Electromagnetic Modeling Framework of Thermal Systems for Real-Time Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Eddy Current-Based Heating
3. The Electromagnetic Real-Time Modeling
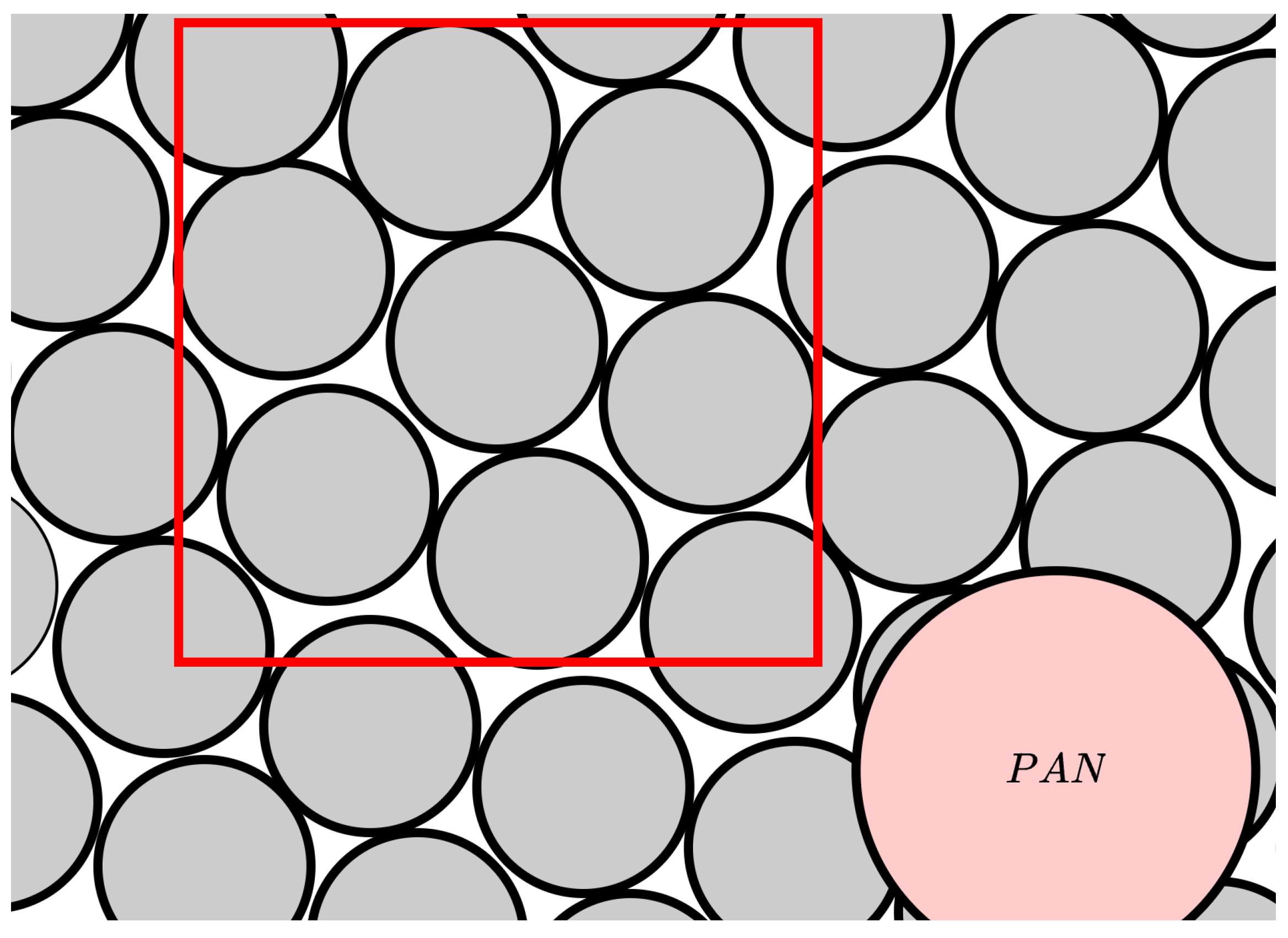
3.1. The FEM Simulation
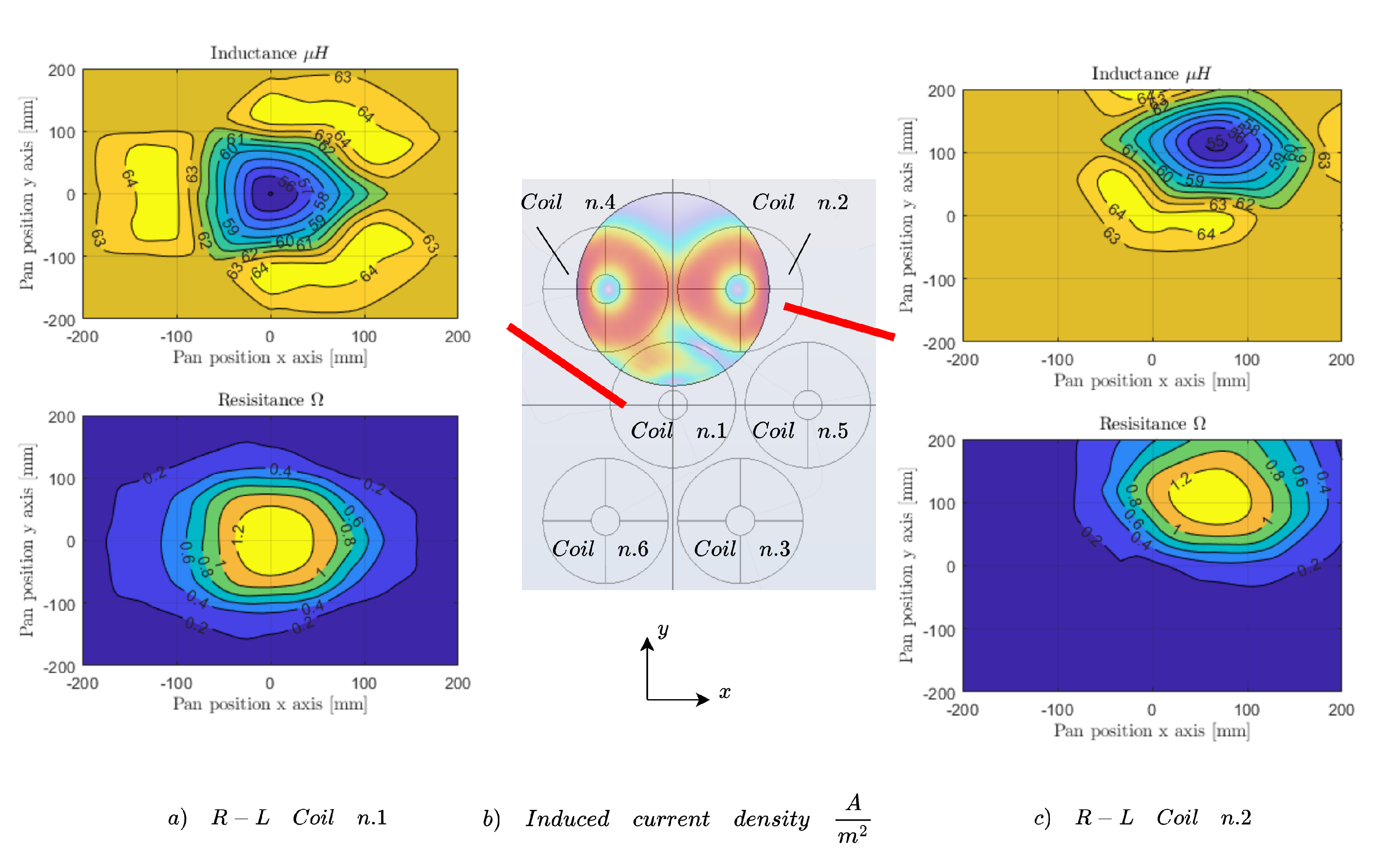
3.2. Parameters Extraction
3.3. Look-Up Table Integration
3.4. Numerical Electromagnetic Results
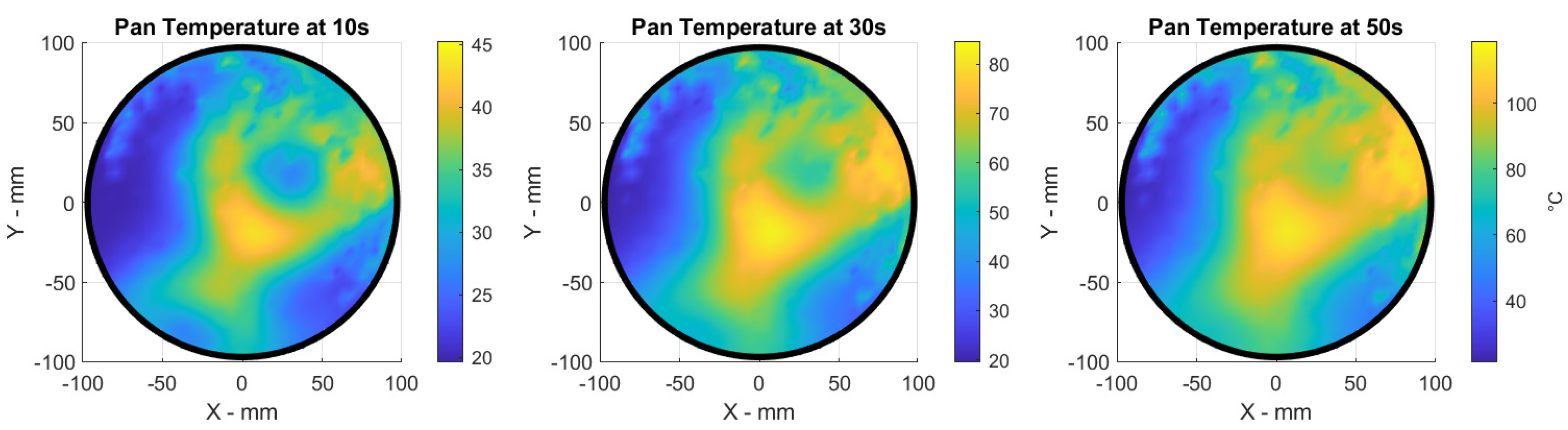
4. The Thermal Real-Time Modeling
Numerical Thermal Results
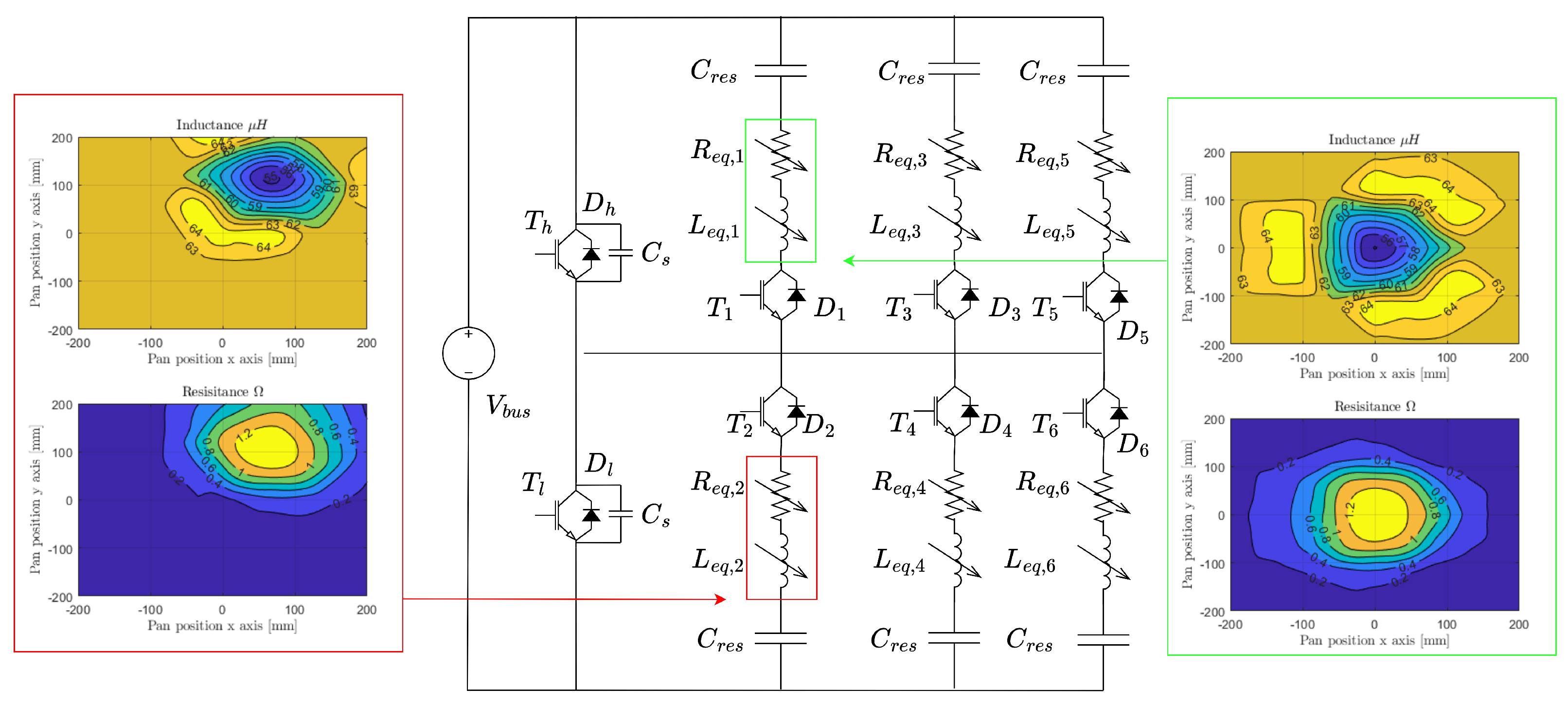
5. Resonant Converter and Control Algorithm
5.1. Setup and Scheme
- Main Core: Acts as a bridge to simulate the resonant converter in an FPGA module, enhancing computational speed.
- Second Core: Implements the regulation scheme and provides switching signals in parallel to an external Microcontroller Unit (MCU).
- Third Core: Analyzes thermal dynamics.
- Last Core: Serves as a bridge between the real-time simulation and an external user interface.
5.2. The Resonant Converter
5.3. The Control Algorithm
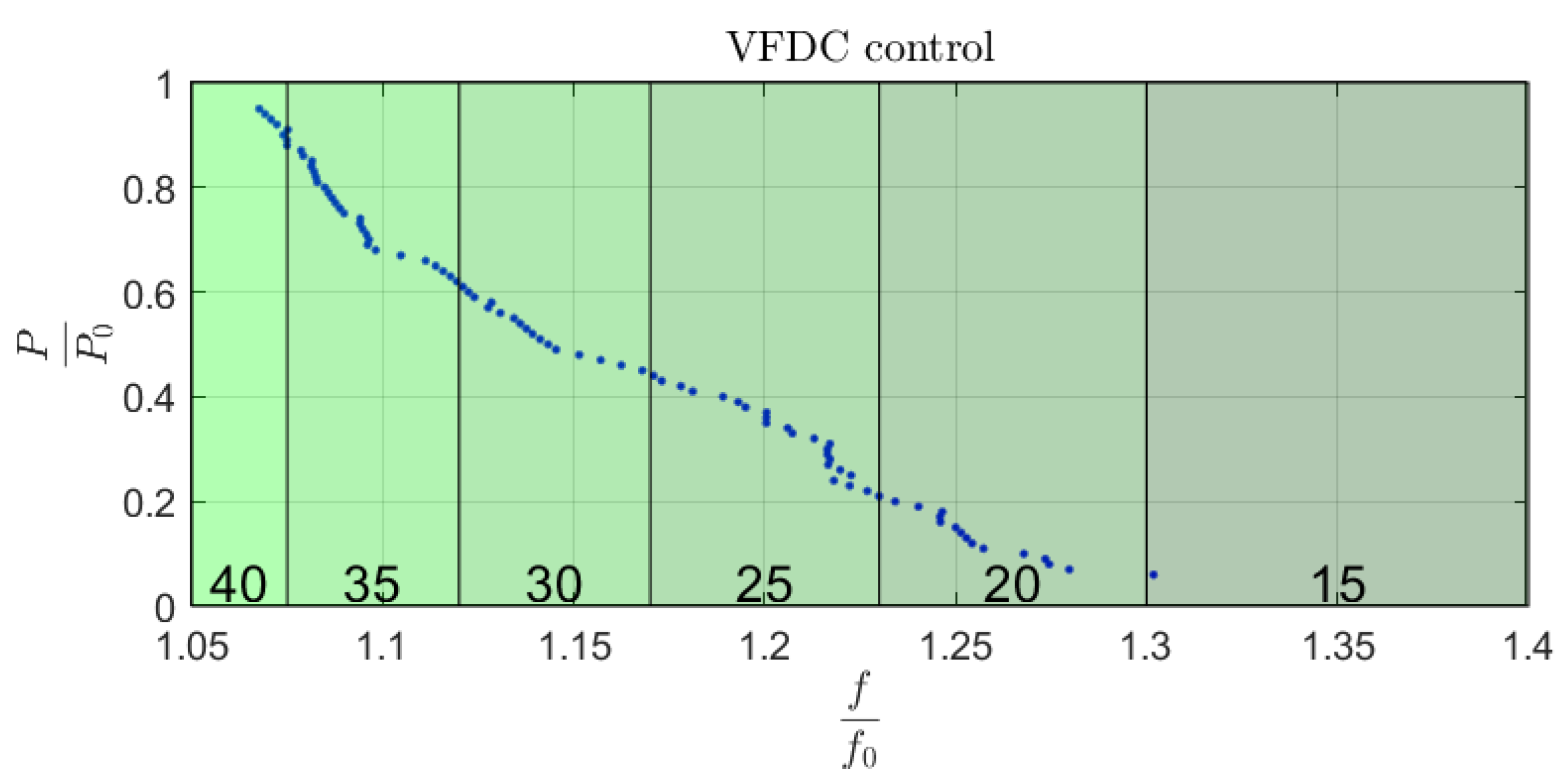
5.3.1. Variable Frequency Duty Cycle
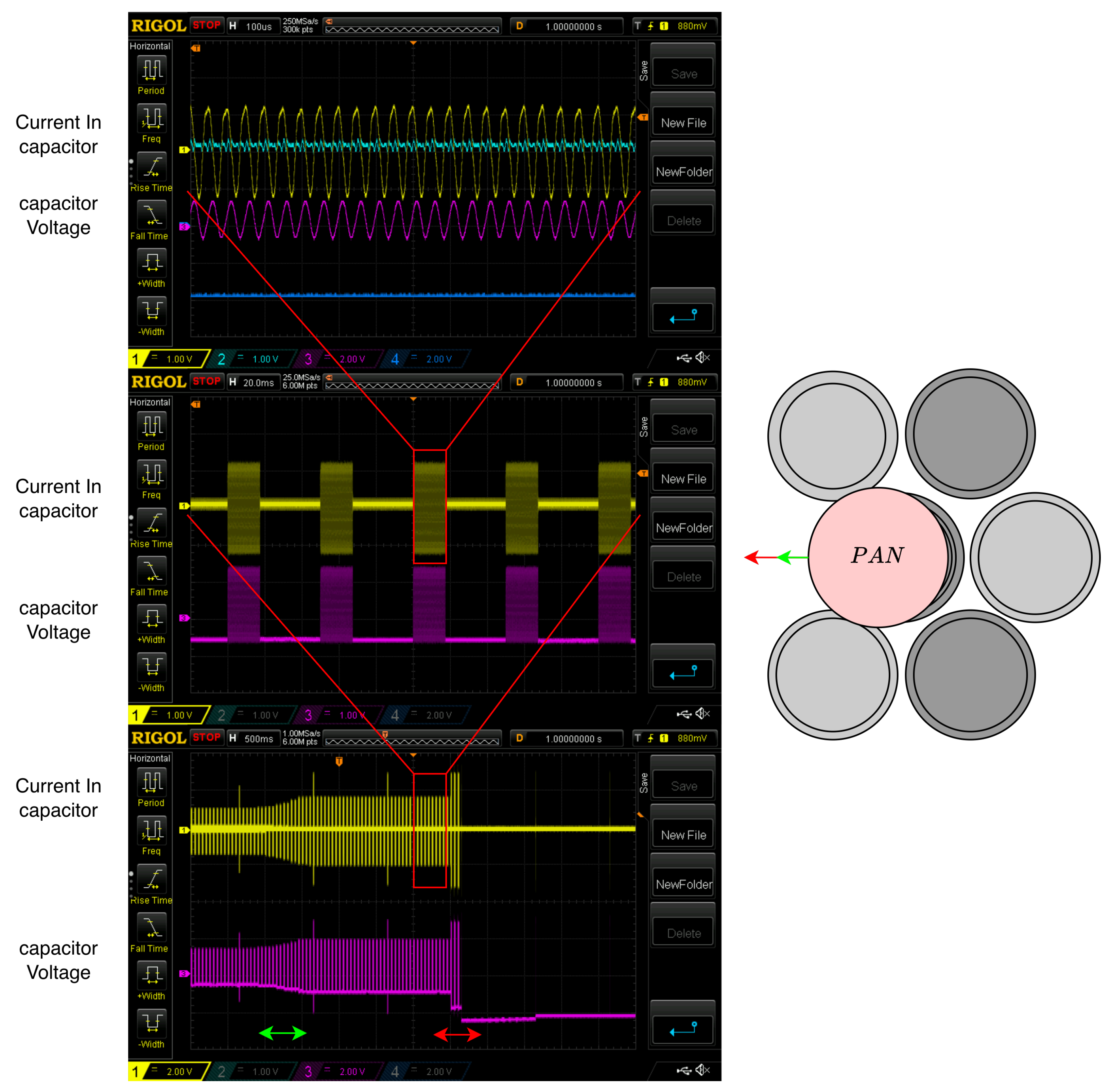
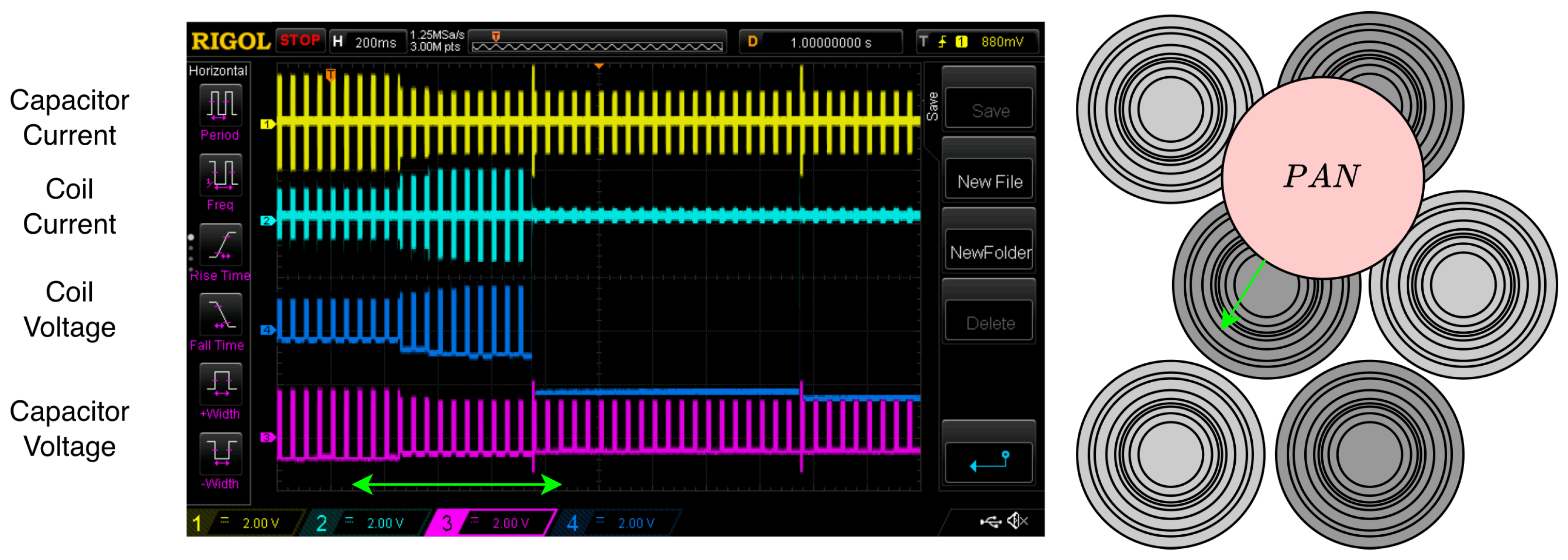
5.3.2. Load Identification
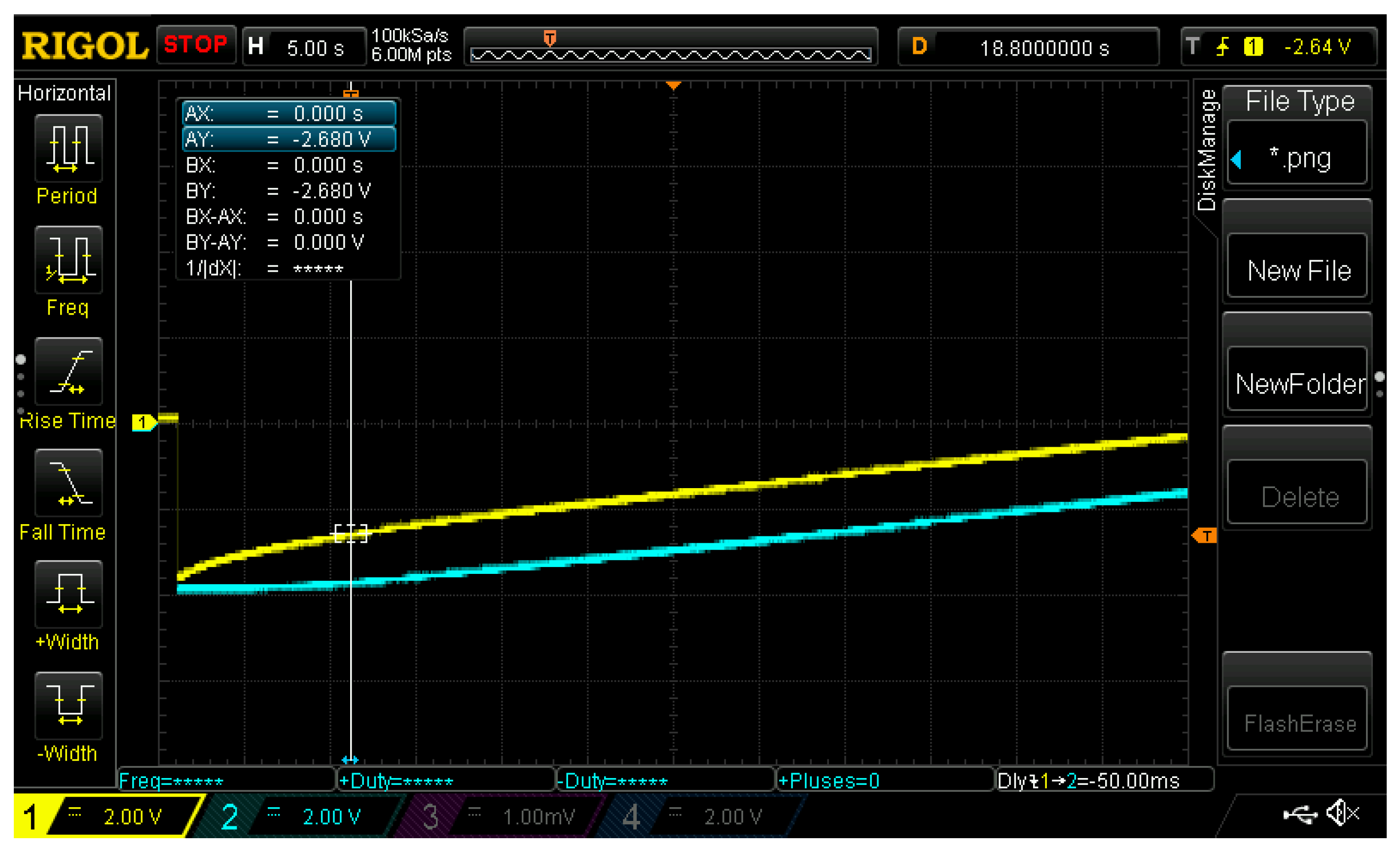
6. Results
7. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prist, M.; Pallotta, E.; Cicconi, P.; Monteriù, A.; Germani, M.; Longhi, S. Induction Mold Heating: Modelling and Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation for Temperature Control. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2018 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/ICPS Europe), Palermo, Italy, 12–15 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zuo, G.; Chen, J.; Wan, M. A rapid control prototyping system design for temperature control of plastic extruder based on labview. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electronics, Communications and Control (ICECC), Ningbo, China, 9–11 September 2011; pp. 2471–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spateri, E.; Gruosso, G. Validation through HIL of an MPC regulator for thermoforming applications. In Proceedings of the IECON 2024—50th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–6 November 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baz, W.; Mayerhofer, L.; Tzscheutschler, P.; Wagner, U. Hardware in the Loop Real-Time Simulation for Heating Systems: Model Validation and Dynamics Analysis. Energies 2018, 11, 3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, X.H.; Kwak, S.K.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, K.A. Comprehensive Electric-Thermal Photovoltaic Modeling for Power-Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation (PHILS) Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 6255–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejeda De La Cruz, A.; Riviere, P.; Marchio, D.; Cauret, O.; Milu, A. Hardware in the loop test bench using Modelica: A platform to test and improve the control of heating systems. Appl. Energy 2017, 188, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhan, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Hardware-in-the-loop Real-time Simulation of High-power Inverter Based on Electro-thermal Coupling Effect. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia), Nanjing, China, 29 November–2 December 2020; pp. 3531–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, S. Fundamentals of Electroheat: Electrical Technologies for Process Heating; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumed, E.; Acero, J.; Lope, I.; Burdío, J.M. Design methodology of high performance domestic induction heating systems under worktop. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaal, M.H.; Abdulbaqi, I.M.; Thejel, R.H. Modeling, design and analysis of an induction heating coil for brazing process using FEM. In Proceedings of the 2016 Al-Sadeq International Conference on Multidisciplinary in IT and Communication Science and Applications (AIC-MITCSA), Baghdad, Iraq, 9–10 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boadi, A.; Tsuchida, Y.; Todaka, T.; Enokizono, M. Designing of suitable construction of high-frequency induction heating coil by using finite-element method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 4048–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.K.; Choi, K.; Roh, H.S.; Hahn, S.Y. Optimal design procedure for a practical induction heating cooker. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2000, 36, 1390–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaboudez, C.; Clain, S.; Glardon, R.; Mari, D.; Rappaz, J.; Swierkosz, M. Numerical modeling in induction heating for axisymmetric geometries. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1997, 33, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spateri, E.; Sabug, L.; Ruiz, F.; Gruosso, G. Efficient Multiobjective Optimization Framework for Induction Heating Systems Design. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 95347–95355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumed, E.; Lope, I.; Acero, J. Induction Heating Adaptation of a Different-Sized Load With Matching Secondary Inductor to Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhance Vertical Displacement. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 6929–6942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J.; Lope, I.; Acero, J. Nonplanar Overlapped Inductors Applied to Domestic Induction Heating Appliances. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 6916–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, O.; Burdio, J.M.; Barragan, L.A.; Acero, J.; Millan, I. Series-Resonant Multiinverter for Multiple Induction Heaters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2860–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, M.; Aslan, S.; Altintas, N.; Sinirlioglu, S. Comparison of Induction Cooker Power Converters. In Proceedings of the 2018 6th International Conference on Control Engineering and Information Technology (CEIT), Istanbul, Turkey, 25–27 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, M.; Zungor, F.; Emre, B.; Oz, B. Quasi Resonant Inverter Load Recognition Method. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 89376–89386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OPAL-RT Technologies. OPAL-RT OP4500 Real-Time Power Grid Digital Simulator. 2014. Available online: https://www.opal-rt.com/hardware/simulators/ (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- Spateri, E.; Ruiz, F.; Gruosso, G. Modelling and Simulation of Quasi-Resonant Inverter for Induction Heating under Variable Load. Electronics 2023, 12, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COMSOL AB. COMSOL Multiphysics; COMSOL AB: Stockholm, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lucia, O.; Burdio, J.M.; Millan, I.; Acero, J.; Barragan, L.A. Efficiency-Oriented Design of ZVS Half-Bridge Series Resonant Inverter With Variable Frequency Duty Cycle Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 1671–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Ye, J.; Liu, G. Novel Prognostics for IGBTs Using Wire-Bond Contact Degradation Model Considering On-Chip Temperature Distribution. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 4411–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gruosso, G.; Spateri, E. Electromagnetic Modeling Framework of Thermal Systems for Real-Time Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulations. Energies 2025, 18, 5752. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215752
Gruosso G, Spateri E. Electromagnetic Modeling Framework of Thermal Systems for Real-Time Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulations. Energies. 2025; 18(21):5752. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215752
Chicago/Turabian StyleGruosso, Giambattista, and Enrico Spateri. 2025. "Electromagnetic Modeling Framework of Thermal Systems for Real-Time Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulations" Energies 18, no. 21: 5752. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215752
APA StyleGruosso, G., & Spateri, E. (2025). Electromagnetic Modeling Framework of Thermal Systems for Real-Time Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulations. Energies, 18(21), 5752. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215752






