Effects of Partial Admission Ratio on the Performance and Flow Characteristics of a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Axial-Flow Turbine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
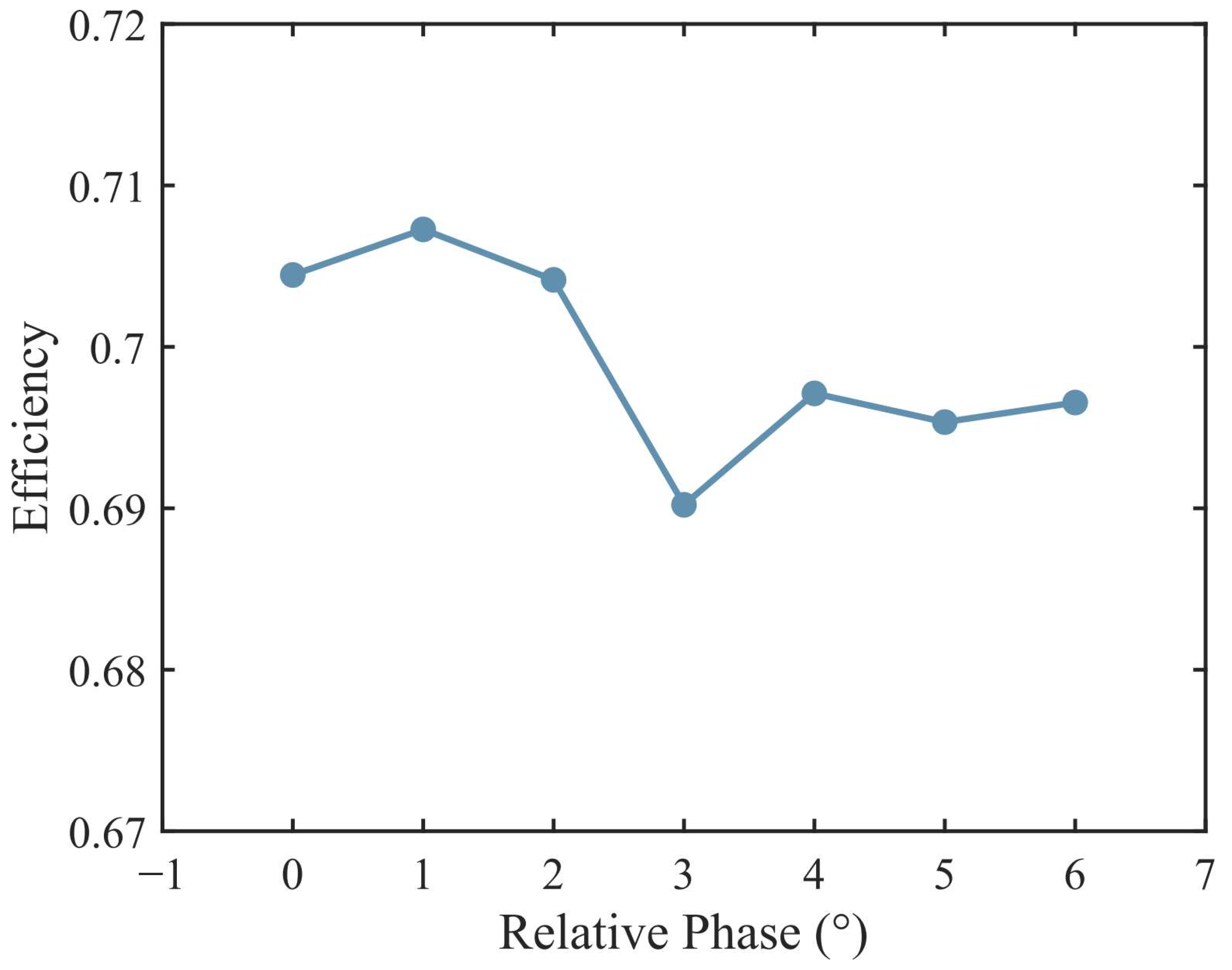
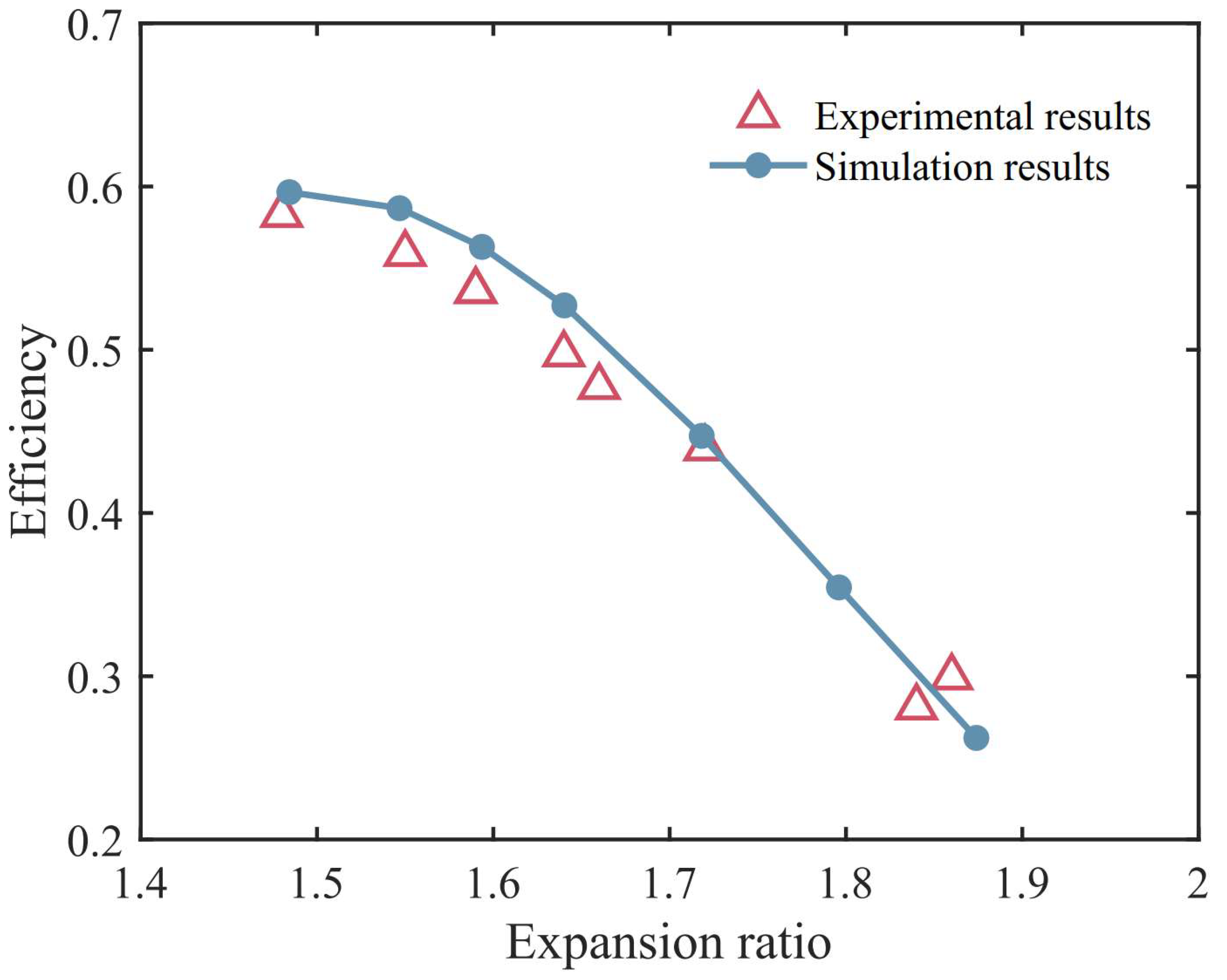
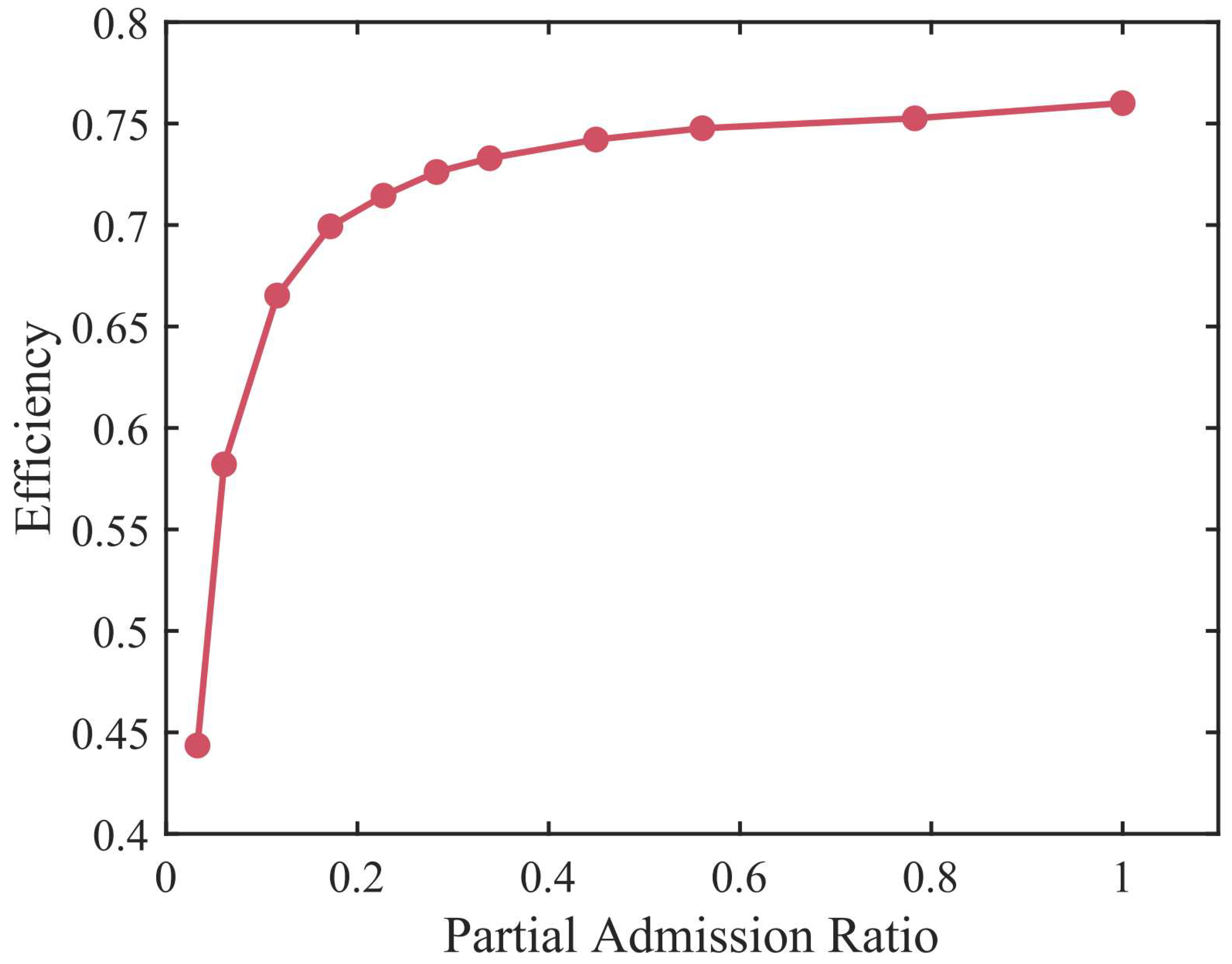
3.1. Performance of the Partial Admission Turbine
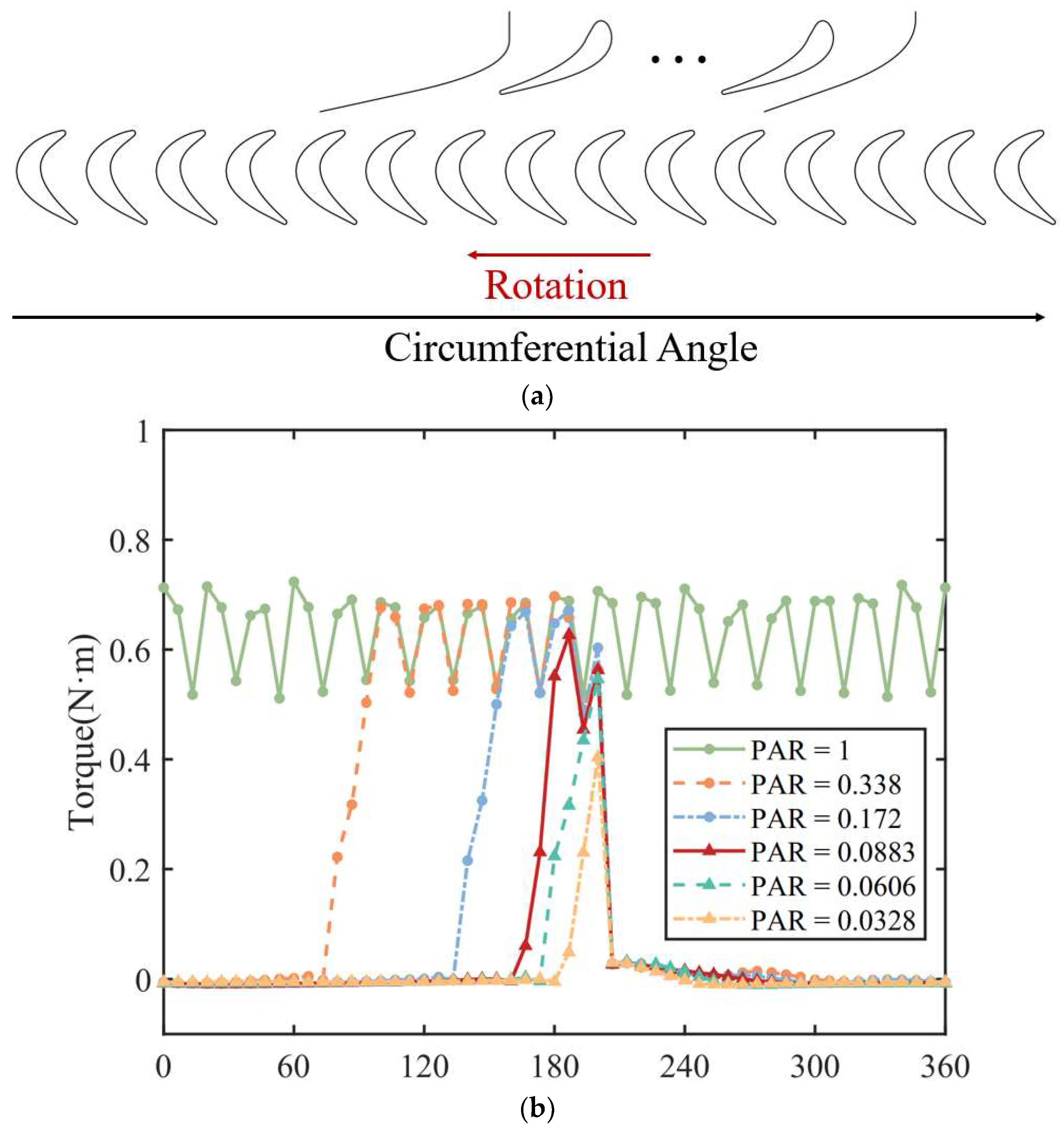
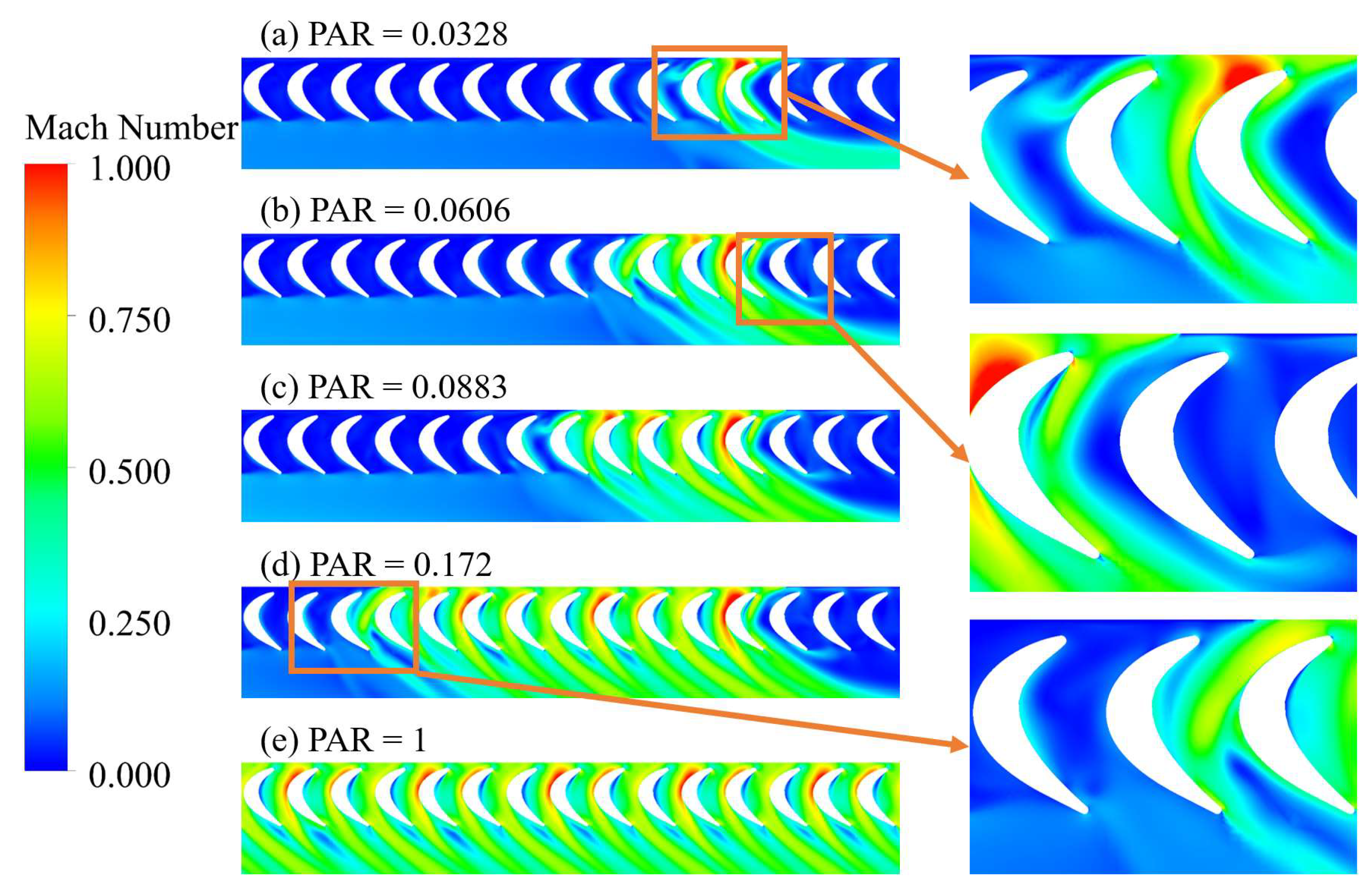
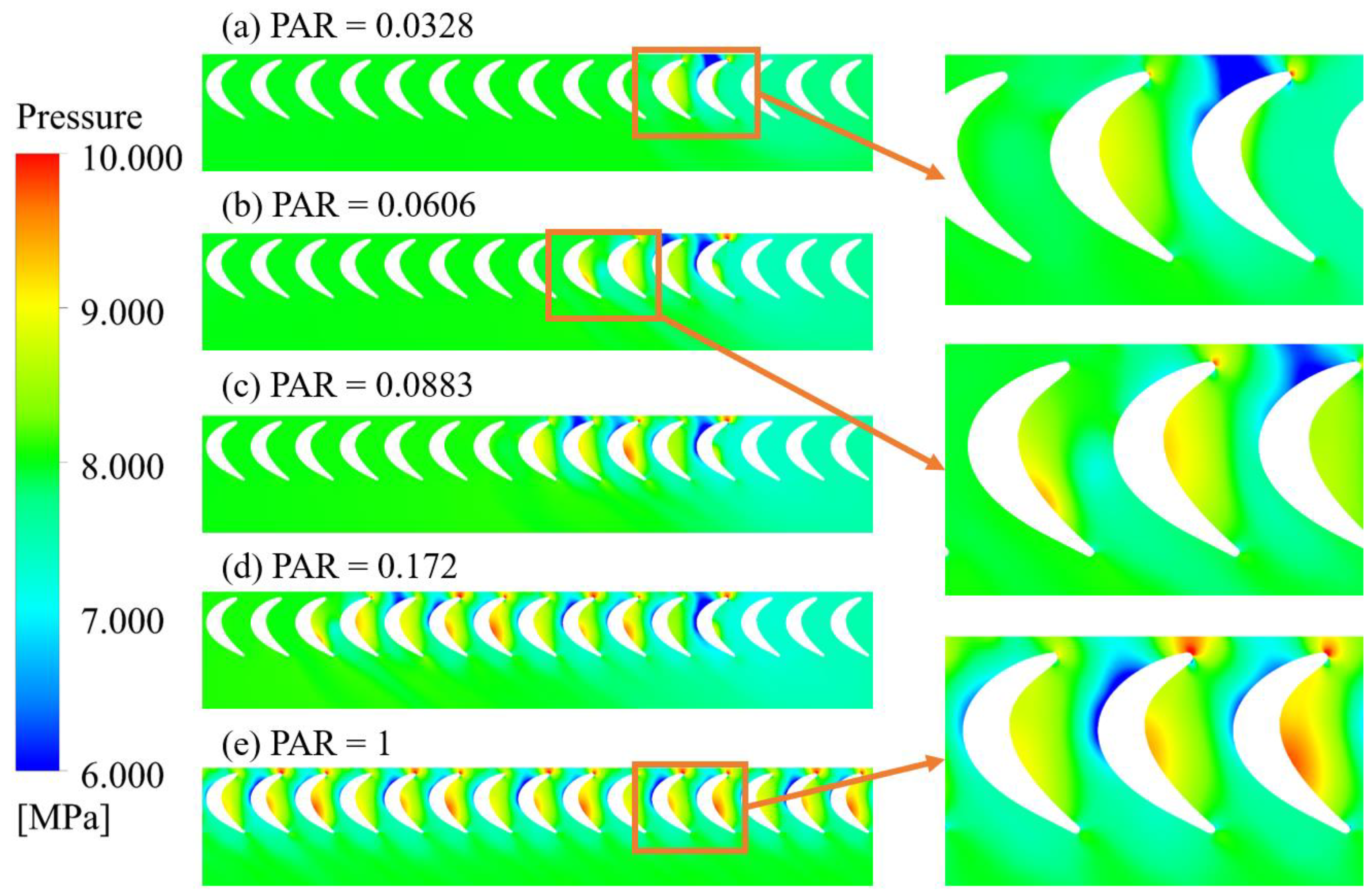
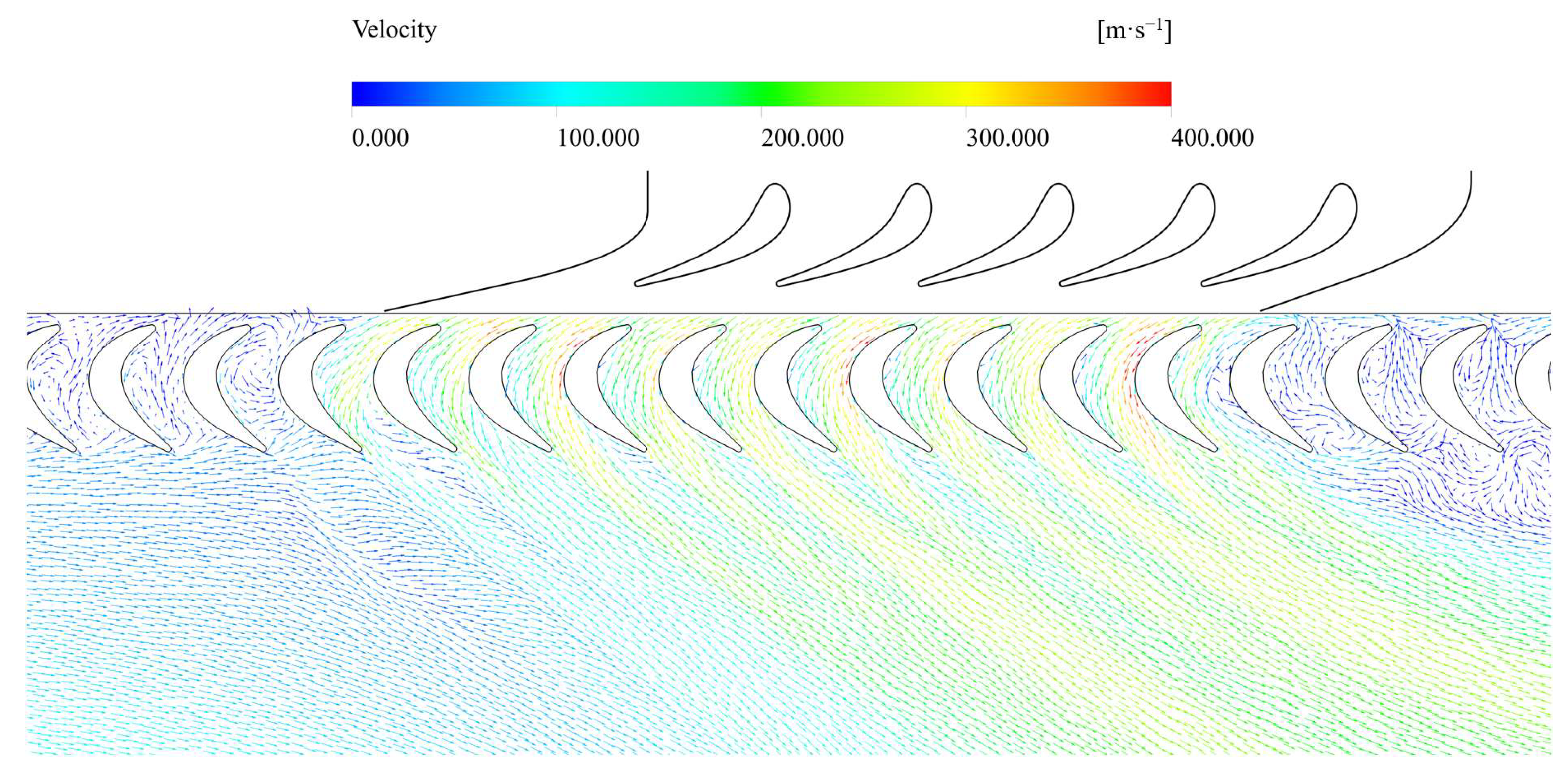
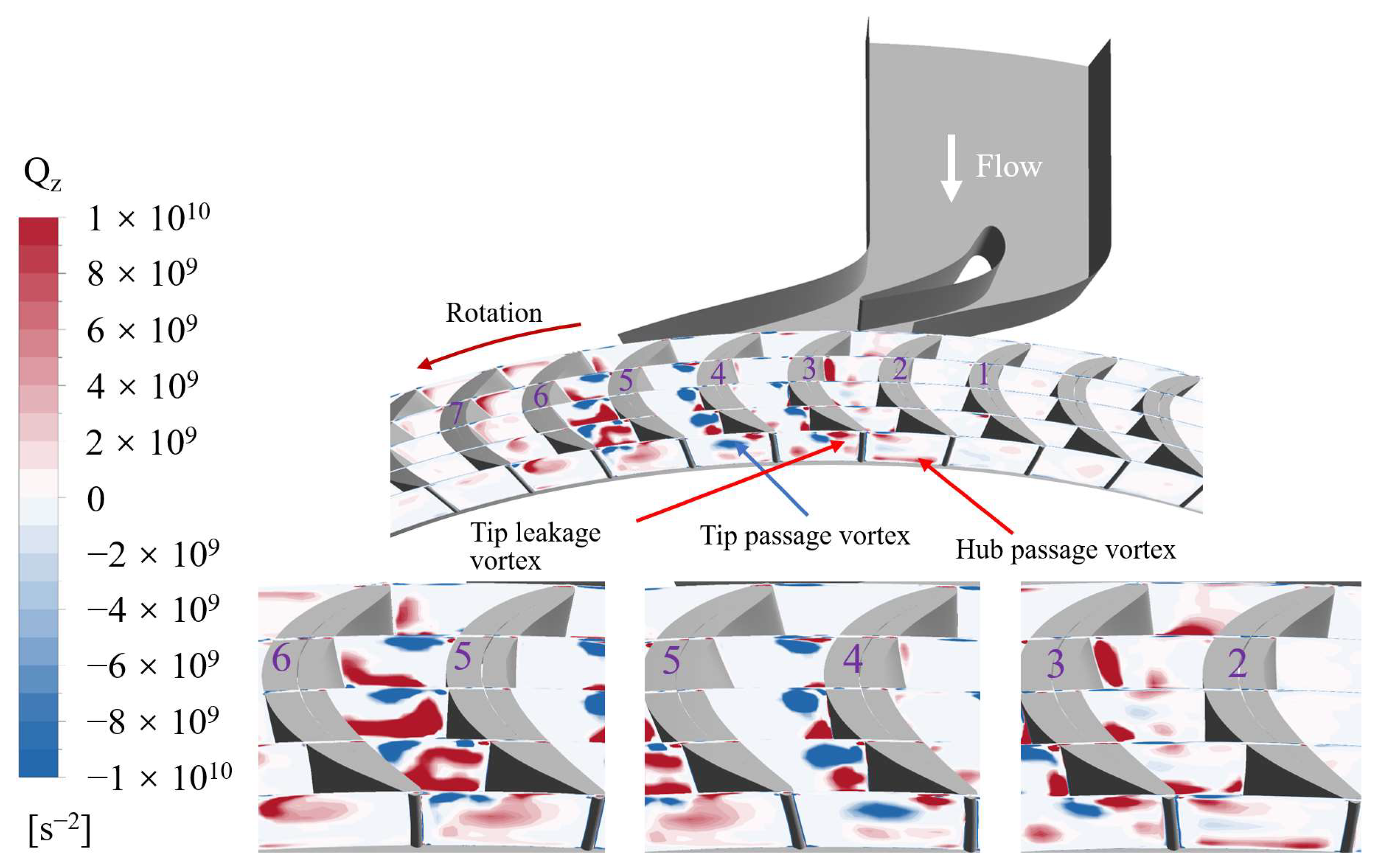
3.2. Flow Field of the Partial Admission Turbine
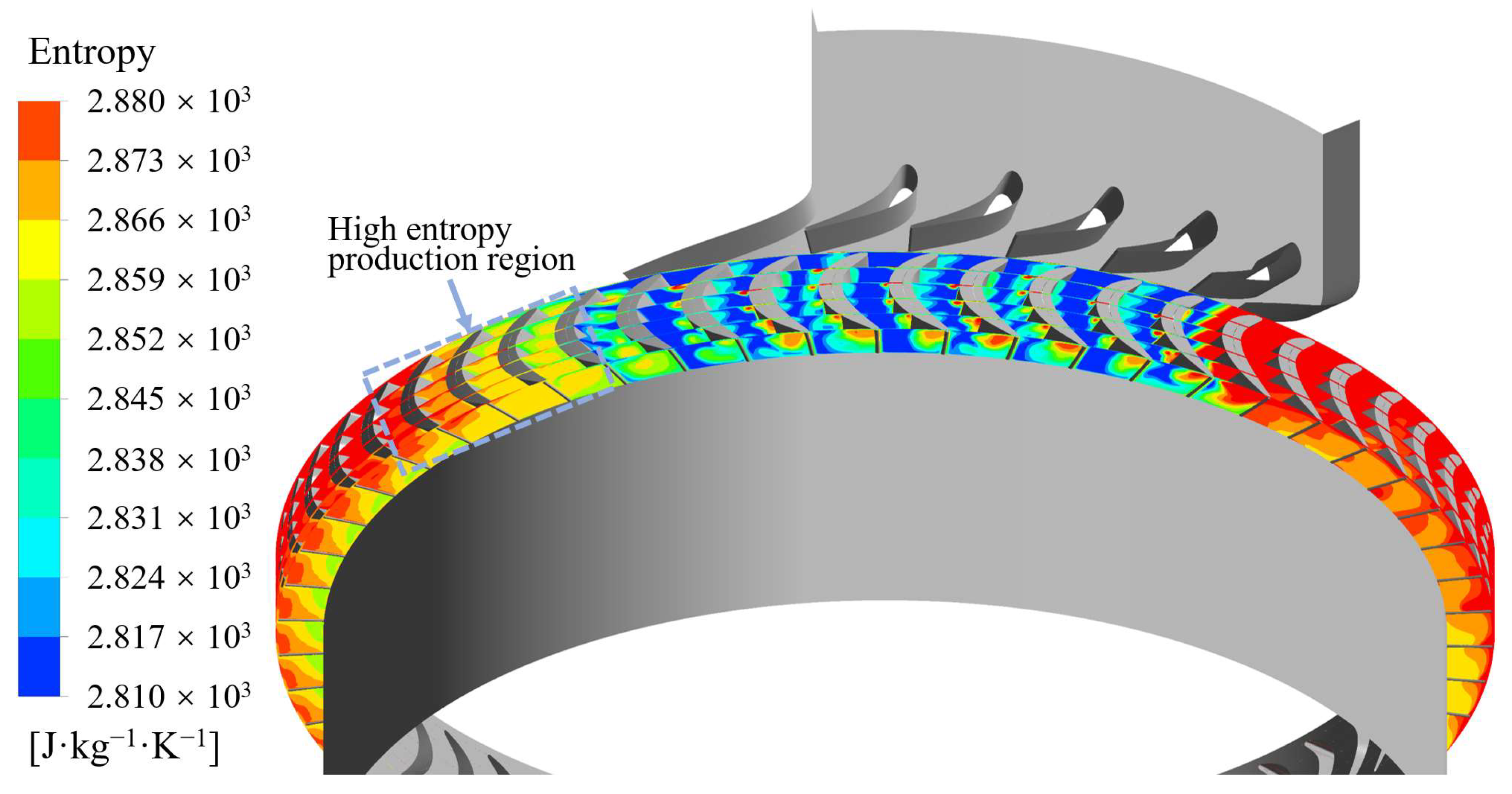
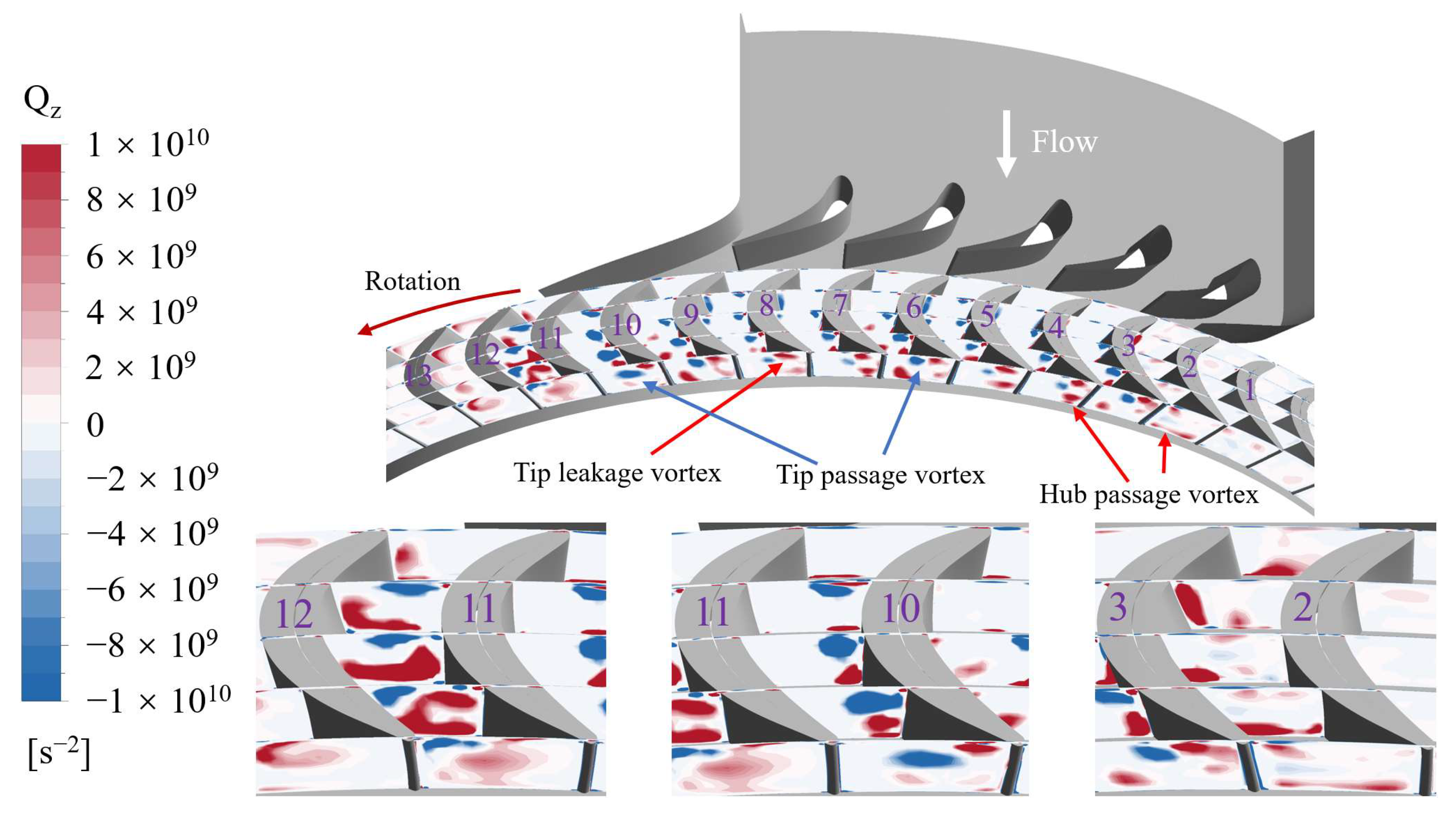
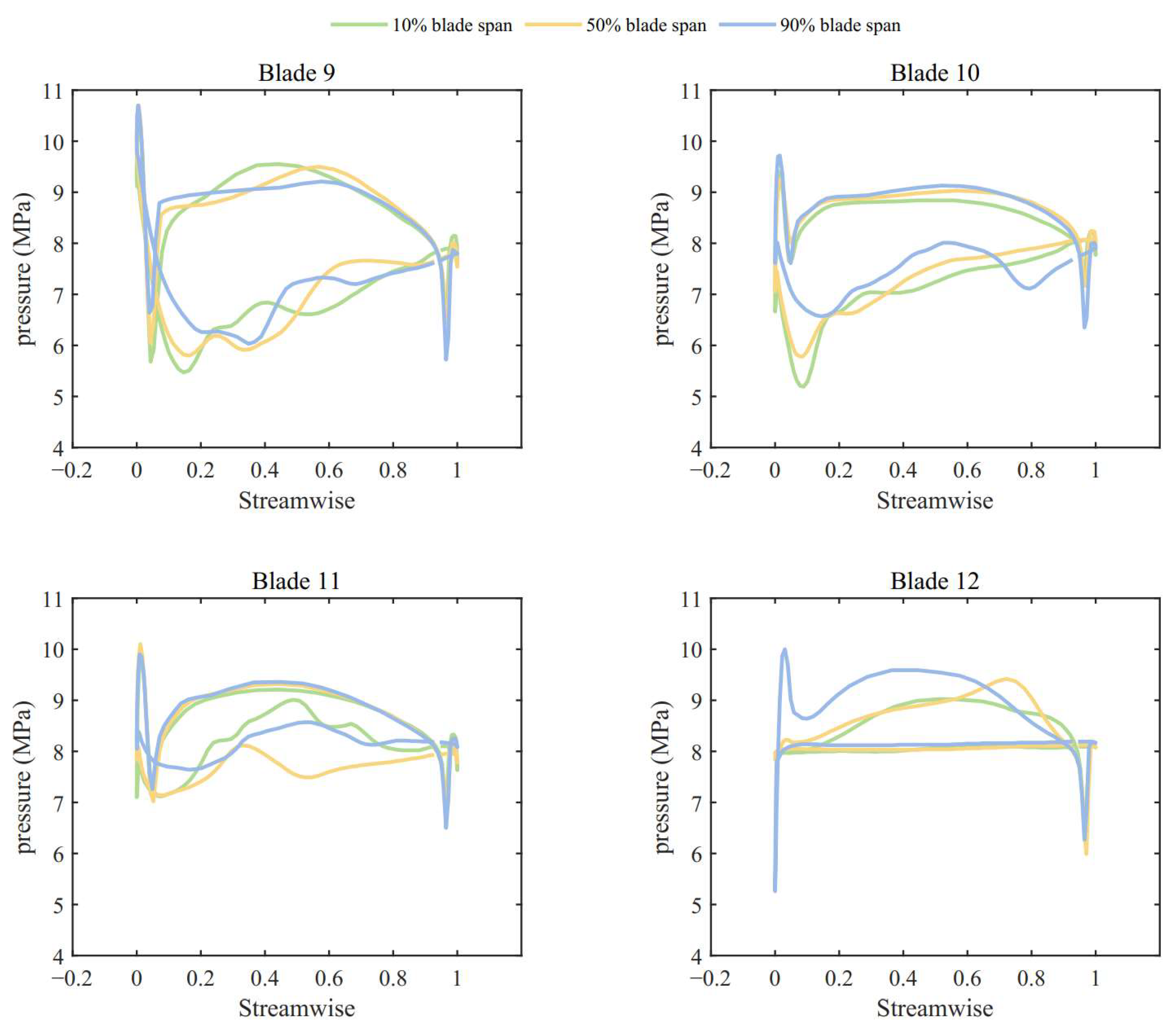
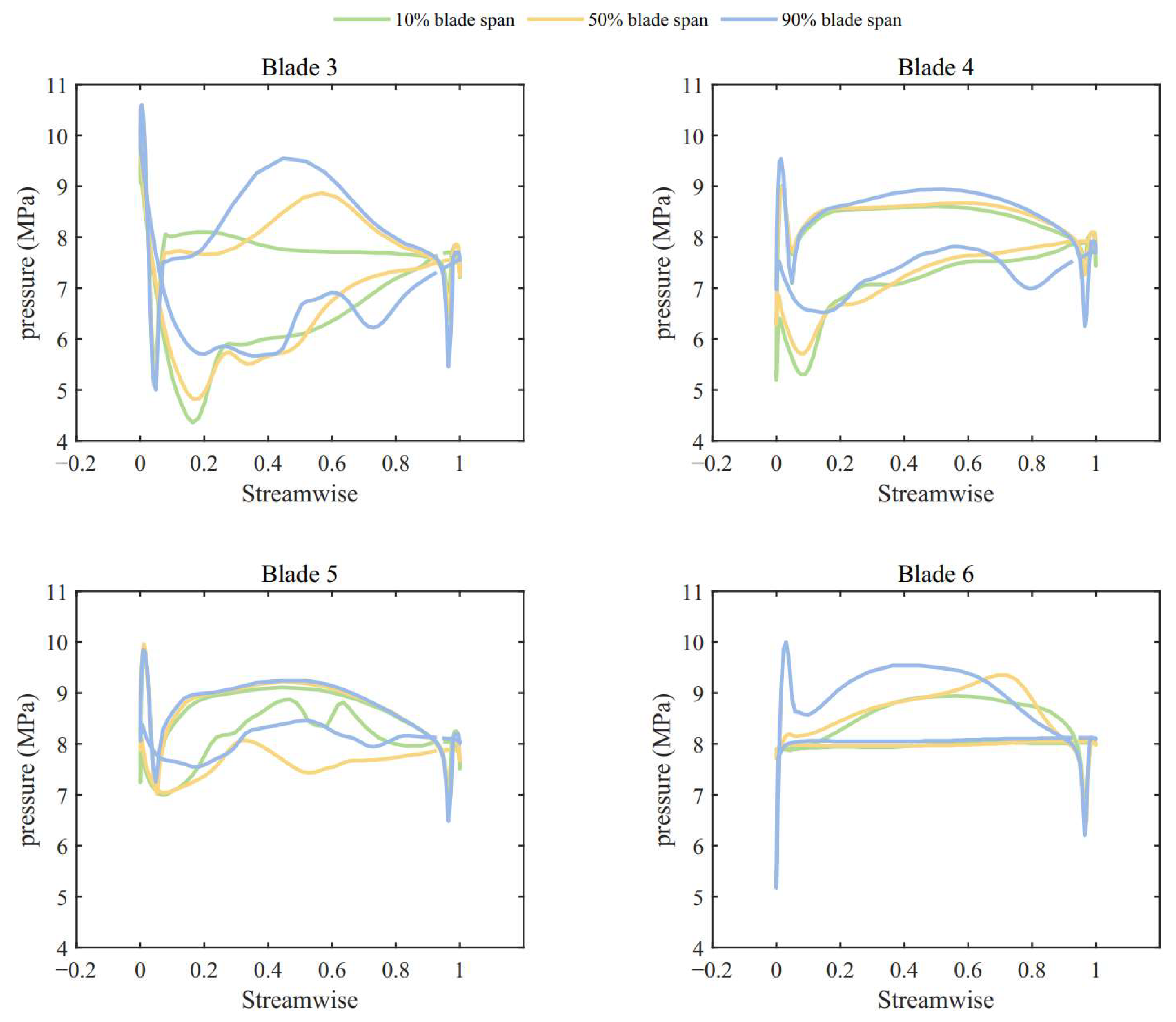
3.3. Effect of Vortex Flow on Turbine Performance
3.3.1. Vortex Flow Characteristics at High Partial Admission Ratio
3.3.2. Vortex Flow Characteristics at Low Partial Admission Ratio
4. Conclusions
- The turbine efficiency decreases as the partial admission ratio decreases, especially when the partial admission ratio is below 0.3, where the efficiency rapidly drops. For the turbine simulated in this study, a partial admission ratio of 0.338 leads to a 2.71 percentage point reduction in efficiency, and a partial admission ratio of 0.172 results in a 6.07 percentage point efficiency drop.
- The torque on the rotor blades suddenly increases to a relatively high level upon entering the active sector. As the blades move from the active sector to the inactive sector, the torque gradually decreases, with about three blade passages showing significantly lower torque compared to full admission conditions. When the partial admission ratio is less than 0.1, the maximum blade torque begins to decrease as the partial admission ratio decreases.
- Vortex structures, including the tip leakage vortex, tip passage vortex, and hub passage vortex, were observed within the rotor passages. As a passage enters the active sector, high-momentum fluid from the nozzle mixes with stagnating fluid. A prominent hub passage vortex develops within the passage. Just before a passage exits the active sector, a tip passage vortex of greater intensity compared to full admission passages is observed, followed by the formation of a large-scale counterclockwise vortex.
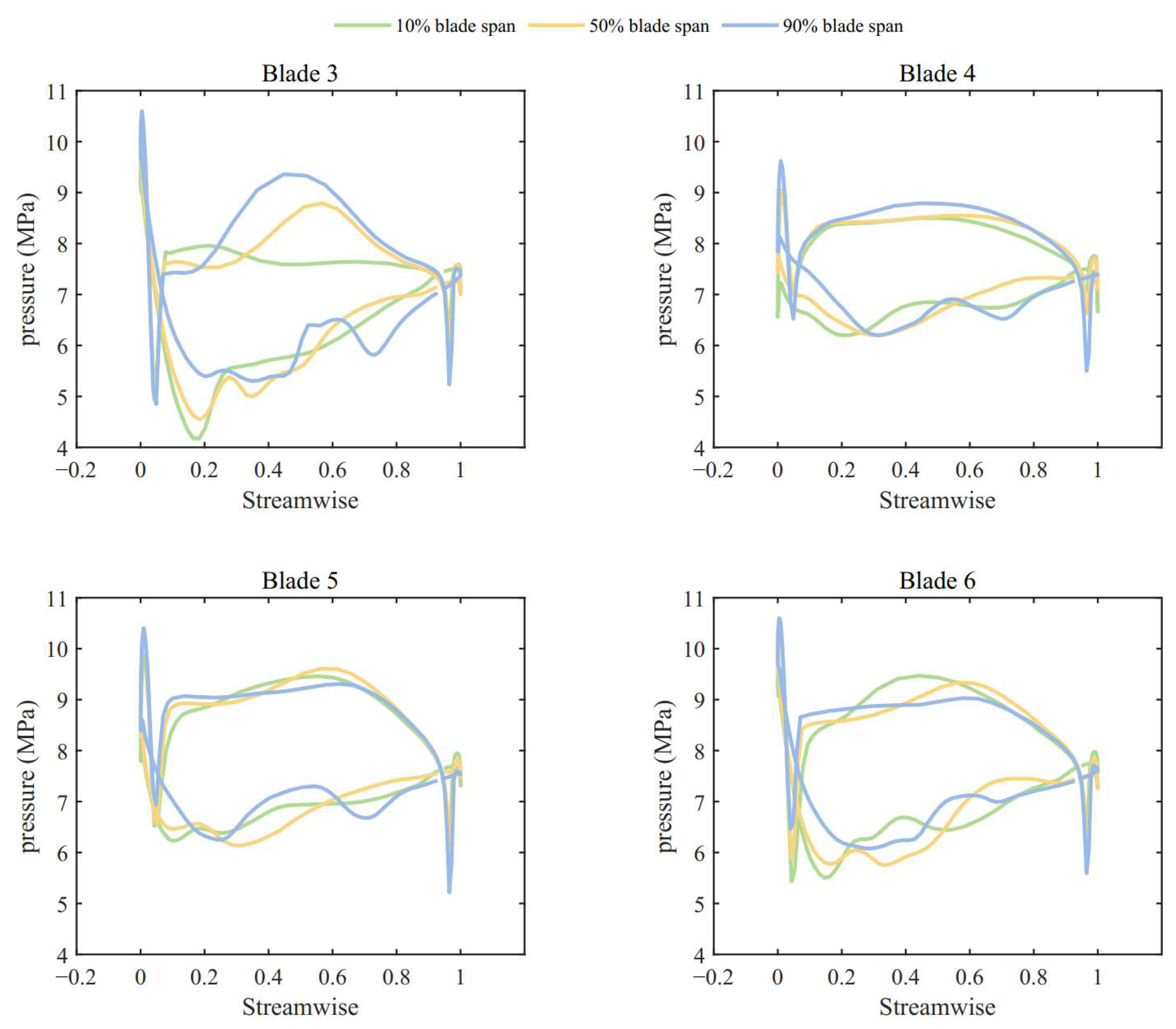
- These vortex patterns significantly influence the blade loading distribution. Compared to full admission conditions, the pressure near the blade root on the pressure side is lower as the blade enters the active sector. Conversely, pressure on the suction side continuously increases as the blade exits the active sector, particularly near the blade root at the 50% axial chord position. These changes in loading contribute to a reduction in the torque generated by the blades. As the partial admission ratio decreases, the flow within blade passages located in the middle of the active sector experiences increased disruption. This effect ultimately leads to a decrease in the maximum blade torque once the partial admission ratio becomes sufficiently small.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| LE | Leading edge |
| PAR | Partial admission ratio |
| S-CO2 | Supercritical carbon dioxide |
| TE | Trailing edge |
References
- Ahn, Y.; Bae, S.J.; Kim, M.; Cho, S.K.; Baik, S.; Lee, J.I.; Cha, J.E. Review of supercritical CO2 power cycle technology and current status of research and development. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2015, 47, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Wang, Y.; Huang, D.G. Supercritical CO2 Brayton cycle: A state-of-the-art review. Energy 2019, 189, 115900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanek, J.; Syblik, J.; Entler, S. Axial sCO2 high-performance turbines parametric design. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 274, 116418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.X.; Sun, L.F.; Han, X.R.; Zhou, Y.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Sun, L. Multi-objective optimization and dynamic characteristic analysis of solid oxide fuel cell—Supercritical carbon dioxide brayton cycle hybrid system. Energy 2024, 313, 133915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, H.Z.; Li, K.L.; Yang, Y.; Sun, S.; Wu, S.S. Off-design operation of supercritical CO2 Brayton cycle arranged with single and multiple turbomachinery shafts for lead-cooled fast reactor. Energy 2024, 299, 131384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Samanta, S.; Ghosh, S. Performance assessment of a biomass-fuelled distributed hybrid energy system integrating molten carbonate fuel cell, externally fired gas turbine and supercritical carbon dioxide cycle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 211, 112740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, K.; Friedman, P.; Dennis, R. (Eds.) Fundamentals and Applications of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publ. Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 1–433. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, J.X.; Liu, S.H.; Liu, M.Y.; Huang, Y.P.; Yuan, F.X.; Zhu, X.L.; Cui, Y.H. Conceptual design and optimization of heat rejection system for nuclear reactor coupled with supercritical carbon dioxide Brayton cycle used on Mars. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2024, 176, 105364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, H.-W.; Wang, D.; Du, C.-H. A novel zero emission combined power and cooling system for concentrating solar power: Thermodynamic and economic assessments and optimization. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 58, 104406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.L.; Tang, G.H.; Luo, K.H.; Fan, Y.H.; Li, X.L.; Sheng, Q. Integration and conversion of supercritical carbon dioxide coal-fired power cycle and high-efficiency energy storage cycle: Feasibility analysis based on a three-step strategy. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 269, 116074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespi, F.; Gavagnin, G.; Sánchez, D.; Martínez, G.S. Supercritical carbon dioxide cycles for power generation: A review. Appl. Energy 2017, 195, 152–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.T.; Bianchi, G.; Chai, L.; Tassou, S.A.; Sayma, A. Review of supercritical CO2 technologies and systems for power generation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 185, 116447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Guo, Y.M.; Zhou, K.H.; Xia, J.X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, P.; Dai, Y.P. Design and performance analysis of compressor and turbine in supercritical CO2 power cycle based on system-component coupled optimization. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 221, 113179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.Z.; Song, J.; Li, X.S.; Ren, X.D.; Gu, C.W. Aerodynamic design and numerical analysis of a radial inflow turbine for the supercritical carbon dioxide Brayton cycle. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 132, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Li, X.S.; Song, J.; Ren, X.D.; Gu, C.W. Design and Analysis of S-CO2 Cycle and Radial Turbine for SOFC Vehicle Waste-Heat Recovery. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 28, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Feng, Z.P.; Li, H.Z.; Yao, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.F. Study on Flow Characteristics of a Turbulent Boundary Layer and Vortex Structure of High Pressure Guide Vanes in SCO2 Turbines. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 28, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Q.Y.; Zhuge, W.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Ma, C.; Gou, J.L.; Wang, W. Vortex Patterns Investigation and Enstrophy Analysis in a Small Scale S-CO2 Axial Turbine. Energies 2021, 14, 6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusitalo, A.; Grönman, A. Analysis of Radial Inflow Turbine Losses Operating with Supercritical Carbon Dioxide. Energies 2021, 14, 3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wen, Y.; Lou, J.; Yang, P.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Design and Thermal-Fluid-Solid Coupling Investigation of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Radial Inflow Turbine. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2022, 56, 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Gunawan, G.; Permana, D.I.; Soetikno, P. Design and numerical simulation of radial inflow turbine of the regenerative Brayton cycle using supercritical carbon dioxide. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Moghazy, M.E.; Zou, Z.P.; Zhang, S.B.; Yao, L.C. Multi-stage radial-outflow supercritical carbon dioxide turbines: Preliminary design and optimization with insights into 3D design and structural considerations. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 265, 125381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H. Review on Research Progress of Partial Admission Turbine. J. Propuls. Technol. 2023, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeley, G.R.; Potts, I. Origins of loss within a multistage turbine environment under conditions of partial admission. In Proceedings of the 1997 International Gas Turbine & Aeroengine Congress & Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 2–5 June 1997; ASME: Little Falls, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, N.; Harada, T.; Imai, Y. Numerical study of partial admission stages in steam turbine (Efficiency improvement by optimizing admission arc position). JSME Int. J. Ser. B 2006, 49, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hushmandi, N.B.; Fransson, T.H. Effects of Multiblocking and Axial Gap Distance on Performance of Partial Admission Turbines: A Numerical Analysis. J. Turbomach. 2011, 133, 031028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, P.; Copeland, C.; Martinez-Botas, R.; Seiler, M. An audit of aerodynamic loss in a double entry turbine under full and partial admission. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2012, 33, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.K.; Xie, Y.H.; Zhang, D. Effects of rotor solidity and leakage flow on the unsteady flow in axial turbine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 128, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Luo, K.; Huang, C.; Zou, A.H.; Li, D.J.; Qin, K. Numerical investigation of partial admission losses in radial inflow turbines. Energy 2022, 239, 121870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalhamid, A.M.K.; Eltaweel, A. Design and analysis of a single-stage supersonic turbine with partial admission. Energy 2024, 309, 133100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.J.; Wang, E.H.; Wang, W.L. Design and analysis of a 1.5 kW single-stage partial-admission impulse turbine for low-grade energy utilization. Energy 2023, 268, 126631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, Y.L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, H.S. Energy loss analysis in two-stage turbine of compressed air energy storage system: Effect of varying partial admission ratio and inlet pressure. Energy 2024, 305, 132214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.X.; Wang, J.K.; Wang, Z.H.; Xi, G. Numerical Study on Unsteady Flow of a Supersonic Partial Admission Impulse Turbine. J. Turbomach. 2025, 147, 071017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Y.; Cai, R.K.; Zhuge, W.L.; Yang, B.J.; Zhang, Y.J. Influence of Real Gas Properties on Aerodynamic Losses in a Supercritical CO2 Centrifugal Compressor. J. Therm. Sci. 2024, 33, 2032–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Shin, H.; Ra, H.S.; Lee, G.; Roh, C.; Lee, B.; Baik, Y.J. Development of the supercritical carbon dioxide power cycle experimental loop in kier. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo: TURBINE Technical Conference and Exposition, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 13–17 June 2016; Volume 9, pp. 433–440. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.; Shin, H.; Cho, J.; Ra, H.S.; Roh, C.; Lee, B.; Lee, G.; Baik, Y.J. Development of the supercritical carbon dioxide power cycle experimental loop with a turbo-generator. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, Charlotte, NC, USA, 26–30 June 2017; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.; Cho, J.; Baik, Y.J.; Cho, J.; Roh, C.; Ra, H.S.; Kang, Y.; Huh, J. Partial admission, axial impulse type turbine design and partial admission radial turbine test for SCO2 cycle. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo: Turbine Technical Conference and Exposition, Charlotte, NC, USA, 26–30 June 2017; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.-S.; Huh, J.-S.; Cho, J.; Shin, H.; Baik, Y.-J. Design and Performance Assessments of a Partial Admission Axial Turbine Using Supercritical Carbon Dioxide. In Proceedings of the ASME 2016 Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting Collocated with the ASME 2016 Heat Transfer Summer Conference and the ASME 2016 14th International Conference on Nanochannels, Microchannels, and Minichannels, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 July 2016; Volume 1A. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.; Shin, H.; Cho, J.; Kang, Y.-S.; Ra, H.-S.; Roh, C.; Lee, B.; Lee, G.; Kim, B.; Baik, Y.-J. Preliminary experimental study of a supercritical CO2 power cycle test loop with a high-speed turbo-generator using R134a under similarity conditions. Front. Energy 2017, 11, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Shin, H.; Cho, J.; Baik, Y.J.; Choi, B.; Roh, C.; Ra, H.S.; Kang, Y.; Huh, J. Design, flow simulation, and performance test for a partial-admission axial turbine under supercritical CO2 condition. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition, Oslo, Norway, 11–15 June 2018; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.D.; Shu, G.Q.; Tian, H.; Shi, L.F.; Zhuge, W.L.; Tao, L. Experiments on a small-scale axial turbine expander used in CO2 transcritical power cycle. Appl. Energy 2019, 255, 113853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.D.; Shu, G.Q.; Tian, H.; Shi, L.F.; Zhuge, W.L.; Zhang, J.; Atik, M.A.R. Development and experimental study of a supercritical CO2 axial turbine applied for engine waste heat recovery. Appl. Energy 2020, 257, 113997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.G.; Tian, H.; Lin, X.; Zeng, X.Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Zhuge, W.L.; Shi, L.F.; Wang, X.; Liang, X.Y.; Shu, G.Q. Demonstration of a small-scale power generator using supercritical CO2. Carbon Energy 2024, 6, e428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS. ANSYS CFX-Solver Modeling Guide; ANSYS: Canonsburg, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Menter, F.R. 2-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, E.W.; Huber, M.L.; McLinden, M.O. Reference fluid thermodynamic and transport properties–refprop. NIST Stand. Ref. Database 2013, 23. Available online: https://www.nist.gov/publications/nist-standard-reference-database-23-reference-fluid-thermodynamic-and-transport (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Sun, H.C.; Li, H.K.; Gao, P.; Hou, F.; Hung, T.-C.; Chang, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-W.; Qin, J. Numerical simulation and low speed experiment of a low partially admitted rate axial turbine for small scale organic Rankine cycle. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 238, 122002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.C.; Wray, A.A.; Moin, P. Eddies, streams, and convergence zones in turbulent flows. In Studying Turbulence Using Numerical Simulation Databases, 2. Proceedings of the 1988 Summer Program 1988; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
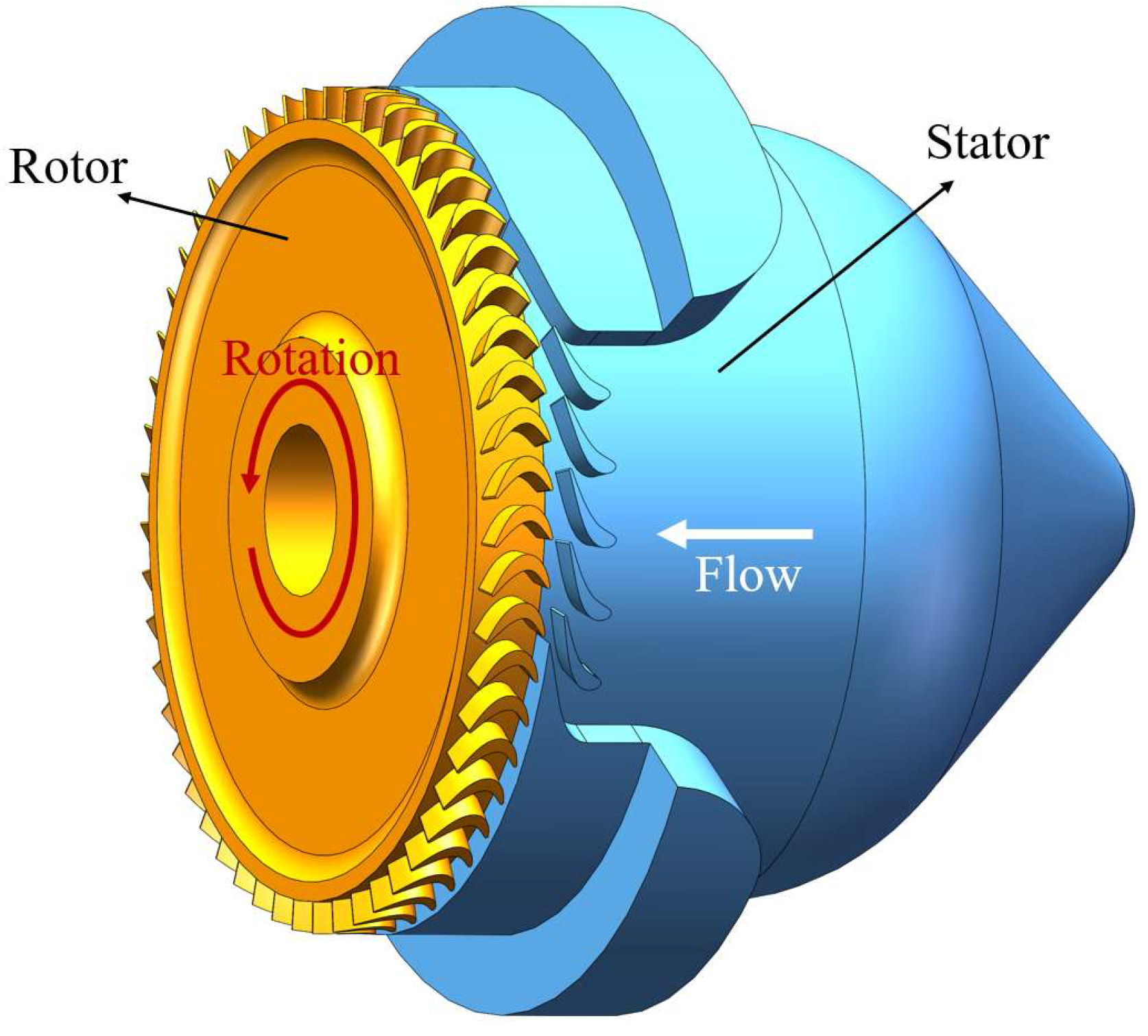
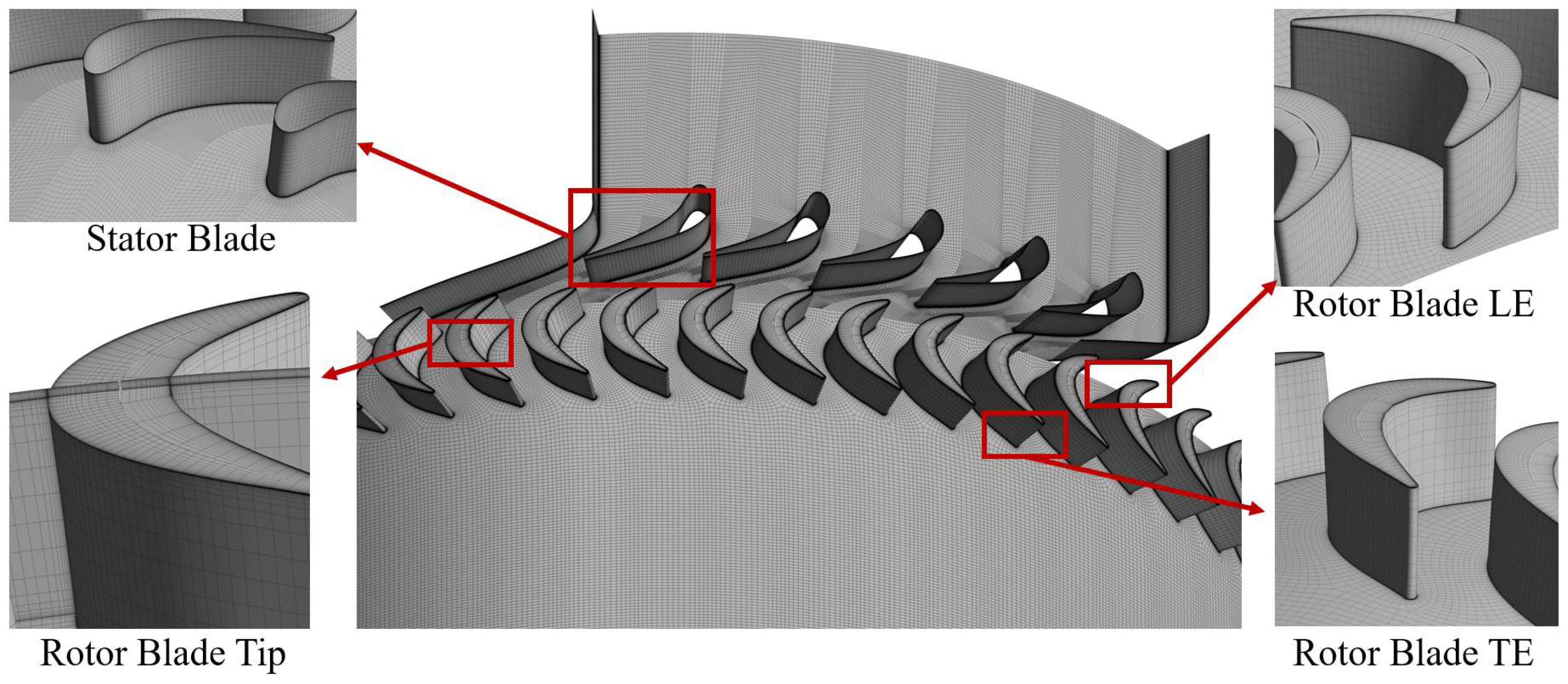
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Turbine inlet temperature | K | 823.15 |
| Turbine inlet pressure | MPa | 14.7 |
| Turbine outlet pressure | MPa | 8.0 |
| Rotational speed | rpm | 55,000 |
| Mass flow rate | kg/s | 3.1 |
| Blade number of the stator | - | 36 |
| Blade number of the rotor | - | 54 |
| Axial chord of the stator blade | mm | 3.8 |
| Axial chord of the rotor blade | mm | 4.7 |
| Hub radius | mm | 29.5 |
| Blade span | mm | 2.5 |
| Number of Mesh | Number of Mesh Elements | Turbine Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh 1 | 6.52 million | 69.43% |
| Mesh 2 | 9.79 million | 69.68% |
| Mesh 3 | 14.68 million | 69.93% |
| Mesh 4 | 17.20 million | 69.99% |
| Mesh 5 | 23.91 million | 70.02% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhuge, W.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Partial Admission Ratio on the Performance and Flow Characteristics of a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Axial-Flow Turbine. Energies 2025, 18, 4259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164259
Hu Z, Jiang H, Zhuge W, Qian Y, Zhang Y. Effects of Partial Admission Ratio on the Performance and Flow Characteristics of a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Axial-Flow Turbine. Energies. 2025; 18(16):4259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164259
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zhuo, Hongsheng Jiang, Weilin Zhuge, Yuping Qian, and Yangjun Zhang. 2025. "Effects of Partial Admission Ratio on the Performance and Flow Characteristics of a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Axial-Flow Turbine" Energies 18, no. 16: 4259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164259
APA StyleHu, Z., Jiang, H., Zhuge, W., Qian, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Effects of Partial Admission Ratio on the Performance and Flow Characteristics of a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Axial-Flow Turbine. Energies, 18(16), 4259. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164259






