Influence of the Porous Transport Layer Surface Structure on Overpotentials in PEM Water Electrolysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Preparation of Catalyst-Coated Membrane
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Different PTLs
2.3. Cell Assembly and Electrochemical Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
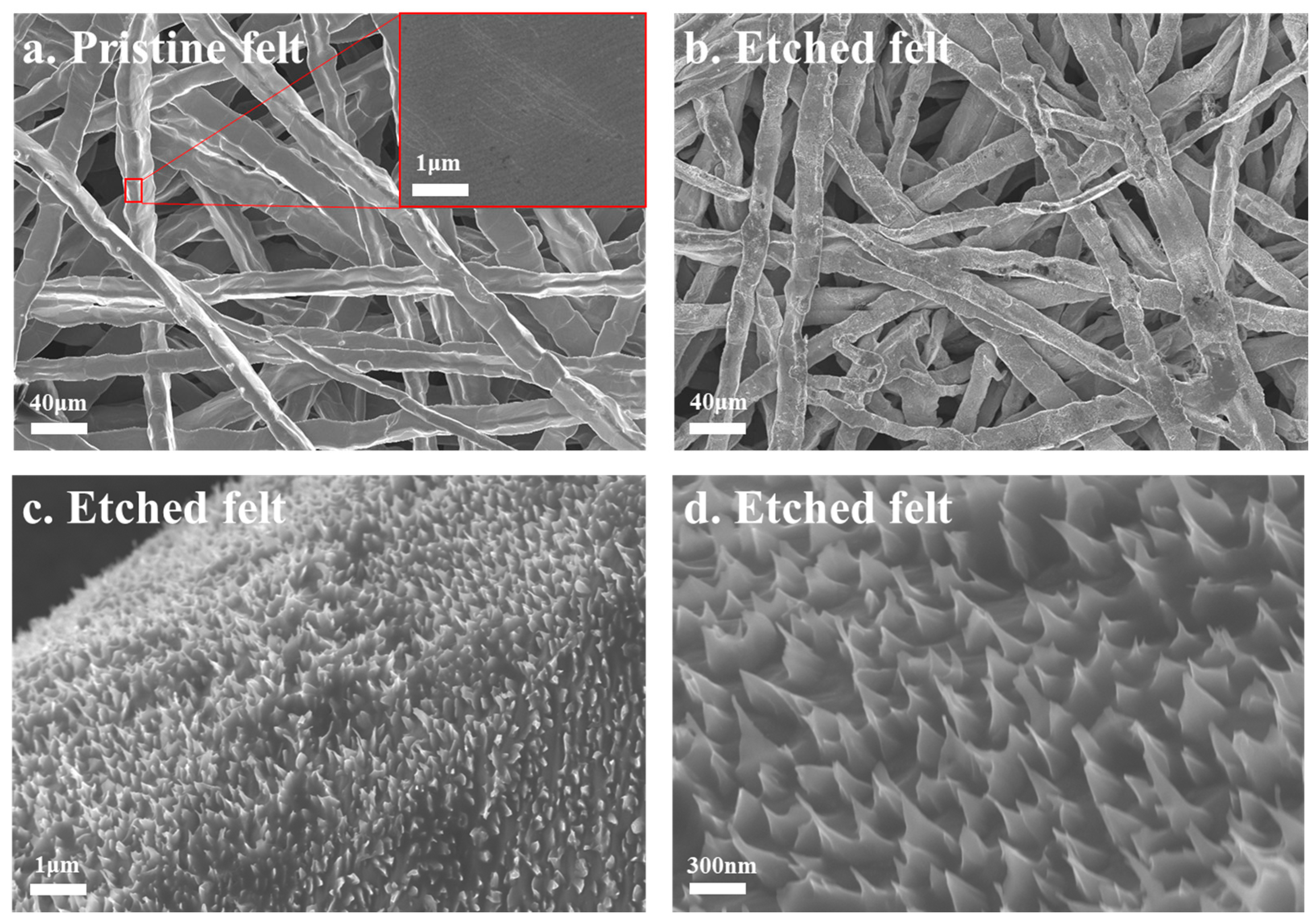
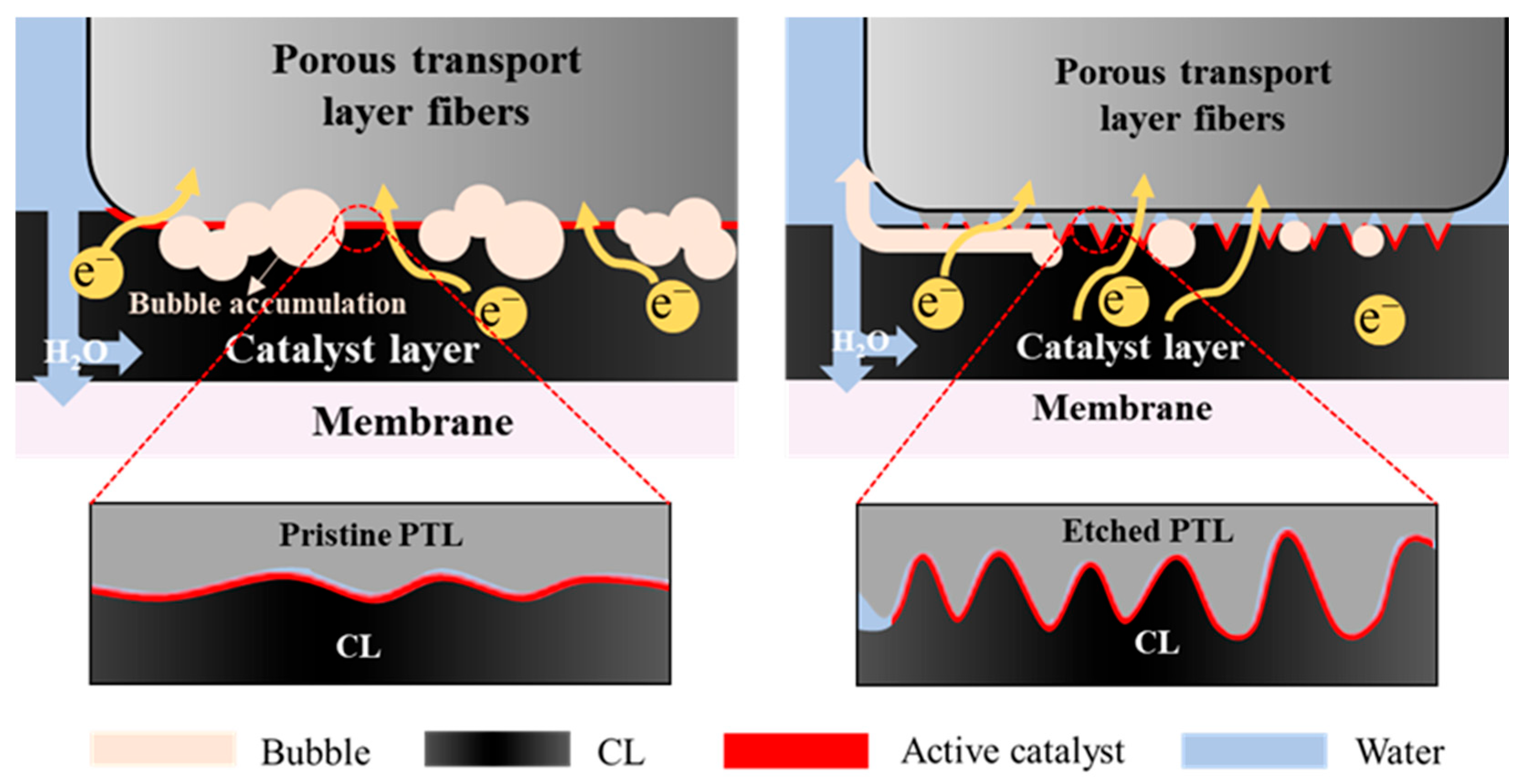
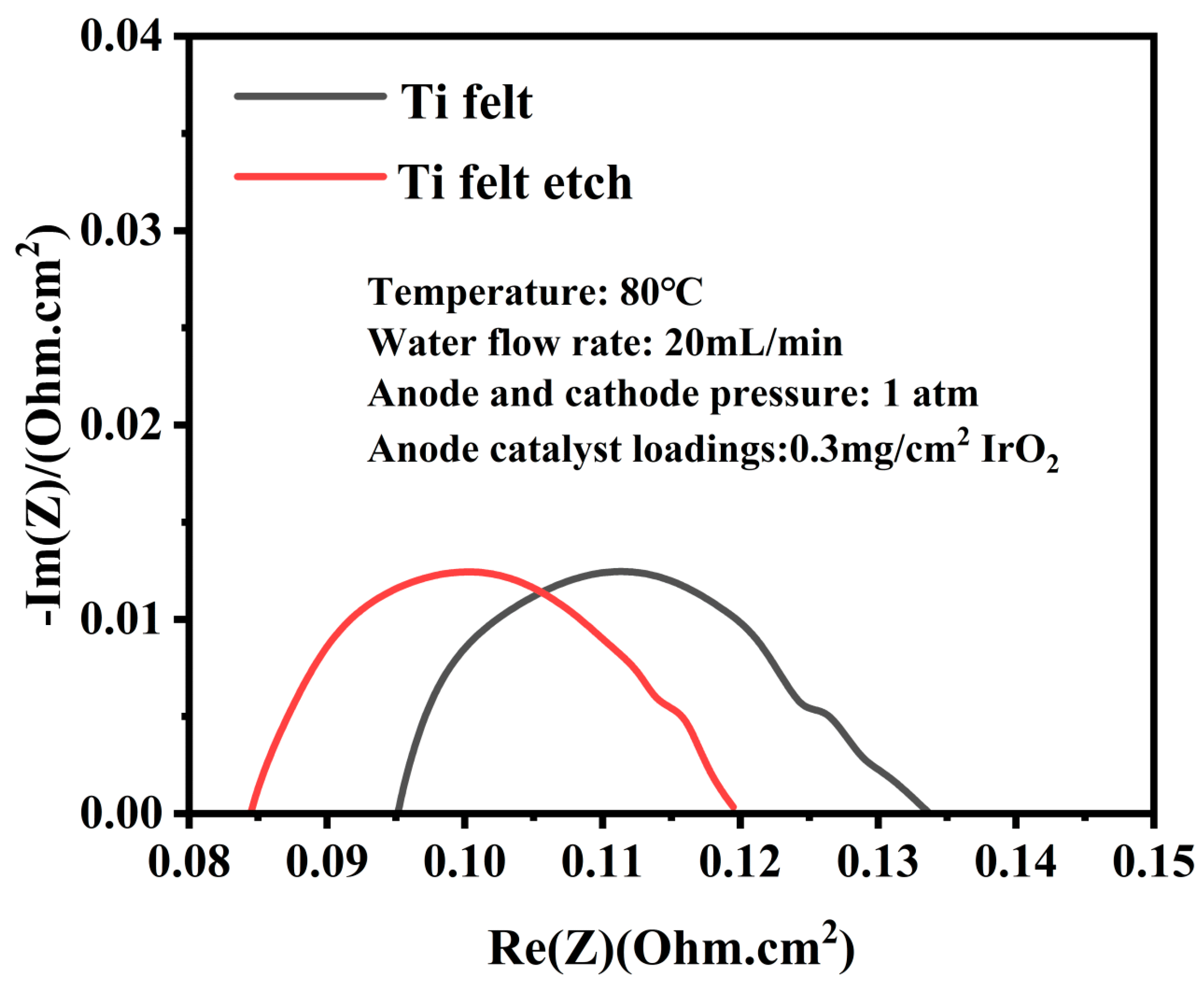
3.1. Acid-Etched Porous Transport Layers
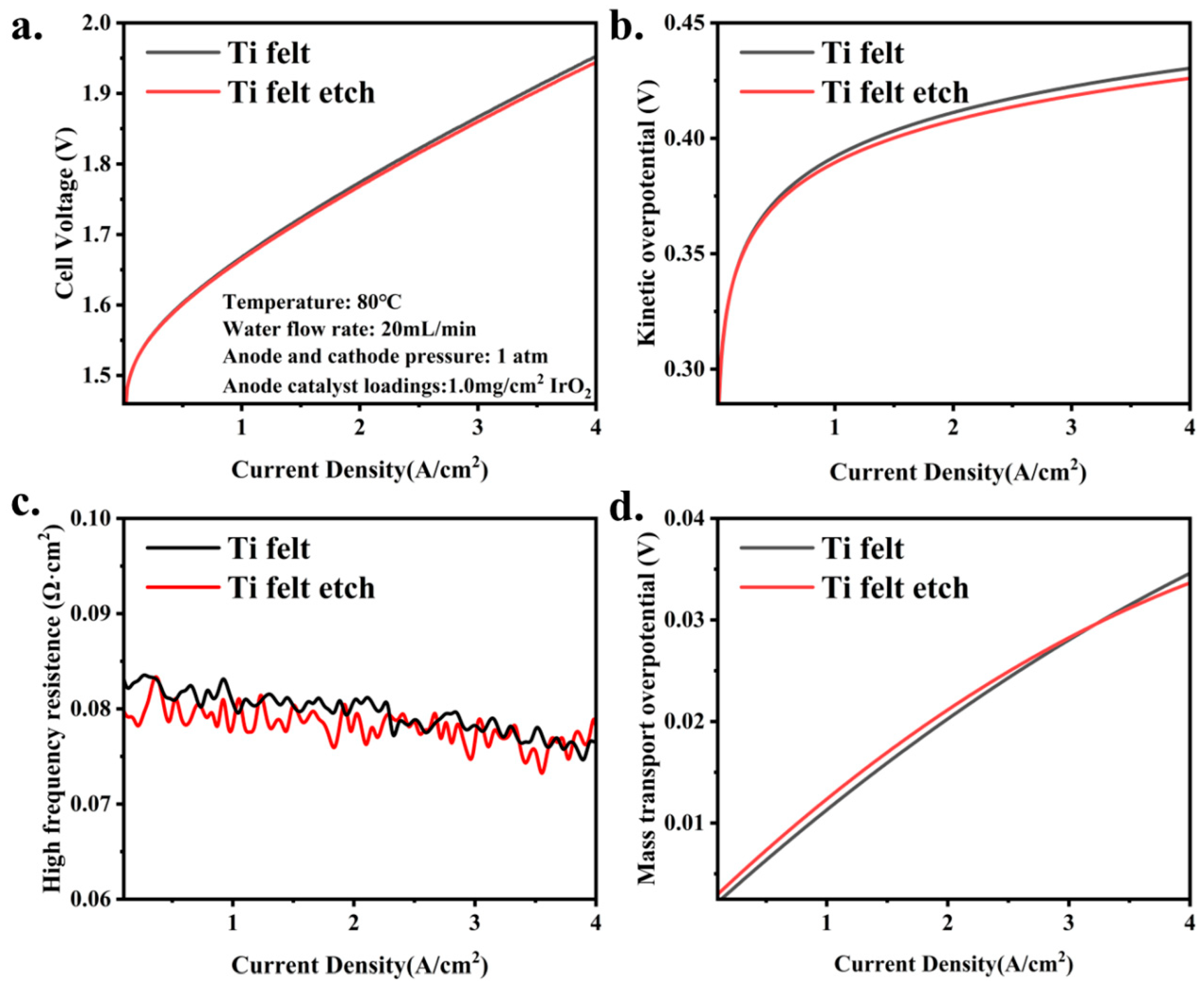
3.2. The Influence of PTL Surface Structure on Cell Performance with High Catalyst Loadings
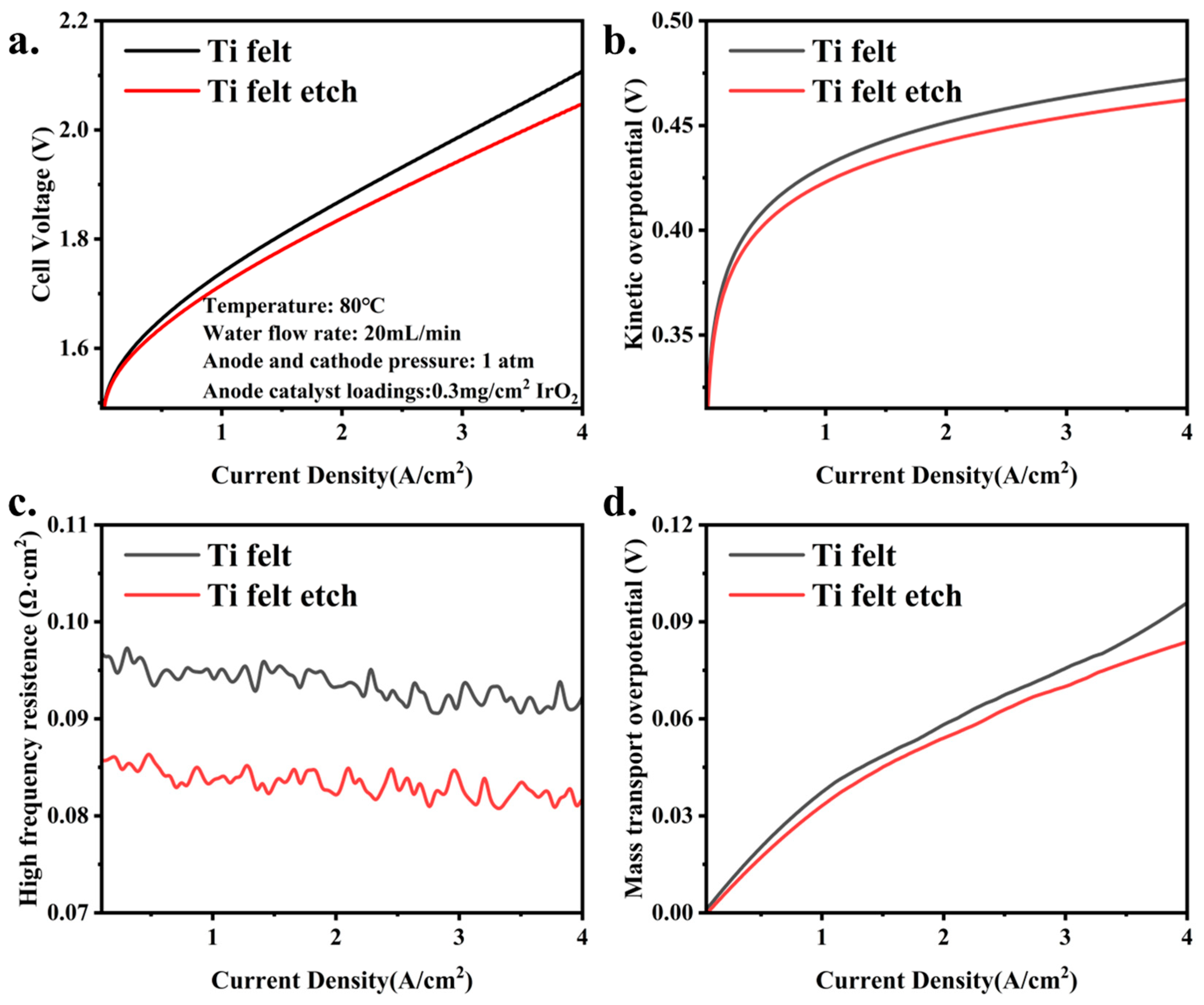
3.3. The Influence of PTL Surface Structure on Cell Performance with Low Catalyst Loadings
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEMWEs | Proton exchange membrane water electrolyzers |
| PTL | Porous transport layer |
| CL | Catalyst layer |
| MPL | Microporous layer |
| CCM | Catalyst-coated membrane |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
| HFR | High-frequency resistance |
| LFR | Low-frequency resistance |
| GDL | Gas diffusion layer |
| SGEIS | Staircase Galvano Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy |
References
- Bernt, M.; Gasteiger, H.A. Influence of Ionomer Content in IrO2/TiO2 Electrodes on PEM Water Electrolyzer Performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, F3179–F3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Hossain, M.M.; Wycisk, R.; Pintauro, P.N. Poly(phenylene sulfonic acid)-expanded polytetrafluoroethylene composite membrane for low relative humidity operation in hydrogen fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2022, 535, 231375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ma, H.; Khan, M.; Hsiao, B.S. Recent Advances and Challenges in Anion Exchange Membranes Development/Application for Water Electrolysis: A Review. Membranes 2024, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttler, A.; Spliethoff, H. Current status of water electrolysis for energy storage, grid balancing and sector coupling via power-to-gas and power-to-liquids: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2440–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehmin, M.N.I.; Husaini, T.; Goh, J.; Sulong, A.B. High-pressure PEM water electrolyser: A review on challenges and mitigation strategies towards green and low-cost hydrogen production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 268, 115985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A.H.A.; Tijani, A.S.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Hanapi, S. An overview of polymer electrolyte membrane electrolyzer for hydrogen production: Modeling and mass transport. J. Power Sources 2016, 309, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langemann, M.; Fritz, D.L.; Mueller, M.; Stolten, D. Validation and characterization of suitable materials for bipolar plates in PEM water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 11385–11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Shao, Z.; Baker, R.T.; Yi, B. Electrochemical investigation of electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction in PEM water electrolyzers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 4955–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandesris, M.; Medeau, V.; Guillet, N.; Chelghoum, S.; Thoby, D.; Fouda-Onana, F. Membrane degradation in PEM water electrolyzer: Numerical modeling and experimental evidence of the influence of temperature and current density. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 1353–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettenmeier, P.; Wang, R.; Abouatallah, R.; Helmly, S.; Morawietz, T.; Hiesgen, R.; Kolb, S.; Burggraf, F.; Kallo, J.; Gago, A.; et al. Durable Membrane Electrode Assemblies for Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzer Systems Operating at High Current Densities. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 210, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, F.N.; Wilberforce, T.; Ijaodola, O.; Ogungbemi, E.; El-Hassan, Z.; Durrant, A.; Thompson, J.; Olabi, A.G. Material degradation of components in polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) electrolytic cell and mitigation mechanisms: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 111, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Mo, J.; Wang, M.; Li, J.; Tian, X. Exploring and understanding the internal voltage losses through catalyst layers in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis devices. Appl. Energy 2022, 317, 119213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, J.; Xia, C.; Wang, P.; Xia, B.Y.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X. Key Components and Design Strategy for a Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzer. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2200130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, L.; Pan, L.; Yan, T.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J. Advances in Oxygen Evolution Electrocatalysts for Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzers. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2103670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Jia, J.; Ma, W.; Yan, X.; Liang, J. Recent advances in key components of proton exchange membrane water electrolysers. Mater. Chem. Front. 2024, 8, 2493–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Ding, L.; Yu, S.; Wang, W.; Capuano, C.B.; Keane, A.; Ayers, K.; Cullen, D.A.; Meyer, H.M.; Zhang, F.-Y. Ionomer-free nanoporous iridium nanosheet electrodes with boosted performance and catalyst utilization for high-efficiency water electrolyzers. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2024, 341, 123298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Mo, J.; Kang, Z.; Dohrmann, Y.; List, F.A., III; Green, J.B., Jr.; Babu, S.S.; Zhang, F.-Y. Fully printed and integrated electrolyzer cells with additive manufacturing for high-efficiency water splitting. Appl. Energy 2018, 215, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazarah, A.; Majlan, E.H.; Husaini, T.; Zainoodin, A.M.; Alshami, I.; Goh, J.; Masdar, M.S. Factors influencing the performance and durability of polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolyzer: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 35976–35989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiber, S.; Balzer, H.; Wierhake, A.; Wirkert, F.J.; Roth, J.; Rost, U.; Brodmann, M.; Lee, J.K.; Bazylak, A.; Waiblinger, W.; et al. Porous Transport Layers for Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolysis Under Extreme Conditions of Current Density, Temperature, and Pressure. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettenmeier, P.; Kolb, S.; Sata, N.; Fallisch, A.; Zielke, L.; Thiele, S.; Gago, A.S.; Friedrich, K.A. Comprehensive investigation of novel pore-graded gas diffusion layers for high-performance and cost-effective proton exchange membrane electrolyzers. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 2521–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Alia, S.M.; Young, J.L.; Bender, G. Effects of various parameters of different porous transport layers in proton exchange membrane water electrolysis. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 354, 136641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettenmeier, P.; Kolb, S.; Burggraf, F.; Gago, A.S.; Friedrich, K.A. Towards developing a backing layer for proton exchange membrane electrolyzers. J. Power Sources 2016, 311, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, T.; De Bruycker, R.; Schmidt, T.J.; Buchi, F.N. Polymer Electrolyte Water Electrolysis: Correlating Porous Transport Layer Structural Properties and Performance: Part I. Tomographic Analysis of Morphology and Topology. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F270–F281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriev, S.A.; Millet, P.; Volobuev, S.A.; Fateev, V.N. Optimization of porous current collectors for PEM water electrolysers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 4968–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusano, S.; Di Blasi, A.; Baglio, V.; Brunaccini, G.; Briguglio, N.; Stassi, A.; Ornelas, R.; Trifoni, E.; Antonucci, V.; Aricò, A. Optimization of components and assembling in a PEM electrolyzer stack. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 3333–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiber, S.; Sata, N.; Morawietz, T.; Ansar, S.A.; Jahnke, T.; Lee, J.K.; Bazylak, A.; Fallisch, A.; Gago, A.S.; Friedrich, K.A. A high-performance, durable and low-cost proton exchange membrane electrolyser with stainless steel components. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Satjaritanun, P.; Taie, Z.; Wiles, L.; Keane, A.; Capuano, C.; Zenyuk, I.V.; Danilovic, N. Insights into Interfacial and Bulk Transport Phenomena Affecting Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzer Performance at Ultra-Low Iridium Loadings. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2102950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.K.; Zhao, B.; Fahy, K.F.; Bazylak, A. Transient Gas Distribution in Porous Transport Layers of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Electrolyzers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 024508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, M.F.; Meier, V.; Kornherr, M.; Gasteiger, H.A. Preparation and Performance Evaluation of Microporous Transport Layers for Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Water Electrolyzer Anodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 074511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, T.; Weber, C.C.; Wrubel, J.A.; Gubler, L.; Pivovar, B.; Buchi, F.N.; Bender, G. Ultrathin Microporous Transport Layers: Implications for Low Catalyst Loadings, Thin Membranes, and High Current Density Operation for Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolysis. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2302786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Schuler, T.; Bender, G.; Sabharwal, M.; Peng, X.; Weber, A.Z.; Danilovic, N. Interfacial engineering via laser ablation for high-performing PEM water electrolysis. Appl. Energy 2023, 336, 120853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasa, B.; Aryal, U.R.; Higashi, S.; Tolouei, N.E.; Lang, J.T.; Erb, B.; Smeltz, A.; Zenyuk, I.V.; Zhu, G. Porous transport layer influence on overpotentials in PEM water electrolysis at low anode catalyst loadings. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. Energy 2025, 361, 124616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.K.; Anderson, G.; Tricker, A.W.; Babbe, F.; Madan, A.; Cullen, D.A.; Arregui-Mena, J.D.; Danilovic, N.; Mukundan, R.; Weber, A.Z.; et al. Ionomer-free and recyclable porous-transport electrode for high-performing proton-exchange-membrane water electrolysis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Du, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, L.; Song, J.; et al. Optimization of power allocation for wind-hydrogen system multi-stack PEM water electrolyzer considering degradation conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 5850–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopata, J.; Kang, Z.; Young, J.; Bender, G.; Weidner, J.W.; Shimpalee, S. Effects of the Transport/Catalyst Layer Interface and Catalyst Loading on Mass and Charge Transport Phenomena in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Water Electrolysis Devices. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 064507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darband, G.B.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Shanmugam, S. Recent advances in methods and technologies for enhancing bubble detachment during electrochemical water splitting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 114, 109300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Lu, Z.; Wan, P.; Kuang, Y.; Sun, X. High-Performance Water Electrolysis System with Double Nanostructured Superaerophobic Electrodes. Small 2016, 12, 2492–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, Y.; Lei, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, X. Nanoarray based “superaerophobic” surfaces for gas evolution reaction electrodes. Mater. Horiz. 2015, 2, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerz, C.; Bensmann, B.; Trinke, P.; Suermann, M.; Hanke-Rauschenbach, R. Local Current Density and Electrochemical Impedance Measurements within 50 cm Single-Channel PEM Electrolysis Cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, F1292–F1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Sui, S.; Zhai, Y. Investigations on high performance proton exchange membrane water electrolyzer. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suermann, M.; Bensmann, B.; Hanke-Rauschenbach, R. Degradation of Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) Water Electrolysis Cells: Looking Beyond the Cell Voltage Increase. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, F645–F652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.-L.; Yu, H.; Reeves, K.S.; Alia, S.M. Identifying electrochemical processes by distribution of relaxation times in proton exchange membrane electrolyzers. J. Power Sources 2025, 628, 235850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Li, K.; Wang, W.; Xie, Z.; Ding, L.; Kang, Z.; Wrubel, J.; Ma, Z.; Bender, G.; Yu, H.; et al. Tuning Catalyst Activation and Utilization Via Controlled Electrode Patterning for Low-Loading and High-Efficiency Water Electrolyzers. Small 2022, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, M.; Meng, Z.; Chen, R.; Song, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhao, S.; Tian, T.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, H. Evolution of the network structure and voltage loss of anode electrode with the polymeric dispersion in PEM water electrolyzer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 673, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, D.; Huynh, A.; Satjaritanun, P.; O’Brien, M.; Shimpalee, S.; Parkinson, D.; Shevchenko, P.; DeCarlo, F.; Danilovic, N.; Ayers, K.E.; et al. Elucidating effects of catalyst loadings and porous transport layer morphologies on operation of proton exchange membrane water electrolyzers. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 308, 121213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padgett, E.; Bender, G.; Haug, A.; Lewinski, K.; Sun, F.; Yu, H.; Cullen, D.A.; Steinbach, A.J.; Alia, S.M. Catalyst Layer Resistance and Utilization in PEM Electrolysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 084512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Hou, B.; Xie, Z.; Yang, G. Influence of the Porous Transport Layer Surface Structure on Overpotentials in PEM Water Electrolysis. Energies 2025, 18, 4396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164396
Yang S, Hou B, Xie Z, Yang G. Influence of the Porous Transport Layer Surface Structure on Overpotentials in PEM Water Electrolysis. Energies. 2025; 18(16):4396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164396
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shufeng, Bin Hou, Zhiqiang Xie, and Gaoqiang Yang. 2025. "Influence of the Porous Transport Layer Surface Structure on Overpotentials in PEM Water Electrolysis" Energies 18, no. 16: 4396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164396
APA StyleYang, S., Hou, B., Xie, Z., & Yang, G. (2025). Influence of the Porous Transport Layer Surface Structure on Overpotentials in PEM Water Electrolysis. Energies, 18(16), 4396. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164396




_Xie.png)

