Line-Start Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: Evolution, Challenges, and Industrial Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Emissions, Efficiency, and Motor Standards
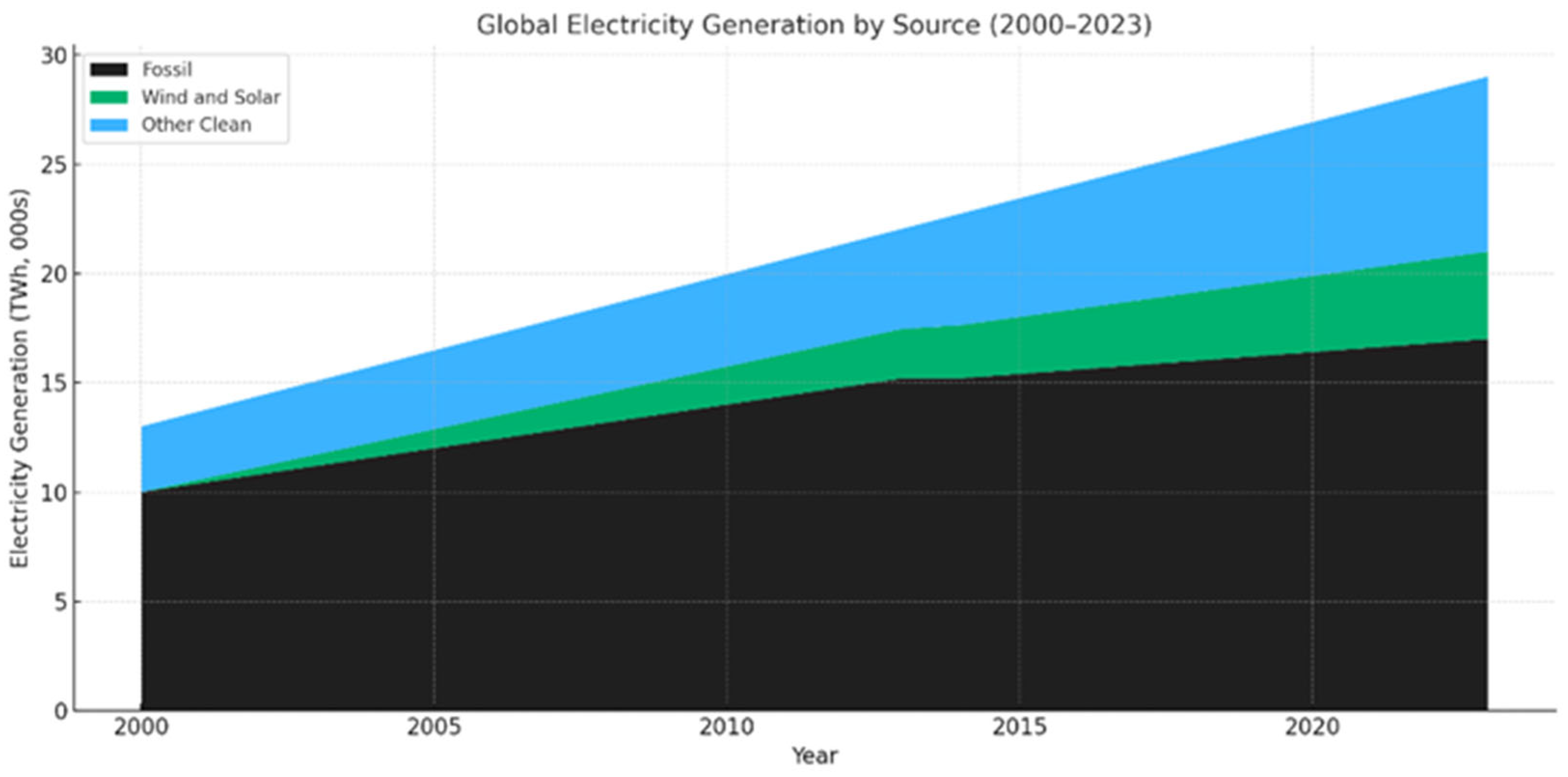
2.1. Energy Consumption and Climate Impact
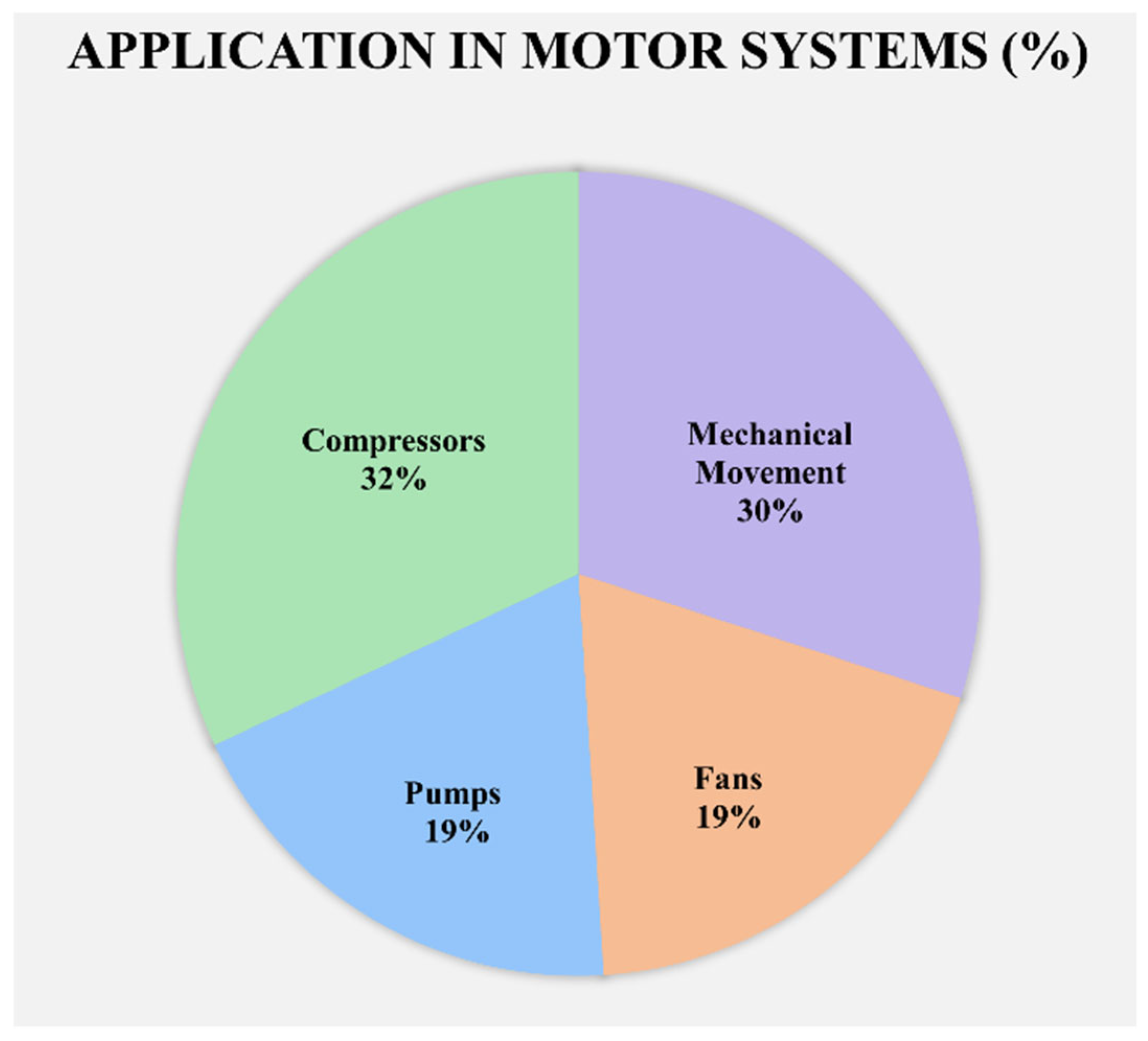
2.2. Electric Motors and Energy Demand
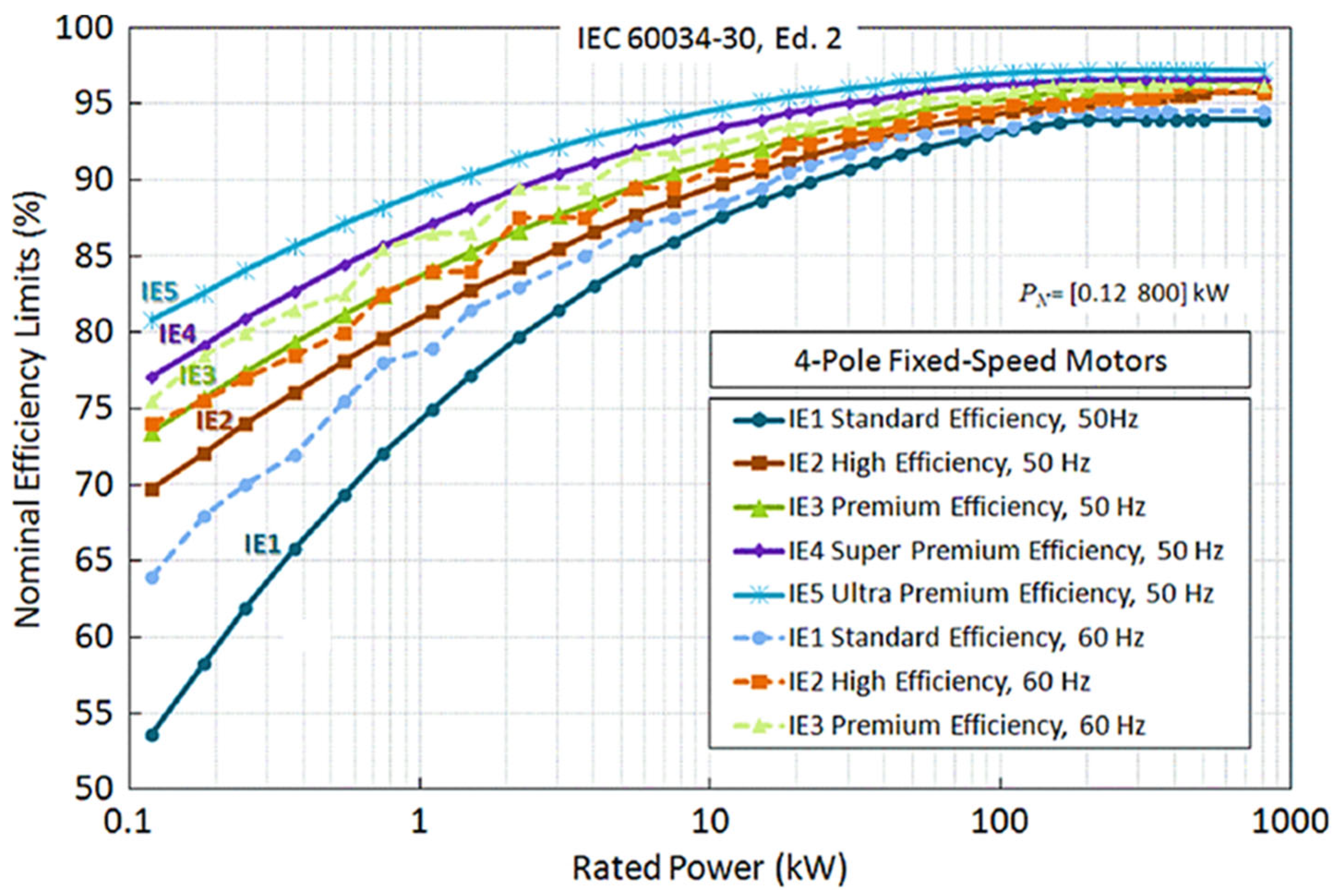
2.3. Efficiency Classes for Electric Motors
3. Fundamentals of LSPMSMs
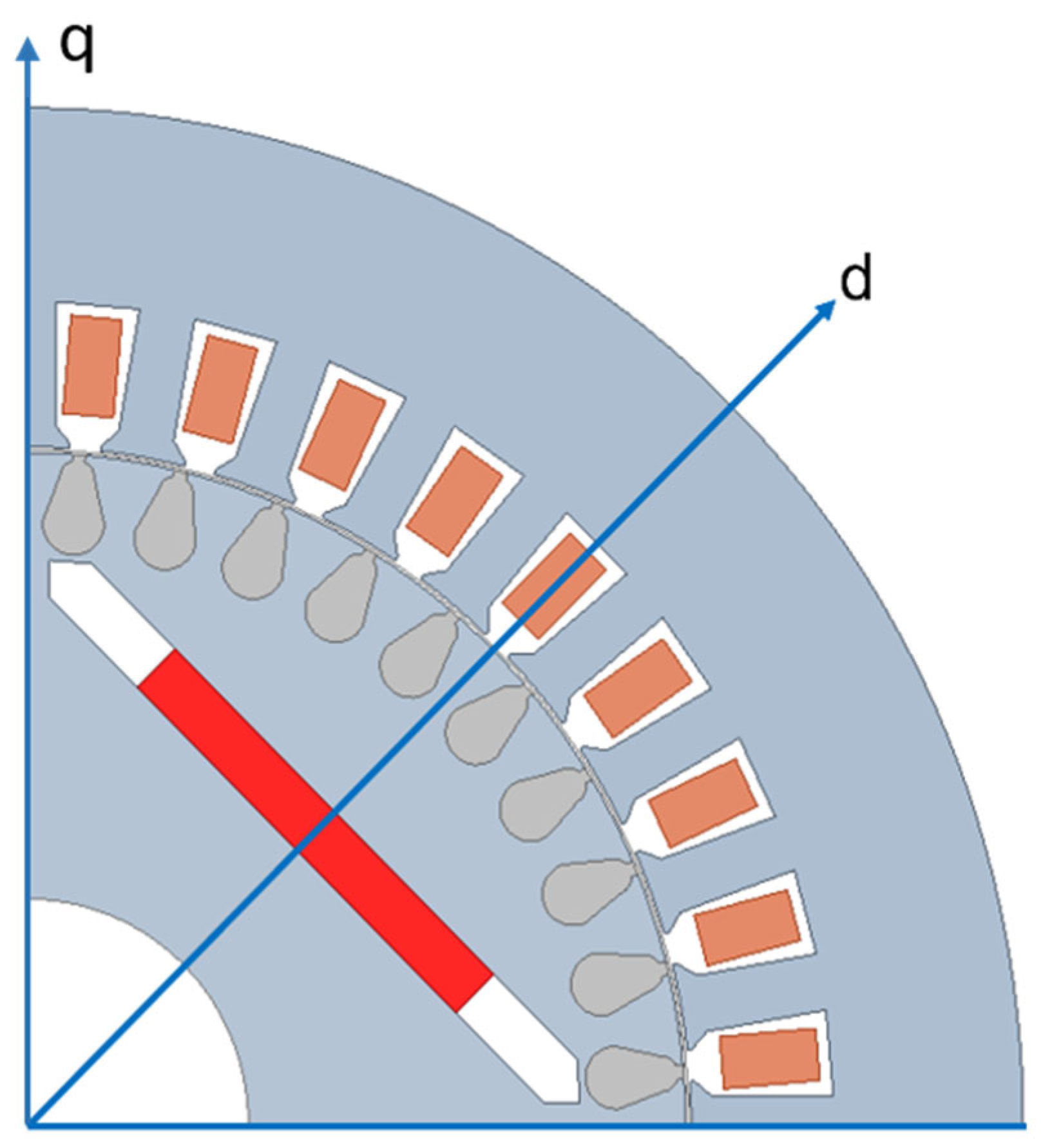
3.1. Operating Theory and Equivalent Circuit
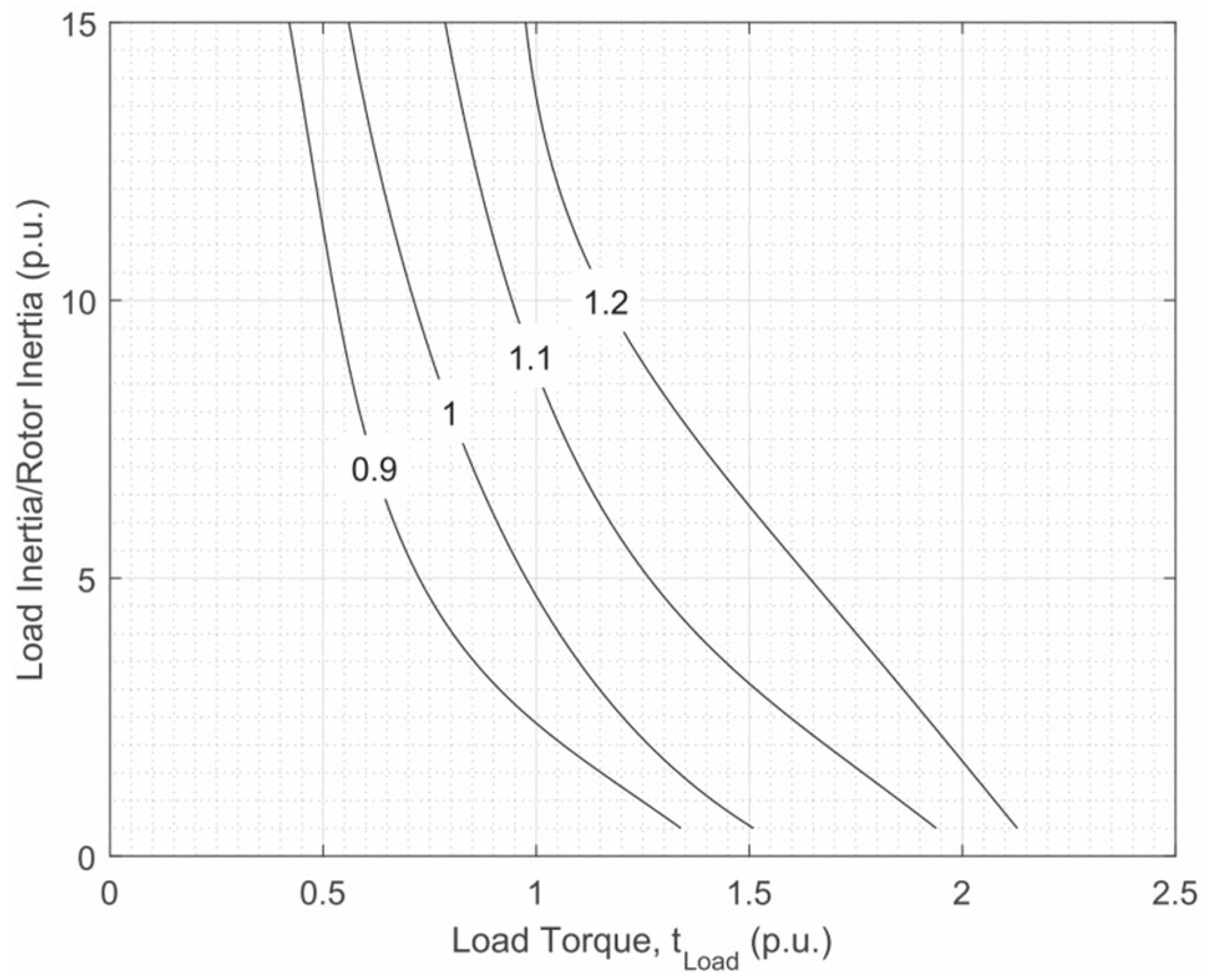
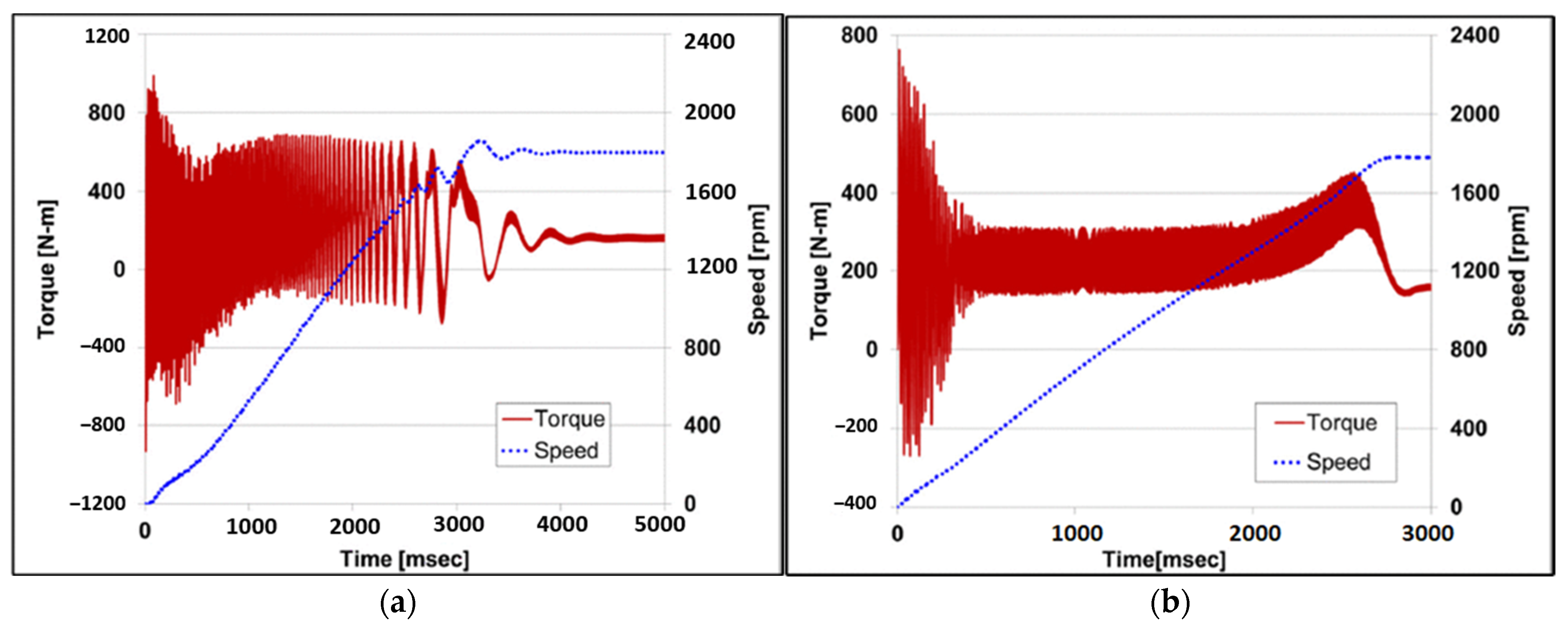
3.2. Startup Behavior and Synchronization Issues
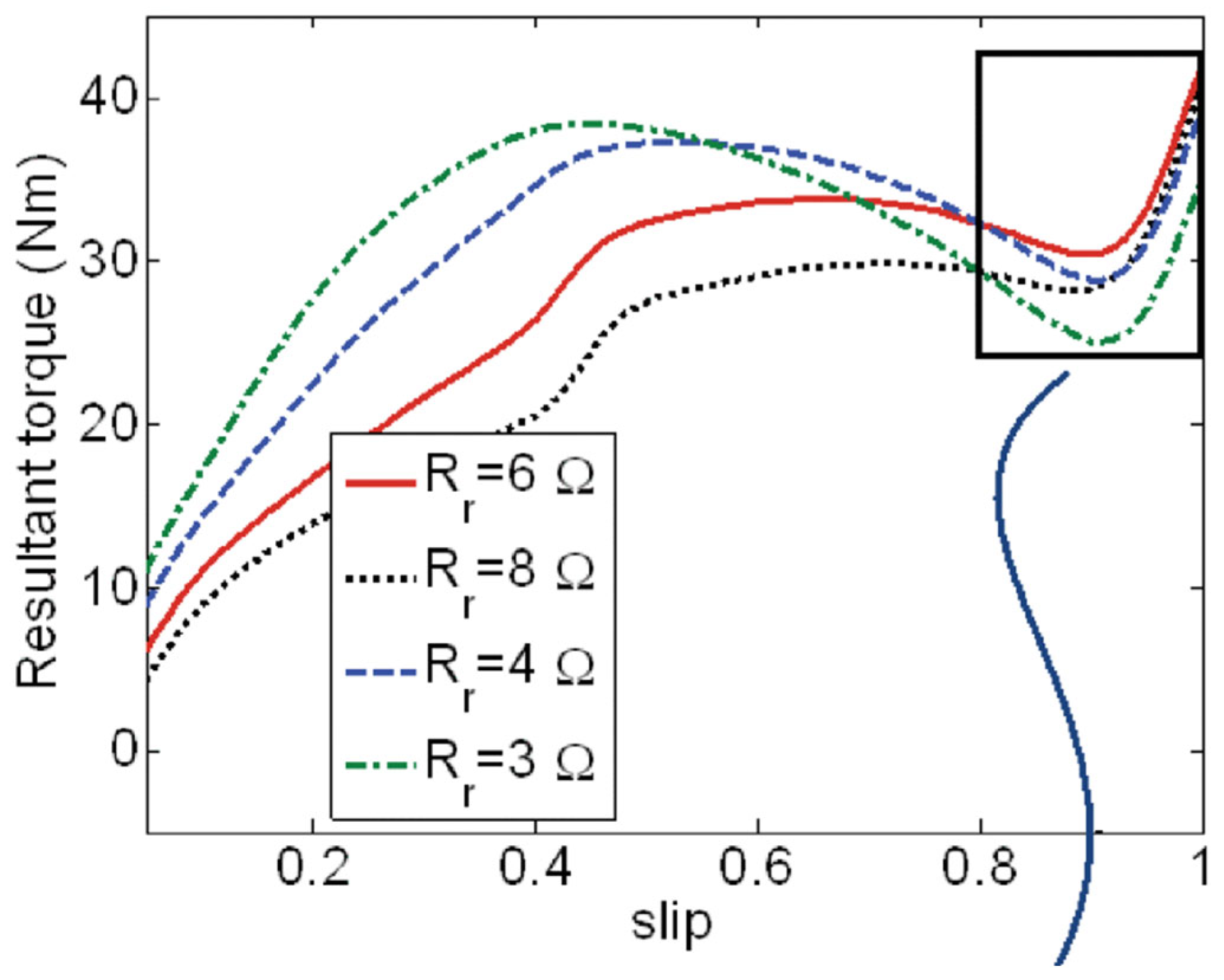
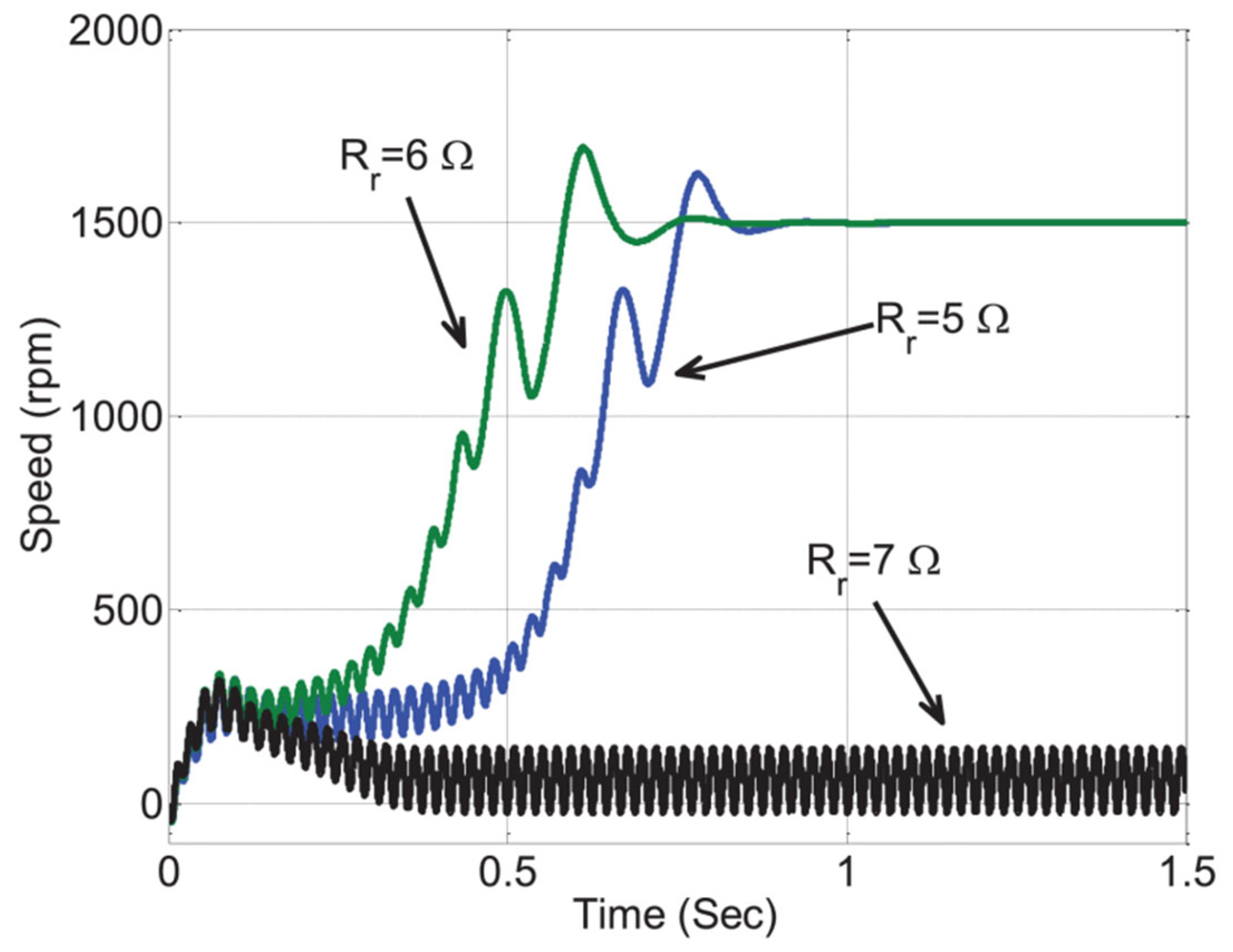
3.3. Effect of Rotor Resistance on Performance
3.4. Influence of Magnetizing Inductance on Performance
3.5. Impact of Supply Voltage on Synchronization
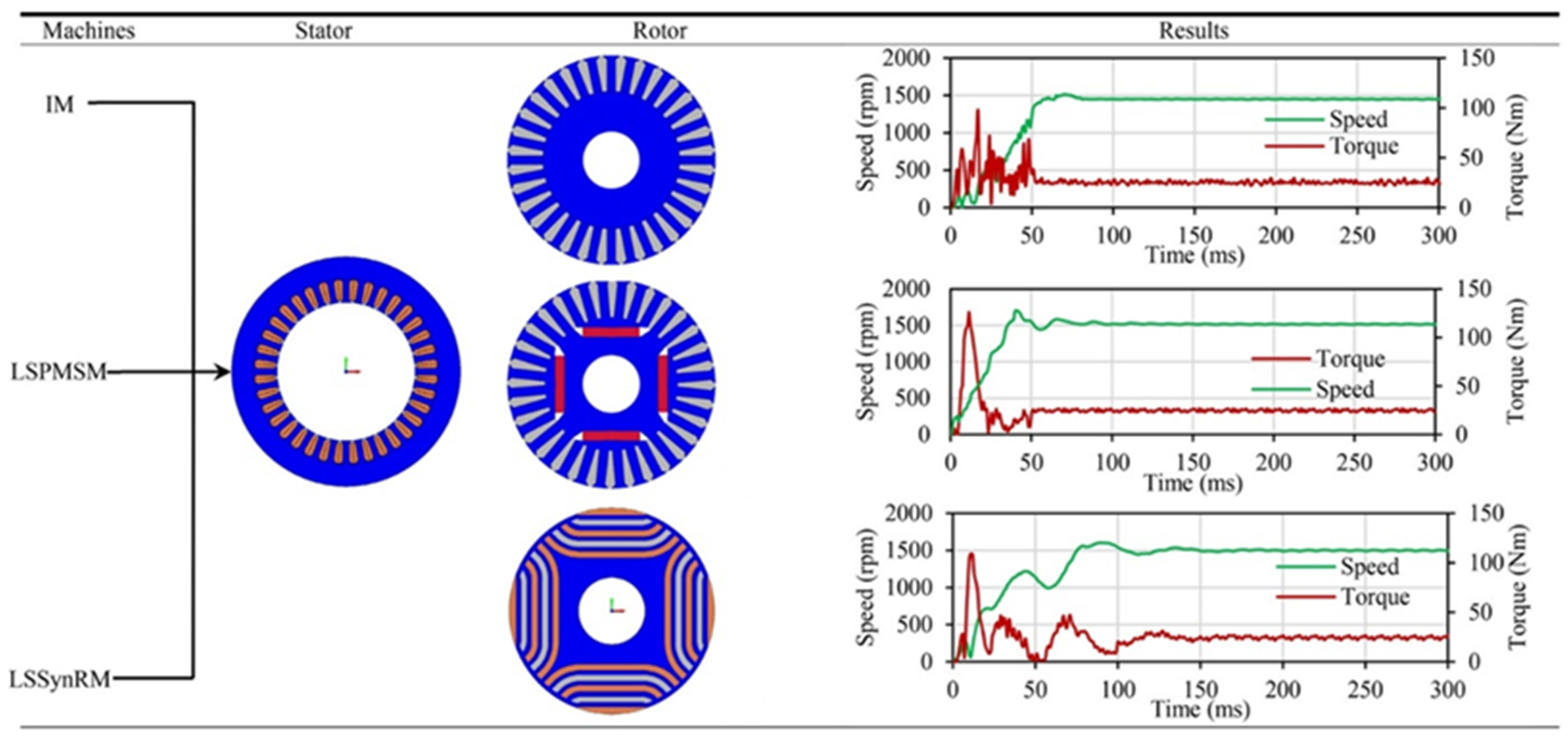
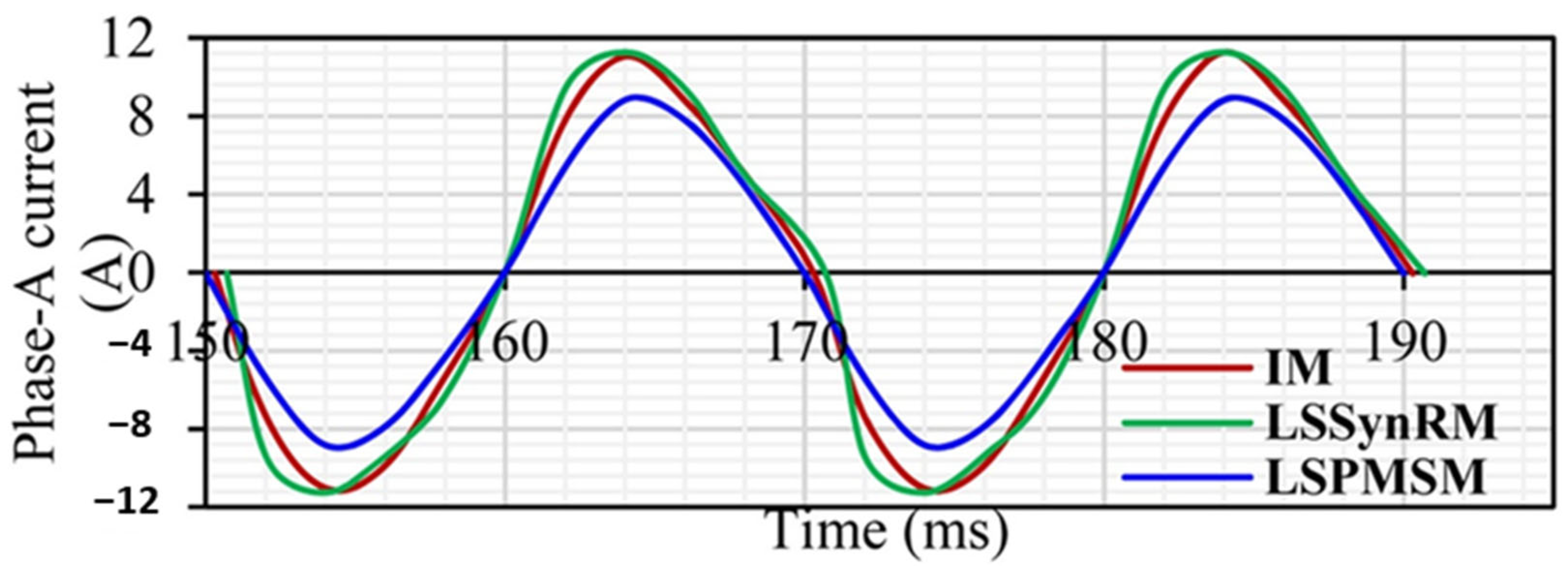
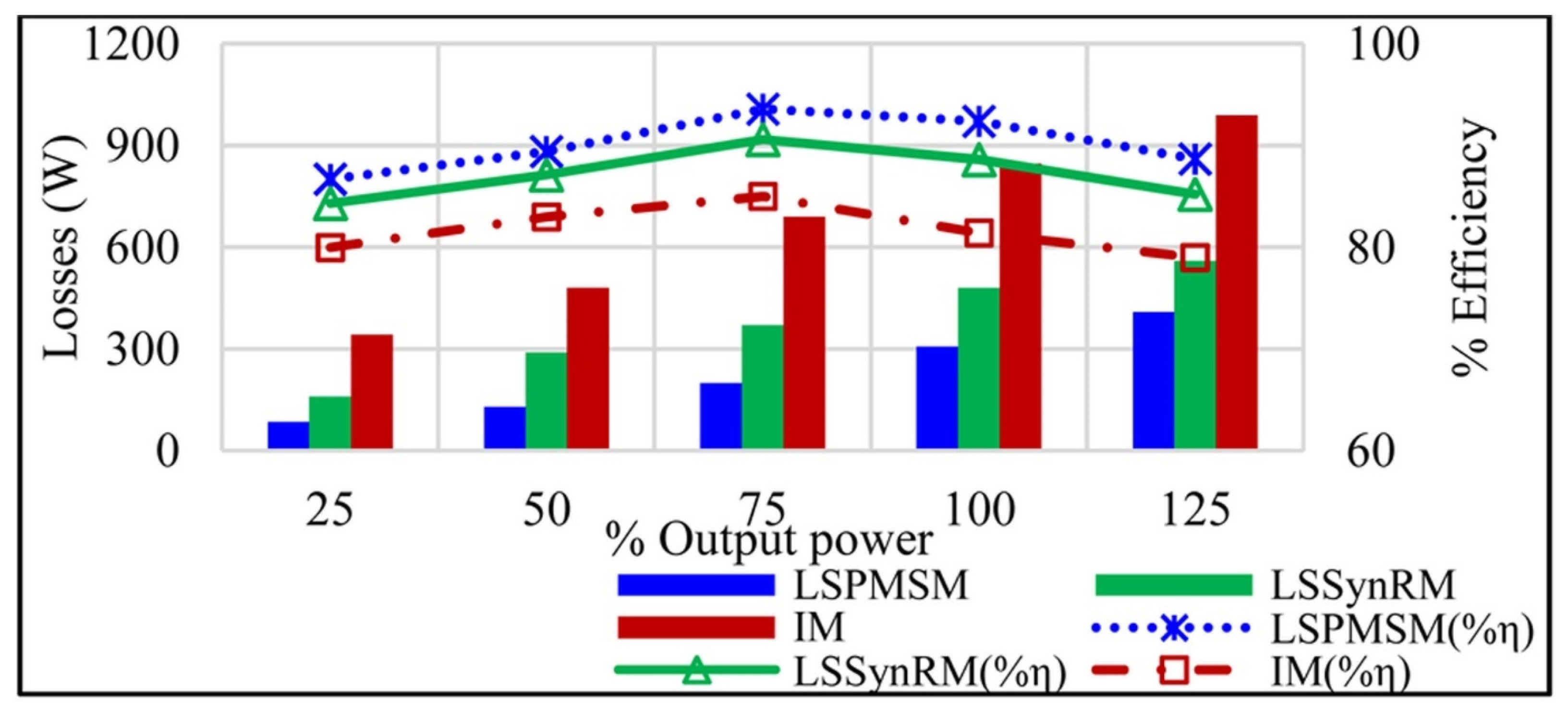
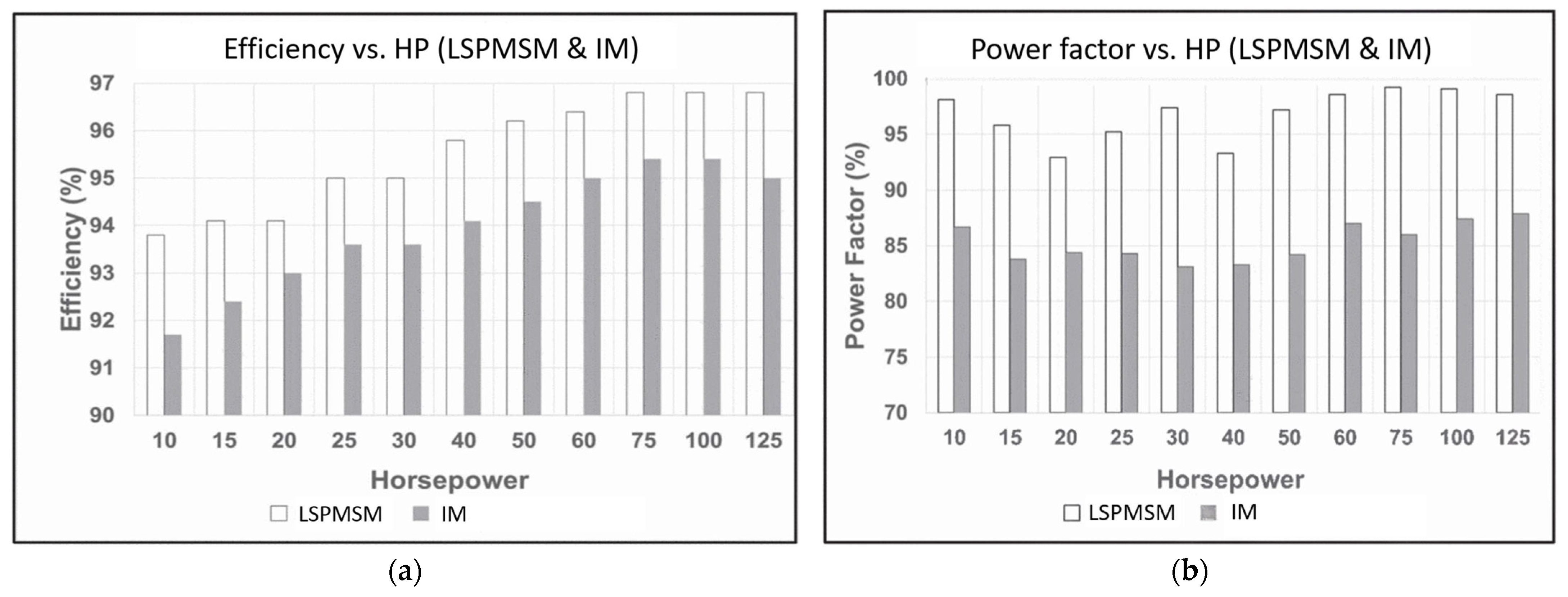
3.6. Performance Comparison with IMs and LSSynRMs
4. Evolution and Innovation in Line-Start PM Motor Design
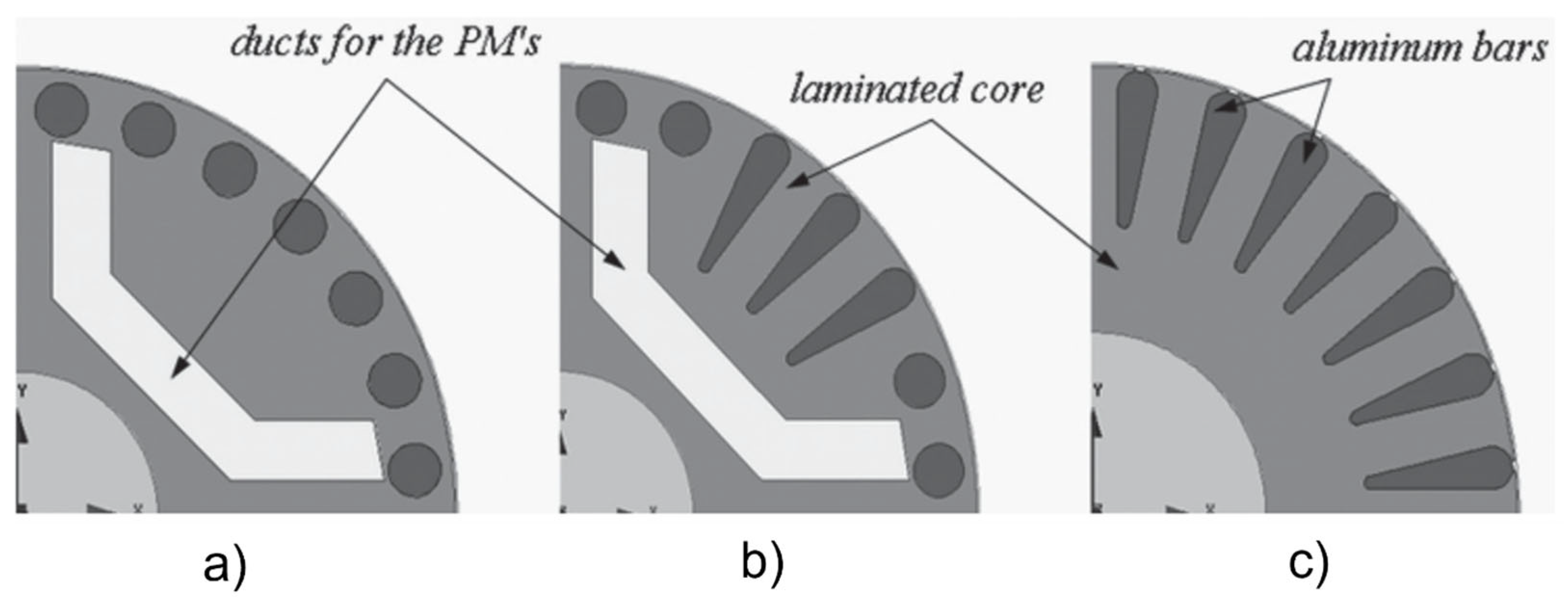
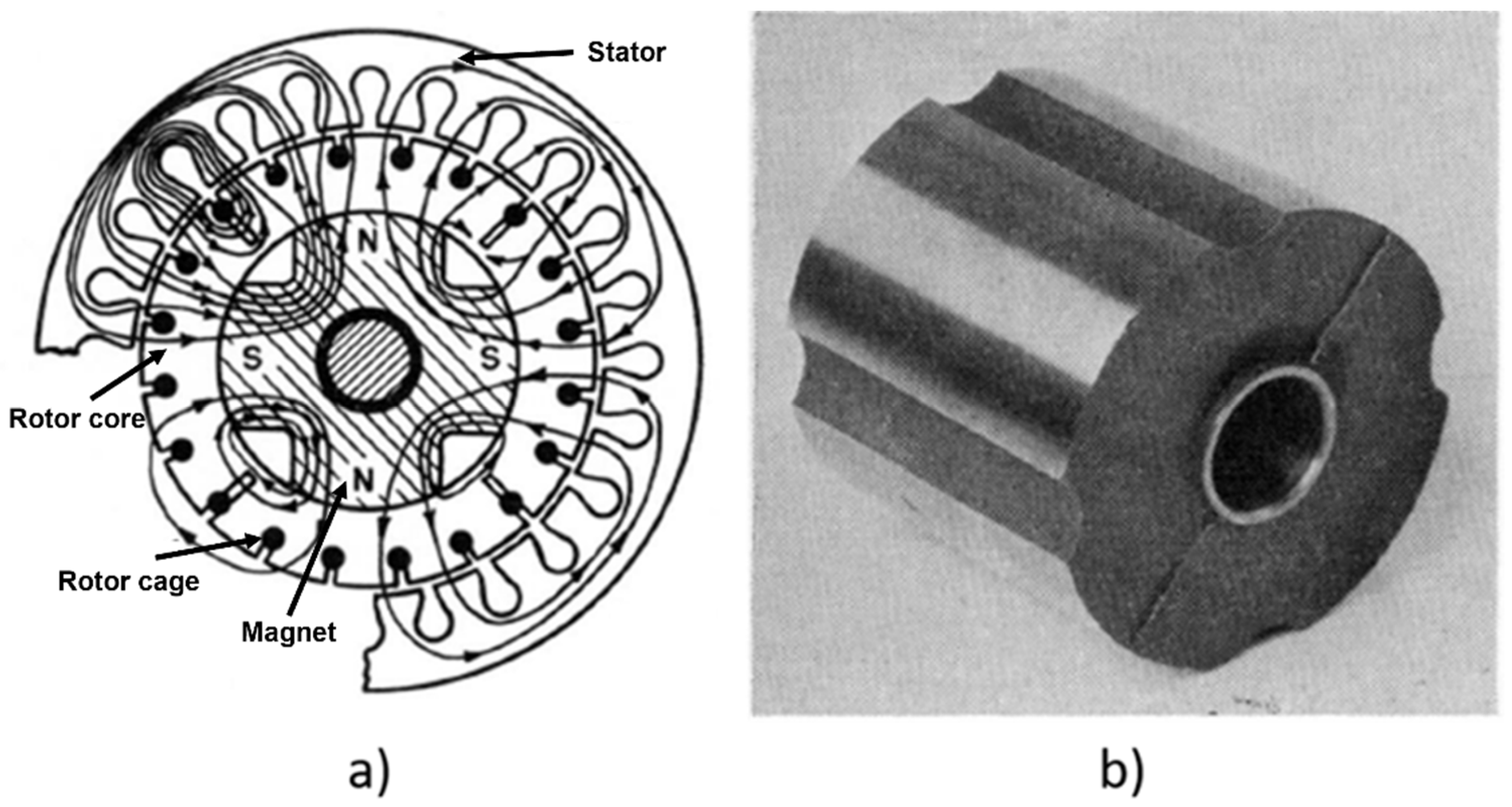
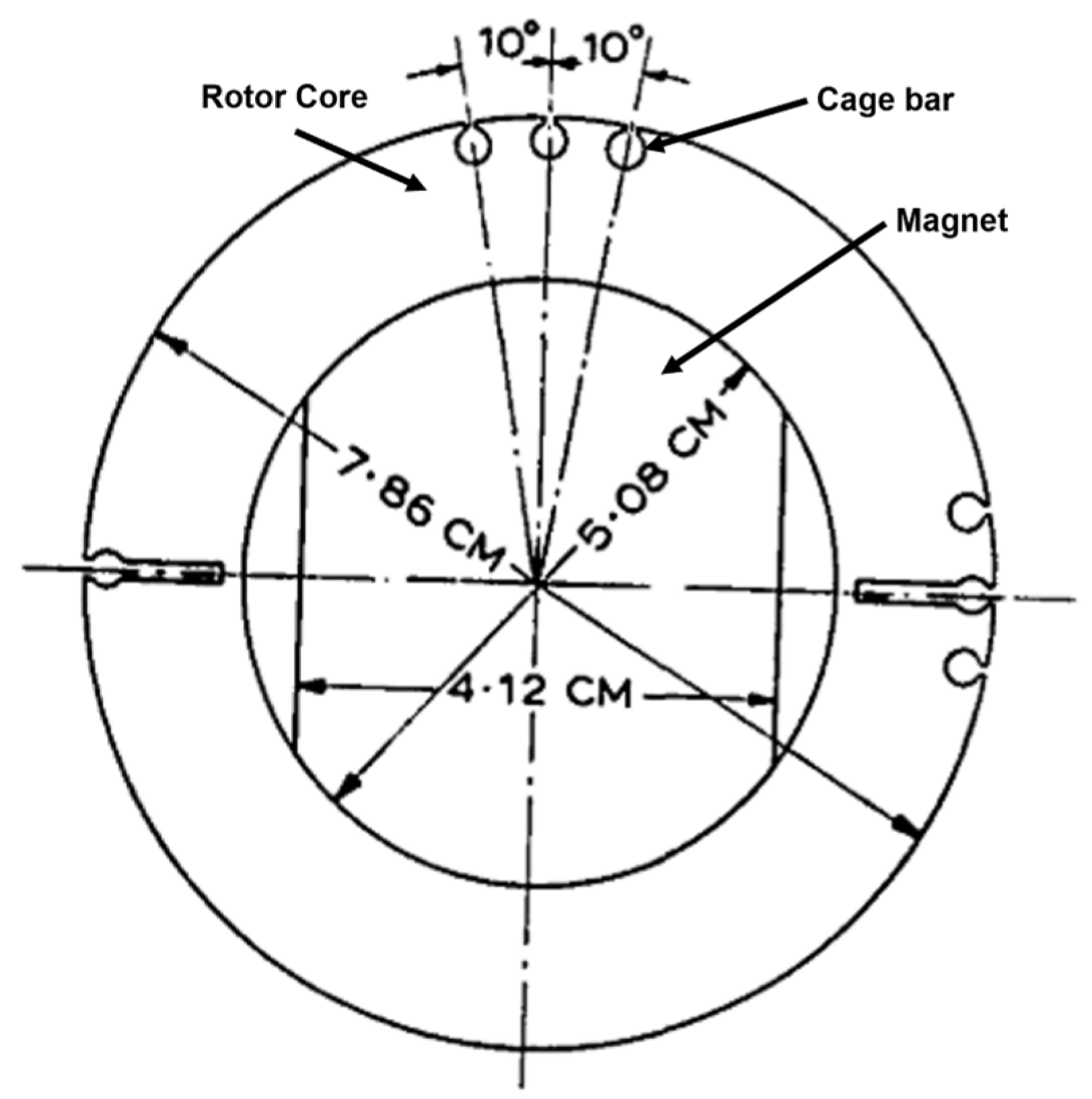
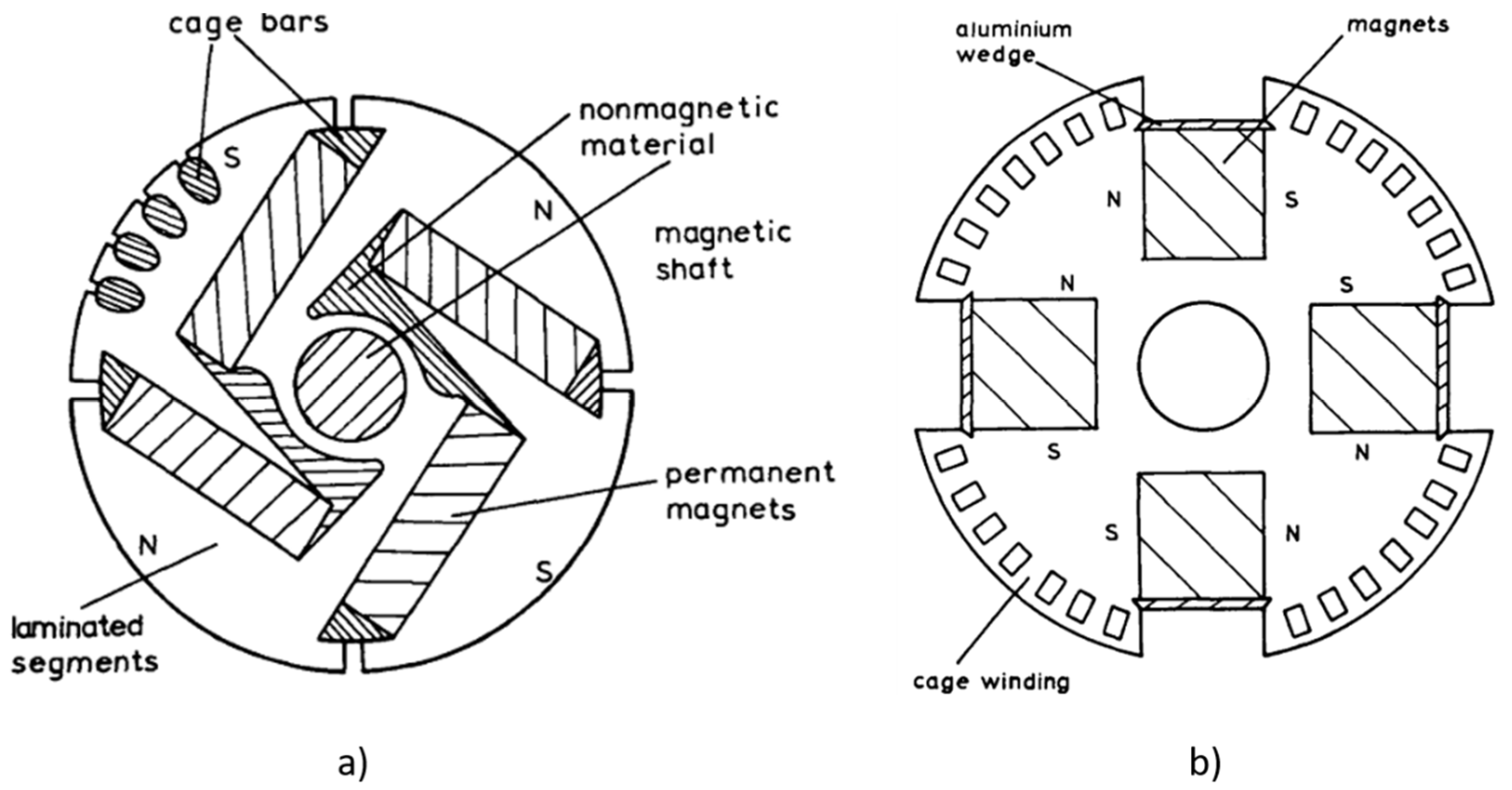
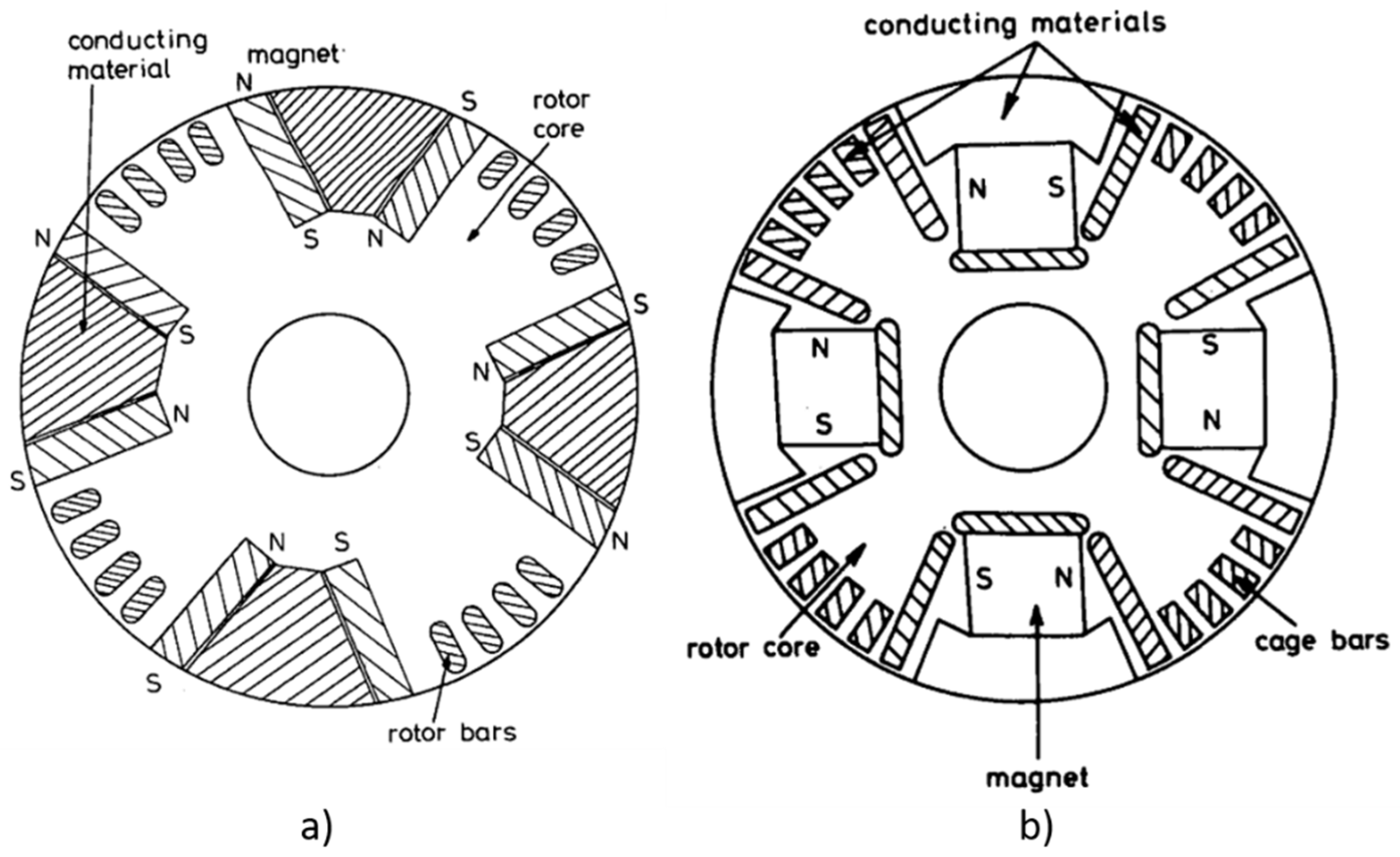
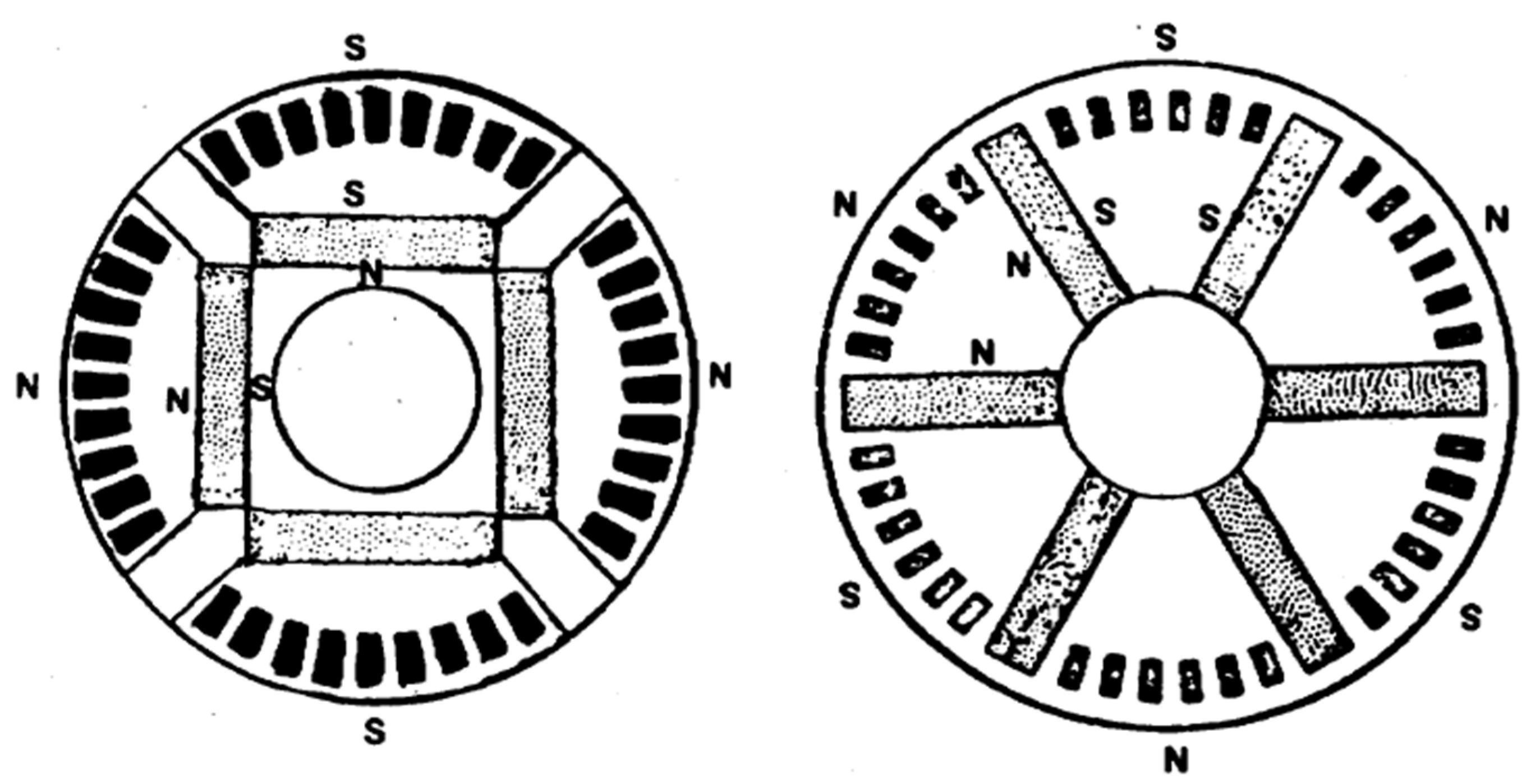
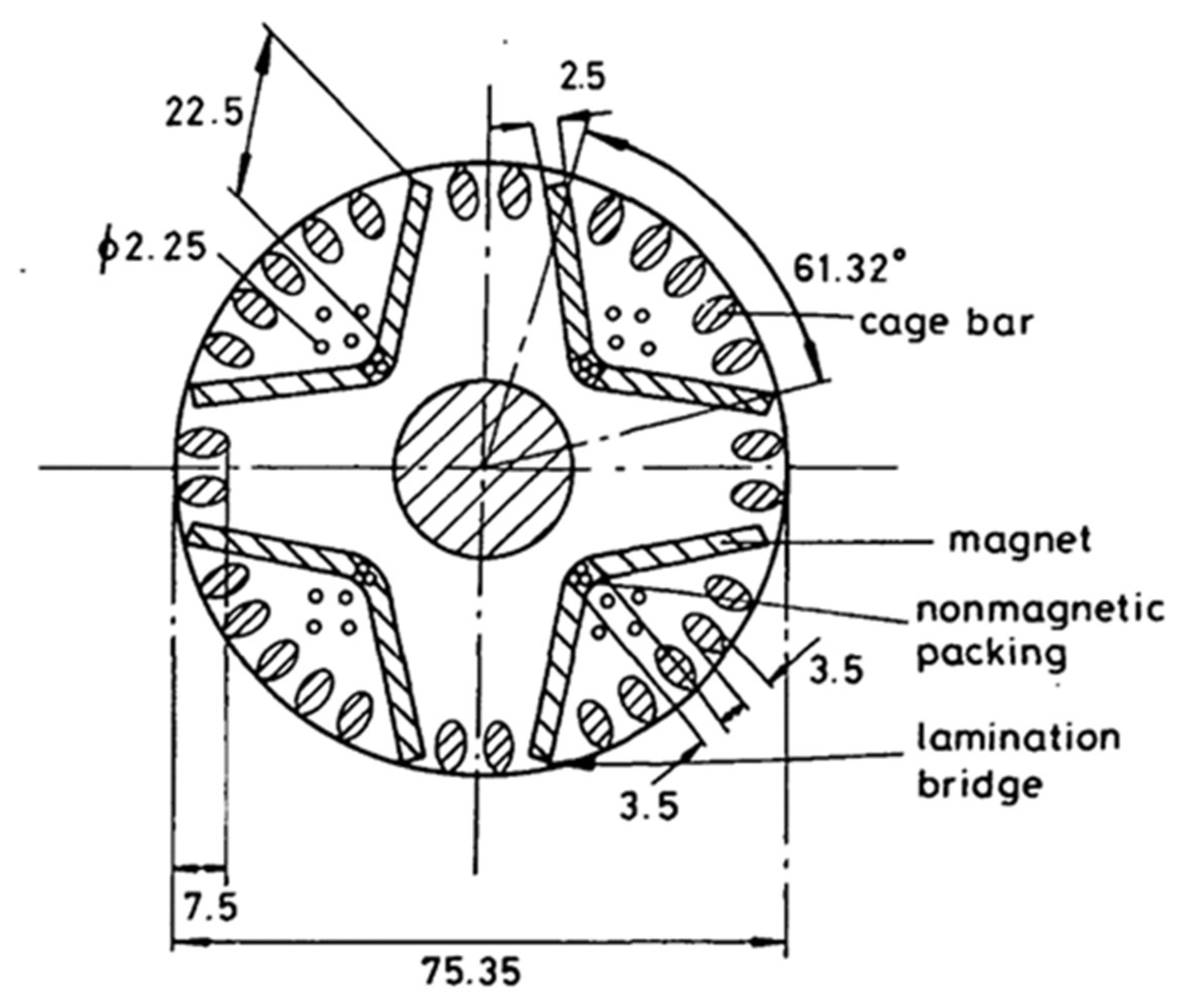
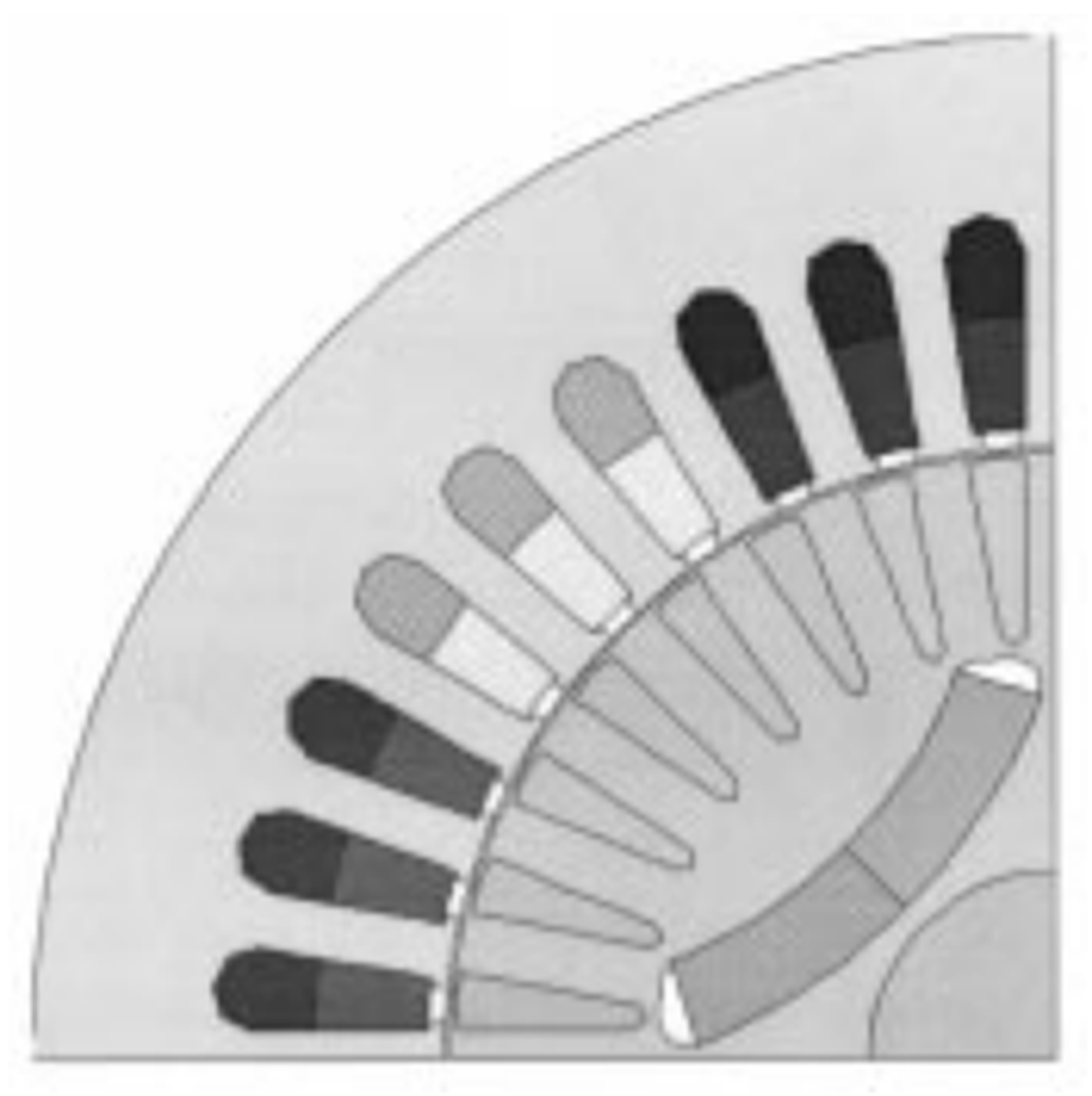
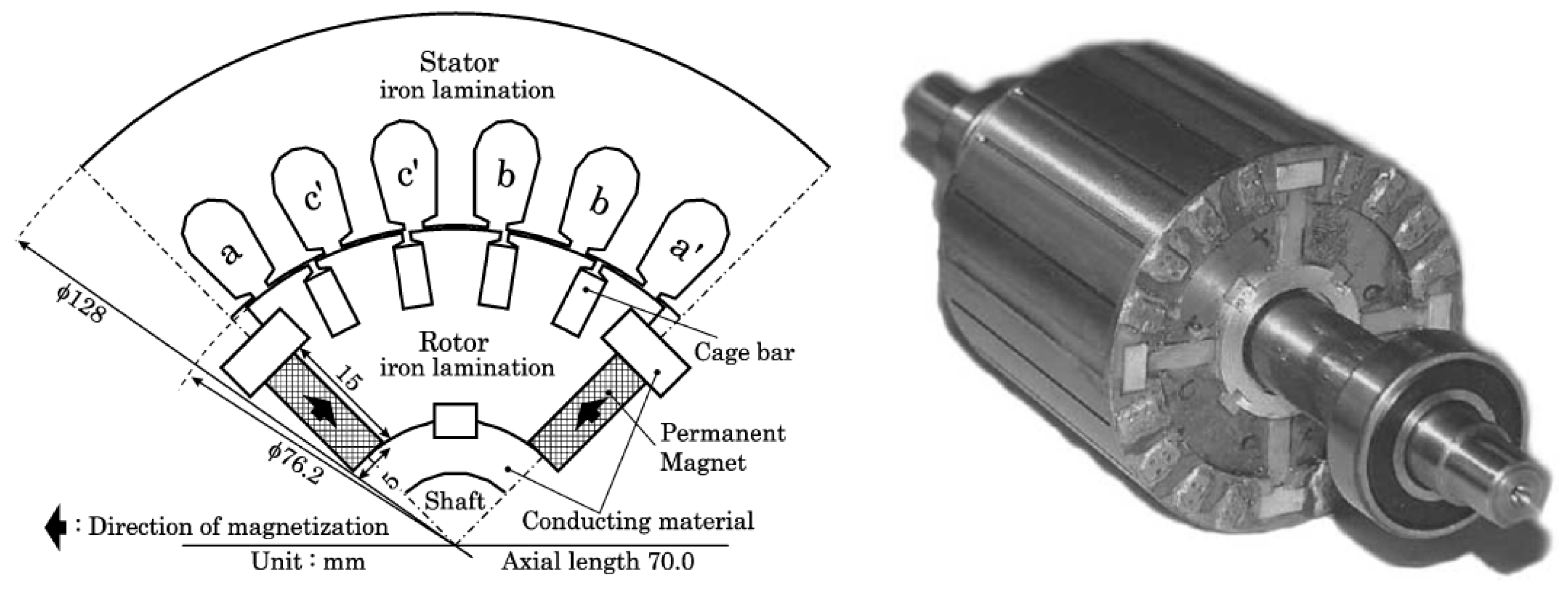
4.1. Historical Rotor Topologies (1950s–2000)
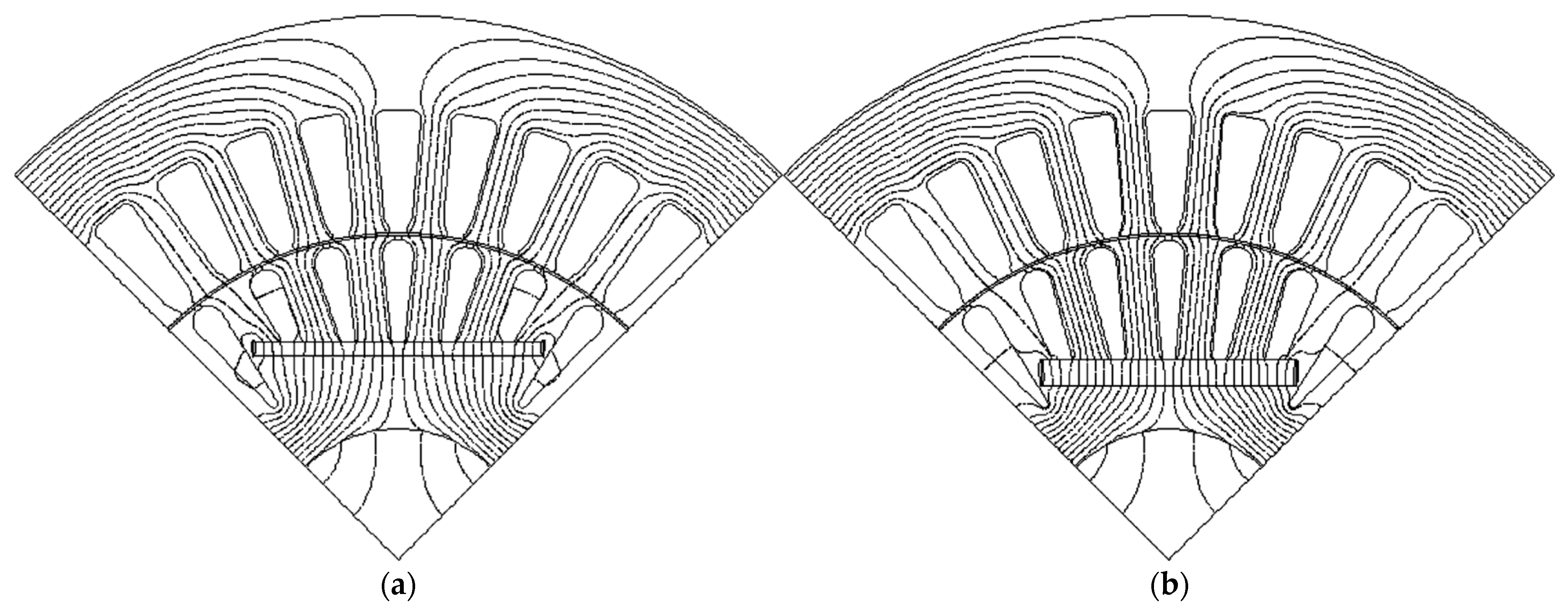
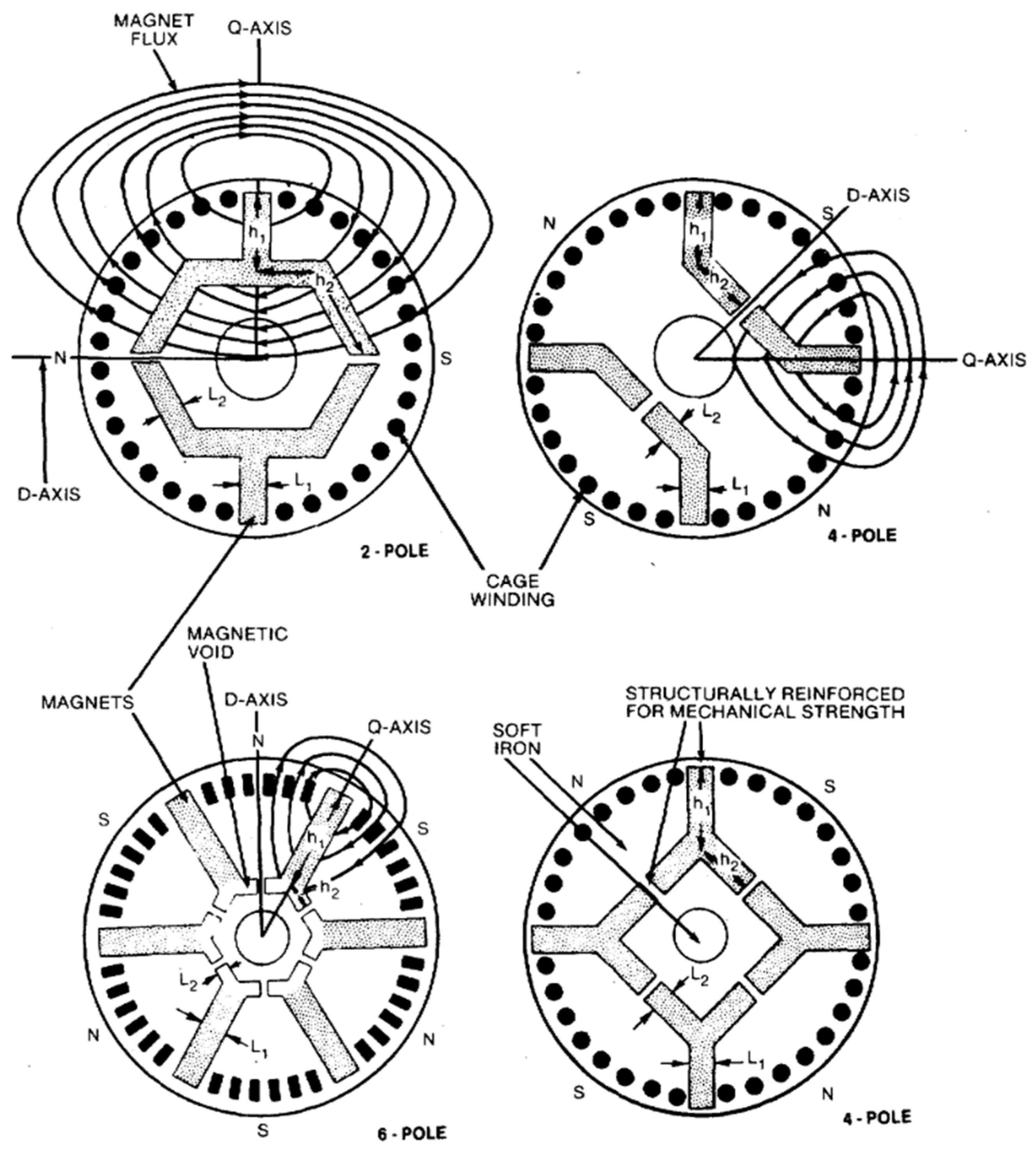
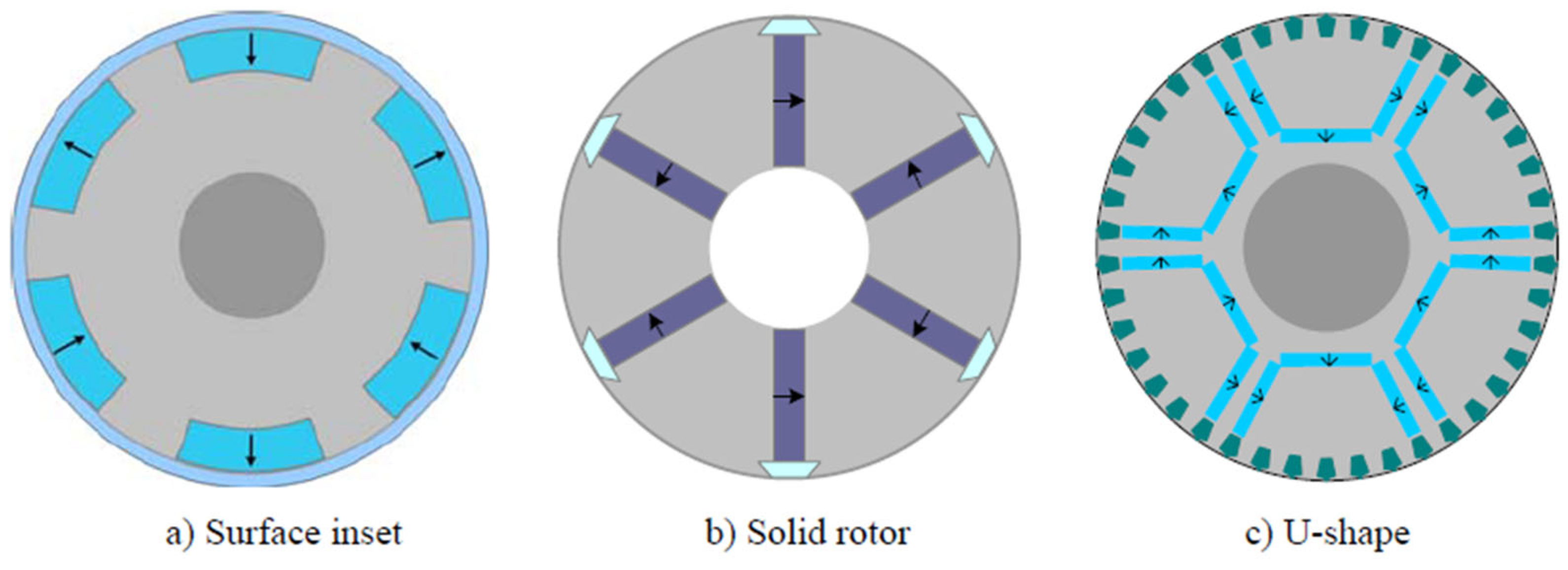
4.2. Modern Rotor Designs
4.3. Emerging Topologies and Startability Solutions
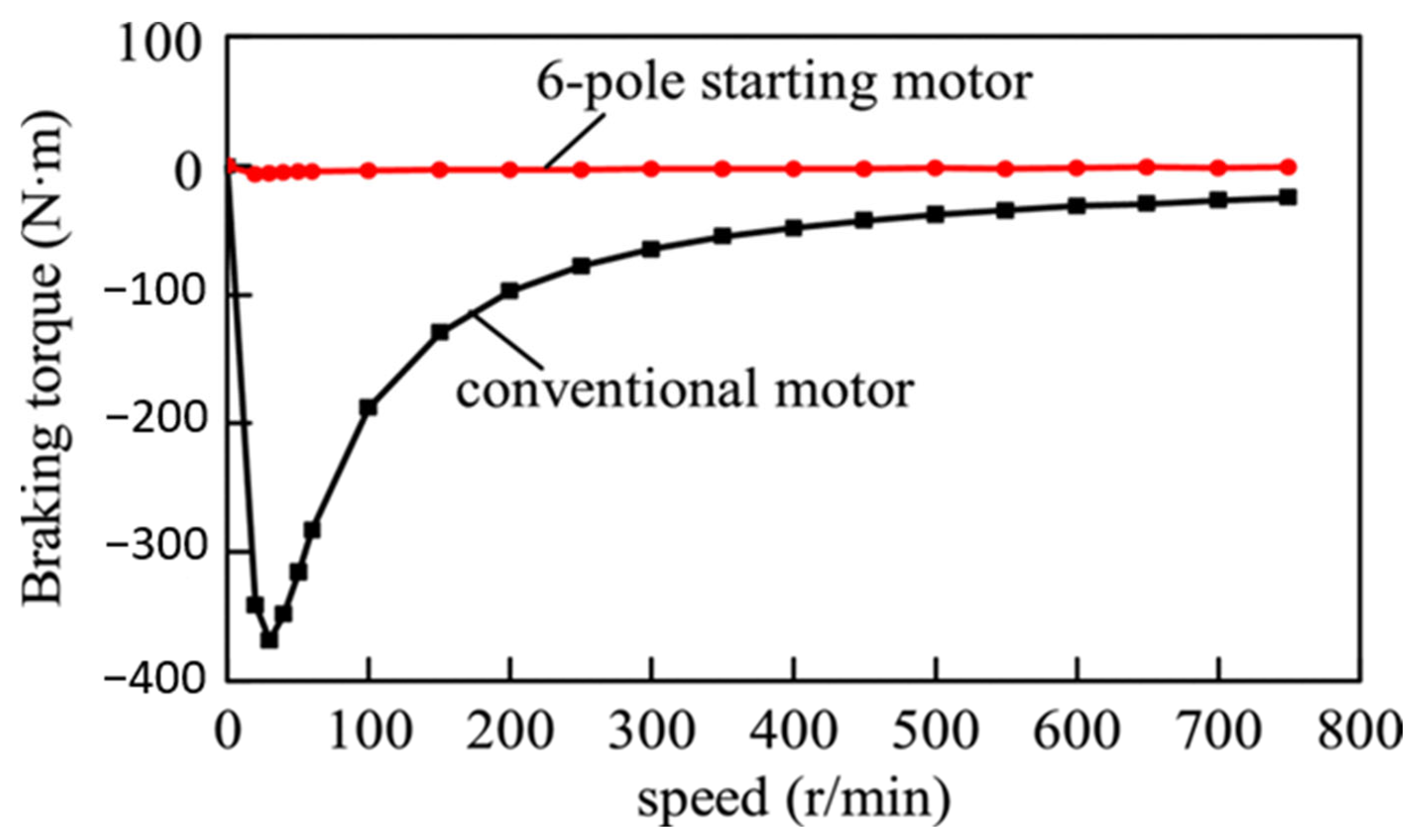
4.3.1. Pole-Changing Configurations
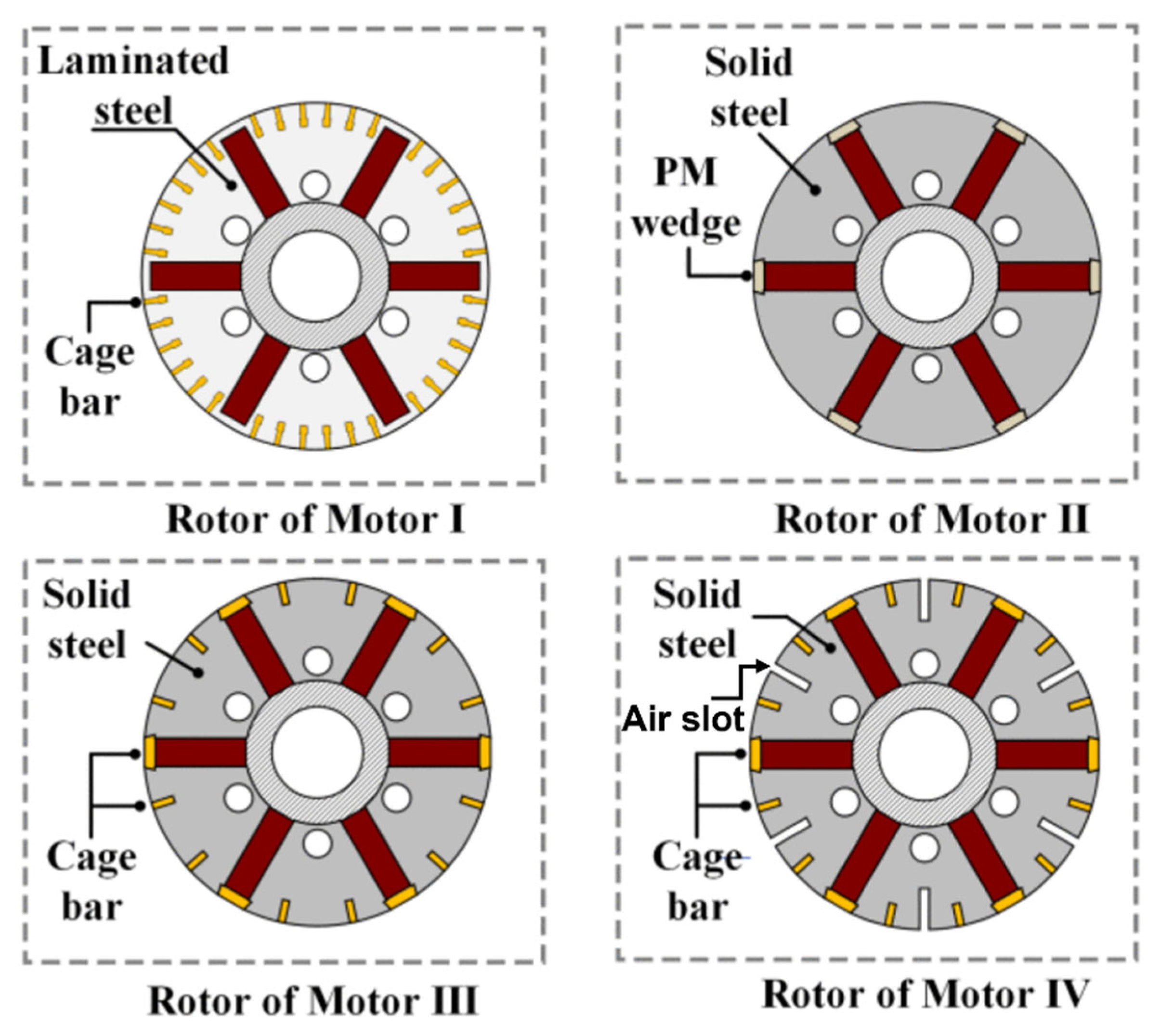
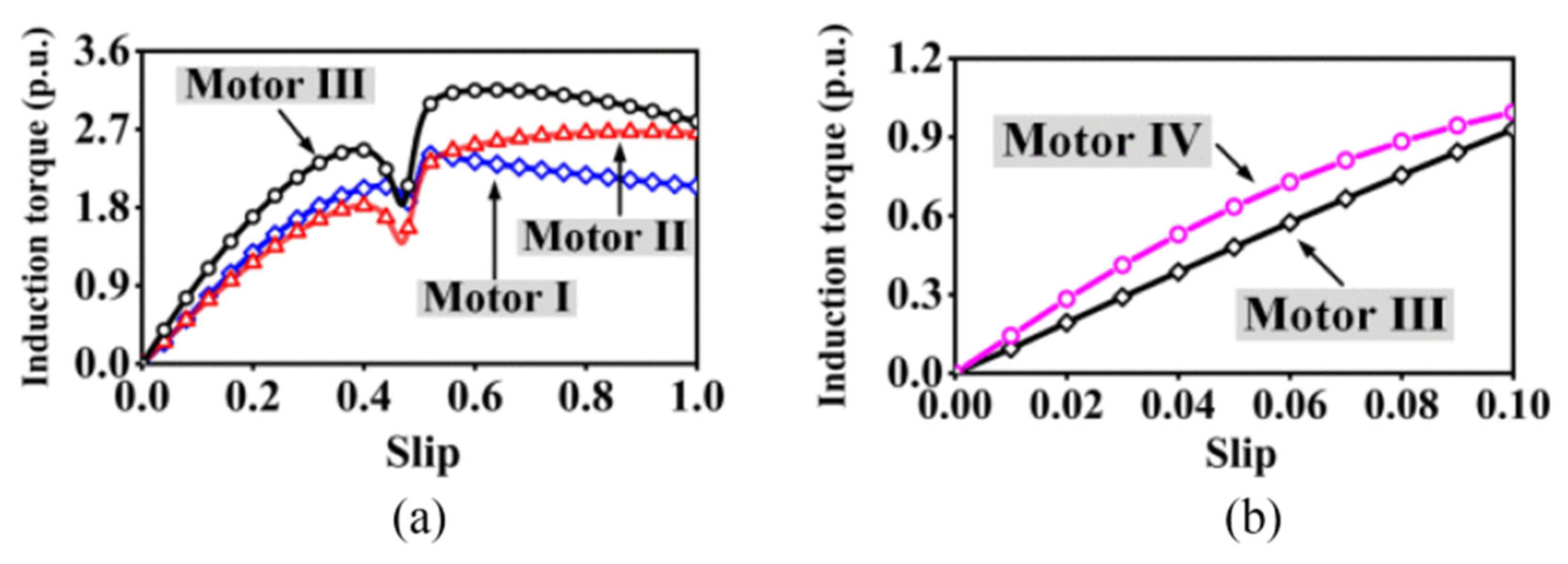
4.3.2. Composite Solid Rotor
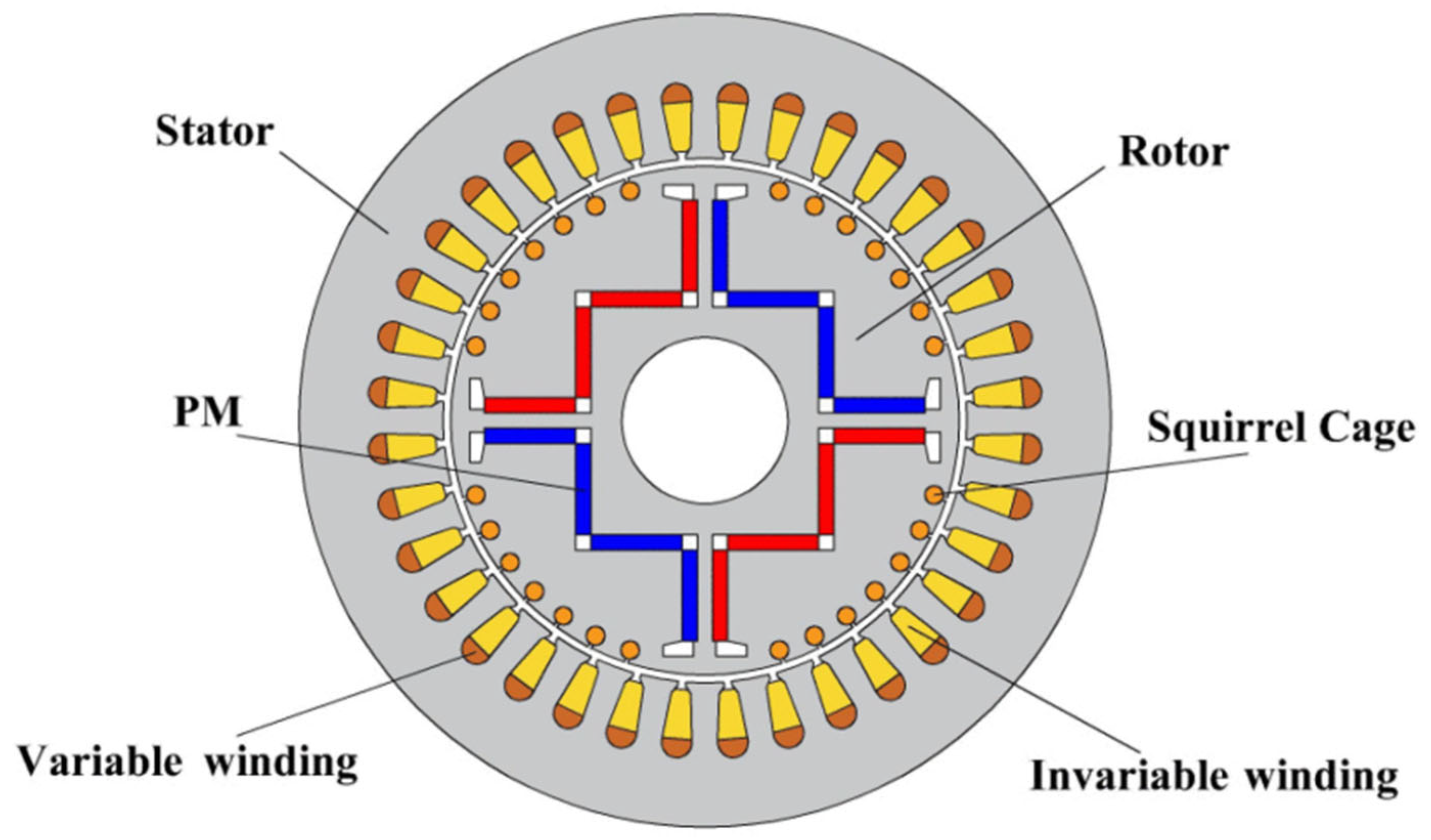
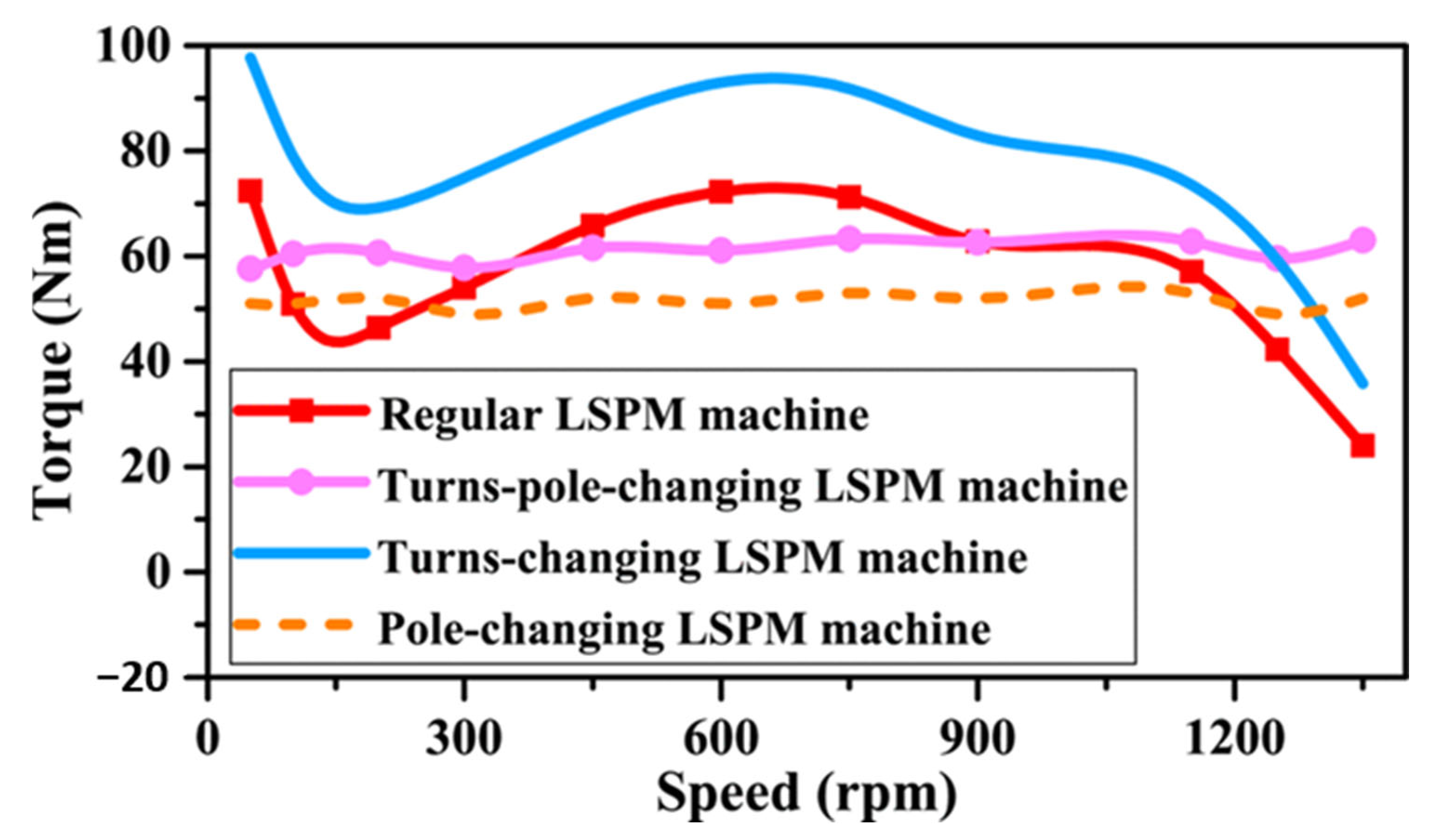
4.3.3. Winding Reconfiguration Technique
4.3.4. Delta-Wye Winding Configuration
5. Industrial Adoption and Economic Viability of LSPMSMs
5.1. Industrial Applications and Commercial Models
5.2. Economic Comparison with IMs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA. World Energy Outlook 2024. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2024 (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- de Souza, D.F.; da Silva, P.P.F.; Sauer, I.L.; de Almeida, A.T.; Tatizawa, H. Life cycle assessment of electric motors—A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 456, 142366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isfahani, A.H.; Vaez-Zadeh, S. Line start permanent magnet synchronous motors: Challenges and opportunities. Energy 2009, 34, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.U.; Chokkalingam, L.N. Review on the evolution of technology advancements and applications of line-start synchronous machines. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElveen, R.F.; Holub, R.; Martin, W.E. Replacing induction motors with caged rotor permanent magnet motors: Application considerations & cost analysis. In Proceedings of the 2017 Petroleum and Chemical Industry Technical Conference (PCIC), Calgary, AB, Canada, 18–20 September 2017; pp. 435–442. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, T. Synchronization of line-start permanent-magnet ac motors. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1984, PAS-103, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palangar, M.F.; Soong, W.L.; Bianchi, N.; Wang, R.-J. Design and optimization techniques in performance improvement of line-start permanent magnet synchronous motors: A review. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. AR6 Synthesis Report: Climate Change 2023. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/syr/ (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy 2024. Available online: https://www.energyinst.org/statistical-review (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Ember. Global Electricity Review 2024. Available online: https://ember-energy.org/latest-insights/global-electricity-review-2024/ (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- IEA. 4E: Policy Guidelines for Motor Driven Units 2016. Available online: https://www.iea-4e.org/projects/the-motor-driven-unit-policy-guidelines/ (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Lu, S.-M. A review of high-efficiency motors: Specification, policy, and technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60034-30; Rotating Electrical Machines—Part 30-3: Efficiency Classes of High Voltage AC Motors (IE-Code). International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- de Almeida, A.T.; Fong, J.; Falkner, H.; Bertoldi, P. Policy options to promote energy efficient electric motors and drives in the EU. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, A.T.; Ferreira, F.J.; Quintino, A. Technical and economical considerations on super high-efficiency three-phase motors. In Proceedings of the 48th IEEE Industrial & Commercial Power Systems Conference, Louisville, KY, USA, 20–24 May 2012; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- EMSA MEPS MAP Export. 2024. Available online: https://www.iea-4e.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/emsa-meps-export-v2.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Rabbi, S.F.; Rahman, M.A. Critical criteria for successful synchronization of line-start IPM motors. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2013, 2, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libert, F.; Soulard, J.; Engstrom, J. Design of a 4-pole line start permanent magnet synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the ICEM 2002: 15th International Conference on Electrical Machines, Brugge, Belgium, 25–28 August 2002; pp. 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- NEMA SM 1; Guide to General-Purpose Synchronous Motors Without Excited Rotor Windings. National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA): Rosslyn, VA, USA, 2021.
- McElveen, R.; Melfi, M.; Daugherty, R. Line start permanent magnet motors-Starting, standards and application guidelines. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Petroleum and Chemical Industry Technical Conference (PCIC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–10 September 2014; pp. 129–139. [Google Scholar]
- Isfahani, A.H.; Vaez-zadeh, S. Rotor resistance for improved start-up performance of line-start permanent-magnet synchronous motors. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–15 June 2018; pp. 832–838. [Google Scholar]
- Jedryczka, C.; Wojciechowski, R.M.; Demenko, A. Finite element analysis of the asynchronous torque in LSPMSM with non-symmetrical squirrel cage winding. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2014, 46, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isfahani, A.H.; Vaez-Zadeh, S. Effects of magnetizing inductance on start-up and synchronization of line-start permanent-magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 47, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wymeerschl, B.; De Belie, F.; Rasmussen, C.B.; Vandevelde, L. The effect of design considerations on the synchronization capability limits of line-start permanent-magnet synchronous motors. In Proceedings of the 2018 XIII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 988–994. [Google Scholar]
- McElveen, R.F.; Budzynski, R.; Jarvinen, J.; Martin, W.E. Solving The Synchronization Problem of Line Start Permanent Magnet Motors. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE IAS Petroleum and Chemical Industry Technical Conference (PCIC), Denver, CO, USA, 26–29 September 2022; pp. 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Merrill, F. Permanent magnet excited synchronous motors. Electr. Eng. 1955, 74, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, D.P.M.; Adkins, B. The permanent-magnet synchronous motor. Proc. IEE-Part A Power Eng. 1962, 109, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, K.; Barnard, W. Novel design of self-starting synchronous motor. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1971, 118, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, K.; Barnard, W.; Jabbar, M. Hybrid permanent-magnet synchronous motors. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1978, 125, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, K.; Jabbar, M. High-field self-starting permanent-magnet synchronous motor. IEE Proc. B (Electr. Power Appl.) 1981, 128, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honsinger, V. The fields and parameters of interior type AC permanent magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Power Appar. Syst. 1982, PAS-101, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, B.; Hamed, S.; Baines, G. Parameters and performance of a high-field permanent-magnet synchronous motor for variable-frequency operation. IEE Proc. B (Electr. Power Appl.) 1985, 132, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A.M.; McClay, C.I. The design of high-efficiency line-start motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2000, 36, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, K.; Rahman, M.A. High-efficiency line-start interior permanent-magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2004, 40, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Takorabet, N.; Sargos, F.-M.; Wang, X. Design and analysis of different line-start PM synchronous motors for oil-pump applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 1816–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elistratova, V. Conception Optimale D’une Gamme de Moteurs Synchrones à Démarrage Direct à Haute Performance Energétique. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Lille Nord-de-France, Lille, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ghahfarokhi, M.M.; Aliabad, A.D.; Boroujeni, S.T.; Amiri, E.; Faradonbeh, V.Z. Analytical modelling and optimisation of line start LSPM synchronous motors. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Ro, J. Analytical modeling for optimal rotor shape to design highly efficient line-start permanent magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 145672–145686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwozdziewicz, M.; Zawilak, J. Induced pole permanent magnet synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Electrical Machines (SME), Naleczow, Poland, 18–21 June 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ugale, R.; Chaudhari, B. A new rotor structure for line start permanent magnet synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Electric Machines & Drives Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 12–15 May 2013; pp. 1436–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Ugale, R.T.; Chaudhari, B.N. Performance enhancement of line start permanent magnet synchronous motor with a special consequent pole rotor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 36, 1972–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyskawinski, W.; Jedryczka, C.; Szelag, W. Influence of magnet and cage shape on properties of the line start synchronous motor with powder hybrid rotor. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Electrical Machines (SME), Naleczow, Poland, 18–21 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Tian, M.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. Analysis of the synchronization process and the synchronization capability for a novel 6/8-pole changing LSPMSM. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 56, 7507806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhao, W.; Li, C. A novel line-start permanent magnet synchronous motor with 6/8 pole changing stator winding. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, X.; Qu, R. Comparison of different types of pole-changing line-start permanent magnet motors. In Proceedings of the 2018 XIII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 2051–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Wang, X.; Li, G. Line-start permanent magnet synchronous motor starting capability improvement using pole-changing method. In Proceedings of the 11th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Hefei, China, 5–7 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Parameters determination and dynamic modelling of line-start permanent-magnet synchronous motor with a composite solid rotor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 13, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Starting performance improvement of line-start permanent-magnet synchronous motor using composite solid rotor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 54, 7400504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Comparative parameters investigation of composite solid rotor applied to line-start permanent-magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 8206305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Design of a large capacity line-start permanent magnet synchronous motor equipped with hybrid salient rotor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 6662–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yan, B.; Wang, X. Dynamic Model of a Line-Start Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Equipped with Hybrid Rotor. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 10, 2974–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, X.; Qu, R. Improvement of starting performance for line-start permanent magnet motors by winding reconfiguration. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 2441–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, X.; Qu, R. Line-start permanent magnet motors with variable coil turns. In Proceedings of the 2018 XIII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 2212–2218. [Google Scholar]
- Biljee, B. SynchroVERT® IE4 Motors. Available online: https://www.bharatbijlee.com/electric-motors/product-range/synchrovert-ie4-motors/ (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- WEG. WQuattro. Available online: https://www.weg.net/catalog/weg/RS/en/Electric-Motors/Low-Voltage-IEC-Motors/Three-Phase/W22-Quattro/WQuattro/p/MKT_WMO_TEXT_IMAGE_3PHASE_TEFC_WQUATTRO (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- SEW Eurodrive. DR…J Synchronous Motors (LSPM Technology). Available online: https://www.sew-eurodrive.es/products/motors/ac_motors/ac_motors_drj_with_lspm_technology/ac_motors_drj_with_lspm_technology.html (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- SISME. LSPM Refrigeration Compressor Motors. Available online: https://sisme.it/en/air-conditioning-and-refrigeration-motors/motors-for-refrigeration-compressors/ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Reuland. Line Start Permanent Magnet Motors. Available online: https://www.reuland.com/line-start-permanent-magnet-motors (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Kazakbaev, V.; Prakht, V.; Dmitrievskii, V.; Oshurbekov, S.; Golovanov, D. Life cycle energy cost assessment for pump units with various types of line-start operating motors including cable losses. Energies 2020, 13, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

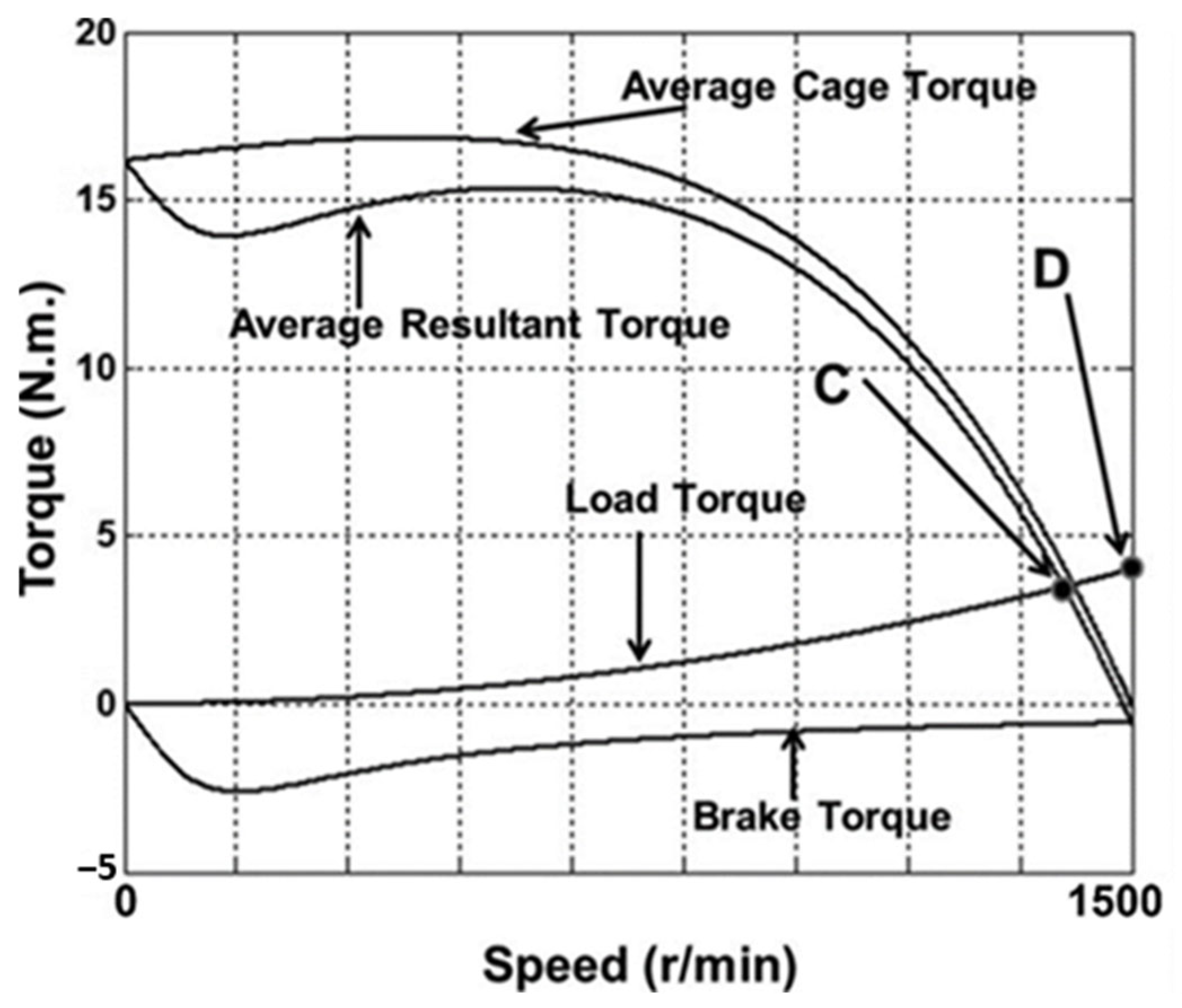
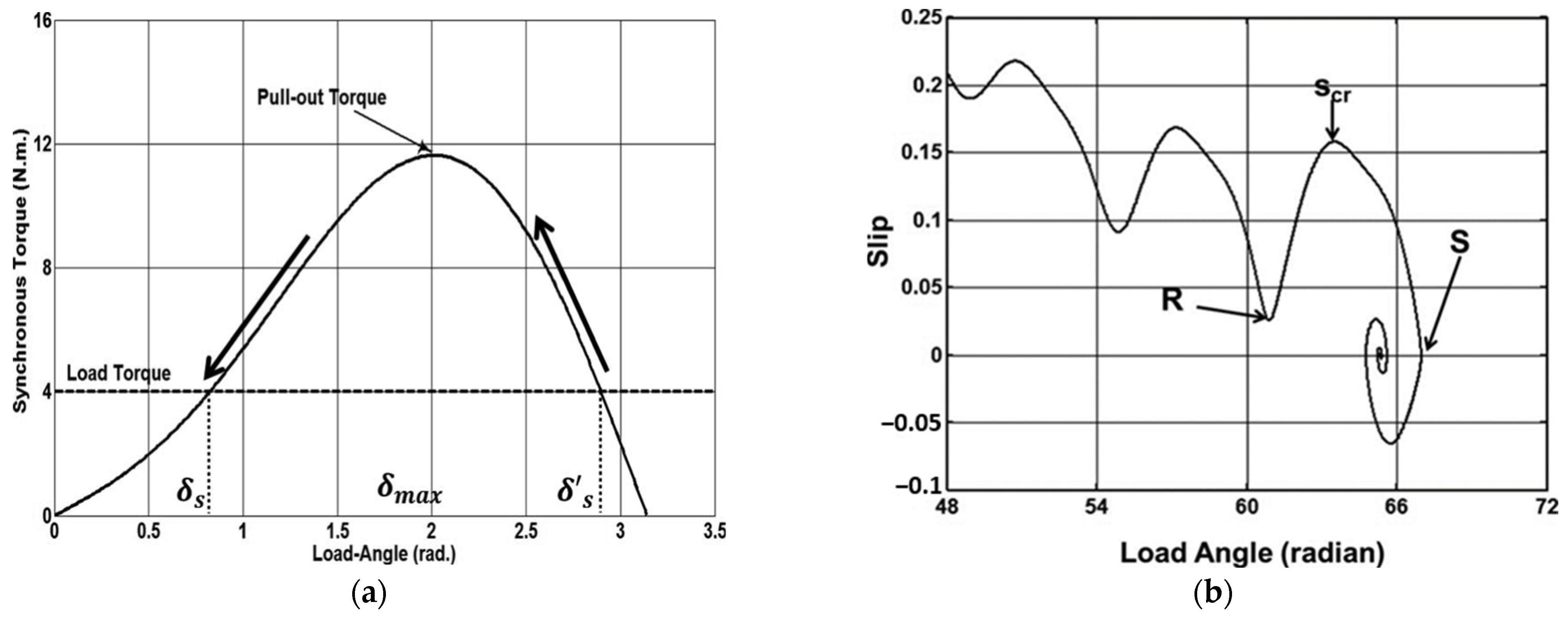
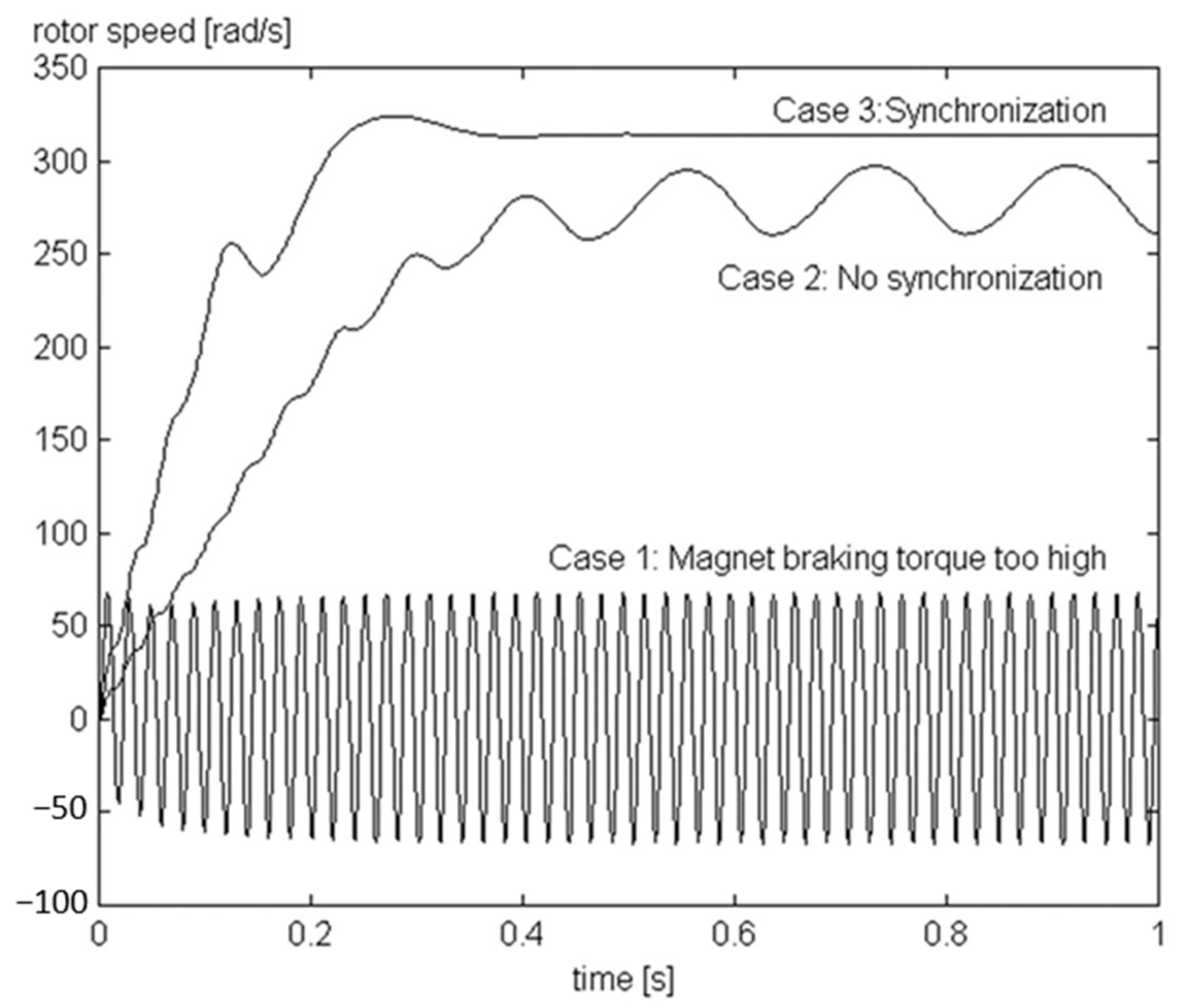
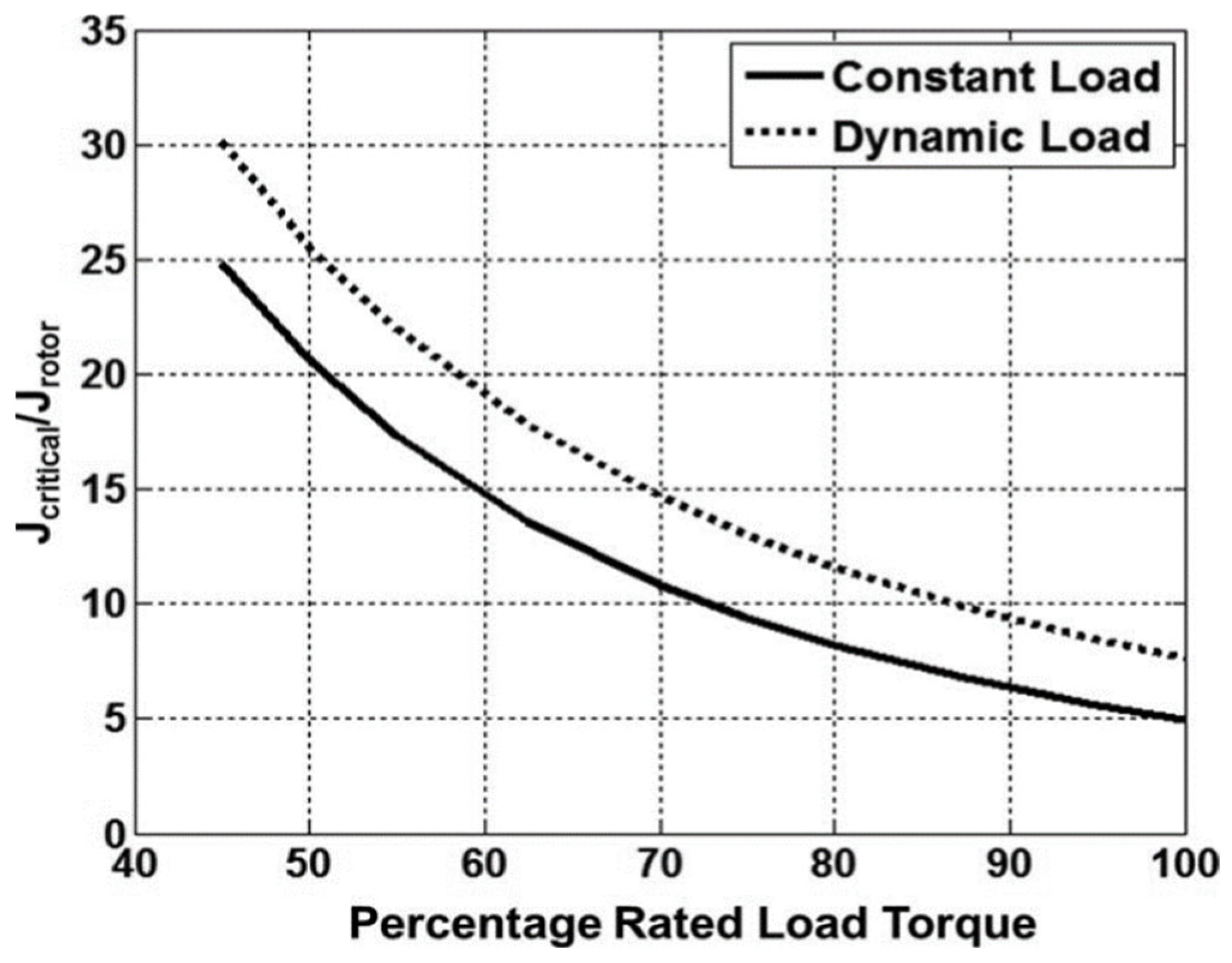

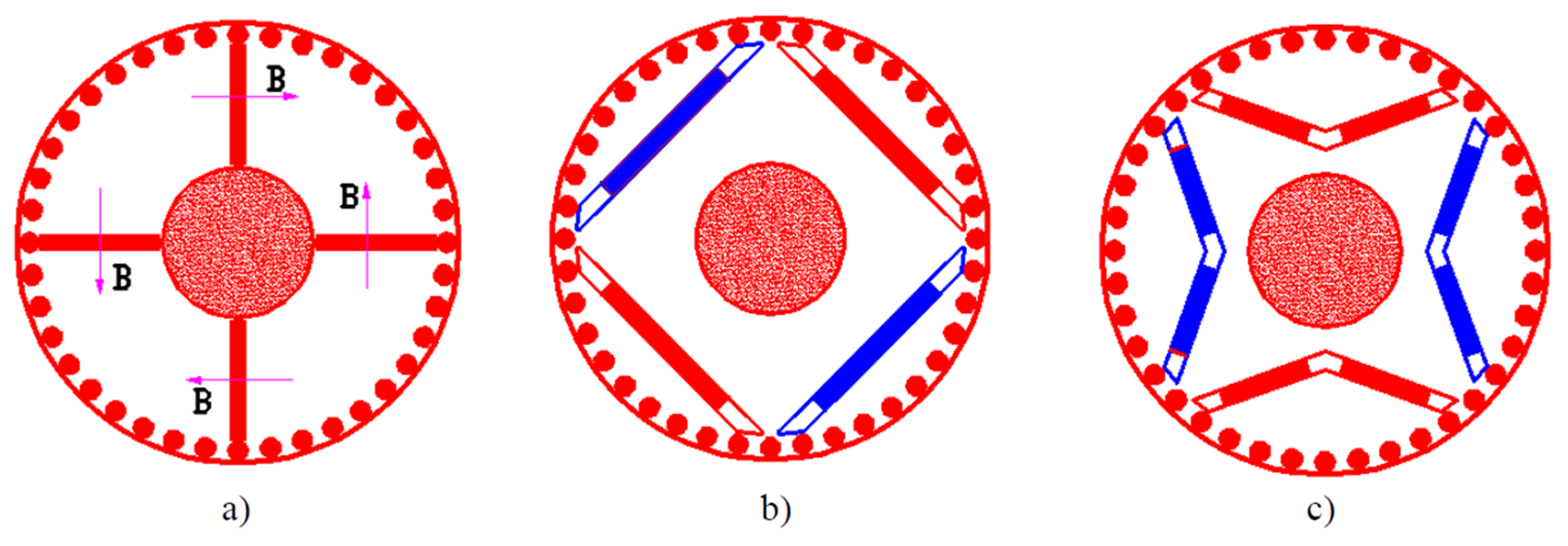

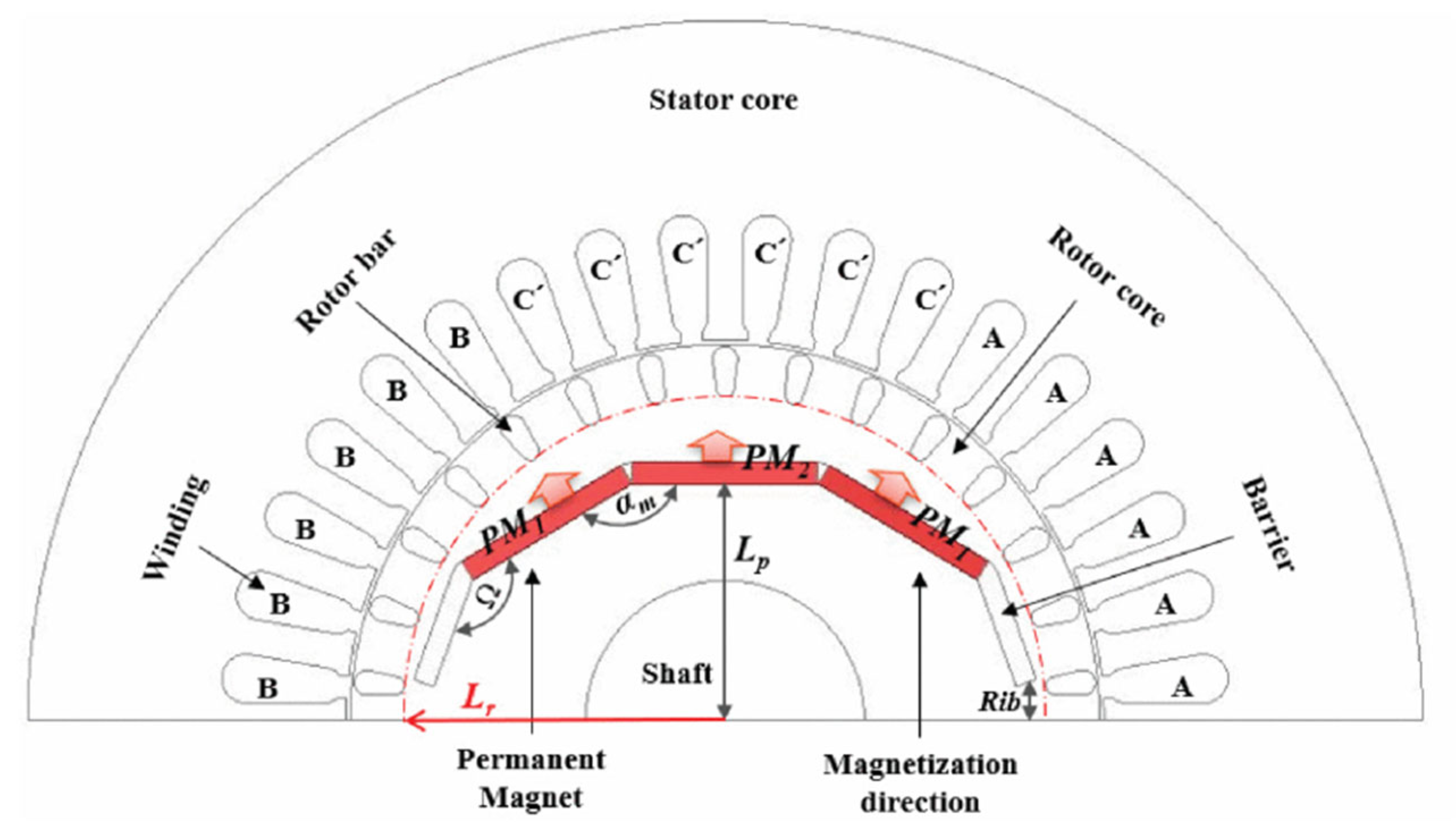

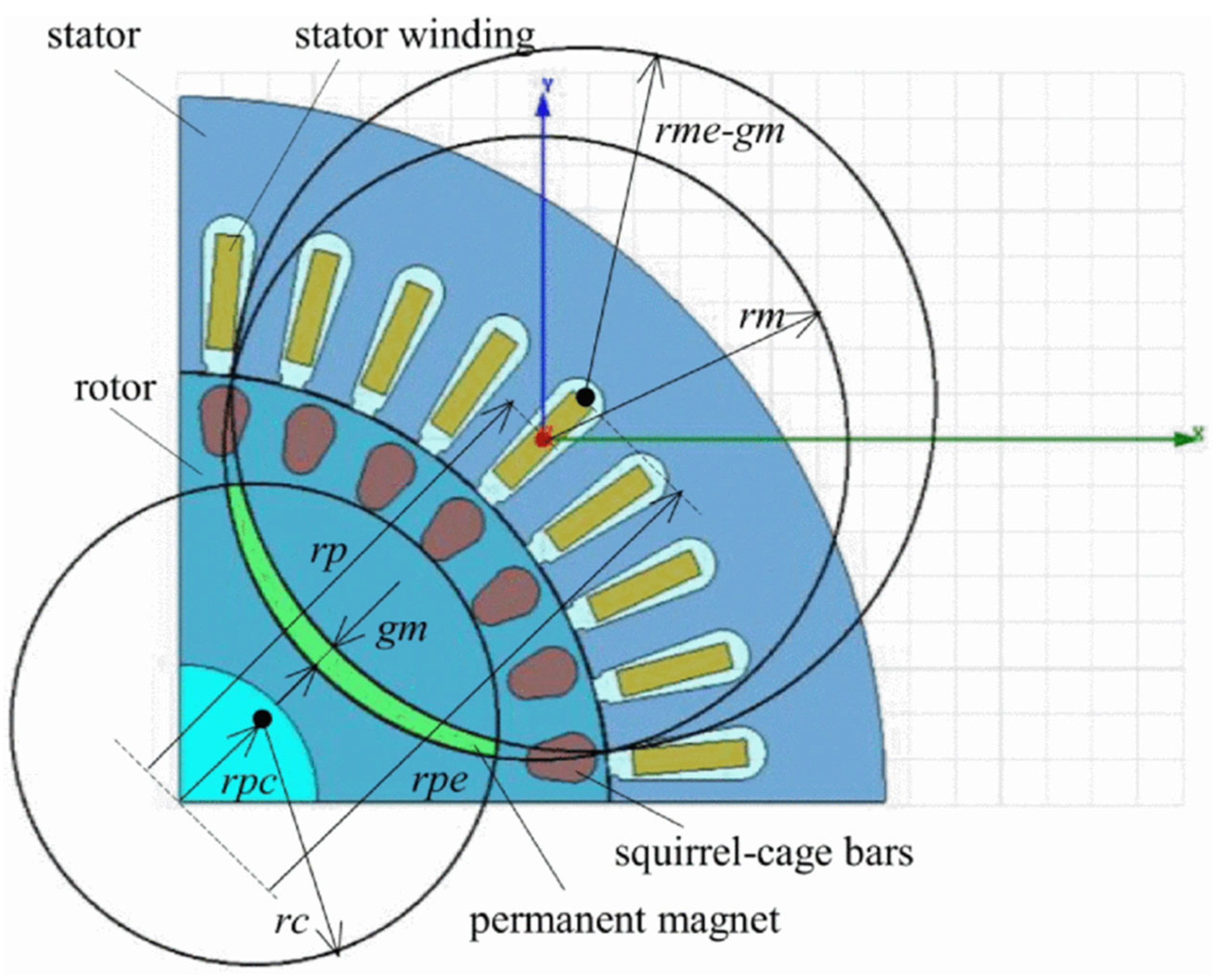
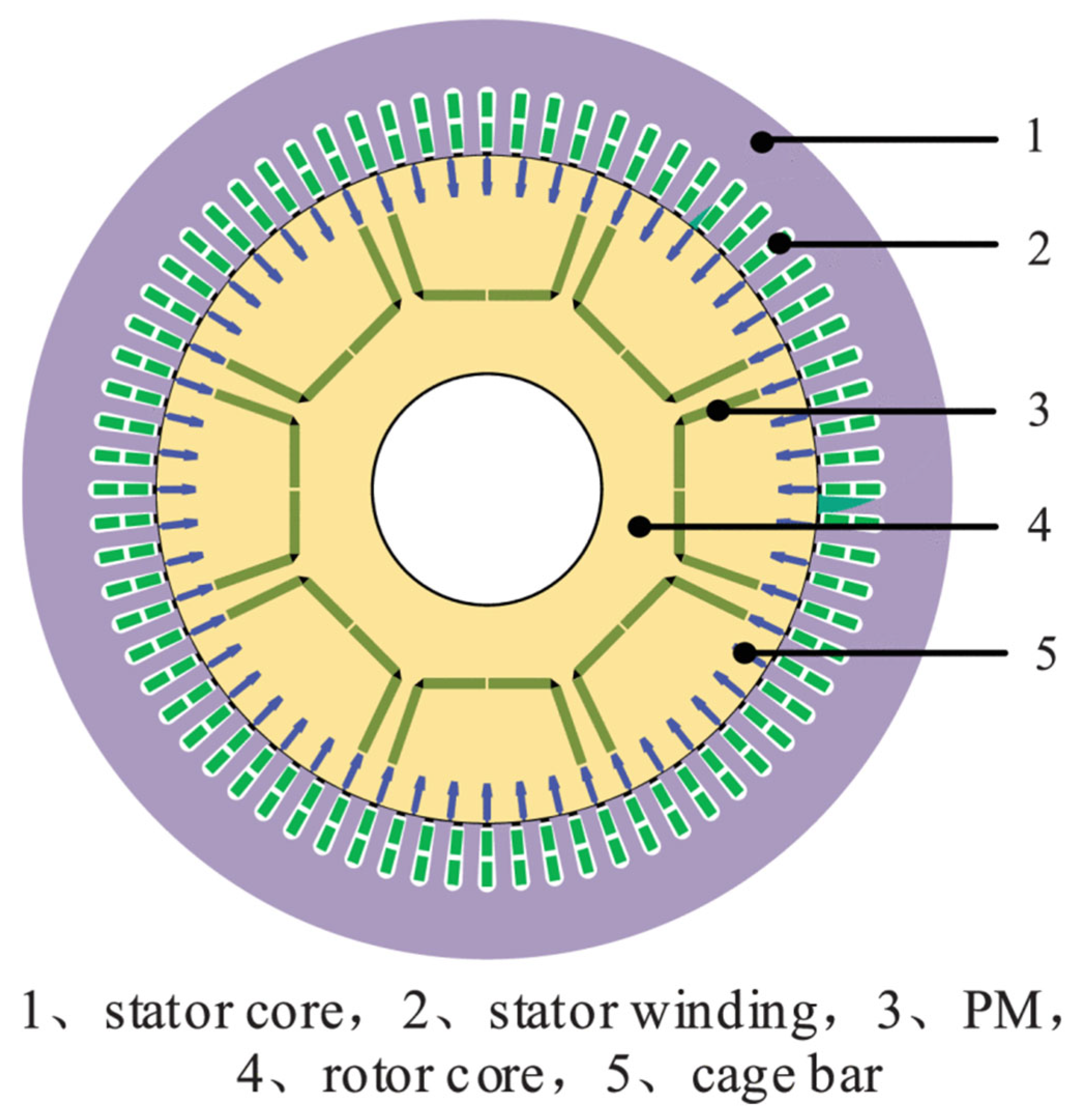
| Motors MEPS Levels | Country/Jurisdiction |
|---|---|
| IE3 | Brazil, Canada, European Union, Japan, Korea, Mexico, Colombia, Saudi Arabia, China, Singapore, Switzerland, Chinese Taipei, Turkey, United States |
| IE2 | Australia, Chile, Ecuador, India, New Zealand |
| Topology | Output Power (kW) | T_avg (Nm) | Speed (rpm) | Power Factor | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6/8 Pole-changing LSPMSM [43] | 30 | 382 | NA | NA | NA |
| Composite solid rotor [50] | 355 | 3390 | NA | NA | NA |
| Turns-changing LSPMSM [52] | 7.5 | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Induced pole rotor [39] | 2 | 12.7 | 1500 | 0.95 | 88.2 |
| Convex-profile LSPMSM [38] | 7.5 | 19 | 3600 | 0.91 | 94.7 |
| Curve-shaped powder material PM [42] | 3.45 | 22 | 1500 | 0.95 | 93 |
| Double-layer U-shaped PM LSPMSM [37] | NA | NA | 1500 | NA | NA |
| Topology | Key Feature | Main Advantage | Drawback |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6/8 Pole-Changing Stator | Switches pole pairs between startup and synchronous mode | Eliminates braking torque, improves startup | Requires dual winding and switching mechanism |
| Composite Solid Rotor | Solid rotor with embedded cage and surface air slots | High torque and strong synchronization capability | Increased rotor weight and manufacturing complexity |
| Turns-Changing Winding | Varies coil turns between startup and steady-state modes | Boosts starting torque | Needs switching control; more complex stator |
| LSPMSM Motor | Efficiency | Power | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| SynchroVERT | IE4 class | 1.5–45 kW | Pump or Fan [54] |
| WQuattro | IE4 class | 0.37–7.5 kW | Replacement of SCIM in Pumps or Fans [55] |
| DRU.J series | IE4 class | 0.25–4 kW | Material Supply in Textile Machinery [56] |
| LSPMSM compressors | IE4 class | 1.86–44.7 kW | Industrial and domestic refrigeration, Air conditioning [57] |
| Reuland LSPMSM | IE4 class | Up to 37 KW | Hoists, cranes, elevators, mixers, and conveyors [58] |
| IEC Class | IE1 | IE2 | IE3 | IE4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motor Technology | SCIM | SCIM | SCIM | LSPM |
| Motor Price with 40% Discount (EUR) | .. | 328 | 378 | 764 |
| Price Difference Compared to IE2 SCIM (EUR) | .. | .. | 50 | 386 |
| Motor Efficiency (%) | 87.0 | 89.0 | 91.5 | 93.5 |
| Consumption by Replacing IE2-Class Motor (kWh/year) | 51,983 | 50,815 | 49,426 | 48,629 |
| Energy Savings by Replacing IE2-Class Motor (kWh/year) | −1168 | 0 | 1388 | 2186 |
| Energy Savings by Replacing IE2-Class Motor (EUR/year) | −81.8 | 0 | 97.2 | 153.0 |
| Simple Payback Time (year) | .. | .. | 0.5 | 2.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ould Lahoucine, Y.; Raute, R.; Caruana, C. Line-Start Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: Evolution, Challenges, and Industrial Prospects. Energies 2025, 18, 4545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174545
Ould Lahoucine Y, Raute R, Caruana C. Line-Start Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: Evolution, Challenges, and Industrial Prospects. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174545
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuld Lahoucine, Yahia, Reiko Raute, and Cedric Caruana. 2025. "Line-Start Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: Evolution, Challenges, and Industrial Prospects" Energies 18, no. 17: 4545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174545
APA StyleOuld Lahoucine, Y., Raute, R., & Caruana, C. (2025). Line-Start Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: Evolution, Challenges, and Industrial Prospects. Energies, 18(17), 4545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174545







