A Review of Upscaling Hydrothermal Carbonization
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Process | Moisture of Feedstock | Process Conditions | Main Product/Purpose | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Fast Pyrolysis | 10–20% |
800 °C or Higher, 0.5–10 s, Limited Oxygen Supply, 1 bar | Bio-oil (60–75%) | [23,24] |
| Intermediate Pyrolysis | <10% |
400–500 °C, 0.5–20 s, Absence of Air, 1 bar | Biochar (25–40%), Bio-oil (35–50%), Gas (20–30%) | [2,24] |
|
Slow Pyrolysis | 15–20% | 300–500 °C, 5 min–12 h, Absence of Air, 1 bar | Solid (25–35%), Liquid (20–30%), Gas (25–35%) | [23] |
| Torrefaction | <10% |
200–300 °C, 0.5–4 h, Absence of Air, 1 bar | Char (80–90%) | [25] |
| HTC | 70–85% |
180–260 °C, 0.5–8 h, Vacuum, 10–60 bar | Hydrochar (50–80%) | [4,5,9] |
| HTL | 70–85% |
260–375 °C, Vacuum, 50–220 bar | Bio-oil, Bio-crude (30–60%) | [5] |
| HTG | 70–85% |
375–800 °C, Vacuum, 220 bar or higher | Syngas (30–80%) | [5] |
| THP | 70–85% | 140 °C–170 °C, 20 min to Several Hours, 6–9 bar | Pre-treatment of AD, Fertilizer | [6] |
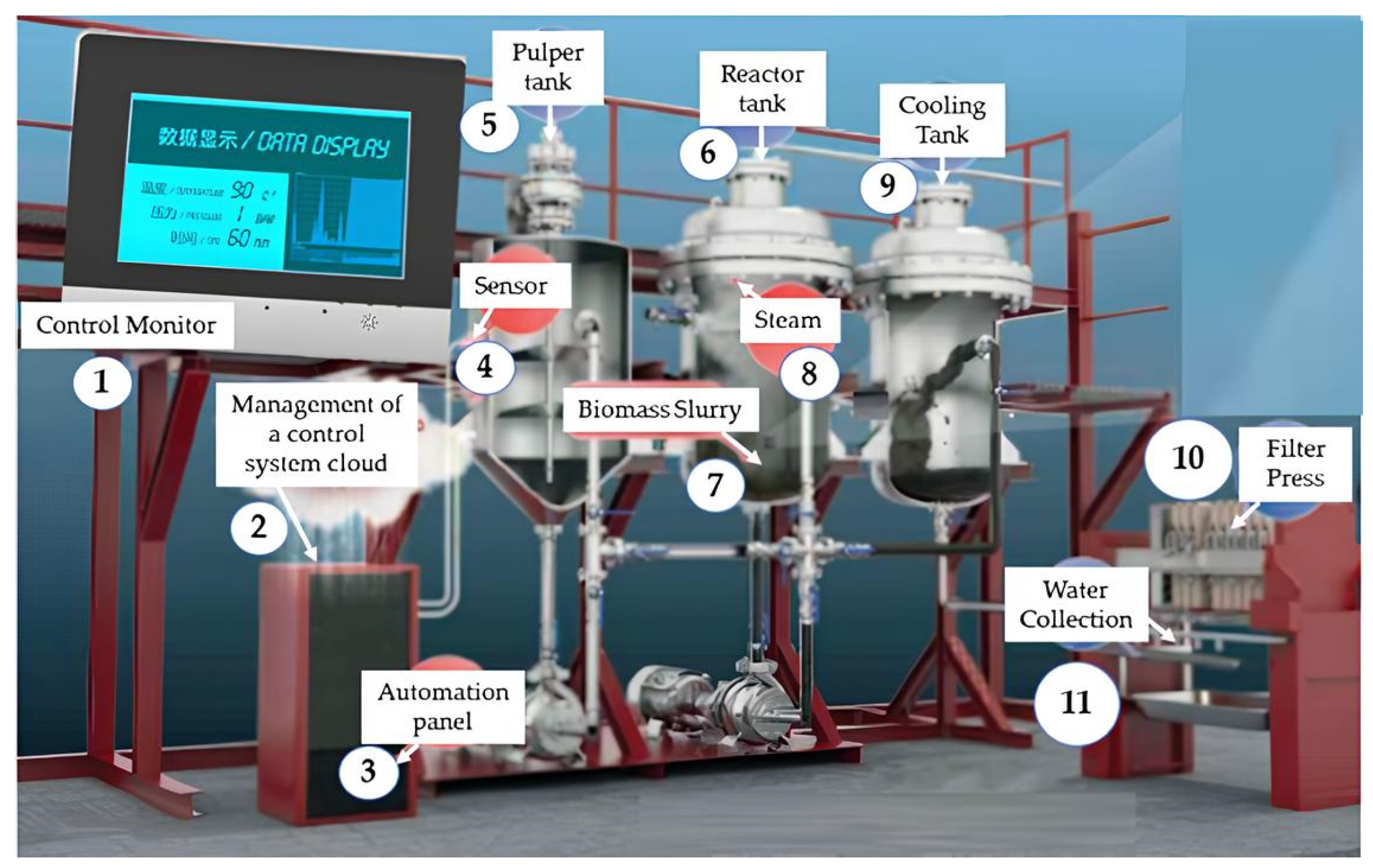
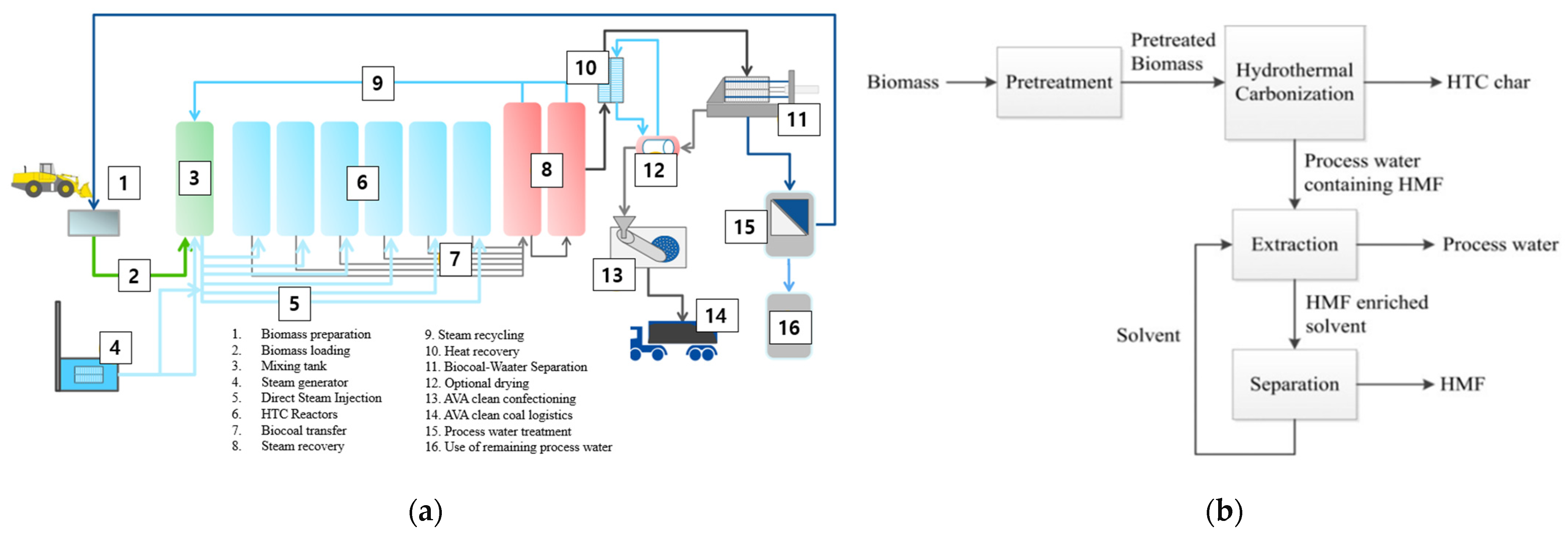
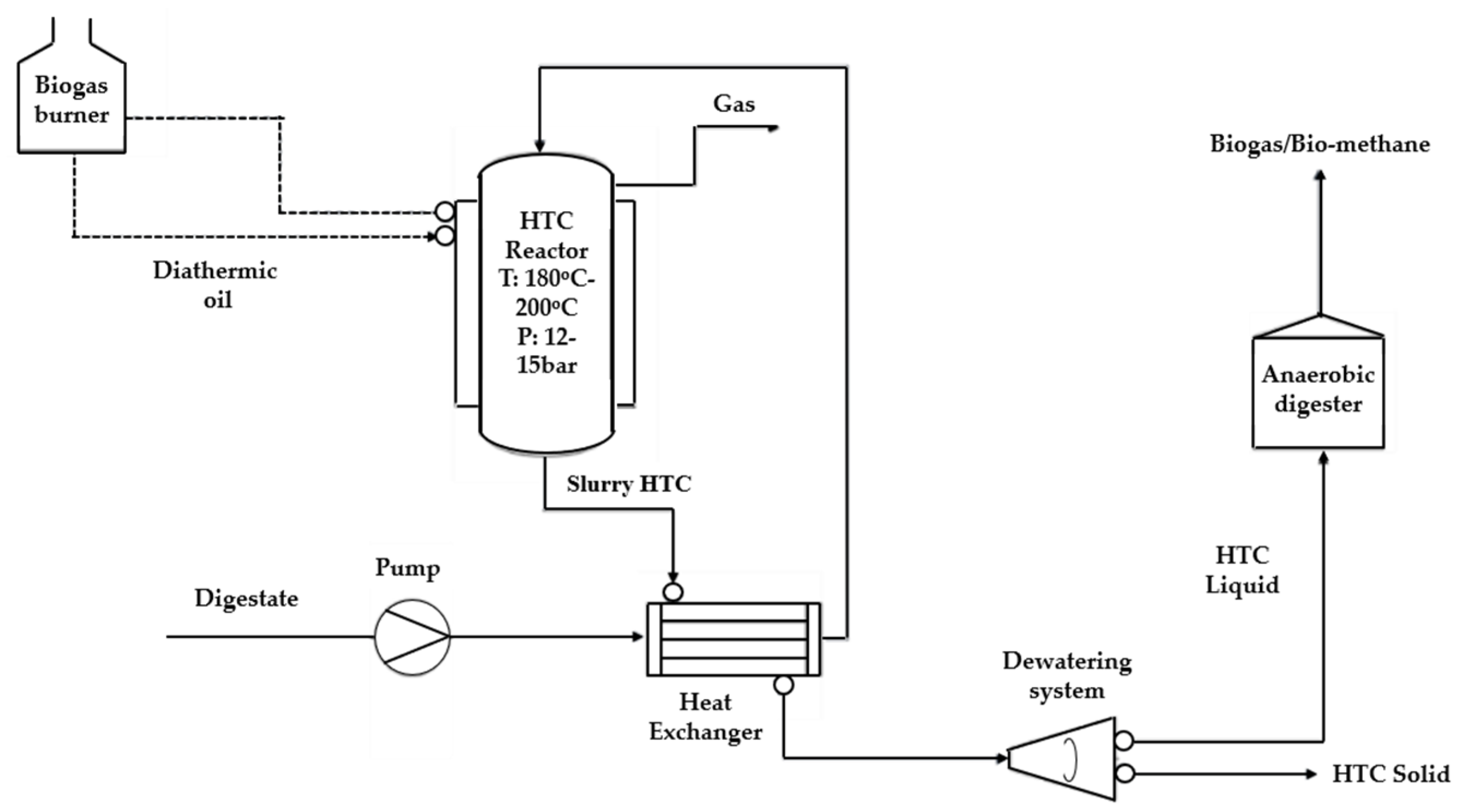
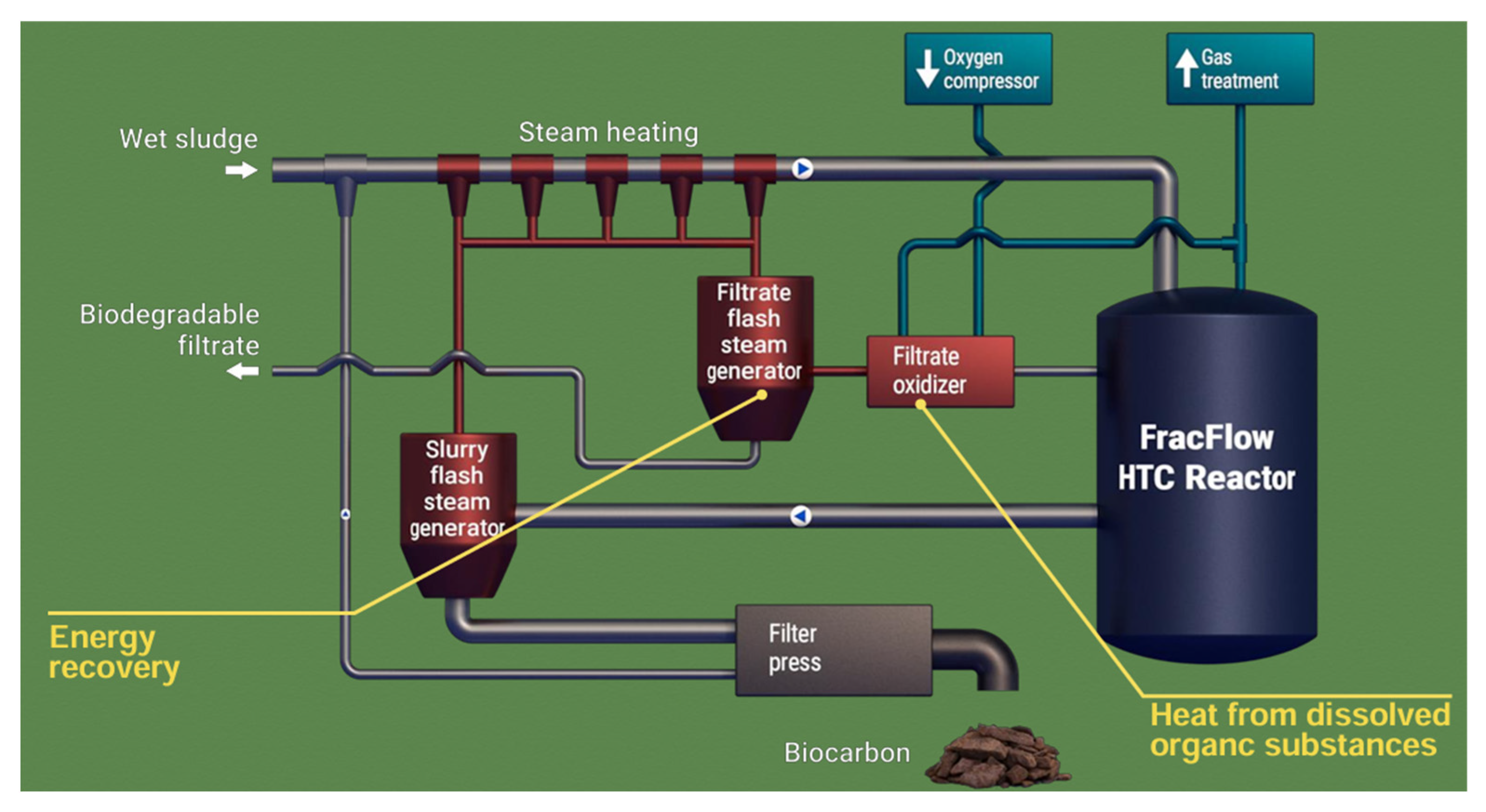
2. Upscaling Case of HTC and Challenges
| Feedstock | Reactor | Process Conditions | Final Products | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper Sludge |
Lab: 0.5 L Pilot: 1000 L Batch |
Lab: 180–240 °C, 2.8–2.4 MPa, 0.5 h Pilot: 197 °C, 1.9 MPa, 0.5 h |
Solid Fuel Lab: Up to 13.6 MJ/kg Pilot: 14.1–14.7 MJ/kg | [26] |
| EFB |
Lab: 2.5 L Pilot: 250 L Batch | 175 °C, 0.5 h, BWR: 1:3 |
Solid Fuel, Lab: 18.5 MJ/kg; Pilot: 18.56 MJ/kg | [27] |
| Corn Stover |
Pilot: 18.75 L Cylindrical Batch | 250 °C, 1–4 h, BWR: 1:10, 1:15, 1:20 |
Biochar Surface Area: 4.35 m2/g, Solid Yield: 31.08–35.82%, | [28] |
| Wood Chips |
Lab: 2 L Pilot: 40 L Semi-continuous |
235–275 °C, 0.5 h |
Solid Fuel HHV: 22–28 MJ/kg | [44] |
|
Swine Manure |
Lab: 4 L (Batch) Pilot: Screw Continuous |
180–250 °C, 0.75 h |
Solid Fuel HHV: 19–21 MJ/kg, FC: 22–24% | [46] |
|
Wood Waste |
Lab: 0.2 L Pilot: 500 L Batch |
220 °C, 1.5 h Catalyst |
Solid Fuel, HHV: 27 MJ/kg | [39] |
| Food Waste and Paper Waste |
Lab: 0.5 L Pilot: 200 L Batch |
Lab: 150–280 °C, 1.3–5.5 Mpa, 0.5 h Pilot: 200 °C, 1.6 MPa, 1 h |
Solid fuel, HHV up to 17.2 MJ/kg | [41] |
| EFB |
Pilot: 1000 L Batch | 200 °C, 20 bar, 0.5 h + Activation (KOH, 800 °C, 1 h, Ar, Air) |
Activated Carbon SSA: 810 m2/g Vpore: 511 cm3/g | [47] |
| Agriculture Residue |
25 L, Autoclave Batch | 180–220 °C, 4 h |
Solid Fuel, Yield of 52.5%, HHV: 26.6 MJ/kg, Biogas: 16.3 L CH4/kg | [61] |
3. Industrial-Scale Review
| Company | Feedstock | Process Type and Capacity | Heating System and Process Conditions | Final Products | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVA-CO2 | Biowaste |
Multi-batch 40,000–50,000 T/year | Steam 220–230 °C, 2.2–2.6 MPa, 5–10 h, Catalyst |
Biocoal, 5-HMF, P Recovery | [90,91,92,93,94] |
| CarboRem | Agro-industrial Digested Sludge |
Semi-continuous 5000 T/year |
Diathermic Oil 190 °C, 1.5 MPa, 1 h |
Biocoal, P Recovery | [95,96] |
| C-Green | Biowaste |
Semi-continuous 33,000 T/year | Steam 200 °C, 2 MPa, 1–4 h | Biocoal, P recovery and Nitrogen Recovery | [97,98,99] |
| TerraNova Energy | Biowaste or Sewage Sludge |
Semi-continuous 14,000 T/year |
Diathermic Oil 180–200 °C, 2–3.5 MPa, 4 h, Catalyst |
Biocoal, P recovery | [8,100,101,102] |
| Ingelia S.L. |
Agricultural Waste, Residential Green Waste |
Semi-continuous 78,000 T/year | Steam 180–220 °C, 1.7–2.4 MPa, 4–8 h |
Biocoal, Biochemical, Fertilizers | [3,8,103,104,105,106,107] |
| HTCycle | Sewage Sludge and Agricultural Waste |
Multi-batch 8000–16,000 T/year | Steam 200–220 °C, 2–2.5 MPa, 4 h |
Biocoal, P recovery, Activated Carbon | [108,109,110] |
| Antaco | Sludge and Paper Mill |
Continuous 31,000–150,000 T/year | Steam 180–250 °C, 1.5–2 MPa, 4–10 h |
Biocoal, Activated Carbon, Biogas | [111,112] |
|
Suncoal Industries | Biowaste |
Semi-continuous
50,000 T/year | Steam 200 °C, 2 MPa, 6–12 h | Biocoal | [8,113,114] |
|
Carbon Solutions | Sewage Sludge |
Semi-continuous 10,000 T/year | 160–250 °C, 1–6 MPa, 1.5 h | Biocoal, Activated Carbon | [115,116] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yaashikaa, P.R.; Kumar, P.S.; Nhung, T.C.; Hemavathy, R.V.; Jawahar, M.J.; Neshaanthini, J.P.; Rangasamy, G. A review on landfill system for municipal solid wastes: Insight into leachate, gas emissions, environmental and economic analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, M.; Sahu, J.N.; Ganesan, P. Effect of process parameters on production of biochar from biomass waste through pyrolysis: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitzl, M.; Corma, A.; Pomares, F.; Renz, M. The hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) plant as a decentral biorefinery for wet biomass. Catal. Today 2015, 257, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, A.; Funke, A.; Titirici, M.M. Hydrothermal conversion of biomass to fuels and energetic materials. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrnčič, M.K.; Kravanja, G.; Knez, Ž. Hydrothermal treatment of biomass for energy and chemicals. Energy 2016, 116, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, P.L.; Udugama, I.A.; Gernaey, K.V.; Young, B.R.; Baroutian, S. Mechanisms, status, and challenges of thermal hydrolysis and advanced thermal hydrolysis processes in sewage sludge treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ischia, G.; Cazzanelli, M.; Fiori, L.; Orlandi, M.; Miotello, A. Exothermicity of hydrothermal carbonization: Determination of heat profile and enthalpy of reaction via high-pressure differential scanning calorimetry. Fuel 2022, 310, 122312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child, M. Industrial-Scale Hydrothermal Carbonization of Waste Sludge Materials for Fuel Production. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Technology, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Zeng, G. A review of the hydrothermal carbonization of biomass waste for hydrochar formation: Process conditions, fundamentals, and physicochemical properties. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauline, A.L.; Joseph, K. Hydrothermal carbonization of organic wastes to carbonaceous solid fuel—A review of mechanisms and process parameters. Fuel 2020, 279, 118472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Zhan, H.; Song, Y.; He, C.; Huang, Y.; Yin, X.; Wu, C. Insights into the evolution of chemical structures in lignocellulose and non-lignocellulose biowastes during hydrothermal carbonization (HTC). Fuel 2019, 236, 960–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Sultana, A.I.; Chambers, C.; Saha, S.; Saha, N.; Kirtania, K.; Reza, M.T. Recent Progress on Emerging Applications of Hydrochar. Energies 2022, 15, 9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavali, M.; Junior, N.L.; de Sena, J.D.; Woiciechowski, A.L.; Soccol, C.R.; Belli Filho, P.; Bayard, R.; Benbelkacem, H.; de Castilhos Junior, A.B. A review on hydrothermal carbonization of potential biomass wastes, characterization and environmental applications of hydrochar, and biorefinery perspectives of the process. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, P.; Stampone, N.; Di Giacomo, G. Evolution and Prospects of Hydrothermal Carbonization. Energies 2023, 16, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Jasrotia, K.; Singh, N.; Ghosh, P.; Srivastava, S.; Sharma, N.R.; Singh, J.; Kanwar, R.; Kumar, A. A comprehensive review on hydrothermal carbonization of biomass and its applications. Chem. Afr. 2020, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, A.; Saha, P.; Reza, M.T. Co-Hydrothermal Carbonization of coal-biomass blend: Influence of temperature on solid fuel properties. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 167, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ge, Y.; Xiao, H.; He, Q.; Wang, W.; Chen, B. Investigation of hydrothermal co-carbonization of waste textile with waste wood, waste-paper, and waste food from typical municipal solid wastes. Energy 2020, 210, 118606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, M.; Novera, T.M.; Tabassum, M.; Islam, M.A.; Islam, M.A.; Hameed, B.H. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of different feedstocks to hydrochar as potential energy for the future world: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 298, 126734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakudze, S.; Chen, J. A critical review on co-hydrothermal carbonization of biomass and fossil-based feedstocks for cleaner solid fuel production: Synergistic effects and environmental benefits. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Bai, L.; Chi, M.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Yu, K.; Liu, Z. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of pretreatment lignocellulose biomass and polyvinyl chloride for clean solid fuel production: Hydrochar properties and its formation mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Yu, Y.; Huang, H.J.; Yu, C.L.; Fang, H.S.; Zhou, C.H.; Yin, X.; Chen, W.H.; Guo, X.C. Efficient conversion of sewage sludge into hydrochar by microwave-assisted hydrothermal carbonization. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, M.C.; Parsons, D.R.; Zein, S.H. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal carbonisation of waste biomass: The effect of process conditions on hydrochar properties. Processes 2022, 10, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Rowbotham, J.S.; Greenwell, C.H.; Dyer, P.W. An introduction to pyrolysis and catalytic pyrolysis: Versatile techniques for biomass conversion. In New and Future Developments in Catalysis: Catalytic Biomass Conversion; Suib, S.L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 173–208. [Google Scholar]
- Kazawadi, D.; Ntalikwa, J.; Kombe, G. A review of intermediate pyrolysis as a technology of biomass conversion for coproduction of bio-oil and adsorption biochar. J. Renew. Energy 2021, 2021, 5533780. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar Tumuluru, J.; Sokhansanj, S.; Hess, J.R.; Wright, C.T.; Boardman, R.D. A review on biomass torrefaction process and product properties for energy applications. Ind. Biotechnol. 2011, 7, 384–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areeprasert, C.; Zhao, P.; Ma, D.; Shen, Y.; Yoshikawa, K. Alternative solid fuel production from paper sludge employing hydrothermal treatment. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusman, M.H.; Sastroredjo, P.N.E.; Prawisudha, P.; Hardianto, T.; Pasek, A.D. A pilot-scale study of wet torrefaction treatment for upgrading palm oil empty fruit bunches as clean solid fuel. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 65, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teribele, T.; Costa, M.E.G.; Sales da Silva, C.D.M.; Pereira, L.M.; Bernar, L.P.; de Castro, D.A.R.; da Costa Assunção, F.P.; Santos, M.C.; de Sousa Brandão, I.W.; Fonseca, C.J.N.; et al. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Corn Stover: Structural Evolution of Hydro-Char and Degradation Kinetics. Energies 2023, 16, 3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Sonil, N.; Guotao, S.; Ling, Q.; Yongqing, G.; Tianle, Z.; Mingqiang, Z.; Runcang, S. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal carbonization of corn stalk for solid biofuel production: Optimization of process parameters and characterization of hydrochar. Energy 2019, 186, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabio, E.; Álvarez-Murillo, A.; Román, S.; Ledesma, B. Conversion of tomato-peel waste into solid fuel by hydrothermal carbonization: Influence of the processing variables. Waste Manag. 2016, 47, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales da Silva, C.D.M.; Rocha de Castro, D.A.; Santos, M.C.; Almeida, H.D.S.; Schultze, M.; Lueder, U.; Hoffmann, T.; Machado, N.T. Process Analysis of Main Organic Compounds Dissolved in Aqueous Phase by Hydrothermal Processing of Açaí (Euterpe Oleracea, Mart.) Seeds: Influence of Process Temperature, Biomass-to-Water Ratio, and Production Scales. Cellulose 2021, 40, 15–6124. [Google Scholar]
- Atallah, E.; Kwapinski, W.; Ahmad, M.N.; Leahy, J.J.; Zeaiter, J. Effect of water-sludge ratio and reaction time on the hydrothermal carbonization of olive oil mill wastewater treatment: Hydrochar characterization. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Cheng, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, H. Effect of residence time on chemical and structural properties of hydrochar obtained by hydrothermal carbonization of water hyacinth. Energy 2013, 58, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, D.; Xiong, L.; Dan, J.; Xu, K.; Yuan, X.; Kan, G.; Ning, X.; Wang, C. Application of catalysts in biomass hydrothermal carbonization for the preparation of high-quality blast furnace injection fuel. Energy 2023, 283, 129147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djandja, O.S.; Liew, R.K.; Liu, C.; Liang, J.; Yuan, H.; He, W.; Feng, Y.; Lougou, B.G.; Duan, P.G.; Lu, X.; et al. Catalytic hydrothermal carbonization of wet organic solid waste: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizamuddin, S.; Baloch, H.A.; Griffin, G.J.; Mubarak, N.M.; Bhutto, A.W.; Abro, R.; Mazari, S.A.; Ali, B.S. An overview of effect of process parameters on hydrothermal carbonization of biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, M.; Zamri, N.M.; May, S.T.; Azizan, M.T.; Aqsha, A.; Sabzoi, N.; Sher, F. Effect of acid catalysts on hydrothermal carbonization of Malaysian oil palm residues (leaves, fronds, and shells) for hydrochar production. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, K.I.; Omorogie, M.O. Biomass-based hydrothermal carbons for catalysis and environmental cleanup: A review. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2022, 15, 162–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.-S.; Yoo, S.-Y.; Kang, I.-K.; Kim, N.; Kim, S.; Lim, H.-B.; Choe, K.; Lee, J.-C.; Yang, H.-I. Analysis of Hydrothermal Solid Fuel Characteristics Using Waste Wood and Verification of Scalability through a Pilot Plant. Processes 2022, 10, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackintosh, A.F.; Jung, H.; Kang, I.K.; Yoo, S.; Kim, S.; Choe, K. Experimental Study on Hydrothermal Polymerization Catalytic Process Effect of Various Biomass through a Pilot Plant. Processes 2021, 9, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Park, K.Y.; Yoshikawa, K. Conversion of municipal solid wastes into biochar through hydrothermal carbonization. Eng. Appl. Biochar 2017, 31, 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- Kruse, A.; Baris, D.; Tröger, N.; Wieczorek, P. Scale-Up in Hydrothermal Carbonization. In Sustainable Carbon Materials from Hydrothermal Processes; Titririci, M.M., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 341–353. [Google Scholar]
- Ischia, G.; Fiori, L. Hydrothermal carbonization of organic waste and biomass: A review on process, reactor, and plant modeling. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 2797–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekman, S.K.; Broch, A.; Robbins, C.; Purcell, R.; Zielinska, B.; Felix, L.; Irvin, J. Process development unit (PDU) for hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) of lignocellulosic biomass. Waste Biomass Valorization 2014, 5, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekman, S.K.; Broch, A.; Felix, L.; Farthing, W. Hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) of loblolly pine using a continuous, reactive twin-screw extruder. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 134, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ipiales, R.P.; Sarrion, A.; Diaz, E.; de la Rubia, M.A.; Diaz-Portuondo, E.; Coronella, C.J.; Mohedano, A.F. Swine manure management by hydrothermal carbonization: Comparative study of batch and continuous operation. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 118062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketwong, T.; Halabaso, E.R.; Nguyen, T.K.A.; Areeprasert, C.; Doong, R.A. Comparative study on pilot-scale production of CuO-loaded activated biochar and hydrochar from oil-palm empty fruit bunches for high-performance symmetric supercapacitor application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 905, 115970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Becker, G.C.; Faweya, N.; Rodriguez Correa, C.; Yang, S.; Xie, X.; Kruse, A. Fertilizer and activated carbon production by hydrothermal carbonization of digestate. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2018, 8, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chi, Y.; Du, K.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, F.; Huang, Q. Hydrothermal Treatment of Food Waste for Bio-fertilizer Production: Regulation of Humus Substances and Nutrient (N and P) in Hydrochar by Feedwater pH. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 2767–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Suvarna, M.; Pan, L.; Tabatabaei, M.; Ok, Y.S.; Wang, X. Wet wastes to bioenergy and biochar: A critical review with future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ran, M.; Fang, G.; Wu, T.; Ni, Y. Biochars from lignin-rich residue of furfural manufacturing process for heavy metal ions remediation. Materials 2020, 13, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliotti, E.; Casini, D.; Rosi, L.; Lotti, G.; Rizzo, A.M.; Chiaramonti, D. Lab-scale pyrolysis and hydrothermal carbonization of biomass digestate: Characterization of solid products and compliance with biochar standards. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 139, 105593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langone, M.; Basso, D. Process waters from hydrothermal carbonization of sludge: Characteristics and possible valorization pathways. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, C.; Alves, O.; Durão, L.; Şen, A.; Vilarinho, C.; Gonçalves, M. Characterization of hydrochar and process water from the hydrothermal carbonization of Refuse Derived Fuel. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäkelä, M.; Forsberg, J.; Söderberg, C.; Larsson, S.H.; Dahl, O. Process water properties from hydrothermal carbonization of chemical sludge from a pulp and board mill. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragón-Briceño, C.I.; Grasham, O.; Ross, A.B.; Dupont, V.; Camargo-Valero, M.A. Hydrothermal carbonization of sewage digestate at wastewater treatment works: Influence of solid loading on characteristics of hydrochar, process water and plant energetics. Renew. Energy 2020, 157, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.E.; Finnerty, G.L.; Camargo-Valero, M.A.; Ross, A.B. Valorisation of macroalgae via the integration of hydrothermal carbonisation and anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.; Ren, S.; Ji, M.; Sompong, O.; Qian, Y.; Luo, G.; Zhang, S. Characterization and biogas production potentials of aqueous phase produced from hydrothermal carbonization of biomass–Major components and their binary mixtures. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzari, F.; Langone, M.; Andreottola, G.; Fiori, L. Methane production from process water of sewage sludge hydrothermal carbonization. A review. Valorising sludge through hydrothermal carbonization. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 947–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.E.; Adams, J.M.; Grasham, O.R.; Camargo-Valero, M.A.; Ross, A.B. An assessment of different integration strategies of hydrothermal carbonisation and anaerobic digestion of water hyacinth. Energies 2020, 13, 5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.; Blöhse, D.; Ramke, H.G. Hydrothermal carbonization of agricultural residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambo, H.S.; Minaret, J.; Dutta, A. Process Water from the Hydrothermal Carbonization of Biomass: A Waste or a Valuable Product? Waste Biomass 2018, 9, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemann, J.; Putschew, A.; Ziegler, F. Hydrothermal carbonization: Process water characterization and effects of water recirculation. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalkopru, A.K.; Kantarli, I.C.; Yanik, J. Effects of spent liquor recirculation in hydrothermal carbonization. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 226, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Li, D.; Lv, M.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Qin, S.; Wang, B.; Cui, X.; Guo, C.; Zhao, P. Influence of process water recirculation on hydrothermal carbonization of rice husk at different temperatures. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.B.; Panigrahi, S.; Vanapalli, K.R.; Cheela, V.S.; Venna, S.; Dubey, B. Study on the process wastewater reuse and valorisation during hydrothermal co-carbonization of food and yard waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stutzenstein, P.; Bacher, M.; Rosenau, T.; Pfeifer, C. Optimization of Nutrient and Carbon Recovery from Anaerobic Digestate via Hydrothermal Carbonization and Investigation of the Influence of the Process Parameters. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 1303–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Yang, B.; Li, H.; Tan, F.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, Q.; He, M.; Ran, Y.; Hu, G. A synergistic combination of nutrient reclamation from manure and resultant hydrochar upgradation by acid-supported hydrothermal carbonization. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal-Uddin, A.T.; Reza, M.T.; Norouzi, O.; Salaudeen, S.A.; Dutta, A.; Zytner, R.G. Recovery and Reuse of Valuable Chemicals Derived from Hydrothermal Carbonization Process Liquid. Energies 2023, 16, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçer, A.T.; İnan, B.; Özçimen, D.; Gökalp, İ. A study of microalgae cultivation in hydrothermal carbonization process water: Nutrient recycling, characterization and process design. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 30, 103048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarpali, M.; Arora, N.; Kuhn, J.N.; Philippidis, G.P. Beneficial use of the aqueous phase generated during hydrothermal carbonization of algae as nutrient source for algae cultivation. Algal Res. 2021, 60, 102485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, G.; Koehler, R.; Poerschmann, J.; Kopinke, F.D.; Weiner, B. Combination of hydrothermal carbonization and wet oxidation of various biomasses. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.T.; Freitas, A.; Yang, X.; Coronella, C.J. Wet air oxidation of hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) process liquid. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3250–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, L.B.S.; Anastasakis, K.; Biller, P. Wet oxidation of aqueous phase from hydrothermal liquefaction of sewage sludge. Water Res. 2022, 209, 117863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilk, M.; Czerwińska, K.; Śliz, M.; Imbierowicz, M. Hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge: Hydrochar properties and processing water treatment by distillation and wet oxidation. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.S.; Sarrión, A.; Baeza, J.A.; Diaz, E.; Calvo, L.; Mohedano, A.F.; Gilarranz, M.A. Integration of hydrothermal carbonization and aqueous phase reforming for energy recovery from sewage sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppi, G.; Pipitone, G.; Pirone, R.; Bensaid, S. Aqueous phase reforming process for the valorization of wastewater streams: Application to different industrial scenarios. Catal. Today 2022, 387, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attasophonwattana, P.; Sitthichirachat, P.; Siripaiboon, C.; Ketwong, T.; Khaobang, C.; Panichnumsin, P.; Ding, L.; Areeprasert, C. Evolving circular economy in a palm oil factory: Integration of pilot-scale hydrothermal carbonization, gasification, and anaerobic digestion for valorization of empty fruit bunch. Appl. Energy 2022, 324, 119766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.B.; Tompsett, G.A.; Partopour, B.; Deskins, N.A.; Timko, M.T. Hydrochar structural determination from artifact-free Raman analysis. Carbon 2020, 167, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chater, H.; Asbik, M.; Koukouch, A.; Mouaky, A.; Bostyn, S.; Sarh, B.; Tabet, F. Analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer inside a batch reactor for hydrothermal carbonization process of a biomass. Energies 2022, 15, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, N.; Özdenkçi, K.; Chianese, S.; Musmarra, D.; De Blasio, C. Process simulation of hydrothermal carbonization of digestate from energetic perspectives in Aspen Plus. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 270, 116215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangaré, D.; Moscosa-Santillan, M.; Aragón Piña, A.; Bostyn, S.; Belandria, V.; Gökalp, I. Hydrothermal carbonization of biomass: Experimental study, energy balance, process simulation, design, and techno-economic analysis. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 14, 2561–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardiambasis, I.O.; Kapetanakis, T.N.; Nikolopoulos, C.D.; Trang, T.K.; Tsubota, T.; Keyikoglu, R.; Khataee, A.; Kalderis, D. Hydrochars as emerging biofuels: Recent advances and application of artificial neural networks for the prediction of heating values. Energies 2020, 13, 4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardani, N.; Hedayati Marzbali, M.; Shah, K.; Zhou, A. Machine learning prediction of the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass during hydrothermal carbonization. Biofuels 2022, 13, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, T.M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Sherif, H.; El-Salam, M.A. Hydrothermal treatment of municipal solid waste into coal in a commercial Plant: Numerical assessment of process parameters. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knötig, P.; Etzold, H.; Wirth, B. Model-based evaluation of hydrothermal treatment for the energy efficient dewatering and drying of sewage sludge. Processes 2021, 9, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Salaudeen, S.; Norouzi, O.; Acharya, B.; Dutta, A. Numerical comparison of a combined hydrothermal carbonization and anaerobic digestion system with direct combustion of biomass for power production. Processes 2020, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.; González-Arias, J.; Pereira, F.J.; Fernández, C.; Cara-Jiménez, J. A techno-economic study of HTC processes coupled with power facilities and oxy-combustion systems. Energy 2021, 219, 119651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Venkatesh, G.; Sandberg, M.; Eskandari, S.; Joseph, S.; Granström, K. A comprehensive environmental life cycle assessment of the use of hydrochar pellets in combined heat and power plants. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucki, M.; Eymann, L.; Gerner, G.; Hartmann, F.; Wanner, R.; Krebs, R. Hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge on industrial scale: Energy efficiency, environmental effects and combustion. J. Energy Chall. Mech. 2015, 2, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Energy of the Future. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?q=ava+co2&oq=ava+co2 (accessed on 5 October 2023).
- Schweiz, Ag. AVA-CO2 develops phosphorus recovery process. Membr. Technol. 2015, 2015, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Kläusli, T. AVA Biochem: Commercialising renewable platform chemical 5-HMF. Green Process. Synth. 2014, 3, 235–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, C.; Konnerth, J.; Sailer-Kronlachner, W.; Solt, P.; Rosenau, T.; van Herwijnen, H.W. Current situation of the challenging scale-up development of hydroxymethylfurfural production. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 3544–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucian, M.; Merzari, F.; Messineo, A.; Volpe, M. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sludge Residues via Carborem C700 Industrial Scale Continuous Operating Plant. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2022, 92, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lucian, M.; Merzari, F.; Gubert, M.; Messineo, A.; Volpe, M. Industrial-scale hydrothermal carbonization of agro-industrial digested sludge: Filterability enhancement and phosphorus recovery. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, F.; Oden, E.; Ohman, F.; C Green Technology AB. Method and System for Hydrothermal Carbonization and Wet Oxidation of Sludge. U.S. Patent 11,724,952, 15 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mäki, E.; Saastamoinen, H.; Melin, K.; Matschegg, D.; Davidis, B.; Spekreijse, J.; Tselepi, V.; Kourkoumpas, D.S.; Axegård, P. Innovative hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) process for a Nordic pulp and paper mill. In Proceedings of the 29th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition, Online, 26–29 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Axegård, P. Towards Industrial Implementation of HTC Treatment of Biosludge. In Proceedings of the Green north HTC conference, Umeå, Sweden, 13–14 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- TerraNova Energy GmbH. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?q=Hydrothermal+Carbonization+and+Thermal+Hydrolysis+-+TerraNova%C2%AEultra+%28terranova-energy.com%29&sca_esv=594172598 (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Buttmann, M. Industrial scale plant for sewage sludge treatment by hydrothermal carbonization in Jining/China and phosphate recovery by terranova® ultra-htc process. In Proceedings of the European Biosolids and Organic Resources Conference, Leeds, UK, 20–21 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, M.; Wetterlund, E. Introducing hydrothermal carbonization to sewage sludge treatment systems—A way of improving energy recovery and economic performance. Waste Manag. 2023, 170, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, M. Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC): Valorisation of Organic Waste and Sludges for Hydrochar Production of Biofertilizers; IEA Bioenergy: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jarnerud, T.; Karasev, A.V.; Wang, C.; Bäck, F.; Jönsson, P.G. Utilization of Organic Mixed Biosludge from Pulp and Paper Industries and Green Waste as Carbon Sources in Blast Furnace Hot Metal Production. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burguete, P.; Corma, A.; Hitzl, M.; Modrego, R.; Ponce, E.; Renz, M. Fuel and chemicals from wet lignocellulosic biomass waste streams by hydrothermal carbonization. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owsianiak, M.; Ryberg, M.W.; Renz, M.; Hitzl, M.; Hauschild, M.Z. Environmental performance of hydrothermal carbonization of four wet biomass waste streams at industry-relevant scales. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6783–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mena Pardo, B.; Doyle, L.; Renz, M.; Salimbeni, A. Industrial Scale Hydrothermal Carbonization: New Applications for Wet Biomass Waste; Ttz Bremerhaven: Bremerhaven, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–71. [Google Scholar]
- HTCycle. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?q=HTCycle&oq=HTCycle (accessed on 25 November 2023).
- HTCycle AG. Europeon Sustainable Phosphorous Platform eNews; HTCycle AG: Murchin, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- HTCycle GmbH. Sewage Sludge Reuse Phosphate Recovery with an Innovative HTC Technology, SMEs; HTCycle GmbH: Murchin, Germany, 2019; p. 3726258. [Google Scholar]
- Antaco. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?q=antaco&sca_esv=594172598 (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Campbell, B.S.; Thorpe, R.B.; Peus, D.; Lee, J. Anaerobic digestion of untreated and treated process water from the hydrothermal carbonisation of spent coffee grounds. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suncoal. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?q=Suncoal&sca_esv=594172598 (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Sekar, P.; Noordermeer, J.W.; Anyszka, R.; Gojzewski, H.; Podschun, J.; Blume, A. Hydrothermally Treated Lignin as a Sustainable Biobased Filler for Rubber Compounds. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 2501–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedner, K.; Rumpel, C.; Steiner, C.; Pozzi, A.; Maas, R.; Glaser, B. Chemical evaluation of chars produced by thermochemical conversion (gasification, pyrolysis and hydrothermal carbonization) of agro-industrial biomass on a commercial scale. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 59, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Richter, R.; Struck, K.; Dinslage, R. Sewage Sludge Disposal; Berlin Water Workshop: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Safril, T.; Safril, B.; Yoshikawa, K. Commercial Demonstration of Solid Fuel Production from Municipal Solid Waste Employing the Hydrothermal Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 2, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, T.T.-T.; Nadeem, A.; Choe, K. A Review of Upscaling Hydrothermal Carbonization. Energies 2024, 17, 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081918
Ho TT-T, Nadeem A, Choe K. A Review of Upscaling Hydrothermal Carbonization. Energies. 2024; 17(8):1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081918
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Thi. Thu-Trang, Ahmad Nadeem, and Kangil Choe. 2024. "A Review of Upscaling Hydrothermal Carbonization" Energies 17, no. 8: 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081918
APA StyleHo, T. T.-T., Nadeem, A., & Choe, K. (2024). A Review of Upscaling Hydrothermal Carbonization. Energies, 17(8), 1918. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081918