The Performance Evaluation of a Hybrid System Combining an Alkaline Fuel Cell with an Inhomogeneous Thermoelectric Generator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Description
- (1)
- The entire hybrid system runs under steady-state conditions [23];
- (2)
- The provision of oxygen and hydrogen are assumed to be perfectly regulated based on the electric current generated, considering that hydrogen can be recycled in practical operations [24];
- (3)
- The ITEG neglects the Thomson effect of thermoelectric elements and permits electric current to flow through the device’s arm [25];
- (4)
- The average Seebeck coefficient of the ITEG is treated as a constant at a constant temperature, and the ITEG’s geometry is assumed to be in its optimal configuration [26].
2.1. Alkaline Fuel Cell
2.2. Inhomogeneous Thermoelectric Generator
2.3. Regenerator
2.4. Hybrid System
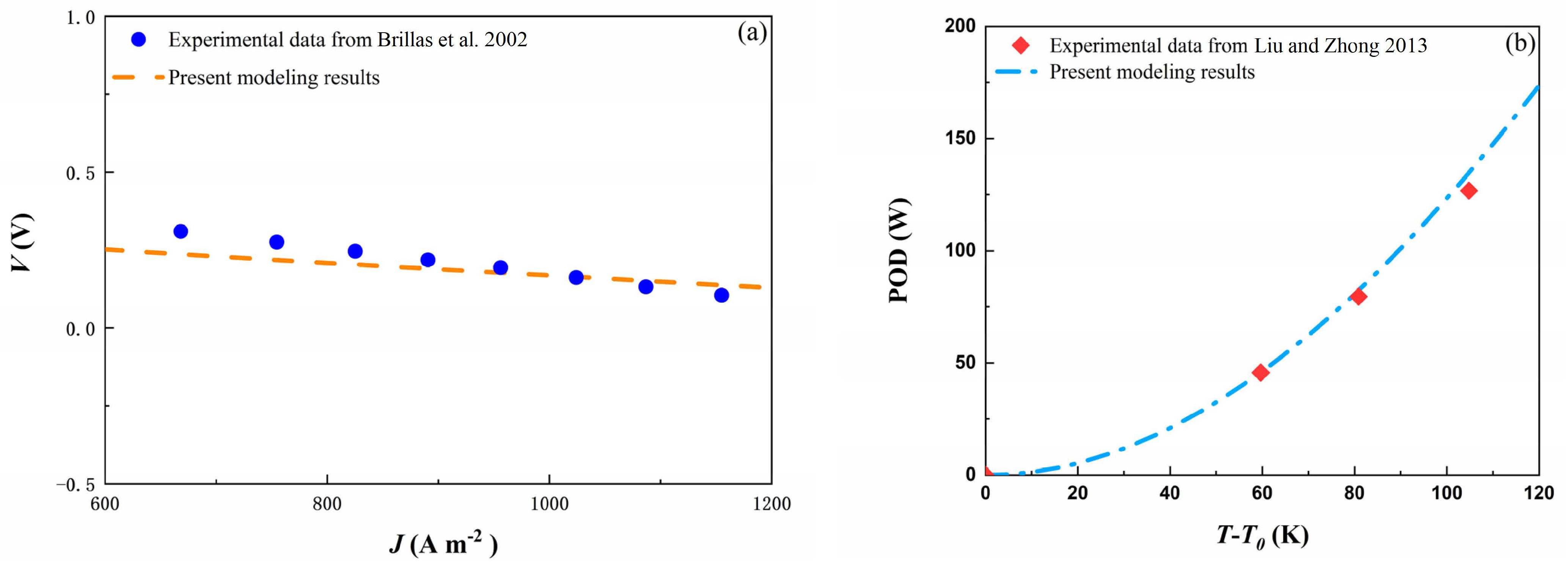
3. Model Validation
4. The Hybrid System’s Generic Performance Characteristics and Competitiveness Assessment
5. Results and Discussion
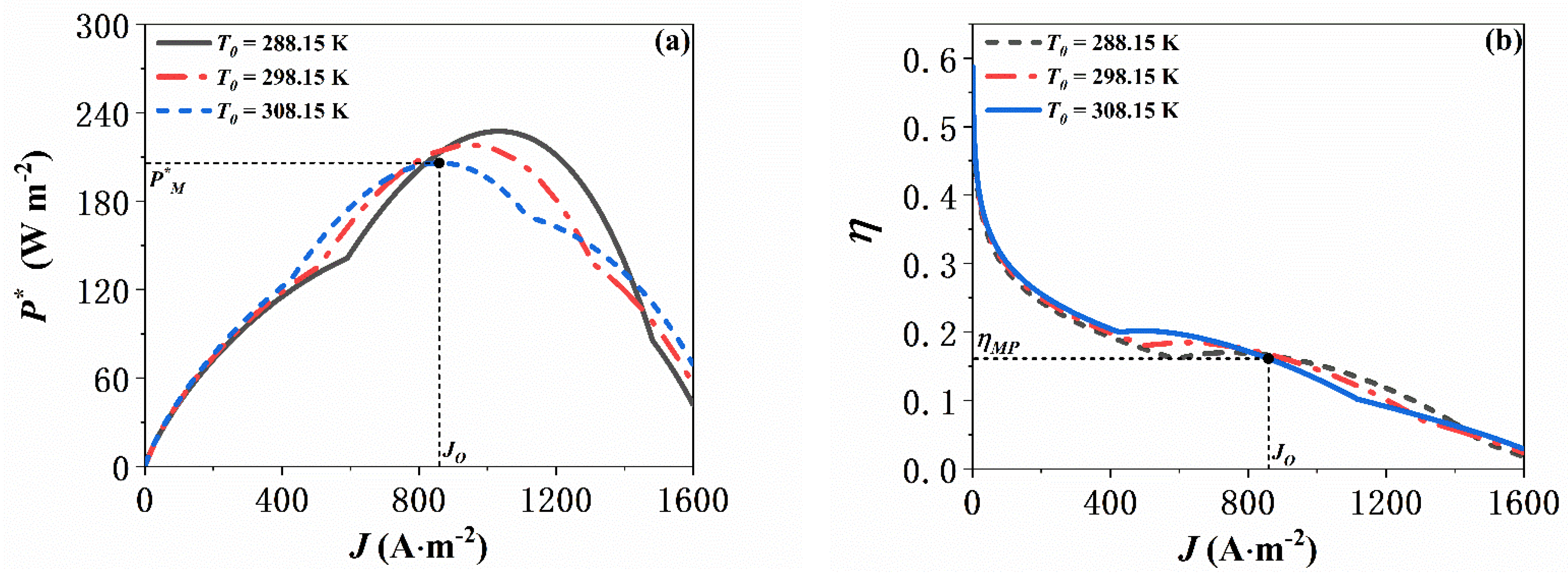
5.1. Effect of the Operating Temperature of the AFC
5.2. Effect of Environmental Temperature
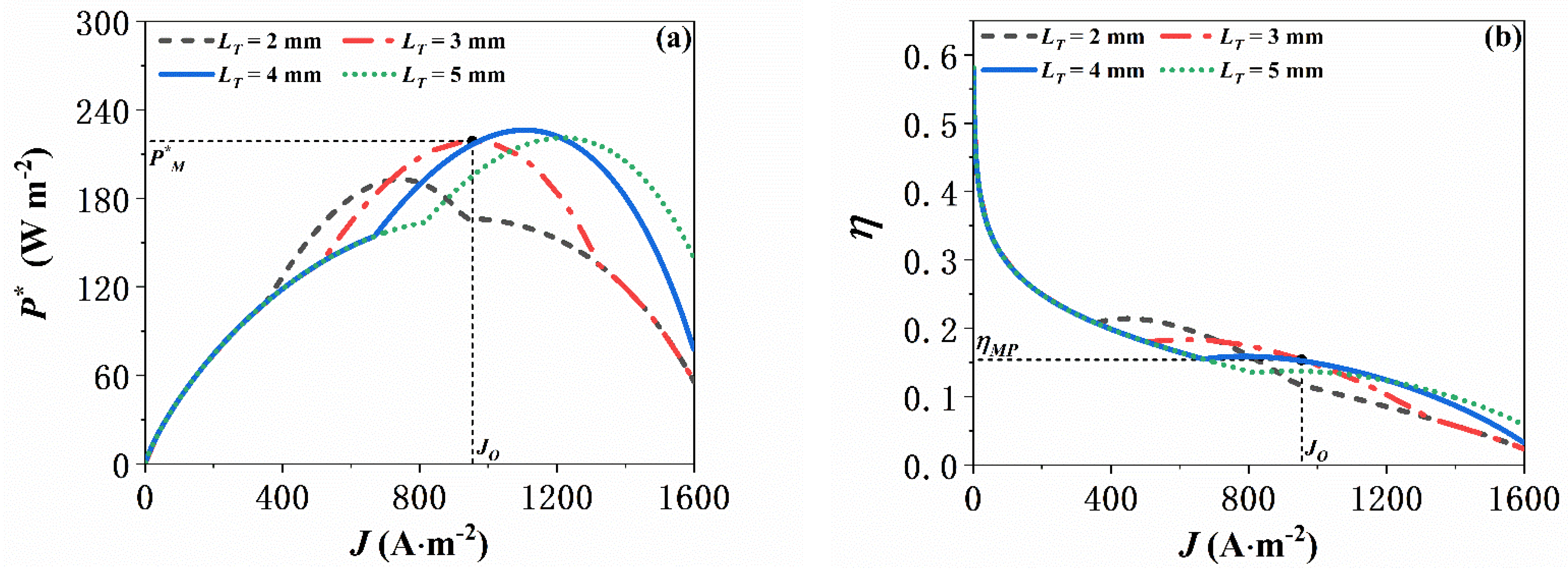
5.3. Effect of the Geometric Characteristics of the ITEG
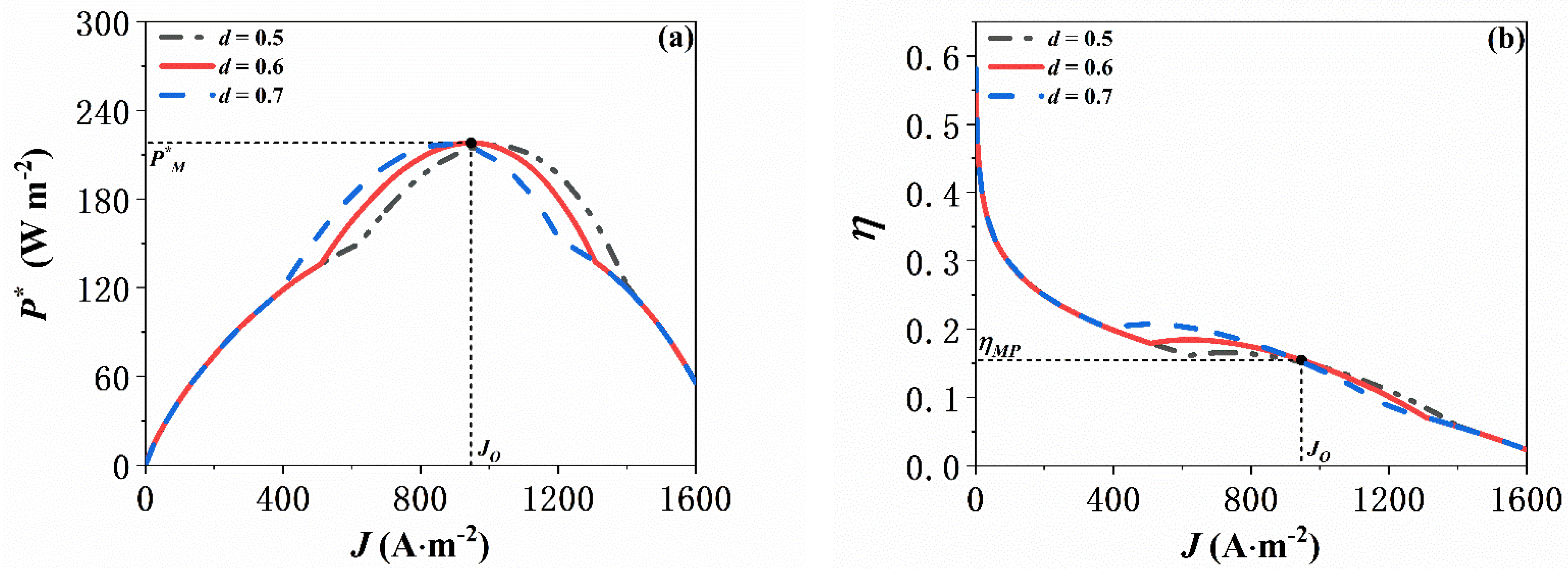
5.4. Effect of the ITEG’s Coefficient of Spatial Inhomogeneity
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zastempowski, M. Analysis and modeling of innovation factors to replace fossil fuels with renewable energy sources—Evidence from European Union enterprises. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 178, 113262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabi, A.G.; Wilberforce, T.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Fuel cell application in the automotive industry and future perspective. Energy 2021, 214, 118955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Hou, S.; Ni, M.; Liao, T. Energetic, exergetic and ecological evaluations of a hybrid system based on a phosphoric acid fuel cell and an organic Rankine cycle. Energy 2021, 217, 119365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamed, K.; Dincer, I. A novel ammonia molten alkaline fuel cell based integrated powering system for clean rail transportation. Energy 2020, 201, 117620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.-Y.; Li, M.-J.; Yang, Y.-W.; He, Y.-L. Achievement of a novel porous non-noble-metal catalyst with excellent oxygen reduction reaction activity: Promoting the commercialization of alkaline fuel cells. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanishi, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Highly conductive mechanically robust high M w polyfluorene anion exchange membrane for alkaline fuel cell and water electrolysis application. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 3812–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Rahman, E. Thermodynamic analysis and optimization of a hybrid power system using thermoradiative device to efficiently recover waste heat from alkaline fuel cell. Renew. Energy 2022, 200, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xiao, L.; Kuang, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Innovative use of air gap membrane distillation to harvest waste heat from alkaline fuel cell for efficient freshwater production: A comprehensive 4E study. Renew. Energy 2024, 225, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhao, H.; Wu, M.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Z. Thermodynamic analysis of a hybrid system integrating an alkaline fuel cell with an irreversible absorption refrigerator. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 10045–10060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Li, Y. An alkaline fuel cell/direct contact membrane distillation hybrid system for cogenerating electricity and freshwater. Energy 2021, 225, 120303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, L.; Liao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J. Exploiting the waste heat from an alkaline fuel cell via electrochemical cycles. Energy 2018, 142, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, J.; Lai, C.; Zhang, H. Recycling alkaline fuel cell waste heat for cooling production via temperature-matching elastocaloric cooler. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 27124–27138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, F.; Zhang, X.; Rahman, E.; Guo, J. Modeling, thermodynamic performance analysis, and parameter optimization of a hybrid power generation system coupling thermogalvanic cells with alkaline fuel cells. Energy 2024, 292, 27124–27138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, K.; Jia, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Linghu, J. Advances in the applications of thermoelectric generators. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 292, 121813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, H.; Ni, M. Performance assessment of a hybrid system integrating a molten carbonate fuel cell and a thermoelectric generator. Energy 2016, 112, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Synergizing perovskite solar cell and thermoelectric generator for broad-spectrum utilization: Model updating, performance assessment and optimization. Energy 2024, 289, 130008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandil, A.; Awad, M.M.; Sultan, G.I.; Salem, M.S. Performance of a photovoltaic/thermoelectric generator hybrid system with a beam splitter under maximum permissible operating conditions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 280, 116795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Hou, S. Achieving a broad-spectrum photovoltaic system by hybridizing a two-stage thermoelectric generator. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 211, 112778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, S.P.; Gunasekaran, D.L.; Jaganathan, G.; Natesan, S.; Muthusamy, S.M.; Kim, S.C.; Kumar, B.; Poongavanam, G.K.; Duraisamy, S. Energy and environmental analysis of a solar evacuated tube heat pipe integrated thermoelectric generator using IoT. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 57835–57850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J. Performance evaluation of an alkaline fuel cell/thermoelectric generator hybrid system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 11756–11762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H.; Kuang, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. A novel photo-thermal-electric hybrid system comprising evacuated U-tube solar collector and inhomogeneous thermoelectric generator toward efficient and stable operation. Energy 2024, 292, 130616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobie, E.A. An introduction to MATLAB. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, tr7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; Ni, M.; Hou, S. Performance evaluation of a novel photovoltaic-electrochemic hybrid system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 195, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hu, Z.; Hou, S. A solar driven hybrid photovoltaic module/direct contact membrane distillation system for electricity generation and water desalination. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 221, 113146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Chen, B.; Dong, F.; Ni, M. Two-stage thermoelectric generators for waste heat recovery from solid oxide fuel cells. Energy 2017, 132, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Wang, C.-C.; Hung, C.-I. Geometric effect on cooling power and performance of an integrated thermoelectric generation-cooling system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 87, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y. Performance analysis of the system integrating a molten carbonate fuel cell and a thermoelectric generator with inhomogeneous heat conduction. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 200, 117729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, S.; Kaushik, S. The influence of Thomson effect in the performance optimization of a two stage thermoelectric generator. Energy 2016, 100, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Alcaide, F.; Cabot, P.-L. A small-scale flow alkaline fuel cell for on-site production of hydrogen peroxide. Electrochimica Acta 2002, 48, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Zhong, Z.-H.; Xiao, L.; Chen, Z.-L. Performance analysis on a novel photovoltaic-hydrophilic modified tubular seawater desalination (PV-HMTSD) system. Desalination 2021, 499, 114829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhong Li, W. An experimental study of a novel prototype for thermoelectric power generation from vehicle exhaust. Distrib. Gener. Altern. Energy J. 2013, 28, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Zhou, J.; Li, N.; Yang, R.; Li, B. Inhomogeneous thermal conductivity enhances thermoelectric cooling. AIP Adv. 2014, 4, 4903547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Anode reaction of AFC [20] | (1) | |
| Cathode reaction of AFC [20] | (2) | |
| Overall electrochemical reaction of AFC [20] | (3) | |
| Maximum possible energy rate released by reactions in AFC [20] | (4) | |
| Reversible cell potential in AFC [20] | (5) | |
| Charge transfer overpotential losses in AFC [20] | (6) | |
| Concentration overpotential losses in AFC [20] | (7) | |
| Ohmic overpotential losses in AFC [20] | (8) | |
| Output voltage of AFC [20] | (9) | |
| PO of AFC [20] | (10) | |
| EE of AFC [20] | (11) |
| Parameter | Symbol | Expression |
|---|---|---|
| Seebeck coefficient () | ||
| Electrical resistivity () | ||
| Thermal conductivity (W K−1 m−2) | ||
| Geometric characteristics (mm) | 2.96 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| () | 96,485 [20] |
| 2 [20] | |
| () | 8.314 [20] |
| () | 0.97 [20] |
| () | 1 [20] |
| () | 1 [20] |
| () | 2000 [20] |
| () | 174,512 [20] |
| () | 5485 [20] |
| () | 0.001 [20] |
| () | 353 [20] |
| () | 298.15 [20] |
| 100% [20] | |
| () | [20] |
| () | 20 [20] |
| 0.5 [21] | |
| () | 1 [21] |
| 3000 [21] |
| Performance Indexes | Energy Efficiency at AFC’s Maximum Output Power Density | Improvement in Output Power Density | Improvement in Energy Efficiency | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid Systems | |||||
| AFC/TEG hybrid system [20] | 204.48 | 13.10% | 23.03% | 10.08% | |
| AFC/TREC hybrid system [11] | 382.26 | 15.80% | 52.90% | 184.68% | |
| AFC/IAR hybrid system [9] | 173.06 | 13.13% | 8.09% | 9.97% | |
| AFC/ITEG hybrid system | 218.04 | 18.46% | 31.19% | 54.61% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, M.; Jin, X. The Performance Evaluation of a Hybrid System Combining an Alkaline Fuel Cell with an Inhomogeneous Thermoelectric Generator. Energies 2024, 17, 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092066
Zhang C, Li H, Zhang X, Shen M, Jin X. The Performance Evaluation of a Hybrid System Combining an Alkaline Fuel Cell with an Inhomogeneous Thermoelectric Generator. Energies. 2024; 17(9):2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092066
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chenjun, Hanqi Li, Xi Zhang, Man Shen, and Xu Jin. 2024. "The Performance Evaluation of a Hybrid System Combining an Alkaline Fuel Cell with an Inhomogeneous Thermoelectric Generator" Energies 17, no. 9: 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092066
APA StyleZhang, C., Li, H., Zhang, X., Shen, M., & Jin, X. (2024). The Performance Evaluation of a Hybrid System Combining an Alkaline Fuel Cell with an Inhomogeneous Thermoelectric Generator. Energies, 17(9), 2066. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17092066





