 | 12 mH |
| C2 | 22 nF | L2 | 60 µH |
| C3 | 22 nF | L3 | 60 µH |
| Component | Value | Component | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| C4 | 10 uF | R1 | 1 Ω |
| C5 | 1 nF | R2 | 1 Ω |
| C6 | 1 nF | L6, L7 | 0.7 µH/m |
| L4 | 50 µH | R3, R4 | 10 mΩ/m |
| L5 | 50 µH |
| Proposer | Fitting Formula | Test Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Ayrton | UA= a + b l + (c + dl)/IA | IA < 100 A l < 10 mm |
| Nottingham | UA = a + b /In A | n is related to the electrode material l: 1~10 mm |
| Paukert | UA = a/I bA | IA: 0.3~100 kA l: 1~200 mm |
| Item | Max Arc Temperature at Different Times/°C | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 s | 1.0 s | 1.5 s | 2.0 s | 2.5 s | 3.0 s | |
| 1 | 2065 | 2068 | 2070 | 2072 | 2073 | 2073 |
| 2 | 3814 | 3817 | 3818 | 3820 | 3820 | 3821 |
| 3 | 21,001 | 20,901 | 20,837 | 20,784 | 20,735 | 20,705 |
| 4 | 5210 | 5174 | 5152 | 5138 | 5129 | 5120 |
| I/A | U/V | Gap/mm | Max Arc Temperature at Different Times/°C | Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 s | 1.5 s | 2.5 s | ||||
| 3 | 312 | 0.8 | 2065 | 2070 | 2073 | With the increase in voltage and current, the temperature of sampling point rises faster, and the risk of arc ignition rises rapidly. The increase in arc gap size limits the temperature rise speed and reduces the fire risk to a certain extent. |
| 8 | 318 | 0.8 | 3814 | 3818 | 3820 | |
| 16 | 318 | 1.1 | 21,001 | 20,837 | 20,735 | |
| 8.5 | 607 | 2.5 | 5210 | 5152 | 5129.3 | |
| Time | Max Arc Temperature at Different Times/°C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 1 s | 20.9 | 45.5 | 20.3 | 66.2 |
| 2 s | 32.1 | 713.3 | 32.9 | 922.4 |
| 3 s | 69.5 | 1315.5 | 66.7 | 1664 |
| Time | Max Arc Temperature at Different Times/°C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 1 s | 20 | 21.4 | 19.9 | 21.8 |
| 2 s | 21.6 | 144.9 | 21.3 | 248.5 |
| 3 s | 31.1 | 906.0 | 30.8 | 1344.9 |
| Particulars | Yan. et al. [29] | Yang et al. [30] | Hu et al. [31] | Wu et al. [15] | This Paper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model used | Cassie arc model | Mayr arc model | Mayr-Cassie arc model | MHD model | MHD model |
| Voltage and current | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Arc gap size | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Heat transfer | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Temperature-time characteristics | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Complexity | Simple | Simple | Medium | Complex | Complex |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Z.; Hou, L.; He, P.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, D. Research on the Fire Risk of Photovoltaic DC Fault Arcs Based on Multiphysical Field Simulation. Energies 2025, 18, 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061396
Xie Z, Hou L, He P, Hu W, Wang Y, Sheng D. Research on the Fire Risk of Photovoltaic DC Fault Arcs Based on Multiphysical Field Simulation. Energies. 2025; 18(6):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061396
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Zhenhua, Linming Hou, Puquan He, Wenxin Hu, Yao Wang, and Dejie Sheng. 2025. "Research on the Fire Risk of Photovoltaic DC Fault Arcs Based on Multiphysical Field Simulation" Energies 18, no. 6: 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061396
APA StyleXie, Z., Hou, L., He, P., Hu, W., Wang, Y., & Sheng, D. (2025). Research on the Fire Risk of Photovoltaic DC Fault Arcs Based on Multiphysical Field Simulation. Energies, 18(6), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18061396







