Assessment of Syngas Storage Tank Hazards Taking Account of the Domino Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Syngas Characteristics
3. Hazards Related to an Uncontrolled Release of Syngas from the Storage Tank
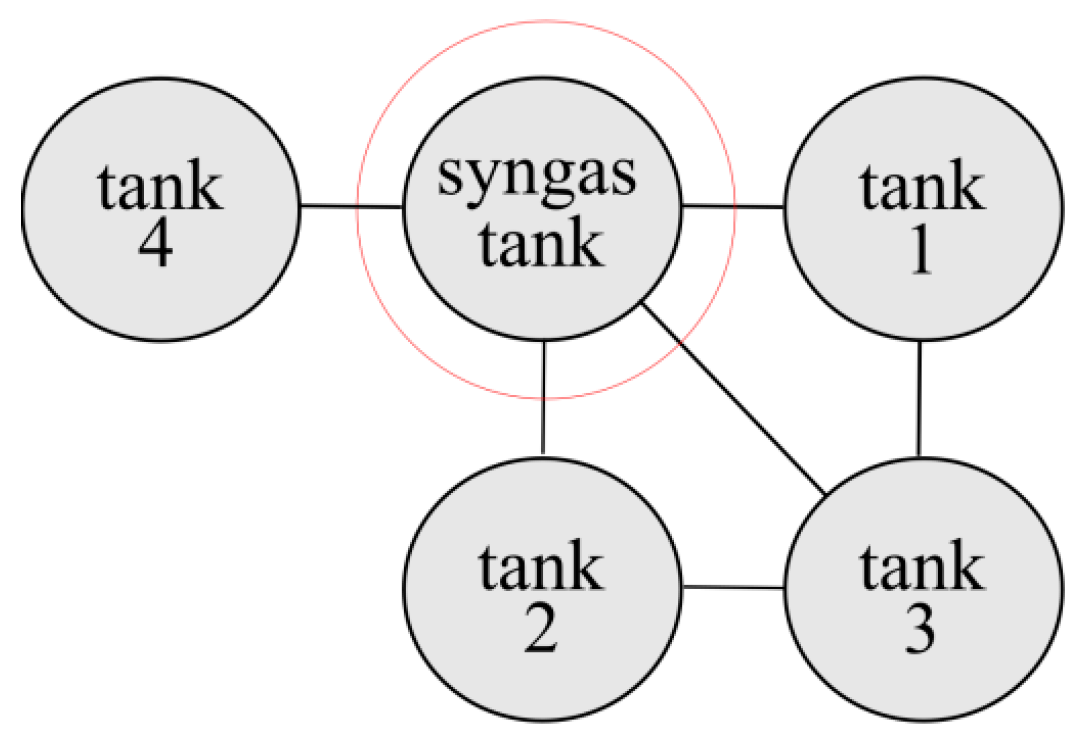
3.1. Synthesis Gas Storage
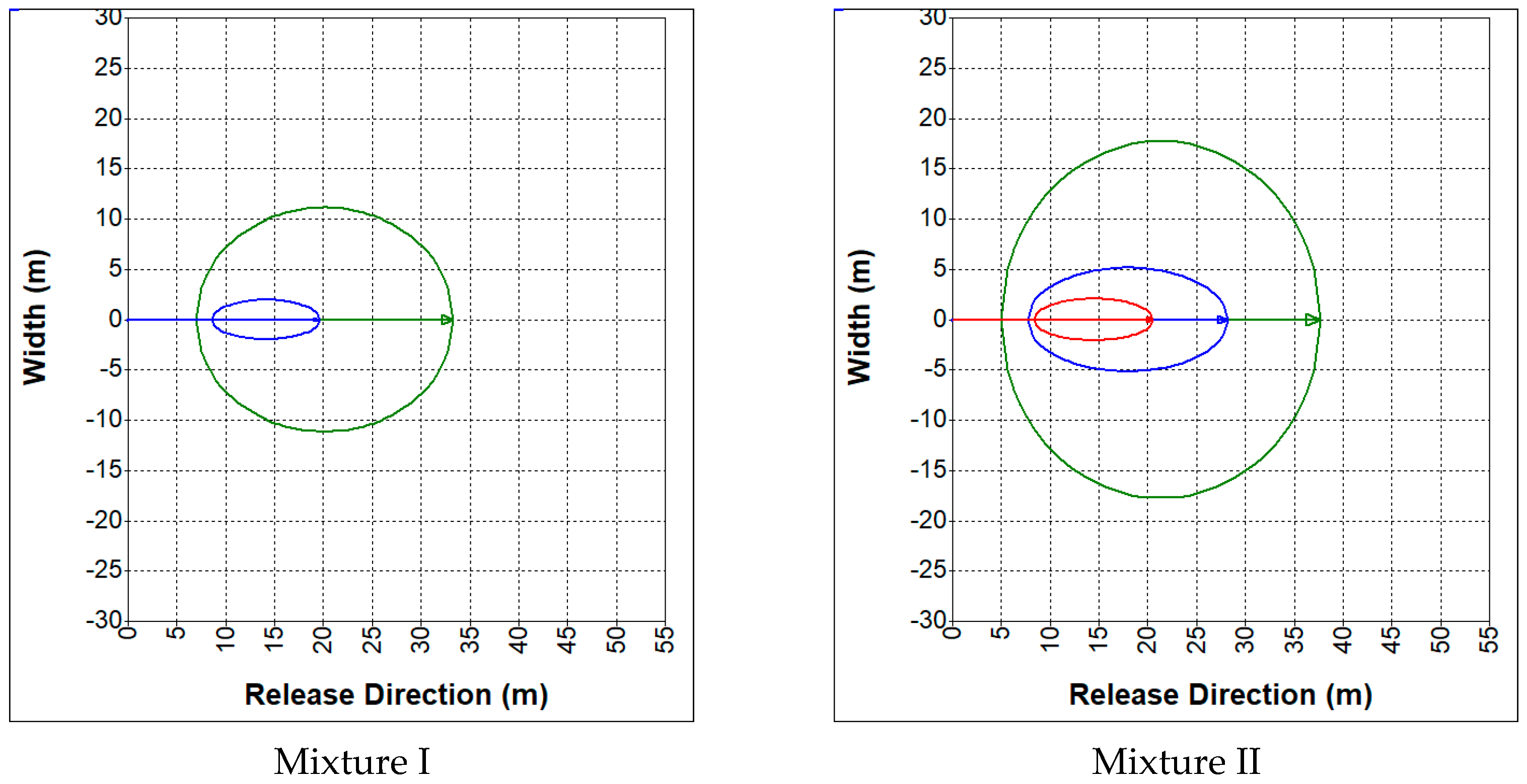
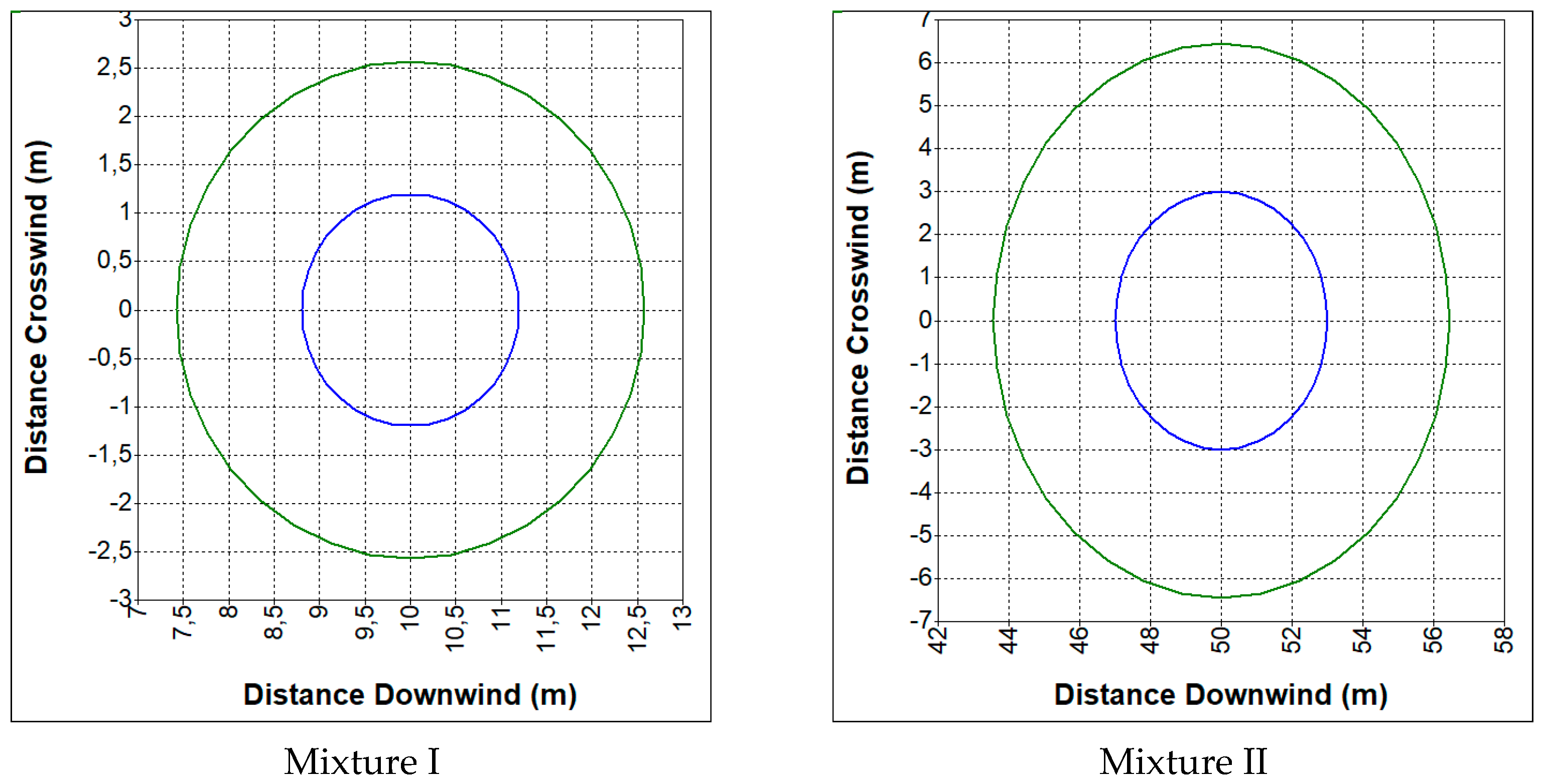
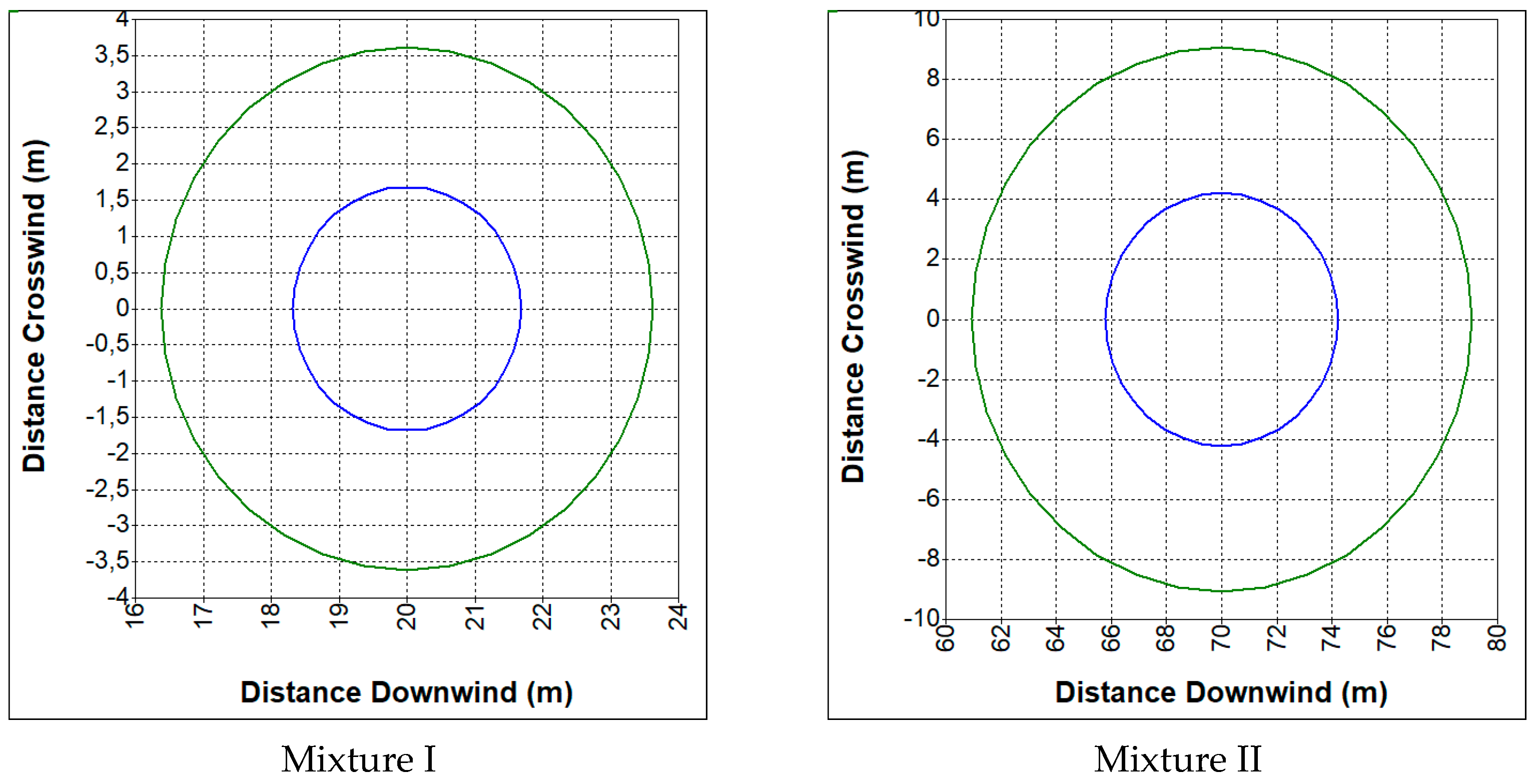
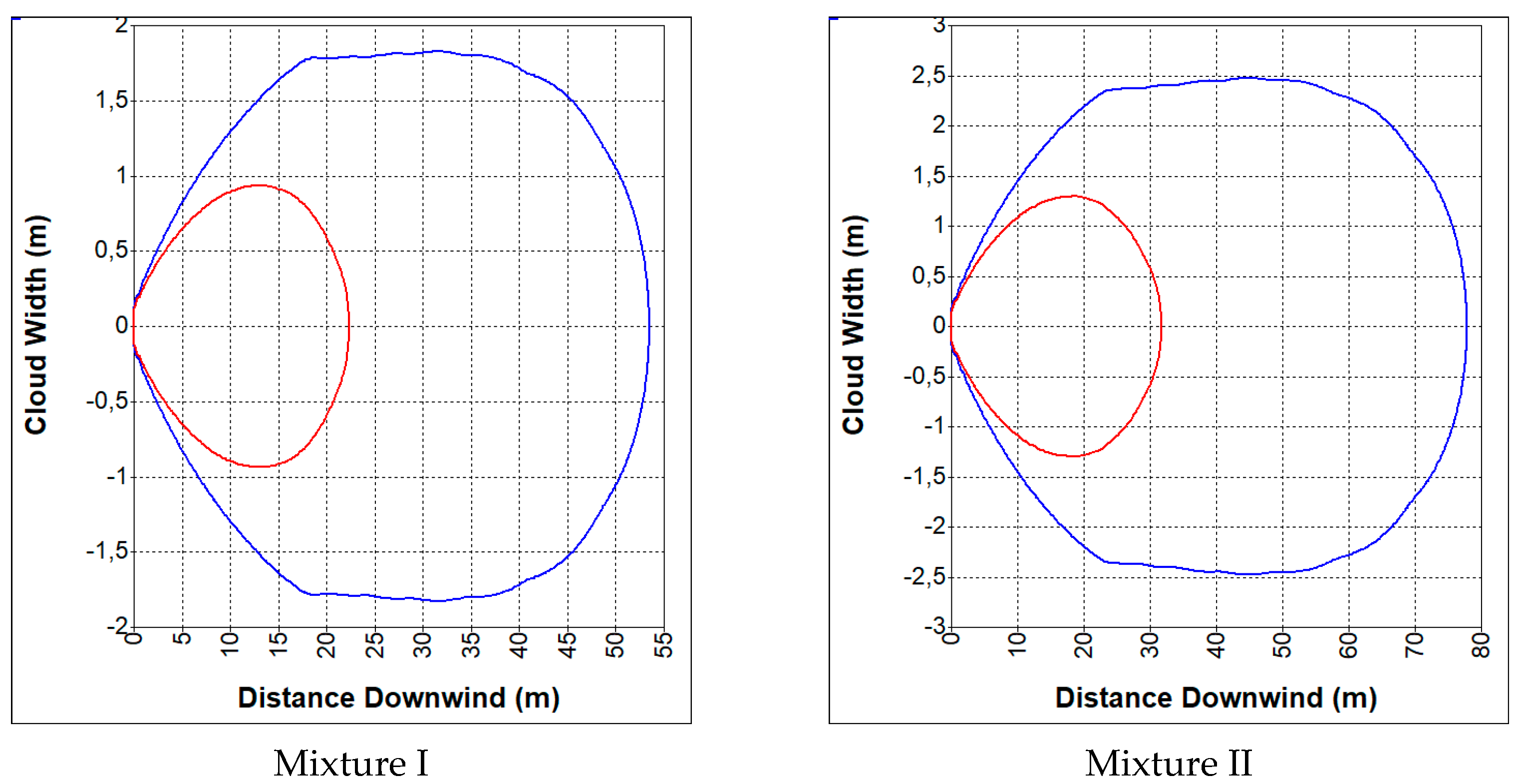
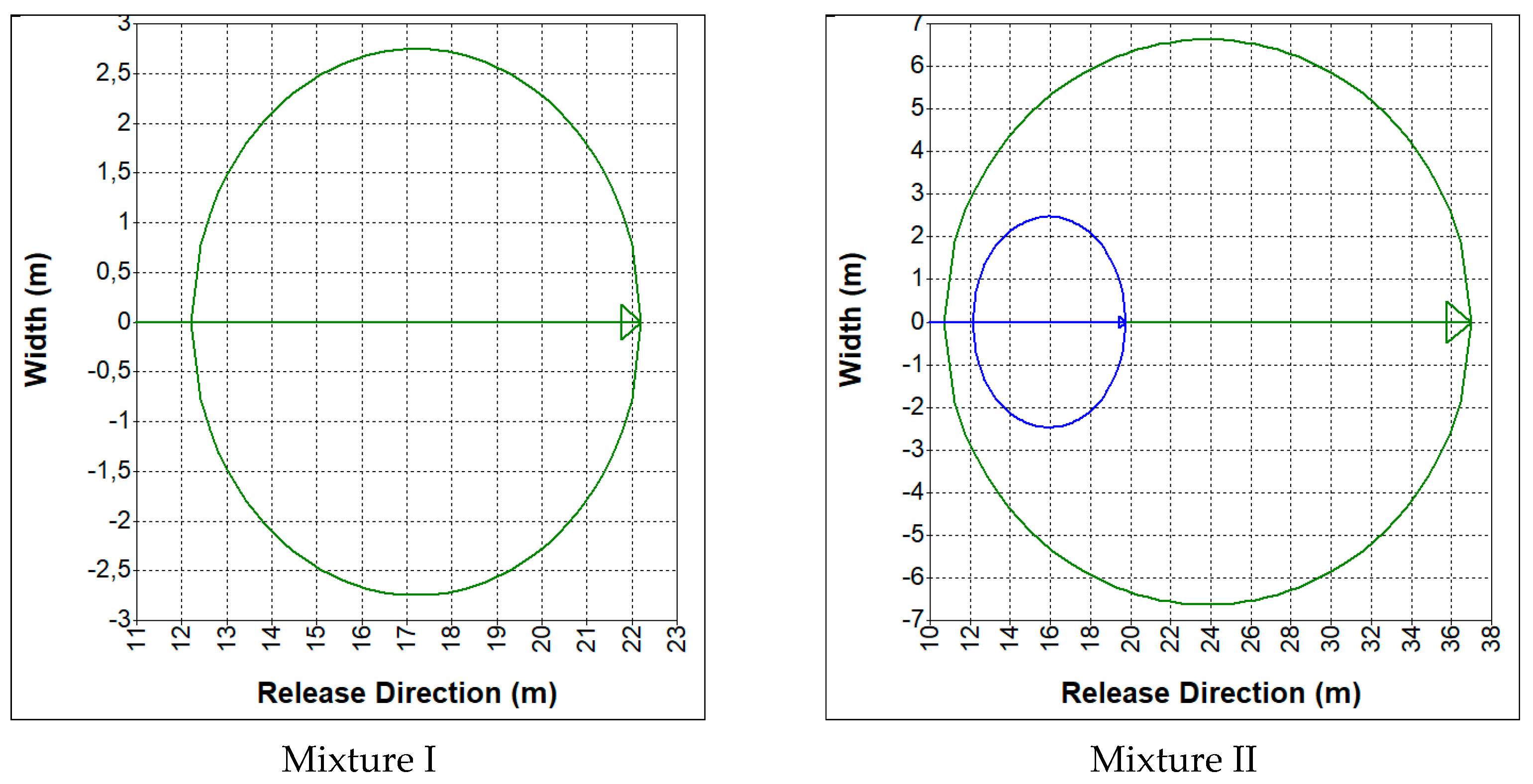
3.2. Hazards Related to an Uncontrolled Release of Synthesis Gas
- CO—19%, CO2—12%, H2—19%, CH4—2%, N2—48% (mixture I);
- CO—23%, CO2—29%, H2—38%, CH4—9.5%, N2—0.5% (mixture II).
4. The Domino Effect
4.1. The Domino Effect Characteristic
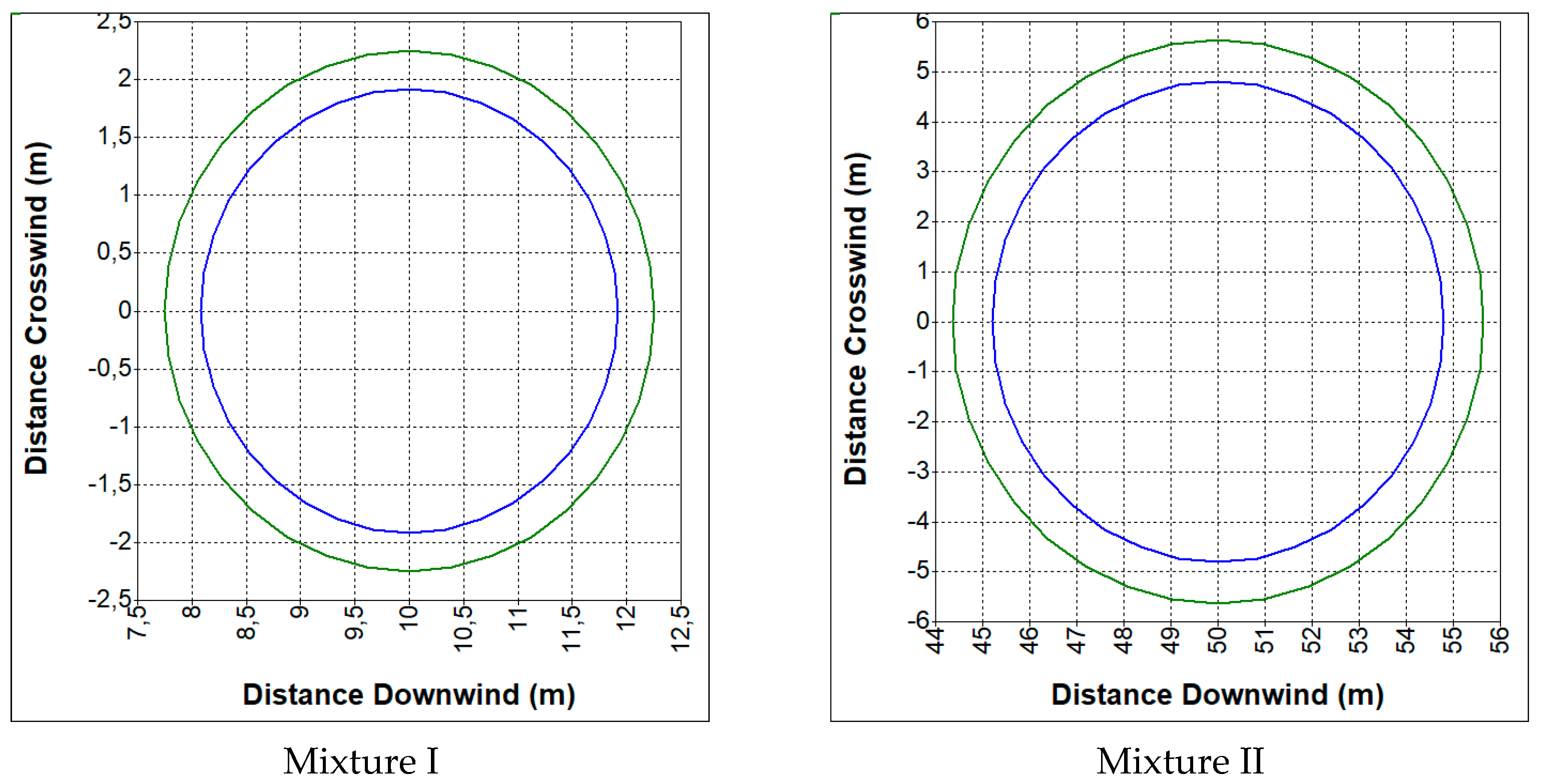
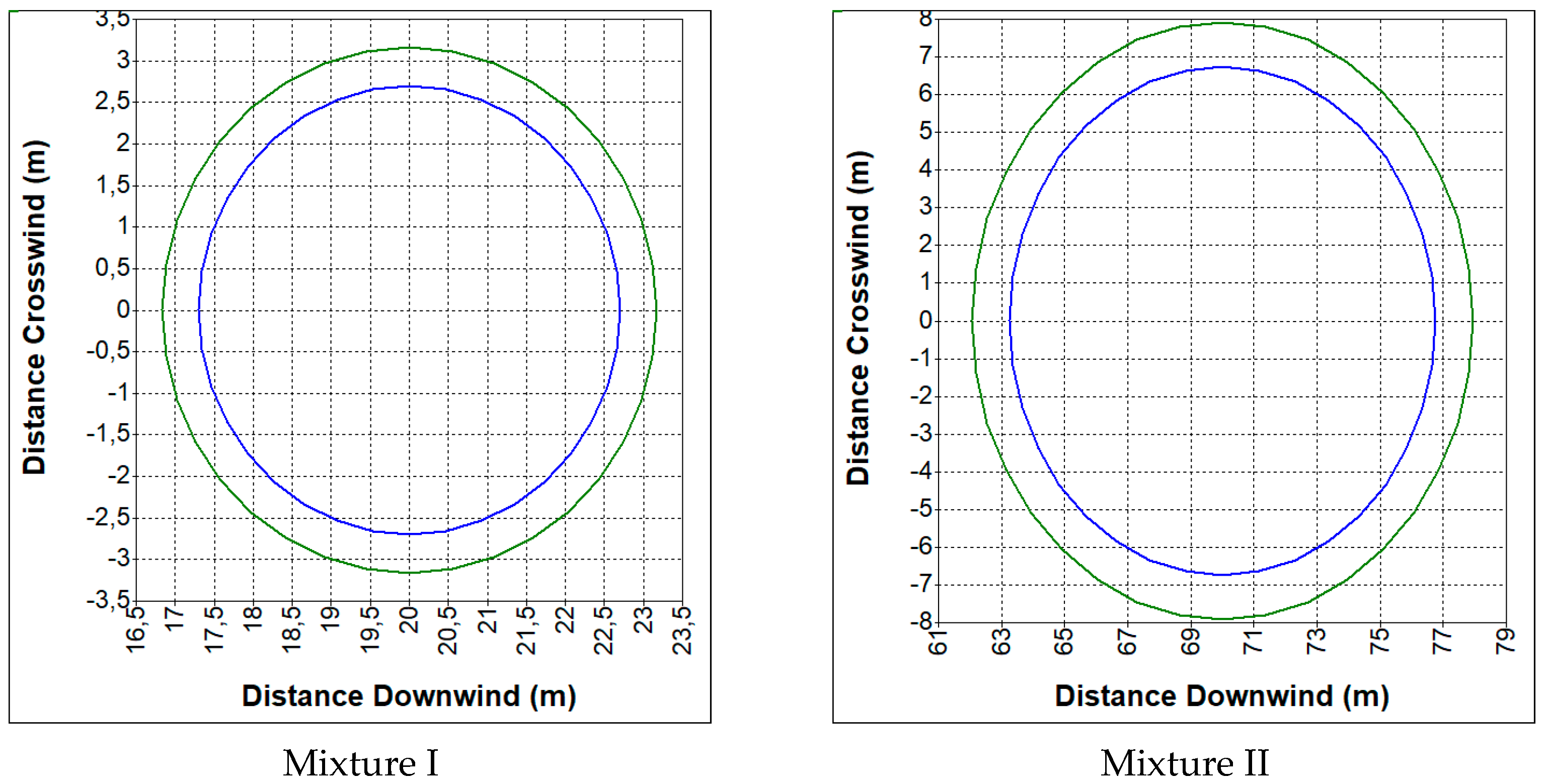
4.2. Range of Zones Causing Another Tank Destruction
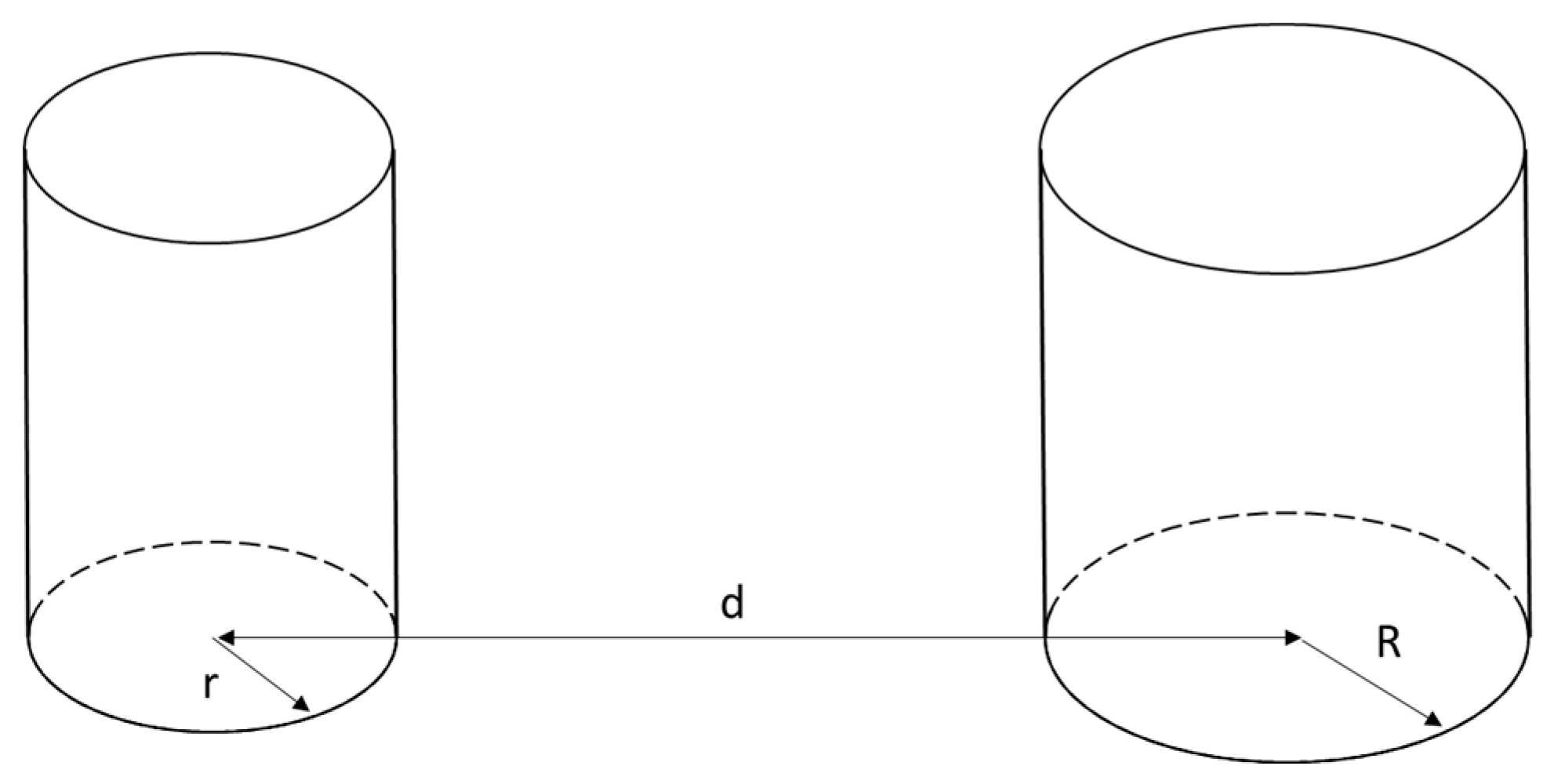
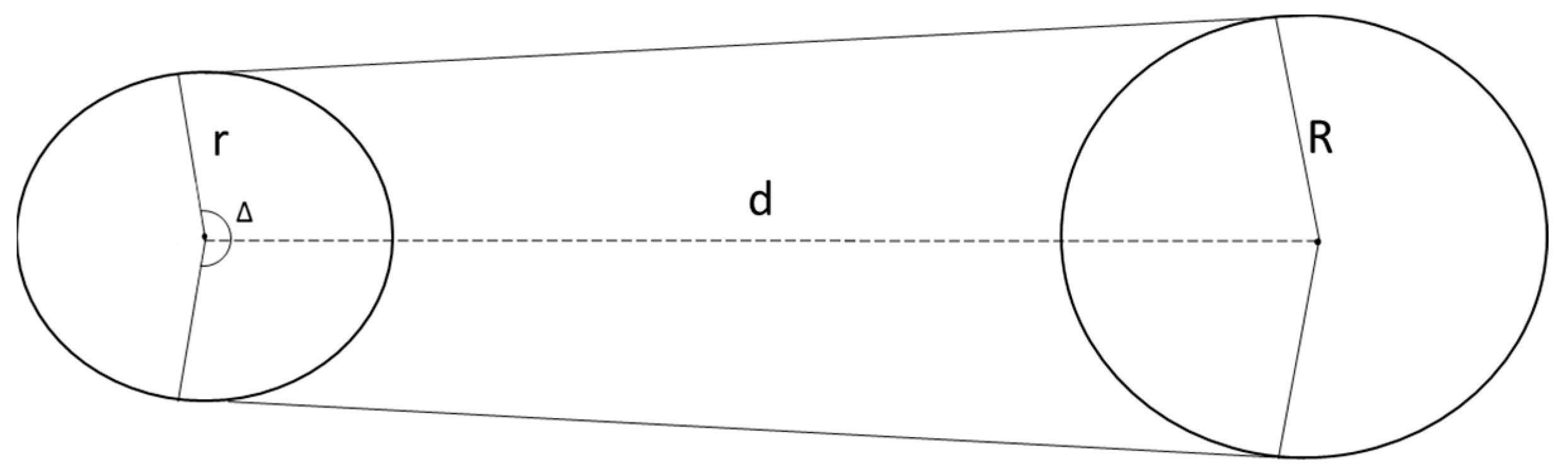
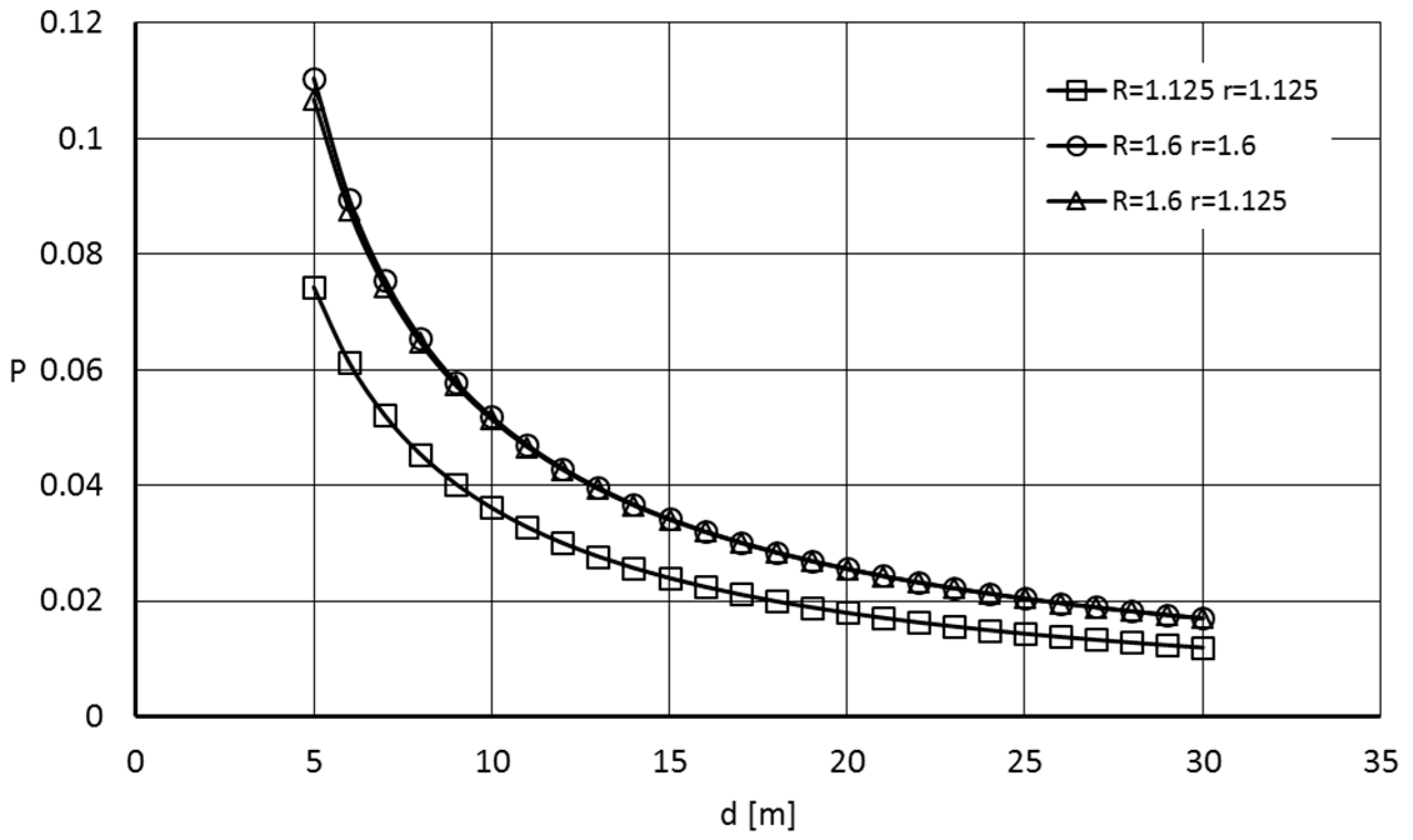
4.3. Probability of Domino Effect Occurrence
- P1—the probability that the hole created due to the failure of Tank A is located on the perimeter facing Tank B,
- P2—the probability that the jet released from the hole in Tank A flows in the direction suitable for the jet to reach Tank B.
- Variant 1: Tank A radius: 1.125 m, Tank B radius: 1.125 m,
- Variant 2: Tank A radius: 1.60 m, Tank B radius: 1.60 m,
- Variant 3: Tank A radius: 1.125 m, Tank B radius: 1.60 m.
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, A.; Gautam, S.; Sharma, T. Effects of operating parameters on coal gasification. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2018, 5, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, R.; Hrbek, J.; Hofbauer, H. Biomass gasification for synthesis gas production and applications of the syngas. Energy Environ. 2014, 3, 343–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Luo, Z.; Krietsch, A.; Wu, D.; Wang, T.; Zhou, S.; Deng, J. Quantitative investigation of explosion behavior and spectral radiant characteristics of free radicals for syngas/air mixtures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolecka, K.; Rusin, A. Analysis of hazards related to syngas production and transport. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 2535–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jithin, E.V.; Raghuram, G.K.S.; Keshavamurthy, T.V.; Velamati, R.K.; Prathap, C.; Varghese, R.J. A review on fundamental combustion characteristics of syngas mixtures and feasibility in combustion devices. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 146, 111178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, M.; Qian, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H. CO rich syngas production from catalytic CO2 gasification-reforming of biomass components on Ni/CeO2. Fuel 2024, 357, 130087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieradzka, M.; Mlonka-Mędrala, A.; Błoniarz, A.; Magdziarz, A. Experimental study of biomass waste gasification: Impact of atmosphere and catalysts presence on quality of syngas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 394, 130290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okati, A.; Khani, M.R.; Shokri, B.; Rouboa, A.; Monteiro, E. Optimizing the operating conditions for hydrogen-rich syngas production in a plasma co-gasification process of municipal solid waste and coal using Aspen Plus. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 26891–26900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anniwaer, A.; Chaihad, N.; Zahra, A.C.A.; Kurnia, I.; Kasai, Y.; Kongparakul, S.; Samart, C.; Kusakabe, K.; Abudula, A.; Guan, G. Utilization of fruit waste for H2-rich syngas production via steam co-gasification with brown coal. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2023, 6, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Vairakannu, P. CO2 based synergistic reaction effects with energy and exergy (2E) analysis of high density polyethylene with high ash bituminous coal for syngas production. Fuel 2022, 311, 122500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, S.; Wen, X.; Guo, Z.; He, W.; Deng, H.; Wang, F. Experimental study of explosion dynamics of syngas flames in the narrow channel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 17808–17820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, S.; Ayoobi, M.; Akkerman, V. Computational Analysis of Premixed Syngas/Air Combustion in Micro-channels: Impacts of Flow Rate and Fuel Composition. Energies 2021, 14, 4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wu, F.; Diao, S.; Wen, X. Unstable combustion behavior of syngas/air mixture with different components in a narrow gap disk reactor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 54, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Coronel, D.A.; Salazar, A.; Pupo-Roncallo, O.R.; Bula, A.; Corredor, L.; Amador, G.; Gonzalez-Quiroga, A. Assessment of the interchangeability of coal-biomass syngas with natural gas for atmospheric burners and high-pressure combustion applications. Energy 2023, 276, 127551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guryanov, A.I.; Evdokimov, O.A.; Burtsev, V.A.; Koshkin, V.I.; Veretennikov, S.V.; Komova, O.V. An experimental study of syngas combustion in a bidirectional swirling flow. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 4503–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamizadeh, K.; Zarei, E.; Yazdi, M.; Ramezanifar, E.; Aliabadi, M.M. A hybrid model for dynamic analysis of domino effects in chemical process industries. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 241, 109654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.T.; Scarponi, G.E.; Cozzani, V.; Khan, F. Dynamic Domino Effect Assessment (D2EA) in tank farms using a machine learning-based approach. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2024, 181, 108556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Khan, F.; Ji, J. A novel approach for domino effects modeling and risk analysis based on synergistic effect and accident evidence. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 203, 107109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zheng, F.; Chen, F.; Pan, W.; Mo, S. Propagation probability of domino effect based on analysis of accident chain in storage tank area. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2019, 62, 103962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinlong, M.; Hongbing, J.; Zhitao, C.; Wenli, X.; Lingbo, Z. Study of the situation deduction of a domino accident caused by overpressure in LPG storage tank area. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2021, 72, 104525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Reniers, G.; Zhang, L. An innovative methodology for quickly modeling the spatial-temporal evolution of domino accident triggered by fire. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2018, 54, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Wabash River Coal Gasification Repowering Project, Topical Report Number 20; The U.S. Department of Energy and Wabash River Coal Gasification Project Joint Venture: West Terre Haute, IN, USA, 2020.
- Apt, J.; Newcomer, A.; Lave, L.B.; Douglas, S.; Dunn, L.M. An Engineering-Economic Analysis of Syngas Storage; DOE/NETL-2008/1331 Draft Final Report; Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Ge, X. Chapter Three–Biogas and Syngas Upgrading. Adv. Bioenergy 2016, 1, 125–188. [Google Scholar]
- Khosravani, H.; Meshksar, M.; Rahimpour, H.R.; Rahimpour, M.R. Chapter 1–Introduction to syngas products and applications. In Advances in Synthesis Gas: Methods, Technologies and Applications; Volume 3: Syngas Products and Usages; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, M.; Raheem, A.; Wang, F.; Wei, J.; Xu, D.; Song, X.; Bao, W.; Huang, A.; Zhang, S.; et al. Syngas Production from Biomass Gasification: Influences of Feedstock Properties, Reactor Type, and Reaction Parameters. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 31620–31631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierorazio, A.J.; Baqer, Q.A. Hazards for Syngas Fires and Explosions. Process Saf. Prog. 2010, 29, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, A.; Braccio, G.; Fiorenza, G.; Marraffa, F.A.; Lamonaca, S.; Giordano, G.; Rotondo, G.; Stecchi, U.; La Scala, M. Classification procedure of explosion risk areas in presence of hydrogen-rich syngas: Biomass gasifier and molten carbonate fuel cell integrated plant. Fuel 2012, 99, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, D.; Sierra, F.; Tola, V. Assessment of energy and economic benefits arising from syngas storage in IGCC power plants. Energy 2013, 58, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Bai, Z.; Li, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, S. Potential of applying the thermochemical recuperation in combined cooling, heating and power generation: Optimized recuperation regulation with syngas storage. Appl. Energy 2024, 353 Pt B, 122128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harm Criteria for People and Property, European Train the Trainer Programme for Responders, HyResponder. 2023. Available online: https://hyresponder.eu/ (accessed on 30 March 2024).
- Stolecka, K.; Rusin, A. Hazards associated with syngas storage. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 137, 01022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PhAST. PHAST v6.7, DNV Software; PhAST: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Song, J.; Zheng, F. Risk analysis on domino effect caused by pool fire in petroliferous tank farm. Procedia Eng. 2018, 211, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, M.; Ren, F.; Li, V.; Xu, W. An Improved Approach to Estimate the Time to Failure for Large Oil Tank in Pool-Fire-Induced Domino Effects by Stress Failure. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2022, 22, 1954–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal, J. Evaluation of the Effects and Consequences of Major Accidents in Industrial Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Naderpoura, M.; Khakzad, N. Texas LPG fire: Domino effects triggered by natural hazards. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 116, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzani, V.; Antiononi, G.; Spadoni, G. Quantitative assessment of domino scenarios by a GIS-based software tool. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2006, 19, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, P. The probability prediction method of domino effect triggered by lightning in chemical tank farm. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 116, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Camacho, J.G.; Pastor, E.; Casal, J.; Amaya-Gomez, R.; Munoz-Giraldo, F. Analysis of domino effect in pipelines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 298, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittiglio, P.; Bragatto, P.; Delle Site, C. Update failure rates and risk management in process industries. Energy Procedia 2014, 45, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rusin, A.; Stolecka-Antczak, K. Assessment of Syngas Storage Tank Hazards Taking Account of the Domino Effect. Energies 2024, 17, 1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081857
Rusin A, Stolecka-Antczak K. Assessment of Syngas Storage Tank Hazards Taking Account of the Domino Effect. Energies. 2024; 17(8):1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081857
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusin, Andrzej, and Katarzyna Stolecka-Antczak. 2024. "Assessment of Syngas Storage Tank Hazards Taking Account of the Domino Effect" Energies 17, no. 8: 1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081857
APA StyleRusin, A., & Stolecka-Antczak, K. (2024). Assessment of Syngas Storage Tank Hazards Taking Account of the Domino Effect. Energies, 17(8), 1857. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081857





