Abstract
This article proposes an improved algorithm for the parameter identification of permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs). An enhanced raccoon optimization algorithm (EROA) was formed by combining the raccoon optimization algorithm (ROA) with the adaptive exploration radius, raccoon-washing-food-inspired, and escaping-predator strategies. First, using some of the functions in IEEE CEC2015, the EROA solution has a large improvement in convergence speed and solution accuracy compared with other algorithms. Second, the EROA solution is more stable under the same conditions, as demonstrated by MATLAB parameter identification simulation. Finally, EROA is applied to motor parameter identification through motor control experiments.
1. Introduction
Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs) are widely used in industry due to their high efficiency and small size [1,2,3]. However, realizing the high-performance control for PMSMs requires accurate motor parameters. For example, model predictive control [4,5] and speed sensorless control [6,7] require accurate motor parameters as a basis. The PMSM parameter identification is categorized into online identification [8,9,10] and offline identification [11,12,13]. Online identification is performed when the motor is integrated into the control system. This method relies on the real-time response of the motor’s input and output, combining the motor control model with the identification algorithm to estimate key parameters. Online identification is often coupled with motor control techniques [14,15] to continuously update the motor parameters. In contrast, offline identification is typically performed when the motor is disconnected from the operating system. This method uses feedback data to estimate the motor’s electrical and mechanical parameters by applying a predetermined signal to the motor. Offline identification is commonly used to initialize parameters before motor startup [16], and it is widely applied in industry.
The main online identification methods are recursive least squares (RLS), model reference adaptive (MRAS), extended Kalman filtering, and high-frequency signal injection. RLS has good mathematical-statistical properties and a wide range of adaptability. In article [17], inductance, flux linkage, and resistance parameters are recognized by a recursive total least-square excitatory and inhibitory learning to update the model parameters of the velocity-free sensor. Reference [18] addresses the rank-deficiency problem in motor parameter identification using the current derivative method in combination with RLS to obtain parameter results. However, RLS requires careful consideration of the convergence speed and solution accuracy of the algorithm. In [19], inductance, resistance, and flux linkages are identified using MRAS. Ref. [20] improves the tracking accuracy of inductance parameters and enhances the precision of speed sensorless control by combining the improved Virtual Rotating Axis High-Frequency Injection (VHFSI) method with MRAS. However, the adaptive rate design process of MRAS is more complex.
In [21], system states and two key motor parameters are estimated using a dual extended Kalman filter. However, this method operates the motor under steady-state conditions, and there is a rank-deficiency issue in the parameter identification process, making it difficult to identify all electrical parameters, particularly for Interior PMSMs (IPMSMs). In [22], motor parameters are obtained by injecting high-frequency sinusoidal voltages into the stationary coordinate system (-axis) to update the model parameters in the position observer. However, high-frequency signals can interfere with motor control, and motor feedback signals are prone to distortion. Reference [23] proposes using a triangle wave injection method to address the rank-deficiency problem in parameter identification, employing RLS to extract multiple motor parameters after receiving the motor feedback signal.
Offline identification methods include finite element analysis (FEA) [24], signal injection [25], and artificial intelligence algorithms [26]. FEA can provide high-precision parameters that accurately reflect the nonlinear characteristics of the motor, but FEA is commonly used in the pre-design stage of the motor. In article [27], the effectiveness of a parameter identification scheme is verified by FEA. However, finite element analysis requires a powerful computing system and is often used when designing engines. In article [16], the amplitude-auto-adjusting signal injection (ASI) method is proposed to recognize the inductance and stator resistance in different states offline. Selecting an appropriate signal injection method is crucial for motor parameter identification, as it helps decouple the parameters in the identification model and compensates for rank deficiencies in the identification process. In this study, the issue of rank deficiency in the identification equation is addressed by injecting different currents into the d-axis. Intelligent algorithms have rapidly developed, and many types of intelligent algorithms have emerged [28]. Depending on the source of inspiration, they can be categorized as swarm-based, evolution-based, physics-based, game-rule-based, and human-social-relationship-based [29]. Artificial intelligence algorithms have outstanding abilities to solve high-dimensional functions, and scholars have applied them to the solution of motor parameters [30]. Commonly, an improved particle swarm algorithm (PSO) performs parameter identification. In article [31], a modified PSO is used to solve the motor parameter identification objective function. In article [32], the particle motion states are improved to form an interactive and dynamically learned PSO to solve for motor parameters.
In recent years, the number of swarm intelligence algorithms has steadily increased, expanding the range of methods available for parameter identification. Ref. [33] employs PSO to identify key motor parameters, enhancing the effectiveness of model predictive control. Ref. [34] uses PSO to optimize the peak cogging torque and no-load back electromotive force (EMF) amplitude, thereby improving motor control performance. Ref. [35] introduces the improved CGCRAO algorithm to enhance parameter identification accuracy, offering new insights in the field. Reference [36] takes into account the negative effects of the drive circuit, such as the dead time of the switching devices, the time delay of the low-pass filter, and angle deviation, to improve the accuracy of parameter identification results.
ROA [37] has a better solution at lower population sizes. In article [38], ROA reduces the scheduling time compared to other algorithms. In article [39], an algorithm based on ROA is implemented for precise localization to improve the accuracy of range measurements. In article [40], ROA is used to significantly improve job scheduling. By improving ROA, motor parameters can be more accurately identified, yielding new insights. To ensure the algorithm meets the requirements of parameter identification, this paper introduces three improvements aimed at enhancing the accuracy and stability of the process.
In this article, the signal injection method combined with intelligent algorithms is used for PMSM parameter identification. Since the direct application of ROA does not solve the problem effectively, this article improves ROA using the adaptive exploration radius, raccoon-washing-food-inspired, and escaping-predator strategies. To validate the effectiveness of EROA, the more classical algorithms ROA, PSO [41], E_WOA [42], and GA [43] were selected for comparison using some of the IEEE CEC 2015 test sets. When compared with recent algorithms such as the Snow ablation optimizer [44] and the Walrus Optimization Algorithm [29], the newly proposed EROA reaches an advanced level of performance. EROA has a large advantage in convergence speed and solution accuracy. Parameter identification objective functions are established in simulation and motor experiments for comparison. EROA can find the motor parameters more quickly.
2. Parameter Identification of PMSM
The parameter identification method in this article is based on the voltage equations in the steady state of the PMSM. To facilitate the analysis, the motor voltage Equation (1), which ignores the effect of core saturation and losses of PMSM, is considered in the rotating coordinate system.
where and are the -axis voltages; and are the -axis currents; are the electromechanical angular velocities; is the stator resistance; and are the -axis inductances; and is the permanent flux linkage. Through PMSM vector control, the motor steadily operates at a certain speed. At this point, the -axis currents of the PMSM remain stable in a very small range. It may be assumed that . From Equation (1), we obtain Equation (2).
Injecting different currents into the d-axis increases the number of equations. The system of full-rank voltage equations is shown in (3), which can be used as a reference model for the motor.
where = 0 A defines the formula subscript as 0, and = −1 A defines the formula subscript as 1. The adjustable model (4) is formed using the PMSM run data and the reference model.
Using the sum of squares of the differences between the reference and adjustable models, we obtain (5) as a fitness function for parameter identification.
When suitable motor parameters are encountered such that the sum of the four functions is 0, the PMSM parameters in (6) are found.
is the fitness of the parameter vector p. In this paper, this function is solved by improving the raccoon optimization algorithm, and the final parameter vector p can be obtained when the function converges to a certain range.
3. Enhanced ROA
3.1. Characteristics of ROA
ROA is mainly characterized by generating two sets of scenarios, and , in two ranges around the initial location , namely the reachable zone radius (RZR) and the visible zone radius (VZR). We compare the fitness values of , , and to obtain their best solution (7).
By comparing the fitness value of the new generation with , the algorithm determines whether to update the globally optimal solution . If no good solution is selected around , we infer that = , which represents no movement in the raccoon location and requires a cumulative migration factor (MF). When MF reaches a certain number of times, the position is forced to update. If a certain number of times is not reached, we generate a different population. We perform the iteration NI times and finally output . To quickly find the optimal solution, it is necessary to rationalize the migration scheme and the new position after the migration.
To improve the algorithm’s accuracy, ROA is improved using the adaptive exploration radius, raccoon-washing-food-inspired, and escaping-predator strategies to form EROA. Figure 1 shows the overall flow of EROA. In Figure 1, i is the current number of iterations; is the current number of times = ; is the raccoon natural community; and , , , and are the values of , , , and for the fitness values, respectively.
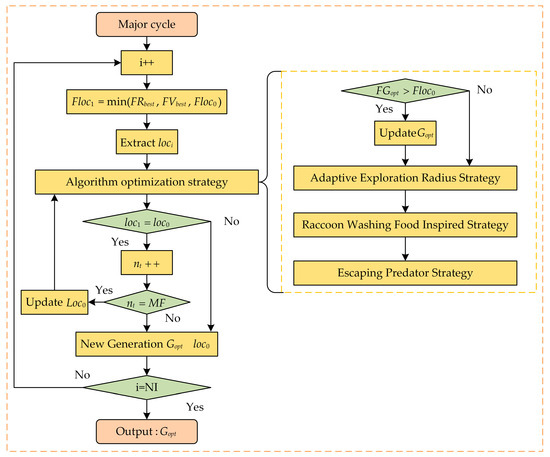
Figure 1.
EROA main loop.
3.2. Adaptive Exploration Radius Strategy
The algorithm uses the adaptive exploration radius strategy to facilitate the solution, as the initial exploration radius is a human-set initial value, but each dimension is almost unpredictable for the problem that requires solving. To improve the convergence accuracy of the algorithm, one approach is to slowly converge the exploration radius during the iteration of the algorithm. The second approach is to explore different positions so that the algorithm can be automatically adjusted to the appropriate exploration radius.
The strategy to decrease the exploration radius with the number of iterations is expressed as (8).
where and constitute the exploration range, and k controls the range of RZR initial values. To adapt the radius of exploration so that the algorithm can automatically learn, we define (9) as follows:
where is the raccoon community, Nop is the set population density, is the adaptive radius updated with iterations, and round is defined to generate random positive integers. To ensure that has self-learning properties, we set (10).
where is the evaluated value of another raccoon that arrives at the new location under the influence of , and rand denotes a 0–1 uniform distribution. The adaptive updating of RZR is performed during the iteration of the algorithm, as shown in (11).
If is updated, the adaptive radii RZR and VZR are updated with . The adaptive exploration radius strategy allows the algorithms to exchange optimal target information during the optimization process, improving the accuracy of the algorithm solution.
3.3. Raccoon-Washing-Food-Inspired Strategy
The raccoons must find a nearby water source to wash their food. From this perspective, the behavior of raccoons searching for wetlands after capturing food is modeled. Assume that the current optimal raccoon is the earliest to find food and arrive at the water source to wash the food, and the other raccoons come relatively late. At this point, the cluster of raccoons by the water edge can be represented as a partial cluster near the optimal raccoon, which produces a better solution by combining the optimal raccoon with the later ones in conjunction with one another. A mathematical model of the process in which the optimal raccoon and other raccoons head out to a nearby water source is established as follows. The small cluster gRZR (12) represents the concentration of raccoons near a given water source.
where the new location of each raccoon is updated according to (13).
Loc(s,:) is the location of another raccoon with the same objective. The smallest (14) is selected in gRZR (12).
The fitness of relative to determines whether is updated, as shown in Equation (15).
This produces better results and improves the algorithm solution accuracy. Using the raccoon-washing-food-inspired strategy, a new generation of raccoons can be provided with a new advantageous position, guiding the algorithm to quickly pursue the optimal goal.
3.4. Escaping-Predator Strategy
A raccoon ducking under attack often creates new possibilities. The raccoon escape strategy is modeled by assuming that a raccoon looks for a direction to quickly escape after being attacked. During this behavior, the ability of the raccoon to arrive at a new safe location implies that the algorithm finds a new target. Failure to do so means that the raccoon fails to escape, and a better target is not found. is the new location of the raccoon after it has escaped, and its update process can be tabulated as shown in (16).
and are the current minimum and maximum ranges of escape of the raccoon, which continuously change as the algorithm iterates; xi is a random integer, and 0 < xi ≤ Nop. The resulting superior solution is used to update the raccoon colony (17).
which can be compared with (18).
Here, the algorithm can greatly jump out of the local optimum and find better results. Under certain conditions, the escaping-predator strategy offers an effective solution for the raccoon’s new location, aiding in the optimization of the algorithm and potentially improving its solution speed.
In summary, this article employs the adaptive exploration radius, raccoon-washing-food-inspired, and predator-escape strategies to enhance ROA, resulting in the generation of EROA.
4. Simulation and Experimental Methods
4.1. Algorithm Testing
To validate the EROA effectiveness, the algorithm was tested through some of the IEEE CEC 2015 function test sets. Five algorithms were set to identical conditions with a total population size of 100 and 1000 iterations: ROA, PSO, E_WOA, GA, and EROA. To approach the dimensionality of the problem of parameter identification, we tested the algorithms by selecting their medium fixed-dimensional multi-peaked test functions . Equations (19)–(27) can be used to express the objective function of the test functions .
Table 1 shows the values of the fixed-dimensional multi-peak test functions .

Table 1.
IEEE CEC2015 test function set.
Figure 2 shows the effect of the test function algorithm iteration. Figure 2 compares the performance of five algorithms—EROA, ROA, PSO, GA, and E_WOA—during the solution process. As shown in Table 1, the dimensions of the 9 IEEE CEC 2015 test set functions represent varying levels of problem difficulty. The dimensions of these functions are similar to those used in the parameter identification process in this study. By comparing these test set functions, the most suitable algorithm for parameter identification can be optimized.
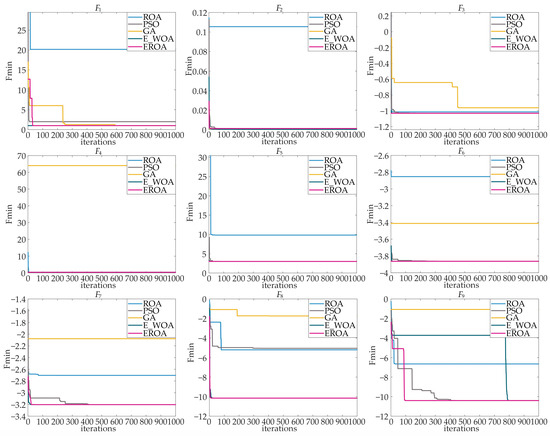
Figure 2.
Test results comparing EROA with other typical algorithms after 1000 iterations.
Equations (19)–(23) represent complex solution functions with 2 or 4 dimensions. The algorithm performance comparison for these functions is shown as in Figure 2. Among the algorithms, GA and ROA show poor optimization performance, while EROA, PSO, and E_WOA exhibit better overall performance and faster convergence.
For the solution process of Equations (24) and (25), represented by in Figure 2, the presence of multiple extreme points in the function makes it easy for the algorithm to fall into local optima. ROA and GA are more susceptible to this issue and fail to reach the optimal value. In contrast, EROA, PSO, and E_WOA perform well by escaping the local optimum and successfully optimizing toward the global optimum.
The objective functions (26) and (27) are more prone to falling into local optima than function (27). The optimization process for these functions is shown in in Figure 2. ROA, GA, PSO, and E_WOA are differently affected by this issue, with EROA demonstrating a clear advantage in escaping the local optimum.
Overall, EROA could quickly find the optimal value during the solution process. Compared with ROA, EROA has a large improvement in solving speed and accuracy. Compared with algorithms such as E_WOA, EROA is leading in . Ten independent experiments were conducted for each algorithm, and the average results are shown in Table 2. As shown in Table 2, there is a significant improvement in EROA compared to ROA. In , , , , , and , EROA, PSO, and E_WOA have identical effects. In and , the value sought by EROA is minimized. In , EROA and PSO have similar effects. Overall, EROA excels compared to other algorithms.

Table 2.
Comparison of EROA with other typical algorithms based on the average value over 10 iterations.
4.2. Simulation Analysis
The PMSM vector control simulation model was built in MATLAB. The motor in this experiment was a surface-mounted PMSM. In the process of identifying the motor parameters, let = = . Table 3 shows the PMSM parameters.

Table 3.
PMSM data sheet.
We set the simulation parameters as follows: DC bus voltage, 150 V; motor angular velocity speed, 40 Hz; and 0.5 s to join the load. Throughout the control process, a current with = 0 A and = −1 A was injected into the d-axis. The two different currents can be separated by 0.1 s to make it easier for the parameter identification algorithm to process the motor operating data. During motor operation, data such as , , , , and were saved to the MATLAB workspace. To test the algorithms, the algorithm population size was set to 20, and the number of iterations was set to 200. Seventy data sets were selected for parameter identification. Table 4 shows the average values of the solution effectiveness of several algorithms, including EROA.

Table 4.
Seven algorithms for solving statistical tables.
From Table 4, EROA had the highest solution accuracy with three parameters within 1% error. ROA had large errors in and , which could not be satisfied. PSO had a similar solving accuracy to EROA. The error of the E_WOA solution was large, which shows that the EROA solution is more stable than the E_WOA solution under identical conditions. At the end of Table 4, two relatively advanced algorithms, WaOA and SAO, are introduced for comparison with the performance of EROA. Under the same conditions, EROA demonstrates comparable solution capabilities to these advanced algorithms, indicating that the optimization approach presented in this paper significantly enhances the performance of the original algorithm.
4.3. Experimentation
Over time, various energy losses within the motor accumulate as heat. Changes in motor temperature lead to nonlinear variations in resistance parameters, which, in turn, affect the conduction current. As an inductive element, the magnitude of the motor stator winding inductance can cause saturation of the winding coil’s magnetic field, leading to changes in inductance. Decoupling control is central to FOC (Field-Oriented Control), and variations in electrical parameters can disrupt this control. This disruption may prevent the accurate regulation of the torque and excitation components, thereby affecting FOC performance. In addition, the demagnetization of the permanent magnets due to high temperatures can cause permanent damage to the motor control. Therefore, parameter identification plays a critical role in motor control.
In order to fully verify the use of EROA to solve PMSM parameter identification, application tests of the algorithm were conducted on the actual motor control platform. The motor control platform was the TMDSHVMTRPFCKIT from Texas Instruments (TI). Figure 3 shows the physical motor control platform.
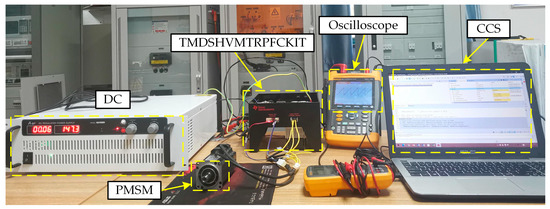
Figure 3.
TMDSHVMTRPFCKIT experimental bench.
The experimental platform was a PMSM control system with TMS320F28335 as the core. The PMSM model number was EMJ-04APB22, and Table 3 shows the main parameters. Motor motion state control was performed using Code Composer Studio (CCS). The inverter DC bus voltage was set to 150 V, and an Interrupt Service Routine frequency of 10 kHz was defined. A segment of motor operating data, including the -axis voltage, current, and , was saved while the motor was stabilized. Due to the tight storage resources inside the chip, 70 sets of motor operation data were saved for this experiment. The operating data in the control chip were uploaded to the host computer through CCS, and the motor recognition function was implemented in MATLAB. Figure 4 shows the motor parameter identification process, a common method for PMSM parameter identification. The motor control platform uses vector control to operate the PMSM. During motor operation, a current is applied to the d-axis, with id set to either 0 A or −1 A. The d-axis current change interval can be referenced through simulation. Memory resources on the motor control chip are used to store the operational data required for parameter identification. Data such as , and are then uploaded via the communication interface between the control board and the computer, enabling MATLAB to process the data. By running EROA to solve the parameter identification fitness function, the motor’s electrical parameters can be obtained.
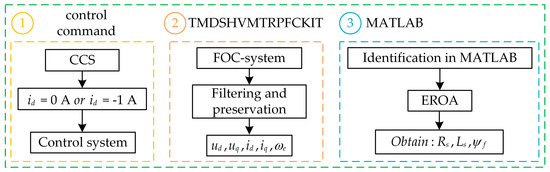
Figure 4.
Experimental process.
In this process, a set of experimental data was selected to compare the effects of EROA, ROA, PSO, GA, and E_WOA. The algorithm parameters were set to populate 20 and 300 iterations. Figure 5 shows the performance of the five intelligent algorithms.
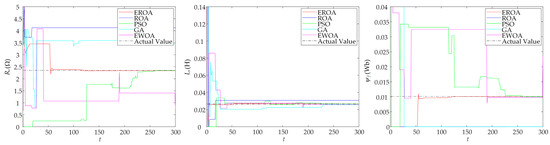
Figure 5.
Comparison diagram of the algorithm iteration process.
When EROA was used to determine the motor parameters, the convergence speed was faster, and the results were more accurate and more stable compared to the other four algorithms. PSO had similar solution accuracy to EROA, but EROA converged more quickly and stabilized at approximately 150 iterations. This algorithm maintained a high accuracy with few iterations and obtained a more optimal solution. This result is consistent with the simulation results. Figure 6 shows the parameter identification results for the 70 sets of data.
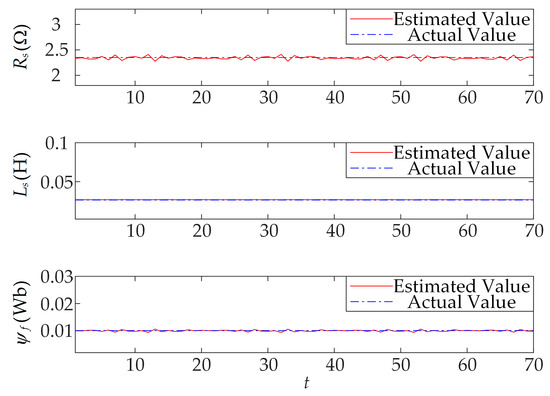
Figure 6.
Results of 70 sets of data identification in MATLAB.
The EROA identification had a more stable effect than the identification of the other algorithms. Table 5 shows the statistical analysis results of the 70 sets of data. As shown in Table 5, this article’s improved raccoon algorithm EROA was used to recognize the motor parameters with average errors of 1% for and and 1.6% for .

Table 5.
Statistical results of the MATLAB identification of 70 sets of data.
In this article, EROA was applied to the motor control system to identify the motor parameters on the motor control platform TMDSHVMTRPFCKIT. Figure 7 shows the parameter identification process. Compared to Figure 4, the key difference in Figure 7 is that the parameter identification process no longer requires computer involvement. This represents a significant innovation of this study, where EROA is applied directly to the motor control chip. The motor control platform is run to collect operational data under and . These data are processed directly within the motor control chip. Following the parameter identification principles outlined in Section 2, the motor operation data are used to construct a parameter identification fitness function. Finally, EROA is run on the motor control chip to obtain the motor’s electrical parameters.
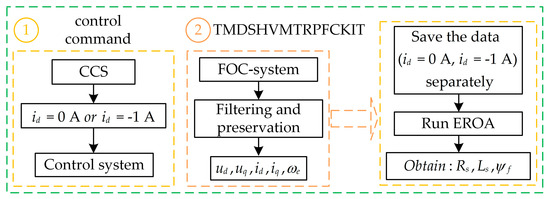
Figure 7.
Parameter identification process on a motor control platform.
We controlled the motor motion state and saved a portion of the motor operation data. The EROA solving algorithm was applied in the motor control chip to solve the motor parameters. To ensure the accuracy of the EROA solution, the population was set at 20, and the number of iterations was set at 400. The obtained motor parameters were imported into the computer for review, and Figure 8 shows the results.
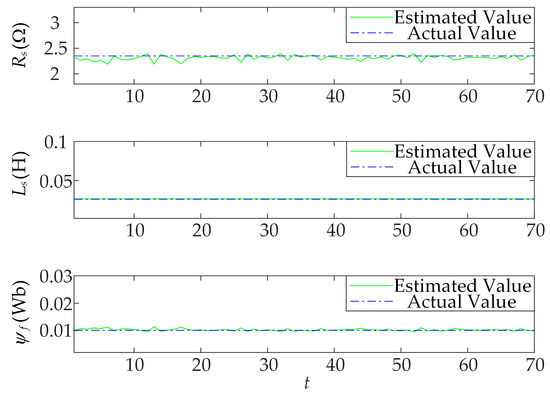
Figure 8.
EROA Recognition Results in the Experimental Platform Chip.
The data therein were analyzed, and Table 6 shows the results. The parameter identification in the motor control system was performed using EROA. The error of the required parameters was within 2%. In summary, this method can be used to monitor changes in motor parameters. EROA can be used to solve the fitness function and determine the motor parameters at regular intervals.

Table 6.
Statistical analysis of the EROA identification results in the experimental platform.
5. Conclusions
In this article, , , and of PMSMs were identified based on an enhanced raccoon optimization algorithm. ROA was improved using the adaptive exploration radius, raccoon-washing-food-inspired, and escaping-predator strategies to form EROA with better solution efficiency. The simulation results show that EROA can achieve faster converge speed and higher robustness than ROA. From the experimental results, EROA can quickly find the motor parameters, which are consistent with the simulation results, and the error of the identification results does not exceed 2%.
In conclusion, this study offers significant implications for the field of motor control. The flexibility of intelligent algorithms has expanded the application scope of parameter identification techniques. In future work, the research will focus on reducing the computational complexity of intelligent algorithms, enhancing the speed and accuracy of parameter identification, and expanding its applications to various contexts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.H. and X.Y.; methodology, J.Z.; software, J.Z.; validation, J.Z., X.Y. and Z.F.; formal analysis, X.Y.; investigation, J.Z.; resources, X.Y.; data curation, J.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.Y.; visualization, X.Y.; supervision, Z.L.; project administration, X.H.; funding acquisition, X.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China General Program, the Henan Province Key R&D Project, the Science and Technology Development Project of Henan Province, and the Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation, grant numbers 62273313, 241111242300, 242102240110, 2023JJ60178, and 2024JJ8046.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, Y.; Liao, W.; Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, M.; Li, C.; Huang, S. A Robust DPCC for IPMSM Based on a Full Parameter Identification Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 7695–7705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Li, B.; Ding, D.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. Virtual-Axis Injection Based Online Parameter Identification of PMSM Considering Cross Coupling and Saturation Effects. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 5791–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, P.; Yang, X. DC Bus Current Sensed Space Vector Pulsewidth Modulation for Three-Phase Inverter. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qiu, J. Adjacent-Vector-Based Model Predictive Control for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors With Full Model Estimation. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, G.; Le, V.D.; Le, C.Q. A Novel Model-Predictive Direct Control for Induction Motor Drives. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2019, 14, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldegiorgis, A.T.; Ge, X.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, H.; Hassan, M. Sensorless Control of Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives Considering Resistance and Permanent Magnet Flux Linkage Variation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 7716–7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, D.; Shen, Y.; Liu, A.; Yang, X.; Zhao, J. Full Speed Range Position-Sensorless Compound Control Scheme for PMSMs. J. Power Electron. 2022, 22, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosch, A.; Wallscheid, O.; Bocker, J. Long-Term Memory Recursive Least Squares Online Identification of Highly Utilized Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors for Finite-Control-Set Model Predictive Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Huang, S.; Niu, F.; Zhang, J. Online Identification of Inductance and Flux Linkage for Inverter-Fed SPMSMs Using Switching State Functions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Chong, E. Transient Performance Improvement of Deadbeat Predictive Current Control of High-Speed Surface-Mounted PMSM Drives by Online Inductance Identification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 12358–12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkkanen, M.; Pescetto, P.; Mölsä, E.; Saarakkala, S.E.; Pellegrino, G.; Bojoi, R. Sensorless Self-Commissioning of Synchronous Reluctance Motors at Standstill Without Rotor Locking. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Qu, L.; Zhan, H.; Xu, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. Self-Commissioning of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives at Standstill Considering Inverter Nonlinearities. IEEE Trans. Power Electronics. 2014, 29, 6615–6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odhano, S.A.; Pescetto, P.; Awan, H.A.A.; Hinkkanen, M.; Pellegrino, G.; Bojoi, R. Parameter Identification and Self-Commissioning in AC Motor Drives: A Technology Status Review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 3603–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, F.; Huang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, Z. Online Inductance Identification Using PWM Current Ripple for Position Sensorless Drive of High-Speed Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 12426–12436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-L.; Liu, G.-R.; Chen, N.-H.; Lou, T.-S. Desensitized Ensemble Kalman Filtering for Induction Motor Estimation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 78029–78036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Wang, G.; Li, C.; Xu, D.G. Offline Parameter Self-Learning Method for General-Purpose PMSM Drives with Estimation Error Compensation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 11103–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Mao, K.; Zheng, S.; Zhou, C.; Zhong, Q. Position Sensorless Drive with Online Parameters Estimation for Magnetic Suspension Centrifugal Compressor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 9384–9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, Z. Overall Electrical Parameters Identification for IPMSMs Using Current Derivative to Avoid Rank Deficiency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 7515–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J. Influence of Nonideal Voltage Measurement on Parameter Estimation in Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 2438–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, B.; Yang, M.; Yang, X.; Guo, X. Decoupling Algorithm for Online Identification of Inductance in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on Virtual Axis Injection Method and Sensorless Control. Energies 2024, 17, 6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kennel, R. General Formulation of Kalman-Filter-Based Online Parameter Identification Methods for VSI-Fed PMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 2856–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, M. Enhancing Low-Speed Sensorless Control of PMSM Using Phase Voltage Measurements and Online Multiple Parameter Identification. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 10700–10710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Yang, P.; Hua, W.; Buja, G. Effects of Triangular Wave Injection and Current Differential Terms on Multiparameter Identification for PMSM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 2943–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.-C.; Lim, D.-K. Novel Method of Deriving Torque and Speed Curve of the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Using Initial State Finite Element Analysis. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8203906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, N.; Wang, G.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. An Offline Parameter Self-Learning Method Considering Inverter Nonlinearity with Zero-Axis Voltage. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 14098–14109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-H.; Wei, H.-L.; Zhong, Q.-C.; Liu, K.; Xiao, X.-S.; Wu, L.-H. Parameter Estimation for VSI-Fed PMSM Based on a Dynamic PSO with Learning Strategies. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 3154–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, G.; Cui, Q.; Xu, D.G. An Impedance Model-Based Multiparameter Identification Method of PMSM for Both Offline and Online Conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajwar, K.; Deep, K.; Das, S. An Exhaustive Review of the Metaheuristic Algorithms for Search and Optimization: Taxonomy, Applications, and Open Challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 13187–13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojovsky, P.; Dehghani, M. A New Bio-Inspired Metaheuristic Algorithm for Solving Optimization Problems Based on Walruses Behavior. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Raahemi, B. Bio-Inspired Feature Selection Algorithms with Their Applications: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 43733–43758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, C.; Shen, A.; Bing, L. Identification of PMSM Parameters with Time-Error Compensated Based on Contractile Factor Anti-Predator PSO. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 10, 4006–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-H.; Wei, H.-L.; Li, X.-H.; Liu, K.; Zhong, Q.-C. Global Identification of Electrical and Mechanical Parameters in PMSM Drive Based on Dynamic Self-Learning PSO. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 10858–10871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, Y. Parameter Identification for SPMSM with Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Using Online PSO. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 10, 4055–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, Y.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Du, J. Multi-Objective Optimization Analysis of Electromagnetic Performance of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on the PSO Algorithm. Energies 2024, 17, 4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jian, X. Parameter Identification of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on CGCRAO Algorithm. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 124319–124330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierczynski, M.; Jakubowski, R.; Kupiec, E.; Niewiara, L.J.; Tarczewski, T.; Grzesiak, L.M. Identification of the Parameters of the Highly Saturated Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM): Selected Problems of Accuracy. Energies 2024, 17, 6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangbari Koohi, S.; Abdul Hamid, N.A.W.; Othman, M.; Ibragimov, G. Raccoon Optimization Algorithm. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 5383–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohi, S.Z.; Hamid, N.A.W.A.; Othman, M.; Ibragimov, G. HATS: HetTask Scheduling. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2023, 11, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, A.; Priya, M.D.; Malar, A.C.J.; Janakiraman, S. Raccoon Optimization Algorithm-Based Accurate Positioning Scheme for Reliable Emergency Data Dissemination under NLOS Situations in VANETs. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 10405–10424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohi, S.Z.; Abdul Hamid, N.A.W.; Othman, M.; Ibragimov, G. ROA-CONS: Raccoon Optimization for Job Scheduling. Symmetry-Basel 2021, 13, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, F.; Walczak, B. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). A Tutorial. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 149, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi-Shahraki, M.H.; Zamani, H.; Mirjalili, S. Enhanced Whale Optimization Algorithm for Medical Feature Selection: A COVID-19 Case Study. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 148, 105858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.H. Genetic Algorithms and the Optimal Allocation of Trials. SIAM J. Comput. 1973, 2, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Liu, S. Snow Ablation Optimizer: A Novel Metaheuristic Technique for Numerical Optimization and Engineering Design. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 225, 120069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).