Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Organic Solid By-Products from Table Olive Processing: Influence of Substrate Mixtures on Overall Process Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrates and Inoculum
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Inoculation Reactor Start-Up
2.2.2. Batch Operation Experiments
2.2.3. Semi-Continuous Operation Experiments
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Statistics Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Inoculation Reactor Monitoring and Control
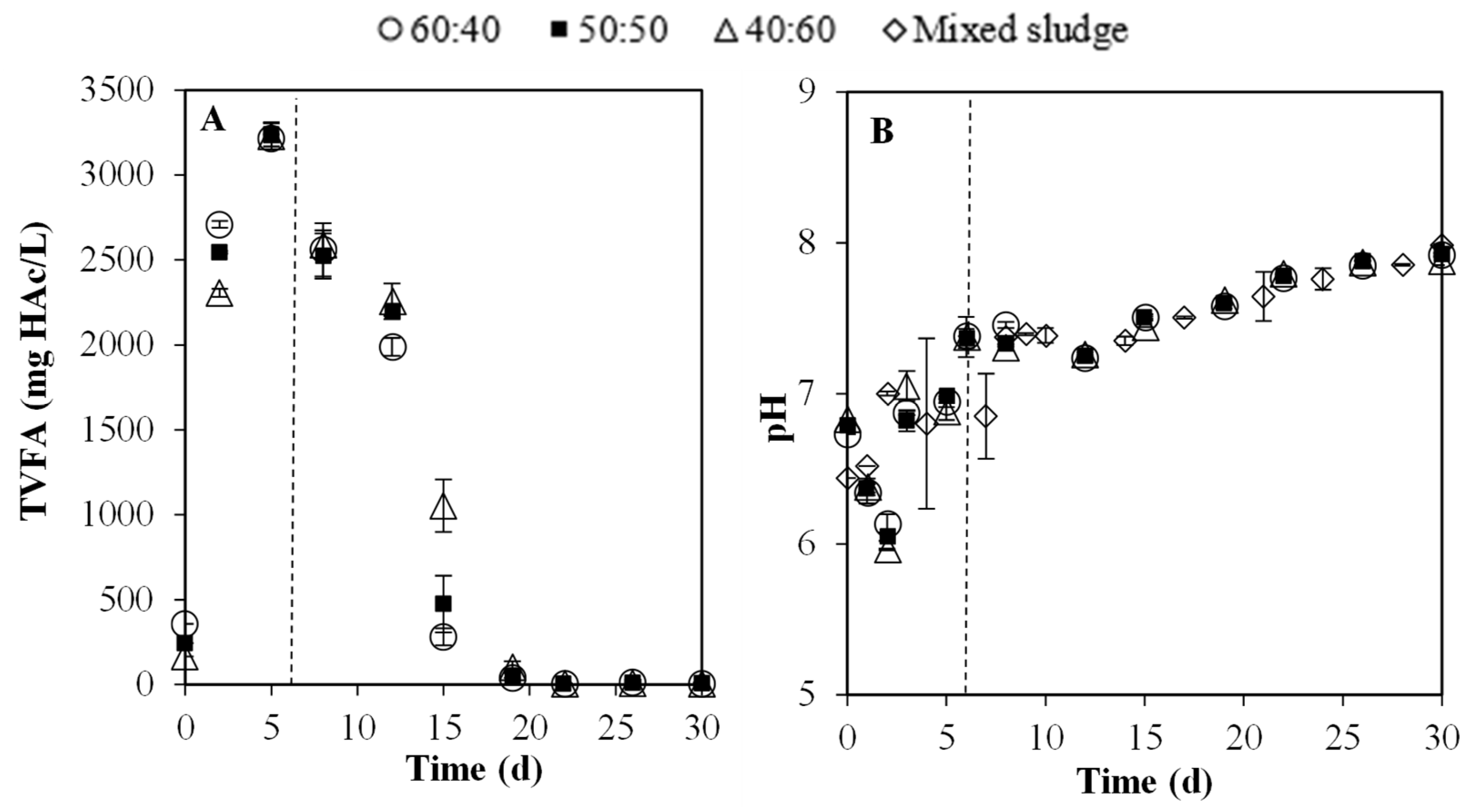
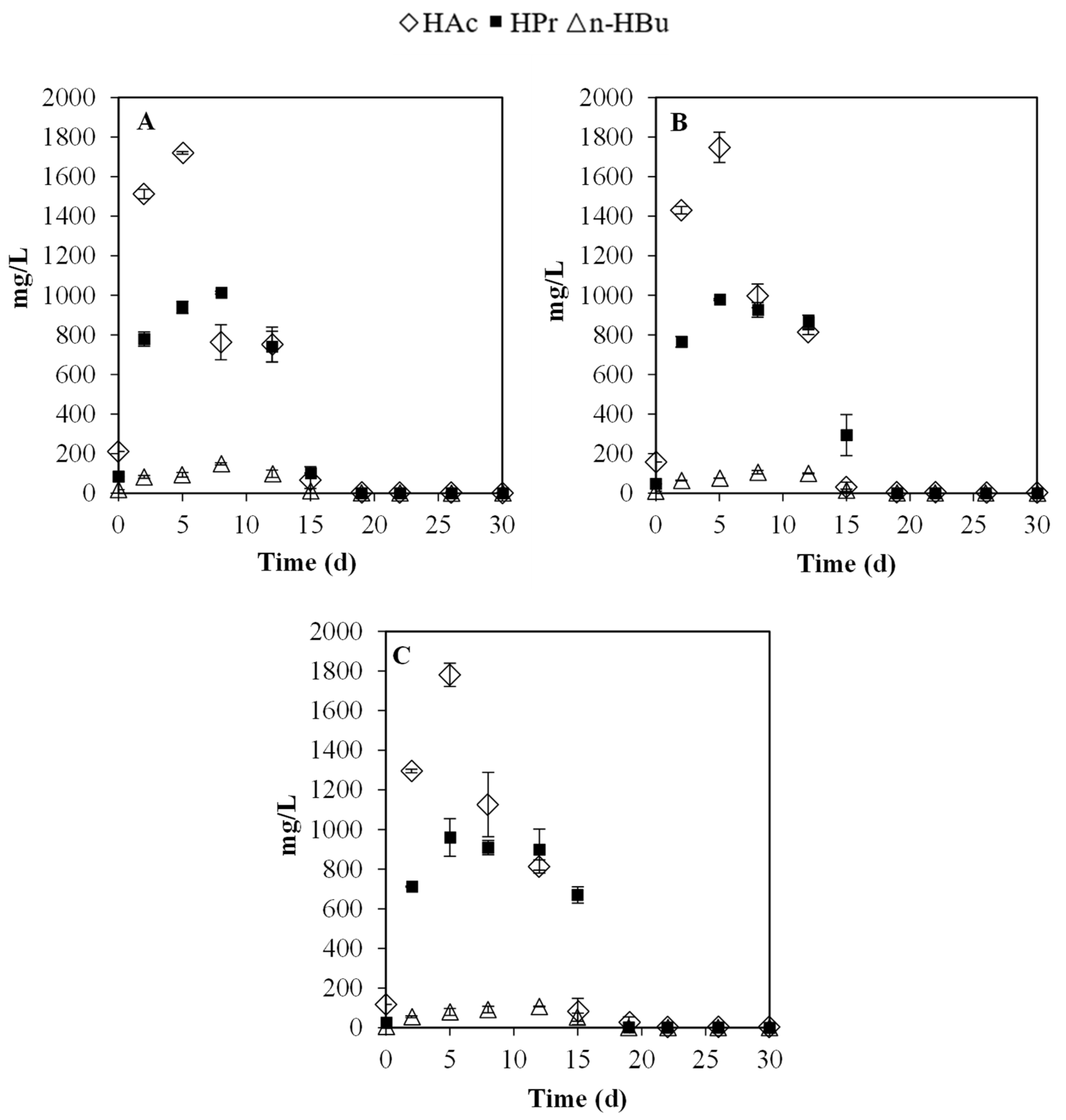
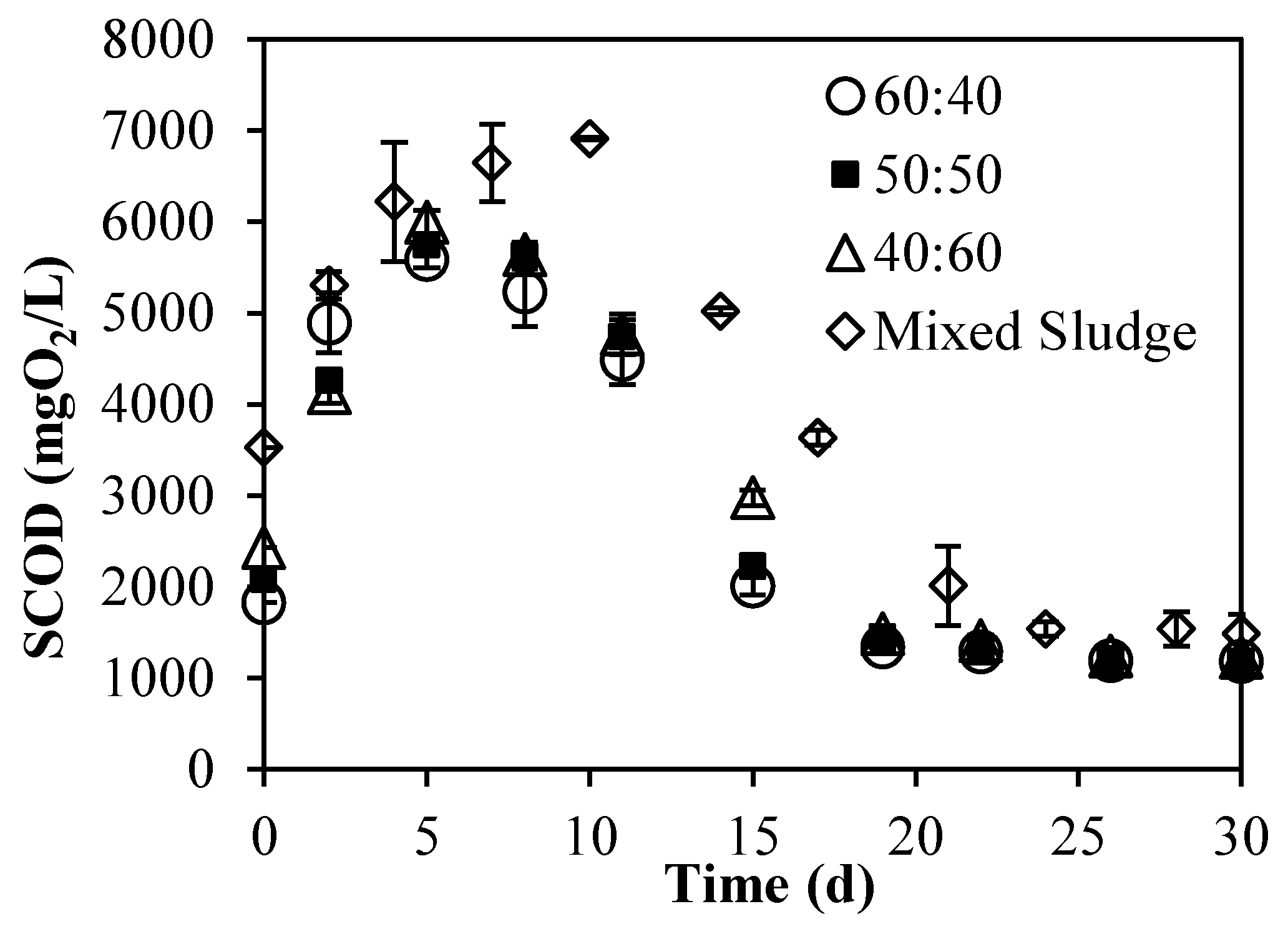
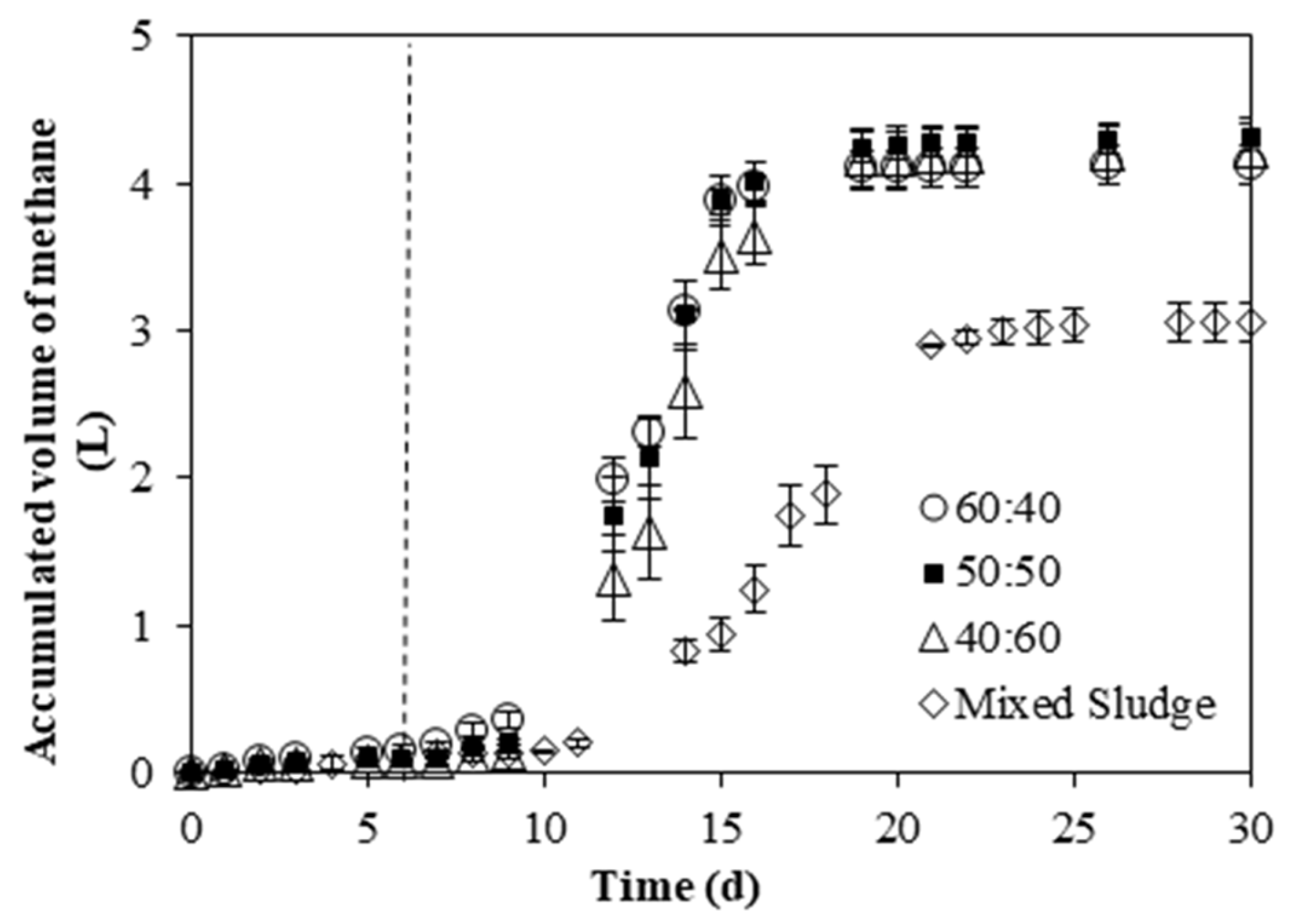
3.2. Batch Experiments: Optimization of Substrate Ratios
3.2.1. Key Physicochemical Parameter: pH and VFA
3.2.2. Evolution of Particulate and Soluble Organic Matter
3.2.3. Methane Production
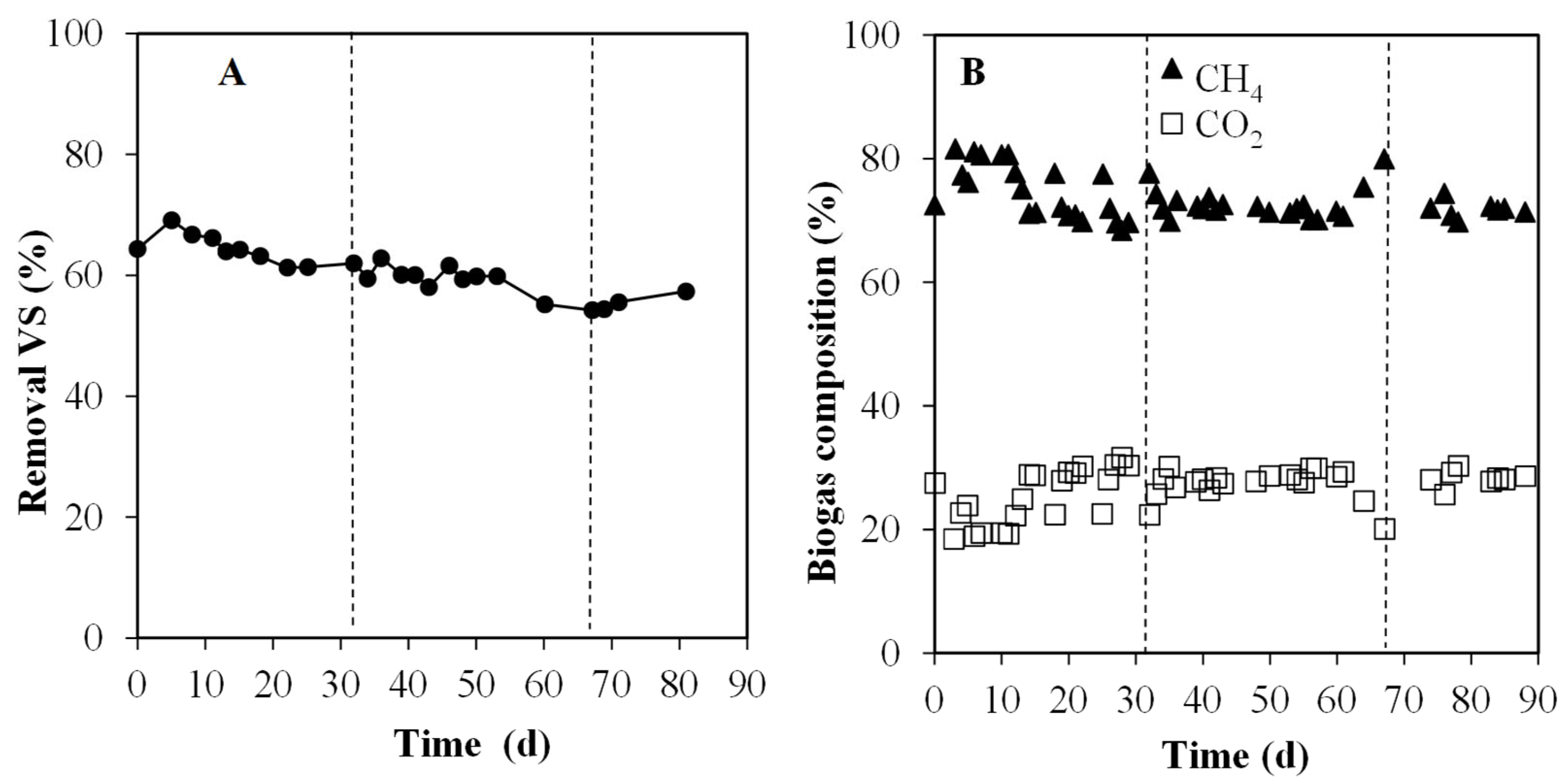
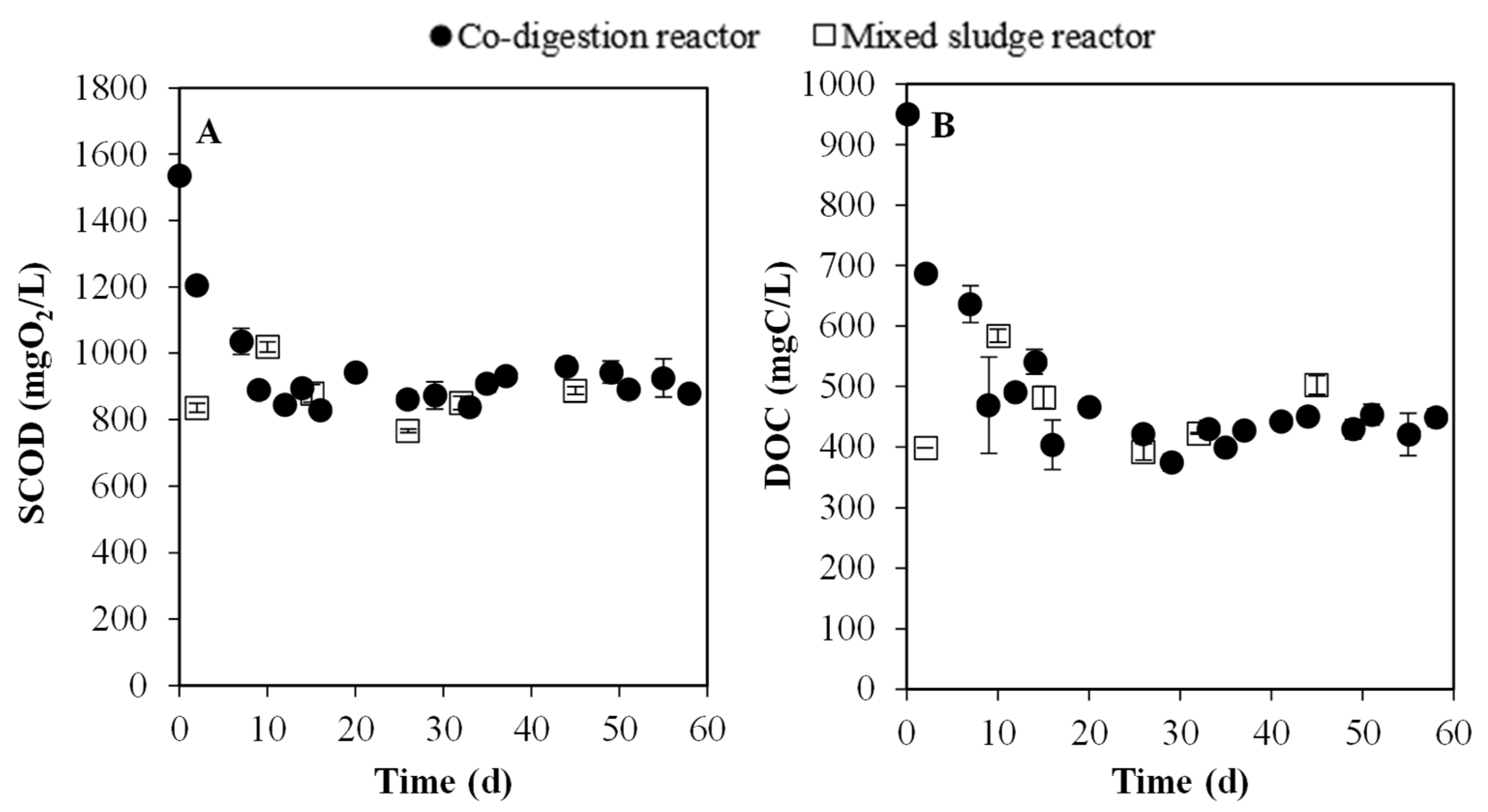
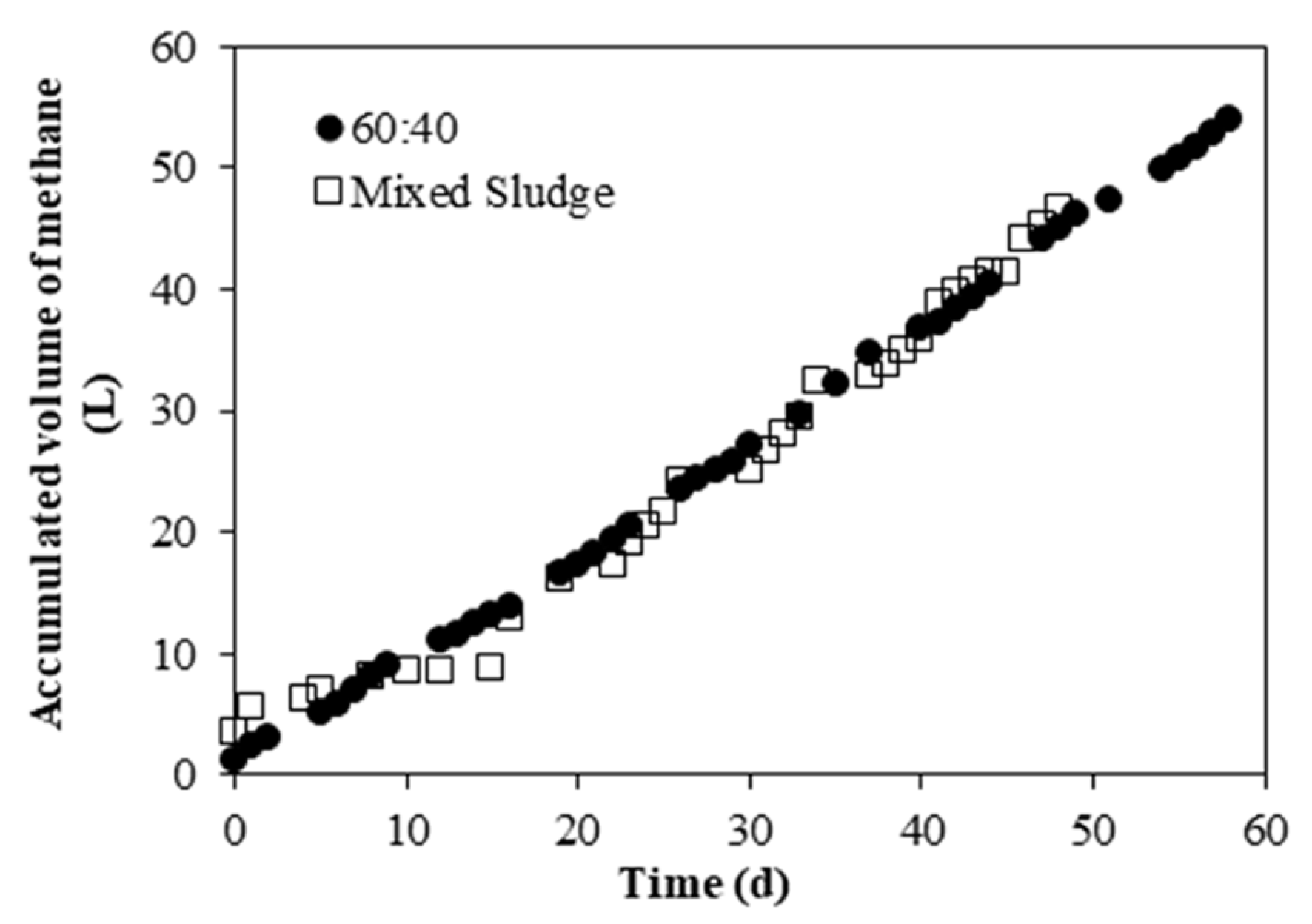
3.3. Semi-Continuous Experiments: Mono- and Co-Digestion Comparison
3.3.1. Evolution of Particulate and Soluble Organic Matter
3.3.2. Methane Production
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Anaerobic Digestion |
| CM | Cattle Manure |
| C/N | Carbon-to-Nitrogen Ratio |
| COD | Chemical Oxygen Demand |
| DOC | Dissolved Organic Carbon |
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| EMASESA | Empresa Metropolitana de Abastecimiento y Saneamiento de Aguas de Sevilla S.A |
| FW | Food Waste |
| GC-FID | Gas Chromatography with Flame Ionization Detector |
| GC-TCD | Gas Chromatography with Thermal Conductivity Detector |
| HRT | Hydraulic Retention Time |
| IVAGRO | Instituto de Investigación Vitivinícola y Agroalimentaria |
| LCFAs | Long-Chain Fatty Acids |
| MAGRAMA | Ministerio de Agricultura Alimentación y Medio Ambiente |
| MITECO | Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico |
| OLRs | Organic Loading Rates |
| OMSW | Olive Mill Solid Waste |
| OSBTOP | Organic Solid By-Products from Table Olive Processing |
| PEMAR | Plan Estatal Marco de Gestión de Residuos |
| 2POMW | Two-Phase Olive Mill Waste |
| SCOD | Soluble Chemical Oxygen Demand |
| TCD | Thermal Conductivity Detector |
| TCOD | Total Chemical Oxygen Demand |
| TNK | Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen |
| TOC | Total Organic Carbon |
| TS | Total Solids |
| TVFA | Total Volatile Fatty Acids |
| VFAs | Volatile Fatty Acids |
| VS | Volatile Solids |
| WWTP | Wastewater Treatment Plant |
References
- Ministerio de Agricultura Alimentación y Medio Ambiente (MAGRAMA). Plan Estatal Marco de Gestión de Residuos (PEMAR); Ministerio de Agricultura, Alimentación y Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 2015; pp. 1–182. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/content/dam/miteco/es/calidad-y-evaluacion-ambiental/planes-y-estrategias/pemaraprobado6noviembrecondae_tcm30-170428.pdf (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico (MITECO). Ministerio Para La Transición Ecológica y El Reto Demográfico, Calidad y Evaluación Ambiental, Prevención y Gestión de Residuos, Flujos de Residuos, Lodos de Depuradora. Available online: https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/calidad-y-evaluacion-ambiental/temas/prevencion-y-gestion-residuos/flujos/lodos-depuradora.html (accessed on 19 September 2024).
- Consejo Oleícola Internacional Estadísticas de Las Aceitunas de Mesa. Available online: https://www.internationaloliveoil.org/que-hacemos/unidad-de-asuntos-econonicos-y-promocion/?lang=es#figures (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Ahring, B.K. Perspectives for Anaerobic Digestion. In Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 81, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyasudeen, K.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Quaik, S.; Ismail, S.A. Prospects of Organic Waste Management and the Significance of Earthworms; Applied Environmental Science and Engineering for a Sustainable Future Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.V.; Yadav Lamba, B.; Tiwari, A.K.; Chen, W.H. Sustainable Biogas Production via Anaerobic Digestion with Focus on CSTR Technology: A Review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2024, 162, 105575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, M.; Barriga, F.; Neumann, P.; Gómez, G.; Vidal, G. Effects of Short Retention Times and Ultrasound Pretreatment on Ammonium Concentration and Organic Matter Transformation in Anaerobic Digesters Treating Sewage Sludge. Fermentation 2024, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borja, R.; Alba, J.; Banks, C.J. Impact of the Main Phenolic Compounds of Olive Mill Wastewater (OMW) on the Kinetics of Acetoclastic Methanogenesis. Process Biochem. 1997, 32, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of Anaerobic Digestion Process: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwietniewska, E.; Tys, J. Process Characteristics, Inhibition Factors and Methane Yields of Anaerobic Digestion Process, with Particular Focus on Microalgal Biomass Fermentation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Induchoodan, T.G.; Haq, I.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Factors Affecting Anaerobic Digestion for Biogas Production: A Review, 1st ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; ISBN 9780323857925. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.Y.; Lay, C.H. Carbon/Nitrogen-Ratio Effect on Fermentative Hydrogen Production by Mixed Microflora. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2004, 29, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, J. Co-Fermentation of Sewage Sludge with Ryegrass for Enhancing Hydrogen Production: Performance Evaluation and Kinetic Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, M.; Luque, B.; Perez, M.; Solera, R. Enhanced Hydrogen Production from Sewage Sludge by Cofermentation with Wine Vinasse. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 15977–15984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Morales, J.L.; Angeriz, R.; Gómez, J.; Suffo, M. Composting of Organic Solid By-Products from Table Olive Processing (OSBTOP). In Proceedings of the 16th International RAMIRAN Conference 2015 on Rural-Urban Symbiosis, Hamburg, Germany, 8–10 September 2015; University of Veterinary Medicine and Pharmacy in Košice: Košice, Slovakia, 2015; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zahan, Z.; Georgiou, S.; Muster, T.H.; Othman, M.Z. Semi-Continuous Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Chicken Litter with Agricultural and Food Wastes: A Case Study on the Effect of Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio, Substrates Mixing Ratio and Organic Loading. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julio Guerrero, I.C.; Peláez Jaramillo, C.A.; Molina Perez, F.J. Evaluación de La Co-Digestión Anaerobia de Lodos de Aguas Residuales Municipales Con Residuos de Alimentos. Rev. ION 2016, 29, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Náthia-Neves, G.; Berni, M.; Dragone, G.; Mussatto, S.I.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Anaerobic Digestion Process: Technological Aspects and Recent Developments. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 2033–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Peng, L.; Wang, D.; Ni, B. The Roles of Free Ammonia (FA) in Biological Wastewater Treatment Processes: A Review. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto-Ikemoto, R.; Matsuura, N.; Honda, R.; Hara-Yamamura, H.; Some, K.; Prak, S.; Koike, K.; Togari, T. Ammonia Tolerance and Microbial Community in Thermophilic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge Initiated with Lignocellulosic Biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezieke, A.H.; Serrano, A.; Clarke, W.; Villa-Gomez, D.K. Bottom Ash from Smouldered Digestate and Coconut Coir as an Alkalinity Supplement for the Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit Waste. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.; Gouveia, B.; Azevedo, A.; Fernandes, E.C.; Duarte, E. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Municipal Mixed Sludge and Mango Peel Biowaste: Performance and Stability Analysis for Different Ratios. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.A.; Romero, L.I.; Wilkie, A.C.; García-Morales, J.L. Mesophilic Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Olive-Mill Waste with Cattle Manure: Effects of Mixture Ratio. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmaciu, I.A.; Ionel, I.; Miutescu, M.C.; Grecu, E. Novel Specifications Regarding Biogas Production from Agriengineering Activities in Romania. AgriEngineering 2024, 6, 3602–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliger, C.; Alves, M.; Andrade, D.; Angelidaki, I.; Astals, S.; Baier, U.; Bougrier, C.; Buffière, P.; Carballa, M.; De Wilde, V.; et al. Towards a Standardization of Biomethane Potential Tests. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methods Standard. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Methods Standard: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Zahedi, S.; Rivero, M.; Solera, R.; Perez, M. Seeking to Enhance the Bioenergy of Municipal Sludge: Effect of Alkali Pre-Treatment and Soluble Organic Matter Supplementation. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, G. Review on Research Achievements of Biogas from Anaerobic Digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi-Banji, A.; Rahman, S. A Review of Process Parameters Influence in Solid-State Anaerobic Digestion: Focus on Performance Stability Thresholds. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohani, S.P.; Havukainen, J. Anaerobic Digestion: Factors Affecting Anaerobic Digestion Process. In Waste Bioremediation. Energy, Environment, and Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. Principles and Potential of the Anaerobic Digestion of Waste-Activated Sludge. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; He, C.; Yu, R.; Shen, D.; Jiao, Y. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Urban Sewage Sludge with Agricultural Biomass. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 6199–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.K.; Suja, F.B.; Zain, S.M.; Pramanik, B.K. The Anaerobic Digestion Process of Biogas Production from Food Waste: Prospects and Constraints. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 8, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Wang, X.; Xi, J.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Linkage of Kinetic Parameters with Process Parameters and Operational Conditions during Anaerobic Digestion. Energy 2017, 135, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Angelidaki, I.; Lv, N.; Ning, J.; Cai, G.; Zhu, G. Deep Insights into the Network of Acetate Metabolism in Anaerobic Digestion: Focusing on Syntrophic Acetate Oxidation and Homoacetogenesis. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, L.; Loh, K.C. Review and Perspectives of Enhanced Volatile Fatty Acids Production from Acidogenic Fermentation of Lignocellulosic Biomass Wastes. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Páez, E.; Serrano, A.; Purswani, J.; Correa-Galeote, D.; Cubero-Cardoso, J.; Fermoso, F.G. Impact on the Microbial Population during Biological Volatile Fatty Acid Production from Olive Mill Solid Waste. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.A.; Fdez-Güelfo, L.A.; Romero-García, L.I.; Wilkie, A.C.; García-Morales, J.L. Start-up of the Mesophilic Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Two-Phase Olive-Mill Waste and Cattle Manure Using Volatile Fatty Acids as Process Control Parameter. Fuel 2022, 325, 124901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lier, J.B.; Grolle, K.C.F.; Frijters, C.T.M.J.; Stams, A.J.M.; Lettinga, G. Effects of Acetate, Propionate, and Butyrate on the Thermophilic Anaerobic Degradation of Propionate by Methanogenic Sludge and Defined Cultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, J.; Yang, X.; Deng, P.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z. Alleviation of Propionic Acid Inhibition and Enhancement of Methane Production in Anaerobic Digestion by Micronano-Bubble Water Supplementation. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 427, 132425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.A.; Fdez-Güelfo, L.A.; Romero-García, L.I.; Wilkie, A.C.; García-Morales, J.L. Co-Digestion of Two-Phase Olive-Mill Waste and Cattle Manure: Influence of Solids Content on Process Performance. Fuel 2022, 322, 124187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliaccia, P.; Gallipoli, A.; Gianico, A.; Montecchio, D.; Braguglia, C.M. Single Stage Anaerobic Bioconversion of Food Waste in Mono and Co-Digestion with Olive Husks: Impact of Thermal Pretreatment on Hydrogen and Methane Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasalari, H.; Gharibi, H.; Darvishali, S.; Farzadkia, M. The Effects of Different Pretreatment Technologies on Microbial Community in Anaerobic Digestion Process: A Systematic Review. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Ping, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, Y. Comparison of Different Sewage Sludge Pretreatment Technologies for Improving Sludge Solubilization and Anaerobic Digestion Efficiency: A Comprehensive Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoyanova, E.; Lundaa, T.; Bochmann, G.; Fuchs, W. Overcoming the Bottlenecks of Anaerobic Digestion of Olive Mill Solid Waste by Two-Stage Fermentation. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Rodríguez, M.J.; Rincón, B.; Fermoso, F.G.; Jiménez, A.M.; Borja, R. Assessment of Two-Phase Olive Mill Solid Waste and Microalgae Co-Digestion to Improve Methane Production and Process Kinetics. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 157, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Lama-Calvente, D.; Fernández-Rodríguez, M.J.; Llanos, J.; Mancilla-Leytón, J.M.; Borja, R. Enhancing Methane Production from the Invasive Macroalga Rugulopteryx Okamurae through Anaerobic Co-Digestion with Olive Mill Solid Waste: Process Performance and Kinetic Analysis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 4113–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, V.; Donoso-Bravo, A.; Chamy-Maggy, R.; Campos, J.L.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Belmonte, M. Factors That Affect Methane Yield Using Raw Olive Alperujo (Unhydrolyzed) as Substrate in BMP Assays. Recycling 2022, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Cardoso, J.; Llamas, M.; Trujillo-Reyes, Á.; Fernández-Prior, Á.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, G. Assessing the Potential of Olive Mill Solid Waste as Feedstock for Methane and Volatile Fatty Acids Production via Anaerobic Bioprocesses. New Biotechnol. 2024, 84, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, J.A.; Fdez-Güelfo, L.A.; Romero-García, L.I.; Wilkie, A.C.; García-Morales, J.L. Mesophilic Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Two-Phase Olive-Mill Waste and Cattle Manure: Optimization of Semi-Continuous Process. Fuel 2022, 328, 125354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Units | OSBTOP 2 | Mixed Sludge 2 | Digested Sludge 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 5.08 (±0.08) | 5.85 (±0.37) | 7.27 (±0.02) |
| EC | mS/cm | 1.41 (±0.01) | 2.66 (±0.41) | 5.49 (±0.04) |
| Moisture | % | 71.51 (±0.07) | 97.20 (±1.68) | 98.18 (±0.19) |
| TS | g/kg | 284.92 (±0.66) | 28.03 (±16.77) | 18.15 (±1.87) |
| VS | g/kg 1 | 273.90 (±0.58) | 20.71 (±11.25) | 10.35 (±1.63) |
| TCOD | gO2/kg 1 | - | 35.32 (±14.40) | 18.52 (±0.47) |
| SCOD | gO2/kg 1 | 11.13 (±0.26) | 3.25 (±1.48) | 0.98 (±0.09) |
| DOC | gC/L | 3.25 (±0.38) | 1.21 (±0.49) | 334.44 (±0.62) |
| TVFA | gHAc/L | 1.15 (±0.50) | 1.94 (±0.43) | 29.51 (±0.58) |
| Organic Matter | % | 96.13 (±0.05) | 75.27 (±3.26) | 56.78 (±3.31) |
| C | % | 55.76 (±2.60) | 43.66 (±1.89) | 32.93 (±3.10) |
| N | % | 1.2 (±0.71) | 6.34 (±0.80) | 8.10 (±0.90) |
| C/N | - | 48.4 (±1.10) | 6.97 (±1.05) | 4.06 (±0.92) |
| Alkalinity | gCaCO3/L | 0.40 (±0.00) | 1.94 (±0.37) | 4.14 (±0.20) |
| TKN | g/kg 1 | 3.28 (±0.13) | 1.44 (±0.36) | 1.47 (±0.01) |
| Ammonia Nitrogen | mgNH3-N/kg 1 | 2.35 (±0.00) | 87.93 (±7.71) | 337.62 (±14.41) |
| Nomenclature | Mixed Sludge % | OSBTOP % | Ratio | C/N Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixed sludge | 100 | 0 | 1:0 | 6.7 |
| 60:40 | 60 | 40 | 3:2 | 20.8 |
| 50:50 | 50 | 50 | 1:1 | 25.0 |
| 40:60 | 40 | 60 | 2:3 | 29.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Domínguez, E.; Rubio, J.Á.; Lyng, J.; Toro, E.; Estévez, F.; García-Morales, J.L. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Organic Solid By-Products from Table Olive Processing: Influence of Substrate Mixtures on Overall Process Performance. Energies 2025, 18, 3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143812
Díaz-Domínguez E, Rubio JÁ, Lyng J, Toro E, Estévez F, García-Morales JL. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Organic Solid By-Products from Table Olive Processing: Influence of Substrate Mixtures on Overall Process Performance. Energies. 2025; 18(14):3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143812
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Domínguez, Encarnación, José Ángel Rubio, James Lyng, Enrique Toro, Fernando Estévez, and José L. García-Morales. 2025. "Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Organic Solid By-Products from Table Olive Processing: Influence of Substrate Mixtures on Overall Process Performance" Energies 18, no. 14: 3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143812
APA StyleDíaz-Domínguez, E., Rubio, J. Á., Lyng, J., Toro, E., Estévez, F., & García-Morales, J. L. (2025). Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Organic Solid By-Products from Table Olive Processing: Influence of Substrate Mixtures on Overall Process Performance. Energies, 18(14), 3812. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18143812








