Bee Bread Granule Drying in a Solar Dryer with Mobile Shelves
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- Justify the drying chamber parameters and its operational modes through mathematical modeling.
- -
- Experimental investigation of moisture variation within the layer of bee bread granules under different drying conditions (airflow rate, mass of granules, and residence time in the chamber).
- -
- A comparative evaluation of drying efficiency using the traditional method (natural shade drying) and the proposed solar dryer.
2. Materials and Methods
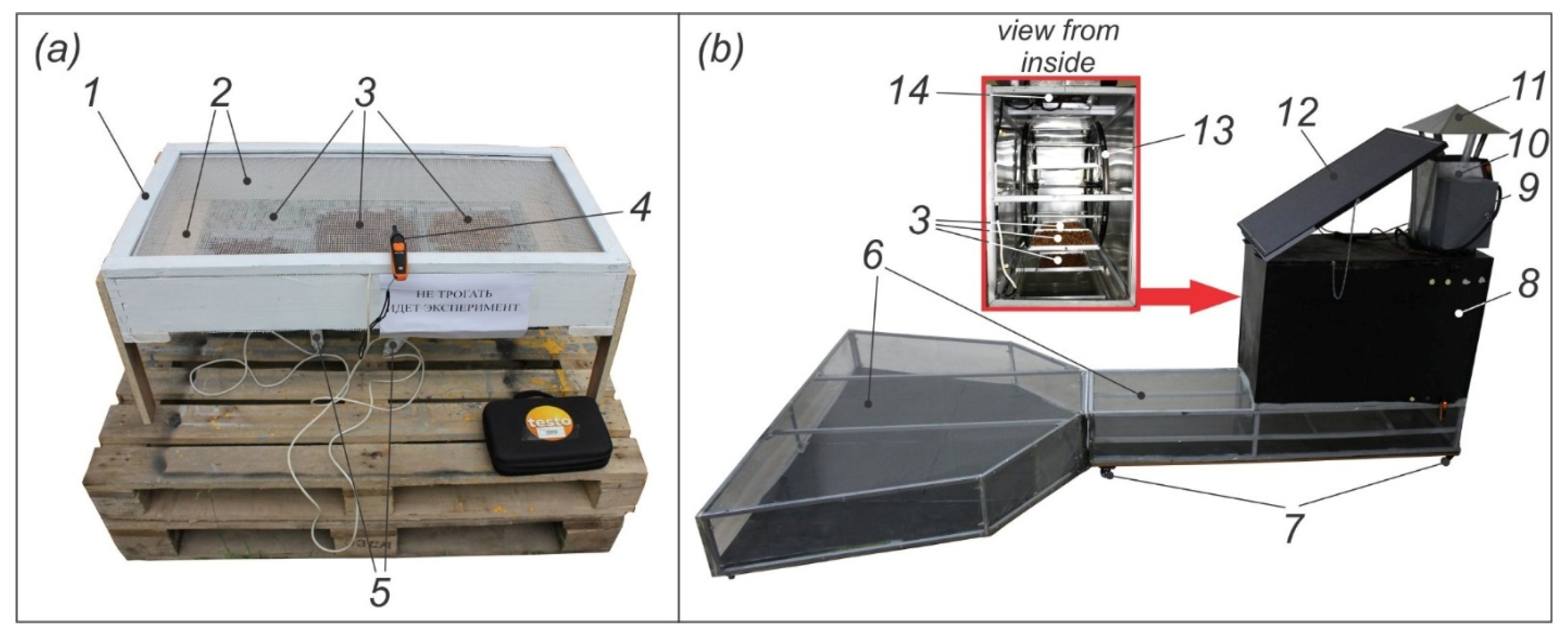
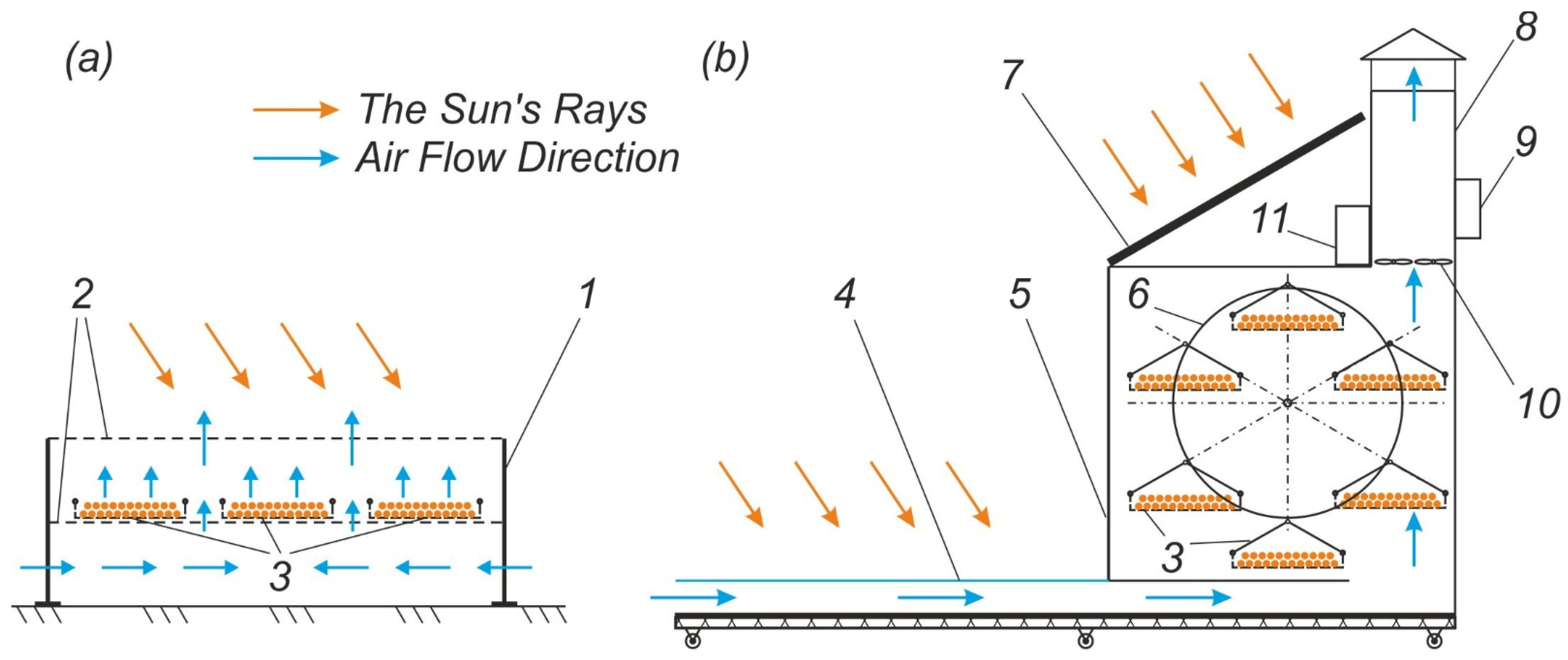
2.1. Principle of Operation of the Developed Solar Dryer for Bee Bread Granules
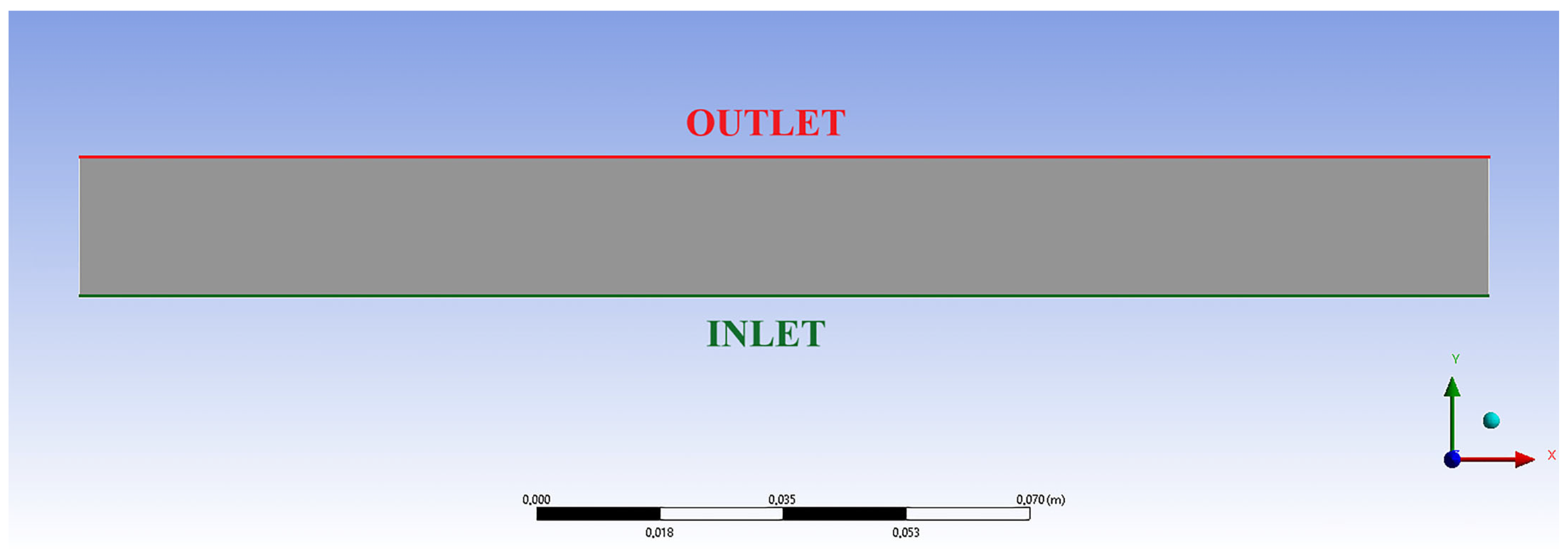
2.2. Numerical Simulation of Heat Exchange Processes During Bee Bread Granule Drying
- —coefficient of temperature conductivity, defined as
- —thermal conductivity;
- —density;
- —the specific heat capacity at constant pressure.
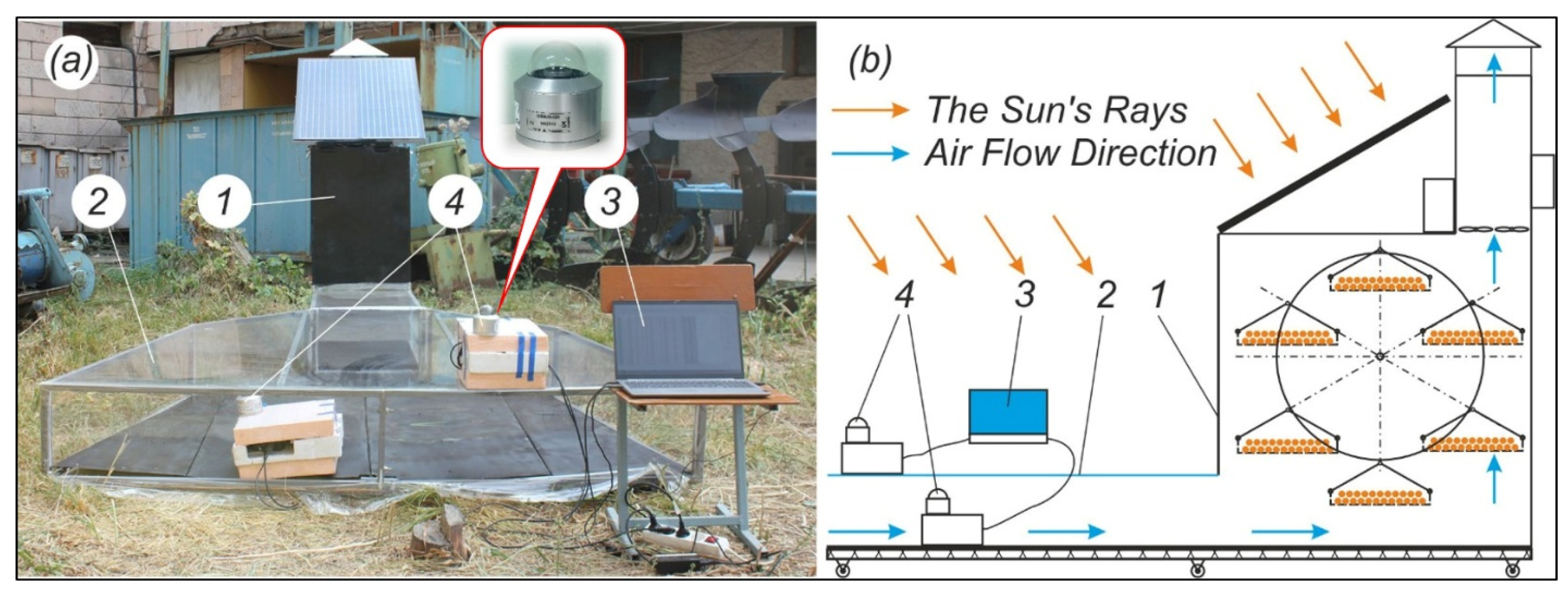
2.3. Experimental Research Methods
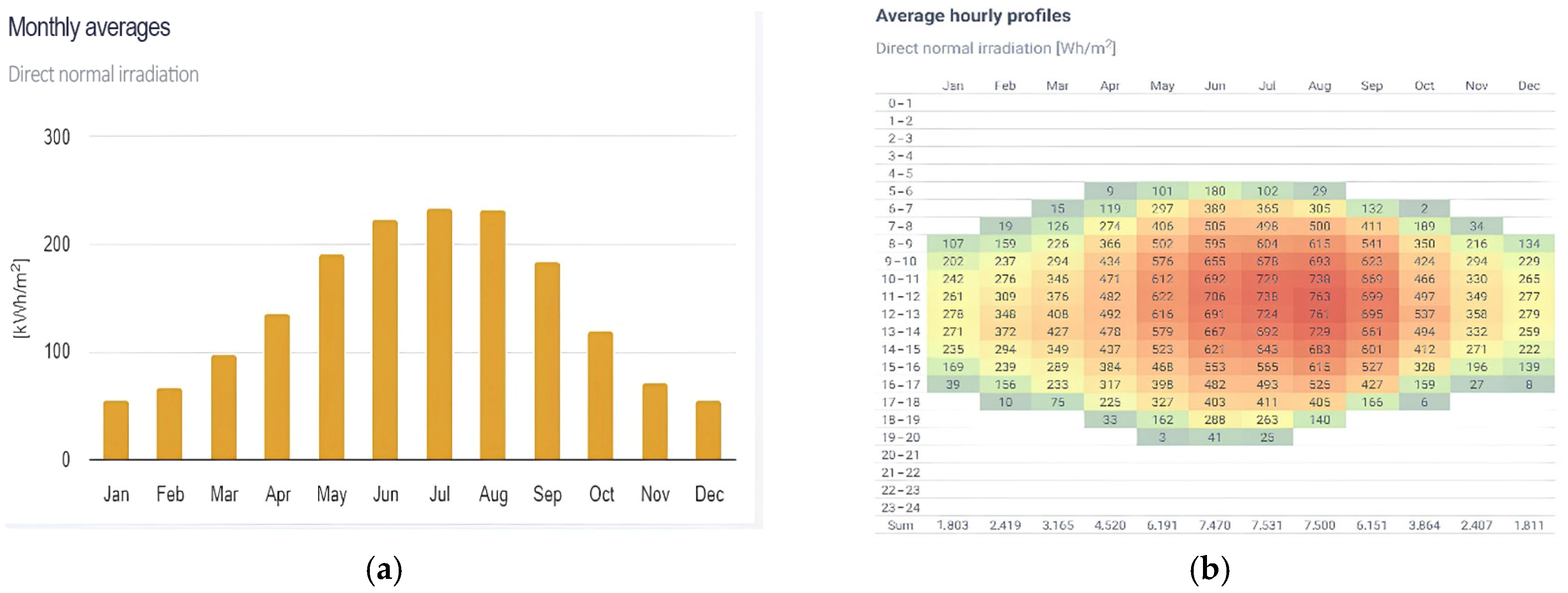
2.3.1. Determination of Solar Radiation in the Study Area
2.3.2. Measurement of Solar Radiation Loss Through the Transparent Film
2.3.3. Investigation of Temperature and Humidity Profiles During Traditional and Solar Drying
3. Study Results
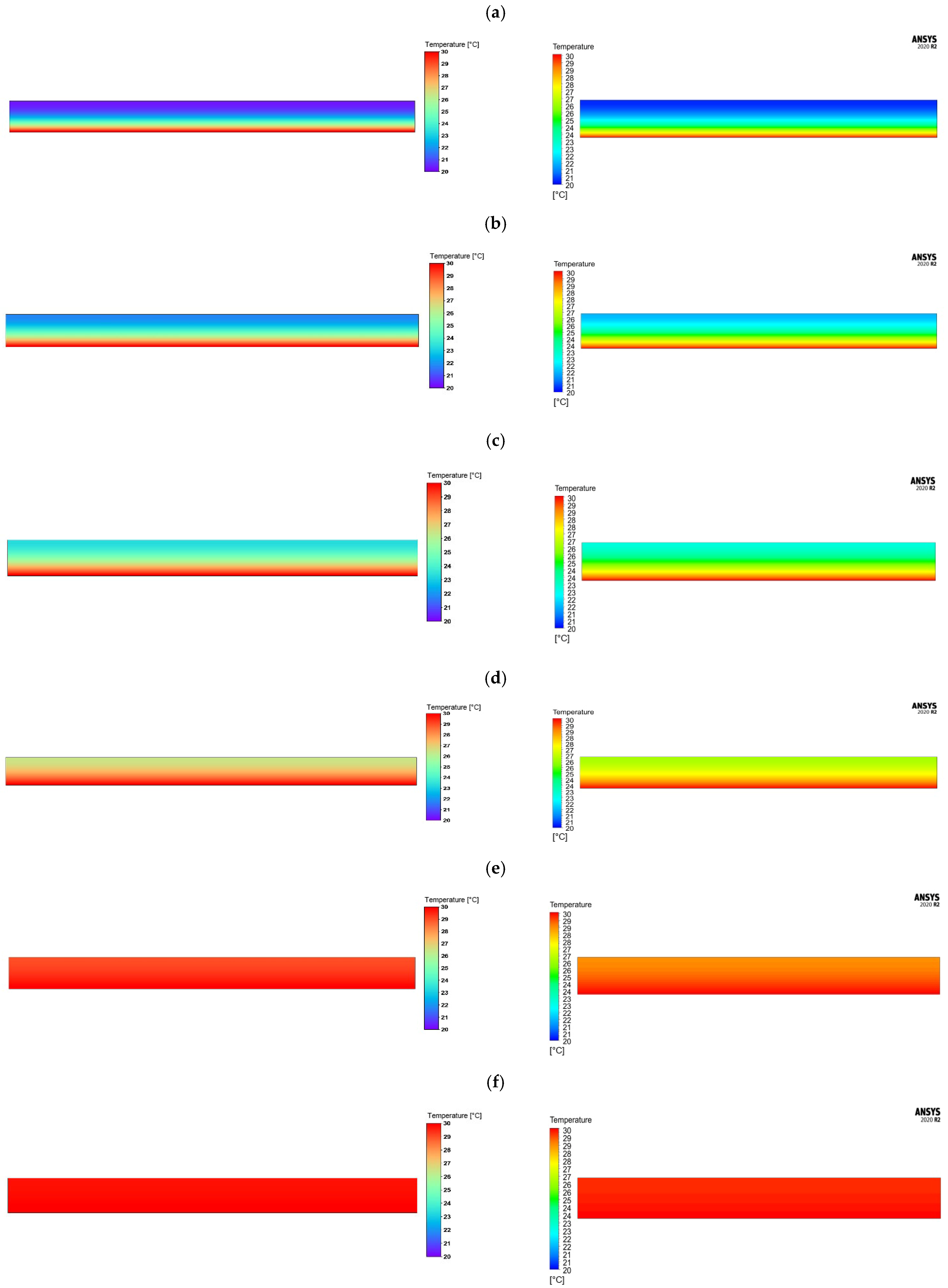
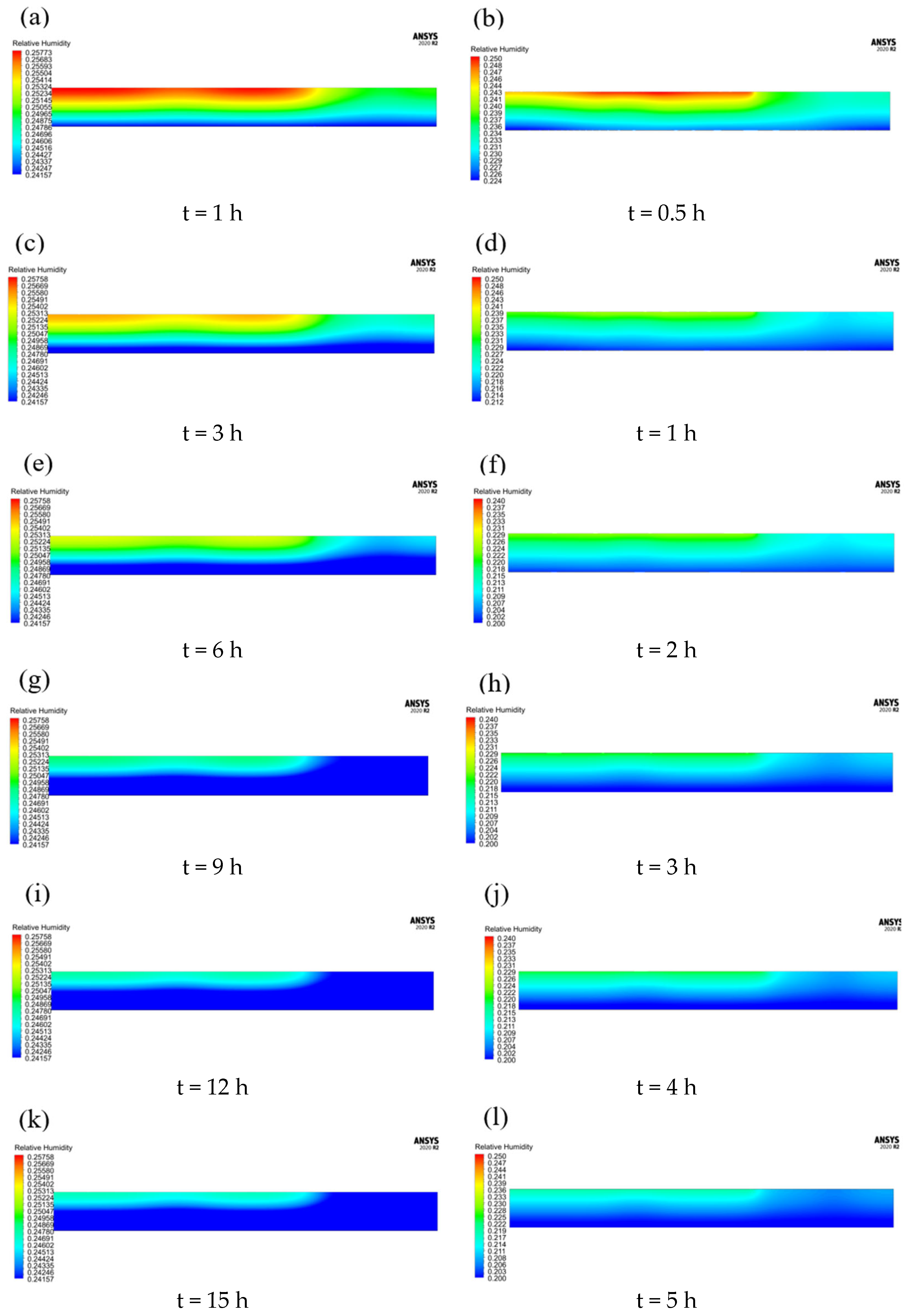
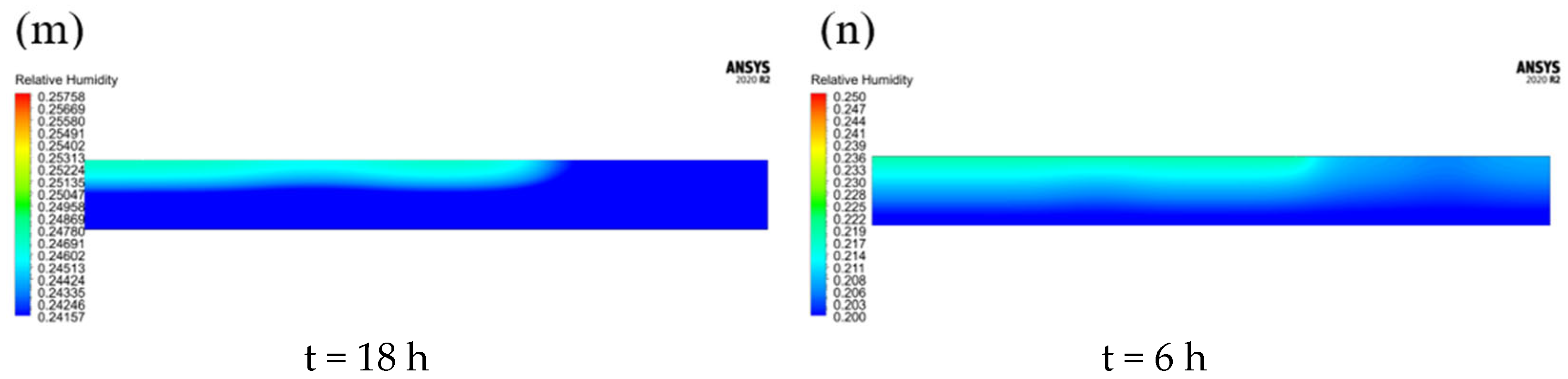
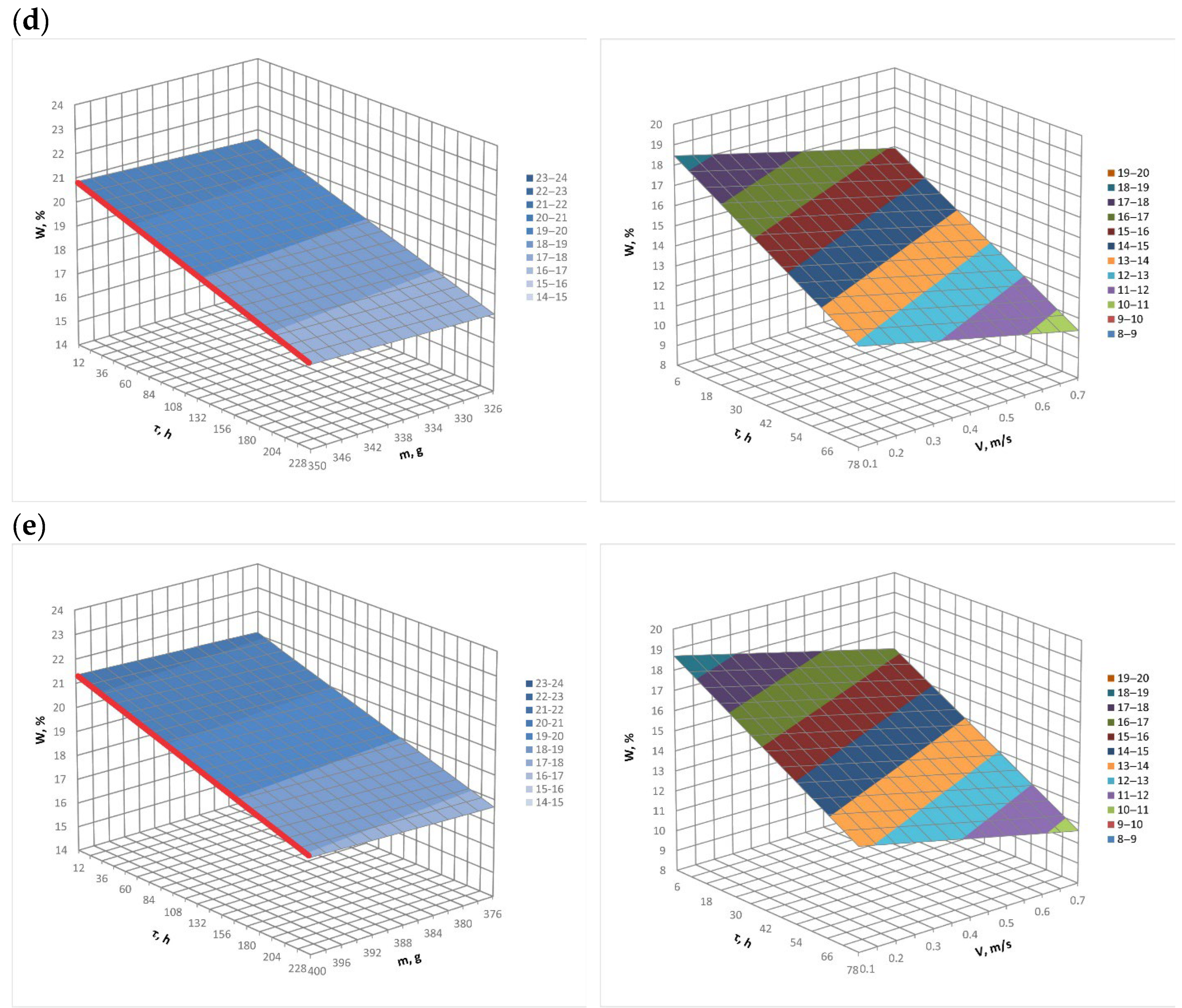
3.1. Numerical Modelling Results
3.2. Results of Experimental Research
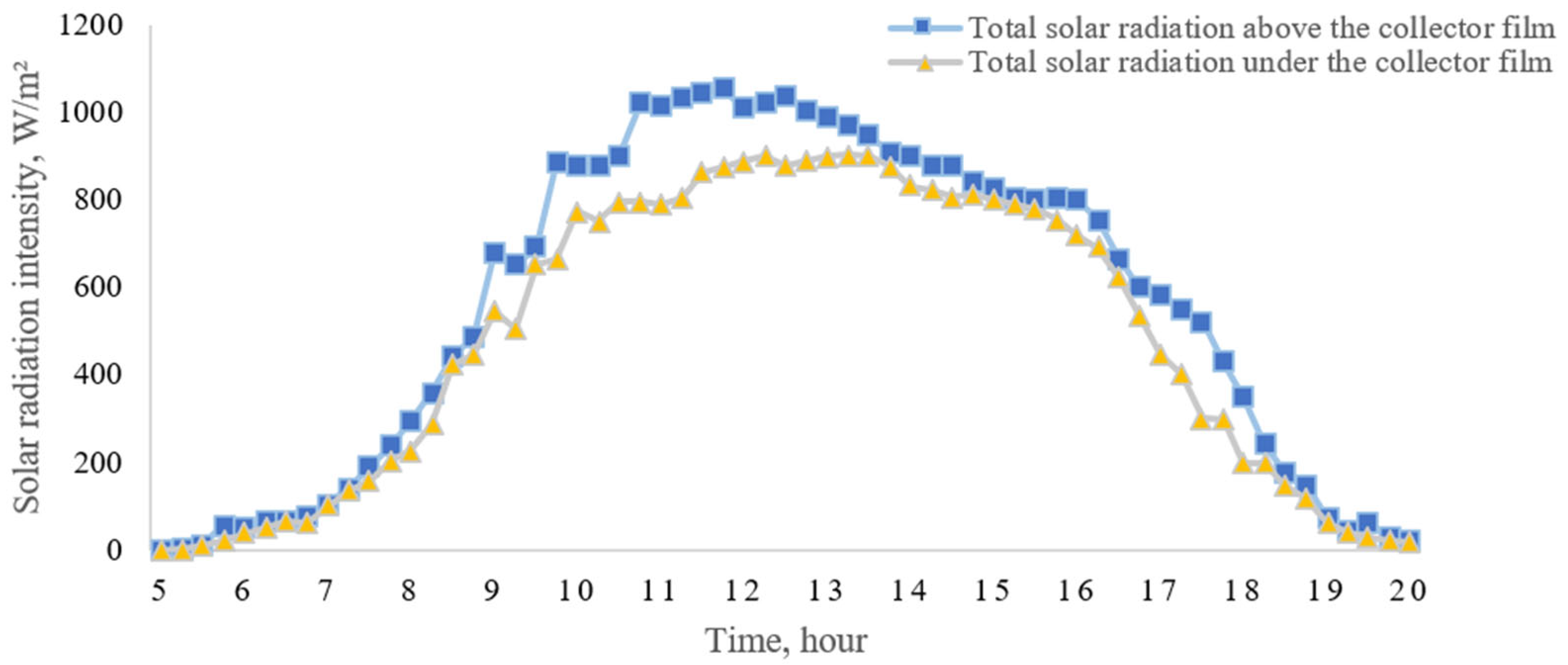
3.2.1. Solar Radiation in the Study Area
3.2.2. Attenuation of Solar Radiation by the Transparent Film
3.2.3. Change in Moisture Content of Bee Bread Granules as a Function of Drying Parameters
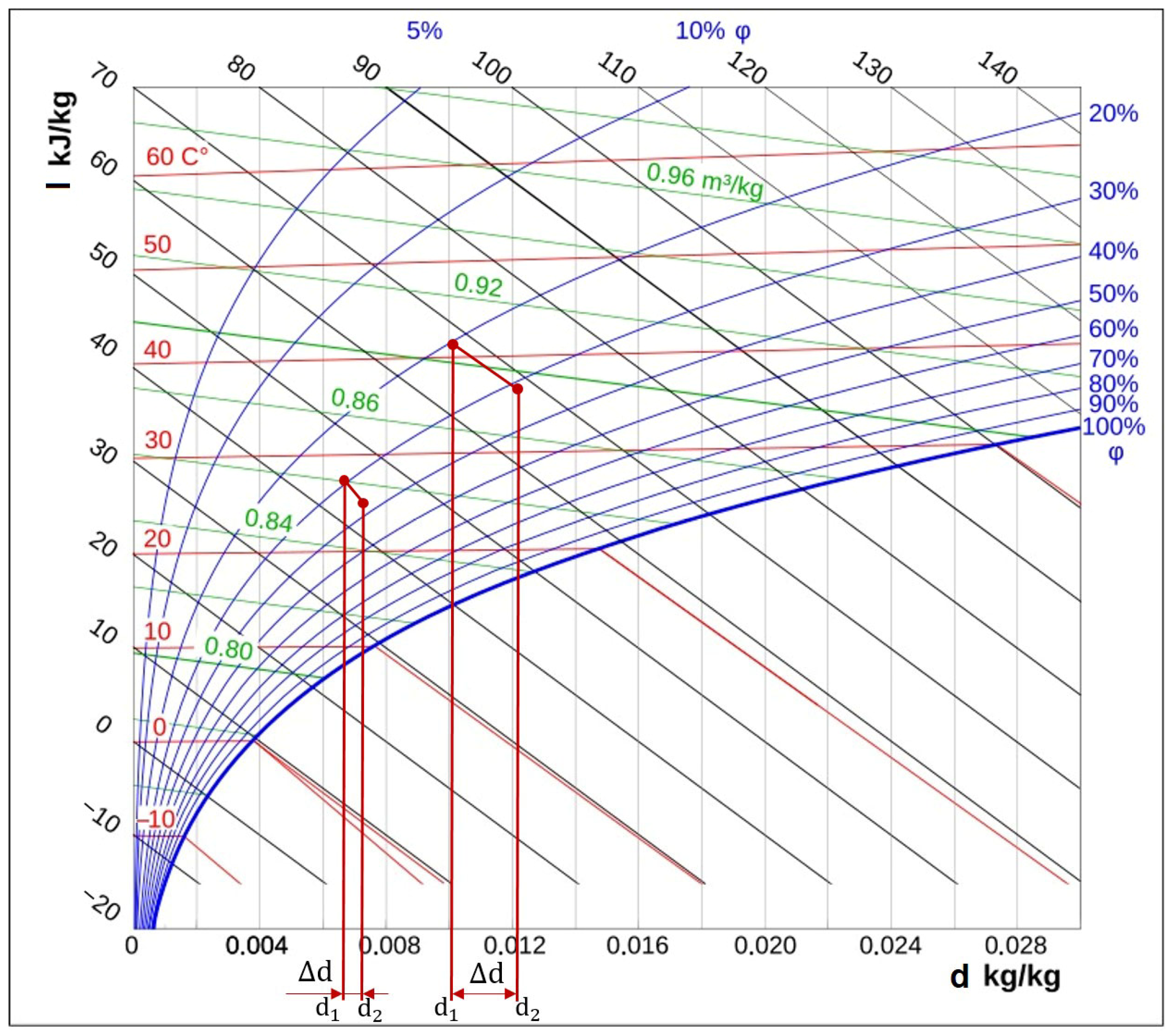
3.3. Change in Moisture Content of the Drying Agent
4. Discussion of Research Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Latin Symbols | |
| m | Meter |
| s | Second |
| Time | |
| Pressure (Pa) | |
| Temperature (°C) | |
| Reference temperature (°C) | |
| Spatial coordinates | |
| Velocity’s components | |
| Concentration | |
| Gravitational acceleration (m/s2) | |
| Heat capacity (J/K) | |
| Greek Symbols | |
| ε | Range |
| Density (kg/m3) | |
| Reference density | |
| Dynamic viscosity | |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | |
| Coefficient of temperature conductivity | |
| Thermal conductivity (W·m−1·K−1) | |
| Diffusion coefficient of concentration | |
| Subscripts | |
| kg | Kilogram |
| g | Gram |
| K | Kelvin |
| kW | Kilowatt |
| V | Volts |
| RH | Relative humidity |
| h | Hour |
| s | Seconds |
| Acronyms | |
| Testo | Measuring instruments |
| HOBO | Data logger |
| GOST | State Standard of the Soviet Union |
| ANSYS | Engineering simulation software |
| Python | Programming language |
References
- Gabriele, M.; Felicioli, A.; Domenici, V.; Sagona, S.; Pucci, L.; Pozzo, L. Phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of tuscan bee pollen of different botanic origins. Ital. J. Food. Sci. 2015, 27, 248–259. [Google Scholar]
- Sattler, J.A.G.; de Melo, I.L.P.; Granato, D.; Araújo, E.; de Freitas, A.d.S.; Barth, O.M.; Sattler, A.; de Almeida-Muradian, L.B. Impact of origin on bioactive compounds and nutritional composition of bee pollen from southern Brazil: A screening study. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Park, H.J.; Chae, Y.; Lim, S. An overview of bee venom acupuncture in the treatment of arthritis. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2005, 2, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.A.-S.M. Studies on bee venom and its medical uses. Int. J. Adv. Res. Technol. 2012, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kieliszek, M.; Piwowarek, K.; Kot, A.M.; Błazejak, S.; Chlebowska-Smigiel, A.; Wolska, I. Pollen and bee bread as new health-oriented products: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 71, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Nanda, V. Composition and functionality of bee pollen: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 82–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mărgăoan, R.; Strant, M.; Varadi, A.; Topal, E.; Yücel, B.; Cornea-Cipcigan, M.; Campos, M.G.; Vodnar, D.C. Bee Collected Pollen and Bee Bread: Bioactive Constituents and Health Benefits. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feas, X.; Vazquez-Tato, M.P.; Estevinho, L.; Seijas, J.A.; Iglesias, A. Organic bee pollen: Botanical origin, nutritional value, bioactive compounds, antioxidant activity and microbiological quality. Molecules 2012, 17, 8359–8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vit, P.; Albore, G.R.D.; Barth, O.M.; Peña-Vera, M.; Pérez-Pérez, E. Characterization of pot-pollen from Southern Venezuela. In Pot-Pollen in Stingless Bee Melittology; Vit, P., Pedro, S.R.M., Roubik, D.W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 361–375. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, S.M.; Mahmud-Ab-Rashid, N.-K.; Zawawi, N. Stingless Bee-Collected Pollen (Bee Bread): Chemical and Microbiology Properties and Health Benefits. Molecules 2021, 26, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, I.L.P.; de Almeida-Muradian, L.B. Stability of antioxidants vitamins in bee pollen samples. Química Nova 2010, 33, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toibazar, D.; Urmashev, B.; Tursynzhanova, A.; Nekrashevich, V.; Daurenova, I.; Niyazbayev, A.; Khazimov, K.; Pegna, F.; Khazimov, M. Bee Bread Drying Process Intensification in Combs Using Solar Energy. Energies 2025, 18, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Dong, Y.; Gu, C.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. Processing technologies for bee products: An overview of recent developments and perspectives. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 727181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, C.V.; da Silva, L.H.M.; Corrêa, D.F.; Rodrigues, A.M. Modeling study for moisture diffusivities and moisture transfer coefficients in drying of passion fruit peel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 85, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.M.; Mayorga, E.Y.; Moreno, F.L. Mathematical modelling of convective drying of fruits: A review. J. Food Eng. 2018, 223, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, L.D.M.S.; Marques, L.G.; Prado, M.M. Performance evaluation of an infrared heating-assisted fluidized bed dryer for processing bee-pollen grains. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2020, 155, 108044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboltins, A. Theoretical study of material drying coefficient. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference Engineering for Rural Development, Jelgava, Latvia, 23–24 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hamed, K.; Mohammed, K.; Iman, G.; Esmail, K.; Robert, R.; Bohdan, D.; Marek, G., Jr. Thermodynamic Evaluation of the Forced Convective Hybrid-Solar Dryer during Drying Process of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Leaves. Energies 2021, 14, 5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macmanus, C.; Ndukwu, M.I.; Inemesit, E.; Ugochukwu, A.; Promise, E.; Lyes, B.; Fidelis, A.; Merlin, S.-T.; Ankur, G. Analysis of the Heat Transfer Coefficient, Thermal Effusivity and Mathematical Modelling of Drying Kinetics of a Partitioned Single Pass Low-Cost Solar Drying of Cocoyam Chips with Economic Assessments. Energies 2022, 15, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazimov, M.Z.; Khazimov, K.M.; Urmashev, B.A.; Tazhibayev, T.S.; Sagyndykova, Z.B. Intensification of the Plant Products Drying Process by Improving Solar Dryer Design. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2018, 27, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, E.E.; Awad Ali, T.O.; Mohsen, A.; Gameh, A.S.; Eissa, S.F.; Mahmoud, M.H.E.; Atef, M.; Mostafa, B.M.; Mohamed, F.T.; Samah, A.T.; et al. Quality evaluation of dried tomato fruit and optimization of drying conditions using a modified solar dryer integrated with an automatic solar collector tracker. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazimov, Z.M.; Bora, G.C.; Khazimov, K.M.; Khazimov, M.Z. Modeling of the motion of free convective drying agent in plastic helio dryer. J. Engin. Thermophys. 2014, 23, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, C.N.; Aruna, K.B. Thermal and environmental analysis of Cucumis sativus drying in a mixed mode solar dryer with combined sensible and latent heat energy storage. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daurenova, I.M.; Toibazar, D.M.; Saparghali, A.Z.; Khazimov, M.Z.; Kasymbaev, B.M.; Chandra, B.G. Effective technology and means of processing honeycombs into bee bread and wax raw materials in Kazakhstan. Res. Results 2024, 2, 523–534. [Google Scholar]
- Khazimov, M.Z.; Pogulyaev, A.D.; Niazbayev, A.K. Helio Dryer with Air Heating Unit for Bee bread. KZ Patent 37476, 15 August 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Testo, S.E. Testo Smart Probes Instruction Manual. 2024. Available online: https://www.testo.com/en-UK/testo-smart-probes-vac-kit/p/0563-0003-10#tab-downloads (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Khazimov, K.; Sagyndykova, Z.; Daurenova, I. Thermal Welding in the Neck of Vacuum Flexible Container with Self-propelled Welding Module. Int. J. Technol. 2024, 15, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazimov, M.Z.; Tazhibayev, T.S.; Francesco, G.P.; Khazimov, K.M.; Turbekova, A.S.; Kurpenov, B.K. Solar Dryer. KZ Patent 30006, 15 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Urmashev, B.A.; Khazimov, K.M.; Temirbekov, A.N. Drying of Vegetable Products in Mobile Solar Dryer with Movable Shelving. J. Engin. Thermophys. 2021, 30, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudasheva, A.B.; Khazimov, M.Z.; Niyazbayev, A.K. Efficient Combustion of the Fixed Coal Layer in an Advanced Combustion Chamber Design for Low-Power Boilers. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 2024, 30, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasner, R.; Walichnowska, P.; Korobka, S.; Shchur, T.; Stukalets, I.; Syrotyuk, S.; Babych, M.; Ptashnyk, V.; Tomporowski, A.; Kruszelnicka, W. Analysis of the Design and Technological Parameters of the Designed Solar Dryer with a Heat Pump. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2024, 18, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Solar Atlas. Available online: https://globalsolaratlas.info/detail?s=42.89568,71.37812&m=site&c=42.895586,71.378174,11, (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- GOST-31776-2012; Bee Bread. Technical Conditions. Inter-State Standard. Standardinform: Moscow, Russia, 2013.
- GOST R 55262-2012; Drying Machines and Installations for Agracultural Purposes. Test Methods. Standartinform: Moscow, Russia, 2015.


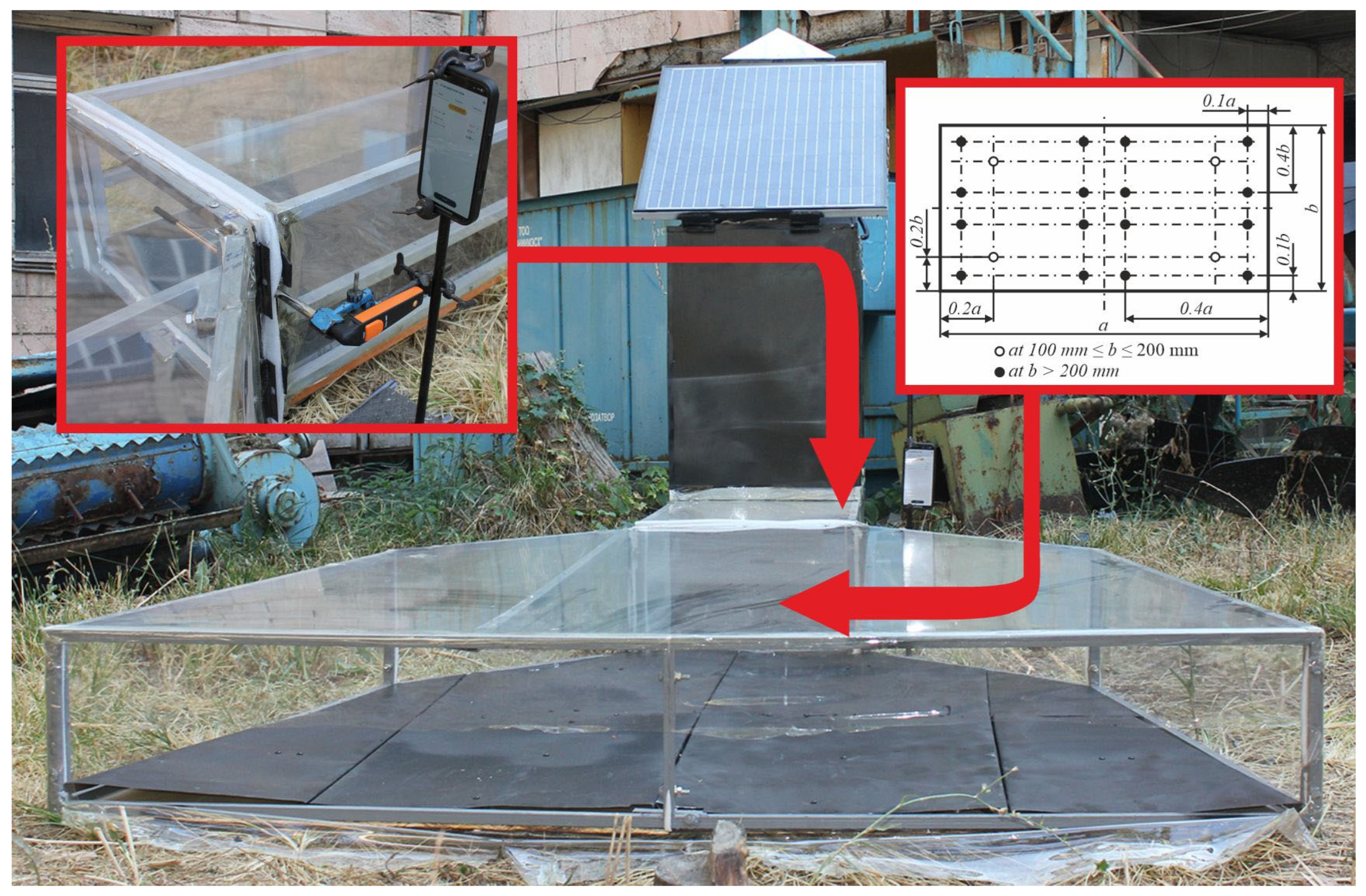
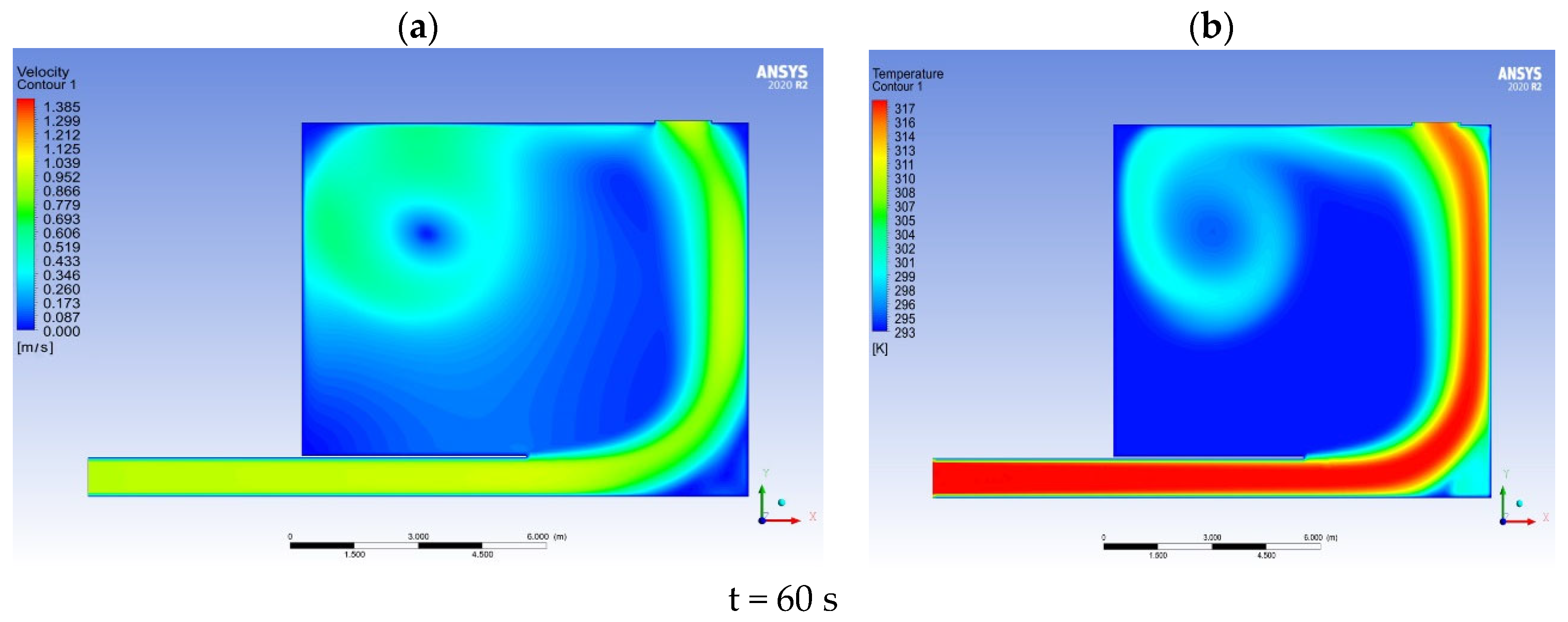
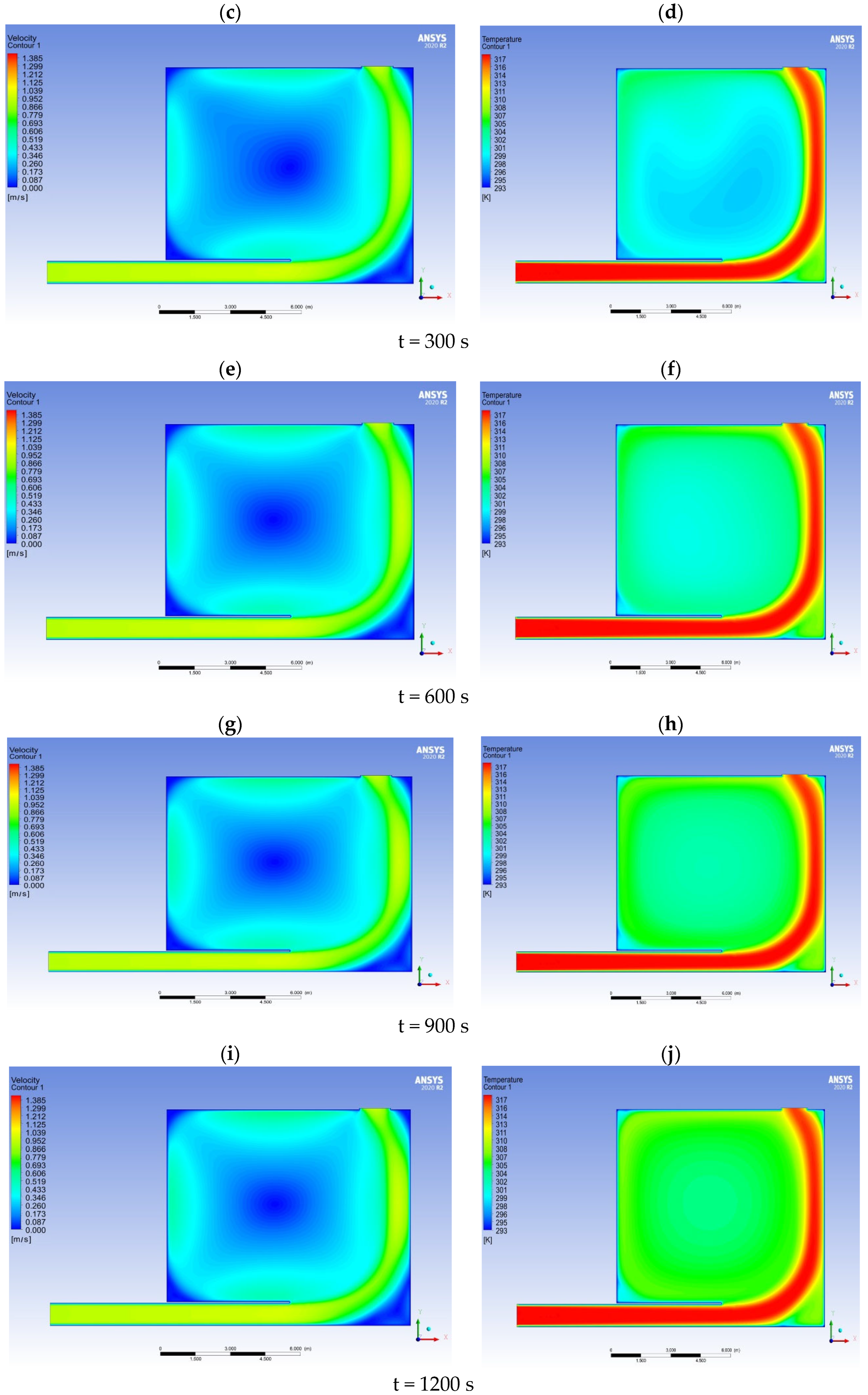
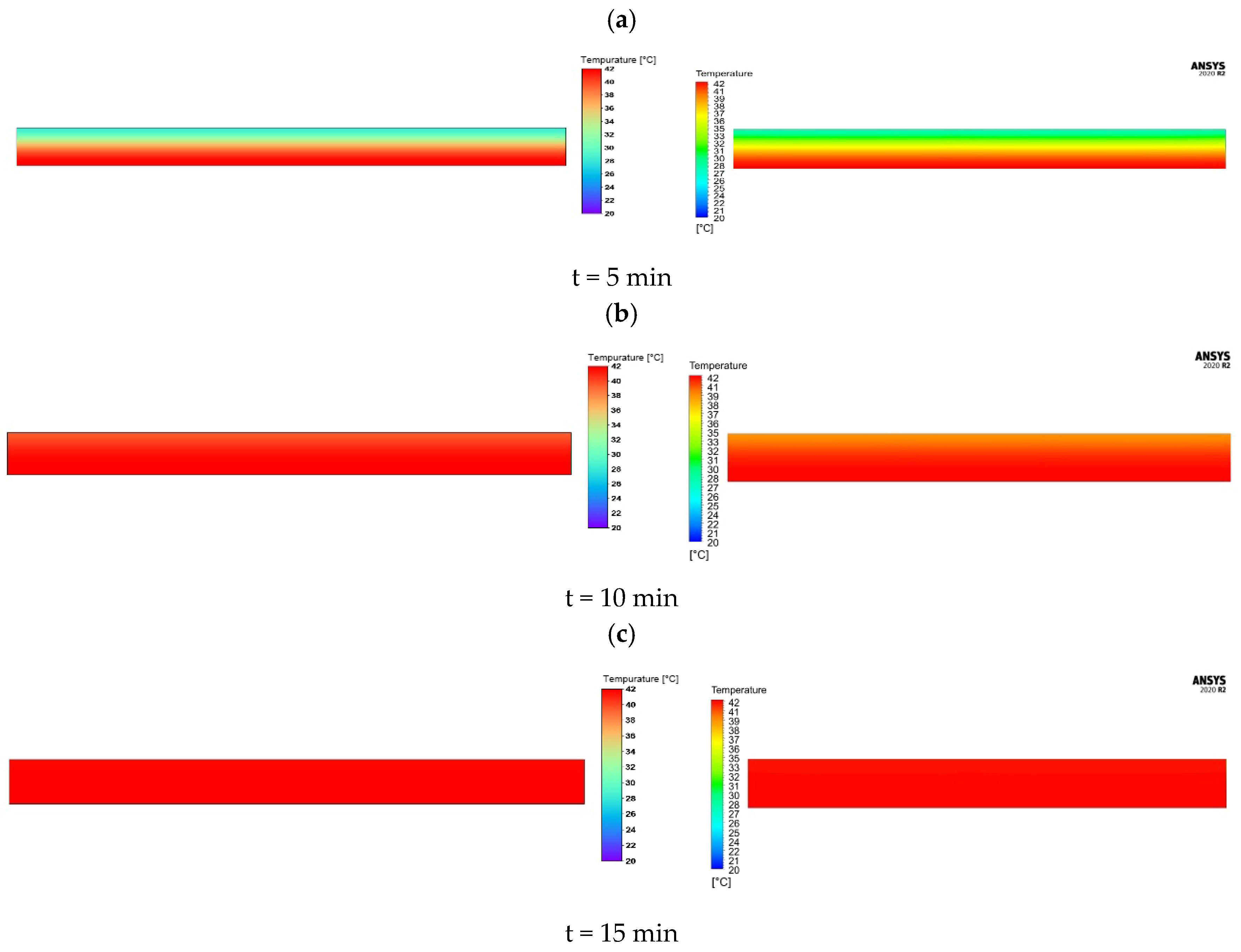

| General Equation | Equation Name |
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
|
| Boundaries | Inside the Solar Dryer Chamber | In Ambient Conditions (Natural Drying) |
|---|---|---|
| Inlet | ||
| Outlet | (Same as solar dryer) Temperature: (Adiabatic) | |
| Walls | (Same as solar dryer) Temperature: (Adiabatic) | |
| Drying Methods | Air Temperature, | Air Velocity, |
|---|---|---|
| Solar dryer | 42 | 0.45 |
| Natural drying | 30 | 0.05 |
| Status of Factors | Coded Values | Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air Flow Velocity, m/s | Exposure Time, h | Bee Bread Mass | ||||
| Solar Dryer | Natural | Solar Dryer | Natural | |||
| Basic level | 0 | 0.44 | 0.05 | 42 | 135 | 280 |
| Range | ε | 0.13 | 0.05 | 18 | 62.5 | 70 |
| Upper level | +1 | 0.57 | 0.05 | 60 | 197.5 | 350 |
| Lower level | −1 | 0.31 | 0.05 | 24 | 72.5 | 210 |
| High point | +1.68 | 0.66 | 0.05 | 72 | 240 | 400 |
| Low point | −1.68 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 12 | 30 | 160 |
| Code mark | xi | x1 | x2 | x3 | ||
| Experiment No | Coded Value x2 | Exposure Time (h) | Coded Value x3 | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | 72.5 | −1 | 210 |
| 2 | +1 | 197.5 | −1 | 210 |
| 3 | −1 | 72.5 | +1 | 350 |
| 4 | +1 | 197.5 | +1 | 350 |
| 5 | −1.68 | 30 | 0 | 280 |
| 6 | +1.68 | 240 | 0 | 280 |
| 7 | 0 | 135 | −1.68 | 160 |
| 8 | 0 | 135 | +1.68 | 400 |
| 9–12 | 0 | 135 | 0 | 280 |
| Experiment No | Coded x1 | Velocity (m/s) | Coded x2 | Time (h) | Coded x3 | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 | 0.31 | −1 | 24 | −1 | 210 |
| 2 | +1 | 0.57 | −1 | 24 | −1 | 350 |
| 3 | −1 | 0.31 | +1 | 60 | −1 | 210 |
| 4 | +1 | 0.57 | +1 | 10 | −1 | 210 |
| 5 | −1 | 0.31 | −1 | 24 | +1 | 350 |
| 6 | +1 | 0.57 | −1 | 24 | +1 | 350 |
| 7 | −1 | 0.31 | +1 | 60 | +1 | 350 |
| 8 | +1 | 0.57 | +1 | 60 | 0 | 280 |
| 9 | −1.68 | 0.22 | 0 | 42 | 0 | 280 |
| 10 | +1.68 | 0.66 | 0 | 42 | 0 | 280 |
| 11 | 0 | 0.44 | −1.68 | 12 | 0 | 280 |
| 12 | 0 | 0.44 | +1.68 | 72 | −1.68 | 160 |
| 13 | 0 | 0.44 | 0 | 42 | +1.68 | 400 |
| 14–20 | 0 | 0.44 | 0 | 42 | 0 | 280 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daurenova, I.; Mustafayeva, A.; Khazimov, K.; Pegna, F.; Khazimov, M. Bee Bread Granule Drying in a Solar Dryer with Mobile Shelves. Energies 2025, 18, 5472. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205472
Daurenova I, Mustafayeva A, Khazimov K, Pegna F, Khazimov M. Bee Bread Granule Drying in a Solar Dryer with Mobile Shelves. Energies. 2025; 18(20):5472. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205472
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaurenova, Indira, Ardak Mustafayeva, Kanat Khazimov, Francesco Pegna, and Marat Khazimov. 2025. "Bee Bread Granule Drying in a Solar Dryer with Mobile Shelves" Energies 18, no. 20: 5472. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205472
APA StyleDaurenova, I., Mustafayeva, A., Khazimov, K., Pegna, F., & Khazimov, M. (2025). Bee Bread Granule Drying in a Solar Dryer with Mobile Shelves. Energies, 18(20), 5472. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205472







