Chance-Constrained Optimal Design of PV-Based Microgrids under Grid Blackout Uncertainties
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A new model is implemented to model the uncertainty of grid blackout starting time and blackout period using kernel density distribution;
- A novel optimal design method utilizing a chance-constrained approach is developed to optimize the sizes of the MG components considering the uncertainties of solar radiation, ambient temperature, and grid blackout;
- An improved method to calculate the utilizing an accurate estimation of the number of lead–acid battery replacements during the MG lifetime by considering the impact of battery state of charge, discharging current, number of cycles, acid stratification, and sulfate crystal structure on the battery lifetime.
2. Modeling the Uncertain Parameters
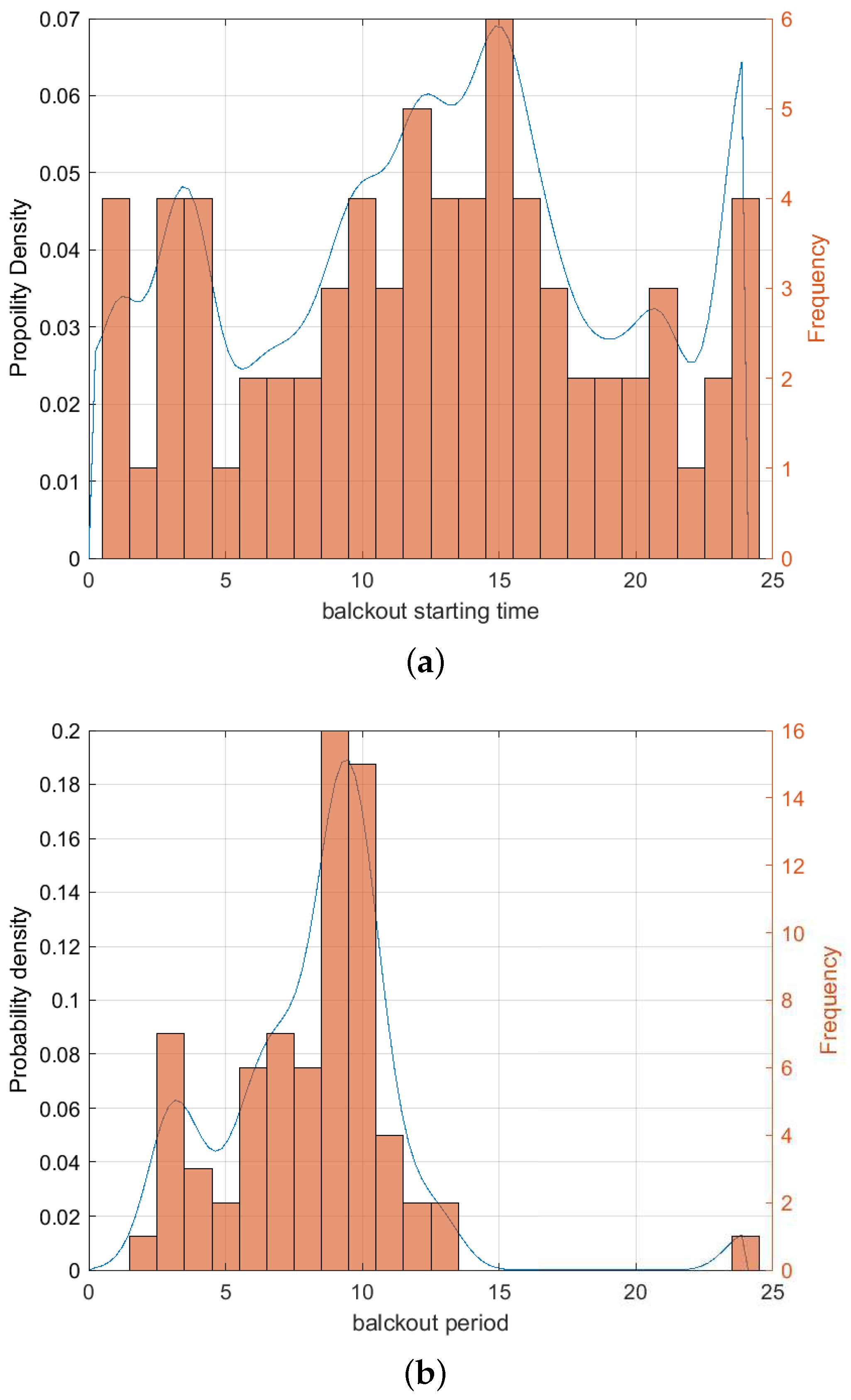
2.1. Blackouts Uncertainty Model
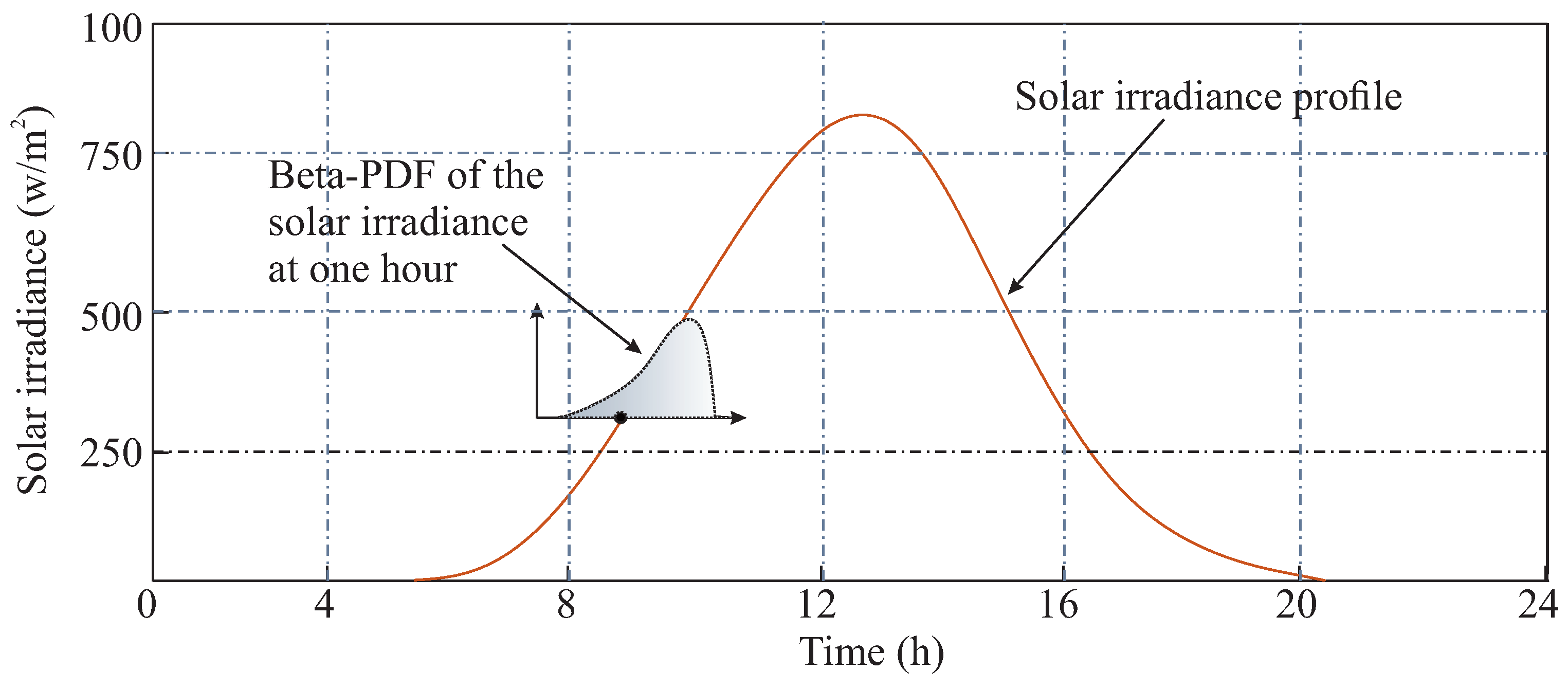
2.2. Solar Irradiance Uncertainty Model
2.3. Ambient Temperature Uncertainty Model
3. Optimization Problem Formulation
3.1. Calculation of LCOE
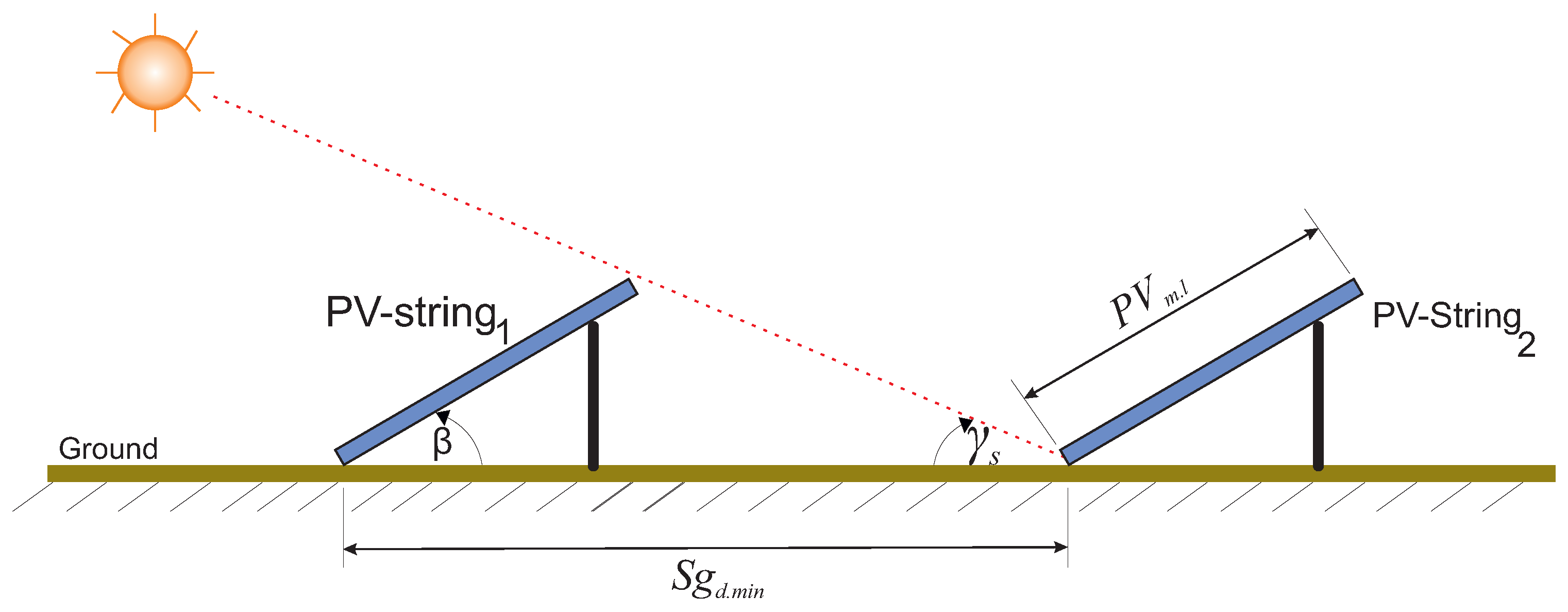
3.2. Optimal Design Constraints
4. Solution Method
5. Case Studies
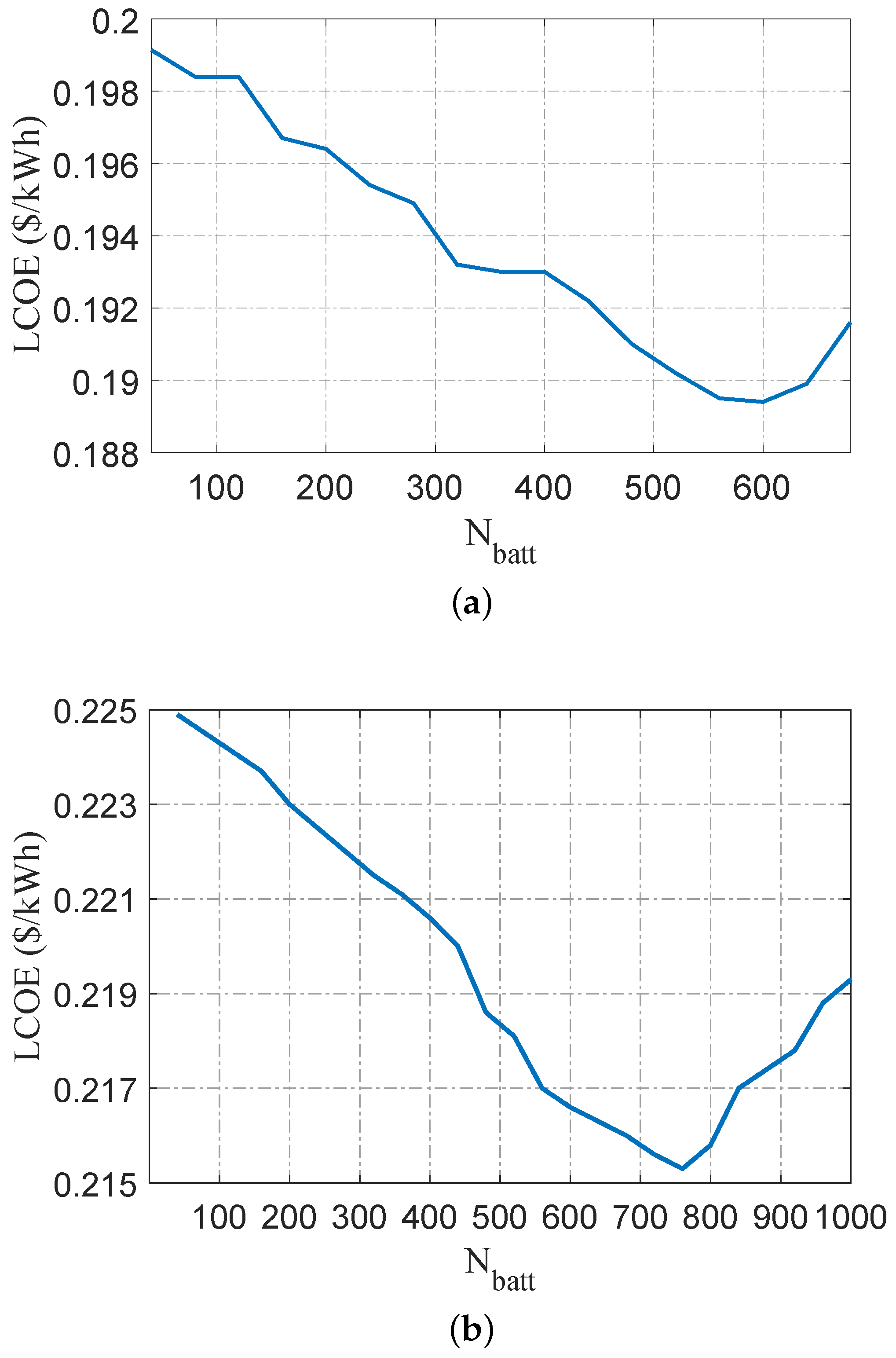
5.1. Optimal Design of a Residential MG
5.2. Optimal Design of an Industrial MG
- Scenario 1: deterministic optimization employing the mean values of grid blackout starting time and duration, solar irradiance, and ambient temperature;
- Scenario 2: stochastic optimization considering the uncertainty of grid blackout starting time and duration, solar irradiance, and ambient temperature;
- Scenario 3: as in Scenario 1, but assume the blackout starts at midnight to include the daily low load period in the grid blackout duration.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aien, M.; Hajebrahimi, A.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M. A comprehensive review on uncertainty modeling techniques in power system studies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, A.; Ismail, F.B.; Lipu, M.H.; Hannan, M. Uncertainty models for stochastic optimization in renewable energy applications. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1543–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamjoo, A.; Maheri, A.; Putrus, G.A. Chance constrained programming using non-Gaussian joint distribution function in design of standalone hybrid renewable energy systems. Energy 2014, 66, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Khajeh, M.G.; Ameri, M. Optimal sizing of a grid independent hybrid renewable energy system incorporating resource uncertainty, and load uncertainty. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 83, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.; Sadeh, J. Optimal sizing of hybrid wind/photovoltaic/battery considering the uncertainty of wind and photovoltaic power using Monte Carlo. In Proceedings of the 2012 11th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering, Venice, Italy, 18–25 May 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1081–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, P.; Banerjee, R.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Optimum sizing of photovoltaic battery systems incorporating uncertainty through design space approach. Sol. Energy 2009, 83, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kedare, S.B.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Optimum sizing of wind-battery systems incorporating resource uncertainty. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 2712–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamjoo, A.; Maheri, A.; Dizqah, A.M.; Putrus, G.A. Multi-objective design under uncertainties of hybrid renewable energy system using NSGA-II and chance constrained programming. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2016, 74, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Jiang, C.; Cai, G.; Huang, N. Optimal sizing of a wind/solar/battery/diesel hybrid microgrid based on typical scenarios considering meteorological variability. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2019, 13, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Gao, F.; Guan, X.; Zhai, Q.; Wu, J. Storage-reserve sizing with qualified reliability for connected high renewable penetration micro-grid. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 7, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Hong, N.; Nguyen-Duc, H. Optimal sizing of energy storage devices in wind-diesel systems considering load growth uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Sustainable Energy Technologies (ICSET), Hanoi, Vietnam, 14–17 November 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, S.; Chan, K.; Luo, X.; Bu, S.; Ding, Z.; Zhou, B. Optimal sizing of energy storage system and its cost-benefit analysis for power grid planning with intermittent wind generation. Renew. Energy 2018, 122, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulgalil, M.A.; Khalid, M.; Alismail, F. Optimal Sizing of Battery Energy Storage for a Grid-Connected Microgrid Subjected to Wind Uncertainties. Energies 2019, 12, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, P. Chance Constrained Programming for Optimal Power Flow Under Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2011, 26, 2417–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, P. Application of sparse-grid technique to chance constrained optimal power flow. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2013, 7, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J.; Mbayed, R.; Salloum, G.; Monmasson, E. Optimal sizing of a residential PV-battery backup for an intermittent primary energy source under realistic constraints. Energy Build. 2015, 105, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijjo, M.; Felgner, F.; Frey, G. Energy Management Scheme for Buildings Subject to Planned Grid Outages. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2016, 3, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Nayar, C.V.; Ashari, M.; Keerthipala, W. A grid-interactive photovoltaic uninterruptible power supply system using battery storage and a back up diesel generator. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2000, 15, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndwali, P.K.; Njiri, J.G.; Wanjiru, E.M. Optimal Operation Control of Microgrid Connected Photovoltaic-Diesel Generator Backup System Under Time of Use Tariff. J. Control. Autom. Electr. Syst. 2020, 31, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falama, R.Z.; Kaoutoing, M.D.; Mbakop, F.K.; Dumbrava, V.; Makloufi, S.; Djongyang, N.; Salah, C.B.; Doka, S.Y. A comparative study based on a techno-environmental-economic analysis of some hybrid grid-connected systems operating under electricity blackouts: A case study in Cameroon. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 251, 114935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cialdea, S.; Orr, J.A.; Emanuel, A.E. Outage Avoidance and Amelioration Using Battery Energy Storage Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilian, A.; Kezunovic, M. Prevention of Power Grid Blackouts Using Intentional Islanding Scheme. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhu, L.; Su, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Tolbert, L.M.; Glass, J.; Bruce, L. Battery and backup generator sizing for a resilient microgrid under stochastic extreme events. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2018, 12, 4443–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tsianikas, S.; Birnie, D.P., III; Coit, D.W. Economic and resilience benefit analysis of incorporating battery storage to photovoltaic array generation. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsianikas, S.; Zhou, J.; Birnie, D.P., III; Coit, D.W. Economic trends and comparisons for optimizing grid-outage resilient photovoltaic and battery systems. Appl. Energy 2019, 256, 113892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alramlawi, M.; Li, P. Design Optimization of a Residential PV-Battery Microgrid with a Detailed Battery Lifetime Estimation Model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soize, C. Stochastic modeling of uncertainties in computational structural dynamics—Recent theoretical advances. J. Sound Vib. 2013, 332, 2379–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C. A tutorial on kernel density estimation and recent advances. Biostat. Epidemiol. 2017, 1, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, A.W.; Azzalini, A. Applied Smoothing Techniques for Data Analysis: The Kernel Approach with S-Plus Illustrations; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 1997; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Voskrebenzev, A.; Riechelmann, S.; Bais, A.; Slaper, H.; Seckmeyer, G. Estimating probability distributions of solar irradiance. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB. Statistics Toolbox User’s Guide; The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- The Humanitarian Impact of Gaza’s Electricity and Fuel Crisis. 2015. Available online: https://www.un.org/unispal/document/auto-insert-204698/ (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Mavromatidis, G.; Orehounig, K.; Carmeliet, J. Uncertainty and global sensitivity analysis for the optimal design of distributed energy systems. Appl. Energy 2018, 214, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, R.; Hennebel, M.; Li, Y.F.; Ruiz, C.; Zio, E. A risk-based simulation and multi-objective optimization framework for the integration of distributed renewable generation and storage. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 37, 778–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, E.; Hutchinson, M. The beta distribution as a probability model for daily cloud duration. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1991, 56, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, B.R.; Jena, D. A sensitivity matrix-based temperature-augmented probabilistic load flow study. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2506–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikmehr, N.; Ravadanegh, S.N. Optimal power dispatch of multi-microgrids at future smart distribution grids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1648–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, G.; Billinton, R. Customer cost of electric service interruptions. Proc. IEEE 1989, 77, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezer, T.; Yaman, R.; Yaman, G. Evaluation of approaches used for optimization of stand-alone hybrid renewable energy systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alramlawi, M.; Gabash, A.; Mohagheghi, E.; Li, P. Optimal operation of hybrid PV-battery system considering grid scheduled blackouts and battery lifetime. Sol. Energy 2018, 161, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alramlawi, M.; Mohagheghi, E.; Li, P. Predictive active-reactive optimal power dispatch in PV-battery-diesel microgrid considering reactive power and battery lifetime costs. Sol. Energy 2019, 193, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, N.N.; Parra, J.A.G.; Valls-Guirado, J.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Optimal displacement of photovoltaic array’s rows using a novel shading model. Appl. Energy 2015, 144, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, K. Photovoltaics: Fundamentals, Technology, and Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Wei, Z.; Chengzhi, L. Optimal design and techno-economic analysis of a hybrid solar–wind power generation system. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geletu, A.; Klöppel, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, P. Advances and applications of chance-constrained approaches to systems optimisation under uncertainty. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2012, 44, 1209–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwekar, U.M.; Kalagnanam, J.R. Efficient sampling technique for optimization under uncertainty. AIChE J. 1997, 43, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovski, G.; Stankovski, M. Model Predictive Controller Employing Genetic Algorithm Optimization of Thermal Processes with Non-Convex Constraints; INTECH Open Access Publisher: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Alramlawi, M.; Gabash, A.; Mohagheghi, E.; Li, P. Optimal Operation of PV-Battery-Diesel MicroGrid for Industrial Loads Under Grid Blackouts. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2018 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/I CPS Europe), Palermo, Italy, 12–15 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Solar Energy Services for Professionals. Available online: http://www.soda-pro.com (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Trading Economics. Available online: http://www.tradingeconomics.com (accessed on 28 February 2024).


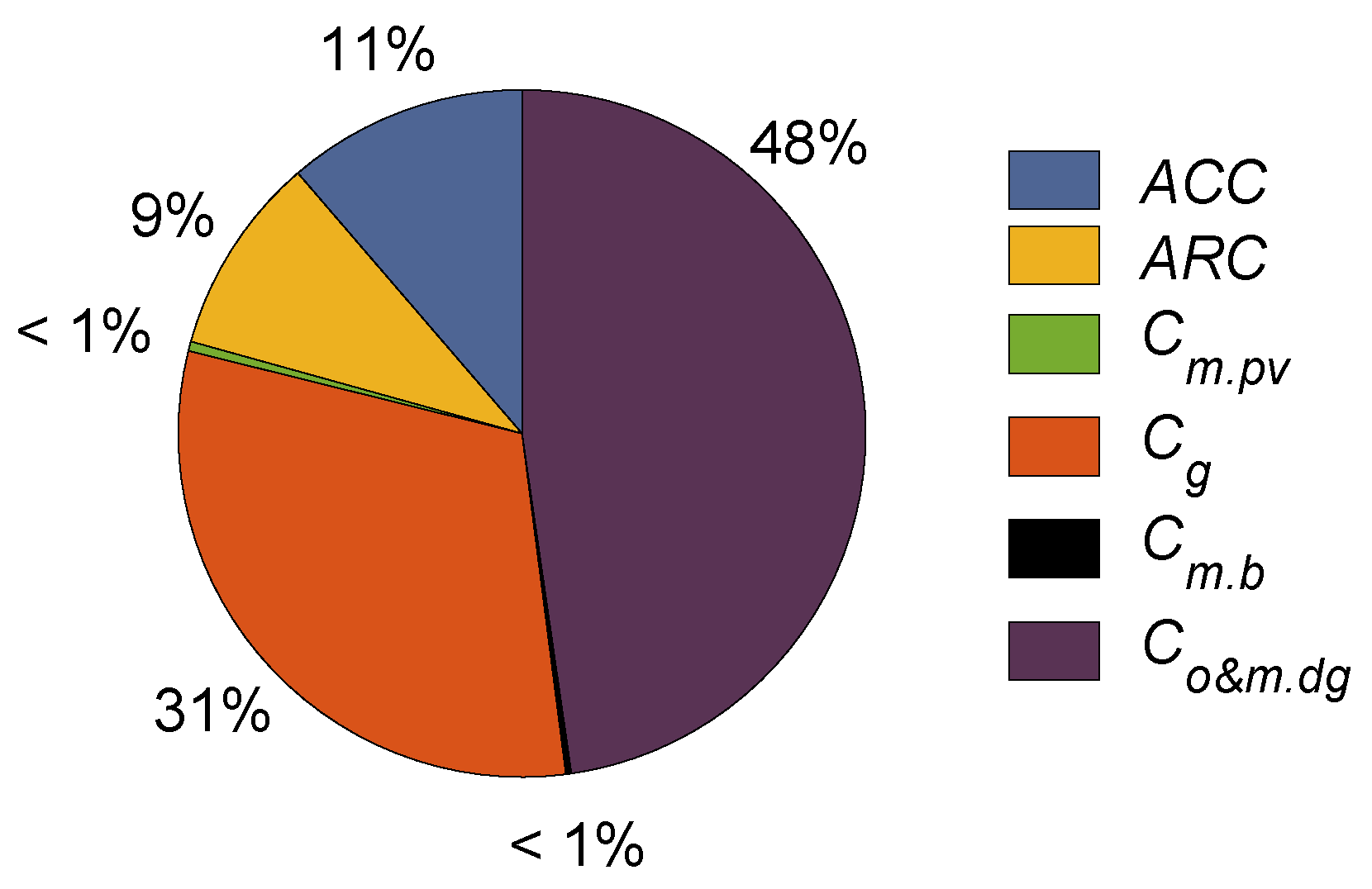

| Parameter | (-) | (-) | ($/l) | ($/kWh) | (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 6.89% | 3.16% | 1.3% | 0.15% | 20 |
| Parameter | Lifetime | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PV array | 550 $/kWp | 0.5% | 20 (years) |
| PV inverter | 300 $/kW | 0.5% | 10 (years) |
| Battery bank | 150 $/kWh | 1% | to be calculated |
| Battery inverter | 300 $/kW | 0.5% | 10 (years) |
| Diesel Generator | 250 $/kW | 8% | 10,000 (h) |
| Parameter | (-) | (-) | (-) | ($/kWh) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deterministic | 8 | 10 | 0.56 | 0.1835 | 27.8 |
| Stochastic | 10 | 12 | 0.68 | 0.2059 | 98 |
| Parameter | Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PV array | 1450 | 1450 | 1450 |
| PV inverter (Kw) | 280 | 280 | 280 |
| Battery size | 568 | 568 | 464 |
| DOD (%) | 76 | 73 | 65 |
| Diesel number | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Diesel generator (Kw) | 60 | 80 | 70 |
| Diesel generator (Kw) | 120 | 170 | 130 |
| Diesel generator (Kw) | 270 | 250 | 220 |
| Battery life (year) | 3.03 | 3.17 | 3.58 |
| LCOE ($/Kw) | 0.1896 | 0.2169 | 0.1729 |
| (%) | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| (%) | 100% | 100% | 16.61% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alramlawi, M.; Li, P. Chance-Constrained Optimal Design of PV-Based Microgrids under Grid Blackout Uncertainties. Energies 2024, 17, 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081892
Alramlawi M, Li P. Chance-Constrained Optimal Design of PV-Based Microgrids under Grid Blackout Uncertainties. Energies. 2024; 17(8):1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081892
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlramlawi, Mansour, and Pu Li. 2024. "Chance-Constrained Optimal Design of PV-Based Microgrids under Grid Blackout Uncertainties" Energies 17, no. 8: 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081892
APA StyleAlramlawi, M., & Li, P. (2024). Chance-Constrained Optimal Design of PV-Based Microgrids under Grid Blackout Uncertainties. Energies, 17(8), 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081892







