Advances in Numerical Reservoir Simulation for In Situ Upgrading of Heavy Oil via Steam-Based Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Simulations for Aquathermolysis of Heavy Crude Oil
2.1. Without Aquathermolysis Reactions
2.2. With Aquathermolysis Reactions
2.3. With Aquathermolysis Reactions and Catalyst Injection
2.4. Main Results of Reservoir Simulations
3. Final Remarks
4. Conclusions
- SAGD dynamics and geomechanics: The critical impact of thermal convection on energy transfer remains a cornerstone of SAGD modeling. Recent studies have quantitatively linked geomechanical changes to steam chamber conformance, showing that caprock integrity can be a limiting factor. Furthermore, incorporating non-condensable gas generation from aquathermolysis is now considered essential for accurate production forecasting, as it directly impacts chamber growth and energy efficiency.
- Advanced reaction kinetics and solvent integration: The transition from basic kinetic models to more sophisticated pathways, including coke formation and different gas generation during catalytic aquathermolysis, has highlighted the need for these latter. The synergy between solvents and aquathermolysis has been a major recent focus, with simulations demonstrating that co-injecting light solvents with catalysts can significantly enhance hydrogen donation and reduce the steam-to-oil ratio (SOR), improving project economics.
- Fluid properties and AI-assisted modeling: The sensitivity of models to relative permeability remains high, increasing the uncertainties of these approaches. A prominent trend since is the application of AI and Machine Learning (ML) to accelerate simulation workflows. These latter are used to optimize well placement and operating parameters in complex, coupled geochemical–geomechanical models, making probabilistic analysis more feasible.
- Emerging hybrid recovery techniques: Hydrogen injection has gained attraction as a method for in situ upgrading with a lower carbon footprint. These simulations consistently show that incorporating the physics of asphaltene adsorption and subsequent permeability alteration is crucial for predicting long-term performance.
5. Future Research Directions
- Full-physics coupling with AI acceleration: While recent studies have begun coupling processes, future work must achieve full integration of geomechanics, thermal, flow, and complex aquathermolysis kinetics. AI/ML should be leveraged not just as a proxy, but to discover new patterns within simulation and field data that can lead to improved physical models and real-time autonomous optimization.
- High-resolution uncertainty quantification: As models become more complex, the number of uncertain parameters grows. A systematic framework for uncertainties combining high-performance computing with advanced sampling techniques is needed to quantify the reliability of forecasts for these capital-intensive projects, moving from deterministic to probabilistic forecasting.
- Modeling for emissions reduction and sustainability: Future simulations must explicitly track carbon generation and account for the fate of injected gases like hydrogen or CO2. This will be essential for evaluating the environmental and economic benefits of novel processes, such as catalytic aquathermolysis with carbon capture, utilization, and storage.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Constant for equilibrium correlation (Equation (1)) | |
| The stoichiometric coefficient for component i | |
| Collision factor for pathway j | |
| Aromatics | |
| Asphaltenes | |
| AQT | Aquathermolysis |
| Constant for equilibrium correlation (Equation (1)) | |
| Bottom hole pressure | |
| Constant for equilibrium correlation (Equation (1)) | |
| Computer Modeling Group | |
| Single pseudo-component responsible for H2S production | |
| Single pseudo-component responsible for CO2 production | |
| cSOR | Cumulative steam-to-oil ratio |
| Cyclic steam stimulation | |
| Distillates | |
| The activation energy for pathway j | |
| Gases | |
| Reactive sulfur species | |
| High-molecular-weight gases | |
| Heavy oil | |
| In situ upgrading technology | |
| Equilibrium constant | |
| Henry’s constant | |
| Reaction rate coefficient for pathway j | |
| Irreversible retention constant | |
| Reversible adsorption retention constant | |
| Reversible desorption retention constant | |
| Light oil | |
| Naphtha | |
| Moles of nanocatalyst in phase p | |
| Moles of nanocatalyst in rock | |
| Number of moles in oil | |
| Total number of moles in phase p | |
| Number of moles in water | |
| Total pressure | |
| p* | Saturation pressure, KPa |
| R | Gas constant = 8.314, J/mol-K (Equations (1) and (2)) |
| Resins | |
| Residue | |
| Reaction rate of component i | |
| Irreversible non-equilibrium retention | |
| Reversible non-equilibrium retention | |
| Universal gas constant | |
| Saturates | |
| Steam-assisted gravity drainage | |
| Steam flooding | |
| Steam with a mixture of catalyst, hydrogen, and vacuum residue | |
| Steam Thermal Advanced Recovery Simulator | |
| Solvent and water-aided electrical heating | |
| Temperature | |
| University of Texas Chemical Compositional | |
| Vacuum gas oil | |
| Mole fraction of the nanocatalyst in rock that is irreversible | |
| Mole fraction of the nanocatalyst in rock that is irreversible in equilibrium | |
| Mole fraction of the nanocatalyst in rock that is reversible | |
| Mole fraction of the nanocatalyst in rock that is reversible in equilibrium | |
| Convective heat transfer coefficient | |
| Heat conductivity | |
| v | Partial molar volume of aqueous solute |
| γg | Activity coefficient of gas solution |
| ϕg | Fugacity coefficient |
| xg | Mole fraction of component in water phase |
| yg | Mole fraction of component in gas phase |
References
- Abdelsalam, Y.I.I.; Akhmetzyanova, L.A.; Galiakhmetova, L.K.; Baimukhametov, G.F.; Davletshin, R.R.; Dengaev, A.V.; Aliev, F.A.; Vakhin, A.V. The Catalytic Upgrading Performance of NiSO4 and FeSO4 in the Case of Ashal’cha Heavy Oil Reservoir. Processes 2023, 11, 2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.K.; Ancheyta, J.; Marroquín, G. Catalytic Aquathermolysis Used for Viscosity Reduction of Heavy Crude Oils: A Review. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2809–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, P.R.; Kallos, M.S.; Gates, I.D. A Review of Pyrolysis, Aquathermolysis, and Oxidation of Athabasca Bitumen. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 131, 270–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraza, O.; Galadima, A. Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil: A Review and Perspective on Catalyst Development. Fuel 2015, 157, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J.G. Enhanced Recovery Methods for Heavy Oil and Tar Sands; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 0127999884. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, K.; Lu, N.; Zhang, Q. Enhanced Oil Recovery Techniques for Heavy Oil and Oilsands Reservoirs after Steam Injection. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 1190–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumanyan, B.P.; Petrukhina, N.N.; Kayukova, G.P.; Nurgaliev, D.K.; Foss, L.E.; Romanov, G.V. Aquathermolysis of Crude Oils and Natural Bitumen: Chemistry, Catalysts and Prospects for Industrial Implementation. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2015, 84, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, G.; Tirado, A.; Yuan, C.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Ancheyta, J. Analysis of Kinetic Models for Hydrocracking of Heavy Oils for In-Situ and Ex-Situ Applications. Fuel 2022, 323, 124322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwofie, M.; Al-Muntaser, A.A.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Suwaid, M.A.; Yuan, C.; Djimasbe, R.; Saeed, S.A. The Effect of Reaction Time and Temperature on the Aquathermolysis Process of Heavy Crude Oil. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhin, A.; Sitnov, S.; Mukhamatdinov, I.; Varfolomeev, M.; Rojas, A.; Sabiryanov, R.; Al-Muntaser, A.; Sudakov, V.; Nurgaliev, D.; Minkhanov, I. Improvement of CSS Method for Extra-Heavy Oil Recovery in Shallow Reservoirs by Simultaneous Injection of in-Situ Upgrading Catalysts and Solvent: Laboratory Study, Simulation and Field Application. In Proceedings of the SPE EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 21–23 March 2022; p. D012S034R002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Lu, N.; Xu, T.; Zhu, G.; Wang, K. A Review on Upgrading and Viscosity Reduction of Heavy Oil and Bitumen by Underground Catalytic Cracking. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 4249–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, B.; Cheng, G.; Yu, X. Experiments and Analysis on Development Methods for Horizontal Well Cyclic Steam Stimulation in Heavy Oil Reservoir with Edge Water. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 188, 106948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarova, A.; Turakhanov, A.; Markovic, S.; Popov, E.; Maksakov, K.; Usachev, G.; Karpov, V.; Cheremisin, A. Thermal Enhanced Oil Recovery in Deep Heavy Oil Carbonates: Experimental and Numerical Study on a Hot Water Injection Performance. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 194, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, S.M.; Khoshooei, M.A.; Ortega, L.C.; Scott, C.E.; Chen, Z.; Pereira-Almao, P. Chemical Insight into Nano-Catalytic in-Situ Upgrading and Recovery of Heavy Oil. Fuel 2020, 278, 118270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, N.; Mejía, J.M. Heavy Oil In-Situ Upgrading Evaluation by a Laboratory-Calibrated EoS-Based Reservoir Simulator. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 196, 107455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, F.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, K.; Pan, H.; Lin, R. Significance of Aquathermolysis Reaction on Heavy Oil Recovery during the Steam-Assisted Gravity Drainage Process. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 5426–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Liu, H.; Cheng, L.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, L. A Modified Model for Aquathermolysis and Its Application in Numerical Simulation. Fuel 2017, 207, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Babadagli, T.; Li, H.A. Catalytic-Effect Comparison Between Nickel and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles During Aquathermolysis-Aided Cyclic Steam Stimulation. SPE—Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2020, 23, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Pu, C. Mechanism of Underground Heavy Oil Catalytic Aquathermolysis. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2018, 53, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, G.; Tirado, A.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Al-muntaser, A.; Suwaid, M.; Yuan, C.; Ancheyta, J. Chemical and Structural Changes of Resins during the Catalytic and Non-Catalytic Aquathermolysis of Heavy Crude Oils. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 230, 212242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado, A.; Félix, G.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Yuan, C.; Ancheyta, J. Definition of Reaction Pathways for Catalytic Aquathermolysis of Liaohe Heavy Crude Oil. Fuel 2023, 333, 126345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Wang, S.G.; Deng, G.Z.; Tang, X.D.; Yang, Z.; Yang, F.X. Catalytic Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil by Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles Prepared via Solvothermal Method. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2025, 186, 106929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temizel, C.; Balaji, K.; Ranjith, R.; Coman, C. Optimization of Steamflooding Heavy Oil Reservoirs Under Uncertainty. In Proceedings of the SPE—Asia Pacific Oil and Gas Conference and Exhibition, Perth, Australia, 25–27 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi-Kiasari, H.; Hemmati-Sarapardeh, A.; Mighani, S.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Sedaee-Sola, B. Effect of Operational Parameters on SAGD Performance in a Dip Heterogeneous Fractured Reservoir. Fuel 2014, 122, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, I.D.; Chakrabarty, N. Optimization of Steam Assisted Gravity Drainage in McMurray Reservoir. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2006, 45, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Jiang, R.; Cui, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W. The Numerical Simulation of Thermal Recovery Considering Rock Deformation in Shale Gas Reservoir. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf. 2019, 138, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulagatov, I.M.; Abdulagatova, Z.Z.; Grigor’ev, B.A.; Kallaev, S.N.; Omarov, Z.M.; Bakmaev, A.G.; Ramazanova, A.E.; Rabadanov, K.M. Thermal Diffusivity, Heat Capacity, and Thermal Conductivity of Oil Reservoir Rock at High Temperatures. Int. J. Thermophys. 2021, 42, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gerritsen, M.G.; Kovscek, A.R. Effects of Reservoir Heterogeneities on the Steam-Assisted Gravity-Drainage Process. SPE Res. Eval. Eng. 2008, 11, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ravalec, M.; Morlot, C.; Marmier, R.; Foulon, D. Heterogeneity Impact on SAGD Process Performance in Mobile Heavy Oil Reservoirs. Oil Gas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 64, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, R.; Guy, N.; Preux, C.; Lerat, O. Analysis of Heavy Oil Recovery by Thermal EOR in a Meander Belt: From Geological to Reservoir Modeling. Oil Gas. Sci. Technol. 2012, 67, 999–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, J.; Cao, M.; Li, A.; Yang, M. Experimental and Numerical Study of Steam-Chamber Evolution during Solvent-Enhanced Steam Flooding in Thin Heavy-Oil Reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 172, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Qu, F.; Liu, Y.; Nian, X.; Chen, Z.; Zou, Y. Numerical Simulation of Steam Injection for Heavy Oil Thermal Recovery. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 3936–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xu, B.; Yuan, Y. Impact of Thermal Pore Pressure on the Caprock Integrity during the SAGD Operation. SPE—Heavy Oil Conf. Can. 2013, 1, 744–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chalaturnyk, R.; Boisvert, J. Sequentially Coupled Thermal-Hydraulic-Mechanical Simulation for Geomechanical Assessments of Caprock Integrity in SAGD. Can. Geotech. J. 2024, 61, 1242–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayache, S.V.; Lamoureux-Var, V.; Michel, P.; Preux, C. Reservoir Simulation of H2S Production during a SAGD Process Using a New Sulfur-Based-Compositional Kinetic Model. In Proceedings of the SPE—Canada Heavy Oil Technical Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 9 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ibatullin, T.R.; Yang, T.; Petersen, E.B.; Chan, M.; Rismyhr, O.; Tollefsen, S. Simulation of Hydrogen Sulfide and Carbon Dioxide Production during Thermal Recovery of Bitumen. In Proceedings of the SPE—Reservoir Characterisation and Simulation Conference and Exhibition, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 9 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bueno Zapata, N.; Morales Mora, O.A.; Mejía Cárdenas, J.M. Practical Kinetic Coupling to Multi-Component and Multi-Phase Flow Transport during in-Situ Heavy Oil Upgrading Processes Using an Equation of State-Based Numerical Reservoir Simulation. In Proceedings of the SPE—Reservoir Characterisation and Simulation Conference and Exhibition, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 17 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanzadeh, H.; Rabiei Faradonbeh, M.; Harding, T. Numerical Simulation of Solvent and Water Assisted Electrical Heating of Oil Sands Including Aquathermolysis and Thermal Cracking Reactions. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 4243–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, G.; Tirado, A.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Al-Muntaser, A.; Suwaid, M.; Ancheyta, J. New Approach to Simulate Long-Term in Situ Aquathermolysis Reaction Combining Noncatalytic and Catalytic Kinetic Models. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 16, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Yuan, Y.; Gu, S.; Yang, X.; Yue, Y.; Cai, J.; Jiang, G. 2D Numerical Simulation of Improving Wellbore Stability in Shale Using Nanoparticles Based Drilling Fluid. Energies 2017, 10, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekhonin, E.; Romushkevich, R.; Popov, E.; Popov, Y.; Goncharov, A.; Pchela, K.; Bagryantsev, M.; Terentiev, A.; Kireev, I.; Demin, S. Advanced Methods of Thermal Petrophysics as a Means to Reduce Uncertainties during Thermal EOR Modeling of Unconventional Reservoirs. Geoscience 2021, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehi, H.; Weng, W.; Li, Z.; Bai, X.S.; Aldén, M. Recent Development in Numerical Simulations and Experimental Studies of Biomass Thermochemical Conversion. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 6940–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, M.; Yang, B.; Liu, W.; Chen, Z. Data-Driven Model for Predicting Production Periods in the SAGD Process. Petroleum 2022, 8, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremon, M.A.; Christie, M.; Gerritsen, M.G. Monte Carlo Simulation for Uncertainty Quantification in Reservoir Simulation: A Convergence Study. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on the Mathematics of Oil Recovery, ECMOR 2018, Barcelona, Spain, 3–6 September 2018; European Association of Geoscientists and Engineers: Bunnik, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jaber, A.K.; Al-Jawad, S.N.; Alhuraishawy, A.K. A Review of Proxy Modeling Applications in Numerical Reservoir Simulation. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Nie, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Wu, W.; Chen, Z. A Critical Review of Reservoir Simulation Applications in Key Thermal Recovery Processes: Lessons, Opportunities, and Challenges. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 7387–7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Suzuki, S. Numerical Simulation of the SAGD Process in the Hangingstone Oil Sands Reservoir. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 1999, 38, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, K.A.; Palmgren, C.; Thimm, H.F. Simulation of Gas Production in SAGD. In Proceedings of the SPE/CIM International Conference on Horizontal Well Technology, OnePetro, Calgary, AB, Canada, 6–8 November 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, K.; Akibayashi, S.; Yazawa, N.; Doan, Q.; Ali, S.M.F. Numerical and Experimental Modelling of the Steam Assisted Gravity Drainage (SAGD) Process. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2001, 40, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalles, C.; Rodríguez, H. Extra Heavy Crude Oil Downhole Upgrading Using Hydrogen Donors under Cyclic Steam Injection Conditions: Physical and Numerical Simulation Studies. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2008, 47, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Perez, A.; Kamp, A.M.; Soleimani, H.; Darche, G. Numerical Simulation of H2S and CO2 Generation during SAGD. In Proceedings of the World Heavy Oil Congress, Calgary, AB, Canada, 14 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kapadia, P.R.; Wang, J.; Kallos, M.S.; Gates, I.D. Reactive Thermal Reservoir Simulation: Hydrogen Sulphide Production in SAGD. In Proceedings of the SPE—Canadian Society of Unconventional Gas, Calgary, AB, Canada, 15 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ayache, S.V.; Lamoureux-Var, V.; Michel, P.; Preux, C. Reservoir Simulation of Hydrogen Sulfide Production during a Steam-Assisted-Gravity-Drainage Process by Use of a New Sulfur-Based Compositional Kinetic Model. SPE J. 2017, 22, 080–093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Yang, Z.; Guo, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Lin, R. Potential Analysis of Enhanced Oil Recovery by Superheated Steam during Steam-Assisted Gravity Drainage. Energy Technol. 2021, 9, 2100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, R.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, W.; Sun, Y.; Bai, Y. Experimental Measurements and Numerical Simulation of H2S Generation during Cyclic Steam Stimulation Process of Offshore Heavy Oil from Bohai Bay, China. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.; Chen, Z.; Pereira Almao, P.; Scott, C.E.; Maini, B. Reservoir Simulation and Production Optimization of Bitumen/Heavy Oil via Nanocatalytic in Situ Upgrading. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 14214–14230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Huang, S.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, X.; Yu, C. An Innovative in Situ Solvent Generation Enhanced SAGD Technique: Mechanism Analysis Based on Numerical Simulation. Fuel 2024, 364, 131020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyne, J.B.; Clark, P.D.; Clarke, R.A.; Koo, J. Aquathermolysis—The Reaction of Organo-Sulphur Compounds during Steaming of Heavy Oil | Repository of the Athabasca River Basin. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Heavy Crude and Tar Sands, Caracas, Venezuela, 7–17 February 1982. Chapter 9. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, R.-S.; Wang, Y.-M.; Kang, Y.-L.; Jia, Y.-L. A Steam Rising Model of Steam-Assisted Gravity Drainage Production for Heavy Oil Reservoirs. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2020, 38, 801–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalles, C.; Vallejos, C.; Vásquez, T.; Martinis, J.; Perez-Perez, A.; Cotte, E.; Castellanos, L.; Rodríguez, H. Extra-Heavy Crude Oil Downhole Upgrading Process Using Hydrogen Donors under Steam Injection Conditions. In Proceedings of the SPE international thermal operations and heavy oil symposium, SPE, Porlamar, Venezuela, 12–14 March 2001; p. SPE-69692. [Google Scholar]
- Hyne, J.B. Aquathermolysis: A Synopsis of Work on the Chemical Reaction Between Water (Steam) and Heavy Oil Sands During Simulated Steam Stimulation; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hyne, J.B.; Tyrer, J.D. Use of Hydrogen-Free Carbon Monoxide with Steam in Recovery of Heavy Oil at Low Temperatures; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Hyne, J.B.; Clark, P.D. Additive for Inclusion in a Heavy Oil Reservoir Undergoing Steam Injection; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, P.D. The Behavior of Various Oil Sands towards High Temperature Steam. In Proceedings of the 4th UNITAR/UNDP International Conference on Heavy Crude and Tar Sands, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 7–12 August 1988; pp. 355–367. [Google Scholar]
- Good, W.K.; Rezk, C.; Felty, B.D. Possible Effects of Gas Caps on SAGD Performance.; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lamoureux-Var, V.; Lorant, F. Method for Constructing a Kinetic Model Allowing the Mass of Hydrogen Sulfide Produced by Aquathermolysis to Be Estimated. U.S. Patent US20070100594A1, 3 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lamoureux-Var, V.; Lorant, F. Experimental Evaluation of H2S Yields in Reservoir Rocks Submitted to Steam Injection. In Proceedings of the IOR 2005—13th European Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Budapest, Hungary, 25–27 April 2005; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Bunnik, The Netherlands; p. cp-12. [Google Scholar]
- Lamoureux-Var, V.; Barroux, C. Using Geochemistry to Address H2S Production Risk Due to Steam Injection in Oil Sands. In Proceedings of the SPE Canada Heavy Oil Conference, SPE, Calgary, AB, Canada, 11–13 June 2013; p. SPE-165437. [Google Scholar]
- Kapadia, P.R.; Wang, J.; Kallos, M.S.; Gates, I.D. New Thermal-Reactive Reservoir Engineering Model Predicts Hydrogen Sulfide Generation in Steam Assisted Gravity Drainage. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 94, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, P.R.; Kallos, M.S.; Gates, I.D. A New Reaction Model for Aquathermolysis of Athabasca Bitumen. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 91, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyne, J.B.; Clark, P.D.; Clarke, R.A.; Koo, J.; Greidanus, J.W. Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oils. Rev. Tec. INTEVEP 1982, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Aliev, F.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Sitnov, S.A.; Ziganshina, M.R.; Onishchenko, Y.V.; Sharifullin, A.V.; Vakhin, A. V In-Situ Heavy Oil Aquathermolysis in the Presence of Nanodispersed Catalysts Based on Transition Metals. Processes 2021, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakhin, A.V.; Aliev, F.A.; Kudryashov, S.I.; Afanasiev, I.S.; Petrashov, O.V.; Sitnov, S.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Nurgaliev, D.K. Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oil in Reservoir Conditions with the Use of Oil-Soluble Catalysts: Part I–Changes in Composition of Saturated Hydrocarbons. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, S.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Ancheyta, J. Kinetic Model for Moderate Hydrocracking of Heavy Oils. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 9409–9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgrave, J.D.M.; Moore, R.G.; Ursenbach, M.G. Comprehensive Kinetic Models for the Aquathermolysis of Heavy Oils. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 1997, 36, PETSOC-97-04-03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Bahonar, M.; Chen, Z. Development of a Thermal Wellbore Simulator with Focus on Improving Heat-Loss Calculations for Steam-Assisted-Gravity-Drainage Steam Injection. SPE—Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2016, 19, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, N.; Wu, K. Impact of Gravity Segregation on Gas Injection Development in Condensate Gas Reservoirs: A Numerical Simulation Study. Processes 2025, 13, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Su, Y.; Li, L.; Mehmood, A.; Wang, H.; Fu, J. The Numerical Simulation and Wellbore Modelling of Steam Injection and Stored Heat Recovery from Light Oil Reservoir. Energy Sources Part. A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 43, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durlofsky, L.J. Upscaling for Compositional Reservoir Simulation. SPE J. 2016, 21, 0873–0887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, Y.; Ahmadi, M. Reservoir Modeling & Simulation: Advancements, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. J. Chem. Pet. Eng. 2023, 57, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.; Maini, B.; Almao, P.P. Propagation of Nanocatalyst Particles Through Athabasca Sands. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2013, 52, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xin, C.; Chen, Y.; Mouhouadi, R.D.; Chen, S. Nanoparticles for Enhancing Heavy Oil Recovery: Recent Progress, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 8057–8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, A.A.; Aboul-Fetouh, M.E.; Gomaa, S.; Aboul-Fotouh, T.M.; Attia, A.M. Optimizing In-Situ Upgrading of Heavy Crude Oil via Catalytic Aquathermolysis Using a Novel Graphene Oxide-Copper Zinc Ferrite Nanocomposite as a Catalyst. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
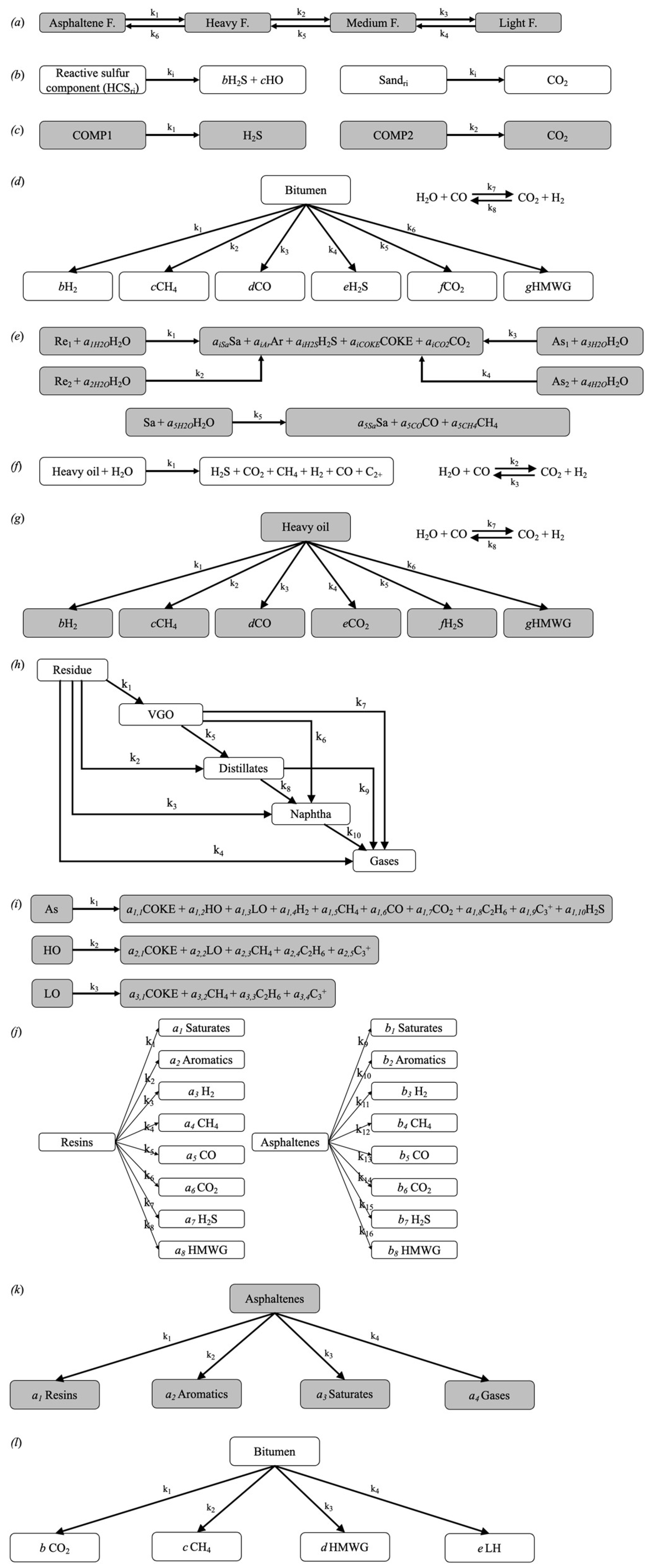
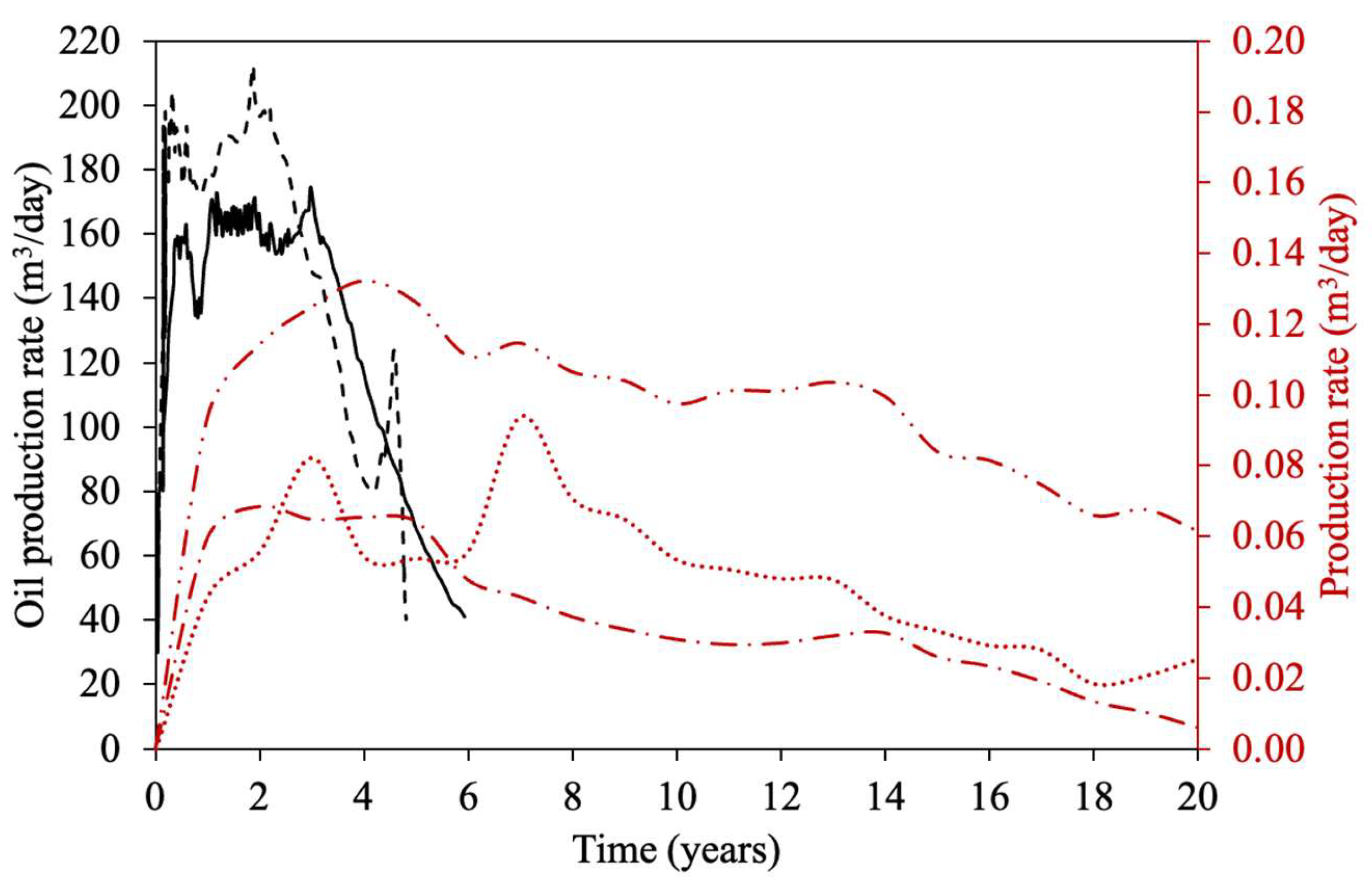

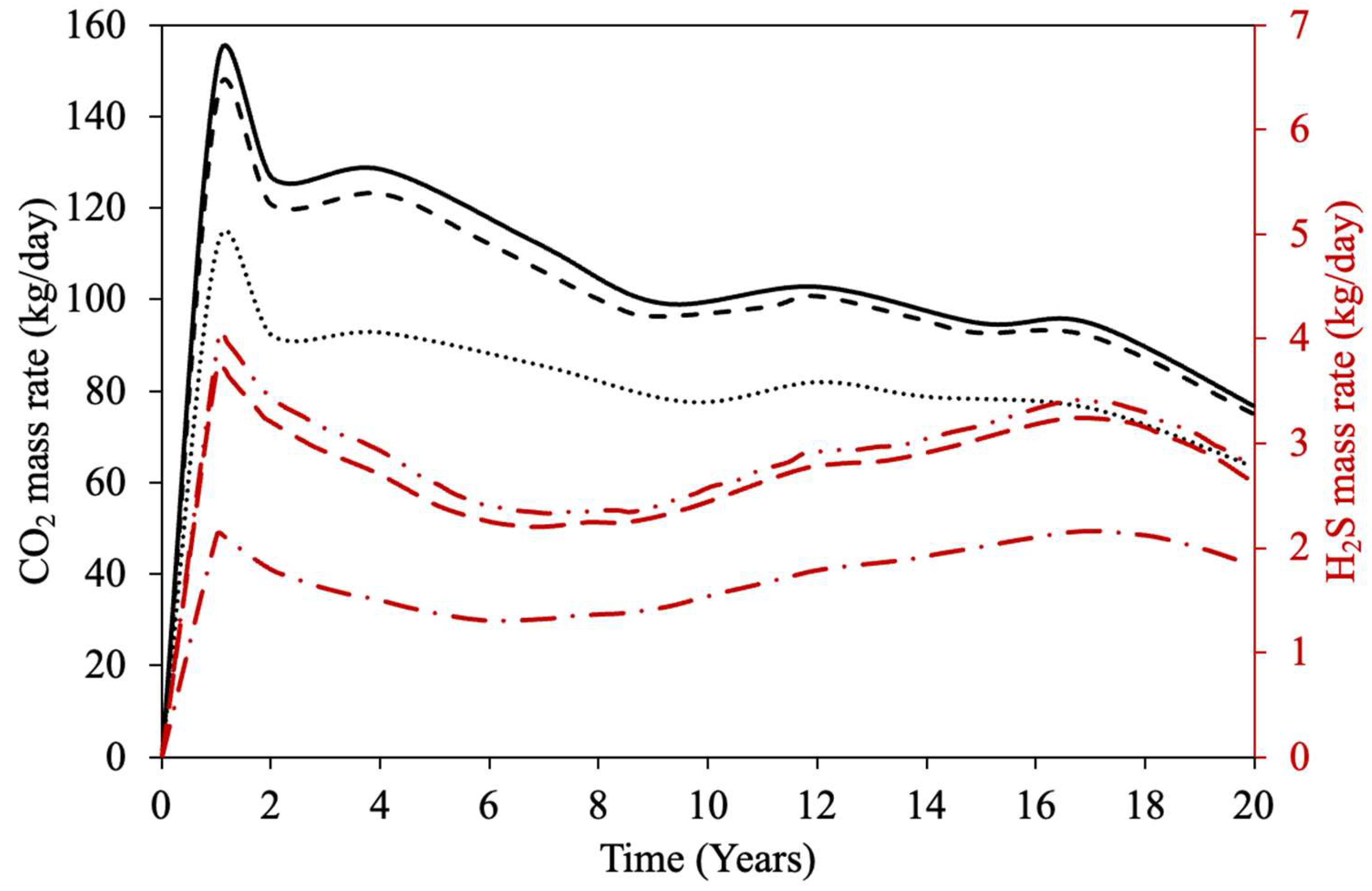
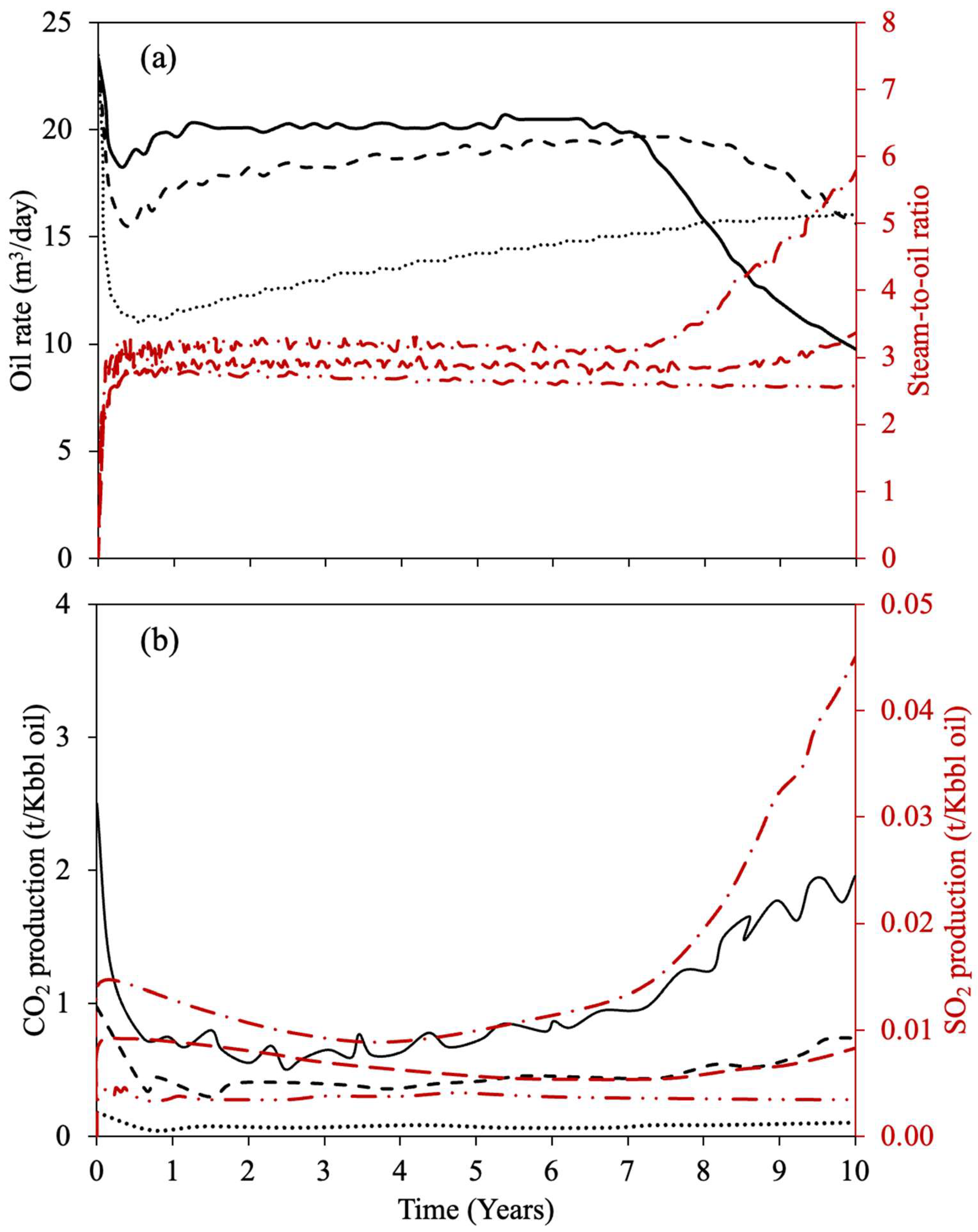
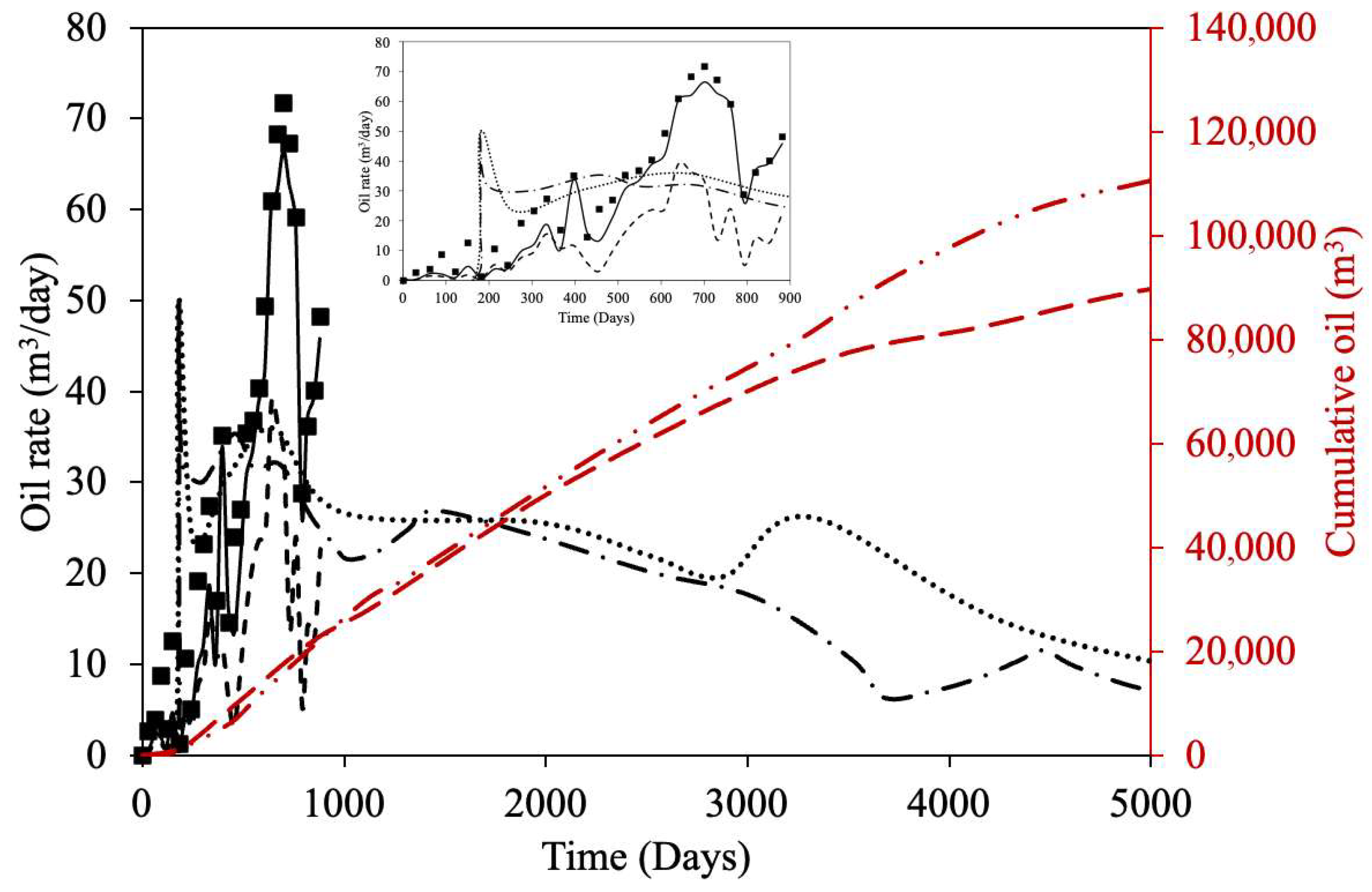
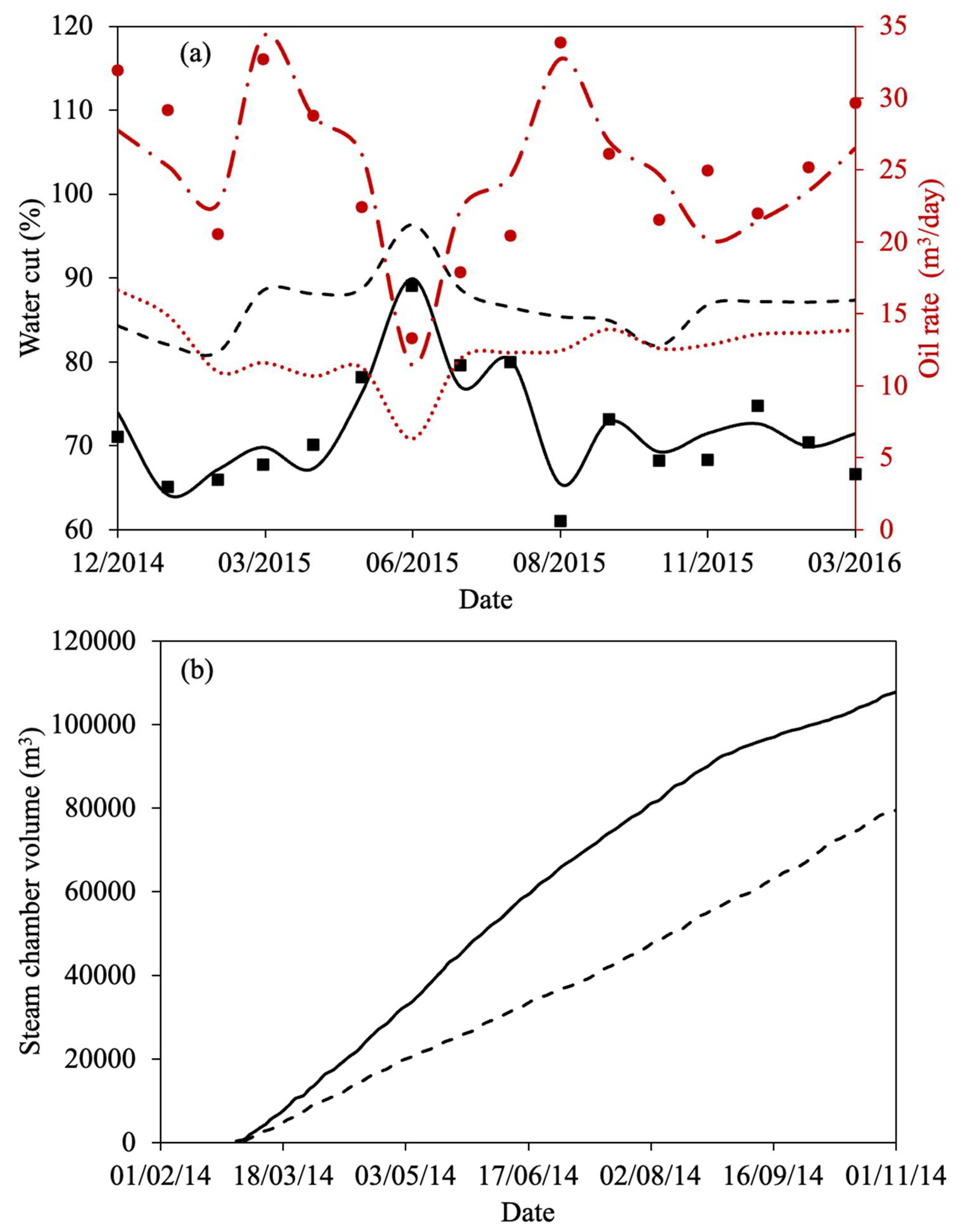

| Property | Ito and Suzuki [47] | Gillis et al. [48] | Sasaki et al. [49] | Ovalles and Rodriguez [50] | Perez-Perez et al. [51] | Ibatullin et al. [36] | Kapadia et al. [52] | Ayache et al. [53] | Zhang et al. [16] | Yuan et al. [54] | Wang et al. [55] | Nguyen et al. [56] | Hassanzadeh et al. [38] | Huang et al. [17] | Bueno et al. [37] | Yang et al. [57] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reservoir | Hangingstone | Hamaca | Athabasca bitumen | Athabasca bitumen | Athabasca bitumen | Athabasca bitumen | ||||||||||
| Top depth (m) | 300 | 300 | 320 | 300 | 110 | 750 | 124 | |||||||||
| Total dimensions (m) | ||||||||||||||||
| x | 50 | 1.5 | 10 | 30 | 420 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.01 | 1 | 30 | 91.44 | 50 | ||||
| y | 500 | 2 | 1 | 50 | 150 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.002 | 50 | 101 | 5.12 | 1.5 | ||||
| z | 30 | 24 | 10 | 800 | 18 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 0.002 | 1 | 1 | 778.76 | 20 | ||||
| Horizontal permeability (mD) | 5000 | 1.42 × 105 | 3000 | 7000 | 2424 | 10,000 | 1860 | 2450 | 3600 | 5000 | 2656 | 1000 | 4000 | |||
| Vertical permeability (mD) | 2500 | 1000 | 3500 | 485 | 3500 | 1800 | 3000 | |||||||||
| Porosity, fraction | 0.3 | 0.38 | 0.33 | 0.3 | 0.33 | 0.37 | 0.2511 | 0.33 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.26 | 0.33 | ||||
| Initial pressure (kPa) | 101.3 | 8000 | 1000 | 2600 | 2900 | 4000 | 2000 | 1300 | 2550 | 1500 | ||||||
| Initial temperature (°C) | 20 | 53 | 10 | 11 | 10 | 17 | 37 | 11 | 7 | 13 | 13 | |||||
| Rock-heat capacity (J/m3-°C) | 1.99 × 106 | 2.63 × 106 | 2.60 × 106 | 2.31 × 106 | 2.60 × 106 | 2.58 × 106 | 1.20 × 106 | 2.60 × 105 | ||||||||
| Rock-thermal conductivity (J/m-s-°C) | 1.16 | 1.17 | 2.5 | 7.64 | 2.75 | 7.64 | 1.89 | 7.22 | 7.64 | |||||||
| Oil density (g/cm3) | 0.998 | 1.013 | 1.001 | 1.0129 | ||||||||||||
| Oil gravity (°API) | 8 | 8.2 | 10 | |||||||||||||
| Oil viscosity (cP) | 1.7 × 106 | 1.5 × 106 | 3.8 × 106 | 654.228 | 35,438 | |||||||||||
| Pay zone (m) | 27.4 | 40 | 30 | 28 | 30 | 30 | ||||||||||
| Initial oil saturation | 1 | 0.87 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.64 | 0.78 | 0.64 | 0.7–0.82 | 0.81 | 0.85 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.75 | |||
| Initial water saturation | 0 | 0.13 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.36 | 0.3–0.18 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.25 | |||
| Maximum BHP (kPa) | 5000 | 3350 | 1000–5000 | 2656 | 2730 | |||||||||||
| Maximum production rate (m3/d) | 40 | |||||||||||||||
| Injection rate (m3/d) | 397.5 | 400 | 192 | 250 | 191 | |||||||||||
| Steam quality (%) | 75 | 90 | 90 | 70 | 95 | 90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwofie, M.; Félix, G.; Tirado, A.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Ancheyta, J. Advances in Numerical Reservoir Simulation for In Situ Upgrading of Heavy Oil via Steam-Based Technologies. Energies 2025, 18, 5639. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215639
Kwofie M, Félix G, Tirado A, Varfolomeev MA, Ancheyta J. Advances in Numerical Reservoir Simulation for In Situ Upgrading of Heavy Oil via Steam-Based Technologies. Energies. 2025; 18(21):5639. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215639
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwofie, Michael, Guillermo Félix, Alexis Tirado, Mikhail A. Varfolomeev, and Jorge Ancheyta. 2025. "Advances in Numerical Reservoir Simulation for In Situ Upgrading of Heavy Oil via Steam-Based Technologies" Energies 18, no. 21: 5639. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215639
APA StyleKwofie, M., Félix, G., Tirado, A., Varfolomeev, M. A., & Ancheyta, J. (2025). Advances in Numerical Reservoir Simulation for In Situ Upgrading of Heavy Oil via Steam-Based Technologies. Energies, 18(21), 5639. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215639









