Abstract
This study presents a novel approach to intensifying the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge through enzymatic pretreatment using hydrolytic enzymes—cellulase and lysozyme. It aims to determine how enzymatic activation affects the efficiency of methane fermentation, defined as the degree of organic matter decomposition and yield and composition of biogas. An experiment was carried out under mesophilic conditions over 20 days, analyzing the physicochemical properties of sludge, biogas production, methane content, and sanitary parameters. The addition of cellulase and lysozyme significantly enhanced process efficiency, increasing both the rate of organic matter degradation and biogas yield. The highest biogas production values (0.73 L·g−1 d.m. for cellulase and 0.72 L·g−1 d.m. for lysozyme) were obtained at a 4% (w/w) enzyme concentration, with a corresponding increase in the degree of organic matter decomposition to 78.7% and 80.0%, respectively. The produced biogas contained 58–61% methane, exceeding the values observed in the control sample, which indicates a positive effect of enzymatic activation on methane selectivity. Enhanced biogas production was attributed to improved hydrolysis of complex organic compounds, resulting in greater substrate bioavailability for methanogenic microorganisms. Moreover, methane fermentation led to the complete elimination of E. coli from all supernatants, confirming the hygienization potential of the process. The results of this study indicate that enzymatic pretreatment may serve as a viable strategy to improve both the energy efficiency and hygienic safety of anaerobic digestion processes, with relevance for future optimization and full-scale wastewater treatment applications.
1. Introduction
Methane fermentation is one of the key processes used in municipal wastewater treatment, enabling not only the stabilization of sewage sludge but also the recovery of energy in the form of biogas [1,2,3]. This process involves the decomposition of organic substances by microorganisms under anaerobic conditions, ultimately leading to the formation of methane, carbon dioxide, and small amounts of hydrogen sulfide and ammonia [4,5]. Methane fermentation is one of the key technologies for sewage sludge disposal in municipal treatment plants, enabling not only reduction in sewage sludge mass but also energy recovery in the form of biogas [6]. The process consists of four main stages: hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis [7]. The key stage limiting the speed of the entire process is hydrolysis, during which complex organic compounds—such as proteins, fats, and carbohydrates—are broken down into simple monomers. Excess sewage sludge, which is a product of biological wastewater treatment, is characterized by a high content of complex organic compounds, including cellulose fibers, proteins, fats, and microorganisms, poorly biodegradable organic compounds, and low susceptibility to fermentation [1,2]. Due to the presence of difficult-to-degrade substances such as cellulose, peptidoglycans, and lignin, the effectiveness of their fermentation is sometimes limited [8,9].
In order to increase the efficiency of methane fermentation of excess sludge, various methods of pretreatment (disintegration) are used, including mechanical methods (ultrasound, homogenization), thermal methods (heat treatment, microwaves), chemical methods (acids, bases, oxidants), and biological methods (enzymes) [10,11,12,13,14,15]. Enzyme use is in line with the principles of the circular economy, contributing to the efficient recovery of energy and nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen [16]. Despite the advantages of enzymatic pretreatment, its industrial implementation faces several challenges, including high enzyme costs, scalability to large sludge volumes, and potential loss of enzymatic activity during processing. Compared to conventional methods such as thermal, mechanical, or chemical pretreatments, enzymatic approaches operate under milder conditions, consume less energy, and offer higher selectivity toward specific substrates, making them more sustainable and compatible with downstream anaerobic digestion.
Hydrolytic enzymes used in the methane fermentation process, such as cellulases and lysozymes, have the ability to break down hard-to-reach organic components contained in the cell structures of microorganisms and sludge matrices [17,18]. Cellulase breaks down cellulose fibers into glucose, improving the availability of carbohydrates for fermentative bacteria, while lysozyme breaks down murein, a component of Gram-positive bacterial cell walls, which can lead to their lysis and the release of cellular material [19,20,21,22]. Cellulase (EC 3.2.1.4) is an enzyme belonging to the glycosidase group that catalyzes the breakdown of β-1,4 glycosidic bonds in cellulose molecules; it is a polysaccharide and the main component of plant cell walls. Thanks to the action of cellulase, cellulose is broken down into glucose and oligosaccharides, which become an easily digestible source of carbon for microorganisms involved in methane fermentation [23,24]. Lysozyme (EC 3.2.1.17) is an enzyme that hydrolyzes β-1,4 bonds between N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid in peptidoglycan, which is the basic component of Gram-positive bacterial cell walls [25,26]. Its use in methane fermentation enables the lysis of bacterial cells, resulting in the release of their contents, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, which can be further decomposed by anaerobic microflora [27].
Enzymatic disintegration can also affect the microbiological composition of sludge. It has been shown that enzymes can lead to the elimination of pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., and Legionella spp., which significantly increases the environmental and sanitary safety of the process [15,27,28]. In studies by Jiang et al. [18], the use of a mixture of enzymes (including lysozyme, lipase, and keratinase) led to a 45% increase in methane production, while in a study by Yang et al. [29], the use of protease and amylase increased the decomposition of organic matter by 68%. This proves that enzymatic disintegration methods have enormous potential in intensifying the anaerobic stabilization processes of sewage sludge.
This study aimed to assess the impact of cellulase and lysozyme on the efficiency of methane fermentation of sewage sludge. Specifically, this study focused on (I) the effect of enzymatic pretreatment on biogas production and methane content, (II) the degree of organic matter decomposition, and (III) the inactivation of pathogenic bacteria, exemplified by Escherichia coli. Despite the growing use of enzymatic pretreatment in anaerobic digestion, there is limited knowledge of how hydrolytic enzymes affect both process performance and microbial safety in sewage sludge, particularly under mesophilic conditions. E. coli was chosen as a model pathogenic bacterium because its presence in sewage sludge is a critical public health concern, and its reduction indicates the potential of fermentation processes to meet regulatory requirements for sludge reuse. This study addresses the gap in understanding how enzymatic pretreatment can simultaneously improve energy recovery and enhance the hygienic quality of sludge. Unlike previous studies [14,22,30] that primarily focused on enzymatic hydrolysis or biogas yield, this work provides a comparative evaluation of cellulase and lysozyme on methane production, organic matter degradation, and pathogen inactivation under mesophilic conditions, highlighting both the practical and hygienic benefits of enzymatic pretreatment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
This study used sewage sludge from a municipal treatment plant that uses activated sludge to carry out biological sewage treatment. The research material was a mixture of excess sludge and fermented sludge, with the fermented sludge serving as inoculum. Samples were taken as instantaneous samples and then combined in appropriate proportions (60%:40% fermented sludge to excess sludge).
Two types of sludge were used in this study: thickened excess sludge, directed to methane fermentation tanks, and digested sludge, collected from the outflow of closed, separate fermentation tanks—used as inoculum to inoculate the excess sludge with fermentative microflora.
The initial physicochemical properties of the sludge and supernatant before fermentation are presented in Table 1. These values provide a baseline for evaluating the effects of enzymatic pretreatment.

Table 1.
Changes in the physicochemical properties of sewage sludge and supernatant before fermentation. Values are presented as mean ± SD for n = 3 independent reactors.
2.2. Enzymes
Two enzymes were used in this study:
- Cellulase (EC 3.2.1.4), derived from Aspergillus niger, (TCI TOKYO CHEMICAL INDUSTRY CO., LTD., 16-12 Nihonbashi-kodemmacho, Chuo-ku, Tokyo 103-0001, Japan) with activity of ≥17,000 U/g,
- Lysozyme (EC 3.2.1.17), a lytic enzyme obtained from chicken egg protein with activity of ≥20,360 U/mg dry weight (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
The enzymes were stored at 2–8 °C in tightly sealed containers, in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
The enzymes were introduced into the sludge in four doses, by weight: 0% (control), 1%, 2%, 3%, and 4% (w/w) in relation to the dry mass of excess sludge introduced into the bioreactor according to Equation (1):
Enzyme dose (%) = enzyme content (g·L−1)/dry mass of excess sewage sludge (g·L−1)
2.3. Fermentation Process
The methane fermentation process was carried out in glass bioreactors with a working capacity of 1 L. In total, 0.7 L of a mixture of excess and fermented sewage sludge was introduced to the rectors. Each variant was carried out in three independent replicates (n = 3). The reactors were closed, deprived of light, placed in a temperature-controlled incubator (37 ± 2 °C) and equipped with a valve for biogas removal.
Before fermentation began, the basic parameters of the sludge mixtures were measured: pH, alkalinity, dry weight, and organic matter content. The process lasted 20 days. The volume of biogas was measured daily using a manometer and calculations based on Boyle’s law. The composition of biogas was determined using a DP-28 BIO analyzer (Nanosens, Wysogotowo, Poland).
2.4. Physicochemical Analyses
The analyses were carried out on samples taken before and after the process. The following parameters were determined:
- -
- pH (potentiometrically)—in accordance with the PN-EN ISO 10523:2012 standard [31].
- -
- Alkalinity (ALK)—titration to pH 4.5.
- -
- Chemical oxygen demand (COD)—NANOCOLOR® VIS II spectrophotometer from MACHEREY NAGEL GmbH & Co. KG, Düren, Germany. (The test is equivalent to EPA 410.4 and APHA 5220D methods [32].)
- -
- Volatile fatty acids (VFAs)—UDK139 Semi-Automatic Steam Distillation Apparatus, VELP, Usmate, Italy (via distillation and titration with NaOH).
- -
- Dry mass (DM)—a weight method in accordance with the PN-EN 12880:2004 standard [33].
All variants were tested in three independent reactors (n = 3). Physicochemical parameters (pH, alkalinity, COD, VFA, dry matter, organic substances) were determined from each reactor before the start of fermentation and after 20 days in triplicate.
2.5. Biogas Production and Composition
The biogas volume was measured every 24 h in each reactor. The qualitative composition (CH4, CO2) was determined four times—after 5, 10, 15, and 20 days—using a gas analyzer (DP-28 BIO). The results were averaged for each variant.
2.6. Microbiological Tests
The number of bacteria was determined in the supernatant samples separated via centrifugation before and after fermentation:
- -
- Escherichia coli—according to ISO 4832:2007, confirmed in Brilliant Green Bile and ColiTest media [34].
Escherichia coli bacteria were selected for study as an indicator microbiological organism due to their widespread occurrence in municipal wastewater. E. coli is a typical representative of Gram-negative fecal bacteria, making it an effective bioindicator of fecal contamination and the presence of pathogens in the water and wastewater environment. E. coli is characterized by relatively high resistance to certain environmental factors, so its elimination may indicate the effectiveness of the sanitation process resulting from methane fermentation or enzymatic action.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
In order to assess the statistical significance of the differences between the control samples and the samples with added enzymes, Student’s t-test (t) for independent samples was used, and a significance level of α = 0.05 was adopted. The critical t-value was determined based on the appropriate degrees of freedom (df = 2), and the calculations were performed using SPSS Statistics software (IBM, version 29).
The results presented in the figures and tables reflect the arithmetic means obtained from three independent experimental repetitions. The removal efficiency was calculated using Equation (2):
where C0 is the initial value, and C is the value after the process.
Removal degree (%) = ((C0 − C)/C0) · 100%
Experimental variability is expressed as standard deviation (σ), calculated according to Equation (3):
where xᵢ is the value from a single repetition, , the mean value, and n, the number of repetitions. Error bars shown in the figures represent standard deviations.
3. Results
3.1. Physical and Chemical Properties of Sewage Sludge
In the control sample, the dry matter concentration before fermentation was 23.78 g·L−1, and it dropped to 12.96 g·L−1 after fermentation. The share of organic substances in the fermented sludge was 41.0%, and the decomposition degree of these substances reached 66.3%. According to the literature, this is a typical level for sludge considered to be well fermented [26].
In the case of sludge with the addition of 1% (w/w) cellulase in relation to dry matter, a 55.6% loss of dry matter was found, with a degree of organic substance decomposition of 66.7%. These differences are not statistically significant. The organic matter content in the sludge after fermentation was 49.8%. In the case of sludge with the addition of 1% (w/w) lysozyme, a 53.1% loss of dry matter was observed, with a degree of organic matter decomposition of 78.6%. The proportion of organic matter in the sludge after fermentation was 30.3%.
The addition of 2% (w/w) cellulase resulted in a statistically significant increase in the degree of organic matter decomposition to 71.0% (td = 12.393). The dry matter concentration in the sludge after the process decreased to 4.58 g·L−1, and the organic matter content was 48.3%. The addition of 2% (w/w) lysozyme resulted in a statistically significant increase in the degree of organic matter decomposition to 79.0% (td = 10.541). The dry matter concentration in the sludge after the process decreased to 3.31 g·L−1, and the organic matter content was 30.8%.
In sewage sludge with the addition of 3% (w/w) cellulase and lysozyme, after 20 days of anaerobic stabilization, a decrease in organic matter content of 77.2 and 77.9%, respectively, was observed. The organic matter content in the fermented sludge was 42.8% for cellulase and 30.7% for lysozyme. The difference compared to the control sample was statistically significant.
The greatest effect was achieved with the use of 4% (w/w) cellulase and lysozyme. In this variant, the dry matter loss was 65.9 and 56.4%, and the share of organic substances in the sludge after fermentation was 41.4 and 30.5% for cellulase and lysozyme, respectively. The observed variations in the effectiveness of cellulase and lysozyme may be related to the complex and heterogeneous composition of sewage sludge. The presence of proteins, fats, polysaccharides, and humic substances may influence enzyme activity by blocking the active sites or changing substrate accessibility. Additionally, hydrolysis products such as soluble sugars and volatile fatty acids may inhibit further enzyme activity through feedback mechanisms. This may partly explain the limited improvement in organic matter decomposition observed at higher enzyme dosages [35].
Table 2 presents the values of the selected physical and chemical properties of the sewage sludge and supernatant, determined after 20 days of the process.

Table 2.
Changes in physicochemical properties of sewage sludge and supernatant after fermentation. Percentages (0–4%) indicate the concentration of the added enzyme in relation to the dry weight of the sludge (% w/w). Values are presented as mean ± SD for n = 3 independent reactors.
These results clearly confirm the greater effectiveness of cellulase in the decomposition of organic matter and mineralization of sludge, while lysozyme, although less effective in terms of degradation, also shows stabilizing potential. The results obtained indicate the validity of the enzymatic activation of sludge as a preliminary stage before methane fermentation.
The concentration of organic compounds, designated as COD, in the supernatant before the start of the process was 1200 mg O2·L−1. After 20 days, the COD content was lower and ranged from 820 to 893 mg O2·L−1. Lysozyme proved to be more effective in reducing COD, which may be due to its specific effect on bacterial cell structures.
After the anaerobic fermentation process was completed, the alkalinity of the supernatant in all samples ranged from 2800 to 3235 mg CaCO3·L−1. The ratio of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) to alkalinity, both in the control sample and in the sample with the addition of enzymes, did not exceed 0.3 after 20 days.
According to literature data and practical experience, for proper fermentation, the ratio of VFA to alkalinity should not exceed 0.3, and the lowest possible value is beneficial for process stability. Under mesophilic fermentation conditions, alkalinity should be in the range of 3000–5000 mg CaCO3·L−1, the VFA concentration in the range of 50–500 mg CH3COOH·L−1, and the pH should be between 7.2 and 8.2 [36,37].
3.2. Biogas Production and Composition During Fermentation
Biogas production was monitored daily over a period of 20 days of fermentation. The effects of cellulase and lysozyme are shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4.
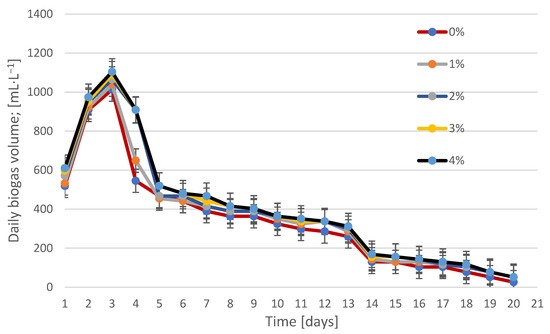
Figure 1.
Productivity of biogas produced on individual days of fermentation using cellulase. Percentages (0–4%) indicate the concentration of the added enzyme in relation to the dry weight of the sludge (% w/w). Values are presented as mean ± SD for n = 3 independent reactors.
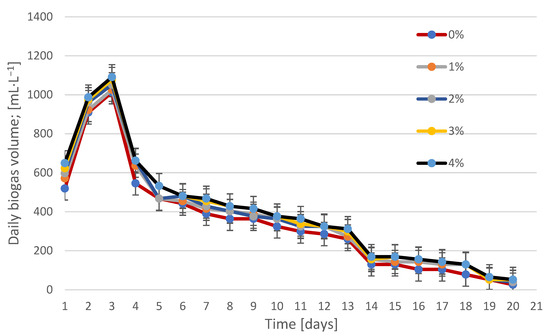
Figure 2.
Productivity of biogas produced on individual days of fermentation using lysozyme. Percentages (0–4%) indicate the concentration of the added enzyme in relation to the dry weight of the sludge (% w/w). Values are presented as mean ± SD for n = 3 independent reactors.
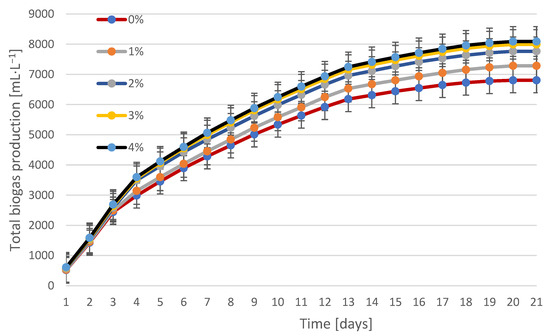
Figure 3.
The biogas yield using cellulase. Percentages (0–4%) indicate the concentration of the added enzyme in relation to the dry weight of the sludge (% w/w). Values are presented as mean ± SD for n = 3 independent reactors.
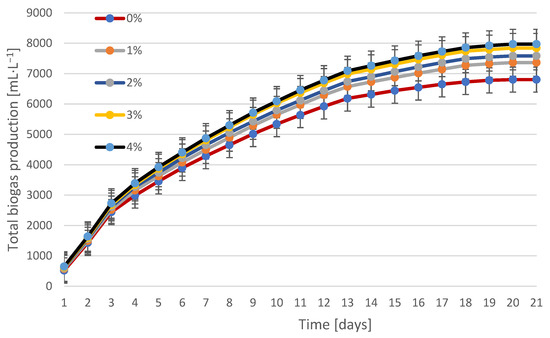
Figure 4.
The biogas yield using lysozyme. Percentages (0–4%) indicate the concentration of the added enzyme in relation to the dry weight of the sludge (% w/w). Values are presented as mean ± SD for n = 3 independent reactors.
The highest instantaneous biogas production was observed on the third day of the process, regardless of the enzyme concentration. The further course of fermentation was characterized by a gradual decrease in daily production. The greatest effect of cellulase was observed at a concentration of 4%, which achieved significantly higher daily values (15–20% on average compared to the control sample). This trend indicates that the enzymatic decomposition of cellulose structures in the initial stage of fermentation increased the availability of components easily assimilated by methanogenic microflora.
In the case of lysozyme, the highest production was also observed on day 3. Higher efficacy was noticeable for concentrations of 3% and 4%, although the differences compared to the control sample were slightly smaller than in the case of cellulase. Lysozyme, by degrading the cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria, could have increased the availability of intracellular material, but the effect was less dynamic than for cellulase. Both curves (Figure 1 and Figure 2) indicate that the greatest differences occurred in the early days of fermentation (up to 6–7 days).
The biogas yield reveals a significant impact of cellulase on the overall efficiency of the process. After 20 days, the largest increase (8090 mL·L−1) was recorded for a concentration of 4%, which was approximately 18% more than in the control sample. Each increase in the enzyme dose resulted in a sharp increase in gas production, although the effect stabilized between doses of 3% and 4%. This indicates possible substrate saturation with the enzyme and limitations resulting from the availability of secondary substrates.
The addition of lysozyme had a positive effect on total biogas production. The maximum production was approximately 7974 mL·L−1 for a 4% enzyme addition, which represents an increase of approximately 17% compared to the control sample.
Analysis of the biogas composition showed that the methane content in biogas obtained from sludge ranged from 58 to 61%, while the carbon dioxide content was between 29 and 30%. For comparison, according to literature data [38], the methane content in biogas ranged from 52.4 to 55.4%, and carbon dioxide, from 28.4 to 29.4%.
Both enzymes showed similar effectiveness in improving methane fermentation efficiency. Both cellulase and lysozyme increased the rate of organic matter decomposition and process stability, with no significant differences in their effects. Similar effects may result from their complementary effects on organic structures—cellulase decomposes fibrous polysaccharides, while lysozyme degrades the cell structures of microorganisms.
3.3. Fermentation Process Parameters
The fermentation process parameters are presented in Table 3. The results indicate that a systematic increase in process efficiency was observed with increasing enzyme concentration. For cellulase, the maximum biogas production value was 0.73 L·g−1 (for a 4% concentration), which represents an increase of over 18% compared to the control sample. For lysozyme, the maximum production reached 0.72 L·g−1, which was slightly lower than for cellulase, but also significantly higher than without the enzyme additive.

Table 3.
Fermentation process parameters. Percentages (0–4%) indicate the concentration of the added enzyme in relation to the dry weight of the sludge (% w/w).
In terms of the degree of organic matter decomposition, cellulase provided an increase from 66.3% (control sample) to 78.7% at the highest concentration. Lysozyme showed even higher potential—up to 80% decomposition, suggesting its high effectiveness in the disintegration of bacterial cell materials.
The results obtained confirm that the use of cellulase and lysozyme can significantly increase the efficiency of methane fermentation of sewage sludge and lead to more stable and efficient biogas production.
The statistical values determining the significance of adding different amounts of enzymes to municipal sludge are presented in Table 4. In the case of total biogas production, the td values for cellulase ranged from 3.018 to 11.524, which means that enzyme doses of 2 to 4% in relation to dry matter caused a statistically significant increase in efficiency compared to the control sample. For lysozyme, at an enzyme concentration of 2%, the td values exceeded the critical value (11.308–11.984), confirming the effect of this enzyme on biogas production. The degree of organic matter decomposition also depended on the enzyme used.

Table 4.
Values of t-Student distribution (td = 4.303). Percentages (0–4%) indicate the concentration of the added enzyme in relation to the dry weight of the sludge (% w/w).
The highest significance in the case of cellulase was obtained for a dose of 4% (td = 14.541), while in the case of lysozyme, statistically significant differences occurred from a concentration of 2%. Regarding dry matter loss, only cellulase at doses of 3 and 4% led to significant results, while in samples with lysozyme, td values were lower than the critical value, indicating no statistically confirmed effect. Analysis of the methane content in biogas did not show any significant differences between the samples with enzymes and the control, as all td values remained below the limit value.
This means that the percentage of CH4 in biogas was stable, regardless of the type and dose of enzyme. In the case of the amount of biogas obtained from 1 g of dry organic matter, both cellulase and lysozyme produced significant differences already at an enzyme dose of 2%. The results obtained indicate that cellulase was more effective in terms of organic matter decomposition and dry matter reduction, while lysozyme had a stronger effect on increasing the amount of biogas per unit of organic matter. In turn, the methane content in the gas remained stable.
3.4. Microbiological Studies
Table 5 shows the number of E. coli bacteria in the supernatant.

Table 5.
Number of E. coli colonies in supernatant. Percentages (0–4%) indicate the concentration of the added enzyme in relation to the dry weight of the sludge (% w/w).
E. coli bacteria were found in the supernatant separated from sewage sludge before the fermentation process. The number of bacteria was 6.7 ± 0.58·103. After 20 days of fermentation, no E. coli bacteria were found in either the supernatant separated from the control sludge or in the samples with added enzymes.
Since no E. coli bacteria were found in the sludge after 20 days of fermentation, it can be assumed that the process itself caused complete or sufficiently significant elimination of these bacteria from the sludge, such that no individual cells were detected using the method employed. Literature data show that methane fermentation can reduce the number of bacteria in sewage sludge. The addition of various hydrolytic enzymes can also reduce the number of bacteria [14]. Lysozyme is an antibacterial agent that causes the lysis of certain bacteria through the enzymatic hydrolysis of peptidoglycans found in the cell walls of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. However, in Gram-negative bacteria, peptidoglycans are protected by a layer of lipopolysaccharide and are therefore not accessible to lysozyme. Lipopolysaccharides inactivate the enzymatic activity of lysozyme. Therefore, the antimicrobial activity of lysozyme against Gram-negative bacteria is lower than against Gram-positive bacteria due to the presence of an outer membrane around the peptidoglycan layer [39,40,41,42]. As E. coli bacteria are Gram-negative, the potential effect of lysozyme would be weaker. In order for cell lysis with lysozyme to occur, a complex must be formed between this enzyme and the bacterial cells. This is influenced by the environmental conditions in which this process takes place, i.e., the pH value, among other things. Studies conducted by Sedov et al. [43] with E. coli bacteria found that the optimal pH for the enzyme to lyse the cells of this bacterium is 8.6. In our studies, the pH of the sewage sludge was slightly lower (7.7), which could have impacted the activity of this enzyme.
4. Discussion
The results clearly indicate that both cellulase and lysozyme contribute to a significant increase in the degree of decomposition of organic matter in sewage sludge.
The highest effects were observed at enzyme doses of 3% and 4%, confirming the effectiveness of enzymatic activation in increasing the bioavailability of substrates for methanogenic microorganisms. Similar observations were made by Córdova O. et al., who reported that pretreatment with a commercial cellulase significantly increased microalgae biogas production, but altered the structure and functionality of microorganisms that live in anaerobic sludge during biomethanation [44]. In our study, the observed plateau between 3% and 4% cellulase dosage suggests similar mechanisms, which is important for the optimization of enzyme dosage and minimization of process costs. This plateau effect may result from limited substrate accessibility or partial inhibition with hydrolysis products. This means that beyond a certain enzyme dose, additional enzyme does not proportionally increase organic matter decomposition or biogas production.
Various studies indicate a positive correlation between enzyme dosage and fermentation efficiency up to a certain threshold. For example, increasing cellulase dosage (up to 1.5% of total dry matter) improved VFA yield, but additional increases may not provide proportional benefits, suggesting a plateau effect [45]. This is consistent with our observations in other enzyme systems (e.g., lipase, papain), where biogas production and organic matter decomposition increased with enzyme dose up to 3–4%, after which the gains stabilized [14,15]. Process stability is further confirmed by maintaining the VFA/alkalinity ratio below the critical value of 0.3 in all samples. From an economic perspective, although enzymatic pretreatment requires financial investment, strategies such as enzyme recycling, optimized dosage, or combined pretreatment methods (e.g., enzymatic + ultrasound or mild thermal pretreatment) could enhance cost-effectiveness and industrial feasibility). The literature indicates that maintaining this parameter at a low level promotes fermentation resistance to sudden organic overloads [46]. Our results suggest that both cellulase and lysozyme not only increase the rate of organic matter degradation but also contribute to greater system stability, which may be particularly important in industrial settings, where the variable composition of the incoming sludge poses a significant challenge for bioreactor operators. Similar conclusions were drawn by Manai et al., who observed that the enzymatic activation of sludge improves not only organic matter degradation but also the process’s resistance to load fluctuations [47]. Taking into account the increase in biogas production by 17–18% compared to the control sample, this result is comparable to the effects obtained in other studies on hydrolysis intensification methods, in which increases of 10–30% were recorded [48,49]. The high methane content in the biogas obtained (58–61%) exceeds the values reported in the literature for standard mesophilic processes (52–55%), which may indicate a beneficial effect of enzymatic activation on the selectivity of metabolic pathways and the reduction in carbon losses in the form of by-products [50]. From the point of view of process optimization, the observed plateau effect indicates the need for balance between the enzyme dose and the actual availability of easily hydrolysable fractions in the sludge, which was also confirmed by Liu et al. (2019) and Luo et al. (2010) [30,51].
The subsequent complete elimination of E. coli bacteria within 20 days of fermentation indicates effective sludge sanitization. This is particularly important in light of legal requirements for limiting pathogens in sludge intended for further environmental use [52]. The lysozyme, despite its limited activity against Gram-negative bacteria, could support the antibacterial effect in combination with unfavorable environmental conditions (pH, presence of fatty acids, metabolites of fermenting bacteria) [25]. In addition to improving biogas yield, enzymatic pretreatment contributes to environmental benefits, including reduced sludge volume and enhanced hygienic safety of the effluent, which is particularly important for meeting regulatory requirements.
Although the results obtained confirm the high efficiency of the enzymes, the limitations of this study should be noted. The experiment was carried out on a laboratory scale, which does not fully capture the complexity of conditions in full-scale installations. Further research is needed to assess the economic viability of enzyme use, the impact of long-term operation on the stability of the process and methanogenic microbiome, and the potential for synergy with other disintegration methods, such as ultrasound or ozonation [53]. Although enzymatic pretreatment requires financial investment, it offers advantages such as lower energy demand and milder process conditions compared with thermal or ultrasonic disintegration. Therefore, enzyme dosage optimization is essential to achieve cost-effective methane enhancement.
5. Conclusions
The addition of lysozyme and cellulase to sewage sludge prior to anaerobic digestion significantly improved the digestion process. This study demonstrated that both enzymes increased the decomposition of organic matter and improved biogas production, confirming the effectiveness of enzymatic activation as a pretreatment strategy. Cellulase showed the highest impact at elevated concentrations, whereas lysozyme exhibited slightly higher potential in the disintegration of bacterial cell materials. Enzyme supplementation also contributed to a reduction in dry matter content and losses during sludge drying. Furthermore, methane fermentation effectively eliminated E. coli, indicating that enzymatic pretreatment may support the hygienization of sewage sludge. These findings highlight the potential of lysozyme and cellulase to improve both the efficiency and stability of sludge anaerobic digestion, with implications for optimizing industrial-scale processes. Moreover, integrating enzymatic pretreatment into wastewater treatment systems aligns with circular economy principles, enabling more efficient energy recovery, nutrient recycling, and production of cleaner digestate with reduced pathogen content, thereby enhancing environmental conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.M.; methodology, B.M., E.P.-N. and A.M.; software, B.M. and E.P.-N.; validation, B.M.; formal analysis, B.M. and M.W.-R.; investigation, B.M. and E.P.-N.; resources, B.M. and E.P.-N.; data curation, B.M. and E.P.-N.; writing—original draft preparation, B.M., E.P.-N., M.W.-R. and A.M.; writing—review and editing, B.M., M.W.-R., E.P.-N. and A.M.; visualization, B.M.; supervision, B.M. and M.W.-R.; project administration, B.M., M.W.-R. and A.M.; funding acquisition, B.M. and M.W.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the scientific subventions of Cardinal Stefan Wyszynski University in Warsaw and Czestochowa University of Technology. The funder of this research was the Ministry of Science and High Education.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Nguyen, V.K.; Chaudhary, D.K.; Dahal, R.H.; Trinh, N.H.; Kim, J.; Chang, S.W.; Hong, Y.; La, D.D.; Nguyen, X.C.; Ngo, H.H.; et al. Review on pretreatment techniques to improve anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Fuel 2021, 285, 119105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, P.; Pesante, S.; Venegas, M.; Vidal, G. Developments in pre-treatment methods to improve anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2016, 15, 173–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.M.; Han, S.K.; Lee, C.Y. Enhancement of methane production in anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge by thermal hydrolysis pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemiński, K.; Frąc, M. Methane fermentation process as anaerobic digestion of biomass: Transformations, stages and microorganisms. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 4127–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, N.A.; Hu, A.; Yu, C.P.; Sharuddin, S.S.; Ramli, N.; Shirai, Y.; Maeda, T. Seeking key microorganisms for enhancing methane production in anaerobic digestion of waste sewage sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5323–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Qiao, W.; Wang, X.; Takayanagi, K.; Shofie, M.; Li, Y.Y. Kinetic characterization of thermophilic and mesophilic anaerobic digestion for coffee grounds and waste activated sludge. Waste Manag. 2015, 36, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrère, H.; Dumas, C.; Battimelli, A.; Batstone, D.J.; Delgenes, J.P.; Steyer, J.P.; Ferrer, I. Pretreatment methods to improve sludge anaerobic degradability: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilli, S.; Bhunia, P.; Yan, S.; LeBlanc, R.J.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Ultrasonic pretreatment of sludge: A review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauknys, R.; Mažeikienė, A.; Paliulis, D. Effect of ultrasound and high voltage disintegration on sludge digestion process. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barjenbruch, M.; Kopplow, O. Enzymatic, mechanical and thermal pre-treatment of surplus sludge. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsamadony, M. Enrich waste activated sludge digestibility via natural enzyme supplementation. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 83, 01012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszograj, S.; Płuciennik-Koropczuk, E. Thermal disintegration of sewage sludge as a method of improving the biogas potential. Energies 2023, 16, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macherzyński, B.; Popowska-Nowak, E.; Włodarczyk-Makuła, M.; Bień, B.; Wszelaka-Rylik, M. Intensification of Energy Production in the Anaerobic Digestion Process of Sewage Sludge Using Enzymatic Disintegration. Energies 2025, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macherzyński, B. Effects of Enzymatic Disintegration on the Decomposition of Organic Compounds During Methane Fer-mentation of Sewage Sludge. Catalysts 2025, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartłomiej, M.; Małgorzata, W.R.; Paweł, G.; Aleksandra, K. Precipitation of Struvite from Supernatants Separated from Enzymatically Disintegrated Digested Sewage Sludge. Catalysts 2025, 15, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, R.T.; Zhang, R.; Teter, S.; McGarvey, J.A. The effect of enzyme addition on anaerobic digestion of Jose Tall Wheat Grass. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4564–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lyu, Q.; Bi, L.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Ji, G.; Huan, G.C.; Xu, L.; Yan, Z. Improvement of sewage sludge anaerobic digestion through synergistic effect combined trace elements enhancer with enzyme pretreatment and microbial community response. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Liu, S.; Xin, F.; Zhou, J.; Jia, H.; Xu, J.; Jiang, M.; Dong, W. Biomethane production from lignocellulose: Biomass recalcitrance and its impacts on anaerobic digestion. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, Y.X.; Chan, Y.J.; Manickam, S.; Chong, M.F.; Chong, S.; Tiong, T.J.; Lim, J.W.; Pan, G.T. Enzymatic pretreatment to enhance anaerobic bioconversion of high strength wastewater to biogas: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Woo, S.G.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.H.; Hwang, S. Evaluation of feasibility of using the bacteriophage t4 lysozyme to improve the hydrolysis and biochemical methane potential of secondary sludge. Energies 2019, 12, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, S.I.; Hwang, S. Enhancement of hydrolysis efficiency and biogas production by treatment of secondary sludge with bacteriophage lysozymes. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 54, 102897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.C.; Sethi, B.K.; Mishra, R.R.; Dutta, S.K.; Thatoi, H.N. Microbial cellulases–Diversity & biotechnology with reference to mangrove environment: A review. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, U.; Sohail, M.; Ghanemi, A. Cellulases: From bioactivity to a variety of industrial applications. Biomimetics 2021, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, N.; Wen, S.; Wang, F.; Nawaz, S.; Raza, J.; Iftikhar, M.; Usman, M. Lysozyme and its application as antibacterial agent in food industry. Molecules 2022, 27, 6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primo, E.D.; Otero, L.H.; Ruiz, F.; Klinke, S.; Giordano, W. The disruptive effect of lysozyme on the bacterial cell wall explored by an in-silico structural outlook. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2018, 46, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christy, P.M.; Gopinath, L.; Divya, D. A review on anaerobic decomposition and enhancement of biogas production through enzymes and microorganisms. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, M. Changes in microbial community during hydrolyzed sludge reduction. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1239218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Luo, K.; Li, X.M.; Wang, D.B.; Zheng, W.; Zeng, G.M.; Liu, J.J. Enhanced efficiency of biological excess sludge hydrolysis under anaerobic digestion by additional enzymes. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2924–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, K.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Ma, X.; Chen, H. Enhancement of excess sludge hydrolysis and decomposition with different lysozyme dosage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN ISO 10523:2012; Jakość Wody—Oznaczanie pH. Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warszawa, Poland, 2012.
- Standard Methods 5220D: Chemical Oxygen Demand, Closed Reflux, Colorimetric Method. Available online: https://www.nemi.gov/methods/method_summary/5716/ (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- PN-EN 12880:2004; Charakterystyka Osadów Ściekowych—Oznaczanie Suchej Pozostałości i Zawartości Wody. Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warszawa, Poland, 2004.
- PN-ISO 4832; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Coliforms—Colony-Count Technique. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Junior, I.V.; de Almeida, R.; Cammarota, M.C. A review of sludge pretreatment methods and co-digestion to boost biogas production and energy self-sufficiency in wastewater treatment plants. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baksi, S.; Sarkar, U.; Villa, R.; Basu, D.; Sengupta, D. Conversion of biomass to biofuels through sugar platform: A review of enzymatic hydrolysis highlighting the trade-off between product and substrate inhibitions. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 55, 102963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardos, L.; Juhasz, A.; Palko, G.Y.; Olah, J.; Barkacs, K.; Zaray, G.Y. Comparing of mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic fermented sewage sludge based on chemical and biochemical tests. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2011, 9, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macherzyński, B.; Włodarczyk-Makuła, M. Evaluation of the possibility of disposal of Coke sludge in the co-fermentation process. Annu. Set Environ. Prot. 2015, 17, 1142–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, T.; Ogez, J.R.; Builder, S.E. Downstream processing of proteins. Biotechnol. Adv. 1983, 1, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, N.; Morrison, D.C. Lipopolysaccharide interaction with lysozyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 4434–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliason, D.J.; Tatini, S.R. Enhanced inactivation of Salmonella typhimurium and verotoxigenic Escherichia coli by nisin at 6·5 °C. Food Microbiol. 1999, 16, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, Y.; Yanagisawa, H. Techniques for the separation of proteins by isoelectric point column chromatography. Bull. Aichi Univ. Educ. 2007, 56, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sedov, S.A.; Belogurova, N.G.; Shipovskov, S.; Levashov, V.A.; Levasho, P.A. Lysis of Escherichia coli cells by lysozyme: Discrimination between adsorption and enzyme action. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 88, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdova, O.; Chamy, R.; Guerrero, L.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, A. Assessing the Effect of Pretreatments on the Structure and Functionality of Microbial Communities for the Bioconversion of Microalgae to Biogas. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreini, G.; Nazari, L.; Ho, D.; Flannery, C.; Elbeshbishy, E.; Santoro, D.; Nakhla, G. Enzymatic pre-treatment for enhancement of primary sludge fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 123071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, L.; Zhen, F.; Liu, H.; Xiao, F.; Sun, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Thermodynamics of volatile fatty acid degradation during anaerobic digestion under organic overload stress: The potential to better identify process stability. Water Res. 2022, 214, 118187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manai, I.; Miladi, B.; El Mselmi, A.; Hamdi, M.; Bouallagui, H. Improvement of activated sludge resistance to shock loading by fungal enzyme addition during textile wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. 2016, 38, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar, N.; Pizzagalli, G.; Coulon, F.; Bajón-Fernández, Y. Enzymes targeting distinct hydrolysis blind-spots of thermal and biological pre-treatments significantly uplift biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 426, 132353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parawira, W. Enzyme research and applications in biotechnological intensification of biogas production. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, Z.; Fattah, M.; Shamkhy, A. Investigation of Solid Waste Generation Rate and Biogas Production. Results Eng. 2024, 23, 102531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Liu, J. Enhanced hydrolysis of excess sludge by external enzymes. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2010, 31, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dz.U. 2019 poz. 1311. Rozporządzenie Ministra Gospodarki Morskiej i Żeglugi Śródlądowej z Dnia 12 lipca 2019 r. w Sprawie Substancji Szczególnie Szkodliwych dla Środowiska Wodnego Oraz Warunków, Jakie Należy Spełnić Przy Wprowadzaniu do Wód Lub do Ziemi Ścieków, a Także Przy Odprowadzaniu Wód Opadowych Lub Roztopowych do Wód lub do Urządzeń Wodnych. Available online: https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/DocDetails.xsp?id=WDU20190001311 (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Liu, Z.; Smith, S. Enzyme Recovery from Biological Wastewater Treatment. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 12, 4185–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).