Research Progress in Multi-Domain and Cross-Domain AI Management and Control for Intelligent Electric Vehicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Innovatively starting from the perspective of the intelligent vehicle domain controller, the research results and application status of DRL algorithms in the four functional domains of intelligent vehicles are sorted out, and the solution ideas regarding DRL algorithms’ application to the difficult problems of intelligent vehicle domain control technology are discussed.
- (2)
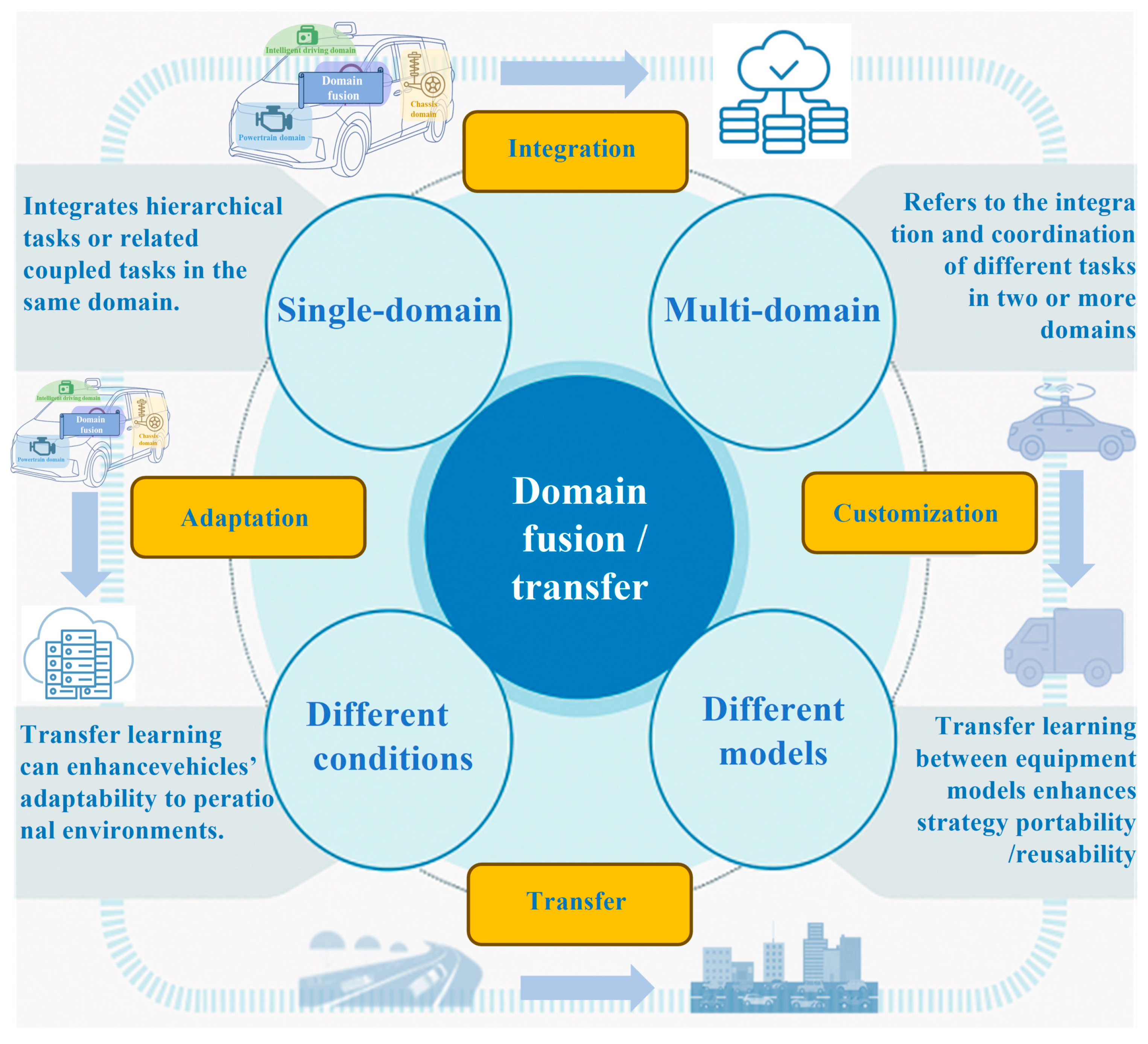
- From the two aspects of single-domain multi-task fusion and multi-domain multi-task fusion, the research progress on cross-domain fusion methods of intelligent vehicles is reviewed, focusing on the research progress of end-to-end algorithm architecture in multi-task fusion in the intelligent driving domain, and summarizing the status of multi-domain fusion research guided by the three elements of “vehicle, road, and person.”
- (3)
- We analyze the limitations and challenges of using the DRL algorithm in solving the technical problems of intelligent vehicle domain control, and explore the application effect and potential of combining the transfer learning method with the DRL algorithm in intelligent vehicle domain control technology.
2. Intelligent Driving Domain
2.1. Target Detection
2.1.1. Vision-Based Target Detection
2.1.2. Radar-Based Target Detection
2.1.3. Fusion-Based Target Detection
2.2. Target Tracking
2.3. Positioning Technology
2.3.1. Vision-Based Positioning Technology
2.3.2. Fusion-Based Positioning Technology
2.4. Trajectory Prediction
2.4.1. Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction
2.4.2. Vehicle Trajectory Prediction
2.5. Decision Planning
2.5.1. Behavioral Decisions
2.5.2. Trajectory Planning
3. Powertrain Domain
3.1. Power Control
3.2. Energy Management
3.3. Thermal Management
4. Chassis Domain
4.1. Steering Control
4.2. Brake Control
4.3. Suspension Control
5. Cockpit Domain
5.1. Personnel Monitoring
5.2. Comfort Control
5.3. Human–Machine Interaction
6. Domain Fusion
6.1. Single-Domain Multi-Task Fusion
6.2. Multi-Domain and Multi-Task Fusion
6.2.1. Fusion with Road (Vehicle Trajectory) as the Target
6.2.2. Fusion with Vehicle (Vehicle Status) as the Target
6.2.3. Integration with People (Drivers and Passengers) as the Goal
7. Domain Transfer
7.1. Transfer Between Different Working Scenarios
7.2. Transfer Between Different Models of Equipment
8. Conclusions
8.1. Intelligence Electric Vehicle Universal Model
8.2. Data Sample Acquisition
8.3. Possibility of Vehicle-Side Model Deployment
8.4. Portability of DRL Algorithms
8.5. Interoperability with Charging Infrastructure
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| DRL | Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DDPG | Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient |
| DQN | Deep Q-Network |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| EMS | Energy Management System |
| DDQN | Double Deep Q-Network |
| SSD | Single Shot MultiBox Detector |
| MARL | Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning |
| GAIL | Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning |
| TL | Transfer Learning |
| ECUs | Electronic Control Units |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| AEB | Automatic Emergency Braking |
| ABS | Anti-lock Braking System |
| DANN | Domain Adversarial Neural Networks |
| E/E | Electronic and Electrical |
| LKA | Large Kernel Attention |
| MTL | Multi-Task Learning |
| R&D | Research and Development |
| SOC | State of Charge |
| GNN | Graph Neural Network |
| SAC | Soft Actor–Critic |
| R-CNN | Region-based CNN |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| IL | Imitation Learning |
| BC | Behavior Cloning |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| PPO | Proximal Policy Optimization |
| ACC | Adaptive Cruise Control |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
References
- Jia, C.; Liu, W.; He, H.; Chau, K.T. Superior energy management for fuel cell vehicles guided by improved DDPG algorithm: Integrating driving intention speed prediction and health-aware control. Appl. Energy 2025, 394, 126195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Xu, B.; Sun, J.; Mujumdar, A.S. Artificial intelligence assisted technologies for controlling the drying of fruits and vegetables using physical fields: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherdoost, H.; Madanchian, M. AI Advancements: Comparison of Innovative Techniques. AI 2024, 5, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, W.; Sulowicz, M.; Feng, Y. Recent Progress on Digital Twins in Intelligent Connected Vehicles: A Review. Elektron. Elektrotech. 2024, 30, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yan, S.; Shen, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hussain, F. Model predictive control system based on direct yaw moment control for 4WID self-steering agriculture vehicle. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.K.; Haerri, J.; Bonnet, C.; Costa, R.F.D. Vehicles as Connected Resources: Opportunities and Challenges for the Future. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2017, 12, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Yu, W.; Ma, M.; Wei, X.; Wang, G. Artificial-Intelligence-Based Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2025, 18, 3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.X.; Chikangaise, P.; Dong, S.W.; Hua, C.W.; Qi, Y.S. Review of intelligent sprinkler irrigation technologies for remote autonomous system. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhou, J.; He, H.; Li, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, K. Health-conscious deep reinforcement learning energy management for fuel cell buses integrating environmental and look-ahead road information. Energy 2024, 290, 130146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Căpriță, H.V.; Selișteanu, D. A Novel Configurable End-to-End Communication Protection Hardware Module for Automotive Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 8949–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, N.; Deka, L.; Paluszczyszyn, D. Container-Based Electronic Control Unit Virtualisation: A Paradigm Shift Towards a Centralised Automotive E/E Architecture. Electronics 2024, 13, 4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Tan, S. Electric Vehicle Integration in Coupled Power Distribution and Transportation Networks: A Review. Energies 2024, 17, 4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, W.; He, H.; Chau, K.T. Deep reinforcement learning-based energy management strategy for fuel cell buses integrating future road information and cabin comfort control. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 321, 119032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, S.; Micallef, C.; Jia, Y.; Shi, Y.; Hughes, D.J. Optimisation and Management of Energy Generated by a Multifunctional MFC-Integrated Composite Chassis for Rail Vehicles. Energies 2020, 13, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachtler, A. Integrated vehicle dynamics control using active brake, steering and suspension systems. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2004, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.R.; Boddupalli, S.; Nath, A.P.D.; Ray, S. Automotive Functional Safety: Scope, Standards, and Perspectives on Practice. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2025, 14, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Bian, Z.; Jin, H.; Zheng, G.; Hu, D.; Sun, Y.; Fan, C.; Xie, W.; Fang, H. Overview of Deep Learning and Nondestructive Detection Technology for Quality Assessment of Tomatoes. Foods 2025, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, K.; Adade, S.Y.-S.S.; Lin, J.; Lin, H.; Chen, Q. Tea grading, blending, and matching based on computer vision and deep learning. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 3239–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, F.; Shu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Feng, C.; Gong, H.; Zhang, C.; Yu, W. Remaining useful life prediction of PEMFC based on matrix long short-term memory. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 111, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Yao, K.; Tang, N. Detection of soluble solid content in apples based on hyperspectral technology combined with deep learning algorithm. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Taha, T.M.; Yakopcic, C.; Westberg, S.; Sidike, P.; Nasrin, M.S.; Hasan, M.; Van Essen, B.C.; Awwal, A.A.S.; Asari, V.K. A State-of-the-Art Survey on Deep Learning Theory and Architectures. Electronics 2019, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunekpeku, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J.; Adade, S.Y.-S.S.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Gel strength prediction in ultrasonicated chicken mince: Fusing near-infrared and Raman spectroscopy coupled with deep learning LSTM algorithm. Food Control 2025, 168, 110916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, W.; He, H.; Chau, K.T. Health-conscious energy management for fuel cell vehicles: An integrated thermal management strategy for cabin and energy source systems. Energy 2025, 333, 137330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhou, J.; Jia, C.; Yi, F.; Zhang, C. Energy sources durability energy management for fuel cell hybrid electric bus based on deep reinforcement learning considering future terrain information. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 52, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Guo, Z.; Li, T.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, C. Dynamic Task Planning for Multi-Arm Harvesting Robots Under Multiple Constraints Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; He, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, K.; Li, M. A novel deep reinforcement learning-based predictive energy management for fuel cell buses integrating speed and passenger prediction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 100, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhan, J.; Duan, C.; Guan, X.; Lu, P.; Yang, K. A Review of Vehicle Detection Techniques for Intelligent Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 3811–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, M.; Onsy, A.; Haikal, A.Y.; Ghanbari, A. Path planning algorithms in the autonomous driving system: A comprehensive review. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2024, 174, 104630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Gao, X.; Yang, F.; Li, Z. Graph Reinforcement Learning-Based Decision-Making Technology for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles: Framework, Review, and Future Trends. Sensors 2023, 23, 8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ali, D.; Cao, W. A Survey on Theories and Applications for Self-Driving Cars Based on Deep Learning Methods. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ma, H.; Smart, E.; Yu, H. Real-Time Performance-Focused Localization Techniques for Autonomous Vehicle: A Review. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 6082–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, D.; Zhu, Q.; Prucka, R. A Review of Reinforcement Learning-Based Powertrain Controllers: Effects of Agent Selection for Mixed-Continuity Control and Reward Formulation. Energies 2023, 16, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, A.H.; Xu, B. A review of reinforcement learning based energy management systems for electrified powertrains: Progress, challenge, and potential solution. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 154, 111833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Miaari, A.; Ali, H.M. Batteries temperature prediction and thermal management using machine learning: An overview. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 2277–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Zeng, J.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Luo, M.; Feng, X.; Xiong, H.; Wu, W. A Review of Automobile Brake-by-Wire Control Technology. Processes 2023, 11, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.-P.; Li, S.-H. Brake-by-wire system for passenger cars: A review of structure, control, key technologies, and application in X-by-wire chassis. Etransportation 2023, 18, 100292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavizadeh, S.A.; Ghaderi, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Hajian, M. Recent Developments in the Vehicle Steer-by-Wire System. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 6, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajunen, A.; Yang, Y.; Emadi, A. Review of Cabin Thermal Management for Electrified Passenger Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 6025–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, W. Functional requirements of automotive head-up displays: A systematic review of literature from 1994 to present. Appl. Ergon. 2019, 76, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Peng, Z.; Yang, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R.; Pang, Z.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y. A review of sensory interactions between autonomous vehicles and drivers. J. Syst. Archit. 2023, 141, 102932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, T.; Zheng, X. A brief analysis of the development process and future trend of automobile headlights. SHS Web Conf. 2023, 165, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Pandey, A.; Sharma, V.; Mishra, S.; Alkhayyat, A. Federated Learning and Blockchain: A Cross-Domain Convergence. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Technological Advancements in Computational Sciences (ICTACS), Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 1–3 November 2023; pp. 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultmann, S.; Quenzel, J.; Behnke, S. Real-time multi-modal semantic fusion on unmanned aerial vehicles with label propagation for cross-domain adaptation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2023, 159, 104286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallaoui, S.; Aglzim, E.-H.; Chaibet, A.; Kribèche, A. Thorough Review Analysis of Safe Control of Autonomous Vehicles: Path Planning and Navigation Techniques. Energies 2022, 15, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Qiu, B.; Ahmad, F.; Kong, C.-W.; Xin, H. A State-of-the-Art Analysis of Obstacle Avoidance Methods from the Perspective of an Agricultural Sprayer UAV’s Operation Scenario. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wei, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, W. Stereo-vision-based multi-crop harvesting edge detection for precise automatic steering of combine harvester. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 215, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, G.; Xie, W.; Tan, J.; Li, Y.; Pu, J.; Chen, L.; Gan, D.; Shi, W. A Survey of Computer Vision Detection, Visual SLAM Algorithms, and Their Applications in Energy-Efficient Autonomous Systems. Energies 2024, 17, 5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Yue, R.; Yao, M.; Shi, J.; Hu, J. Seedling-YOLO: High-Efficiency Target Detection Algorithm for Field Broccoli Seedling Transplanting Quality Based on YOLOv7-Tiny. Agronomy 2024, 14, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wu, G.; Barth, M.J.; Liu, Y.; Sisbot, E.A.; Oguchi, K. PillarGrid: Deep Learning-Based Cooperative Perception for 3D Object Detection from Onboard-Roadside LiDAR. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 8–12 October 2022; pp. 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Niu, Q. Multi-Sensor Fusion in Automated Driving: A Survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 2847–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Pan, S.; Li, J.; Deng, Y. RPFA-Net: A 4D RaDAR Pillar Feature Attention Network for 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 3061–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimi, H.; Akilan, T.; Khalid, M.A.S. Fast Traffic Sign and Light Detection using Deep Learning for Automotive Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Western New York Image and Signal Processing Workshop (WNYISPW), Rochester, NY, USA, 22 October 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fan, H.; Jiang, G.; Jiang, D.; Liu, Y.; Tao, B.; Yun, J. RGBD-SLAM Based on Object Detection with Two-Stream YOLOv4-MobileNetv3 in Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 2847–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Niu, S.; Lan, T.; Liu, B. PCT: Large-Scale 3d Point Cloud Representations Via Graph Inception Networks with Applications to Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 4395–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lei, J.; Lan, H.; Al-Jawari, A.; Wei, X. DuEqNet: Dual-equivariance network in outdoor 3D object detection for autonomous driving. 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.13577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, D.; Fang, J.; Yin, J.; Bin, Z.; Zhang, L. FusionPainting: Multimodal Fusion with Adaptive Attention for 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 22 September 2021; pp. 3047–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, K.; Cheng, H. An Object Detection Method Enhanced by Sparse Point Cloud for Low Illumination in Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 8–12 October 2022; pp. 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xu, N.; Zhou, J.; Shi, J.; Diao, Z. Vision-based navigation and guidance for agricultural autonomous vehicles and robots: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 205, 107584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.-m.; Cai, J.-r.; Sun, L.; Ye, C. A Preliminary Discrimination of Cluster Disqualified Shape for Table Grape by Mono-Camera Multi-Perspective Simultaneously Imaging Approach. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chan, P.H.; Baris, G.; Higgins, M.D.; Donzella, V. Analysis of Automotive Camera Sensor Noise Factors and Impact on Object Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 22210–22219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wu, J.; Li, P. Real-Time Detection and Location of Potted Flowers Based on a ZED Camera and a YOLO V4-Tiny Deep Learning Algorithm. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Gu, J. Research on Robot Visual Servo Control Based on Image Identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Modeling, Simulation and Optimization Technologies and Applications (MSOTA2016), Xiamen, China, 18–19 December 2016; pp. 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M. Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. CVPR 2001, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001; p. I. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 881, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felzenszwalb, P.; McAllester, D.; Ramanan, D. A discriminatively trained, multiscale, deformable part model. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, R.; Sambath, M. A comprehensive review on two-stage object detection algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Quantum Technologies, Communications, Computing, Hardware and Embedded Systems Security (iQ-CCHESS), Kottayam, India, 15–16 September 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, H.; Xu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Real-time vehicle target detection in inclement weather conditions based on YOLOv4. Front. Neurorobot. 2023, 17, 1058723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Meng, F. Improved object detection via large kernel attention. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 240, 122507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, S.; Li, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. An Improving Faster-RCNN With Multi-Attention ResNet for Small Target Detection in Intelligent Autonomous Transport With 6G. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 7717–7725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Fang, H.; Shao, F.; Hu, C.; Meng, F. Vehicle Detection in Congested Traffic Based on Simplified Weighted Dual-Path Feature Pyramid Network with Guided Anchoring. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 53219–53231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tang, J.; Liao, Q. A study on radar target detection based on deep neural networks. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2019, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, H. Point Cloud-Based Analysis of Integrated Drone-Based Tracking, Mapping, and Anomaly Detection for GPS-Denied Environments; University of British Columbia Library: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; He, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Li, Z.; Han, Y. A Novel Method for Improving Point Cloud Accuracy in Automotive Radar Object Recognition. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 78538–78548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, H.; Shen, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zheng, X. Individual nursery trees classification and segmentation using a point cloud-based neural network with dense connection pattern. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 328, 112945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Chang, K.; Dong, S.; Tang, J.; Wang, A.; Huang, R.; Jia, Y. Rapid image detection and recognition of rice false smut based on mobile smart devices with anti-light features from cloud database. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 218, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C.; Liu, F.; Qi, L.; Tie, Y. LRT-CLUSTER: A New Clustering Algorithm Based on Likelihood Ratio Test to Identify Driving Genes. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2023, 15, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Kropfreiter, T.; Meyer, F. A BP Method for Track-Before-Detect. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diskin, T.; Beer, Y.; Okun, U.; Wiesel, A. CFARnet: Deep learning for target detection with constant false alarm rate. Signal Process. 2024, 223, 109543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranft, B.; Stiller, C. The Role of Machine Vision for Intelligent Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2016, 1, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravallika, A.; Hashmi, M.F.; Gupta, A. Deep Learning Frontiers in 3D Object Detection: A Comprehensive Review for Autonomous Driving. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 173936–173980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, M.; Du, J.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, S.S.; Xie, W. A Task-Driven Scene-Aware LiDAR Point Cloud Coding Framework for Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 8731–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shuang, F.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, J. DenseKPNET: Dense Kernel Point Convolutional Neural Networks for Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, L.A. ITS Sensors and Architectures for Traffic Management and Connected Vehicles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuanyuan, Z.; Bin, Z.; Cheng, S.; Haolu, L.; Jicheng, H.; Kunpeng, T.; Zhong, T. Review of the field environmental sensing methods based on multi-sensor information fusion technology. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2024, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Meng, Y.; Yang, G.; Feng, H.; Yang, M.; Zhu, Q.; Xue, H.; Wang, B. Monitoring leaf nitrogen content in rice based on information fusion of multi-sensor imagery from UAV. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 2327–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Feng, C.; Xie, X.; Shi, B.; Lu, H.; Lv, Y.; Yang, M.; Niu, Z. Multi-Sensor Fusion and Cooperative Perception for Autonomous Driving: A Review. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2023, 15, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, J.; Zeng, T. A Review of Environmental Perception Technology Based on Multi-Sensor Information Fusion in Autonomous Driving. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Dong, H.; Shao, Z. A Survey of the Multi-Sensor Fusion Object Detection Task in Autonomous Driving. Sensors 2025, 25, 2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Tian, X. Automatic cruise system for water quality monitoring. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csiszar, O. Ordered Weighted Averaging Operators: A Short Review. IEEE Syst. Man Cybern. Mag. 2021, 7, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yang, H.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chai, X. Wheat biomass, yield, and straw-grain ratio estimation from multi-temporal UAV-based RGB and multispectral images. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 234, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto-Cubero, A.J.; Gómez-Espinosa, A.; Escobedo Cabello, J.A.; Cuan-Urquizo, E.; Cruz-Ramírez, S.R. Sensor Data Fusion for a Mobile Robot Using Neural Networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tian, D.; Duan, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, D.; Cao, D. CL3D: Camera-LiDAR 3D Object Detection With Point Feature Enhancement and Point-Guided Fusion. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 18040–18050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, T.; Li, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Bai, X. EPNet++: Cascade Bi-Directional Fusion for Multi-Modal 3D Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 8324–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, M. Multi-Scale Vehicle Detection and Tracking Method in Highway Scene. In Proceedings of the 2020 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Hefei, China, 22–24 August 2020; pp. 2066–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shang, Z.; Li, R.; Cui, B. Adaptive Sliding Mode Path Tracking Control of Unmanned Rice Transplanter. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zeng, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhou, J.; Tomizuka, M.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Ye, N. PNAS-MOT: Multi-Modal Object Tracking With Pareto Neural Architecture Search. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 4377–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E.; Xue, J.; Chen, T.; Jiang, S. Robust Trajectory Tracking Control of an Autonomous Tractor-Trailer Considering Model Parameter Uncertainties and Disturbances. Agriculture 2023, 13, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Han, X.; Guo, W. Uncertain multi-objective programming approach for planning supplementary irrigation areas in rainfed agricultural regions. Irrig. Drain. 2025, 74, 1193–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, H. A 3D Multiobject Tracking Algorithm of Point Cloud Based on Deep Learning. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8895696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Ding, S.; Xia, J.; Xing, G. Adaptive disturbance observer-based fixed time nonsingular terminal sliding mode control for path-tracking of unmanned agricultural tractors. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 246, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Tang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wang, J.; Lu, H. Improving multiple object tracking with single object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2021; pp. 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Xing, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Fan, J. Deep Spatial and Temporal Network for Robust Visual Object Tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassaballah, M.; Kenk, M.A.; Muhammad, K.; Minaee, S. Vehicle Detection and Tracking in Adverse Weather Using a Deep Learning Framework. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 4230–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Niu, J.; Cui, J.; Fu, Z.; Ouyang, Z. Fast Segmentation-Based Object Tracking Model for Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the Algorithms and Architectures for Parallel Processing, New York, NY, USA, 2–4 October 2020; pp. 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.; Wei, M.; Wu, Y. High-precision and real-time visual tracking algorithm based on the Siamese network for autonomous driving. Signal Image Video Process. 2023, 17, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Xing, J.; Milan, A.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Kim, T.-K. Multiple object tracking: A literature review. Artif. Intell. 2021, 293, 103448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, X.; Zhan, J. High-Precision Motion Detection and Tracking Based on Point Cloud Registration and Radius Search. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 6322–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Guo, G.; Wang, H.; Deng, H. One-shot multi-object tracking using CNN-based networks with spatial-channel attention mechanism. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 153, 108267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Xia, Z.; Gu, J.; Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, W. High-precision apple recognition and localization method based on RGB-D and improved SOLOv2 instance segmentation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1403872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Shi, L.; Yang, W.; Ge, H.; Wei, X.; Ding, Y. Multi-Feature Fusion Recognition and Localization Method for Unmanned Harvesting of Aquatic Vegetables. Agriculture 2024, 14, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogni, C.; Cascone, L.; Nappi, M.; Pero, C. IoT-enabled Biometric Security: Enhancing Smart Car Safety with Depth-based Head Pose Estimation. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2024, 20, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, F.; Guan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, H.; Cheng, K. Development of a combined harvester navigation control system based on visual simultaneous localization and mapping-inertial guidance fusion. J. Agric. Eng. 2024, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ni, D.; Li, K. RFID-Based Vehicle Positioning and Its Applications in Connected Vehicles. Sensors 2014, 14, 4225–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkendi, Y.; Seneviratne, L.; Zweiri, Y. State of the Art in Vision-Based Localization Techniques for Autonomous Navigation Systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 76847–76874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. ASD-SLAM: A Novel Adaptive-Scale Descriptor Learning for Visual SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 19 October–13 November 2020; pp. 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, H. Beyond cross-view image retrieval: Highly accurate vehicle localization using satellite image. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 17010–17020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibebu, H.; De-Silva, V.; Artaud, C.; Pina, R.; Shi, X. Towards Interpretable Camera and LiDAR Data Fusion for Autonomous Ground Vehicles Localisation. Sensors 2022, 22, 8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhuang, Y.; Huai, J. Multi-sensor fusion for robust localization with moving object segmentation in complex dynamic 3D scenes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 124, 103507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalioglu, Y.; Turan, M.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Deep learning-based robust positioning for all-weather autonomous driving. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, R. Research Status and Prospects on Plant Canopy Structure Measurement Using Visual Sensors Based on Three-Dimensional Reconstruction. Agriculture 2020, 10, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabziev, E. Determining the Location of an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Based on Video Camera Images. Adv. Inf. Syst. 2021, 5, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersü, C.; Petlenkov, E.; Janson, K. A Systematic Review of Cutting-Edge Radar Technologies: Applications for Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs). Sensors 2024, 24, 7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Ye, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C. An improved visual SLAM based on affine transformation for ORB feature extraction. Optik 2021, 227, 165421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Refai, R.; Nandakumar, K. A unified model for face matching and presentation attack detection using an ensemble of vision transformer features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2023; pp. 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.; Sheng, B.; Yang, P.; Li, P.; Shen, R.; Feng, D.D. Deep convolutional neural networks for human action recognition using depth maps and postures. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 49, 1806–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Nie, Q.; Shen, H. 3D Scene Geometry-Aware Constraint for Camera Localization with Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 4211–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W. Domain-Invariant Similarity Activation Map Contrastive Learning for Retrieval-Based Long-Term Visual Localization. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, H.; Liang, L.; Shi, W.; Xie, G.; Lu, X.; Hei, X. TransBoNet: Learning camera localization with Transformer Bottleneck and Attention. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 146, 109975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ahmad, N.S. A Comprehensive Review on Sensor Fusion Techniques for Localization of a Dynamic Target in GPS-Denied Environments. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 2252–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, A.; Amiri, W.A.; Mahmoud, M.; Swieder, B.; Hasan, S.R.; Guo, T.N. Survey of Navigational Perception Sensors’ Security in Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 104937–104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrun, S.; Montemerlo, M. The Graph SLAM Algorithm with Applications to Large-Scale Mapping of Urban Structures. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2006, 25, 403–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Wan, G.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, X.; Yuan, P.; Song, S. Deepvcp: An end-to-end deep neural network for point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; She, R.; Wang, S.; Tay, W.P.; Navarro, D.N.; Hartmannsgruber, A. Location Learning for AVs: LiDAR and Image Landmarks Fusion Localization with Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 8–12 October 2022; pp. 3032–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Akhtar, N.; Anwar, S.; Mian, A. UnLoc: A Universal Localization Method for Autonomous Vehicles using LiDAR, Radar and/or Camera Input. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Detroit, MI, USA, 1–5 October 2023; pp. 5187–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Li, P.; Fu, Z.; Xu, S.; Shi, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, C. Int2: Interactive trajectory prediction at intersections. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 8536–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipfl, M.; Hertlein, F.; Rettinger, A.; Thoma, S.; Halilaj, L.; Luettin, J.; Schmid, S.; Henson, C. Relation-based Motion Prediction using Traffic Scene Graphs. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 8–12 October 2022; pp. 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.; Cai, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Lee, D.H. Multimodal Vehicular Trajectory Prediction with Inverse Reinforcement Learning and Risk Aversion at Urban Unsignalized Intersections. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 12227–12240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.; Li, X.; Rosman, G.; Gilitschenski, I.; Meireles, O.; Karaman, S.; Rus, D. A Deep Concept Graph Network for Interaction-Aware Trajectory Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 8992–8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Broszio, H.; Sester, M.; Yang, M.Y. GATraj: A graph- and attention-based multi-agent trajectory prediction model. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 205, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Kweon, N.; Yang, C.; Kim, D.; Shon, H.; Choi, J.; Huh, K. DSA-GAN: Driving Style Attention Generative Adversarial Network for Vehicle Trajectory Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 1515–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Chen, K.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Hou, B.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xiong, G.; Wang, Z. Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction Based on Deep Convolutional LSTM Network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 3285–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Huynh, D.Q.; Reynolds, M. PoPPL: Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction by LSTM With Automatic Route Class Clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.J.; Shih, C.S.; Lin, C.W.; Chen, C.W.; Tsung, P.K. Trajectory Prediction at Unsignalized Intersections using Social Conditional Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Bingxian, L.; Xiangcheng, W. SGAMTE-Net: A pedestrian trajectory prediction network based on spatiotemporal graph attention and multimodal trajectory endpoints. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 31165–31180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, T.; Zemmouri, E.; Bouzid, A. STM-GCN: A spatiotemporal multi-graph convolutional network for pedestrian trajectory prediction. J. Supercomput. 2023, 79, 20923–20937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakzar, M.; Bond, A.; Rakotonirainy, A.; Trespalacios, O.O.; Dehkordi, S.G. Driver influence on vehicle trajectory prediction. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 157, 106165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Lv, C.; Cao, D. Personalized Vehicle Trajectory Prediction Based on Joint Time-Series Modeling for Connected Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Zheng, N.; Wang, S. A Flexible and Explainable Vehicle Motion Prediction and Inference Framework Combining Semi-Supervised AOG and ST-LSTM. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 840–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, S.E.; Yang, B.; Wang, Z.; Nakano, K. Structural Transformer Improves Speed-Accuracy Trade-Off in Interactive Trajectory Prediction of Multiple Surrounding Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 24778–24790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, K.; Dai, X.; Xu, J.; Xi, J.; Ai, R.; Wang, Y.; Gu, W.; Sun, C. Safety-Balanced Driving-Style Aware Trajectory Planning in Intersection Scenarios with Uncertain Environment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 2888–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Choi, J.; Kum, D. SCALE-Net: Scalable Vehicle Trajectory Prediction Network under Random Number of Interacting Vehicles via Edge-enhanced Graph Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October–24 January 2021; pp. 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarting, W.; Alonso-Mora, J.; Rus, D. Planning and Decision-Making for Autonomous Vehicles. Annu. Rev. Control Robot. Auton. Syst. 2018, 1, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhao, H. Joint Imitation Learning of Behavior Decision and Control for Autonomous Intersection Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Detroit, MI, USA, 1–5 October 2023; pp. 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Teng, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, R. Design of bionic goat quadruped robot mechanism and walking gait planning. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wu, J.; Sun, B.; Leng, X.; Miao, W.; Gao, Z.; Li, W. Intelligent vehicle decision-making strategy integrating spatiotemporal features at roundabout. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 273, 126779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Ma, Z. Modeling of working environment and coverage path planning method of combine harvesters. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feraco, S.; Luciani, S.; Bonfitto, A.; Amati, N.; Tonoli, A. A local trajectory planning and control method for autonomous vehicles based on the RRT algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 AEIT International Conference of Electrical and Electronic Technologies for Automotive (AEIT Automotive), Turin, Italy, 18–20 November 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R.; Ashari, A.E.; Huber, M. CHAMP: Integrated Logic with Reinforcement Learning for Hybrid Decision Making for Autonomous Vehicle Planning. In Proceedings of the 2023 American Control Conference (ACC), San Diego, CA, USA, 31 May–2 June 2023; pp. 3310–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirchevska, B.; Pek, C.; Werling, M.; Althoff, M.; Boedecker, J. High-level Decision Making for Safe and Reasonable Autonomous Lane Changing using Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 2156–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Yuan, S. Graph convolution-based deep reinforcement learning for multi-agent decision-making in interactive traffic scenarios. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 8–12 October 2022; pp. 4074–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fotouhi, A.; Pan, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. Deep reinforcement learning-based eco-driving control for connected electric vehicles at signalized intersections considering traffic uncertainties. Energy 2023, 279, 128139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xu, S.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, X. Action-Oriented Deep Reinforcement Learning Method for Precast Concrete Component Production Scheduling. Buildings 2025, 15, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevly, D.; Cao, X.; Gordon, M.; Ozbilgin, G.; Kari, D.; Nelson, B.; Woodruff, J.; Barth, M.; Murray, C.; Kurt, A.; et al. Lane Change and Merge Maneuvers for Connected and Automated Vehicles: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2016, 1, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.; Jung, C.; Lee, S.; Shim, D.H. Learning to Drive at Unsignalized Intersections using Attention-based Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Indianapolis, IN, USA, 22 September 2021; pp. 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Angah, O.; Liu, Z.; Ban, X. Hybrid deep reinforcement learning based eco-driving for low-level connected and automated vehicles along signalized corridors. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2021, 124, 102980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Sun, Z.; Ji, A. A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach for Automated On-Ramp Merging. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 25th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Macau, China, 8–12 October 2022; pp. 3800–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- En, L.; Zheng, M.; Yaoming, L.; Lizhang, X.; Zhong, T. Adaptive backstepping control of tracked robot running trajectory based on real-time slip parameter estimation. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; He, Y.; Lin, X. An Overview of Motion-Planning Algorithms for Autonomous Ground Vehicles with Various Applications. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2024, 8, 179–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrakazas, C.; Quddus, M.; Chen, W.-H.; Deka, L. Real-time motion planning methods for autonomous on-road driving: State-of-the-art and future research directions. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 60, 416–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yao, D.; Li, B.; Li, L. A Survey of Trajectory Planning Methods for Autonomous Driving—Part I: Unstructured Scenarios. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 9, 5407–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Schneider, J.; Dolan, J.M. Behavior Planning at Urban Intersections through Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 2667–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Song, W. Conflict-constrained Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning Method for Parking Trajectory Planning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 9421–9427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Han, T.; Alhajyaseen, W.K.M.; Iryo-Asano, M.; Nakamura, H. Can automated driving prevent crashes with distracted Pedestrians? An exploration of motion planning at unsignalized Mid-block crosswalks. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2022, 173, 106711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Huang, B.; Liu, T.; Lin, X. Highway Decision-Making and Motion Planning for Autonomous Driving via Soft Actor-Critic. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 4706–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yang, D.; Xu, S.; Peng, H.; Li, B.; Feng, S.; Zhao, D. Highway Exiting Planner for Automated Vehicles Using Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.C.; Xu, X.; Shen, Y.J.; Liu, Y.L. Modeling and test on height adjustment system of electrically-controlled air suspension for agricultural vehicles. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2016, 9, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, T.; Yang, B. Adaptive Controller of PEMFC Output Voltage Based on Ambient Intelligence Large-Scale Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 6063–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Guo, R.; Xue, X.; Hong, Z.; Luo, M.; Wong, P.K.; Liu, J.J.R.; Wang, X. Application-oriented mode decision for energy management of range-extended electric vehicle based on reinforcement learning. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 226, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yi, F.; Hu, D.; Lu, D.; Wu, G.; Zhang, C.; Deng, B.; Cao, D. An intelligent control method for PEMFC air supply subsystem to optimize dynamic response performance. Fuel 2024, 361, 130697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, M.-A.; Boulet, B. Improving gearshift controllers for electric vehicles with reinforcement learning. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 169, 104654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Hong, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Jia, Q. Double deep Q-network guided energy management strategy of a novel electric-hydraulic hybrid electric vehicle. Energy 2023, 269, 126858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lv, Z.; Ye, J. The Optimization of RBFNN Gearshift Controller Parameters for Electric Vehicles Using PILCO Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 92807–92821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, N.; Kolmanovsky, I.; Girard, A. Energy-Efficient Autonomous Vehicle Control Using Reinforcement Learning and Interactive Traffic Simulations. In Proceedings of the 2020 American Control Conference (ACC), Denver, CO, USA, 1–3 July 2020; pp. 3029–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbel, L.; Ayalew, B.; Ivanco, A.; Loiselle, K. Driver Assistance Eco-driving and Transmission Control with Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 American Control Conference (ACC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 8–10 June 2022; pp. 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Hu, D.; Wang, J.; Wei, W.; Zhang, X. A Data-Driven Vehicle Speed Prediction Transfer Learning Method with Improved Adaptability Across Working Conditions for Intelligent Fuel Cell Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 10881–10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Cai, Y.; Lai, L. Energy Saving Performance of Agricultural Tractor Equipped with Mechanic-Electronic-Hydraulic Powertrain System. Agriculture 2022, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Huang, P.; Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Peng, J. Driving style-aware energy management for battery/supercapacitor electric vehicles using deep reinforcement learning. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 109199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xia, C.; Jiang, D.; Sun, Y. Development and Testing of the Power Transmission System of a Crawler Electric Tractor for Greenhouses. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2020, 36, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Jia, T.; Hu, X.; Huang, Y.; Deng, Z.; Pu, H. Naturalistic Data-Driven Predictive Energy Management for Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Pi, D.; Lin, X.; Grzesiak, L.M.; Hu, X. Battery Health-Aware and Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Energy Management for Naturalistic Data-Driven Driving Scenarios. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 948–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.; He, D. Deep reinforcement learning based energy management for a hybrid electric vehicle. Energy 2020, 201, 117591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Chen, J.; Pu, H.; Liu, T.; Khajepour, A. Double Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Energy Management for a Parallel Hybrid Electric Vehicle with Engine Start–Stop Strategy. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 1376–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sauer, D.U. Battery Thermal- and Health-Constrained Energy Management for Hybrid Electric Bus Based on Soft Actor-Critic DRL Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 3751–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Cui, W.; Shi, Y. Deep Reinforcement Learning Based PHEV Energy Management with Co-Recognition for Traffic Condition and Driving Style. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 3026–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Guo, R.; Lee, J.; Moura, S.; Casals, L.C.; Jiang, S.; Shi, J.; Harris, S.; Zhang, T.; Chung, C.Y.; et al. Immediate remaining capacity estimation of heterogeneous second-life lithium-ion batteries via deep generative transfer learning. Energy Environ. Sci. 2025, 18, 7413–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, B.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, H.; Han, L.; Jiao, K. A Data-Driven Approach to Lifespan Prediction for Vehicle Fuel Cell Systems. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 5049–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Ma, R.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, G.; Su, L.; Chang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Liang, Z.; Cao, T.; et al. Generative learning assisted state-of-health estimation for sustainable battery recycling with random retirement conditions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J. Investigation of optimal operating temperature for the PEMFC and its tracking control for energy saving in vehicle applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 249, 114842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhai, C.; Gao, Y.; Dou, H.; Zhao, X.; He, Y.; Wang, X. Planting uniformity performance of motor-driven maize precision seeding systems. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2022, 15, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; He, L.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, Y. Reinforcement learning-based control for the thermal management of the battery and occupant compartments of electric vehicles. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2024, 8, 588–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraireh, M. Thermal Management in Electric Vehicles: Modeling and Prospects. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2023, 41, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Kim, J.W.; Ahn, C.; Gim, J. Reinforcement Learning-based Controller for Thermal Management System of Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Merced, CA, USA, 1–4 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmandzadeh, Z.; Abbasi, M.H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, B. Electric Vehicle Battery Thermal Management Under Extreme Fast Charging with Deep Reinforcement Learning. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5011679 (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, T. An optimal coordinated proton exchange membrane fuel cell heat management method based on large-scale multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 6054–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billert, A.M.; Frey, M.; Gauterin, F. A Method of Developing Quantile Convolutional Neural Networks for Electric Vehicle Battery Temperature Prediction Trained on Cross-Domain Data. IEEE Open J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 3, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, G. Real-Time Battery Thermal Management for Electric Vehicles Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 14060–14072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Song, R.; Ji, D.; Wang, Y.; Pan, F. Hierarchical thermal management for PEM fuel cell with machine learning approach. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 236, 121544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Huang, C.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C. A dynamic tire model based on HPSO-SVM. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zheng, Z.A.; Chen, J. Research on the Control Strategy for Handling Stability of Electric Power Steering System with Active Front Wheel Steering Function. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2024, 8, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Zhou, B.; Wu, X.; Cui, Q.; Zheng, K. Steering collision avoidance and lateral stability coordinated control based on vehicle lateral stability region. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2024, 239, 1699–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Liu, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X. Design and Control of Personalized Steering Feel for Steer-by-Wire Systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 6288–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, B.; Chen, Z. A velocity adaptive steering control strategy of autonomous vehicle based on double deep Q-learning network with varied agents. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 139, 109655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasala, A.; Byrne, D.; Miesbauer, P.; O’Hanlon, J.; Heraty, P.; Barry, P. Trajectory based lateral control: A Reinforcement Learning case study. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 94, 103799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao-zhong, W.; Yao, L.; Zhi-jun, C.; Peng, L. Human-machine integration method for steering decision-making of intelligent vehicle based on reinforcement learning. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2022, 22, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cheng, S.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z. A model free controller based on reinforcement learning for active steering system with uncertainties. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2021, 235, 2470–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, G.A.P.; Marcos, L.B.; Bueno, J.N.A.D.; de Resende, N.F.; Terra, M.H.; Grassi, V., Jr. Vision-based robust control framework based on deep reinforcement learning applied to autonomous ground vehicles. Control Eng. Pract. 2020, 104, 104630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L. Design of an Electronically Controlled Fertilization System for an Air-Assisted Side-Deep Fertilization Machine. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Du, C. Human–Machine Shared Steering Decision-Making of Intelligent Vehicles Based on Heterogeneous Synchronous Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; He, X.; Lv, C. Human-Guided Deep Reinforcement Learning for Optimal Decision Making of Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 6595–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X. Switching in Sliding Mode Control: A Spatio-Temporal Perspective. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2025, 12, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, G.A.; Al-Ammar, E.A.; Hasanien, H.M.; Ko, W.; Lee, S.M.; Turky, R.A.; Tostado-Véliz, M.; Jurado, F. Circle Search Algorithm-Based Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control for MPPT of Different Commercial PV Modules. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 33109–33128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, F.R.; Luan, T.H.; Zhang, Y. A Decision-Making Strategy for Vehicle Autonomous Braking in Emergency via Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 5876–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanti, M.P.; Mangini, A.M.; Martino, D.; Olivieri, I.; Parisi, F.; Popolizio, F. Safety and Comfort in Autonomous Braking System with Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Prague, Czech Republic, 9–12 October 2022; pp. 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Gan, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Ji, Y. Vehicle ride comfort optimization in the post-braking phase using residual reinforcement learning. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023, 58, 102198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantripragada, V.K.T.; Kumar, R.K. Deep reinforcement learning-based antilock braking algorithm. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2023, 61, 1410–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, V.S.; Kasad, R.; Agrawal, K. Autonomous braking and throttle system: A deep reinforcement learning approach for naturalistic driving. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.06696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theunissen, J.; Tota, A.; Gruber, P.; Dhaens, M.; Sorniotti, A. Preview-based techniques for vehicle suspension control: A state-of-the-art review. Annu. Rev. Control 2021, 51, 206–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Mao, H.; Xue, X.; Ding, S.; Qiao, B. Optimized design and test for a pendulum suspension of the crop spray boom in dynamic conditions based on a six DOF motion simulator. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, J.B.; DeBoer, B.; Bubbar, K. Adaptive control and reinforcement learning for vehicle suspension control: A review. Annu. Rev. Control 2024, 58, 100974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lian, R.J. Intelligent Control of Active Suspension Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, Y. Advancements in semi-active automotive suspension systems with magnetorheological dampers: A review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yin, Z.; Xia, Z.; Wang, W.; Shangguan, W.-B.; Rakheja, S. Control Strategy of Semi-Active Suspension Based on Road Roughness Identification. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2024, 8, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Han, S.Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J. Adaptive Vibration Control of Vehicle Semi-Active Suspension System Based on Ensemble Fuzzy Logic and Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Prague, Czech Republic, 9–12 October 2022; pp. 2627–2632. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, L.; Yibin, L.; Xuewen, R.; Shuaishuai, Z.; Yanfang, Y. Semi-Active Suspension Control Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 9978–9986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.; Seo, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Choi, J. Suspension Control Strategies Using Switched Soft Actor-Critic Models for Real Roads. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cui, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, K. Enhancing vehicle ride comfort through deep reinforcement learning with expert-guided soft-hard constraints and system characteristic considerations. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 59, 102328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannusch, T.; Shannon, D.; Völler, M.; Murphy, F.; Mullins, M. Cars and distraction: How to address the limits of Driver Monitoring Systems and improve safety benefits using evidence from German young drivers. Technol. Soc. 2021, 66, 101628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, C.; Chang, F.; Liu, H.; Huan, H. JHPFA-Net: Joint Head Pose and Facial Action Network for Driver Yawning Detection Across Arbitrary Poses in Videos. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 11850–11863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, M.M.; Shoitan, R.; Cho, Y.-I.; Abdallah, M.S. Visual-Based Children and Pet Rescue from Suffocation and Incidence of Hyperthermia Death in Enclosed Vehicles. Sensors 2023, 23, 7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.C.; Zhao, X.L.; Lin, H.Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Guo, J.I.; Fan, C.P. YOLO Deep-Learning Based Driver Behaviors Detection and Effective Gaze Estimation by Head Poses for Driver Monitor System. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 12th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Nara, Japan, 10–13 October 2023; pp. 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Liu, P.X.; Li, D. Vision-Based Fatigue Driving Recognition Method Integrating Heart Rate and Facial Features. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 3089–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistolesi, F.; Baldassini, M.; Lazzerini, B. Speech-Based Detection of In-Car Escalating Arguments to Prevent Distracted Driving. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData), Sorrento, Italy, 15–18 December 2023; pp. 5330–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. Solving Pediatric Vehicular Heatstroke with Efficient Multi-Cascaded Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics and Computer Engineering (ICCECE), Guangzhou, China, 15–17 January 2021; pp. 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashisht, S.; Rakshit, D. Recent advances and sustainable solutions in automobile air conditioning systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusey, J.; Hintea, D.; Gaura, E.; Beloe, N. Reinforcement learning-based thermal comfort control for vehicle cabins. Mechatronics 2018, 50, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Qiu, C.; Lu, D.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Xue, H. An intelligent thermal comfort control strategy for air conditioning of fuel cell vehicles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 248, 123286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-G.; Kwon, O. Reinforcement Learning Based Power Seat Actuation to Mitigate Carsickness of Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the HCI International 2023 Posters, Copenhagen, Denmark, 23–28 July 2023; pp. 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, A.Ş.; Ince, I.F.; Baydargil, H.B.; Garip, I.; Ozturk, O. Deep learning based automatic vertical height adjustment of incorrectly fastened seat belts for driver and passenger safety in fleet vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2021, 236, 639–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, E.R.; Bajcsy, R.; Gregor, M.; Huang, I.; Villegas, I.; Kurillo, G. On the Development of an Acoustic-Driven Method to Improve Driver’s Comfort Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 2923–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Ge, X.; Li, J.; Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, R. Intelligent cockpits for connected vehicles: Taxonomy, architecture, interaction technologies, and future directions. Sensors 2024, 24, 5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishavan, H.H.; Behzadi, M.M.; Lohan, D.J.; Dede, E.M.; Kim, I. Closed-Loop Brain Machine Interface System for In-Vehicle Function Controls Using Head-Up Display and Deep Learning Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 6594–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachara, F.; Kopinski, T.; Gepperth, A.; Handmann, U. Free-hand gesture recognition with 3D-CNNs for in-car infotainment control in real-time. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 20th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Yokohama, Japan, 16–19 October 2017; pp. 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Paillat, L.; Kim, S.C. Vehicle Control on an Uninstrumented Surface with an Off-the-Shelf Smartwatch. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 3366–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjape, A.; Patwardhan, Y.; Deshpande, V.; Darp, A.; Jagdale, J. Voice-Based Smart Assistant System for Vehicles Using RASA. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Networks and Security (ICCINS), Mylavaram, India, 22–23 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewalegama, M.P.; Zoysa, A.D.S.d.; Kodikara, L.M.; Dissanayake, D.M.J.C.; Kuruppu, T.A.; Rupasinghe, S. Deep Learning-Based Smart Infotainment System for Taxi Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Congress on Human-Computer Interaction, Optimization and Robotic Applications (HORA), Ankara, Turkey, 9–11 June 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Fang, H.; Wang, H. Blockchain-Based Internet of Vehicles: Distributed Network Architecture and Performance Analysis. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 4640–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; Luo, X.; Qu, X.; Green, P. Human-Like Decision Making of Artificial Drivers in Intelligent Transportation Systems: An End-to-End Driving Behavior Prediction Approach. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2022, 14, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Sun, J.; Yao, K.; Xu, M.; Dai, C. Multi-task convolutional neural network for simultaneous monitoring of lipid and protein oxidative damage in frozen-thawed pork using hyperspectral imaging. Meat Sci. 2023, 201, 109196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.; Gaber, M.M.; Elyan, E.; Jayne, C. Imitation learning: A survey of learning methods. ACM Comput. Surv. 2017, 50, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawke, J.; Shen, R.; Gurau, C.; Sharma, S.; Reda, D.; Nikolov, N.; Mazur, P.; Micklethwaite, S.; Griffiths, N.; Shah, A.; et al. Urban Driving with Conditional Imitation Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. Vision-Based Trajectory Planning via Imitation Learning for Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 October 2019; pp. 2736–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, G.C.K.; Antonelo, E.A. Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning for End-to-End Autonomous Driving on Urban Environments. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Orlando, FL, USA, 5–7 December 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Lv, C. Conditional Predictive Behavior Planning with Inverse Reinforcement Learning for Human-Like Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 7244–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; He, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Wei, Z.; Li, K. Learning-based model predictive energy management for fuel cell hybrid electric bus with health-aware control. Appl. Energy 2024, 355, 122228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, Z.; Han, Z.; Sun, W.; He, L. A Decision-Making System for Cotton Irrigation Based on Reinforcement Learning Strategy. Agronomy 2024, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Sun, Q.; Li, S.E.; Kum, D.; Yin, Y.; Wei, J.; Gu, T. End-to-End Autonomous Driving Through Dueling Double Deep Q-Network. Automot. Innov. 2021, 4, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, C. Smooth Actor-Critic Algorithm for End-to-End Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the 2020 American Control Conference (ACC), Denver, CO, USA, 1–3 July 2020; pp. 3242–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liao, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Lu, R. Deep Reinforcement Learning on Autonomous Driving Policy with Auxiliary Critic Network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 3680–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, S.E.; Tomizuka, M. Interpretable End-to-End Urban Autonomous Driving with Latent Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 5068–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Song, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, M. Stabilization Approaches for Reinforcement Learning-Based End-to-End Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 4740–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Lei, N.; Li, B.; Li, R.; Wang, Z. Integrated Thermal and Energy Management of Connected Hybrid Electric Vehicles Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 4594–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Huangfu, Y.; Xu, L.; Pang, S. Online energy management strategy considering fuel cell fault for multi-stack fuel cell hybrid vehicle based on multi-agent reinforcement learning. Appl. Energy 2022, 328, 120234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, S.; Ma, Y.; Yang, N.; Yan, Q.; Xiang, C. Multiobjective optimization of longitudinal dynamics and energy management for HEVs based on nash bargaining game. Energy 2023, 262, 125422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Lu, Y.; Pi, D.; Yin, G.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, F.; Feng, J.; Zhou, C. A Decentralized Cooperative Control Framework for Active Steering and Active Suspension: Multi-Agent Approach. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 1414–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Pi, W.; Wang, Q.; Lin, F.; Zhang, C. Integrated Control of Active Front Wheel Steering and Active Suspension Based on Differential Flatness and Nonlinear Disturbance Observer. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 4813–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Deng, K.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, G.; Li, X. Robust control for active suspension system under steering condition. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2017, 60, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchamna, R.; Youn, E.; Youn, I. Combined control effects of brake and active suspension control on the global safety of a full-car nonlinear model. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2014, 52, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, A.; Bagheri, A.; Azadi, S. Integrated vehicle dynamics control using semi-active suspension and active braking systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part K J. Multi-Body Dyn. 2017, 232, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termous, H.; Shraim, H.; Talj, R.; Francis, C.; Charara, A. Coordinated control strategies for active steering, differential braking and active suspension for vehicle stability, handling and safety improvement. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2018, 57, 1494–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Shu, X.; Zhang, J.; Yi, F.; Jia, C.; Zhang, C.; Kong, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, G. A deep learning method based on CNN-BiGRU and attention mechanism for proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance degradation prediction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 94, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhao, X.; Luo, W.; Bai, X.; Xu, L.; Jiang, H. Microwave detection technique combined with deep learning algorithm facilitates quantitative analysis of heavy metal Pb residues in edible oils. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 6005–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateria, S.; Subagdja, B.; Tan, A.-h.; Quek, C. Hierarchical reinforcement learning: A comprehensive survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, Y.; Wang, Q.; Pan, W.; Ming, Z. Joint Optimization of Sensing, Decision-Making and Motion-Controlling for Autonomous Vehicles: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 4642–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, Q.; He, H. Cooperative energy management and eco-driving of plug-in hybrid electric vehicle via multi-agent reinforcement learning. Appl. Energy 2023, 332, 120563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y. Reinforcement Learning and Deep Learning Based Lateral Control for Autonomous Driving [Application Notes]. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2019, 14, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porav, H.; Newman, P. Imminent Collision Mitigation with Reinforcement Learning and Vision. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 958–964. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, S.; Yang, K.; Wei, C.; Tang, X. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Integrated Control of Hybrid Electric Vehicles Driven by Lane-Level High-Definition Map. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, 10, 1642–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, K.; Toyoda, M.; Liu, T.; Hu, X. Visual Detection and Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Car Following and Energy Management for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 2501–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Peng, J.; Dong, H.; Tan, H.; Ding, F. Hierarchical reinforcement learning based energy management strategy of plug-in hybrid electric vehicle for ecological car-following process. Appl. Energy 2023, 333, 120599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.; Xiong, X.; Yang, F.; Sun, W.; Yu, Y.; Wang, P. An Energy-Efficient Driving Method for Connected and Automated Vehicles Based on Reinforcement Learning. Machines 2023, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, K.; Zhao, K. Coordinated Longitudinal and Lateral Motions Control of Automated Vehicles Based on Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for On-Ramp Merging; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PE, USA, 2024; ISSN 0148-7191. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Shu, H.; Tang, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, W. Deep reinforcement learning-based multi-objective control of hybrid power system combined with road recognition under time-varying environment. Energy 2022, 239, 122123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wu, G.; Mao, L. Preview Control of Semi-Active Suspension with Adjustable Damping Based on Machine Vision. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 16th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Chengdu, China, 1–4 August 2021; pp. 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, C.; Liao, F.; Zhu, M. A hierarchical framework for improving ride comfort of autonomous vehicles via deep reinforcement learning with external knowledge. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2023, 38, 1059–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Li, S.; Tang, X.; Yang, K.; Lin, X. Battery thermal- and cabin comfort-aware collaborative energy management for plug-in fuel cell electric vehicles based on the soft actor-critic algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 283, 116889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, D.H.; Lee, J.Y. Augmented Reality-Based Navigation Using Deep Learning-Based Pedestrian and Personal Mobility User Recognition—A Comparative Evaluation for Driving Assistance. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 62200–62211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Yin, G.; Zhang, H. Human–Machine Shared Control for Path Following Considering Driver Fatigue Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 7250–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Li, J.; Tei, K.; Honiden, S. Towards Personalized Autonomous Driving: An Emotion Preference Style Adaptation Framework. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Agents (ICA), Kyoto, Japan, 13–15 December 2021; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y.; Gu, Y. A comparison review of transfer learning and self-supervised learning: Definitions, applications, advantages and limitations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 242, 122807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Sun, C.; Fu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, R.; Han, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, G.; Zhang, X.; et al. Battery Cross-Operation-Condition Lifetime Prediction via Interpretable Feature Engineering Assisted Adaptive Machine Learning. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 3269–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Lin, K.; Jain, A.K.; Zhou, J. Transfer Learning in Deep Reinforcement Learning: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 13344–13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Tao, S.; Fan, H.; He, K.; Liu, X.; Tao, Y.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y. Data-driven capacity estimation for lithium-ion batteries with feature matching based transfer learning method. Appl. Energy 2024, 353, 121991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.Y.; Liu, P.; Xiao, T.; Zhao, W.; Tang, X.L. A review of deep domain adaptation: General situation and complex situation. ACTA Autom. Sin. 2021, 47, 515–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Q.; Ma, J.; Yu, H. Domain adaptive object detection for autonomous driving under foggy weather. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2023; pp. 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Chung, W.H. Cooperative Neighboring Vehicle Positioning Systems Based on Graph Convolutional Network: A Multi-Scenario Transfer Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the ICC 2022—IEEE International Conference on Communications, Seoul, Korea, 16–20 May 2022; pp. 3226–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Liu, T.; Mu, X.; Cao, D. Driving Tasks Transfer Using Deep Reinforcement Learning for Decision-Making of Autonomous Vehicles in Unsignalized Intersection. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Huang, C.; Yin, G.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, H.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Xie, H. A transfer-based reinforcement learning collaborative energy management strategy for extended-range electric buses with cabin temperature comfort consideration. Energy 2024, 290, 130097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang Dinh, V.; Munir, F.; Azam, S.; Yow, K.-C.; Jeon, M. Transfer learning for vehicle detection using two cameras with different focal lengths. Inf. Sci. 2020, 514, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ji, Z.; Chang, Y.; Li, S.; Qu, X.; Cao, D. ML-ANet: A Transfer Learning Approach Using Adaptation Network for Multi-label Image Classification in Autonomous Driving. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 34, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, R.; Tan, H.; Peng, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y. Cross-Type Transfer for Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Hybrid Electric Vehicle Energy Management. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 8367–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; He, H.; Su, Q. Towards a fossil-free urban transport system: An intelligent cross-type transferable energy management framework based on deep transfer reinforcement learning. Appl. Energy 2024, 363, 123080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Li, K.; Sima, C.; Zhu, X.; Chai, S.; Du, S.; Lin, T.; Wang, W. Planning-oriented autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17853–17862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, D.R.; VinayKarthik, B.C. Deep Learning based Object Detection Model for Autonomous Driving Research using CARLA Simulator. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Smart Electronics and Communication (ICOSEC), Trichy, India, 7–9 October 2021; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
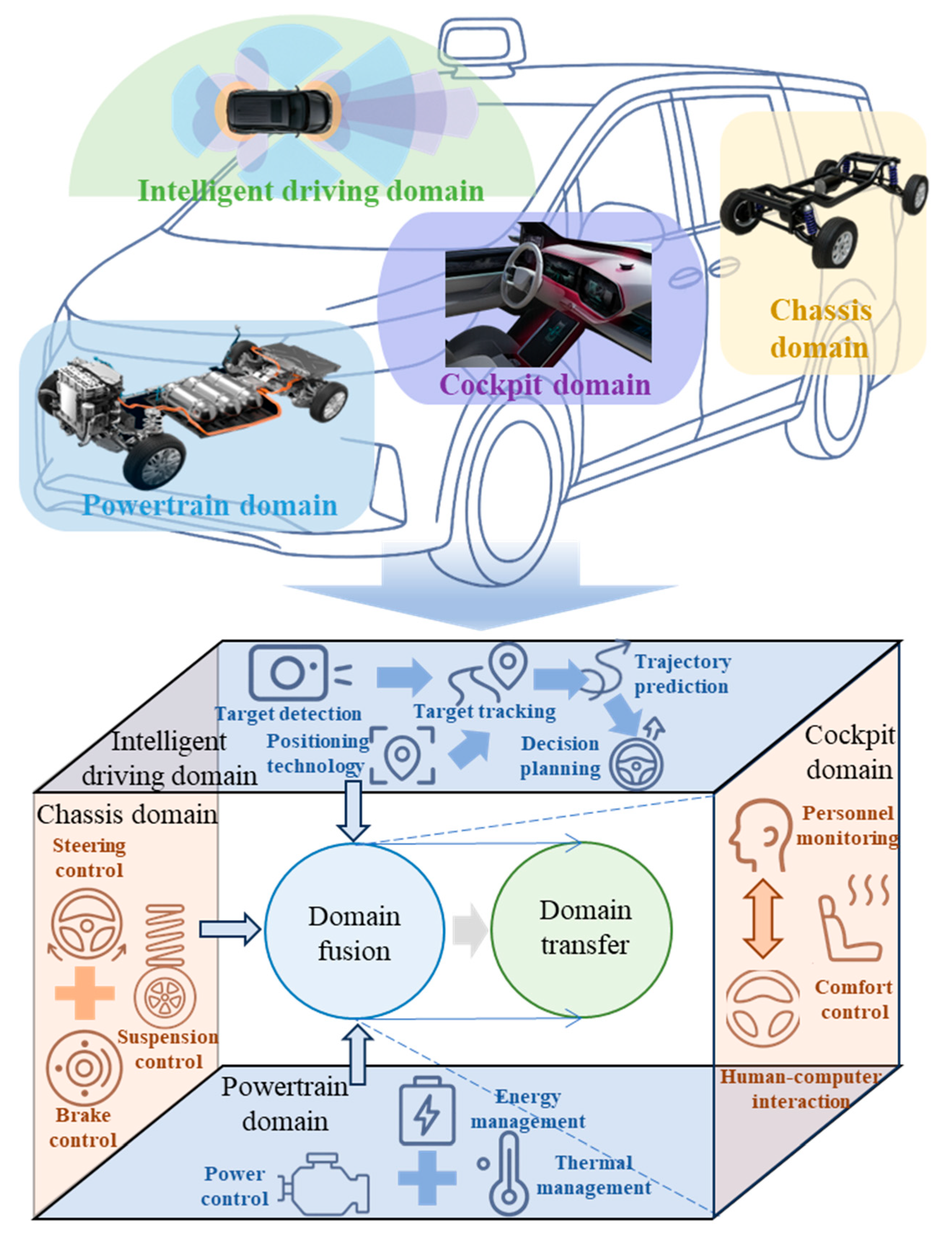
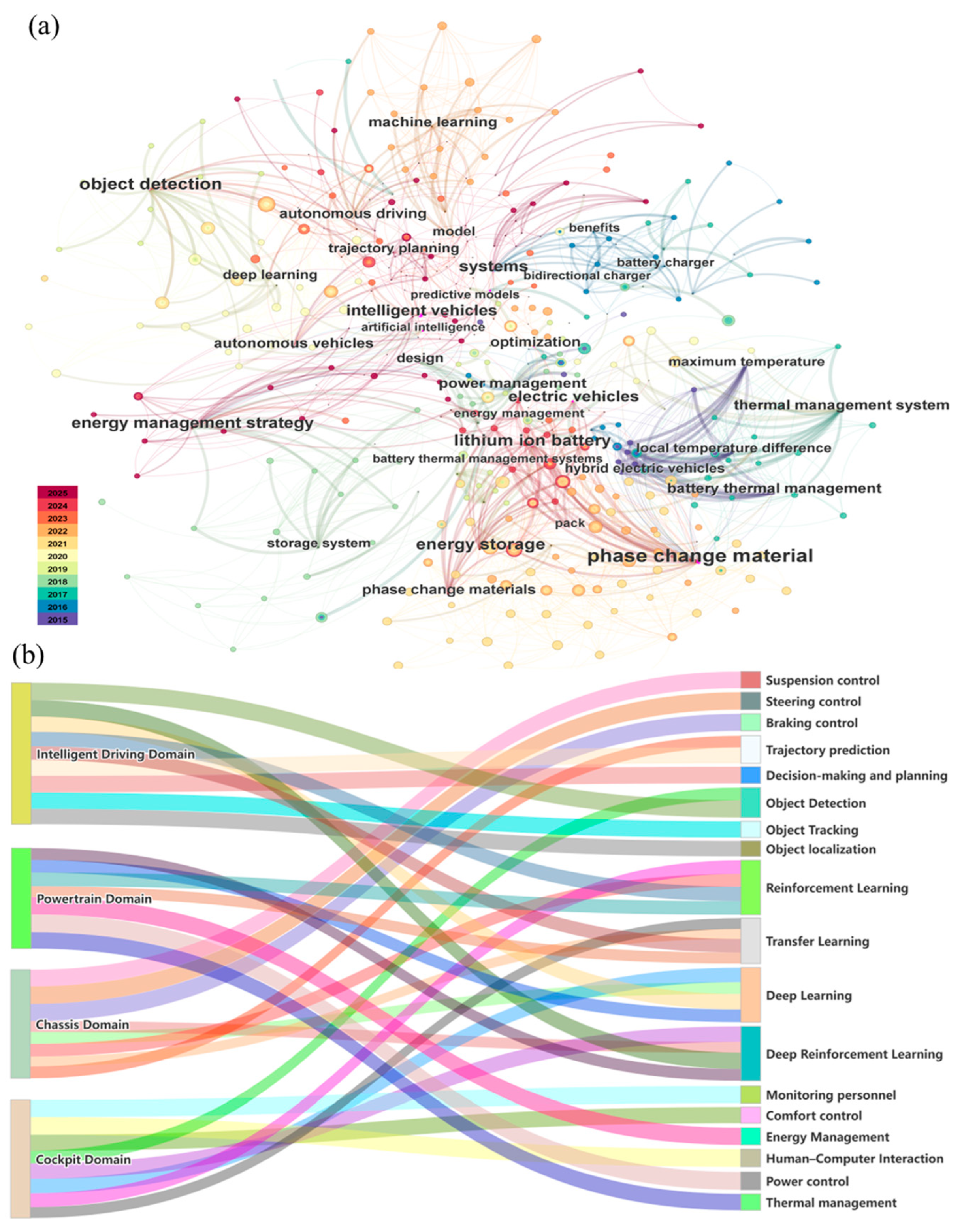
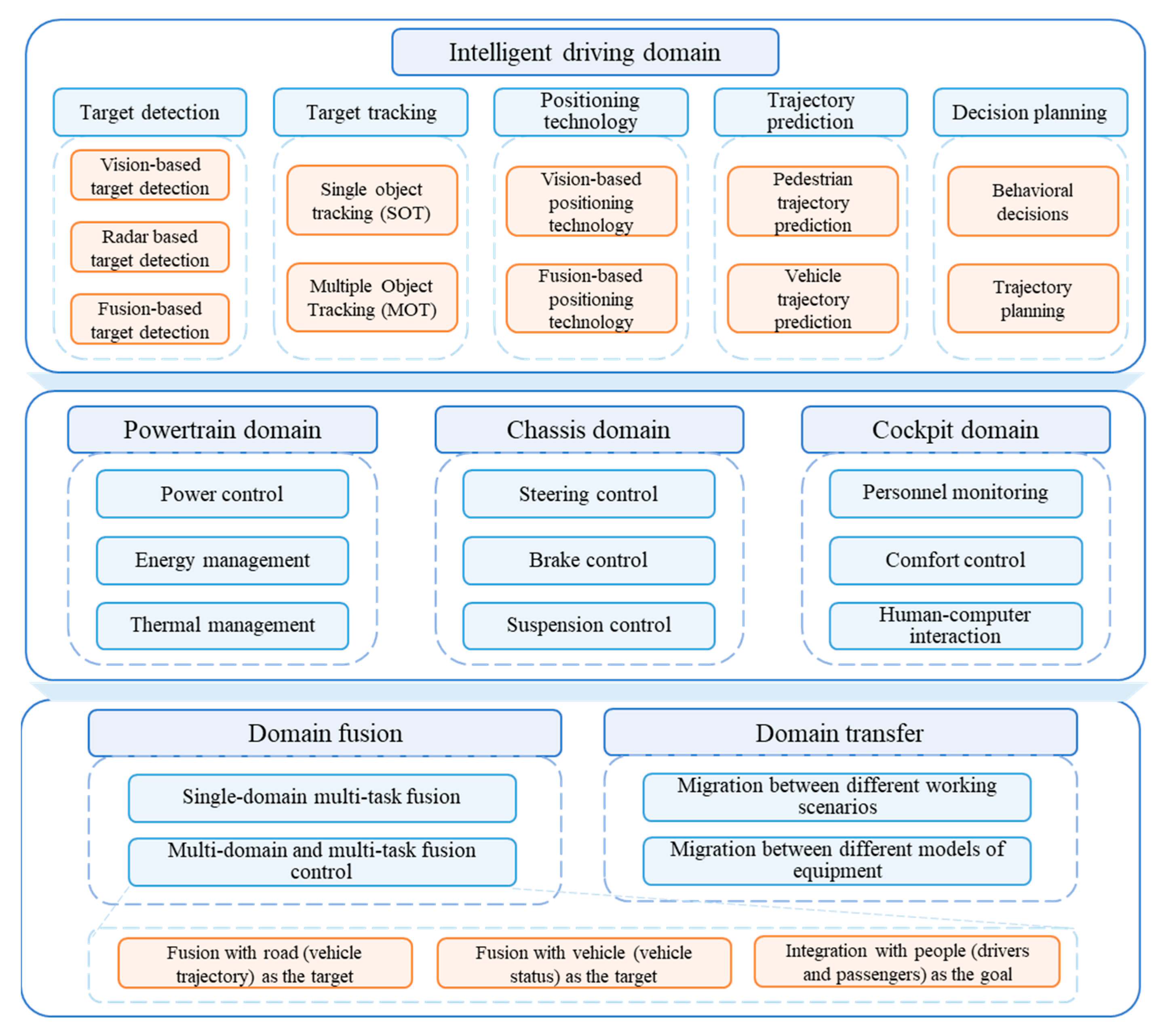
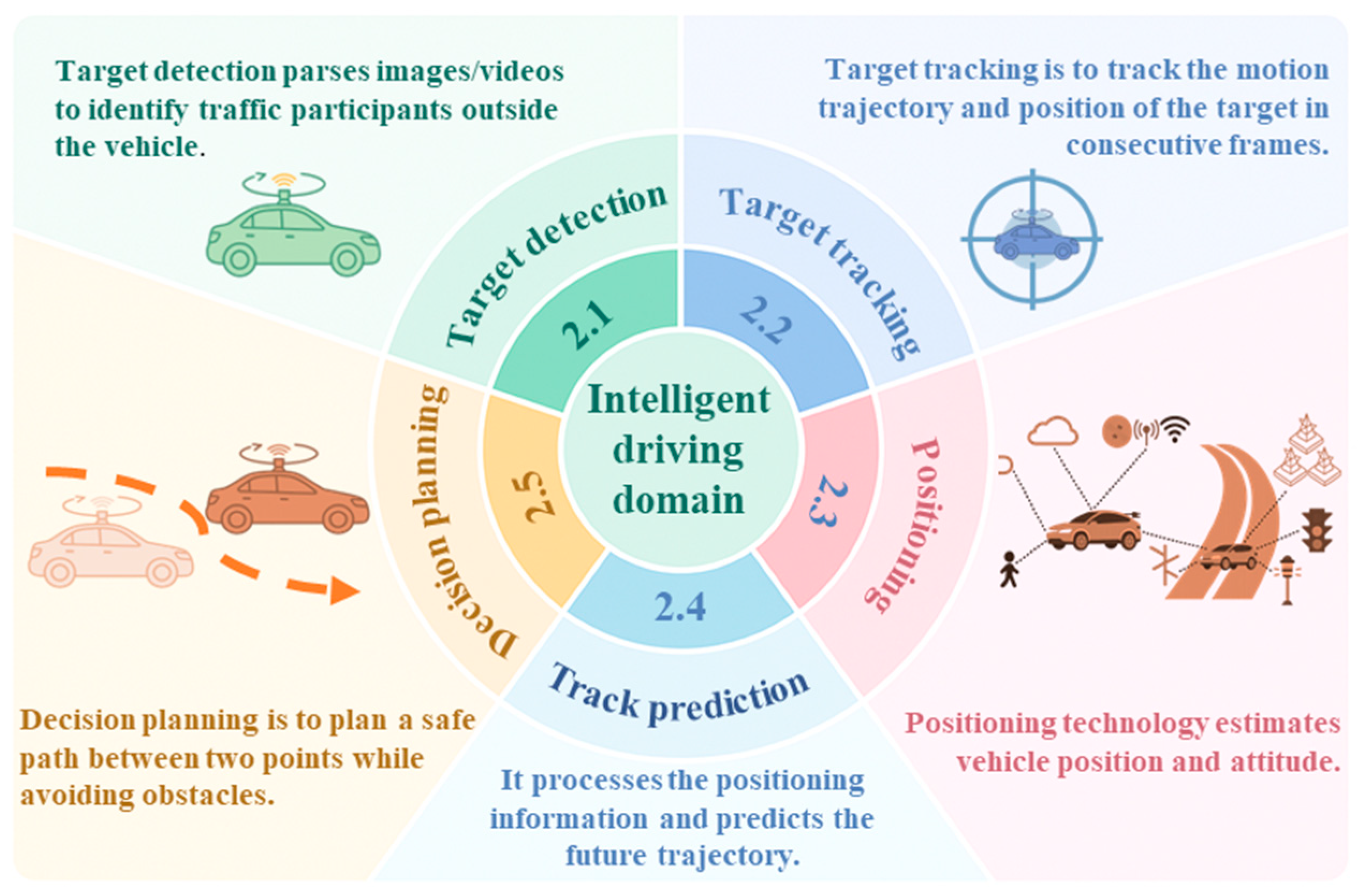
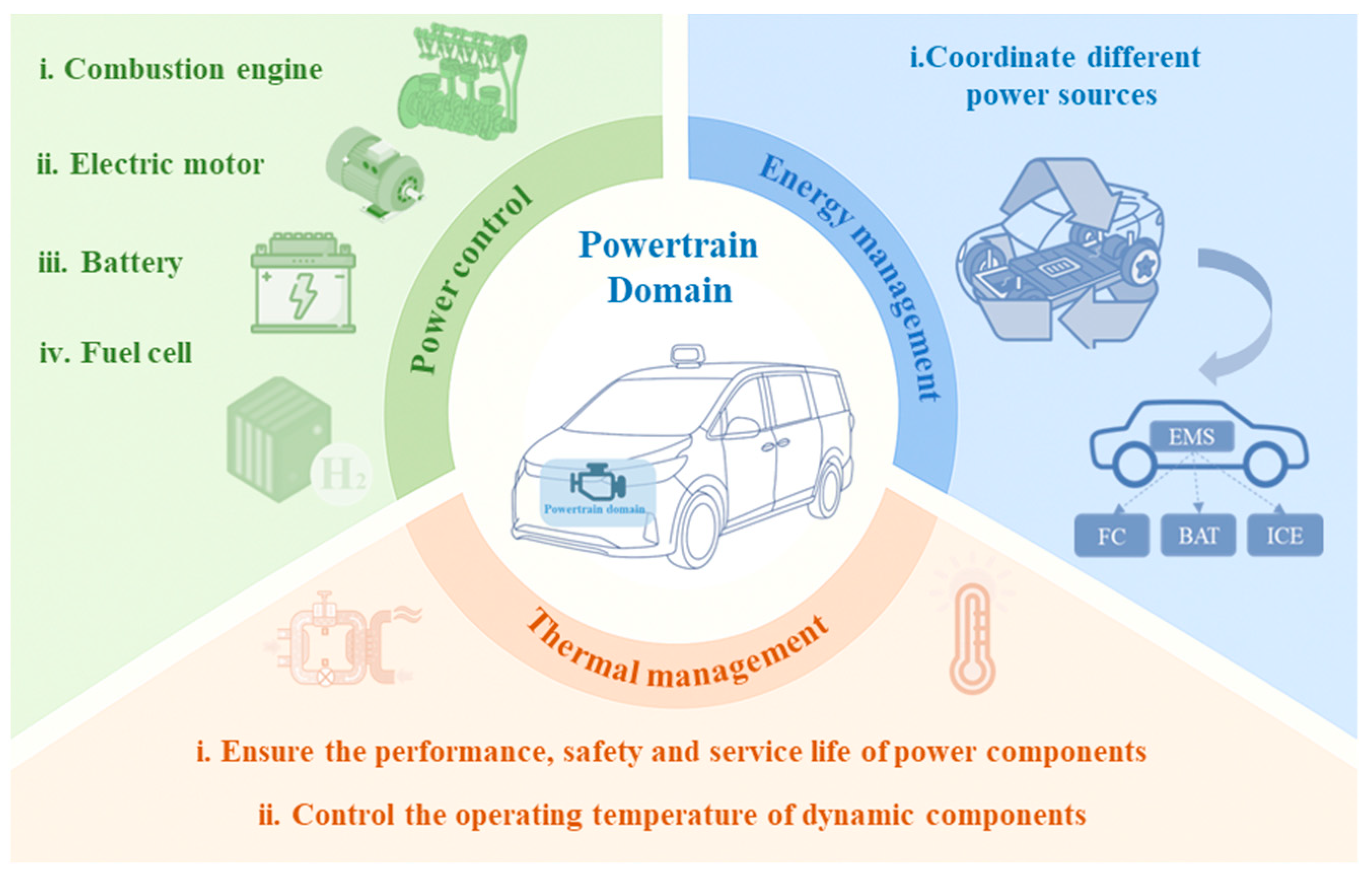
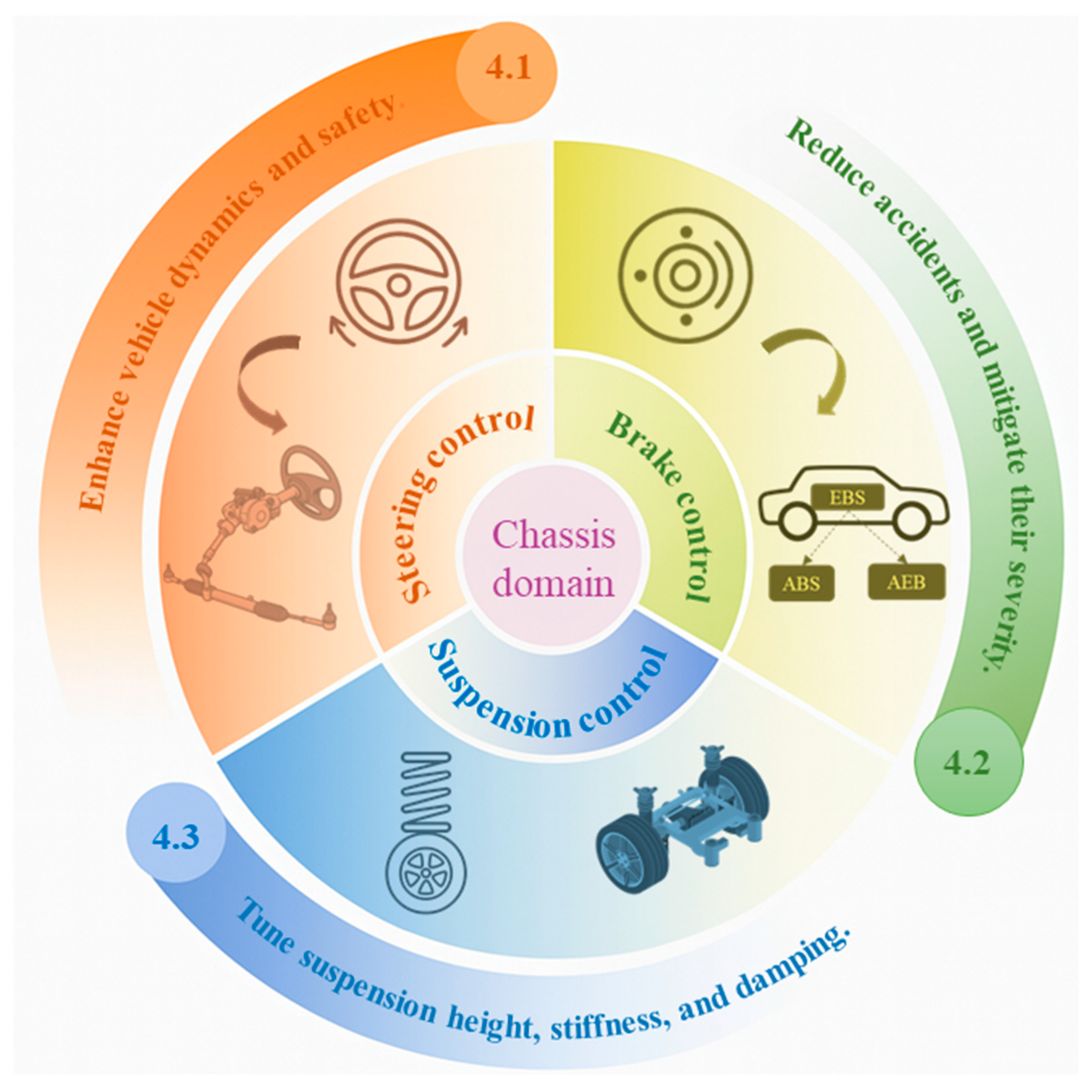
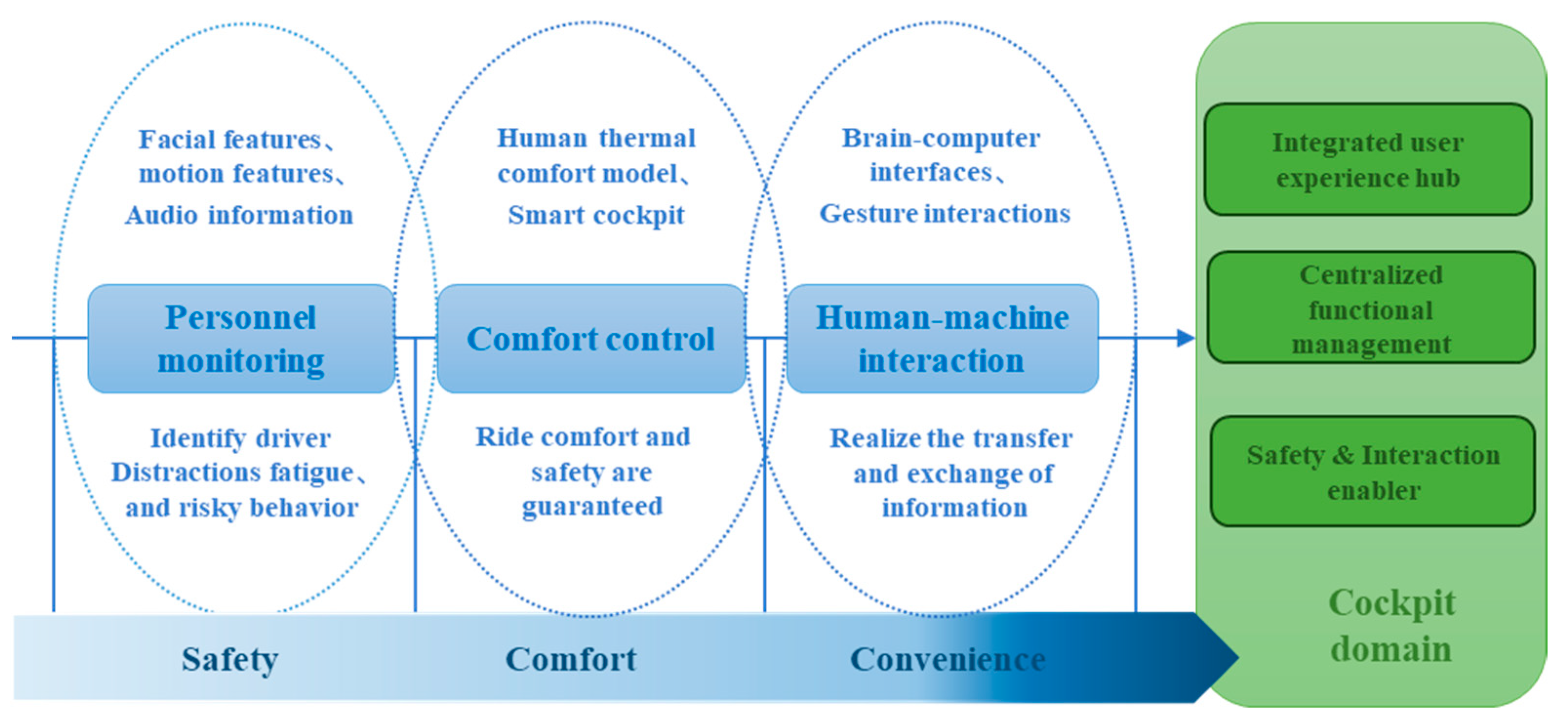
| Category | Strengths | Limitations | Typical Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Value-Based | High sample efficiency in discrete spaces. Stable with replay buffers. Simple to implement. | Cannot directly handle continuous actions. Overestimation bias in vanilla forms. Weak for stochastic policies. | Discrete control, low-dimensional actions, tabular tasks. |
| Policy-Gradient | Direct stochastic policy optimization. Handles continuous/discrete actions. Good exploration in high-entropy tasks. | High gradient variance. Slow in early methods. Prone to sub-optimal convergence. | Continuous control, constrained actions. |
| Actor–Critic | Balances bias variance. High sample efficiency. Supports continuous/discrete actions. | More complex networks. Critic error can destabilize. Sensitive to hyperparameters. | Real-world control, multi-agent, sparse-reward tasks. |
| Ref. | Functional Domain | Application of DRL | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | Intelligent driving domain | Yes | Based on the classification of sensor types and algorithms, the automotive target detection methods in recent years are summarized. |
| [28] | Intelligent driving domain | Yes | In the conclusion, the development of algorithms for vehicle trajectory planning in recent years is discussed. |
| [29] | Intelligent driving domain | Yes | The application of different RL algorithms in behavioral decision making in different autonomous driving scenarios is summarized. |
| [30] | Intelligent driving domain | Yes | Summarizes the application of RL and DRL algorithms in multiple tasks of vehicles such as obstacle detection, scene recognition, lane detection, navigation, and path planning |
| [31] | Intelligent driving domain | No | / |
| [32] | Powertrain domain | Yes | The effects of different RL algorithm actions and reward function setting choices on the performance of the powertrain controller are analyzed. |
| [33] | Powertrain domain | Yes | An analysis and review of RL-based EMS research was conducted according to different types of hybrid vehicle architectures. |
| [34] | Powertrain domain | Yes | This study explores approaches for predicting battery temperatures and optimizing their thermal control. |
| [35] | Chassis domain | No | / |
| [36] | Chassis domain | No | / |
| [37] | Chassis domain | No | / |
| [38] | Cockpit domain | Yes | Various automotive cabin thermal modeling techniques are discussed, and control technologies for cabin thermal management in different weather conditions are evaluated. |
| [39] | Cockpit domain | No | / |
| [40] | Cockpit domain | No | / |
| [41] | Body domain | No | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Partial occlusion and overlap issues | Yes | [49] | Fusion of information from multiple 3D lidars to enhance situational awareness of occluded objects in dense scenes. |
| Radar sensor noise interference | Yes | [51] | Only the RPFA-Net method of 4D radar is used. |
| Long distance, small target | Yes | [52] | Uses MobileNet V2 to replace its original backbone and only uses the first two feature mapping layers of Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD) to improve small object detection performance. |
| Detection speed is slow | Yes | [53] | Constructed a model that can quickly generate a global sparse graph and construct a dense graph. |
| Changing scenes | Yes | [54] | The 3D environment is partitioned into voxels, and a novel graph-based initialization network is introduced that encodes the points residing within. |
| Changes in vehicle perspective | Yes | [55] | The dual equivariance of the model can extract local and global equivariance features, respectively, thereby alleviating the impact of vehicle steering. |
| Low detection accuracy | Yes | [56] | 2D RGB imagery is integrated with 3D point clouds at the semantic level to boost 3D object-detection accuracy. |
| Strong light, low light | Yes | [57] | A sparse point-cloud–image fusion strategy is adopted, and fog augmentation is added to the dataset images. |
| Camera image is blurry | No | / | / |
| Photo stitching technology | No | / | / |
| Bad weather | No | / | / |
| Color fusion environment is high | No | / | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target scale changes | Yes | [95] | By embedding an improved SNIPER sampling strategy within Faster R-CNN, our method achieves reliable vehicle detection across variable scales. |
| Tracking inefficiencies | Yes | [97] | Applies neural architecture search to uncover efficient tracking models that cut real-time latency. |
| Target is partially occluded | Yes | [100] | An object detector extracts an oriented 3D bounding box from the point cloud, after which similarity-based re-identification matches it to known instances. |
| Changes in appearance features | Yes | [103] | A single target tracking model is designed, which can obtain the temporal variation characteristics of video targets across frames. |
| Affected by sunlight, bad weather | Yes | [104] | The scheme consists of three stages: illumination enhancement, reflectance component enhancement, and linear weighted fusion. |
| Background interference problem | Yes | [105] | Using position-normalized features, a general convolutional layer is used to enhance the object contour. |
| High target appearance similarity | No | / | / |
| Limited tracking capabilities | No | / | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positioning reliability | Yes | [116] | To improve the distinguishability and matching of feature descriptors, an effective multi-level intensity map representation is adopted, and a new sampling method based on coverage fraction is proposed. |
| Positioning accuracy is not high | Yes | [117] | A panoramic camera was added next to the positioning camera to assist gaze control. |
| Changes in vehicle perspective | Yes | [118] | The compressed representation mode explains the learned features and processes, significantly reducing translation and rotation errors. |
| Error accumulation problem | Yes | [119] | Uses PointPillars to detect and remove objects, then performs lidar odometry and mapping for a more static mapping. |
| Affected by sunlight, bad weather | Yes | [120] | An effective multi-scale feature discriminator is proposed for adversarial training. The features of visual sensors and radar are fused together. |
| Map data overfitting problem | No | / | / |
| Dependency on HD maps | No | / | / |
| High-speed positioning delay | No | / | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact of complex road environment | Yes | [137] | Traffic scenes are modeled in the form of spatial semantic scene graphs to make various predictions about traffic participants. |
| Multimodal prediction | Yes | [138] | The system unites a multimodal trajectory generator with modules for inverse reinforcement learning and risk avoidance. |
| Multi-agent interaction problem | Yes | [139] | Explicitly modeling interactions using graph structures can lead to better predictions of agent interactions. |
| Predicting real-time constraints | Yes | [140] | An attention-based graph model GATraj is proposed, which balances prediction accuracy and inference speed well. |
| Trajectory uncertainty | Yes | [141] | A driving style attention generative adversarial network is proposed. |
| Prediction reliability is not high | No | / | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human-like decision planning | Yes | [154] | High- and low-level policies are co-learned from human demos. |
| Cognitive reasoning questions | Yes | [159] | Combining hand-designed logic with data-driven reinforcement learning agents. |
| Planning optimality problem | Yes | [160] | Designing a safety mechanism for lane-changing decisions of autonomous vehicles on highways. |
| Vehicle interaction | Yes | [161] | A general graph reinforcement learning (GRL) framework is proposed to solve the decision-making problem in interactive traffic scenarios on highways. |
| Multi-objective optimization | Yes | [162] | An eco-driving planning method based on a hierarchical framework is proposed to reduce energy consumption while ensuring driving safety. |
| Difficult to satisfy personalization | No | / | / |
| Self-learning and self-performing | No | / | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security issues | Yes | [19] | A twin-delay DDPG strategy smooths torque delivery, steadies training, and supports safe, energy-efficient driving. |
| Environmental adaptability issues | Yes | [178] | This algorithm adds environmental intelligent exploration to the original DDPG algorithm. |
| Inefficient power switching | Yes | [179] | By defining the action as the mode choice, the method uses a continuous state space and richer decision criteria, enabling more precise mode transitions. |
| Slow response problem | Yes | [180] | Control method of fuel cell gas supply subsystem based on DRL to optimize dynamic response performance. |
| Intent and state are difficult to identify | No | / | / |
| Smoothness problem | No | / | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consider the driver’s intentions | Yes | [188] | A semi-supervised SVM classifier identifies driver types and derives driving-style features. |
| Low utilization rate of information | Yes | [190] | Wavelet neural network is used to predict future traffic information, generate long-term global driving state. |
| Lifetime optimization | Yes | [191] | Weighs the fuel consumption cost, battery aging cost, and state of charge (SOC) sustainability reward function under different weight coefficients. |
| Optimality problem | Yes | [192] | The designed EMS for updating the weights of the Q neural network shows close to the global optimal fuel economy in different driving cycles. |
| Powertrain status optimization | Yes | [193] | The comprehensive synchronous control of multiple components is realized in the mixed motion space through the dual DRL algorithm |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-system collaboration | Yes | [201] | A novel RL-based cooling control strategy is proposed to coordinately control the passenger compartment and battery cold plate. |
| Temperatures are difficult to track | Yes | [203] | Tuned for fast convergence on multiple-input problems, minimizing tracking error and power consumption. |
| Thermal runaway issues | Yes | [204] | By modelling fine-grained, vehicle-level battery dynamics, the method curbs pack aging. |
| Low efficiency of waste heat reuse | No | / | / |
| Module temperature uniformity | No | / | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Not very robust | Yes | [214] | Generate a generalized reinforcement learning agent by selecting vehicle parameters and path trajectories as the state space. |
| Human–machine co-driving control | Yes | [215] | Make the optimal driving rights allocation based on the driver’s steering angle, the vehicle’s autonomous steering angle, and vehicle–road information. |
| Optimal steering parameters | No | / | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Braking timeliness | Yes | [224] | A DDPG-based AEB control method is proposed to manage the vehicle’s speed change through braking action. |
| Braking stability | Yes | [225] | The strategy enhances ride comfort by modulating brake torque to suppress body pitch and longitudinal oscillations across varied braking scenarios. |
| Braking timing problem | No | / | / |
| Brake energy recovery | No | / | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time lag problem | Yes | [233] | An adaptive suspension system is introduced, combining random road-profile detection with semi-active control technology. |
| Poor adaptability and robustness | Yes | [234] | To meet the differing performance demands of various road conditions, we craft a fuzzy-logic reward that dynamically steers the optimization objective. |
| Nonlinear phenomena | No | / | / |
| Synergy of posture and comfort | No | / | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Person’s head turning | Yes | [239] | This method synthesizes realistic frontal faces through the FF-Module module, which can be used to capture facial movements in any posture, and integrates head posture attributes and facial morphology through the GK-Module module. |
| False alarm problem | Yes | [240] | By improving four DL models to detect children, pets, and adults, respectively, the problem of false alarms can be avoided while improving accuracy. |
| Driver interaction behavior | No | / | / |
| Noise interference problem | No | / | / |
| Privacy leakage issue | No | / | / |
| Expression and Difference | No | / | / |
| Difficult Questions | Application of DRL | Ref. | Main Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental changes | Yes | [246] | Takes into full account factors such as air temperature, external air temperature, and temperature of the passengers, and controls the air outlet temperature. |
| Difference in comfort | Yes | [247] | A human thermal comfort model is embedded, and its comfort scores serve as the optimization target for the PPO-driven cabin HVAC controller. |
| Comfort and mood changes | No | / | / |
| Degree of intelligence | No | / | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, D.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wei, W.; Ji, S.; Ruan, H.; Yi, F.; Jia, C.; Hu, D.; Tang, K.; et al. Research Progress in Multi-Domain and Cross-Domain AI Management and Control for Intelligent Electric Vehicles. Energies 2025, 18, 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174597
Lu D, Chen Y, Sun Y, Wei W, Ji S, Ruan H, Yi F, Jia C, Hu D, Tang K, et al. Research Progress in Multi-Domain and Cross-Domain AI Management and Control for Intelligent Electric Vehicles. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174597
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Dagang, Yu Chen, Yan Sun, Wenxuan Wei, Shilin Ji, Hongshuo Ruan, Fengyan Yi, Chunchun Jia, Donghai Hu, Kunpeng Tang, and et al. 2025. "Research Progress in Multi-Domain and Cross-Domain AI Management and Control for Intelligent Electric Vehicles" Energies 18, no. 17: 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174597
APA StyleLu, D., Chen, Y., Sun, Y., Wei, W., Ji, S., Ruan, H., Yi, F., Jia, C., Hu, D., Tang, K., Huang, S., & Wang, J. (2025). Research Progress in Multi-Domain and Cross-Domain AI Management and Control for Intelligent Electric Vehicles. Energies, 18(17), 4597. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174597