Optimal Sliding Mode Control of Modular Multilevel Converters Considering Control Input Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model of the MMC
3. Formulation of Optimal Sliding Mode Control for MMCs
3.1. Performance Index and Optimization Problem Formulation
3.2. Solving QP Problem for Arm Voltage References Determination Using the Infeasible Active-Set Method
| Algorithm 1: Infeasible active-set method [25,27] |
| Input: |
| 1: Compute H and F according to (29) and (31). |
| 2: ; ; ; ; |
| 3: Flag 0; |
| 4: while Flag == 0 do |
| 5: ; ; |
| 6: ; ; |
| 7: Compute , and from (42), (43) and (44). |
| 8: if |
| 9: ; |
| 10: Flag 1; |
| 11: end if |
| 12: ; |
| 13: ; |
| 14: ; |
| 15: end while |
| Output: |
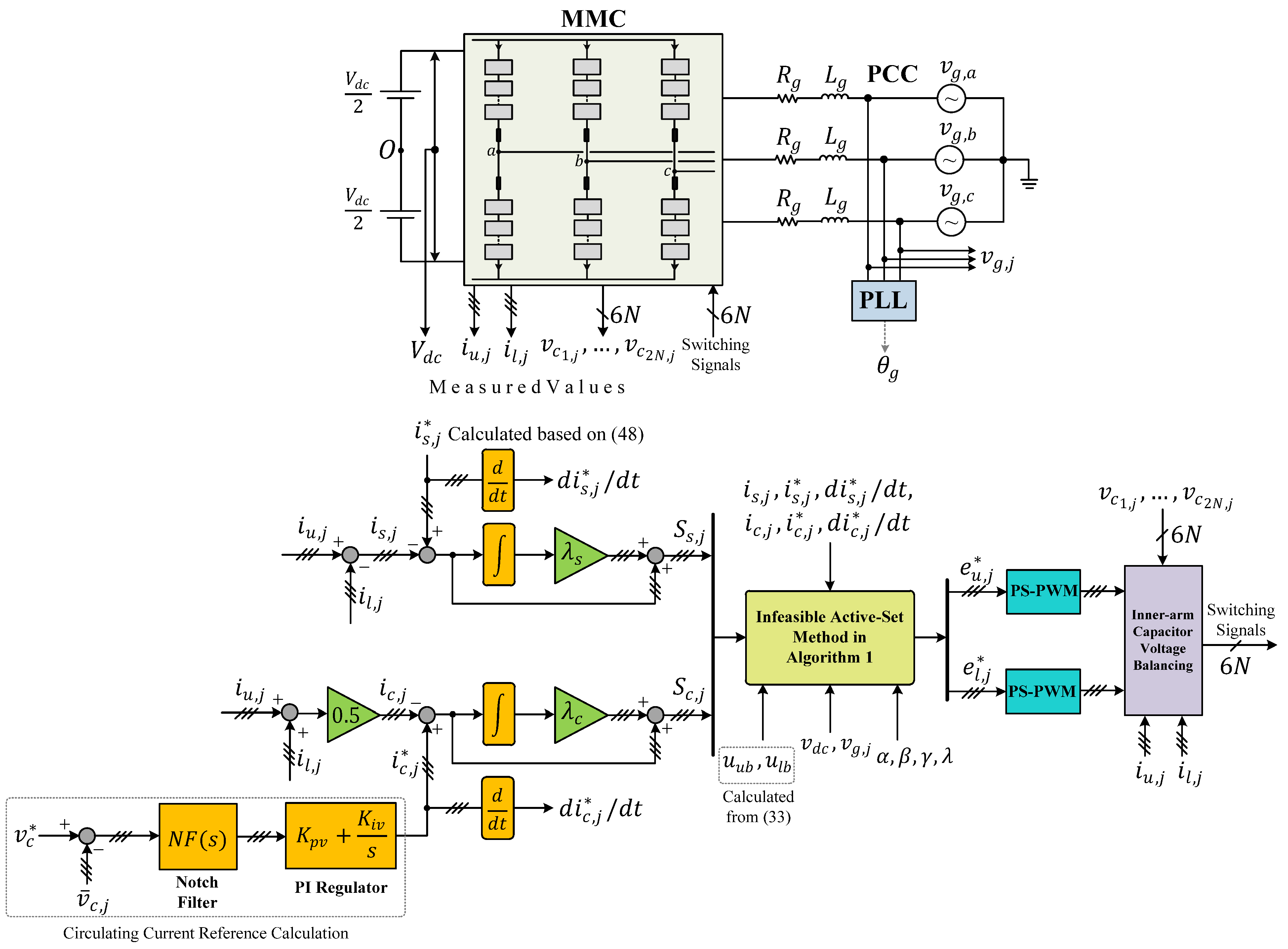
4. Reference Calculation and Low-Level Control Strategy
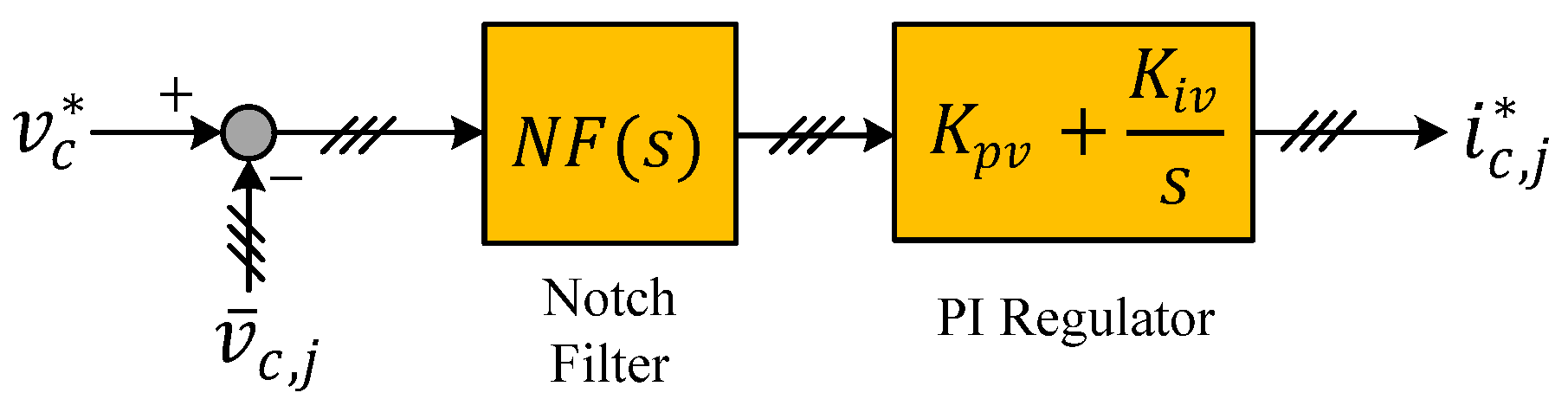
4.1. Reference Values
4.2. Modulation and Inner-Arm Capacitor Voltage Balancing Strategy
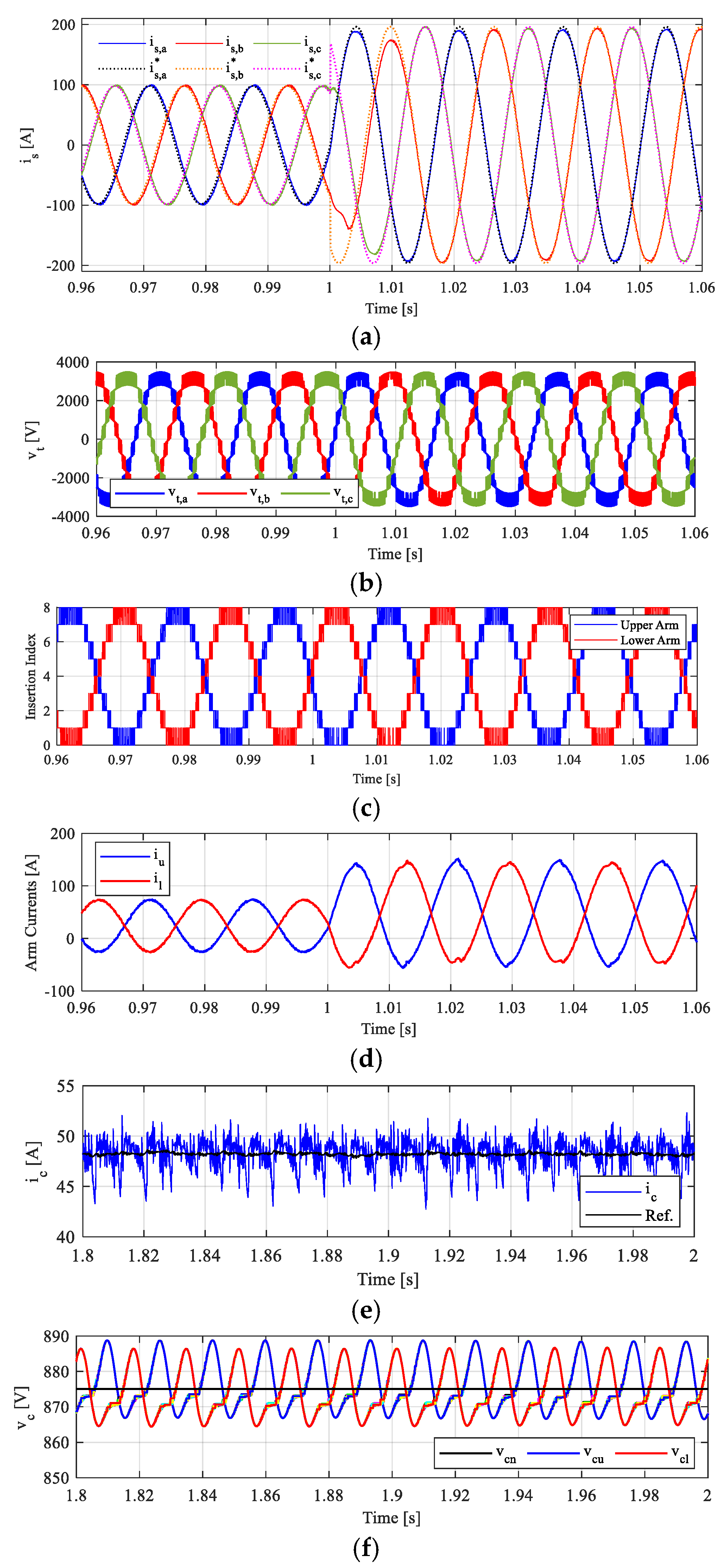
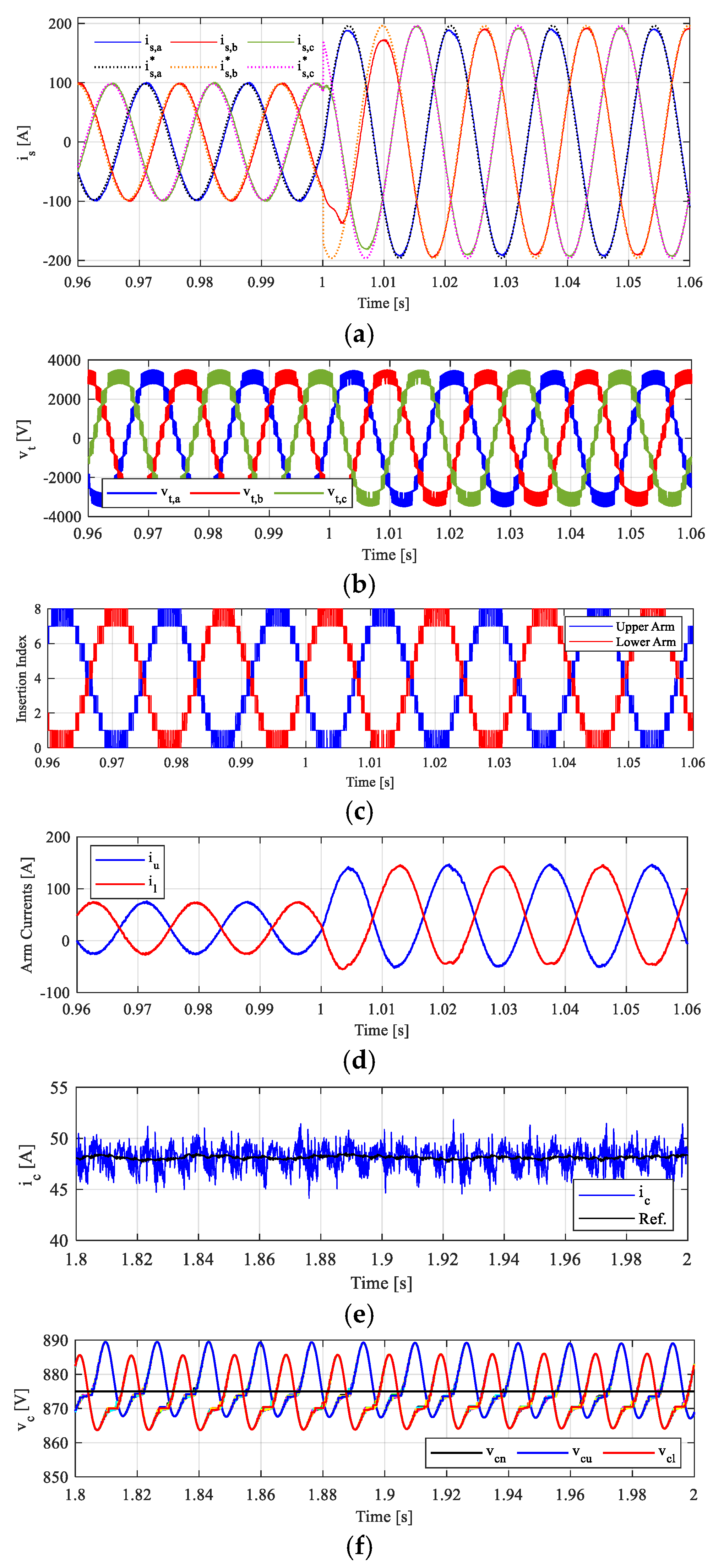
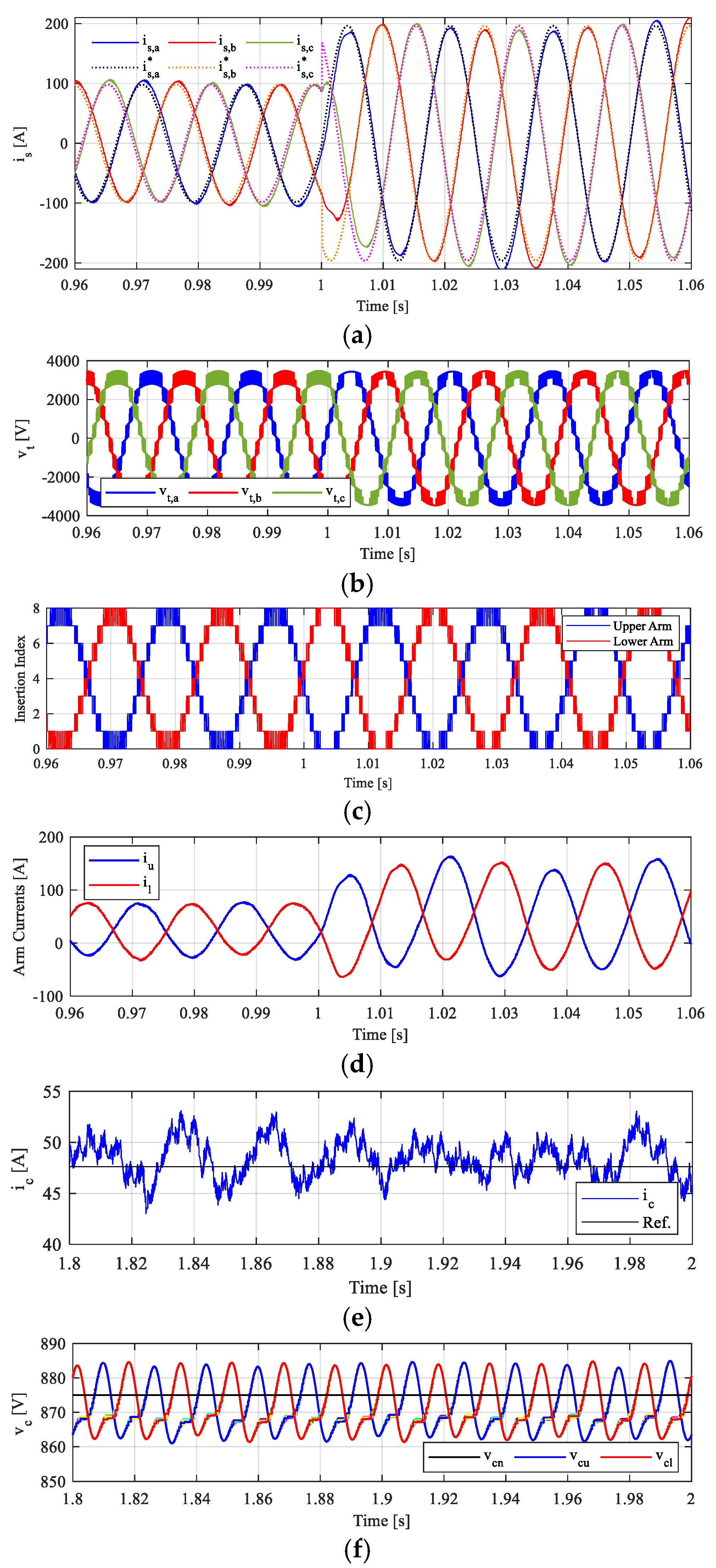
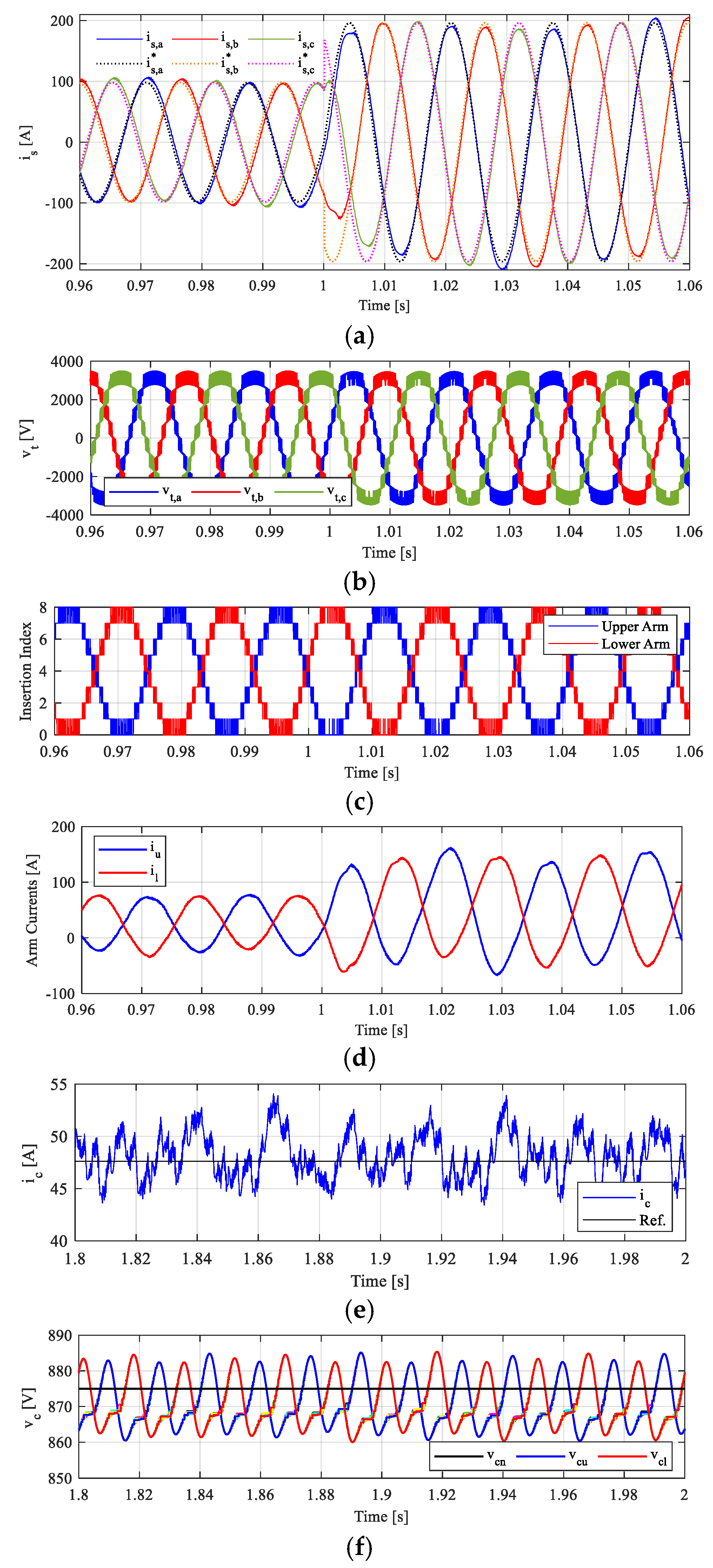
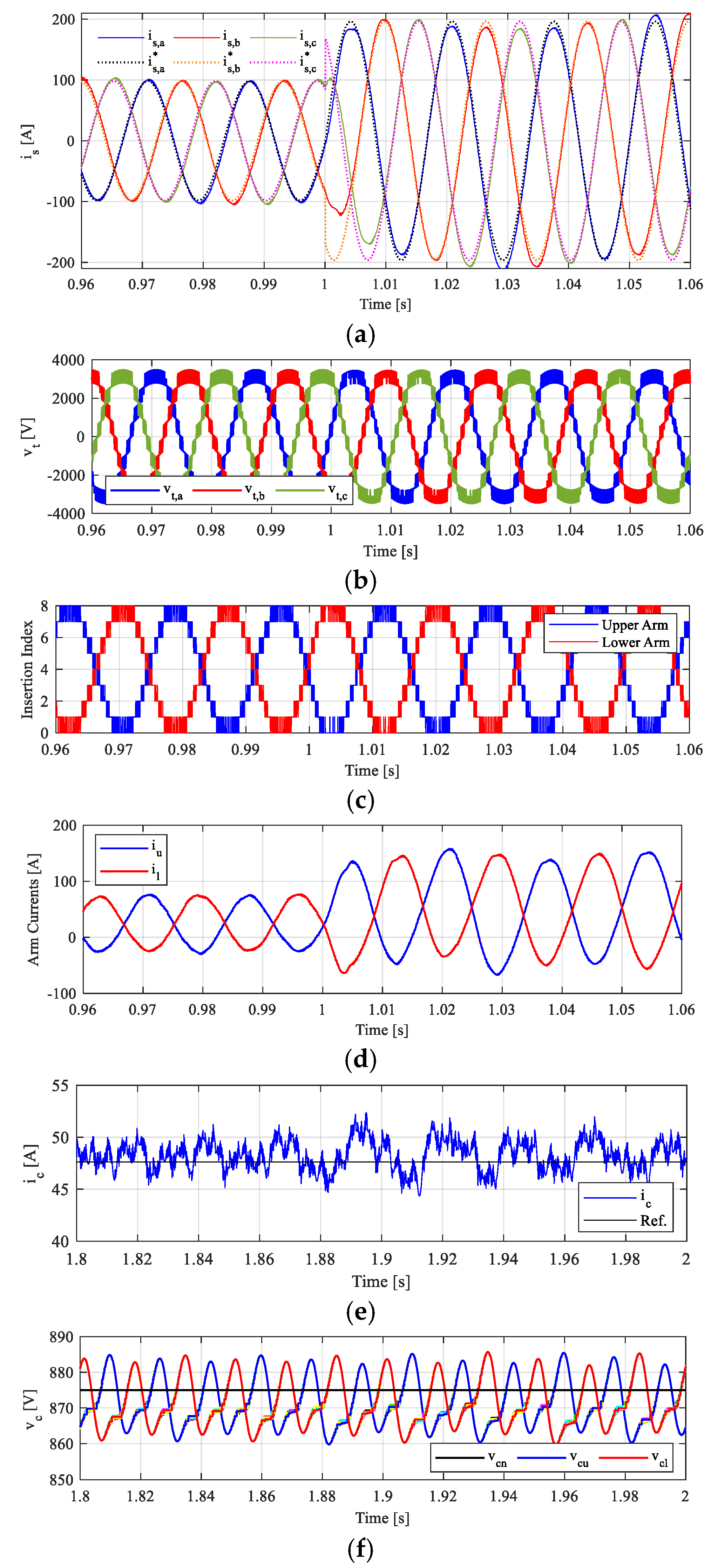
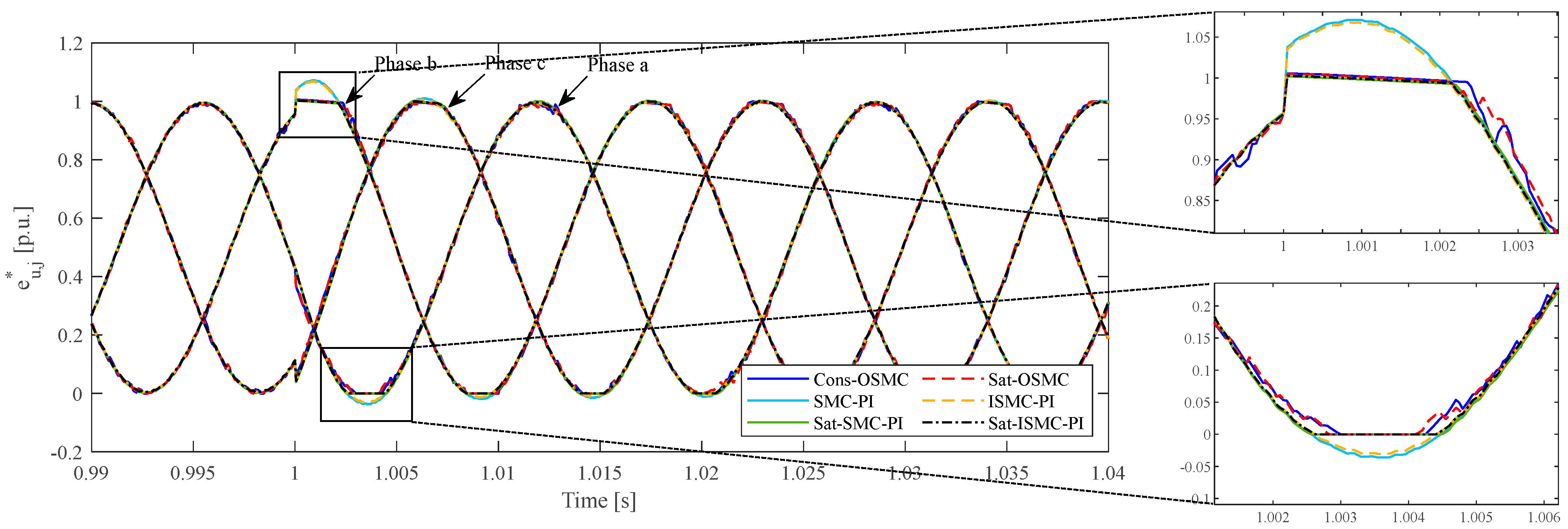
5. Simulation Results and Discussion
Dynamic and Steady-State Performance Under Transient Due to AC-Side Power Change
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Picas, R.; Zaragoza, J.; Pou, J.; Ceballos, S. Reliable Modular Multilevel Converter Fault Detection with Redundant Voltage Sensor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou, G.; Pou, J.; Ceballos, S.; Picas, R.; Zaragoza, J.; Agelidis, V.G. Control of Circulating Currents in Modular Multilevel Converters Through Redundant Voltage Levels. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 7761–7769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedifard, M.; Iravani, R. Dynamic Performance of a Modular Multilevel Back-to-Back HVDC System. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2010, 25, 2903–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupertino, A.F.; Farias, J.V.M.; Pereira, H.A.; Seleme, S.I.; Teodorescu, R. Comparison of DSCC and SDBC Modular Multilevel Converters for STATCOM Application During Negative Sequence Compensation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 2302–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Wang, H.; Song, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Ren, B.; Wang, Z. HB and FB MMC Based Onshore Converter in Series-Connected Offshore Wind Farm. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 2646–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.A.; Arancibia, D.; Kouro, S.; Rodriguez, J. Modular Multilevel Converter with Integrated Storage for Solar Photovoltaic Applications. In Proceedings of the IECON 2013—39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Soong, T.; Lehn, P.W. Evaluation of Emerging Modular Multilevel Converters for BESS Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2014, 29, 2086–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, P.; Tang, Y. Feedback Linearization Based Current Control Strategy for Modular Multilevel Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Dekka, A.; Wu, B.; Zargari, N. Modular Multilevel Converters: Analysis, Control and Applications; Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, L.; Yao, W.; Lu, Z. Circulating Harmonic Current Elimination of a CPS-PWM Based Modular Multilevel Converter with Plug-In Repetitive Controller. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2083–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouybary, H.S.; Khaburi, D.A.; El Hajjaji, A.; Mabwe, A.M. Modular Multilevel Converter Current Control Using Linear Matrix Inequality (LMI) Approach. In Proceedings of the PEDSTC, Tehran, Iran, 30 January–1 February 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara, M.; Maeda, R.; Akagi, H. Control and Analysis of the Modular Multilevel Cascade Converter Based on Double-Star Chopper-Cells (MMCC-DSCC). IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riar, B.S.; Geyer, T.; Madawala, U.K. Model Predictive Direct Current Control of Modular Multilevel Converters: Modeling, Analysis, and Experimental Evaluation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhum, H.; Watson, A.J.; Rivera, M.; Zanchetta, P.; Wheeler, P. Model Predictive Control of a Modular Multilevel Converter with Reduced Computational Burden. Energies 2024, 17, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, C.; Yi, W.; Luo, B.; Cheng, Z. Model Predictive Control of Modular Multilevel Converter Based on Fixed Switch State Set for Offshore Wind Power. J. Eng. 2023, 2023, e12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-C.; Lai, Y.-M.; Tse, C.K. Sliding Mode Control of Switching Power Converters: Techniques and Implementation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Saeedifard, M.; Perez, M.A. Sliding Mode Control of the Modular Multilevel Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshani, H.; Farrokhi, M. Optimal Sliding-Mode Control of Linear Systems with Uncertainties and Input Constraints Using Projection Neural Network. Optim. Control Appl. Methods 2018, 39, 963–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, C.; Lu, H.; Li, M. Adaptive Reaching Law Based Sliding Mode Control for Electromagnetic Formation Flight with Input Saturation. J. Frankl. Inst. 2016, 353, 2398–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Capello, E. Reaching Law-Based SMC for Spacecraft Applications with Actuators Constraints. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2021, 6, 2036–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, M.; Wu, Q.; Shao, S. Dynamic Surface Control for a Class of Stochastic Non-Linear Systems with Input Saturation. IET Control Theory Appl. 2016, 10, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, W.; Zeb, K.; Khan, M.A.; Ishfaq, M.; Khan, I.; ul Islam, S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, G.S.; Lee, C. Control of Output and Circulating Current of Modular Multilevel Converter Using a Sliding Mode Approach. Energies 2019, 12, 4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.Y.; Subroto, R.K.; Wang, C.Z.; Lian, K.L. An Improved Sliding Mode Control with Integral Surface for a Modular Multilevel Power Converter. Energies 2022, 15, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouybary, H.S.; Khaburi, D.A.; El Hajjaji, A.; Mabwe, A.M. A Comparative Study of Current Control Strategies for Modular Multilevel Converters. In Proceedings of the EPE’23 ECCE Europe, Aalborg, Denmark, 4–8 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kunisch, K.; Rendl, F. An Infeasible Active Set Method for Quadratic Problems with Simple Bounds. SIAM J. Optim. 2003, 14, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Leon, J.I.; Perez, M.A.; Franquelo, L.G.; Marquez, A.; Vazquez, S. Model Predictive Control of Modular Multilevel Converters Using Quadratic Programming. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 7012–7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Tian, W.; Yang, Q.; Chai, N.; Rodriguez, J.; Kennel, R.; Heldwein, M.L. Model Predictive Control of a Modular Multilevel Converter Considering Control Input Constraints. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex Optimization, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S.J. Numerical Optimization, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, M.A. Practical Optimization Methods: With Mathematica Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Xiao, Q.; Zhou, D.; Qiu, H.; Tang, Y. Modulated Model Predictive Control for Modular Multilevel Converters with Easy Implementation and Enhanced Steady-State Performance. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 9107–9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zama, A.; Mansour, S.A.; Frey, D.; Benchaib, A.; Bacha, S.; Luscan, B. A Comparative Assessment of Different Balancing Control Algorithms for Modular Multilevel Converter (MMC). In Proceedings of the 18th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’16 ECCE Europe), Karlsruhe, Germany, 5–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dekka, A.; Wu, B.; Zargari, N.R.; Lizana, R. Dynamic Voltage Balancing Algorithm for Modular Multilevel Converter: A Unique Solution. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Saeedifard, M. Reduced Switching-Frequency Voltage-Balancing Strategies for Modular Multilevel HVDC Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2013, 28, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jones, E.A.; Wang, F. The Impact of Voltage-Balancing Control on Switching Frequency of the Modular Multilevel Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 2829–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Parameters | ||
| Rated line-to-line RMS grid voltage | 4160 | V |
| Grid fundamental frequency () | 60 | Hz |
| Grid filter inductance () | 8 | mH |
| MMC Parameters | ||
| Rated power | 1 | MVA |
| DC-bus voltage () | 7 | kV |
| Arm inductance (L) | 5 | mH |
| Equivalent arm resistance (R) | 0.1 | Ω |
| Number of submodules per arm (N) | 8 | --- |
| Submodule capacitance (C) | 8 | mF |
| SM capacitor nominal voltage () | 875 | V |
| Control Parameters | ||
| Fundamental sample time | 2 | |
| Carrier frequency () | 500 | Hz |
| Leg-level balancing proportional gain () | 3.8 | A·V−1 |
| Leg-level balancing integral gain () | 30 | A·V−1·s−1 |
| Cons-OSMC | Sat-OSMC | SMC-PI | ISMC-PI | Sat-SMC-PI | Sat-ISMC-PI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAE of in transient | Phase a: 0.29 | Phase a: 0.31 | Phase a: 0.77 | Phase a: 0.80 | Phase a: 0.69 | Phase a: 0.77 |
| Phase b: 0.64 | Phase b: 0.68 | Phase b: 0.85 | Phase b: 0.96 | Phase b: 0.81 | Phase b: 0.91 | |
| Phase c: 0.36 | Phase c: 0.39 | Phase c: 0.86 | Phase c: 0.91 | Phase c: 0.78 | Phase c: 0.85 | |
| IAE of in steady-state | Phase a: 2.04 | Phase a: 2.06 | Phase a: 3.15 | Phase a: 2.99 | Phase a: 3.76 | Phase a: 2.79 |
| Phase b: 2.04 | Phase b: 2.02 | Phase b: 3.04 | Phase b: 3.01 | Phase b: 3.45 | Phase b: 2.67 | |
| Phase c: 1.98 | Phase c: 2.00 | Phase c: 3.22 | Phase c: 2.95 | Phase c: 3.90 | Phase c: 2.74 | |
| THD of in steady-state | 4.27% | 3.03% | 5.00% | 4.32% | 6.45% | 4.25% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheikhi Jouybary, H.; Arab Khaburi, D.; El Hajjaji, A.; Mpanda Mabwe, A. Optimal Sliding Mode Control of Modular Multilevel Converters Considering Control Input Constraints. Energies 2025, 18, 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112757
Sheikhi Jouybary H, Arab Khaburi D, El Hajjaji A, Mpanda Mabwe A. Optimal Sliding Mode Control of Modular Multilevel Converters Considering Control Input Constraints. Energies. 2025; 18(11):2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112757
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheikhi Jouybary, Homa, Davood Arab Khaburi, Ahmed El Hajjaji, and Augustin Mpanda Mabwe. 2025. "Optimal Sliding Mode Control of Modular Multilevel Converters Considering Control Input Constraints" Energies 18, no. 11: 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112757
APA StyleSheikhi Jouybary, H., Arab Khaburi, D., El Hajjaji, A., & Mpanda Mabwe, A. (2025). Optimal Sliding Mode Control of Modular Multilevel Converters Considering Control Input Constraints. Energies, 18(11), 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18112757






