Sensorless Induction Motor Control Based on an Improved Full-Order State Observer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Rotor Flux Linkage Model of IM Described by Voltage and Current
2.1. Current-Based Rotor Flux Linkage Model of IM
2.2. Voltage-Based Rotor Flux Linkage Model of IM
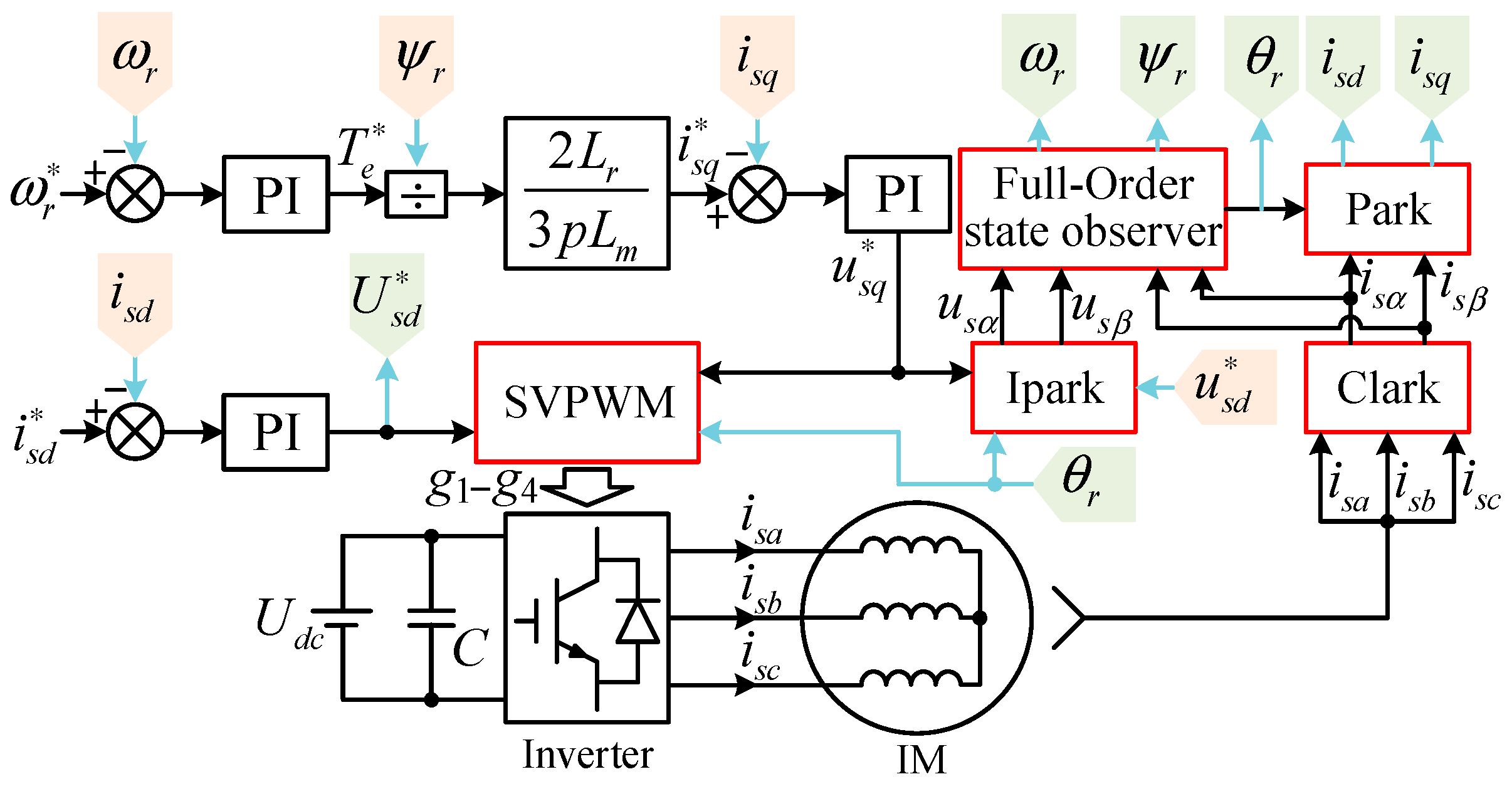
3. Adaptive Full-Order State Observer for IM
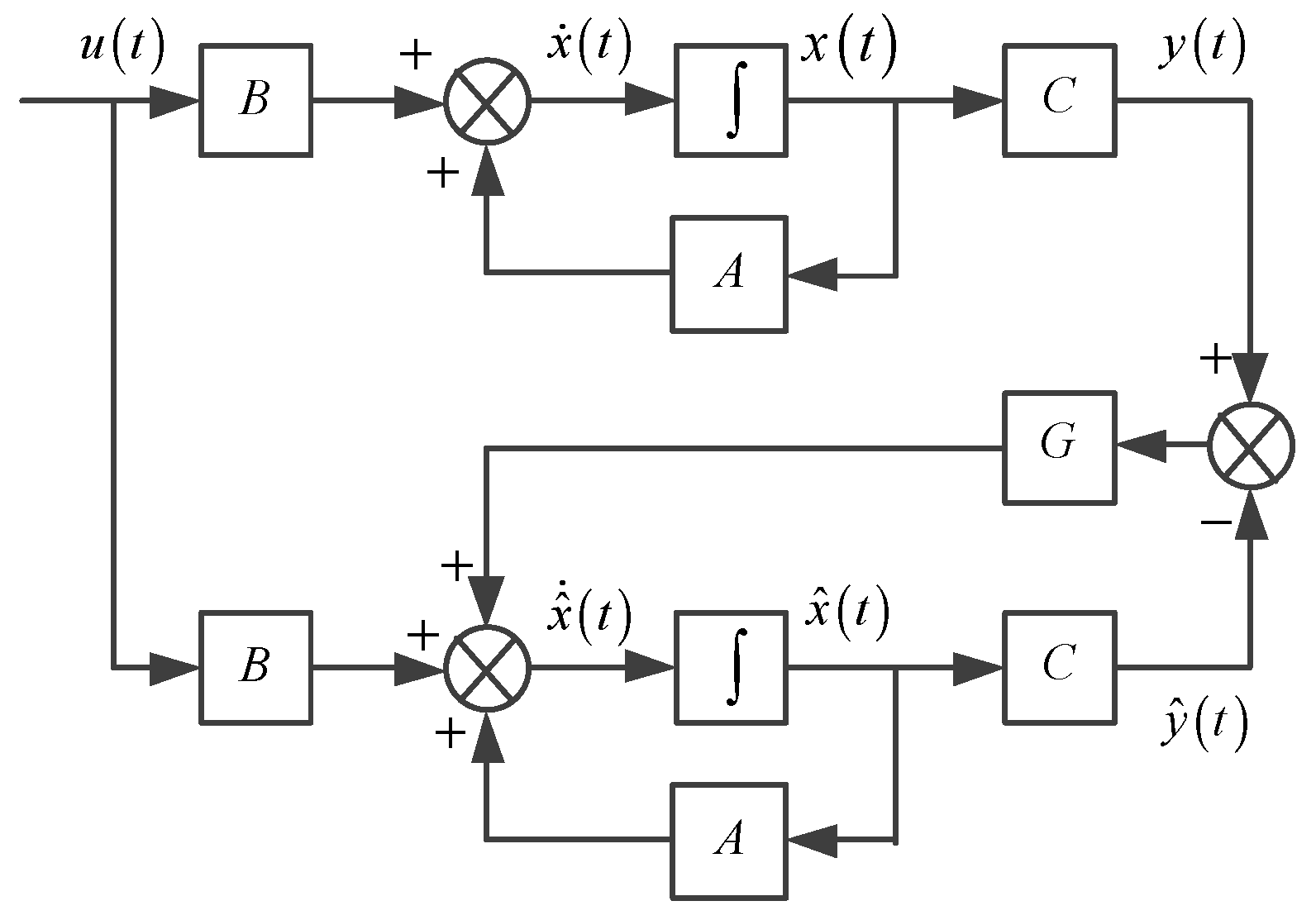
3.1. Principle of Full-Order State Observer
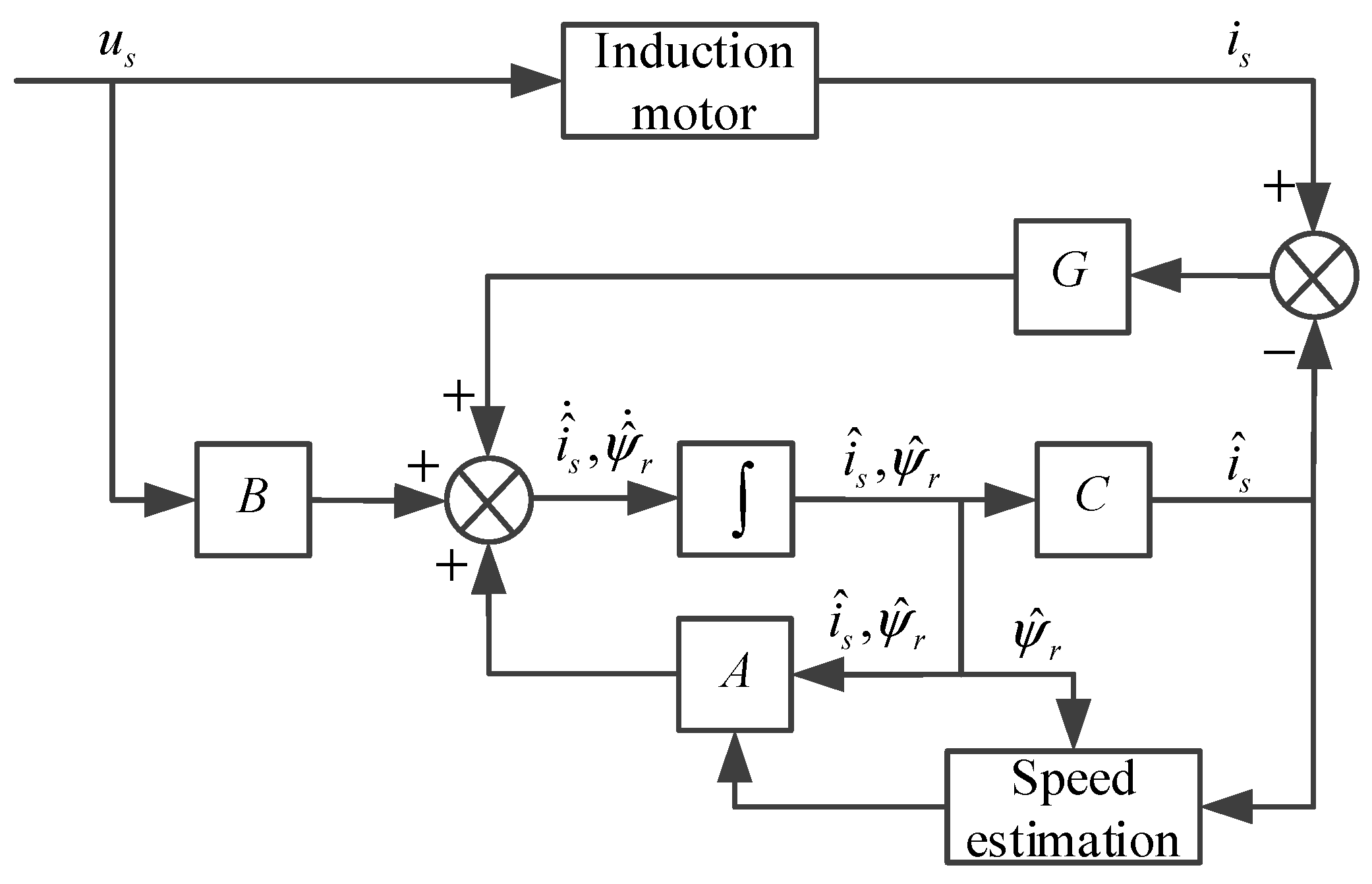
3.2. Full-Order State Observer for IM
3.3. Solution for Feedback Matrix
4. Simplification for Feedback Matrix and Speed Estimation
4.1. Simplification for Feedback Matrix
4.2. Speed Estimation Based on Current Error and Lyapunov Theory
5. Improvement in Low-Speed Performance of Full-Order State Observer
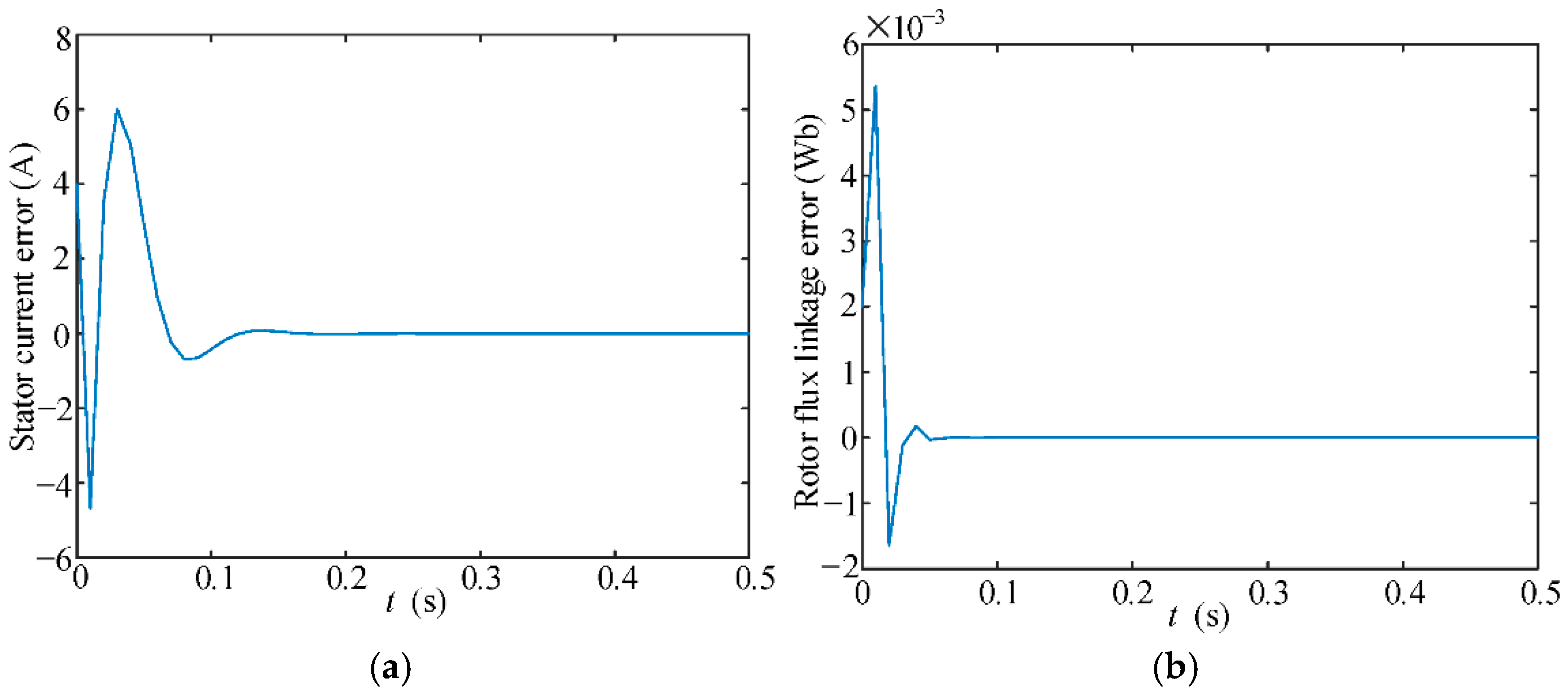
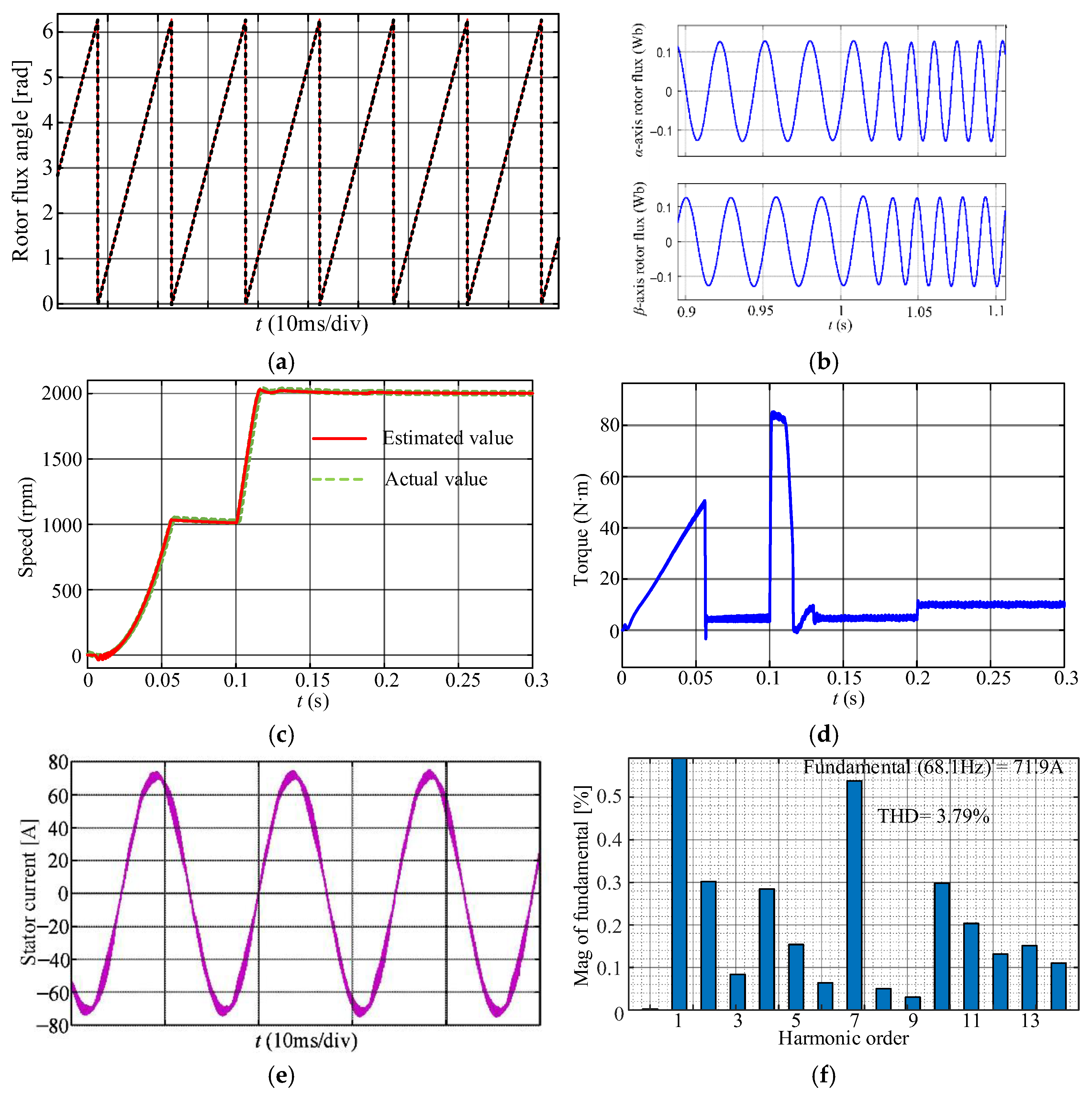
6. Simulation Verification
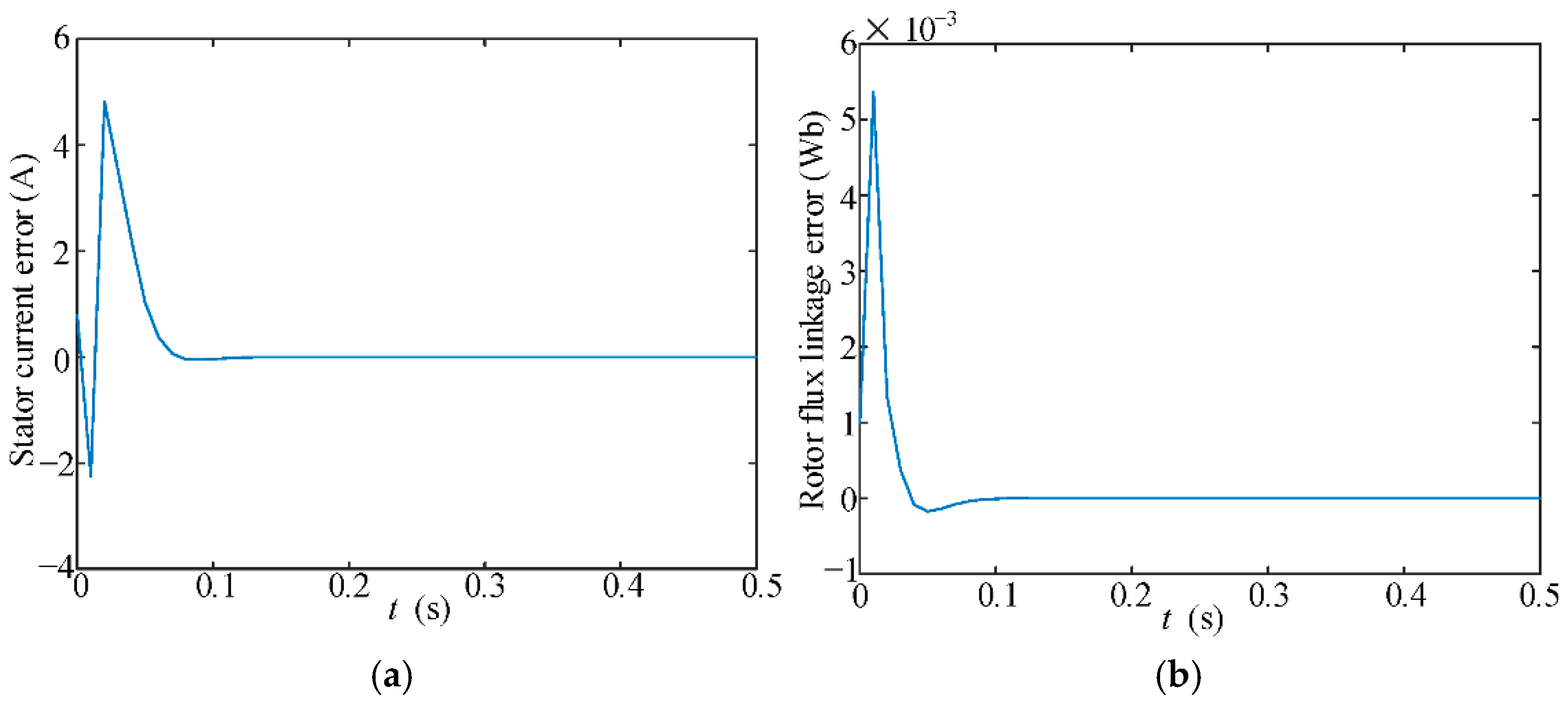
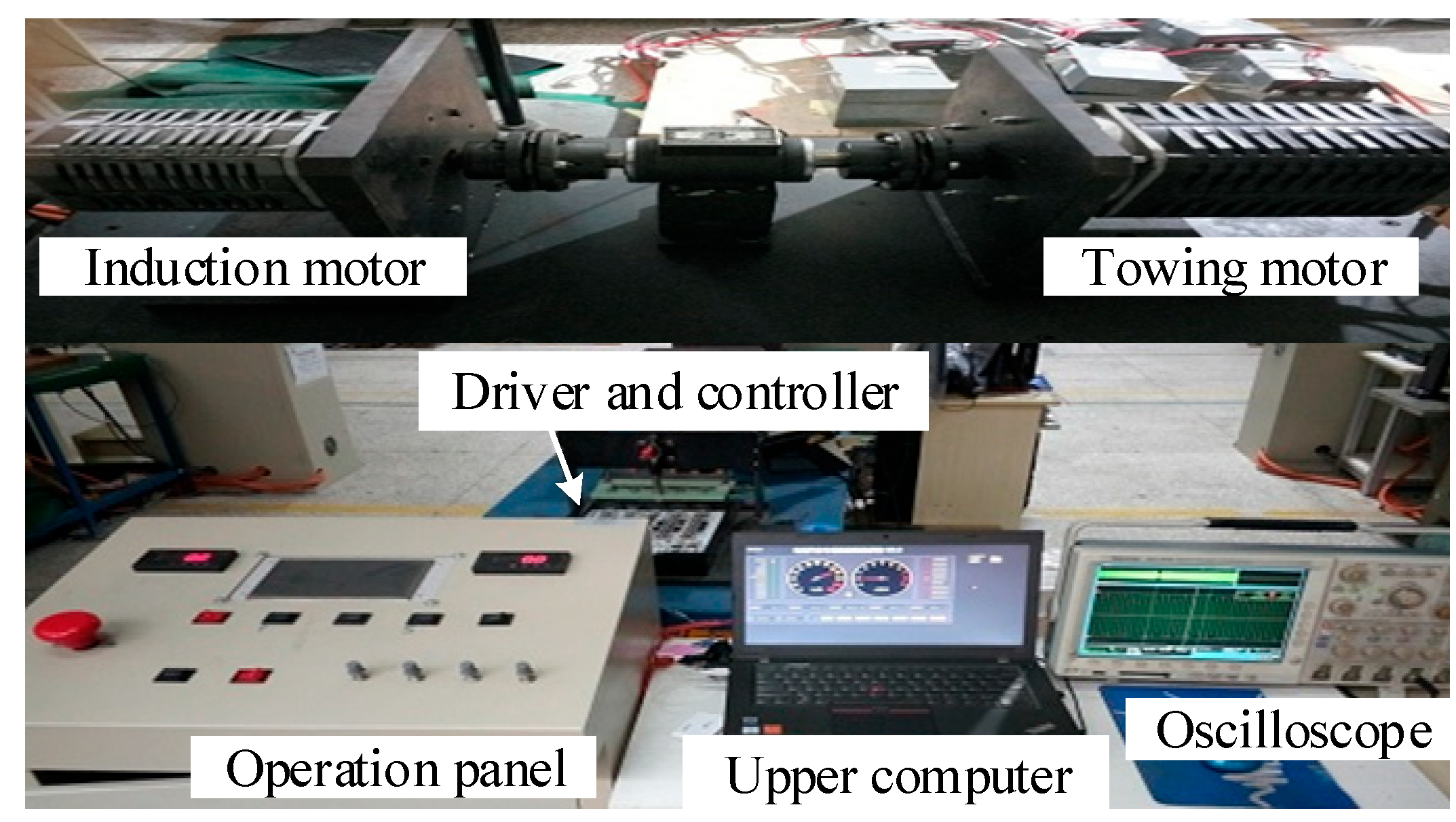
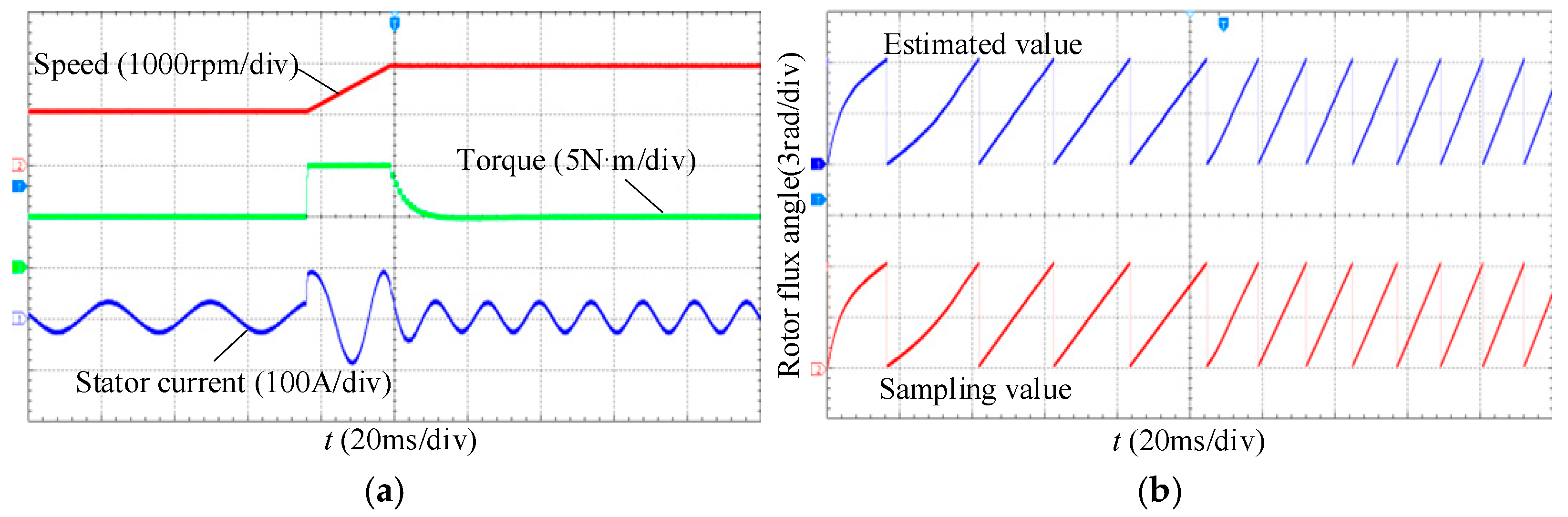
7. Experimental Verification
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Q.; Yi, L.; Long, X.; Luo, L.; Miao, Y. Dead-Time Free Modulation Scheme for IM Drive System Fed by Voltage Source Inverter. Energies 2024, 17, 3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.-H.; Song, C.-H.; Won, Y.-J.; Park, J.-C.; Kim, H.-S.; Park, H.-R. Magnetizing Inductance Estimation Method of Induction Motor for EV Traction Considering Magnetic Saturation Changes According to Current and Slip Frequency. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2024, 60, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Huang, R.; Liu, S.; Liu, C. Analysis of Winding-Connection Sequence in Multiphase Series-End Winding Motor Drives for Leg-Current Stress Reduction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2025, 21, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Song, Y.; Qi, W.; Guo, Q.; Li, X. Real-Time Global Optimal Energy Management Strategy for Connected PHEVs Based on Traffic Flow Information. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 20032–20042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, H.; Yuan, L. An Enhanced DC Preexcitation With Effective Flux-Linkage Control for the High-Power Induction Motor Drive System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 2375–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Lan, P.; Xiang, S. Investigation on thermal management of cylindrical lithium-ion batteries based on interwound cooling belt structure. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 340, 119962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagam, V.S.R.; Devabhaktuni, S. An Isolation Transformer-less Single DC Source fed Dual 5-leg Inverter Controlled 5-Phase Induction Motor with Modified Direct Torque Control. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2024, 22, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, X. A Double Vector Model Predictive Torque Control Method Based on Geometrical Solution for SPMSM Drive in Full Modulation Range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 5558–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Sasamura, T.; Morita, T. Sensorless Speed Control of Ultrasonic Motors Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 4023–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, P.; Miao, Y. Overlap Time Compensation and Characteristic Analysis for Current Source Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverter. Energies 2024, 17, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meira, M.; Bossio, G.R.; Verucchi, C.J.; Ruschetti, C.R.; Bossio, J.M. Speed Estimation During the Starting Transient of Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.; Roy, S.B. Closed-Loop Reference Model Based Distributed Model Reference Adaptive Control for Multi-Agent Systems. IEEE Control. Syst. Lett. 2021, 5, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, D. Speed and flux observer based on adaptive linear neuron for induction motor. J. Power Electron. 2023, 23, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerdali, E. Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter for Speed-Sensorless Control of Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwasilu, F.; Jung, J.-W. Enhanced Fault-Tolerant Control of Interior PMSMs Based on an Adaptive EKF for EV Traction Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5746–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhuang, W.; Li, B.; Li, K.; Xia, T.; Hu, B. Integration of Planning and Deep Reinforcement Learning in Speed and Lane Change Decision-Making for Highway Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2025, 11, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komurcugil, H.; Zhang, Z.; Bayhan, S. Guest Editorial Special Section on Recent Advances on Sliding Mode Control and Its Applications in Modern Industrial Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalavarthi, A.; Singh, B. Sensorless Speed Control of SRM Drive Using Optimized Neural Network Model for Rotor Position Estimation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2024, 39, 2158–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, J.; Lu, M. The Hall Sensors Fault-Tolerant for PMSM Based on Switching Sensorless Control With PI Parameters Optimization. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 114048–114059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davari, S.A.; Khaburi, D.A.; Wang, F.; Kennel, R.M. Using Full Order and Reduced Order Observers for Robust Sensorless Predictive Torque Control of Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3424–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Gao, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, D. Robustness Improvement of Speed Estimation in Speed-Sensorless Induction Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 2525–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Xu, Q.; Yang, T.; Tu, Y. Internal Model Current Decoupling Control Strategy for Induction Motors. Energies 2025, 18, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| s3 | s2 | s1 | s0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | m2 | m1−m0/m2 | m0 |
| m1 | m0 | 0 | 0 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated voltage | 72 V |
| Rated frequency | 50 Hz |
| Rated power | 30 kW |
| Rated current | 200 A |
| Stator resistance | 0.052 Ω |
| Rotor resistance | 0.035 Ω |
| Stator leakage inductance | 16.3 μH |
| Rotor leakage inductance | 27.5 μH |
| Magnetic inductance | 1.43 mH |
| Number of pole pairs | 2 |
| Category | Part Number | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| DC power supply | PR300-4 (YOKOGAWA, Tokyo, Japan) | 72 V |
| Switching tubes (IGBT) | IPB042N10N (Infineon, Munich, Germany) | 100 V/100 A |
| Current sensors | MLX91205 (MELEXIS, Brussels, Belgium) | / |
| Digital signal controller | TMS320F28035 (Texas Instruments, Dallas, TX, USA) | / |
| Encoder | OIH (Tamagawa, Tokyo, Japan) | 2500 C/T |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Q.; Xu, Q.; Luo, L.; Tu, Y.; Song, W. Sensorless Induction Motor Control Based on an Improved Full-Order State Observer. Energies 2025, 18, 4374. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164374
Xie Q, Xu Q, Luo L, Tu Y, Song W. Sensorless Induction Motor Control Based on an Improved Full-Order State Observer. Energies. 2025; 18(16):4374. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164374
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Qiuyue, Qiwei Xu, Lingyan Luo, Yuxiaoying Tu, and Wuyu Song. 2025. "Sensorless Induction Motor Control Based on an Improved Full-Order State Observer" Energies 18, no. 16: 4374. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164374
APA StyleXie, Q., Xu, Q., Luo, L., Tu, Y., & Song, W. (2025). Sensorless Induction Motor Control Based on an Improved Full-Order State Observer. Energies, 18(16), 4374. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164374







