Techno-Economic Analysis and Power Take-Off Optimization of a Wave Energy Converter Adjacent to a Vertical Seawall
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
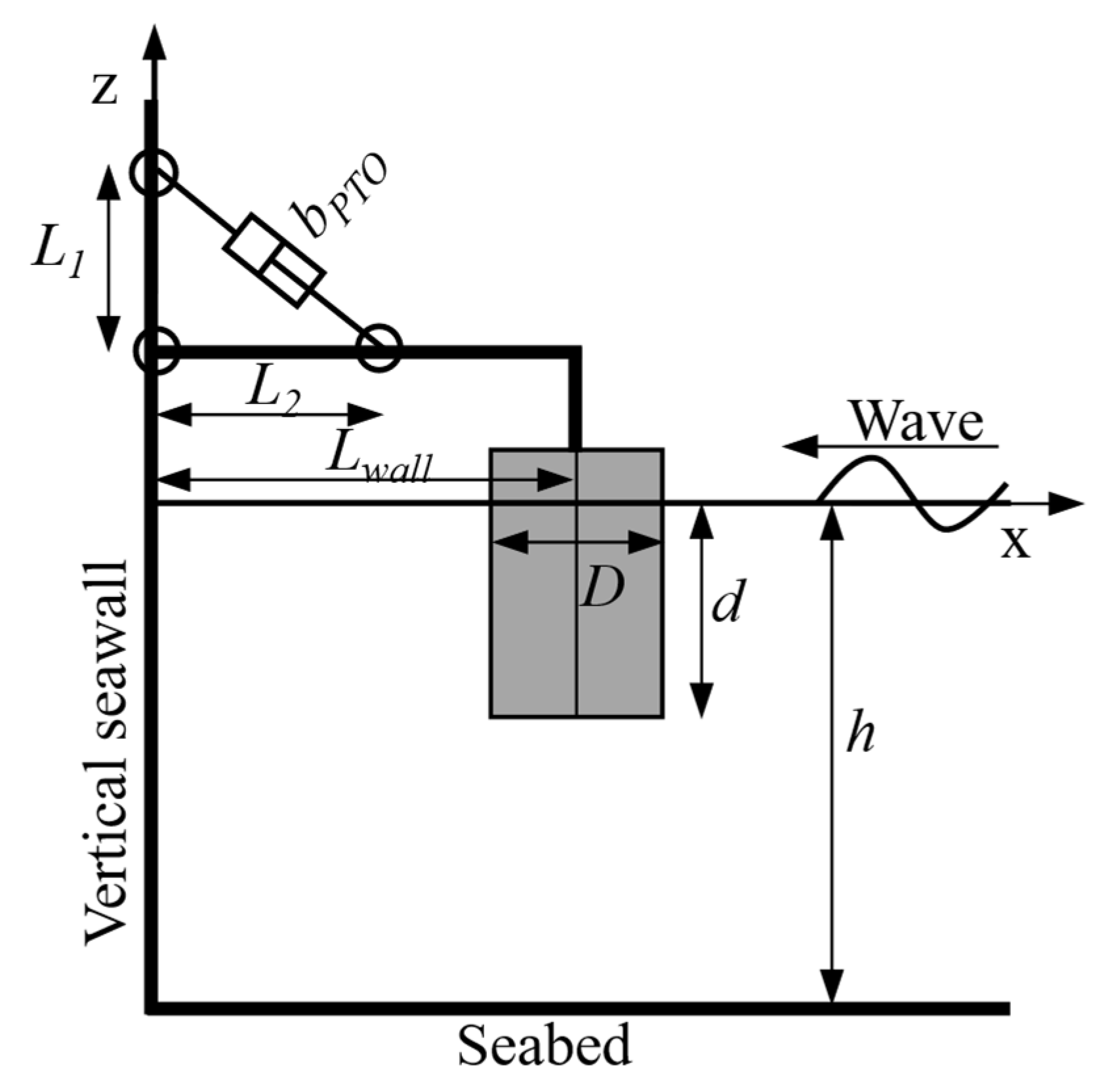
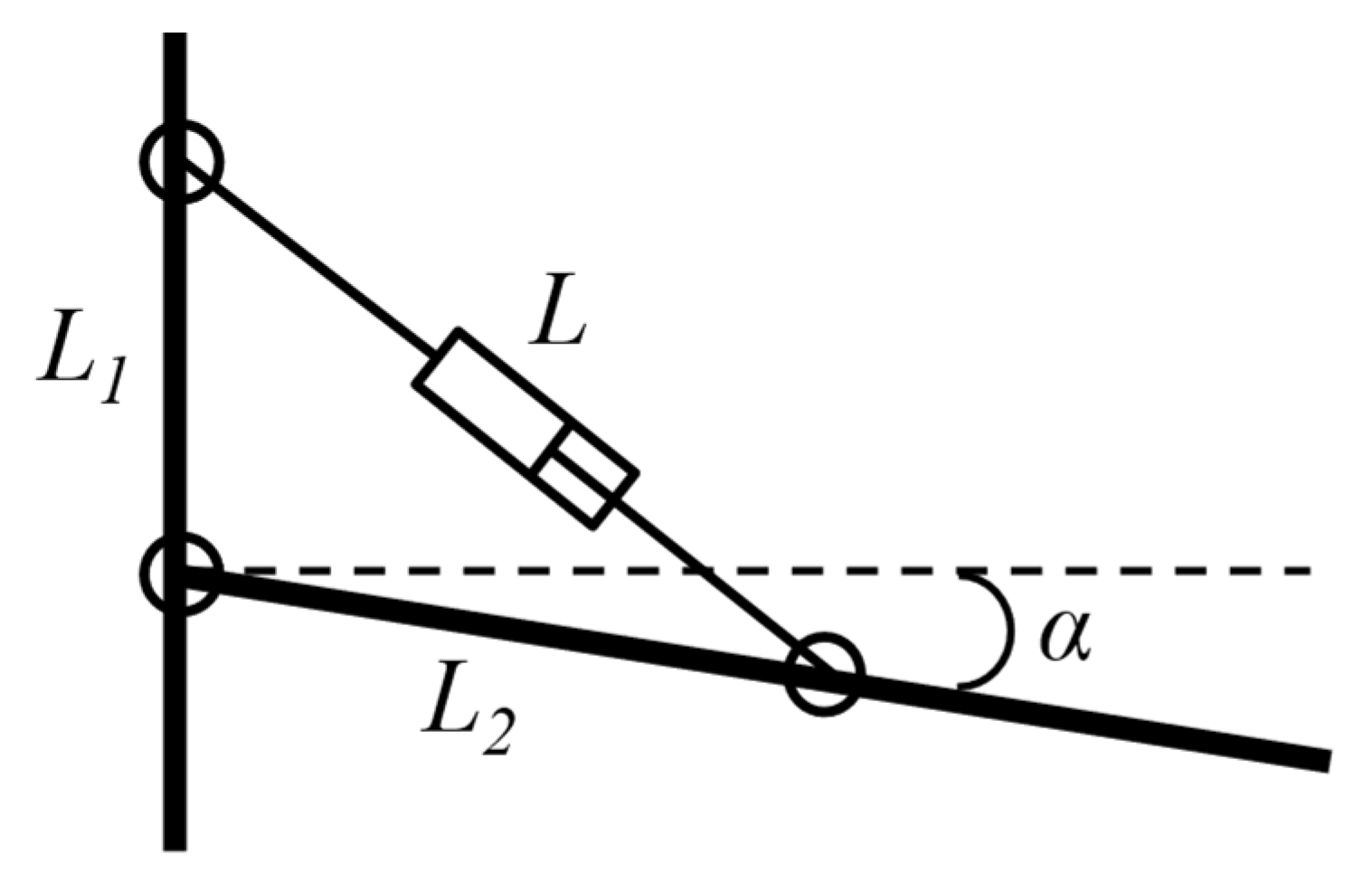
2.1. Geometry and Kinematics of the PTO System Frames
2.2. Hydrodynamic Modeling
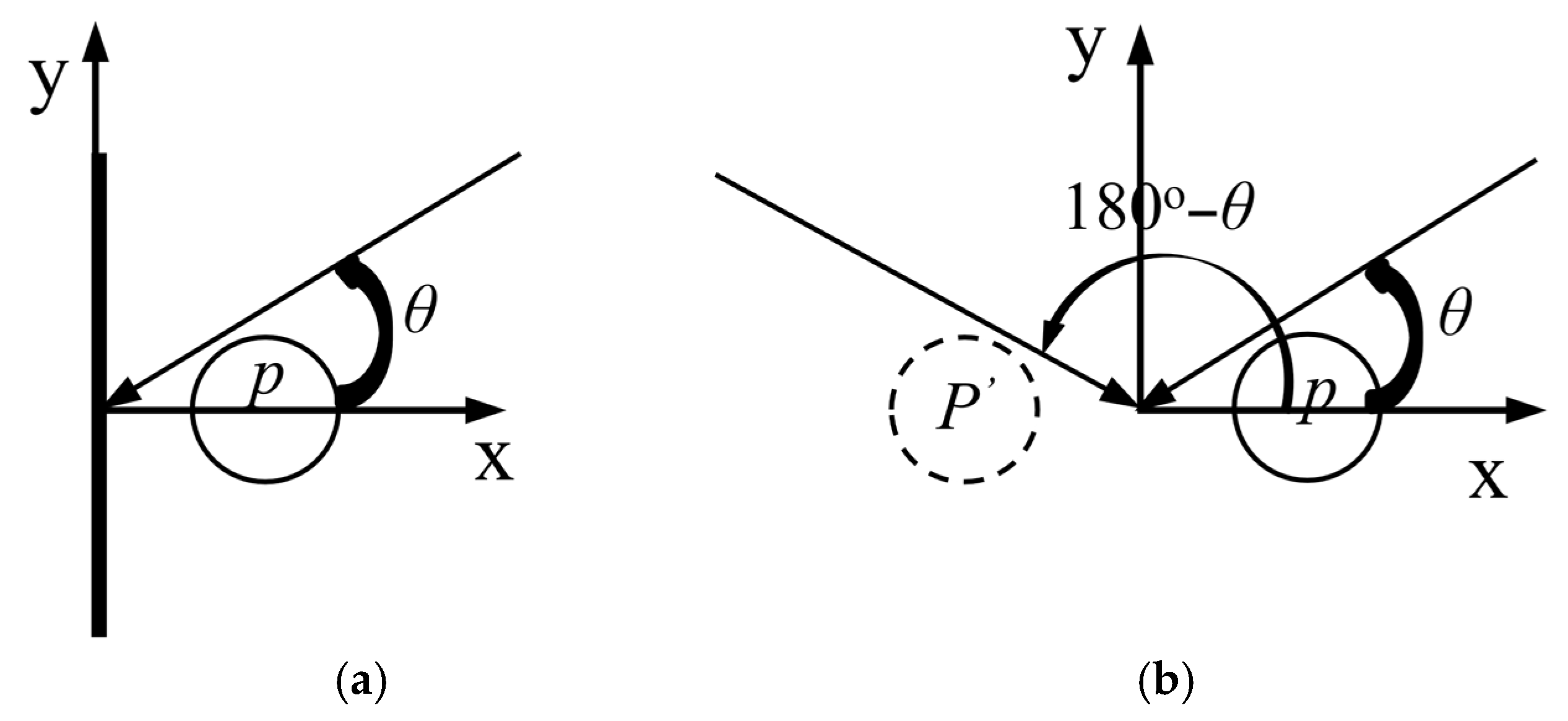
2.3. Image Method
2.4. Equation of Heave Motion
2.5. Wave Power Extraction
2.6. PTO Damping
2.6.1. Optimal PTO Damping
2.6.2. A Fixed PTO Damping
2.7. Techno-Economic Metrics
2.8. Weighted Sum Model (WSM)
2.9. Parameters for Analysis
2.10. Techno-Economic Analysis and PTO Optimization
3. Results and Discussions
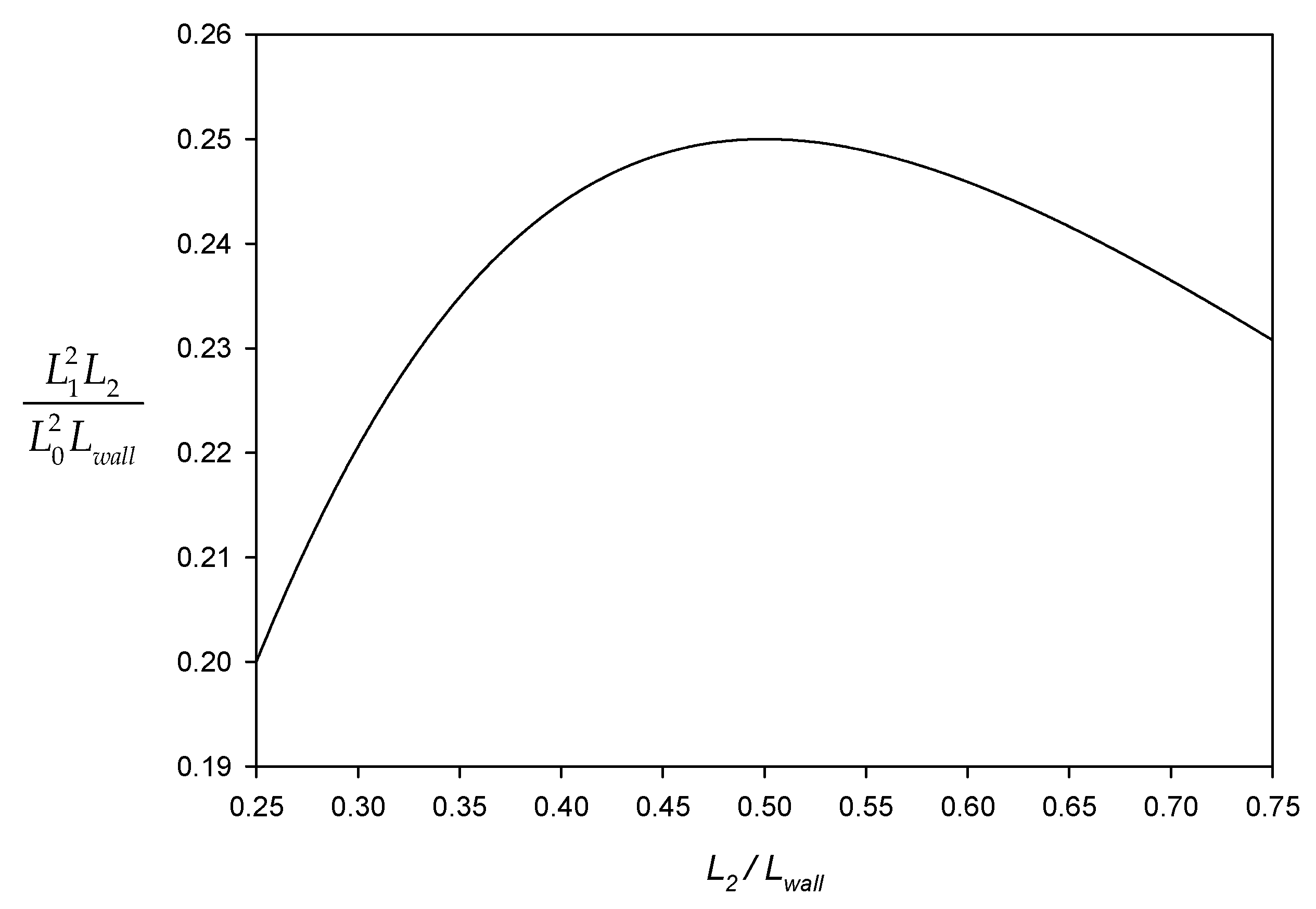
3.1. Optimal Hinge Position
3.2. Optimal Arm Length
3.3. Techno-Economic Analysis
3.4. Power Take-Off Optimization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| LCoE | Levelized cost of energy |
| MCDA | Multi-criteria decision analysis |
| PTO | Power take-off |
| RAO | Response amplitude operator |
| TPL | Technology performance level |
| TRL | Technology readiness level |
| WEC | Wave energy converter |
| WSM | Weighted sum model |
References
- Mustapa, M.A.; Yaakob, O.B.; Ahmed, Y.M.; Rheem, C.K.; Koh, K.K.; Adnan, F.A. Wave energy device and breakwater integration: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reabroy, R.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Zang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, M.; Sun, K.; Tiaple, Y. Hydrodynamic response and power efficiency analysis of heaving wave energy converter integrated with breakwater. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 195, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R. Design, simulation, and testing of a novel hydraulic power take-off system for the Pelamis wave energy converter. Renew. Energy 2006, 31, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, Y. Analysis for wave power capture capacity of two interconnected floats in regular waves. J. Fluids Struct. 2017, 75, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Hu, S.; He, H.; Zheng, S.; Chen, H.; Yang, S.; Ji, Z. Structural optimization on the oscillating-array-buoys for energy-capturing enhancement of a novel floating wave energy converter system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 228, 113693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Lewis, A. Power takeoff optimization for maximizing energy conversion of wave-activated bodies. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 41, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, P.C.; Dang, T.D.; Ahn, K.K. Assessment of a Hybrid Wind–Wave Energy Converter System in Nearshore Deployment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, F.; Ambühl, S.; Fischer, B.; Kofoed, J.P. Balancing power output and structural fatigue of wave energy converters by means of control strategies. Energies 2014, 7, 2246–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Koo, W. Dynamic response analysis of a wavestar-type wave energy converter using augmented formulation in Korean nearshore areas. Processes 2021, 9, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, S.; He, H.; Chen, H. Influence of Central Platform on Hydrodynamic Performance of Semi-Submerged Multi-Buoy Wave Energy Converter. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jusoh, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.Z.; Daud, M.Z.; Yusop, Z.M.; Albani, A. An estimation of hydraulic power take-off unit parameters for wave energy converter device using non-evolutionary NLPQL and evolutionary GA approaches. Energies 2020, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; He, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Sensitivity analysis of geometric characteristics on the cavity-buoy for energy capture efficiency enhancement of a semi-submersible floating-array-buoy wave energy converter system. Ocean Eng. 2024, 294, 116735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Xue, G.; Liu, Y. Influence of hydraulic PTO parameters on power capture and motion response of a floating wind-wave hybrid system. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukogeorgaki, E.; Chatjigeorgiou, I.K. Hydrodynamic performance of an array of truncated cylinders in front of a vertical wall. Ocean Eng. 2019, 189, 106407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.L.; Ning, D.Z.; Liang, D.F. Experimental investigation on hydrodynamic performance of a breakwater-integrated WEC system. Ocean Eng. 2019, 171, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ning, D. Hydrodynamic study of a novel breakwater with parabolic openings for wave energy harvest. Ocean Eng. 2019, 182, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konispoliatis, D.N.; Mavrakos, S.A.; Katsaounis, G.M. Theoretical evaluation of the hydrodynamic characteristics of arrays of vertical axisymmetric floaters of arbitrary shape in front of a vertical breakwater. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konispoliatis, D.N.; Mavrakos, S.A. Wave power absorption by arrays of wave energy converters in front of a vertical breakwater: A theoretical study. Energies 2020, 13, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecher, A.; Kofoed, J.P. Handbook of Ocean Wave Energy; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Ringwood, J.V. Geometric optimisation of wave energy conversion devices: A survey. Appl. Energy 2021, 297, 117100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirigu, S.A.; Foglietta, L.; Giorgi, G.; Bonfanti, M.; Cervelli, G.; Bracco, G.; Mattiazzo, G. Techno-Economic optimisation for a wave energy converter via genetic algorithm. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Polinder, H.; Laguna, A.J.; Wellens, P.; Miedema, S.A. The influence of sizing of wave energy converters on the techno-economic performance. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Têtu, A.; Fernandez Chozas, J. A proposed guidance for the economic assessment of wave energy converters at early development stages. Energies 2021, 14, 4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, E.; Petracca, E.; Paduano, B.; Moscoloni, C.; Giorgi, G.; Sirigu, S.A. Estimating the Cost of Wave Energy Converters at an Early Design Stage: A Bottom-UP Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Sheng, W.; De Silva, D.G.; Aggidis, G. A review of the levelized cost of wave energy based on a techno-economic model. Energies 2023, 16, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giassi, M.; Göteman, M.; Thomas, S.; Engström, J.; Eriksson, M.; Isberg, J. Multi-parameter optimization of hybrid arrays of point absorber wave energy converters. In Proceedings of the 12th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference (EWTEC), Cork, Ireland, 27–31 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- David, D.R.; Kurniawan, A.; Wolgamot, H.; Hansen, J.E.; Rijnsdorp, D.; Lowe, R. Nearshore submerged wave farm optimisation: A multi-objective approach. Appl. Ocean Res. 2022, 124, 103225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusov, M.A.; Thwaites, J.; Kurniawan, A.; Orszaghova, J.; Wolgamot, H. New cost-effectiveness metric for wave energy converters: Extensive database and comparisons. In Proceedings of the 14th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference. Technical Committee of the European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference, Plymouth, UK, 5–9 September 2021; p. 2188-1-2188-10. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Ning, D.; Gou, Y.; Zhou, Z. Wave energy converter optimization based on differential evolution algorithm. Energy 2022, 246, 123433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, J. Ocean wave energy converters: Technical principle, device realization, and performance evaluation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 141, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cradden, L.; Kalogeri, C.; Barrios, I.M.; Galanis, G.; Ingram, D.; Kallos, G. Multi-criteria site selection for offshore renewable energy platforms. Renew. Energy 2016, 87, 791–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.K.; Cho, S.; Cho, I.H. The Optimal Design of an Inclined Porous Plate Wave Absorber Using an Artificial Neural Network Model. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handoko, D.; Mesran, M.; Nasution, S.D.; Yuhandri, Y.; Nurdiyanto, H. Application of Weight Sum Model (WSM) in determining special allocation funds recipients. Int. J. Inform. Comput. Sci. 2017, 1, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesode, P.; Barve, S.; Wankhede, S.V.; Jadhav, D.R.; Pawar, S.K. Titanium alloy selection for biomedical application using weighted sum model methodology. Mater. Today: Proc. 2023, 72, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.K.; Cho, I.H. Cost-Effective Optimization of an Array of Wave Energy Converters in Front of a Vertical Seawall. Energies 2023, 17, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babarit, A. Impact of long separating distances on the energy production of two interacting wave energy converters. Ocean Eng. 2010, 37, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.H.; Kim, M.H. Hydrodynamic performance evaluation of a wave energy converter with two concentric vertical cylinders by analytic solutions and model tests. Ocean Eng. 2017, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.Z.; Hu, J.J.; Sun, K.; Liu, Y.; Collu, M. Motion response and energy conversion performance of a heaving point absorber wave energy converter. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 553295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.K.; Cho, I. New Strategy on Power Absorption of a Concentric Two-Body Wave Energy Converter. Energies 2023, 16, 3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R. Dynamics of Marine Vehicles; John Wiley & Sons Incorporated: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1978; Chapter 6. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, J.N. Marine Hydrodynamics, 40th Anniversary Edition; The MIT Press: London, UK, 2018; Chapter 6. [Google Scholar]
- Goda, Y. Statistical variability of sea state parameters as a function of a wave spectrum. Coast. Eng. Jpn. 1988, 31, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.H. Latching control technology for improvement of extracted power from wave energy converter. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Energy 2015, 18, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Temiz, I.; Pan, J.; Eriksson, M.; Boström, C. Damping studies on PMLG-based wave energy converter under oceanic wave climates. Energies 2021, 14, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
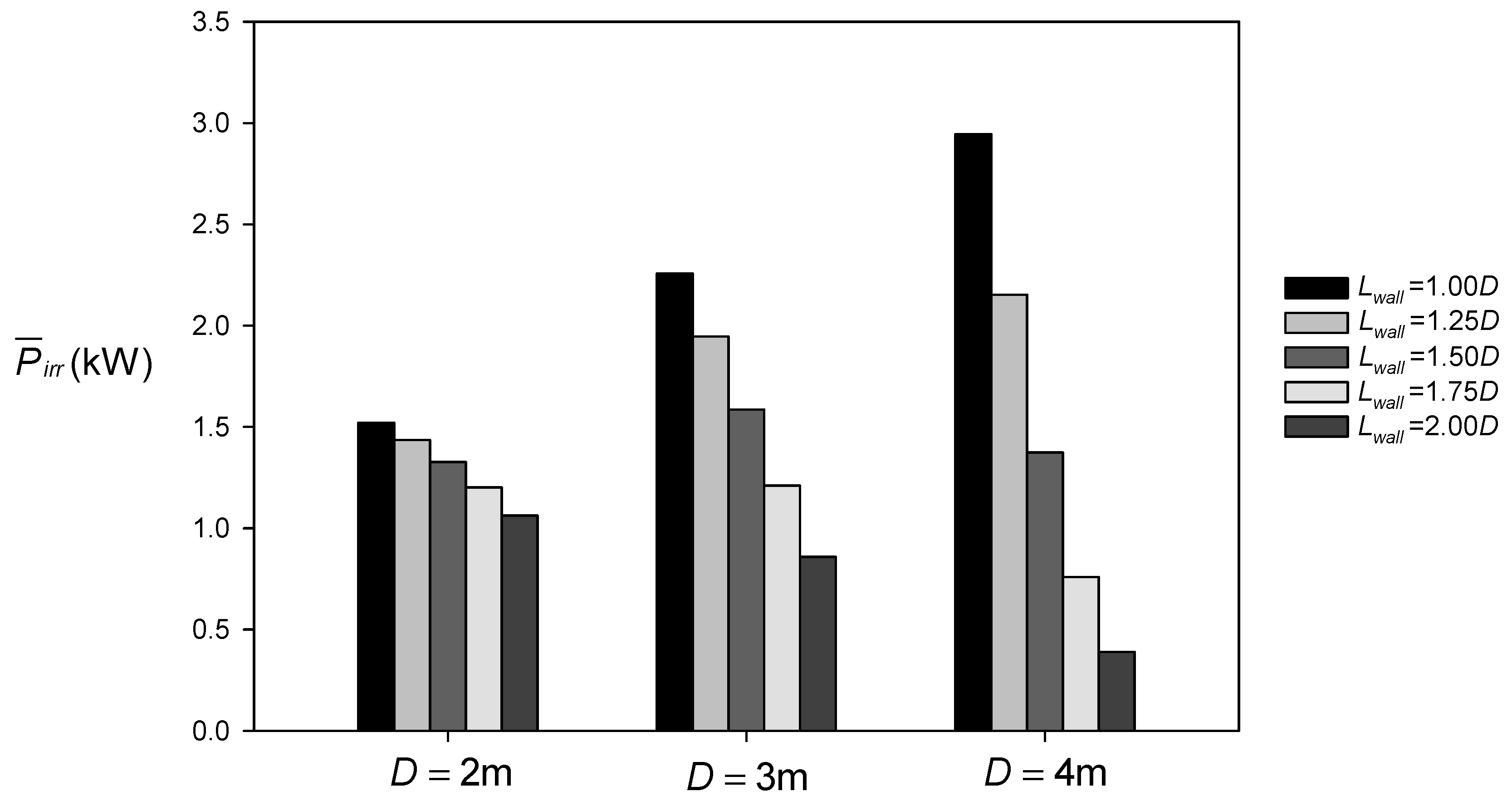
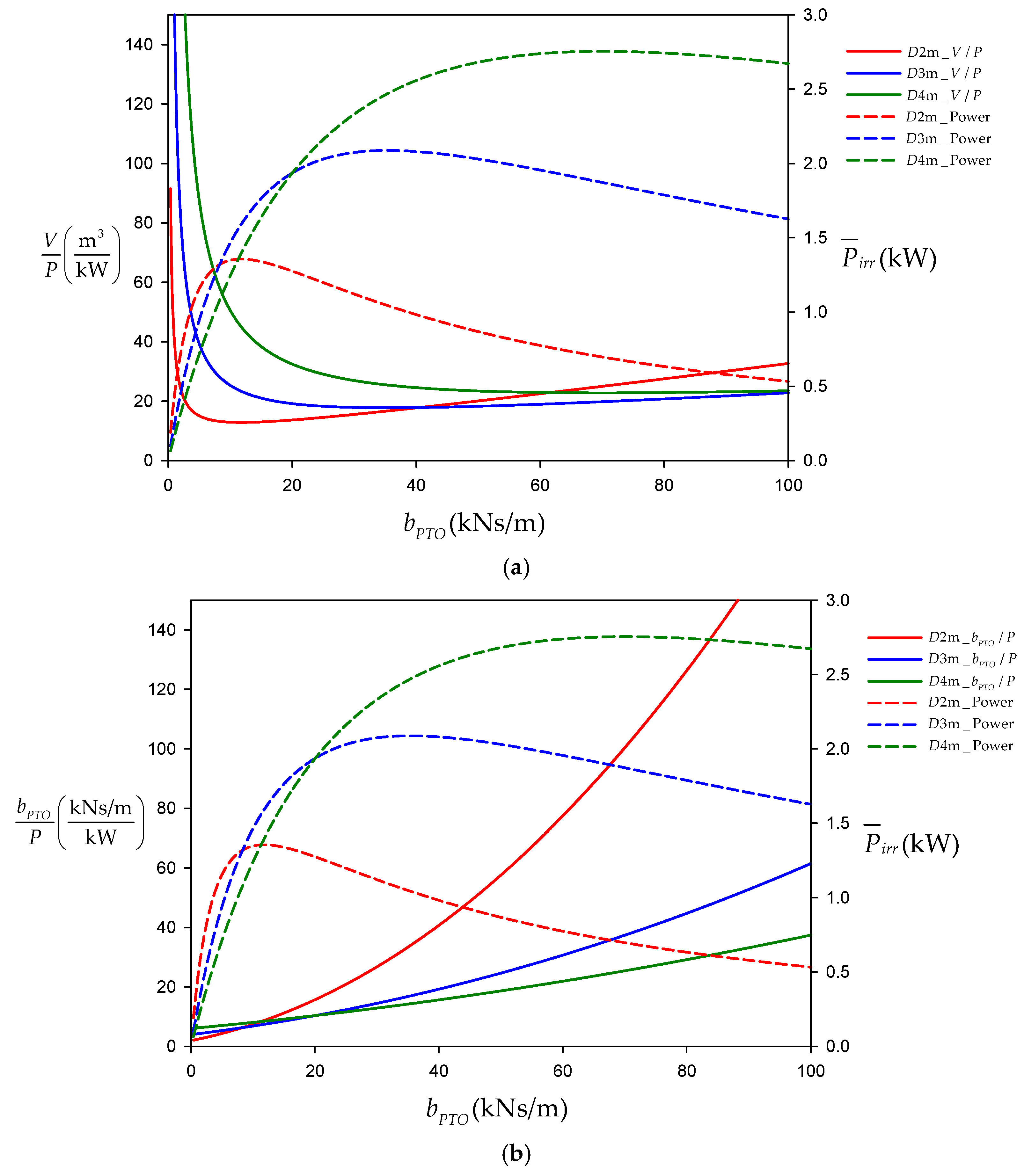
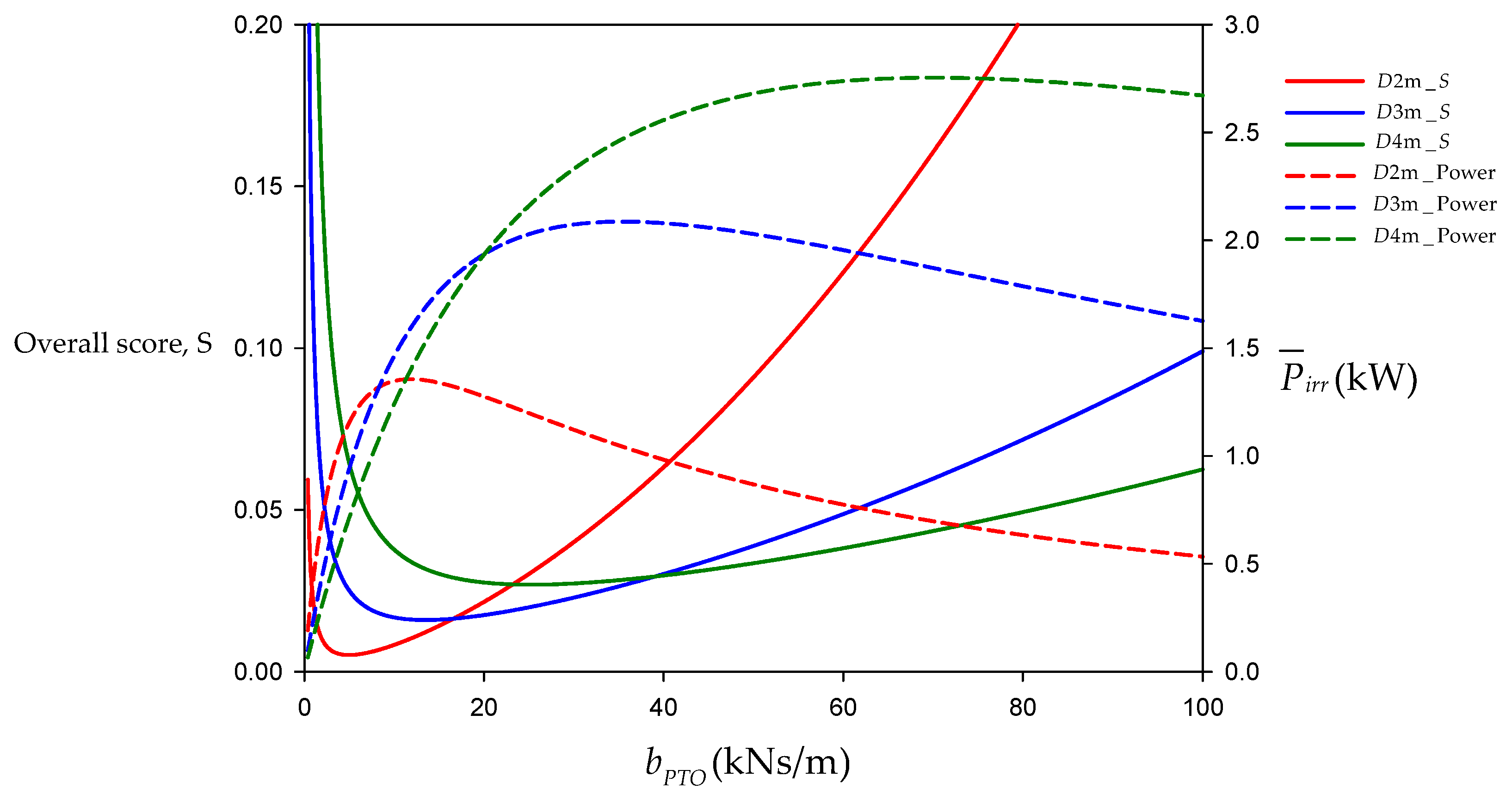
| D = 2 m | 4.99 | 1.15 |
| D = 3 m | 13.57 | 1.69 |
| D = 4 m | 25.35 | 2.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Natarajan, S.K.; Cho, I.H. Techno-Economic Analysis and Power Take-Off Optimization of a Wave Energy Converter Adjacent to a Vertical Seawall. Energies 2025, 18, 4246. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164246
Natarajan SK, Cho IH. Techno-Economic Analysis and Power Take-Off Optimization of a Wave Energy Converter Adjacent to a Vertical Seawall. Energies. 2025; 18(16):4246. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164246
Chicago/Turabian StyleNatarajan, Senthil Kumar, and Il Hyoung Cho. 2025. "Techno-Economic Analysis and Power Take-Off Optimization of a Wave Energy Converter Adjacent to a Vertical Seawall" Energies 18, no. 16: 4246. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164246
APA StyleNatarajan, S. K., & Cho, I. H. (2025). Techno-Economic Analysis and Power Take-Off Optimization of a Wave Energy Converter Adjacent to a Vertical Seawall. Energies, 18(16), 4246. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18164246





