Abstract
While Forgetting Factor Recursive Least Square (FFRLS) algorithms with evaluation mechanisms have been developed to address SOC-dependent parameter mapping shifts and their efficacy has been proven in Li-ion batteries, their applicability to lithium–sulfur (Li-S) batteries remains uncertain due to different electrochemical characteristics. This study critically evaluates the applicability of a Fisher information matrix-constrained FFRLS framework for online parameter identification in Li-S battery equivalent circuit network (ECN) models. Experimental validation using distinct drive cycles showed that the identification results of polarization-related parameters are significantly biased between different current excitations, and root mean square error (RMSE) variations diverge by 100%, with terminal voltage estimation errors more than 0.05 V. The parametric uncertainty under variable excitation profiles and voltage plateau estimation deficiencies confirms the inadequacy of such approaches, constraining model-based online identification viability for Li-S automotive applications. Future research should therefore prioritize hybrid estimation architectures integrating electrochemical knowledge with data-driven observers, alongside excitation capturing specifically optimized for Li-S online parameter observability requirements and cell nonuniformity and aging condition consideration.
1. Introduction
Lithium–sulfur (Li-S) batteries represent a highly promising chemistry for high-gravimetric energy density applications, offering a theoretical energy density of 2500 Wh/kg [1,2]. Although the practically achievable energy density is typically reported to be approximately 600 Wh/kg—significantly lower than the theoretical maximum yet still 2–3 times greater than that of commercial lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, this potential drives significant research focused on fundamental material understanding, cell construction, and electrochemical behavior to reveal underlying mechanisms and enhance performance [3,4,5,6,7,8]. While electrochemistry is central to these efforts, advancing Li-S technology towards practical deployment necessitates the concurrent development of engineering science and techniques, alongside evaluating the feasibility of adapting existing Li-ion battery engineering technologies for Li-S applications [9,10,11,12,13,14].
Currently, model-based battery management systems (BMSs) deployed utilize equivalent circuit network (ECN) models for online estimation of critical states such as state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH), ensuring pack safety and reliability [15,16,17]. ECNs represent a computationally efficient framework that balances model fidelity with processing complexity [18]. These lumped electrical models employ discrete components—including voltage sources, resistors, and capacitors—to simulate battery current–voltage dynamics. The SOC-dependent parameters characterize open-circuit voltage (OCV), ohmic resistance, and polarization/hysteresis effects [19,20]. These parameters are conventionally identified offline by experimental datasets, then embedded as static lookup tables or empirical functions within onboard microprocessors [21].
However, battery degradation significantly alters their mapping relationship [22,23]. While Kalman filter-based techniques can mitigate state estimation errors through data fusion, inaccurate model parameters introduce non-negligible estimation errors, particularly for end-of-life batteries [24]. Meanwhile, power allocation in battery-integrated hybrid energy systems depends on precise parameter estimation and prediction capability. Inaccurate state and parameter estimation under extreme conditions may escalate into critical safety hazards [25,26,27]. Consequently, developing online parameter identification methods for ECN-based Li-S battery management represents a crucial research direction to ensure long-term operational safety [1,28].
The ECN constitutes a single-input–single-output (SISO) system, where dynamic current–voltage behavior is mathematically represented through state-space formulations corresponding to the circuit topology [29,30]. While theoretically, increased ECN complexity can capture broader dynamic characteristics for wider application scope, this does not guarantee the online identifiability of all parameters. Previous studies have evaluated identifiability in mainstream ECNs, including the Rint, Thevenin, dual-polarization (DP), and Randles models, revealing that the Rint and Thevenin models exhibit global parameter identifiability (yielding unique solutions), whereas theDP and Randles models demonstrate only local identifiability due to structural nonuniqueness, hindering reliable online identification [31]. The Thevenin model’s additional resistor–capacitor (RC) pair improves polarization dynamics representation compared to the Rint model, although it remains substantially less accurate than the DP and Randles models in characterizing dynamic responses [32].
Forgetting Factor Recursive Least Squares (FFRLS) algorithms are frequently employed in the literature for online parameter identification in Thevenin models due to their computational efficiency [33,34,35]. However, accurate identification of specific parameters necessitates excitation by current profiles featuring particular frequencies and amplitudes. Real-world deployments expose FFRLS to estimation instability under random load profiles [35], often inducing insufficient excitation in critical frequency–amplitude bands, leading to high sensitivity to sensor noise. To mitigate insufficient excitation effects in online identification, derivative-based methods leveraging metrics such as Hessian matrix eigenvalues, Fisher information matrix eigenvalues, and sensitivity matrix rank have been proposed. Among these, Fisher matrix-based approaches demonstrate enhanced robustness for parameter identification in Li-ion battery applications [36,37,38]. Nevertheless, these methods fundamentally rely on the quasi-linear characteristic exhibited by the OCV-SoC curves of Li-ion batteries: despite being inherently nonlinear, the OCV universally demonstrates a monotonically increasing relationship with SoC, exhibiting relatively mild nonlinearity.
The substantially more complex reaction mechanisms of Li-S batteries compared to Li-ion systems—notably the “shuttle effect” arising from dissolution and migration of intermediate polysufiede and the distinct low/high-voltage plateau regions—introduce significant nonlinearities into the OCV and impedance characteristics [1,10]. While the Fisher information matrix has proven effective for quantitatively assessing excitation sufficiency and guiding parameter updates in Li-ion batteries [39], its application to Li-S batteries raises concerns regarding parameter identifiability under such complex OCV and impedance characteristics [40]. Consequently, it remains prudent to critically revisit Fisher matrix-based FFRLS algorithms despite their validated efficacy in Li-ion battery applications.
Therefore, this study employs experimental Li-S battery data to assess the applicability and accuracy of Fisher information matrix-based FFRLS algorithms for online parameter identification. This article is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the method combining the FFRLS and the Fisher matrix evaluation from battery cell modeling to the FFRLS algorithm and Fisher information matrix. Section 3 gathers Li-S battery data from experiments to perform an analysis of the performance of this method across various operating scenarios, thereby discussing its applicability and accuracy in Li-S applications. Finally, Section 4 concludes and explores the future directions.
2. Methodology
This section demonstrates the FFRLS method, incorporating Fisher information matrix analysis and Cramér–Rao lower-bound (CRB) constraints. According to the ECN modeling method reported in [1,40], this study selects the Thevenin model containing a first-order resistance–capacitance (1RC) network. Figure 1 presents a diagram illustrating this approach.
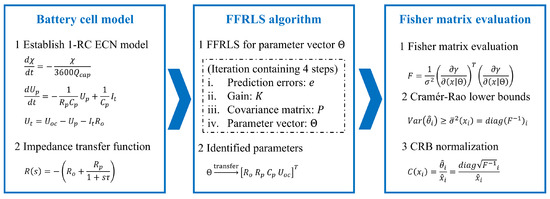
Figure 1.
Diagram of the FFRLS-Fisher matrix approach for online model parameter identification.
2.1. Battery Cell Modeling
In experimental conditions, the terminal voltage response of the Li-S cell to a current impulse, depicted in Figure 2a, exhibits distinct dynamic behavior. During the discharge pulse, the cell voltage displays an initial sudden drop, followed by a nonlinear decline that transitions into stability. Following pulse termination, an immediate voltage jump occurs, succeeded by a gradual recovery phase until the open-circuit voltage (OCV) is restored; these dynamic behaviors arise from the SOC-dependent variations in OCV and cell impedance.
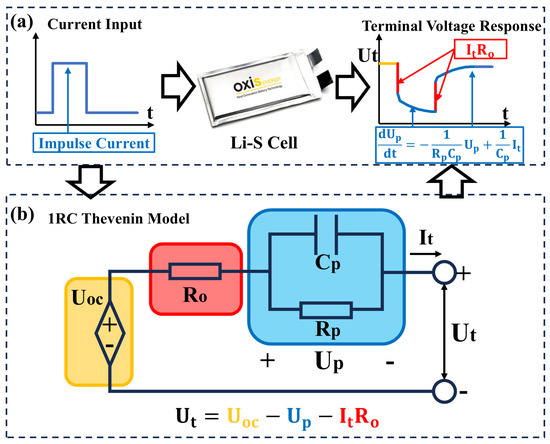
Figure 2.
(a) Current impulse and cell response voltage, and (b) the 1RC Thevenin model.
The Thevenin model containing a first-order resistance–capacitance (1RC) circuit network is generally applied to describe this dynamic response in online applications [3], as depicted in Figure 2b. The voltage source represents the open-circuit voltage (V); the resistor indicates the internal ohmic resistance to describe the voltage’s abrupt drop and jump exhibited in the voltage response curve. The RC pair combining polarization resistance and capacitance ( and ) describes the polarization behaviors, i.e., the nonlinear decline and gradual recovery phases. These model parameters strongly depend on the cell SOC level. Assuming the discharge current is defined as the positive direction, the model state-space function can be expressed as
where is the cell SOC (0∼1), is the cell capacity (Ah), is the polarization voltages (V), and is the terminal voltage (V). The state-space function corresponding to the terminal voltage response segments is illustrated in Figure 2a.
, , , and are not only the SOC-dependent variables but also influenced by cell degradation; they are generally identified and optimized offline based on laboratory testing datasets to date, remaining unchanged throughout the entire service life of battery packs. To mitigate the impact of parameter drift cause by cell aging on state estimation accuracy, studies proposed the FFRLS algorithm that can identify these parameters online during operation processes.
2.2. FFRLS Algorithm
Although the Li-S cell model is a time-variant system, the parameters identified online (, , , and ) exhibit quasi-static characteristics within estimation windows on the order of seconds due to the slow temporal evolution of the SOC and SOH. Consequently, this algorithm assumes the time derivatives of these parameters are negligible (approximately zero), and parameter updates are governed by a forgetting factor (FF). Based on Equation (1), the transfer function of the cell impedance can be written as
where is the cell impedance and . In online implementation, the embedded code generally employs a discrete format with the sample time T for compatibility with computation in microprocessors. The bilinear transformation is a common method for converting continuous transfer functions to discrete ones, and the conversion function is
The discrete transfer function can be expressed as Equation (4), combining Equations (2) and (3):
where
The observed discrete state-space function can be arranged as follows:
where
RLS methods for identification can be expressed:
where
Measured time-series voltage and current values can be presented in compact vector and matrix format:
Therefore, the identified results can be expressed as
where
Details about battery-based FFRLS applications have been widely discussed in [1,2], and the operational processes are demonstrated in Algorithm 1. In this algorithm, e is the difference between estimated and measured terminal voltages; is the gain vector, where is the forgetting factor (it is set to 0.95 in this study).
| Algorithm 1 FFRLS |
| Input:
, , , 1: Prediction errors: 2: Gain: 3: Covariance matrix update: 4: Parameter vector update: Output: |
Once is optimized by the algorithm, the online model parameter is directly identified, as depicted in Equation (5), and , , and can be derived as
Consequently, this recursive method eliminates the need for historical data storage by dynamically updating the covariance matrix P at each sampling time to optimize parameters as new measurements arrive. The voltage–current–parameter relationship is governed by the ECN model, where a forgetting factor enhances time-varying parameter tracking; subsequent set-wise updates of the gain K, covariance matrix P, and parameter vector estimates enable online adaptation through recursive computation.
2.3. Fisher Information Matrix
The accuracy of the parameter identification is strongly correlated with the excitation and response information richness (i.e., measured currents and voltages) in the frequency domain. The Fisher information matrix provides a mathematical approach to quantify information sufficiency by evaluating the derivative of online-identified model parameters. It can be expressed as
where indicates the variance of the Gaussian distribution error of measured voltages, x is the model parameter vector , and Y is the system output. The deviation at time can be depicted as an equation using the Jacobian matrix format:
where
In Equation (10), and are the RLS-estimated parameters. The diagonal elements of the inverse Fisher information matrix constitute the theoretical lower bounds (CRBs) for the variances of unbiased parameter estimates. These CRBs establish a criterion: estimated parameter variances may approach but cannot fall below their respective CRB, where smaller CRB values indicate higher theoretical identification precision. This can be demonstrated by using an inequality equation as follows:
Here, denotes the CRB for the i-th identified parameters, corresponding to the i-th diagonal element of . The current-series excitation constitutes a sufficient input at numerically small CRB values. Given the significant magnitude differences among parameters, this study adopts CRB normalization to enable direct comparison across parameters, expressed as
Upon receiving data corresponding to a 1% SOC change, initial conditions are established using model parameters from the reserved lookup table and their associated data-sufficiency index . The FFRLS algorithm is executed at each data point, and then CRBs are computed as the data-sufficiency metric, which requires a data series for Fisher information matrix calculation and voltage variance estimation. Within this, individual parameters exhibit distinct sensitivity profiles, necessitating independent selection of optimal data points rather than simultaneous multi-parameter optimization. The corresponding model parameter represents the averaged value within the SOC range, though acquired data may not contain the theoretical optimum. Hence, the algorithm continuously compares current CRB values against historical minima, updating the lookup table and index only when lower bounds are approached, thereby enabling progressive refinement toward globally optimal parameter estimation through adaptive data selection.
Although validated for Li-ion batteries under specific scenarios—notably with information-rich excitation [41], such as an HPPC test profile—this method faces two questions that necessitate further accuracy assessment for Li-S applications: significant discrepancies in the OCV and impedance characteristics between Li-S and Li-ion chemistries, and insufficient verification under actual operating conditions. Hence, the following section experimentally evaluates the method’s performance in Li-S batteries to address these considerations.
3. Results
The Li-S cell employed in this study (supplied by OXIS Energy Ltd., Abingdon, UK) features specifications detailed in Table 1. Experimental data and test implementation were provided by Advanced Vehicle Engineering Center (AVEC), Cranfield University, UK. The experimental configuration incorporated a programmable power source/sink, applying specified current profiles while measuring terminal voltage, coupled with a thermal chamber maintaining 25 °C operational temperature (equipment detailed in [9,42]). Two drive-cycle profiles were implemented, from fully charged to fully discharged states, with time-domain data sampled at 1 Hz. Figure 3 presents the corresponding current patterns and voltage responses. Furthermore, the running environment of the algorithm was MATLAB/Simulink.

Table 1.
Basic parameters of the Li-S battery cell.
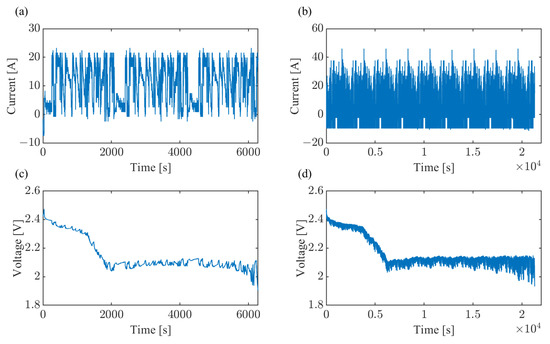
Figure 3.
Experimental data: (a,c) are current profile 1 and corresponding voltage response; (b,d) are current profile 2 and corresponding voltage response.
Figure 4 presents the identification results for the parameters , , , and under two current profiles. The parameters obtained from profile 1 exhibit significantly greater fluctuation than those from profile 2, particularly in the and estimations. This demonstrates how varying current sequences in real-world applications yield divergent identification outcomes, especially for polarization-related parameters. Such variations arise because polarization dynamics are difficult to capture within narrow 1% SOC intervals for fast-discharge operations.
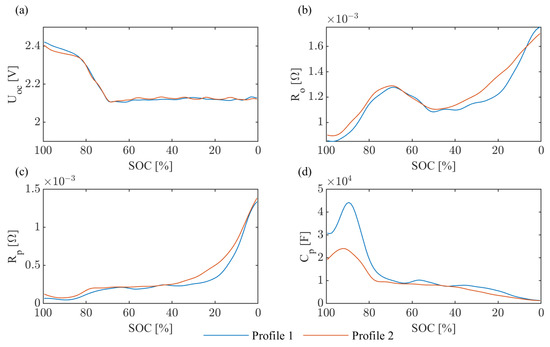
Figure 4.
Parameter identification results under two current profiles: (a) , (b) , (c) , and (d) .
To validate the online identification accuracy, a Li-S ECN model was implemented in MATLAB/Simulink with the estimated parameters configured. Figure 5 compares simulated terminal voltages against experimental measurements for both current profiles. Voltage discrepancies fluctuate within 0.13 V (profile 1) and 0.08 V (profile 2); with root mean square error (RMSE) quantified as
where and denote measured and estimated voltages, respectively. The computed RMSE values of 0.0254 (profile 1) and 0.0122 (profile 2) demonstrate better parameter identification accuracy under the conditions of profile 2.
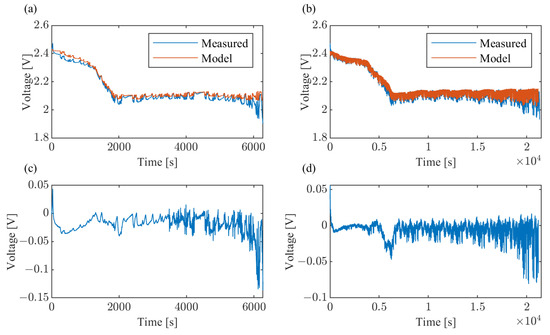
Figure 5.
Terminal voltage comparison between the ECN model and measured values under two current profiles: (a) terminal voltages from profile 1, (b) terminal voltages from profile 2, (c) two voltage discrepancies of profile 1, and (d) two voltage discrepancies of profile 2.
The better parameter identification accuracy observed under the conditions of profile 2 stems from richer frequency-domain excitation characteristics. Fast Fourier transform (FFT) analysis of both current profiles (Figure 6) reveals that profile 2 exhibits significantly enhanced spectral energy distribution across frequency bands essential for cell parameter identification. Specifically, profile 2 maintains more than two times greater magnitudes in the range 0.05∼0.3, corresponding to dominant polarization dynamics, compared to profile 1. Such excitation enables more complete estimation capability of the system dynamics through greater-magnitude excitation conditions. The frequency-domain performance directly translates to improved parameter estimation fidelity, as confirmed by the 52% reduction in RMSE values between profiles.
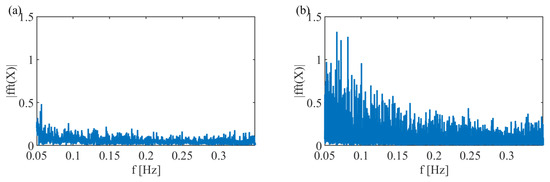
Figure 6.
Fast Fourier transform for current excitation in (a) profile 1 and (b) profile 2.
4. Discussion
The results in Figure 5 confirm this approach can identify Li-S cells’ OCV and impedance parameters online, and the achieved RMSE values for profiles 1 and 2 (0.0254 V and 0.0122 V) demonstrate voltage prediction accuracy comparable to relevant prior Li-ion studies documented in [40]. Despite that, the identified parameters exhibit significant sensitivity to excitation variations. The parametric values identified under different current profiles demonstrate substantial divergence, particularly for polarization-related parameters (approximately 20% and 50% in some SOC intervals). This instability exists despite CRB constraints theoretically guaranteeing identifiable minimum bounds. In automotive applications, where load currents perform stochastic frequency characteristics, this uncertainty introduces estimation error propagation risks for battery-state estimation.
As seen in Figure 5, parameter estimation accuracy degrades at OCV “inflection” points (approximately SOC 70%) and voltage “plateaus” (SOC: 0∼70%), with terminal voltage errors reaching 0.05 V, representing 70% of the SOC range. Within the SOC range of 10∼70%, the OCV of Li-S batteries varies by merely 0.1 V (2.0∼2.1 V). This probably creates an ill-conditioned estimation problem. While Kalman filtering techniques partially compensate, their linear approximation assumptions would break down in these regions, leading to difficultly in mitigating such errors.
The convergence of these challenges, including parametric excitation dependence and estimation inaccuracy, reveals limitations in transferring such online parameter identification frameworks to Li-S batteries. The observed 0.05 V estimation fluctuation in critical “plateau” regions constrains the state-estimation fidelity. Furthermore, although the combination of Fisher matrix evaluation and CRB is applied, the results in Figure 5 confirm a loss of identifying accuracy in the “plateau” regions. Given the demonstrated parameter identification uncertainties and estimation deficiencies, the evaluated methodology proves unsuitable for reliable Li-S battery parameter estimation online. Until these limitations are addressed, ECM model-based online parameter identification for Li-S batteries remains a substantial challenge in automotive applications.
5. Conclusions
This study critically evaluates the applicability of the FFRLS algorithm, enhanced with a Fisher information matrix analysis and CRB constraints, for online parameter identification with ECN models of Li-S batteries. Experimental validation using distinct drive cycles revealed that identification accuracy is governed by the richness of current excitation. Significant discrepancies (20∼50%) were observed in polarization-related parameters across specific state-of-charge (SOC) intervals, and RMSE variations exceeded 100% between profiles, with voltage fluctuations confined within approximately 0.05 V. These parametric uncertainties and estimation deficiencies within voltage plateau regions exceed acceptable thresholds for automotive Li-S applications. Therefore, overcoming these limitations necessitates prioritized future research directions: (1) developing hybrid estimation architectures that integrate electrochemical knowledge with data-driven observers, specifically targeting plateau regions; (2) designing excitation capture specifically optimized for Li-S online parameter observability requirements; and (3) evaluating state estimation performance of the developed algorithm under conditions of cell nonuniformity and aging. Until these advancements are realized, model-based battery management for Li-S systems will remain challenging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.G. and Y.G.; methodology, N.G.; software, N.G.; validation, X.Y.; investigation, N.G., Y.G., and Y.Y.; resources, Y.G.; writing—original draft preparation, N.G. and Y.G.; supervision, Y.G.; funding acquisition, D.Y., B.W., and H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Education Scientific Research Project for Middle-age and Young Teachers of Fujian Province grant number JAT220346, Science and Technology Research Project of Xiamen University of Technology grant number YKJ22036R and YKJ24014R, and Xiamen Human Resources and Social Security grant number [2024]241-1.
Data Availability Statement
Additional questions can be forwarded to the corresponding author; the article contains the original contributions made throughout the study.
Acknowledgments
Thanks for Advanced Vehicle Engineering Center (AVEC), Cranfield University supporting a part of the Li-S experimental dataset, during the preparation of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Li-S | Lithium–sulfur |
| ECN | Equivalent circuit network |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| BMS | Battery management system |
| Li-ion | Lithium-ion |
| SOC | State of charge |
| SOH | State of health |
| OCV | Open-circuit voltage |
| SISO | Single input–single output |
| DP | Dual polarization |
| RC | Resistor–capacitor |
| FF | Forgetting factor |
| FFRLS | Forgetting factor recursive least square |
| CRB | Cramér–Rao lower bound |
References
- Fotouhi, A.; Auger, D.J.; Propp, K.; Longo, S.; Wild, M. A review on electric vehicle battery modelling: From Lithium-ion toward Lithium–Sulphur. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 1008–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotouhi, A.; Auger, D.J.; O’Neill, L.; Cleaver, T.; Walus, S. Lithium-sulfur battery technology readiness and applications—A review. Energies 2017, 10, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörfler, S.; Walus, S.; Locke, J.; Fotouhi, A.; Auger, D.J.; Shateri, N.; Abendroth, T.; Härtel, P.; Althues, H.; Kaskel, S. Recent progress and emerging application areas for lithium–sulfur battery technology. Energy Technol. 2021, 9, 2000694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Whitehouse, J.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, C. Experimental study of battery passive thermal management system using copper foam-based phase change materials. Int. J. Thermofluids 2023, 17, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, B.Q.; Zhang, X.Q.; Huang, J.Q.; Zhang, Q. A perspective toward practical lithium–sulfur batteries. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Chen, H.; Cui, Y. Formulating energy density for designing practical lithium–sulfur batteries. Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbonaite, S.; Poux, T.; Novák, P. Progress towards commercially viable Li–S battery cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1500118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Yu, M. Flexible solid-state lithium-sulfur batteries based on structural designs. Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 57, 429–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shateri, N.; Shi, Z.; Auger, D.J.; Fotouhi, A. Lithium-sulfur cell state of charge estimation using a classification technique. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 70, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Lu, J. Lithium-sulfur batteries for commercial applications. Chem 2018, 4, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, H.; Wang, C. Algorithm-driven optimization of lithium-ion battery thermal modeling. J. Energy Storage 2023, 65, 107388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Auger, D.J.; Fotouhi, A.; Hale, C.J. A new topology for electric all-terrain vehicle hybrid battery systems using low-frequency discrete cell switching. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 9, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Marinescu, M.; Walus, S.; Offer, G.J. Modelling transport-limited discharge capacity of lithium-sulfur cells. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 219, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shateri, N.; Auger, D.J.; Fotouhi, A.; Brighton, J. Charging characterization of a high-capacity lithium-sulfur pouch cell for state estimation: An experimental approach. Energy Storage 2023, 5, e412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Gong, Y.; Fotouhi, A.; Auger, D.J. A novel hybrid electrochemical equivalent circuit model for online battery management systems. J. Energy Storage 2024, 99, 113142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, C. A novel hybrid battery thermal management system for prevention of thermal runaway propagation. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 9, 5028–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Propp, K.; Auger, D.J.; Fotouhi, A.; Longo, S.; Knap, V. Kalman-variant estimators for state of charge in lithium-sulfur batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 343, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Luo, G.; Ricco, M.; Swierczynski, M.; Stroe, D.I.; Teodorescu, R. Overview of lithium-ion battery modeling methods for state-of-charge estimation in electrical vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Gao, W.; Han, X.; Ouyang, M.; Lu, L.; Guo, D. An accurate parameters extraction method for a novel on-board battery model considering electrochemical properties. J. Energy Storage 2019, 24, 100745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Liu, G.; Lu, L.; Li, J.; Han, X. Enhancing the estimation accuracy in low state-of-charge area: A novel onboard battery model through surface state of charge determination. J. Power Sources 2014, 270, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotas, R.; Iliadis, P.; Nikolopoulos, N.; Rakopoulos, D.; Tomboulides, A. Dynamic battery modeling for electric vehicle applications. Batteries 2024, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.K.; Mathew, M.; Janhunen, S.; Panchal, S.; Raahemifar, K.; Fraser, R.; Fowler, M. A comprehensive equivalent circuit model for lithium-ion batteries, incorporating the effects of state of health, state of charge, and temperature on model parameters. J. Energy Storage 2021, 43, 103252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, S.; Gladwin, D.; Stone, D. A systematic review of lumped-parameter equivalent circuit models for real-time estimation of lithium-ion battery states. J. Power Sources 2016, 316, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, B.; Etse-Dabu, B.; Xiong, X. A novel adaptive extended Kalman filtering and electrochemical-circuit combined modeling method for the online ternary battery state-of-charge estimation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 9720–9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.K.; Mevawalla, A.; Aziz, A.; Panchal, S.; Xie, Y.; Fowler, M. A review of lithium-ion battery thermal runaway modeling and diagnosis approaches. Processes 2022, 10, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Read, E.; Chen, Y.; Dai, Y.; Marco, J.; Shearing, P.R. Numerical and experimental characterization of nail penetration induced thermal runaway propagation in 21700 lithium-ion batteries: Exploring the role of interstitial thermal barrier materials. J. Energy Chem. 2025, 109, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ping, P.; Zhao, X.; Chu, G.; Sun, J.; Chen, C. Thermal runaway caused fire and explosion of lithium ion battery. J. Power Sources 2012, 208, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, F.; Schaltz, E.; Stroe, D.I.; Gismero, A.; Farjah, E. An enhanced equivalent circuit model with real-time parameter identification for battery state-of-charge estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 3743–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotouhi, A.; Auger, D.J.; Propp, K.; Longo, S. Lithium–sulfur battery state-of-charge observability analysis and estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 5847–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotouhi, A.; Auger, D.J.; Propp, K.; Longo, S. Electric vehicle battery parameter identification and SOC observability analysis: NiMH and Li-S case studies. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, N.; Duan, B.; Zhang, C. A novel fractional variable-order equivalent circuit model and parameter identification of electric vehicle Li-ion batteries. ISA Trans. 2020, 97, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Xiong, R.; Guo, H.; Li, S. Comparison study on the battery models used for the energy management of batteries in electric vehicles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 64, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Sun, F.; Zou, Y.; Peng, H. Online estimation of an electric vehicle lithium-ion battery using recursive least squares with forgetting. In Proceedings of the 2011 American Control Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 935–940. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, R.; Xu, Y.; Guo, H. Online model-based estimation of state-of-charge and open-circuit voltage of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles. Energy 2012, 39, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Z.; Xia, B.; Wang, W.; Sun, W.; Lai, Y.; Wang, M. A novel method for lithium-ion battery online parameter identification based on variable forgetting factor recursive least squares. Energies 2018, 11, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Fathy, H.K. Fisher identifiability analysis for a periodically-excited equivalent-circuit lithium-ion battery model. In Proceedings of the 2014 American Control Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 4–6 June 2014; pp. 274–280. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A.P.; Bitzer, M.; Imre, Á.W.; Guzzella, L. Experiment-driven electrochemical modeling and systematic parameterization for a lithium-ion battery cell. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 5071–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Stefanopoulou, A.G. Analytic bound on accuracy of battery state and parameter estimation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberger, M.J.; Anstrom, J.; Brennan, S.; Fathy, H.K. Maximizing parameter identifiability of an equivalent-circuit battery model using optimal periodic input shaping. In Proceedings of the Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, San Antonio, TX, USA, 22–24 October 2014; Volume 46186, p. V001T19A004. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Auger, D.J.; Perinpanayagam, S. Enhanced online identification of battery models exploiting data richness. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Systems for Aircraft, Railway, Ship Propulsion and Road Vehicles & International Transportation Electrification Conference (ESARS-ITEC), Venice, Italy, 28–31 March 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, R.; Wang, S.; Yu, C.; Xia, L. An estimation method for lithium-ion battery SOC of special robots based on Thevenin model and improved extended Kalman. Energy Storage Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 695. [Google Scholar]
- Shateri, N.; Auger, D.J.; Fotouhi, A.; Brighton, J.; Du, W.; Owen, R.E.; Brett, D.J.; Shearing, P.R. Investigation of the effect of temperature on lithium-sulfur cell cycle life performance using system identification and x-ray tomography. Batter. Supercaps 2022, 5, e202200035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
