This section presents the experimental validation of the proposed algorithm’s capability for estimating generator inertia, using MATLAB 2022b and a maximum of 12 parallel MATLAB workers. Performance comparisons are conducted against the conventional M-H algorithm on both the IEEE 39-bus and IEEE 68-bus benchmark systems. The ground truth values of the generator inertia time constants are taken directly from the dynamic models specified in the standard IEEE 39-bus and 68-bus test systems. The simulation employs a time step of s and simulates a three-phase line-to-ground fault at 1 s after simulation initiation. The fault is cleared after a brief duration, and the total simulation time is 6 s. This setup provides sufficient post-disturbance dynamic response for inertia estimation. For both the M-H and MCMC Hammer algorithms, the initial of samples are discarded as burn-in to ensure convergence toward the target posterior distribution. All random processes in the experiment, including initialization, walker selection, and proposal generation, are performed without setting a random seed. This allows assessment of algorithm robustness under purely stochastic conditions. All experiments are executed on a workstation equipped with an Intel Core i7-13790 processor (Intel Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA), 32 GB RAM.
The comparative analysis focuses on two key performance metrics: estimation accuracy relative to known system parameters and computational efficiency in terms of execution time. The parameter
a in (
14) is set to 2. The PMU measurement errors,
, are assumed to follow mutually independent Gaussian distributions with means of 0 and a standard deviation of
. We assume that the prior distributions of the inertia time constants follow Gaussian distributions, with means deviating by approximately
from the actual inertia time constants, and the standard deviation set to
of the corresponding means. In the
mth iteration of the M-H algorithm, the proposal distribution
q is set as a Gaussian distribution with means of
and a standard deviation of
.
4.1. Estimation in IEEE 39-Bus System
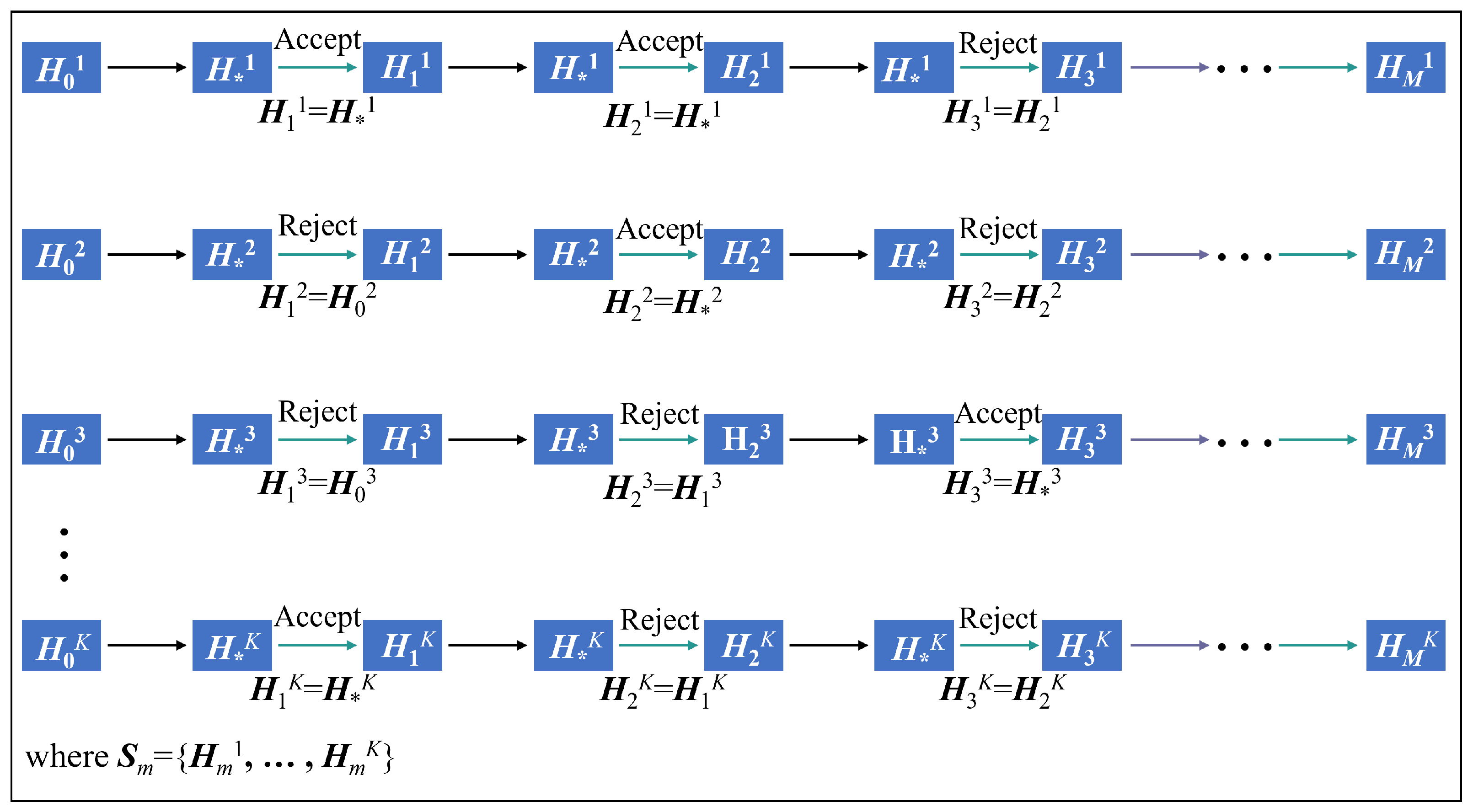
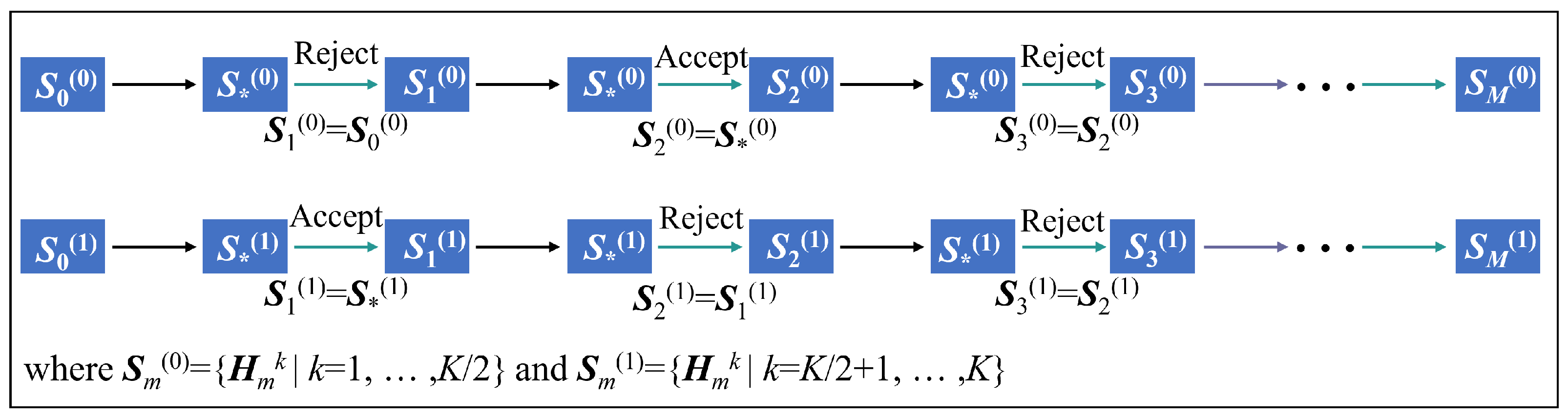
In this part of the study, we apply the proposed algorithms, including the MCMC Hammer algorithm, the parallel MCMC Hammer algorithm, and the M-H algorithm, to the IEEE 39-bus system. The fault occurs on Bus 15 and Bus 16. Both algorithms use a total of 50,000 samples. Specifically, for the M-H algorithm, , and for the MCMC Hammer algorithm, .
The estimation results of the three algorithms are presented in
Table 1, which shows the MAP points and estimation errors of the inertia time constants for each generator obtained by the different methods. In terms of computational efficiency, the parallel MCMC Hammer algorithm achieves the shortest computation time of 142.61 s, demonstrating significant advantages in processing speed. In contrast, both the standard MCMC Hammer and M-H algorithms require considerably longer computation times of 301.97 s and 297.02 s, respectively, showing a nearly identical computational cost. Furthermore, among the 35,000 collected samples, only 3478 unique samples were generated by the M-H algorithm, indicating a high level of sample redundancy and poor exploration efficiency. In comparison, the standard MCMC Hammer and its parallel version produced 18,408 and 18,354 unique samples, respectively, highlighting their superior mixing behavior and sampling diversity.
The experimental findings clearly demonstrate the effectiveness of all three algorithms in estimating the inertia time constants of synchronous generators within the IEEE 39-bus test system. Specifically, the M-H algorithm yields an average estimation error of across the ten generators, with the maximum and minimum errors reaching and , respectively. In comparison, the MCMC Hammer algorithm achieves significantly improved accuracy, with an average error of only . Its worst-case error is limited to , while the best-case error is as low as , indicating a high level of precision. The parallel implementation of the MCMC Hammer algorithm also maintains strong performance, producing an average error of , with maximum and minimum errors of and , respectively.
Beyond point accuracy, the reliability of the estimation results is also critically important. As shown in
Table 2, the M-H algorithm consistently exhibits greater standard deviations and wider credible intervals, suggesting higher variability and reduced confidence in the inferred inertia parameters. In contrast, both versions of the MCMC Hammer algorithm produce more concentrated posterior distributions, reflecting greater robustness and reliability in their estimates.
The superior performance of the MCMC Hammer algorithms can be attributed to their advanced sampling mechanisms. The ensemble sampling approach enables more thorough exploration of the parameter space, leading to more accurate estimation of the posterior distribution. The remarkable efficiency of the parallel implementation stems from its ability to distribute computational load across multiple processors while maintaining sampling effectiveness. This makes it particularly suitable for real-time applications where both accuracy and speed are crucial. Although the absolute differences in estimation accuracy may appear minor, the combined advantages of precision and computational efficiency position the parallel MCMC Hammer as the most practical choice for modern power system operation.
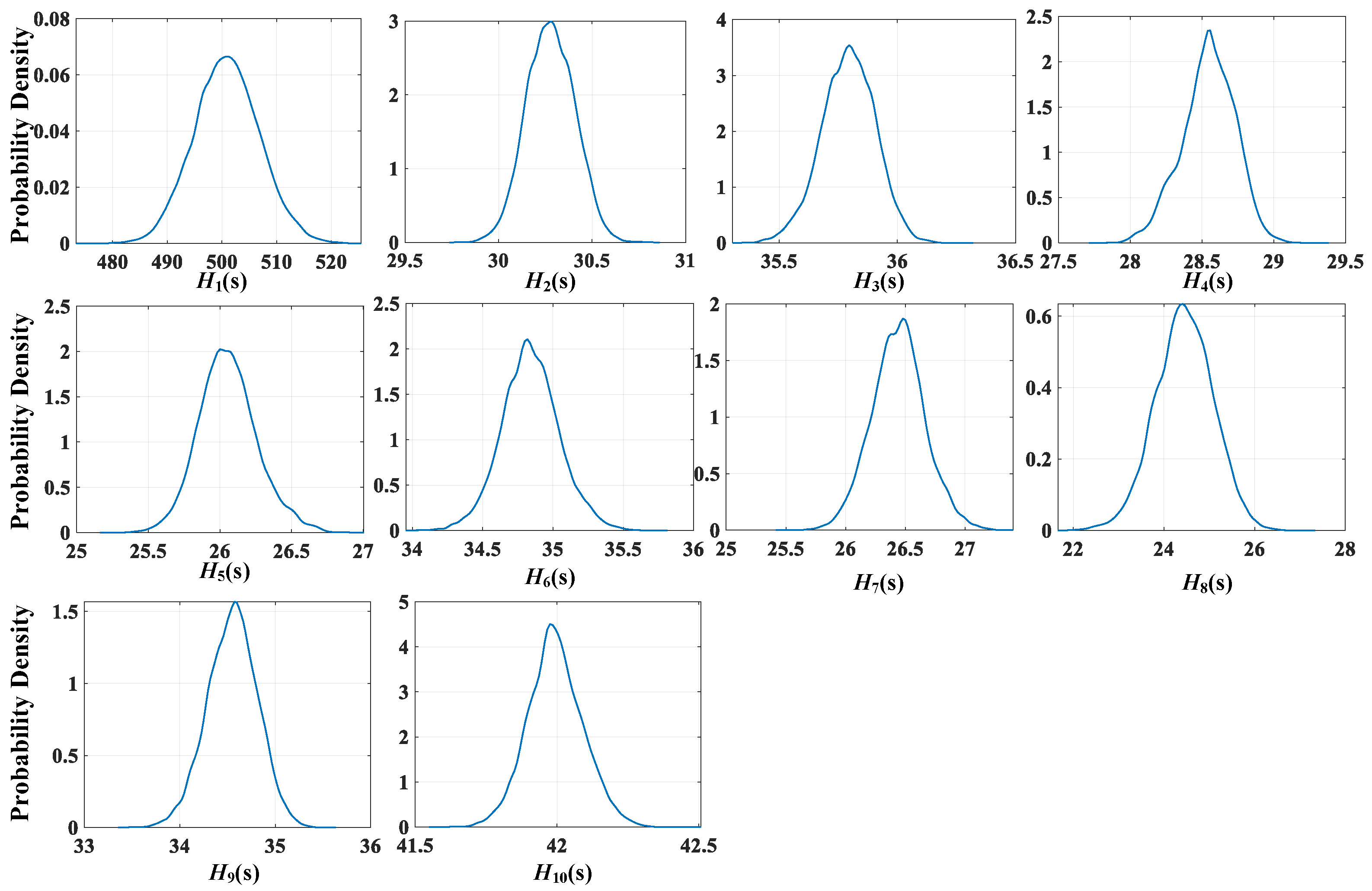
The Bayesian inference framework can also provide their complete posterior distributions of the inertia time constants, as demonstrated in
Figure 4. The figure clearly visualizes the probability density functions of the posterior distributions for each generator’s inertia time constant. The varying widths of the distributions reflect different confidence levels in the estimation between generators, providing useful information on the reliability of the values obtained. The results reveal an important finding regarding the distribution characteristics: While the prior distributions of inertia time constants were initially assumed to be Gaussian, the posterior distributions obtained through the MCMC Hammer algorithm demonstrate significantly non-Gaussian characteristics.
This observation fundamentally validates the necessity of employing advanced random sampling techniques to approximate rather than relying on simplified distributional assumptions. The divergence between the assumed Gaussian priors and the complex, often skewed or multimodal posterior distributions underscores several critical aspects of the estimation problem. First, it highlights the inherent nonlinearity in the relationship between power system dynamics and inertia parameters, which cannot be adequately captured through conventional Gaussian approximations. Second, it demonstrates how measurement data and system constraints can fundamentally reshape the parameter distributions in ways that simple analytical forms cannot represent. Third, the results prove that the MCMC Hammer algorithm successfully captures these complex distributional features through its sophisticated sampling mechanism, which would be impossible under traditional Gaussian assumptions.
4.2. Estimation in IEEE 68-Bus System
In this part, we further compare the performance of the algorithms on the IEEE 68-bus system. In this case, the fault is applied between Bus 32 and Bus 33. To address the increased dimensionality, the total number of samples used by both algorithms is set to 100,000. Specifically, for the M-H algorithm, we set M = 100,000, while for the MCMC Hammer algorithm, we set = 100,000.
The experimental results presented in
Table 3 and
Table 4 provide a comprehensive comparison of the three algorithms’ performance in estimating generator inertia time constants for the IEEE 68-bus system. Although all three methods operate with the same total number of samples, namely 100,000, the M-H algorithm exhibits substantial estimation errors across multiple generators. This performance disparity highlights its limitations when applied to high-dimensional parameter spaces, where convergence efficiency and sampling accuracy become critical. In contrast, both the standard MCMC Hammer algorithm and its parallel implementation consistently demonstrate superior estimation performance across all generators, maintaining errors below
throughout the IEEE 68-bus test system.
Specifically, the M-H algorithm yields an average inertia estimation error of for the 16 generators, with individual errors ranging from a minimum of to a maximum of . The standard MCMC Hammer algorithm significantly improves upon this performance, reducing the average error to just . Its most accurate estimate deviates by only from the true value, while even the largest deviation does not exceed . The parallel MCMC Hammer algorithm delivers comparably strong results, achieving an average error of , with errors ranging from to .
In addition to estimation accuracy, uncertainty quantification results further underscore the advantages of the proposed algorithms. The M-H algorithm exhibits noticeably larger standard deviations and wider credible intervals, indicating high uncertainty in its estimates. In contrast, both the standard and parallel MCMC Hammer algorithms produce significantly narrower credible intervals. These tighter intervals suggest that the sample distributions are more concentrated around the true values, meaning the inferred inertia parameters have higher statistical confidence. This reflects the robustness and reliability of the MCMC Hammer-based methods, particularly when precise and trustworthy parameter estimation is required for system monitoring and control.
From a computational perspective, the proposed parallel MCMC Hammer algorithm offers a clear advantage. It completes the entire estimation process in s, considerably faster than the standard MCMC Hammer, which takes s, and the M-H algorithm, which requires s. The parallel implementation, therefore, not only enhances estimation accuracy but also improves practical applicability for large-scale and real-time power system analysis. In addition, out of the 70,000 collected samples, the M-H algorithm yielded only 9121 unique samples, reflecting significant redundancy and poor mixing performance. In contrast, the standard MCMC Hammer and its parallel variant produced 30,952 and 30,939 unique samples, respectively. This demonstrates the proposed method’s superior ability to efficiently explore high-dimensional posterior distributions and generate diverse, informative samples.
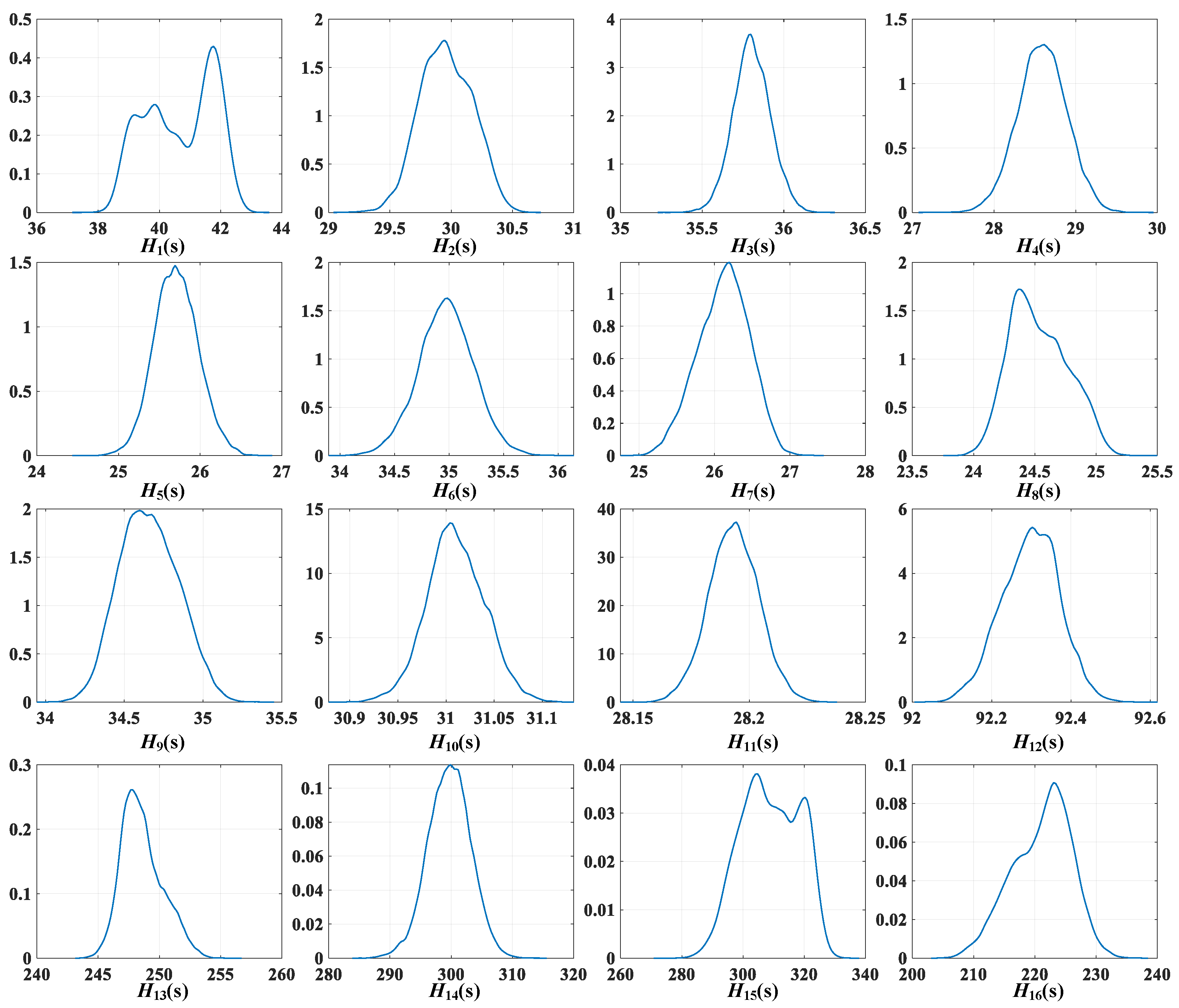
The posterior distributions of the generator inertia constants in the IEEE 68-bus system, obtained using the parallel MCMC Hammer algorithm, are shown in
Figure 5. An important observation from the posterior analysis is the presence of multimodal distributions for certain inertia parameters. To quantitatively validate and characterize this multimodality, the Hartigan Dip Test is applied to the posterior samples of each generator’s inertia. This statistical test evaluates the departure of a given empirical distribution from unimodality by computing the dip statistic, denoted as
, which represents the maximum vertical distance between the empirical distribution function and the best-fitting unimodal distribution. Typically, a
value greater than
indicates significant evidence against unimodality. The computed dip statistics for all generators are summarized in
Table 5. Notably, generators 1 and 15 exhibit dip values well above the
threshold, confirming the presence of multimodal features in their posterior distributions. This observation reinforces the inherently non-Gaussian nature of the inferred parameter distributions, which poses substantial challenges for the M-H algorithm.
The traditional M-H algorithm demonstrates fundamental limitations when applied to such complex estimation problems. The degraded performance of the M-H algorithm in this higher-dimensional system originates from its single-chain sampling mechanism, which struggles to adequately explore the complex posterior distributions of multiple coupled inertia parameters. The method’s sensitivity to manually tuned proposal distributions becomes increasingly problematic as system dimensionality grows, often resulting in inefficient exploration of the parameter space and convergence to suboptimal solutions.
The MCMC Hammer algorithm addresses these challenges through its innovative ensemble-based sampling approach. The method’s stretch move mechanism generates informed, geometry-adaptive proposals by leveraging the relative positions of walkers in the ensemble. This strategy provides several advantages for power system parameter estimation. First, the affine-invariant property ensures consistent performance regardless of parameter scaling or correlation structure. Second, the ensemble automatically adapts to the local geometry of the posterior distribution, enabling efficient exploration of anisotropic parameter spaces. Third, the parallel implementation maintains these benefits while significantly improving computational efficiency through distributed walker updates.
These results conclusively demonstrate the superiority of the parallel MCMC Hammer algorithm for inertia estimation in large-scale power systems. By combining high estimation accuracy with significant computational efficiency gains, the proposed method addresses two of the most critical challenges in modern power system analysis. The algorithm’s ensemble-based sampling strategy enables effective exploration of complex, high-dimensional parameter spaces, ensuring accurate identification of generator inertia time constants even in systems with heterogeneous dynamic behaviors. Furthermore, the parallelized implementation substantially reduces computational time without sacrificing estimation quality, making the method particularly well-suited for real-time or near-real-time applications. This advantage is especially important for modern power grids with increasing penetration of renewable energy sources, where rapid and precise inertia estimation is vital for maintaining frequency stability and ensuring system reliability. The consistent performance observed across generators with varying inertia values further validates the robustness and versatility of the proposed approach. These qualities position the parallel MCMC Hammer algorithm as a highly promising and preferred solution for parameter estimation tasks in large-scale, complex power networks, offering a strong foundation for future developments in dynamic system monitoring and control.