Attention Mechanism-Based Micro-Terrain Recognition for High-Voltage Transmission Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
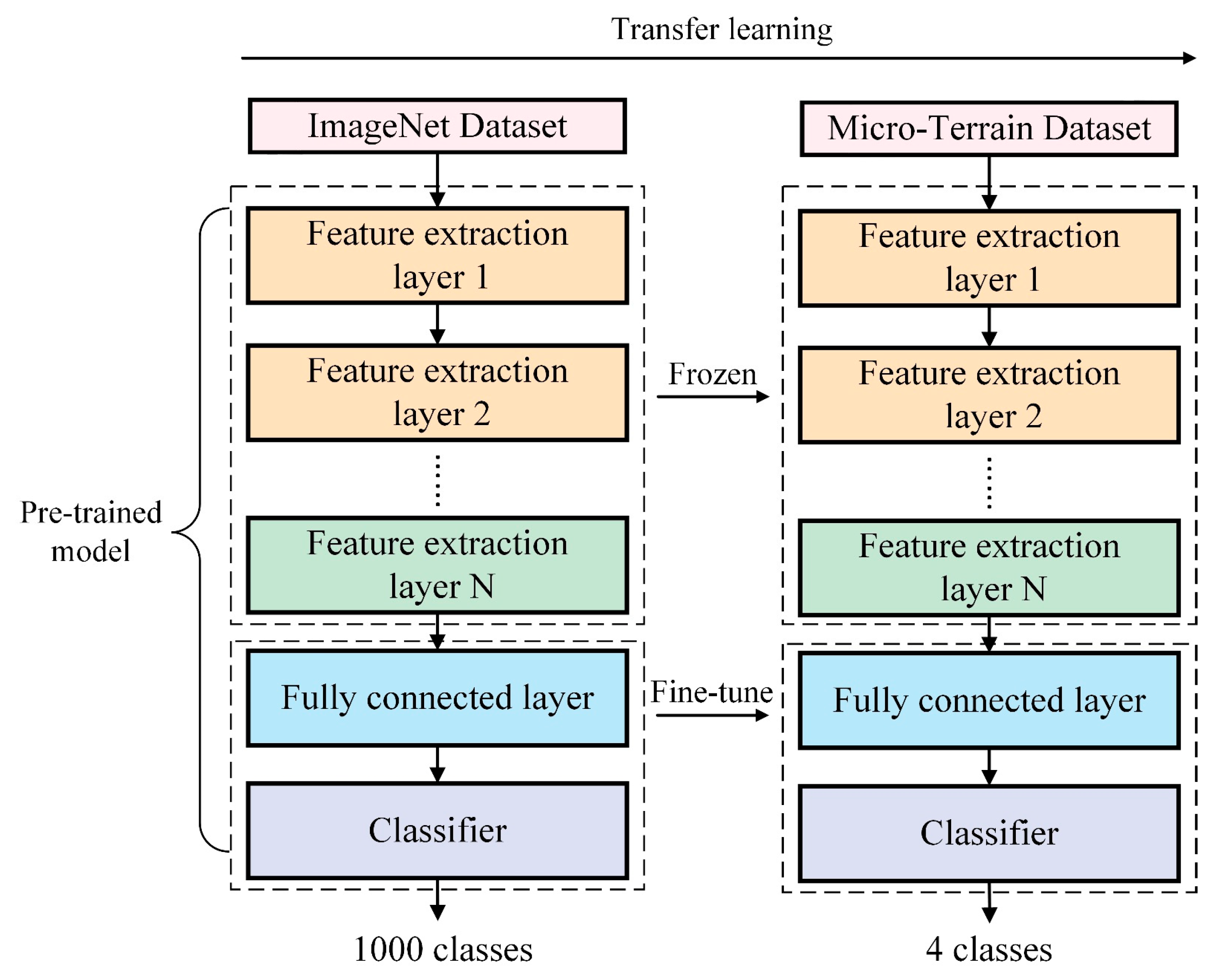
2. Methodology
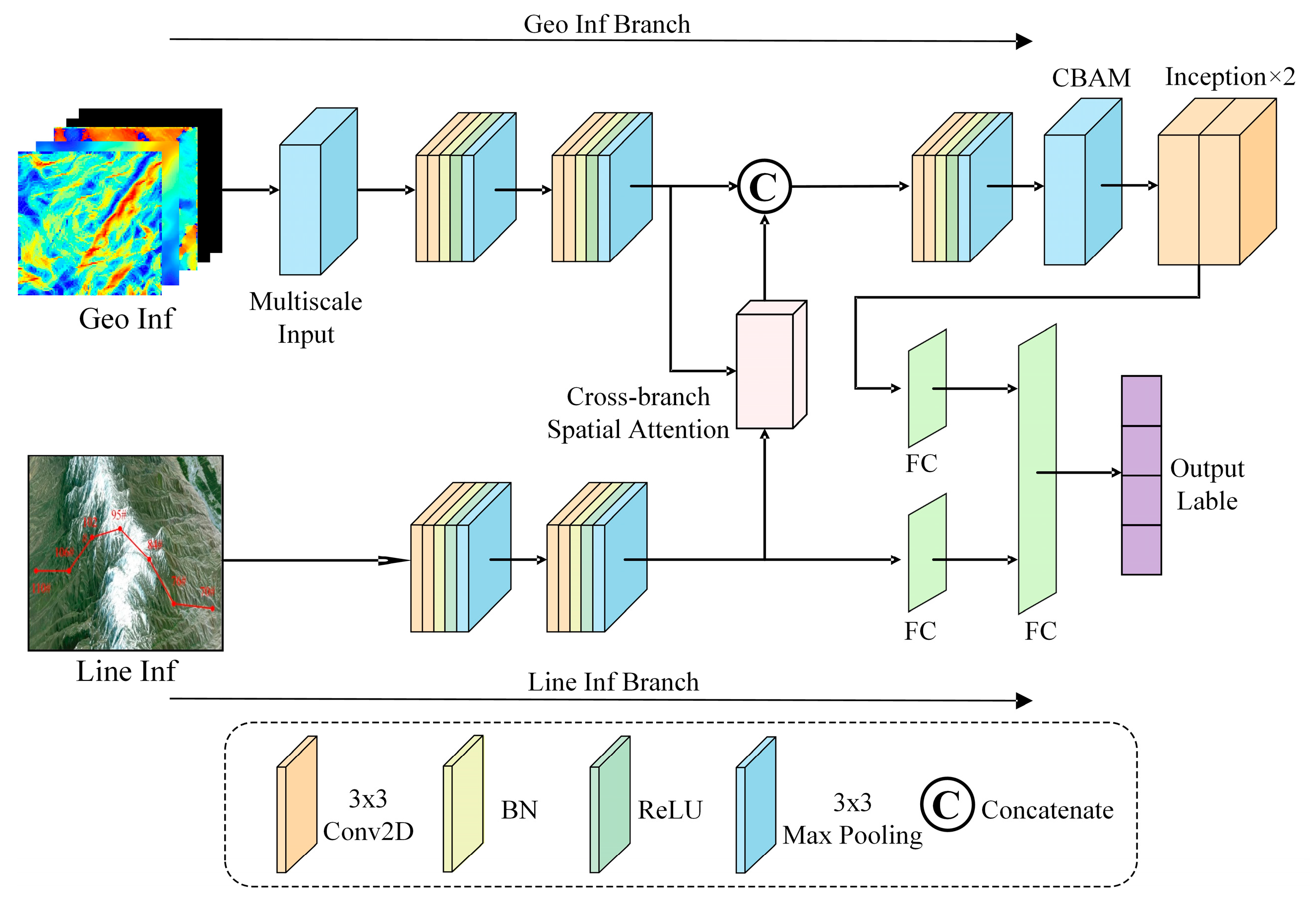
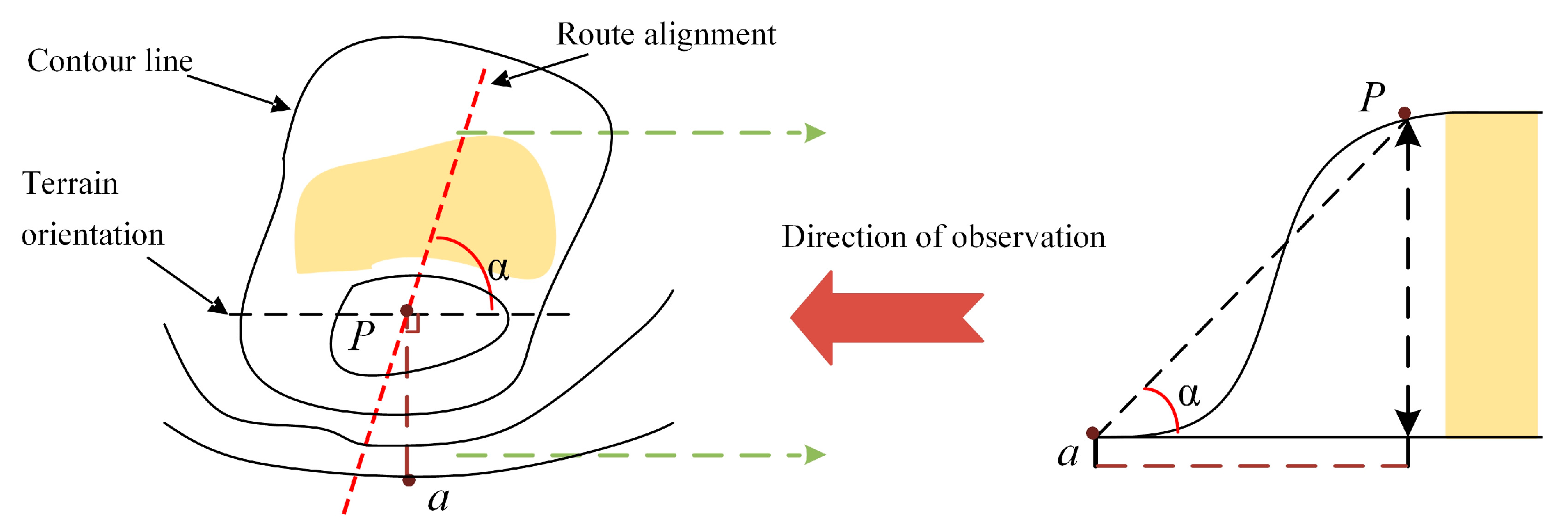
2.1. Input Data Formulation and Dual-Branch Structure
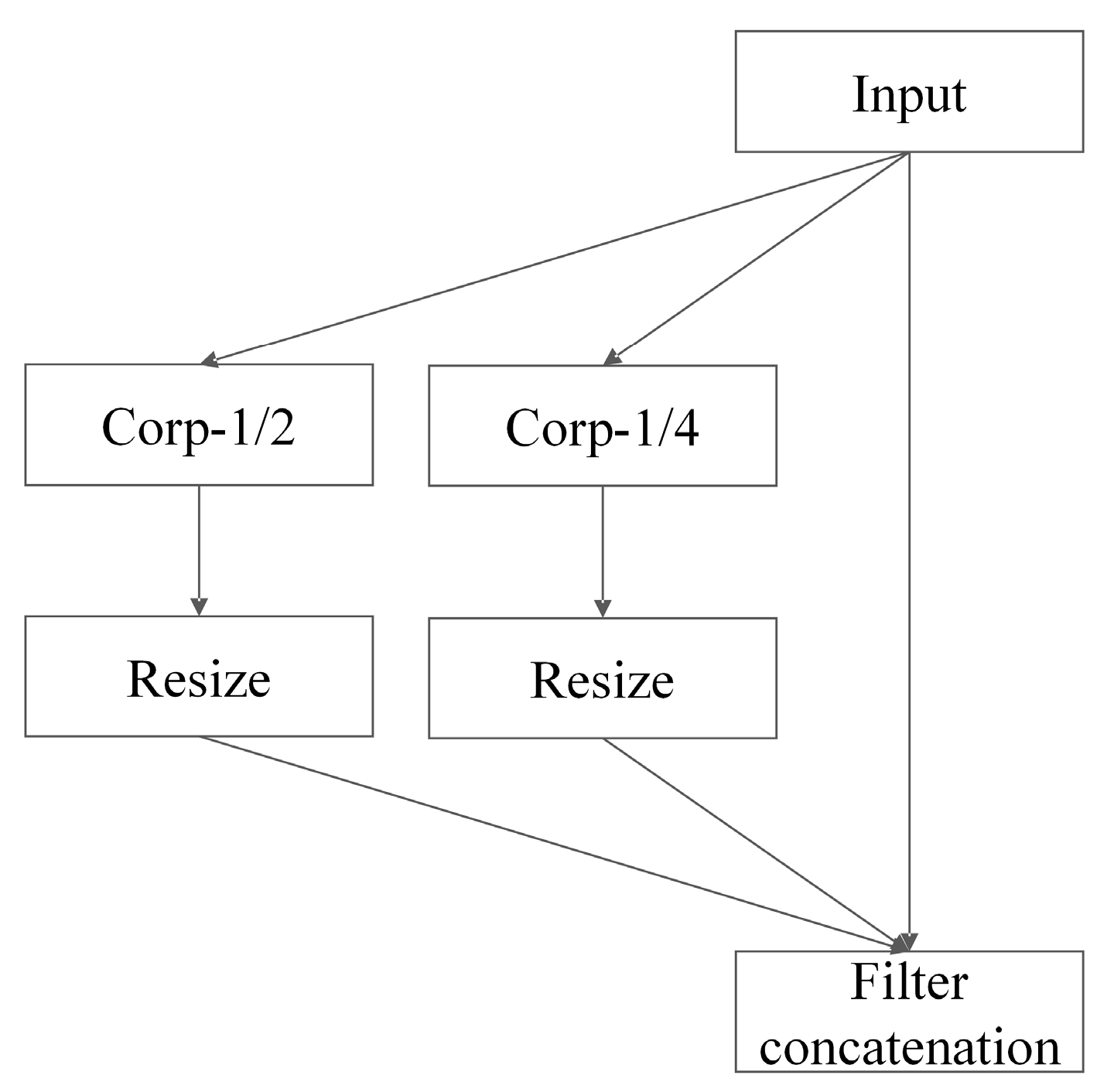
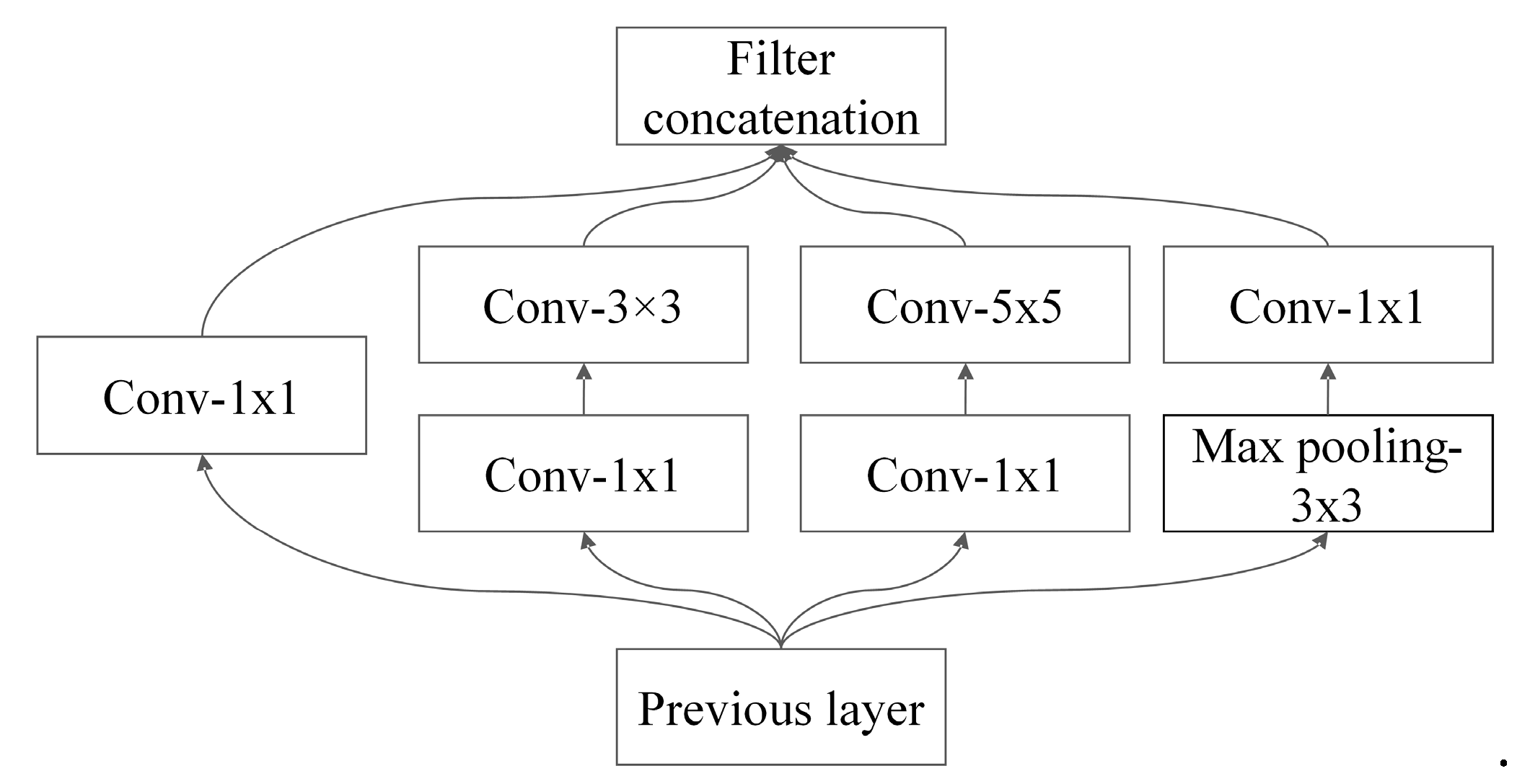
2.2. Multi-Scale Module
2.3. Attention Mechanisms
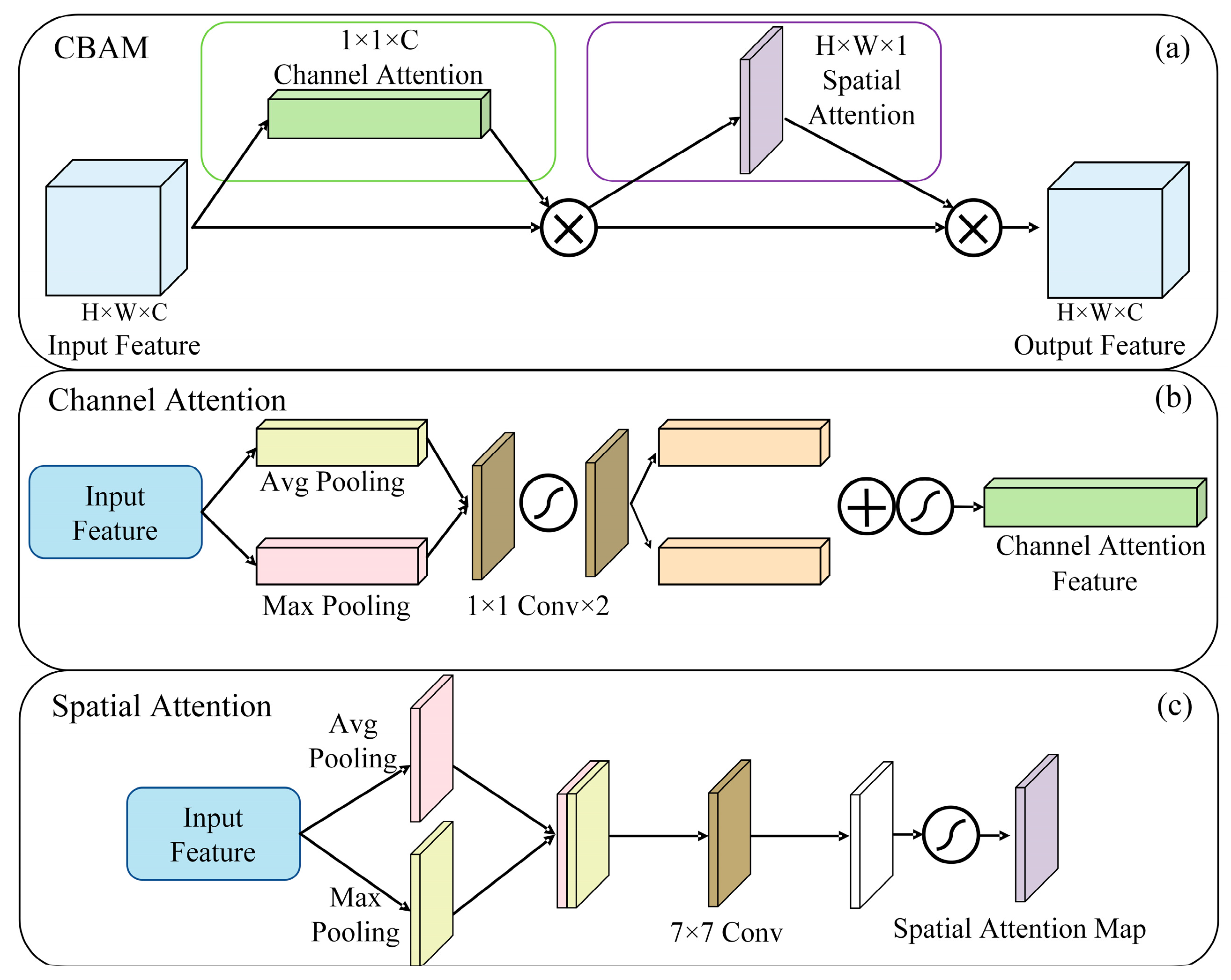
2.3.1. Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM)
2.3.2. Cross-Branch Spatial Attention Module
3. Experiment
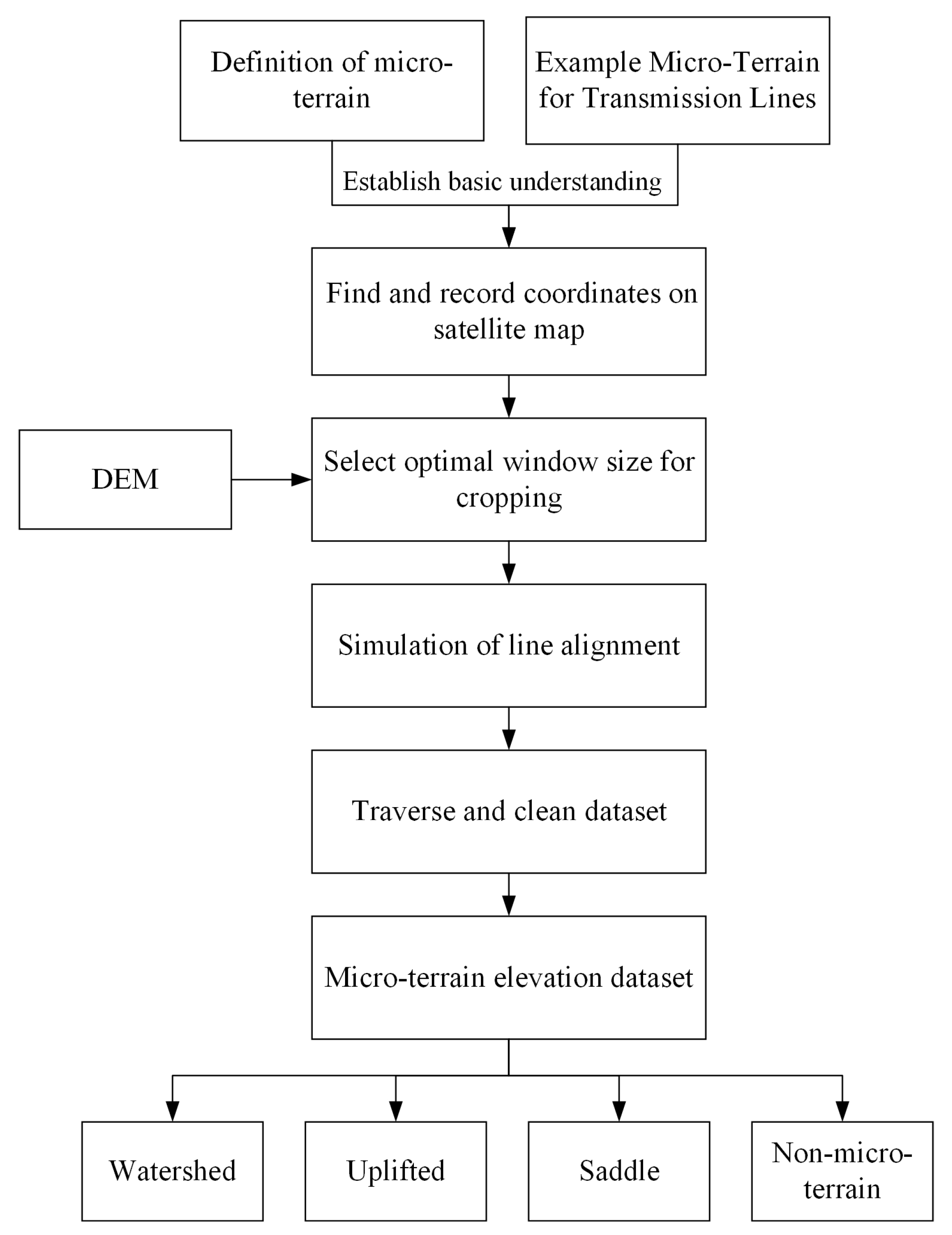
3.1. The National DEM Data Source
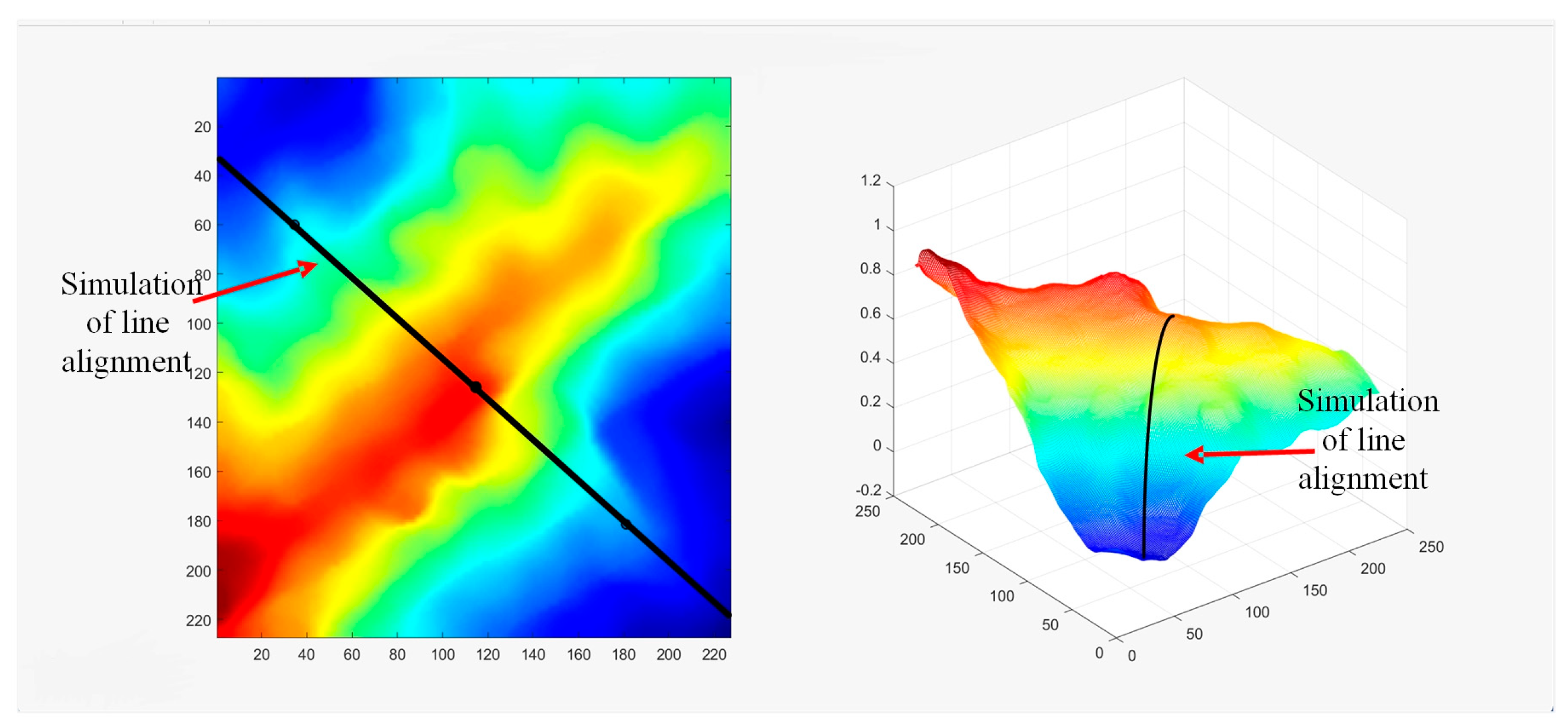
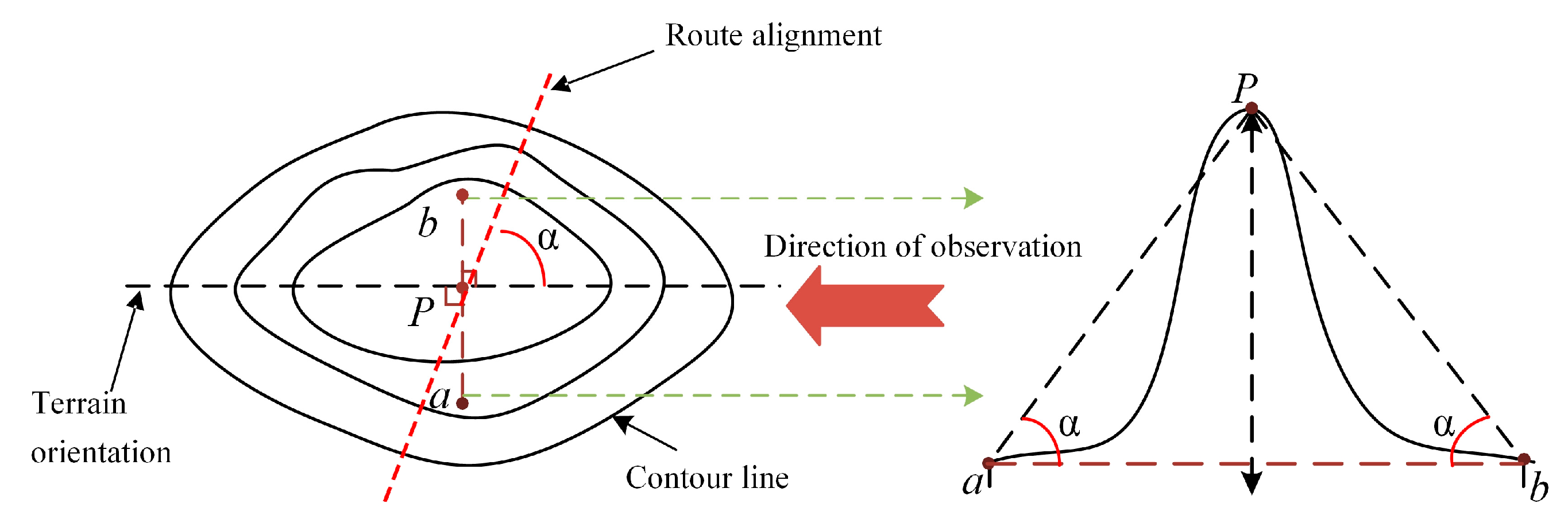
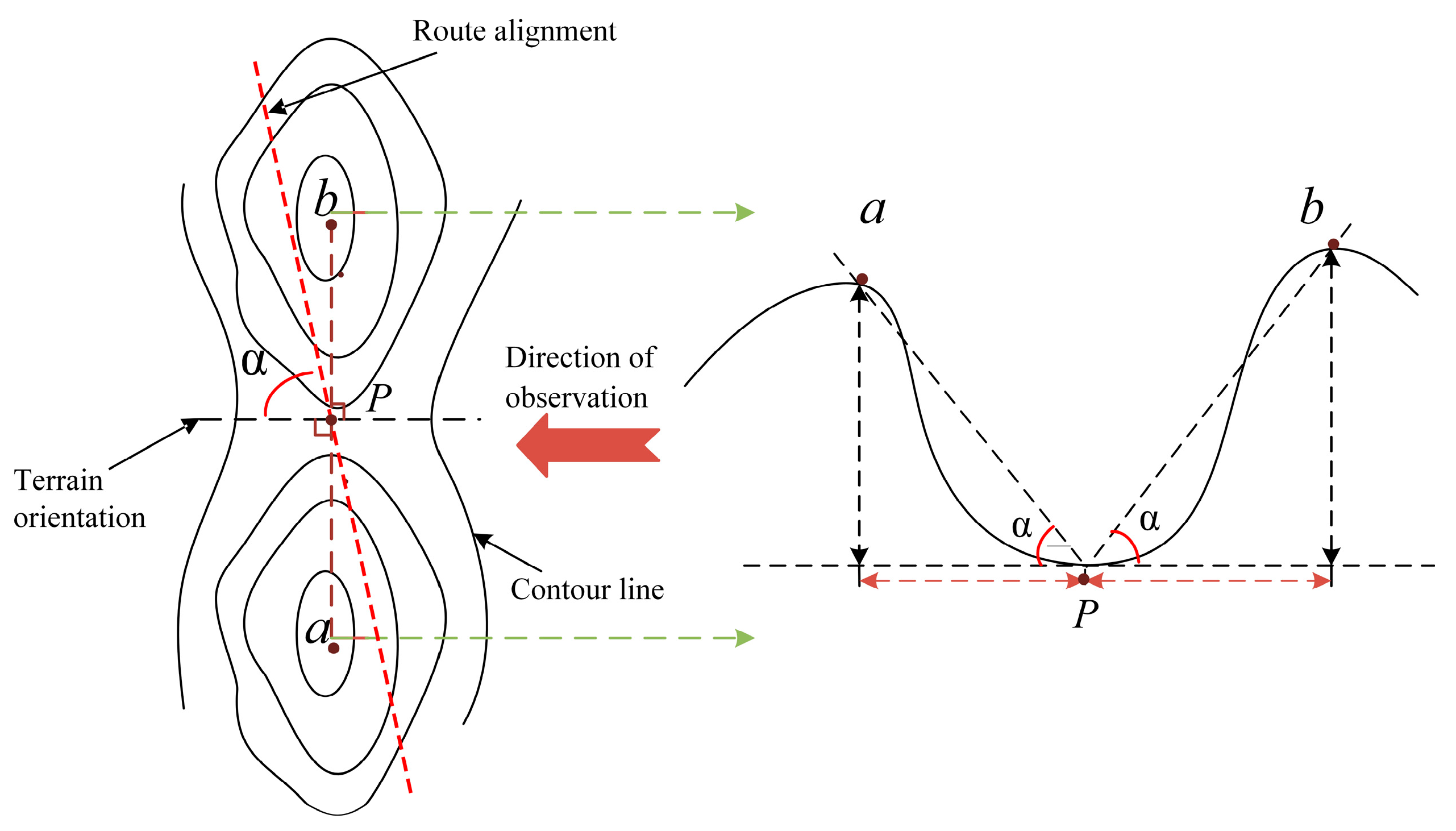
3.2. Micro-Terrain Elevation Dataset
3.3. Micro-Terrain Instance Test Dataset
3.4. Evaluation Metrics
3.5. Model Parameter Configuration
4. Results
4.1. Ablation Study
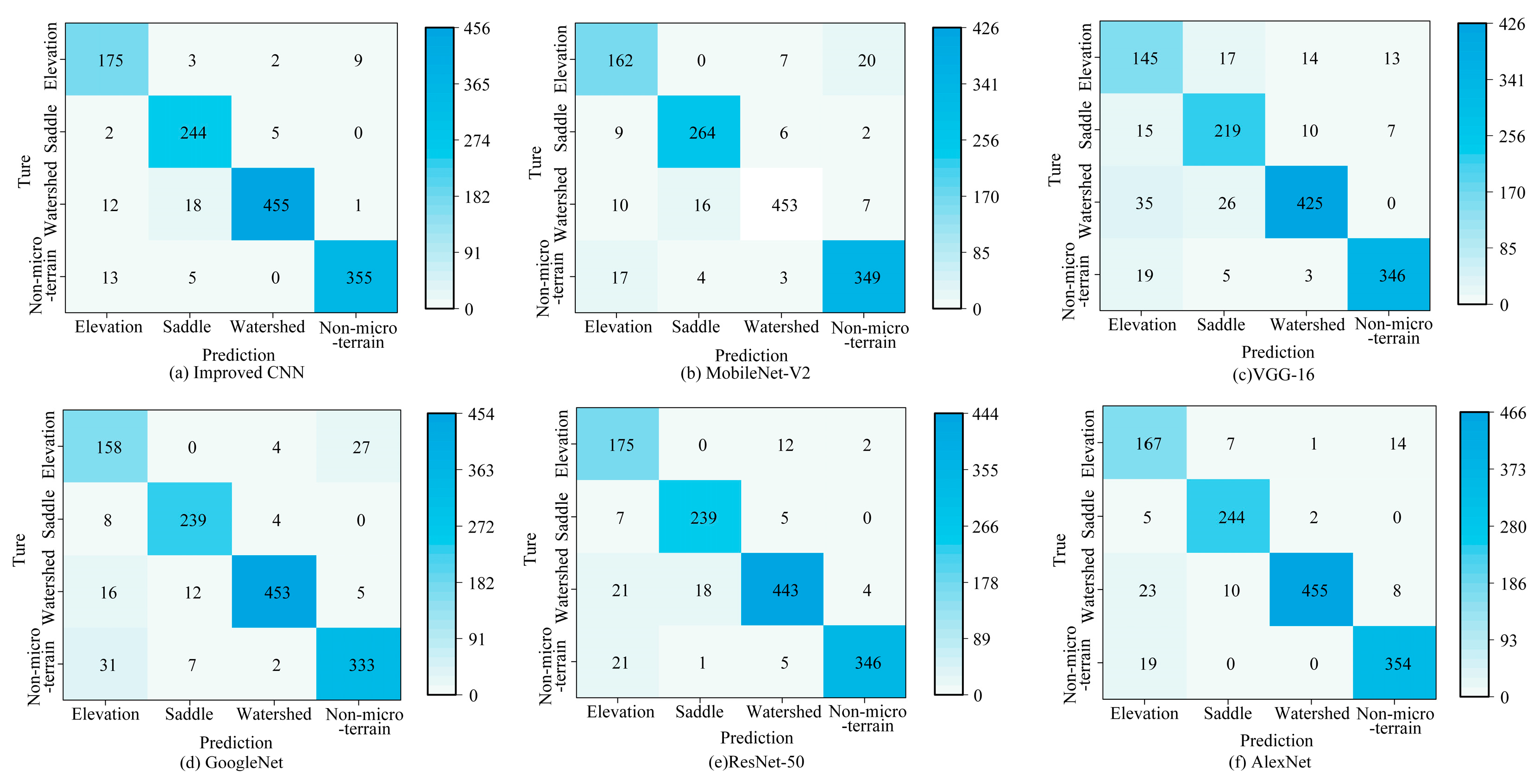
4.2. Comparative Experiment
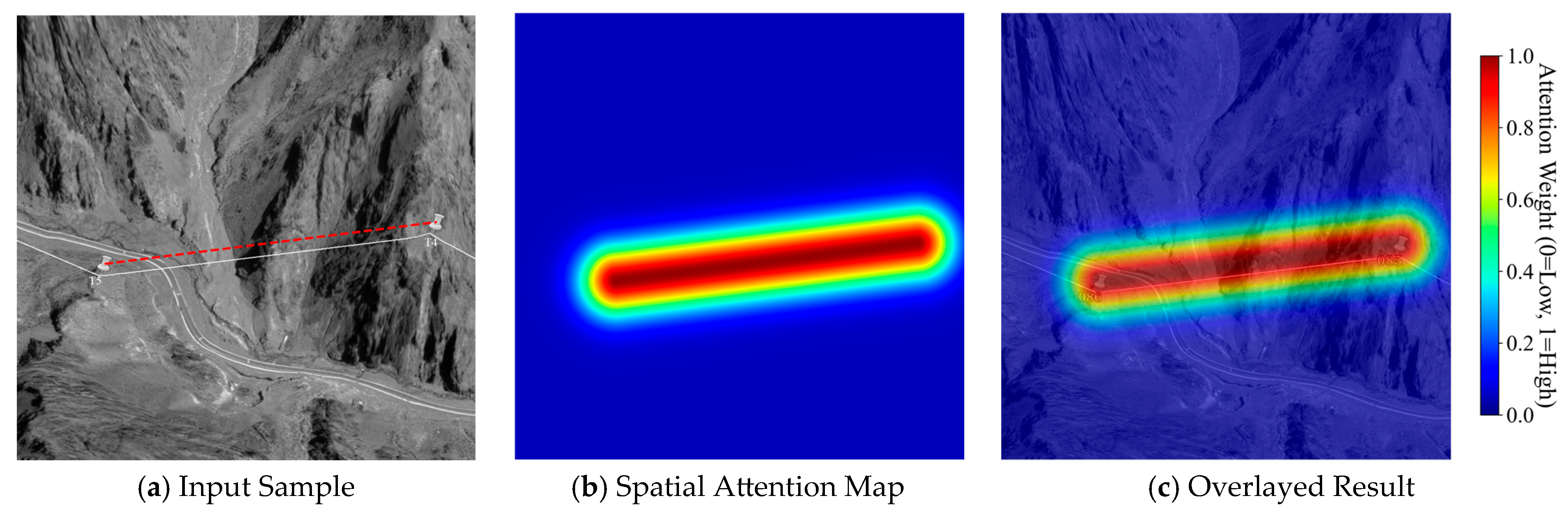
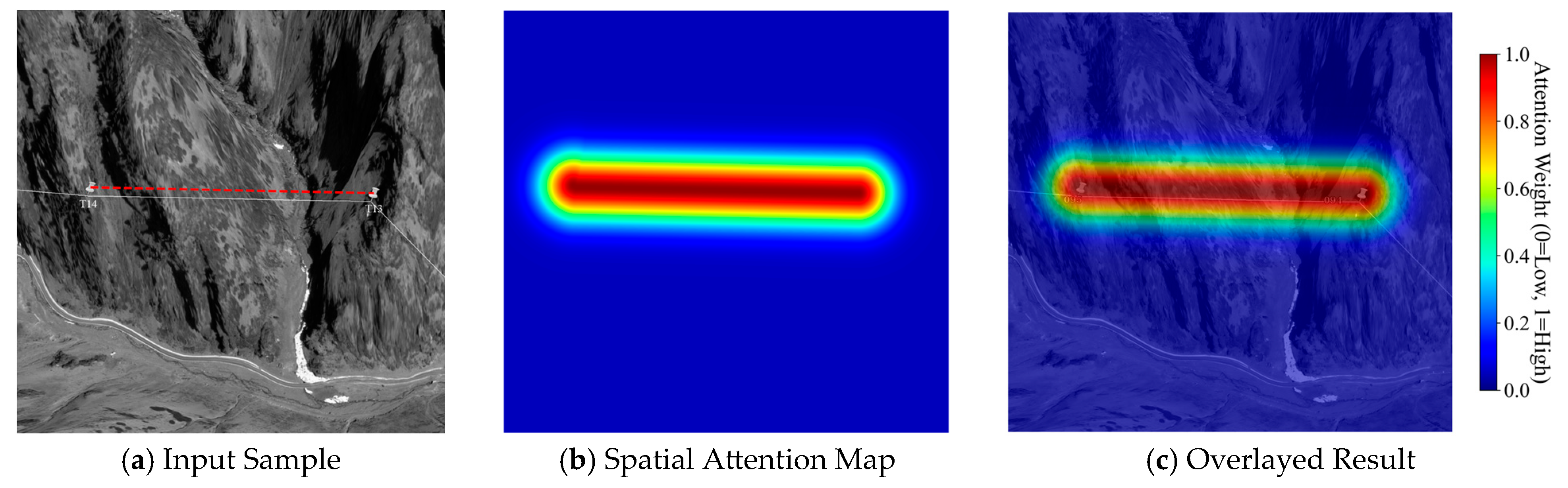
4.3. Visualization of the Spatial Attention Mechanism
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xi, J. Statement at the General Debate of the 75th Session of the United Nations General Assembly; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Available online: https://news.un.org/zh/story/2020/09/1067222 (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Chen, Y.; Yan, B.; Yu, M.; Huang, G.; Qian, G.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Mo, R. Wind tunnel study of wind turbine wake characteristics over two-dimensional hill considering the effects of terrain slope and turbine position. Appl. Energy 2025, 380, 125044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, D.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, X. Analysis of solar radiation differences for High-Voltage transmission lines on Micro-Terrain Areas. Energies 2024, 17, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, J. Predicting Ice Thickness of Transmission Lines Using Gaussian Regression Process and Micrometeorological Parameters: A Machine Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Workshop on Electromagn: Applications and Student Innovation Competition (iWEM), Harbin, China, 15–18 July 2023; pp. 263–265. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Feng, T.; Cai, Z.; Lian, X.; Tang, W. Vulnerability Assessment for Power Transmission Lines under Typhoon Weather Based on a Cascading Failure State Transition Diagram. Energies 2020, 13, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Hu, J.; Shu, L. Thinkings on the Restrike of Ice and Snow Disaster to the Power Grid. High Volt. Eng. 2018, 44, 463–469. [Google Scholar]
- Tabas, D.; Fang, J.; Porte-Agel, F. Wind Energy Prediction in Highly Complex Terrain by Computational Fluid Dynamics. Energies 2019, 12, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Hu, C. An optimized detection model for micro-terrain around transmission lines. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Magd, S.A.A.; Ali, S.A.; Pham, Q.B. Spatial modeling and susceptibility zonation of landslides using random forest, naïve bayes and K-nearest neighbor in a complicated terrain. Earth Sci. Inform. 2021, 14, 1227–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Huang, F.; Du, Y.; Liu, D.; Cao, Z. Regional terrain complexity evaluation based on GIS and K-means clustering model: A case study of Ningdu County, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 300, 022025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, Z.A.; Park, U. A Drone Based Transmission Line Components Inspection System with Deep Learning Technique. Energies 2020, 13, 3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Du, Q.; Bi, Z. Research on DEM geomorphic factor terrain recognition algorithm using probabilistic neural networks based on tactile systems. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 2024, 46, 2174–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, N.; Shen, R. Directed Positive Negative Terrain Structure Graph Attention Network for Genetic Landform Recognition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 62, 4501915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suneetha, M.; Sujitha, A.V.S.P.; Shameera, M.; Kalyan, M.R. Object Based Terrain Classification Using Deep Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2024 15th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kamand, India, 24–28 June 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Zhang, H. Transmission Line Geological Hazard Detection Based on UAV LiDAR DEM and InSAR. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Smart Electrical Grid and Renewable Energy (SEGRE), Changsha, China, 16–19 June 2023; pp. 470–475. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, X. Study on transmission line icing prediction based on micro-topographic correction. AIP Adv. 2022, 12, 085103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, V.; Montaña, J.; Candelo, J.; Quintero, C. Estimation of the shielding performance of transmission lines considering effects of landform, lightning polarity and stroke angle. Electr. Eng. 2017, 100, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaraperumal, R.; Raj, M.N.; Pazhanivelan, S.; Jagadesh, M.; Selvi, D.; Muthumanickam, D.; Jagadeeswaran, R.; Karthikkumar, A.; Kanna, S.K. Data mining techniques for LULC analysis using sparse labels and multisource data integration for the hilly terrain of Nilgiris district, Tamil Nadu, India. Earth Sci. Inform. 2025, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.B.; Babiceanu, R.F. Deep CNN-based visual defect detection: Survey of current literature. Comput. Ind. 2023, 148, 103911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Cao, S.; Wang, X.; Xie, S. A hyperspectral image classification method based on the nonlocal attention mechanism of a multiscale convolutional neural network. Sensors 2023, 23, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, C.; Song, G.; Li, L.; Zhao, G.; Lu, W.; Jiang, G.; Sun, Q. DB-MFENet: A Dual-Branch Multi-Frequency Feature Enhancement Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Duan, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Classification of hyperspectral image based on double-branch dual-attention mechanism network. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, R.; Wang, W.; Luo, Q.; Tu, C. Hyperspectral image classification based on double-branch multi-scale dual-attention network. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- ASF DAAC. ASF Data Search. Available online: https://search.asf.alaska.edu/ (accessed on 26 July 2025).
- GB/T 50548-2018; Survey Specification for 330 kV~750 kV Overhead Transmission Lines. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development and State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2018. Available online: https://ebook.chinabuilding.com.cn/zbooklib/bookpdf/probation?SiteID=1&bookID=111990 (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- DL/T 741-2019; Operating Code for Overhead Transmission Line. National Energy Administration: Beijing, China, 2019. Available online: https://www.doc88.com/p-74959496509292.html (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Huang, C.; Yin, K.; Liang, X.; Gui, L.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Y. Study of direct and indirect risk assessment of landslide impacts on ultrahigh-voltage electricity transmission lines. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Micro-Terrain Type | Training Dataset (80%) | Validation Dataset (20%) | Total Sample Count |
|---|---|---|---|
| Watershed | 1944 | 486 | 2430 |
| Saddle | 1000 | 0251 | 1251 |
| Uplifted | 158 | 189 | 947 |
| Non-micro-terrain | 1494 | 373 | 1867 |
| Total | 5196 | 1299 | 6495 |
| Category Number | Micro-Terrain Type | Sample Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Watershed | 28 |
| 2 | Saddle | 61 |
| 3 | Uplifted | 41 |
| Total | 3 | 130 |
| Hyperparameter | Improved CNN Model | Transfer Learning Models |
|---|---|---|
| Optimizer | Adam | Adam |
| 0.9 | 0.9 | |
| 0.999 | 0.999 | |
| 10−8 | 10−8 | |
| 10−3 | 10−3 | |
| Batch Size | 128 | 128 |
| Training Epochs | 100 | 8 |
| Dataset | CNN | Dual-Branch | Attention Module | Multi-Scale | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micro-terrain elevation validation dataset | √ | 90.6 | |||
| √ | √ | 93.2 | |||
| √ | √ | √ | 94.4 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 93.5 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 95.6 | |
| Micro-terrain instance test dataset | √ | 89.3 | |||
| √ | √ | 91.4 | |||
| √ | √ | √ | 93.7 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 92.6 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 94.8 |
| Watershed | Saddle | Uplifted | Non | OA | AA | Kappa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 93 | 94.8 | 88.9 | 91.4 | 92.2 | 92 | 0.8963 |
| Improve CNN | 95.2 | 97.2 | 92.6 | 93.6 | 94.6 | 94.5 | 0.9289 |
| VGG-16 | 92.8 | 87.3 | 76.7 | 87.5 | 87.4 | 86.1 | 0.8331 |
| GoogleNet | 89.3 | 95.2 | 83.6 | 93.2 | 91.1 | 90.3 | 0.8221 |
| MobileNet-V2 | 93.6 | 93.2 | 85.7 | 93.2 | 92.3 | 91.4 | 0.8975 |
| ResNet-50 | 93 | 95.2 | 92.6 | 91.2 | 92.7 | 93 | 0.9064 |
| AlexNet | 94.9 | 97.2 | 88.4 | 91.6 | 93.2 | 93 | 0.9095 |
| Watershed | Saddle | Uplifted | OA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 89.3 | 93.4 | 82.9 | 89.3 |
| Improve CNN | 96.4 | 93.4 | 90.2 | 92.8 |
| VGG-16 | 85.7 | 88.5 | 78 | 84.7 |
| GoogleNet | 82.1 | 91.8 | 80.5 | 86.3 |
| MobileNet-v2 | 96.4 | 90.2 | 87.8 | 90.8 |
| ResNet-50 | 100 | 93.4 | 82.9 | 91.8 |
| AlexNet | 92.9 | 90.2 | 87.8 | 90.1 |
| Tower | Micro-Terrain | Tower | Micro-Terrain |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No | 11 | No |
| 2 | No | 12 | No |
| 3 | No | 13 | Saddle |
| 4 | Saddle | 14 | Saddle |
| 5 | Saddle | 15 | No |
| 6 | No | 16 | No |
| 7 | No | 17 | No |
| 8 | No | 18 | No |
| 9 | No | 19 | No |
| 10 | No | 20 | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mo, K.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Wei, R. Attention Mechanism-Based Micro-Terrain Recognition for High-Voltage Transmission Lines. Energies 2025, 18, 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174495
Mo K, Zheng H, Zhang Z, Jiang X, Wei R. Attention Mechanism-Based Micro-Terrain Recognition for High-Voltage Transmission Lines. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174495
Chicago/Turabian StyleMo, Ke, Hualong Zheng, Zhijin Zhang, Xingliang Jiang, and Ruizeng Wei. 2025. "Attention Mechanism-Based Micro-Terrain Recognition for High-Voltage Transmission Lines" Energies 18, no. 17: 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174495
APA StyleMo, K., Zheng, H., Zhang, Z., Jiang, X., & Wei, R. (2025). Attention Mechanism-Based Micro-Terrain Recognition for High-Voltage Transmission Lines. Energies, 18(17), 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174495









