Effective Degradation of Metronidazole through Electrochemical Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: Mechanistic Insights and Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (i)
- To examine the influence of operational parameters, specifically current density and PMS dosage, on the degradation efficiency of EC-PMS-BDD and EC-PMS-DSA systems (EC is the abbreviation of the electrochemical system).
- (ii)
- To systematically investigate the sources and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), including •OH, SO4•−, and 1O2 in these processes, elucidating their respective oxidation mechanisms.
- (iii)
- To utilize the Box–Behnken Design model to assess the optimal conditions leading to the highest MNZ removal efficiency.
- (iv)
- To analyze the structural characteristics of MNZ byproducts generated during the degradation processes and evaluate the environmental implications concerning other organic pollutants.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Setup and Procedures
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results
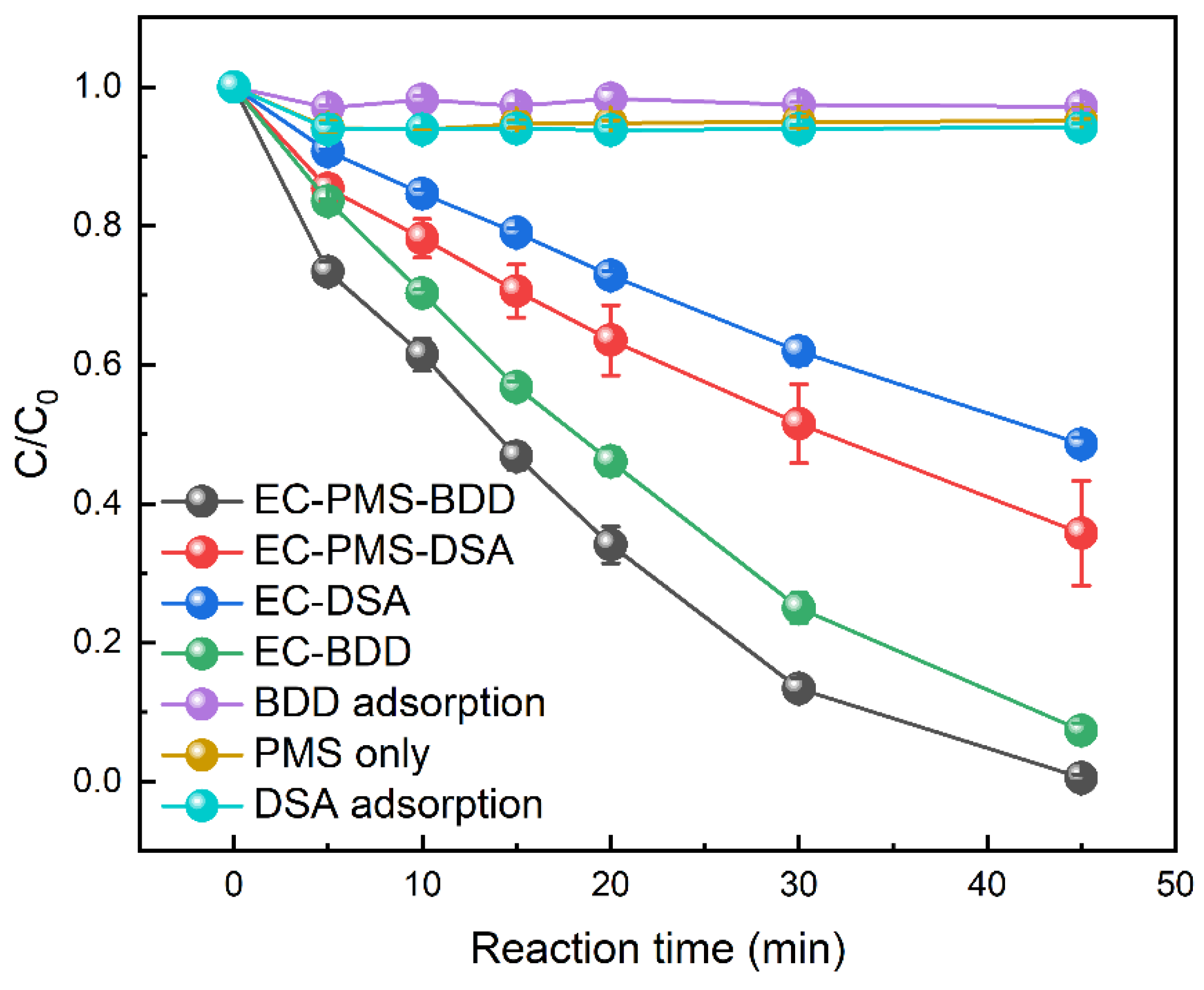
3.1. Removal Efficiency of MNZ in Various Processes
3.2. Optimization of Electrochemical Reaction Parameters
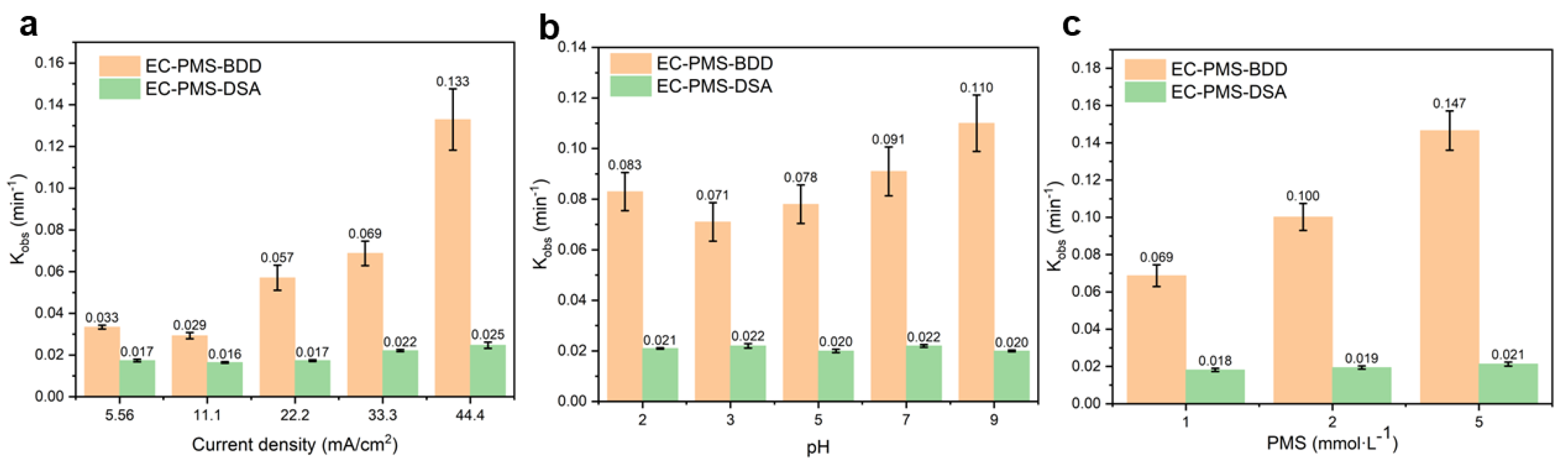
3.2.1. Effect of Current Density
3.2.2. Effect of Initial pH
3.2.3. Effect of PMS Dosage
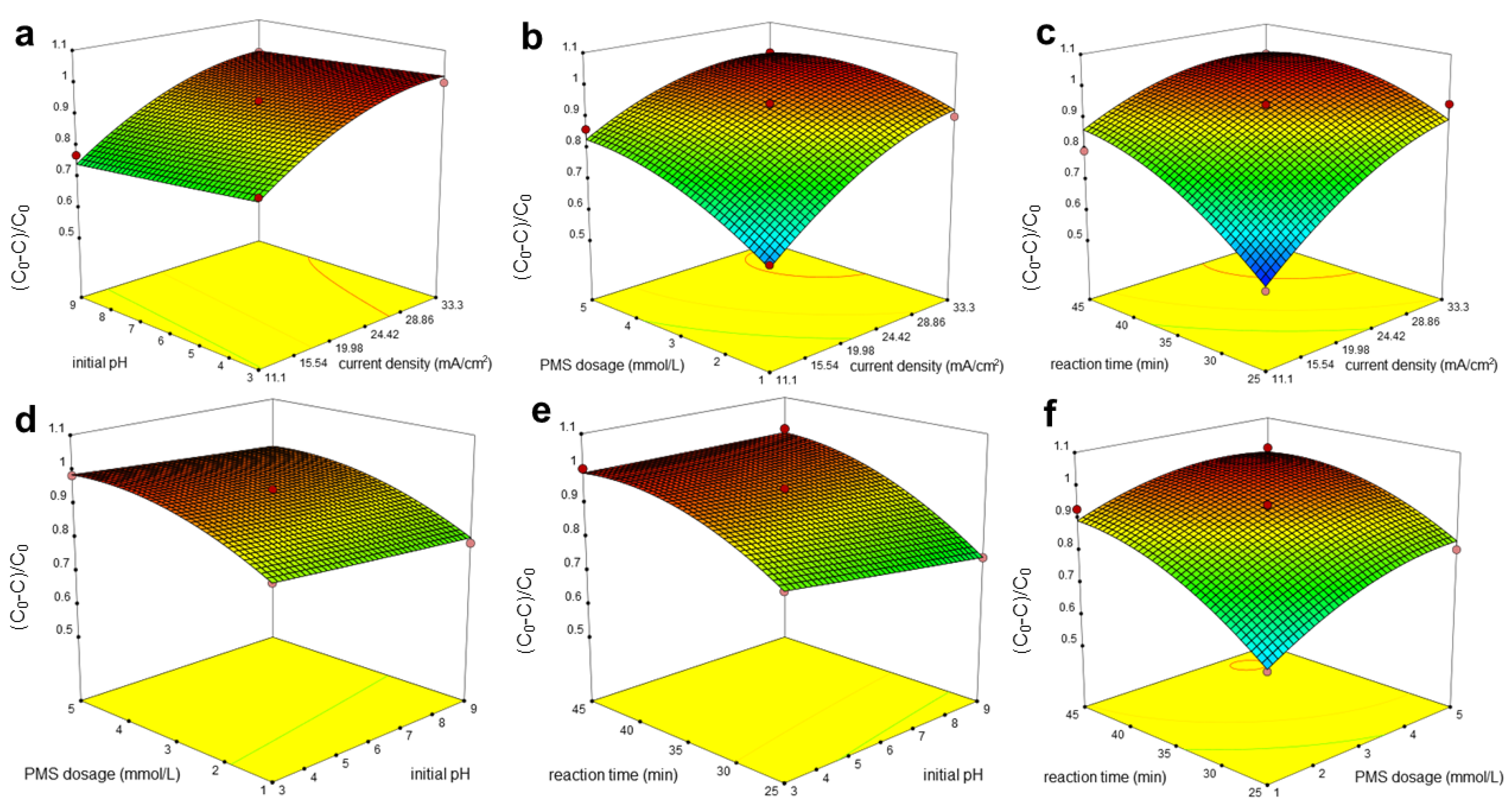
3.3. Optimum Conditions by RSM
3.4. Mechanism Study
3.4.1. EPR Test
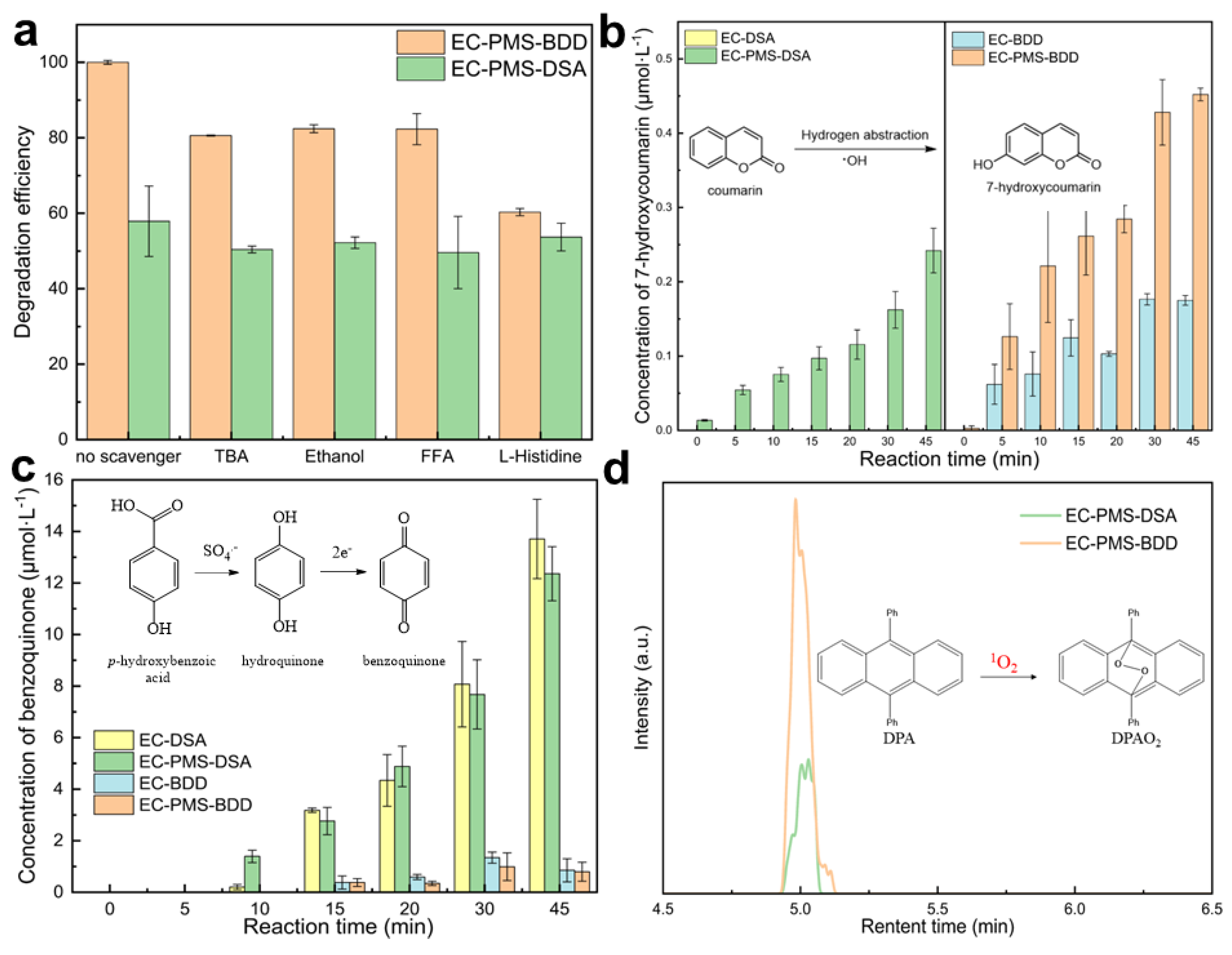
3.4.2. Quenching Experiments
3.4.3. Chemical Probe Experiments
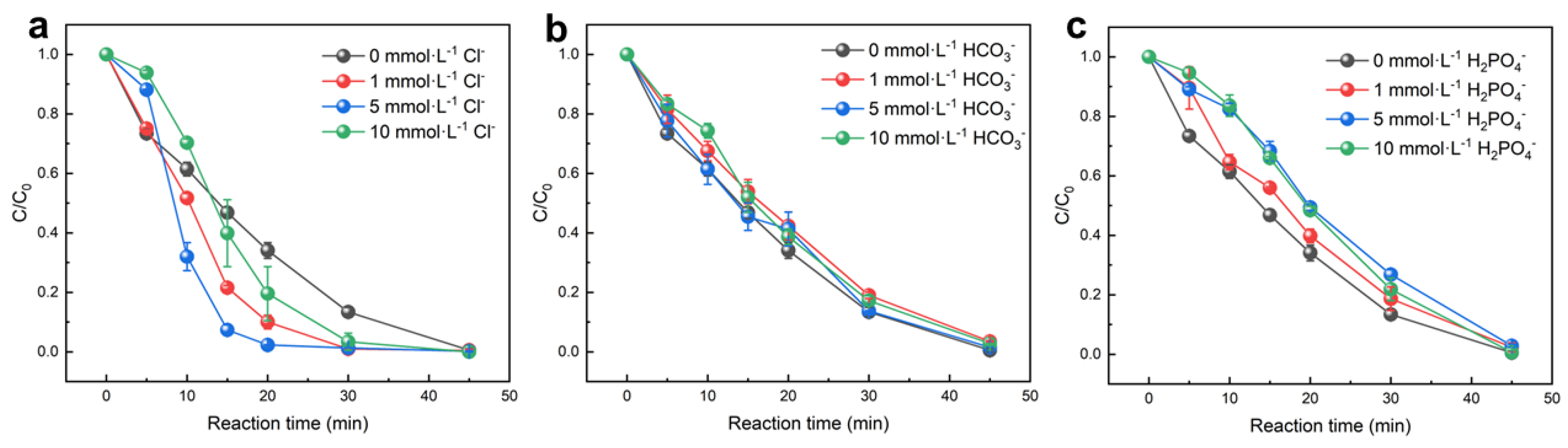
3.5. Effects of Different Water Matrics
3.5.1. Effect of Cl− Addition
3.5.2. Effect of HCO3− Addition
3.5.3. Effect of H2PO4− Addition
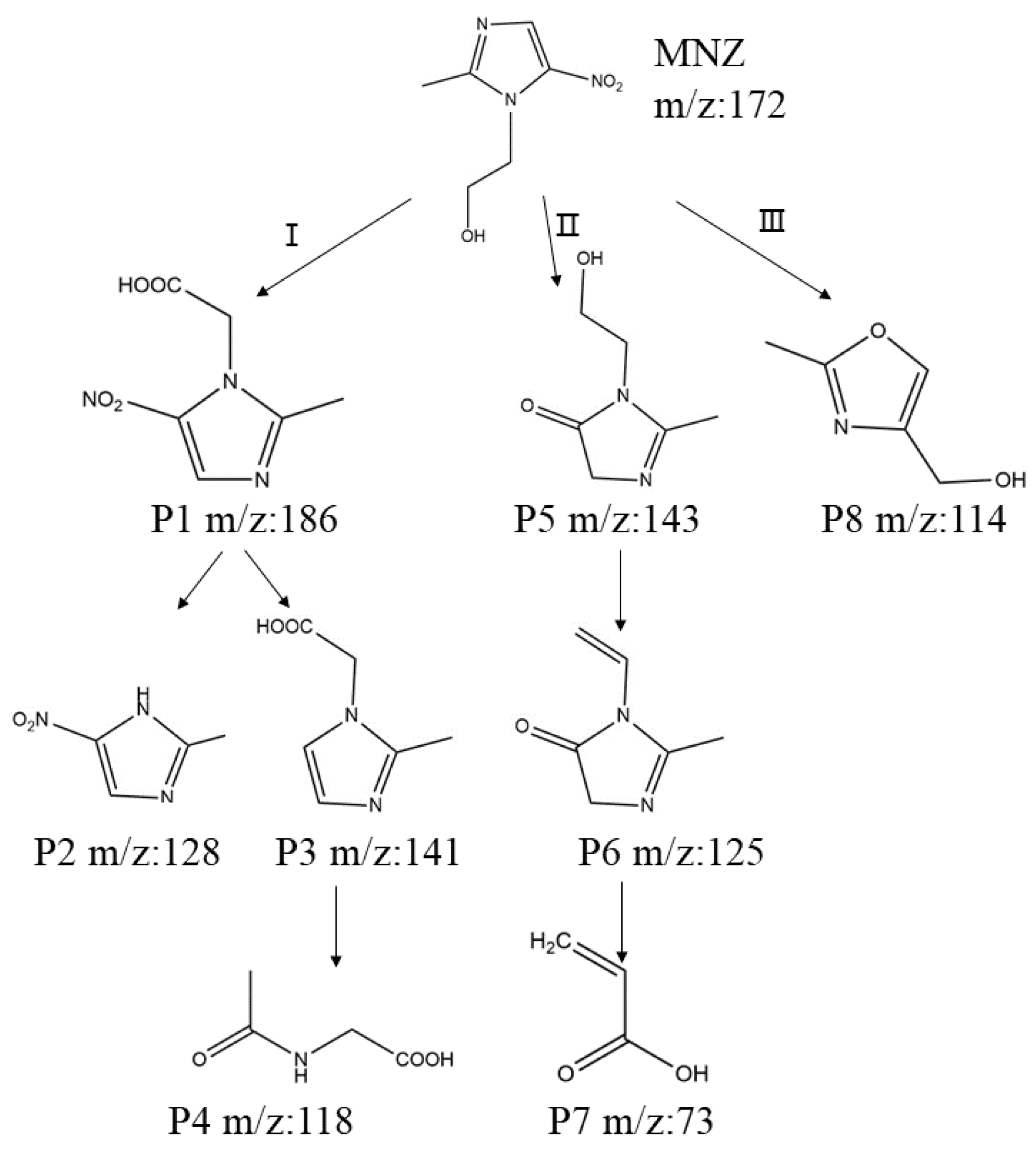
3.6. Analysis of MNZ Byproducts
3.6.1. Proposed Pathway of MNZ Degradation
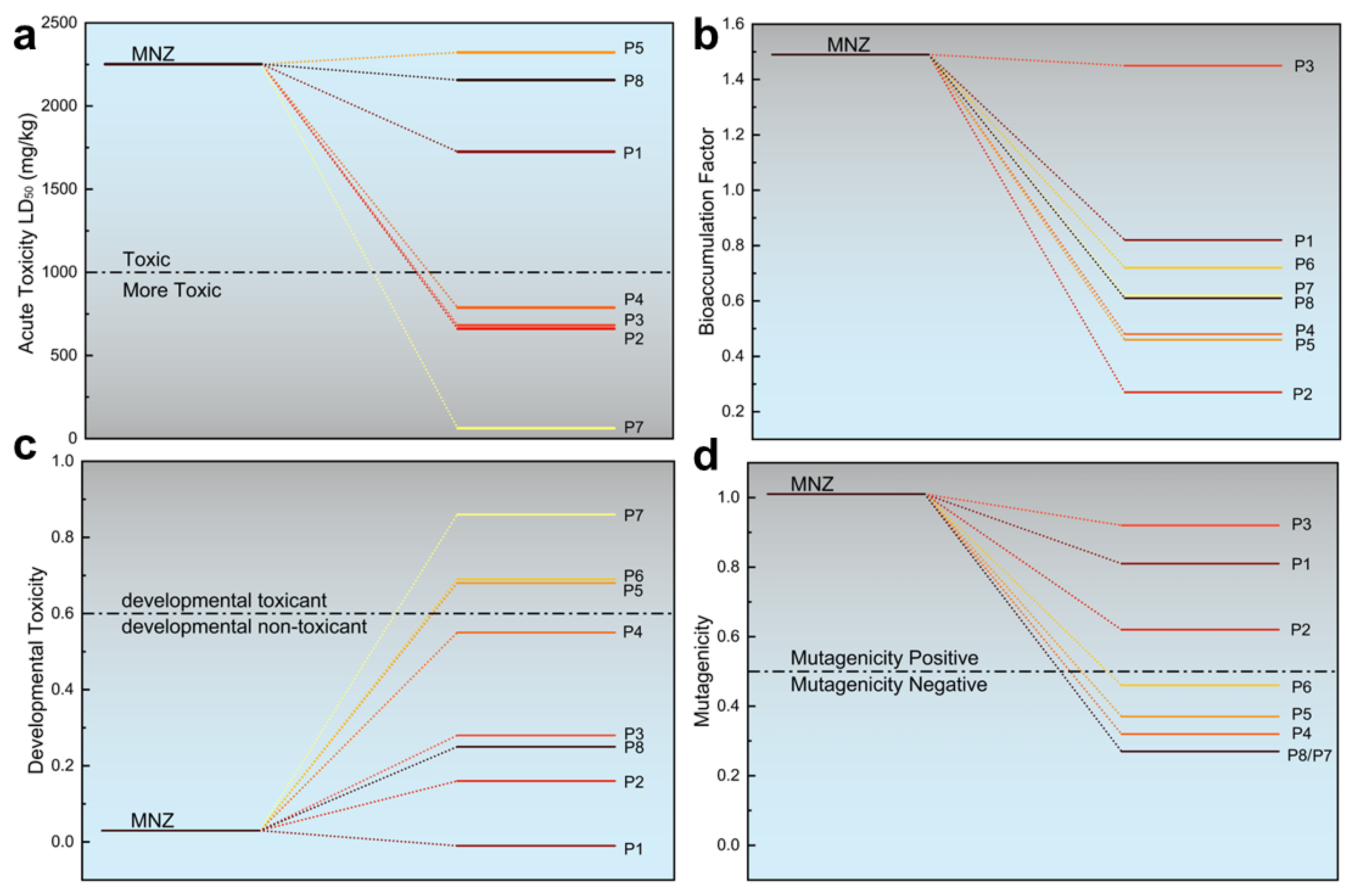
3.6.2. Toxicity Evaluation
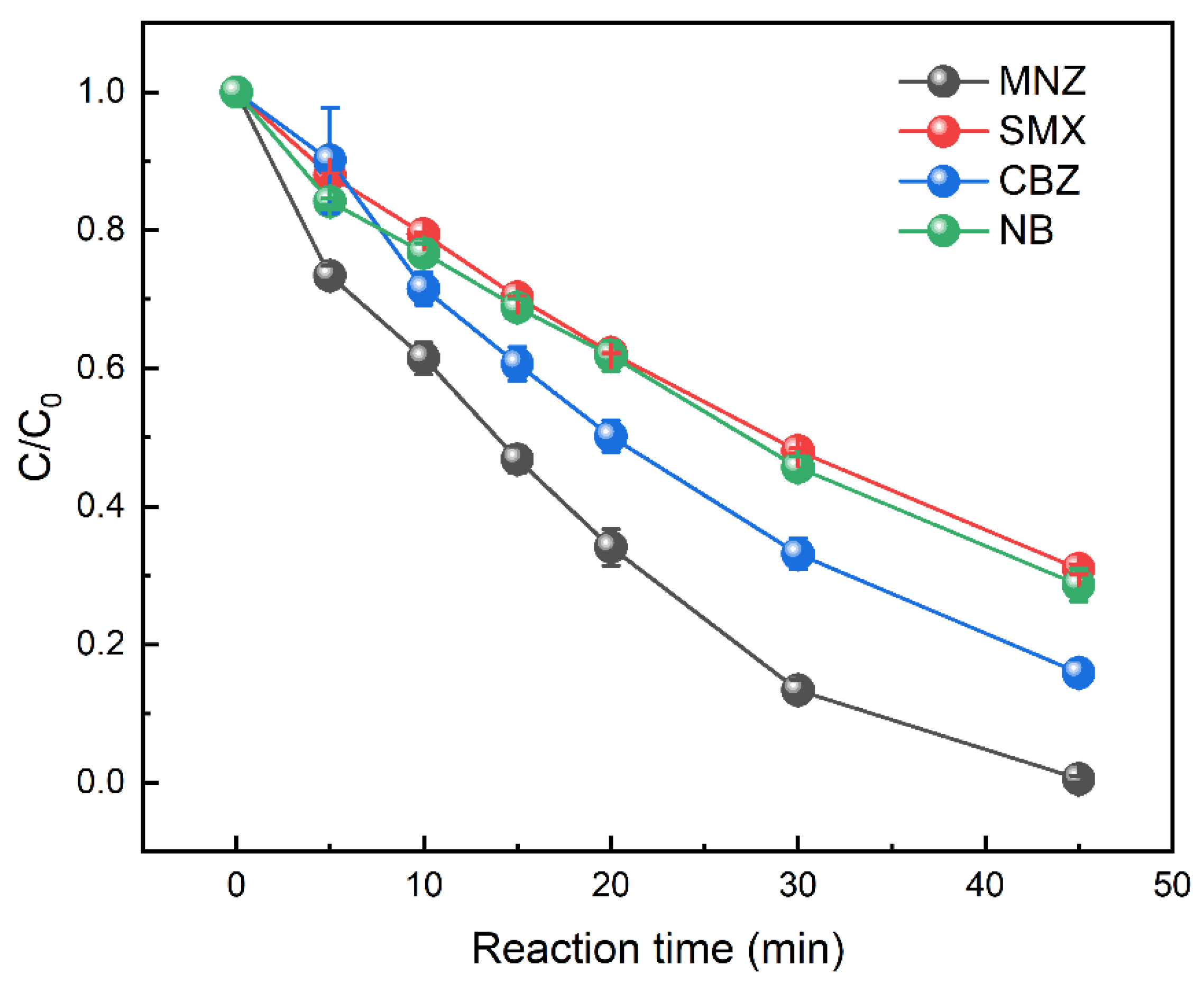
3.7. Removal Efficiency of Other Persistent Organic Pollutants
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Neghi, N.; Kumar, M.; Burkhalov, D. Synthesis and application of stable, reusable TiO2 polymeric composites for photocatalytic removal of metronidazole: Removal kinetics and density functional analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodhar, U.; Reddy, M.V. Impact of pharmaceutical industry treated effluents on the water quality of river Uppanar, South east coast of India: A case study. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerer, K. Resistance in the environment. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moteshaker, P.; Rokni, S.; Farnoodian, N.; Mohassel Akhlaghi, N.; Saadi, S.; Ahmadidoust, G.; Yousefi, A. Application of response surface methodology for optimization of electrochemical process in metronidazole (MNZ) removal from aqueous solutions using stainless steel 316 (SS316) and lead (Pb) anodes. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2020, 18, 20200055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Fu, K.; Deng, H.; Shi, J. Degradation of metronidazole by UV/chlorine treatment: Efficiency, mechanism, pathways and DBPs formation. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.; Fu, K.; Pan, Y.; Liu, J.; Deng, H.; Shi, J. Comparison of Ag and AgI-Modified ZnO as Heterogeneous Photocatalysts for Simulated Sunlight Driven Photodegradation of Metronidazole. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Y. Simultaneous determination of metronidazole, chloramphenicol and 10 sulfonamide residues in honey by LC-MS/MS. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, T. Fabrication of magnetic CuFe2O4@PBC composite and efficient removal of metronidazole by the photo-Fenton process in a wide pH range. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, D.; Ma, X.; Ma, Z. A novel ZnO/biochar composite catalysts for visible light degradation of metronidazole. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Shah, M. Characterisation and bioremediation of wastewater: A review exploring bioremediation as a sustainable technique for pharmaceutical wastewater. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsiou, V.; Filippidis, N.; Mantzavinos, D.; Poulios, I. Heterogeneous and homogeneous photocatalytic degradation of the insecticide imidacloprid in aqueous solutions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 86, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilla, S.; Kaçar, K.Y.; Linden, K.G. Degradation of the pharmaceutical metronidazole via UV, Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Zhou, M.; Du, X.; Xu, X. Enhanced mechanism of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation by electrochemical activation of persulfate on Blue-TiO2 nanotubes anode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, D.S.; Srivastava, V.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Kumar, M. Detoxification of water and wastewater by advanced oxidation processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Yuzhu, X. Electrochemical oxidation technology: A review of its application in high-efficiency treatment of wastewater containing persistent organic pollutants. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 44, 102308. [Google Scholar]
- Radjenovic, J.; Sedlak, D.L. Challenges and Opportunities for Electrochemical Processes as Next-Generation Technologies for the Treatment of Contaminated Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11292–11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, P.; Yadav, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Dubey, B.K. Chlorine mediated indirect electro-oxidation of ammonia using non-active PbO2 anode: Influencing parameters and mechanism identification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Wang, L.; Xue, Q.; Hu, Z.; Pan, B. Multivariate optimization of the pulse electrochemical oxidation for treating recalcitrant dye wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 230, 115851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglada, A.; Urtiaga, A.; Ortiz, I. Contributions of electrochemical oxidation to waste-water treatment: Fundamentals and review of applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Makoś, P.; Boczkaj, G. Treatment of bitumen post oxidative effluents by sulfate radicals based advanced oxidation processes (S-AOPs) under alkaline pH conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczkaj, G.; Fernandes, A. Wastewater treatment by means of advanced oxidation processes at basic pH conditions: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 320, 608–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Dionysiou, D.D. Sulfate radical-based ferrous–peroxymonosulfate oxidative system for PCBs degradation in aqueous and sediment systems. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 85, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zekun, D. Enhanced degradation of contaminants of emerging concern by electrochemically activated peroxymonosulfate: Performance, mechanism, and influencing factors. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128938. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Tang, S.; Yuan, D.; Tang, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, N.; Rao, Y. Improved degradation of anthraquinone dye by electrochemical activation of PDS. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 177, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Shan, L.; Zhang, W.; Shao, X.; Niu, R. Degradation efficiencies of azo dye Acid Orange 7 by the interaction of heat, UV and anions with common oxidants: Persulfate, peroxymonosulfate and hydrogen peroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazime, R.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Ferronato, C.; Salvador, A.; Jaber, F.; Chovelon, J. Comparative study of imazalil degradation in three systems: UV/TiO2, UV/K2S2O8 and UV/TiO2/K2S2O8. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 144, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, X.; Liu, W.; Sun, W.; Cai, M.; Ye, Z.; Yang, C.; Lu, Z.; Li, C. Medium pressure UV-activated peroxymonosulfate for ciprofloxacin degradation: Kinetics, mechanism, and genotoxicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Yao, F.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Yi, K.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Wang, D. Recent advances in photo-activated sulfate radical-advanced oxidation process (SR-AOP) for refractory organic pollutants removal in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lominchar, M.A.; Santos, A.; De Miguel, E.; Romero, A. Remediation of aged diesel contaminated soil by alkaline activated persulfate. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, N.; Tang, H. Sulfate radicals induced degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A with nanoscaled magnetic CuFe2O4 as a heterogeneous catalyst of peroxymonosulfate. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 129, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, X.; Dong, X.; Zhang, X.; Tan, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zheng, S.; Li, C. Synergistic activation of peroxymonosulfate via in situ growth FeCO2O4 nanoparticles on natural rectorite: Role of transition metal ions and hydroxyl groups. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.B.H.; Yang, M.; Liu, R.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Anaerobically-digested sludge disintegration by transition metal ions-activated peroxymonosulfate (PMS): Comparison between Co2+, Cu2+, Fe2+ and Mn2+. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujar, S.K.; Divyapriya, G.; Gogate, P.R.; Nidheesh, P.V. Environmental applications of ultrasound activated persulfate/peroxymonosulfate oxidation process in combination with other activating agents. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 780–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, L.; Sun, X. Catalytic degradation of acid red B in the system of ultrasound/peroxymonosulfate/Fe3O4. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaesang, L.; Urs, V.G.; Jae-Hong, K. Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation: Critical Assessment of Opportunities and Roadblocks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3064–3081. [Google Scholar]
- Wacławek, S.; Lutze, H.V.; Grübel, K.; Padil, V.V.; Černík, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Chemistry of persulfates in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 310, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Yan, L.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Yang, T. Electrochemical activation of persulfates at BDD anode: Radical or nonradical oxidation? Water Res. 2018, 128, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Tien, H.; Bui, D.N.; Manh, T.D.; Tram, N.T.; Ngo, V.D.; Mwazighe, F.M.; Hoang, H.Y.; Le, V.T. Electrochemical degradation of indigo carmine, P-nitrosodimethylaniline and clothianidin on a fabricated Ti/SnO2-Sb/Co-βPbO2 electrode: Roles of radicals, water matrices effects and performance. Chemosphere 2022, 313, 137352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fan, S.; Jin, C.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Ji, J.; She, Z. Electrochemical degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride in sulfate solutions on boron-doped diamond electrode: The accumulation and transformation of persulfate. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Cui, Y.H.; Feng, Y.J.; Xie, Z.M.; Gu, J.D. Reaction pathways and mechanisms of the electrochemical degradation of phenol on different electrodes. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1972–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christos, C. Electrocatalysis in the electrochemical conversion/combustion of organic pollutants for waste water treatment. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.J.; Li, X.Y. Electro-catalytic oxidation of phenol on several metal-oxide electrodes in aqueous solution. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simond, O.; Comninellis, C. Anodic oxidation of organics on Ti/IrO2 anodes using Nafion(R) as electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 1997, 42, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Huang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, I.Y. Understanding the electro-cocatalytic peroxymonosulfate-based systems with BDD versus DSA anodes: Radical versus nonradical dominated degradation mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 309, 123120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; El-Din, M.G. Insight into in-situ radical and non-radical oxidative degradation of organic compounds in complex real matrix during electrooxidation with boron doped diamond electrode: A case study of oil sands process water treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 279, 119366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, A.; Keller, J.; Tait, S.; Radjenovic, J. Removal of Persistent Organic Contaminants by Electrochemically Activated Sulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14326–14333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ding, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Electrochemical activation of peroxymonosulfate with ACF cathode: Kinetics, influencing factors, mechanism, and application potential. Water Res. 2019, 159, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBeath, S.T.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Graham, N.J.D. Application of boron-doped diamond electrodes for the anodic oxidation of pesticide micropollutants in a water treatment process: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 2090–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Dai, C.; Tian, X.; Nie, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, Y. Effects of Lewis acid-base site and oxygen vacancy in MgAl minerals on peroxymonosulfate activation towards sulfamethoxazole degradation via radical and non-radical mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, C.B.; Fu, X.Z.; Cui, S.; Lu, J.Y.; Liu, H.Q.; Li, W.W. Interactions between chlorophenols and peroxymonosulfate: pH dependency and reaction pathways. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J.; Gao, Y.; Ma, J.; Pang, S.Y.; Li, J.; Lu, X.T.; Yuan, L.P. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Benzoquinone: A Novel Nonradical Oxidation Process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12941–12950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, L. Dolomite as a low-cost peroxymonosulfate activator for the efficient degradation of tetracycline: Performance, mechanism and toxicity evolution. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Chen, T.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Zou, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, F.; Zhai, P.; Xia, M.; Liu, M. Degradation of norfloxacin by calcite activating peroxymonosulfate: Performance and mechanism. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, F.; Liu, Z.; Kang, X.; Cheng, C.; Mao, X.; Li, R.; Lin, H.; Zhang, H. Electro-enhanced heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate via acceleration of Fe(III)/Fe(II) redox cycle on Fe-B catalyst. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 377, 138073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, W.; Li, Y.; He, D.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, J.; You, X.; Wang, K.; Zhou, G.; Peng, G. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by pyrophosphate for the degradation of AO7 at neutral pH. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 47549–47560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Sun, H.Y.; Zhang, S.; Su, X. Structure-property relationship and mechanism of peroxymonosulfate activation by nitrogen-doped biochar for organic contaminant oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 609, 15294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhou, L.; Ferronato, C.; Chovelon, J. Non-activated peroxymonosulfate oxidation of sulfonamide antibiotics in water: Kinetics, mechanisms, and implications for water treatment. Water Res. 2018, 147, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Hussain, I.; Huang, R. Insight into the degradation of methomyl in water by peroxymonosulfate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Sheng, B.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, R.; Xiao, D.; Liu, J. Deciphering the degradation/chlorination mechanisms of maleic acid in the Fe(II)/peroxymonosulfate process: An often overlooked effect of chloride. Water Res. 2018, 145, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Jing, Y.; Chaplin, B.P. Development and Characterization of Ultrafiltration TiO2 Magneli Phase Reactive Electrochemical Membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1428–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinea, E.; Arias, C.; Cabot, P.L.; Garrido, J.A.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Centellas, F.; Brillas, E. Mineralization of salicylic acid in acidic aqueous medium by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes using platinum and boron-doped diamond as anode and cathodically generated hydrogen peroxide. Water Res. 2008, 42, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; Martinez-Huitle, C.A. Nature, Mechanisms and Reactivity of Electrogenerated Reactive Species at Thin-Film Boron-Doped Diamond (BDD) Electrodes During Electrochemical Wastewater Treatment. Chemelectrochem 2019, 6, 2379–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Bu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Kabutey, F.T.; Wei, L.; Dionysiou, D.D. Electrochemical activation of persulfate on BDD and DSA anodes: Electrolyte influence, kinetics and mechanisms in the degradation of bisphenol A. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Gao, S.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Xia, X. Enhanced performance of LaFeO3 perovskite for peroxymonosulfate activation through strontium doping towards 2,4-D degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayla, M.; Ju, Y.Y.; Jeanluc, A.A. Estimation of Singlet Oxygen Quantum Yield Using Novel Green-Absorbing Baird-type Aromatic Photosensitizers. Photochem. Photobiol. 2021, 98, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Liu, F.; Xinyuan, D.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C.; Offiong, N.O.; Bi, Y.; Zeng, W.; Ren, H. Removal of metronidazole from wastewater by electrocoagulation with chloride ions electrolyte: The role of reactive chlorine species and process optimization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soufan, M.; Deborde, M.; Delmont, A.; Legube, B. Aqueous chlorination of carbamazepine: Kinetic study and transformation product identification. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5076–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Y.; Bao, Z.C.; Barker, J.R. Free Radical Reactions Involving Cl•, Cl2−•, and SO4−• in the 248 nm Photolysis of Aqueous Solutions Containing S2O82− and Cl. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 108, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Y.; Barker, J.R. Hydrogen Peroxide Photolysis in Acidic Aqueous Solutions Containing Chloride Ions. II. Quantum Yield of HO•(Aq) Radicals. J. Phys. Chem. A 2003, 107, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Cui, X.; Yan, B.; Song, Y.; Li, N.; Chen, G.; Wang, S. Effect of phosphates on oxidative species generation and sulfamethoxazole degradation in a pig manure derived biochar activated peroxymonosulfate system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Liu, X.; Liu, B.; Akram, M.; Li, Y.; Pan, J.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Xu, X. Effect of phosphate on peroxymonosulfate activation: Accelerating generation of sulfate radical and underlying mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 298, 120532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhu, X.J.; Shanshan, Y.; Tian, S.; Li, Y.; Bo, L.; Pan, Z.; Li, H. Novel strategy for the efficient degradation of organic contaminants using porous graphite electrodes: Synergistic mechanism of anodic and cathodic reactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.L.; Fu, C.; Juang, R. Removal of metronidazole by TiO2 and ZnO photocatalysis: A comprehensive comparison of process optimization and transformation products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 28285–28295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Wavelength (nm) | Mobile Phase A | Mobile Phase B | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrapure Water (%) | 0.1% (v/v) Acetic Acid Solution (%) | Acetonitrile (%) | Methyl Alcohol (%) | ||
| MNZ | 318 | 80 | N.A. | 20 | N.A. |
| SMX | 265 | N.A. | 60 | 40 | N.A. |
| CBZ | 284 | 60 | N.A. | 40 | N.A. |
| BA | 230 | 50 | N.A. | 50 | N.A. |
| NB | 262 | N.A. | 50 | 50 | N.A. |
| p-HBA/p-BQ | 246 | 70 | N.A. | 30 | N.A. |
| Coded Levels | A: Current Density (mA/cm2) | B: Initial pH | C: PMS Dosage (mmol·L−1) | D: Reaction Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 (Low) | 11.1 | 3 | 1 | 25 |
| 0 (Medium) | 22.2 | 6 | 3 | 35 |
| 1 (High) | 33.3 | 9 | 5 | 45 |
| Standard Order | Run Order | Current Density (mA/cm2) | pH (1) | PMS Dosage (mmol·L−1) | Reaction Time (min) | MNZ Removal Rate (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 1 | 22.2 | 6 | 5 | 45 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 33.3 | 3 | 3 | 35 | 1 |
| 27 | 3 | 22.2 | 6 | 3 | 35 | 0.94103 |
| 23 | 4 | 22.2 | 3 | 3 | 45 | 1 |
| 19 | 5 | 11.1 | 6 | 5 | 35 | 0.86044 |
| 26 | 6 | 22.2 | 6 | 3 | 35 | 0.9398 |
| 22 | 7 | 22.2 | 9 | 3 | 25 | 0.74029 |
| 29 | 8 | 22.2 | 6 | 3 | 35 | 0.9407 |
| 15 | 9 | 22.2 | 3 | 5 | 35 | 0.98338 |
| 28 | 10 | 22.2 | 6 | 3 | 35 | 0.9426 |
| 3 | 11 | 11.1 | 9 | 3 | 35 | 0.76985 |
| 14 | 12 | 22.2 | 9 | 1 | 35 | 0.78515 |
| 4 | 13 | 33.3 | 9 | 3 | 35 | 0.98794 |
| 17 | 14 | 11.1 | 6 | 1 | 35 | 0.6179 |
| 11 | 15 | 11.1 | 6 | 3 | 45 | 0.79368 |
| 16 | 16 | 22.2 | 9 | 5 | 35 | 0.92868 |
| 5 | 17 | 22.2 | 6 | 1 | 25 | 0.6271 |
| 20 | 18 | 33.3 | 6 | 5 | 35 | 0.9948 |
| 18 | 19 | 33.3 | 6 | 1 | 35 | 0.9013 |
| 9 | 20 | 11.1 | 6 | 3 | 25 | 0.54074 |
| 25 | 21 | 22.2 | 6 | 3 | 35 | 0.9412 |
| 21 | 22 | 22.2 | 3 | 3 | 25 | 0.81912 |
| 12 | 23 | 33.3 | 6 | 3 | 45 | 0.99603 |
| 24 | 24 | 22.2 | 9 | 3 | 45 | 1 |
| 10 | 25 | 33.3 | 6 | 3 | 25 | 0.94412 |
| 6 | 26 | 22.2 | 6 | 5 | 25 | 0.805 |
| 13 | 27 | 22.2 | 3 | 1 | 35 | 0.84191 |
| 1 | 28 | 11.1 | 3 | 3 | 35 | 0.80368 |
| 7 | 29 | 22.2 | 6 | 1 | 45 | 0.9258 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p Value Prob > F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.43 | 14 | 0.031 | 32.24 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A-current density | 0.17 | 1 | 0.17 | 179.54 | <0.0001 | |
| B-initial pH | 4.648 × 10−3 | 1 | 4.648 × 10−3 | 4.84 | 0.0450 | |
| C-initial PMS concentration | 0.064 | 1 | 0.064 | 65.79 | <0.0001 | |
| D-reaction time | 0.13 | 1 | 0.13 | 133.92 | <0.0001 | |
| AB | 1.185 × 10−4 | 1 | 1.185 × 10−4 | 0.12 | 0.7305 | |
| AC | 5.553 × 10−3 | 1 | 5.553 × 10−3 | 5.79 | 0.0305 | |
| AD | 0.010 | 1 | 0.010 | 10.53 | 0.0059 | |
| BC | 1.061 × 10−6 | 1 | 1.061 × 10−6 | 1.106 × 10−3 | 0.9739 | |
| BD | 1.554 × 10−3 | 1 | 1.554 × 10−3 | 1.62 | 0.2240 | |
| CD | 2.830 × 10−3 | 1 | 2.830 × 10−3 | 2.95 | 0.1079 | |
| A2 | 0.020 | 1 | 0.020 | 20.79 | 0.0004 | |
| B2 | 3.487 × 10−6 | 1 | 3.487 × 10−6 | 3.634 × 10−3 | 0.9528 | |
| C2 | 0.015 | 1 | 0.015 | 15.25 | 0.0016 | |
| D2 | 0.021 | 1 | 0.021 | 22.30 | 0.0003 | |
| Residual | 0.013 | 14 | 9.596 × 10−4 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 0.013 | 10 | 1.343 × 10−3 | 1307.41 | <0.0001 | significant |
| Pure Error | 4.109 × 10−6 | 4 | 1.027 × 10−6 | |||
| Cor Total | 0.45 | 28 |
| Pollutant | Current Intensity (A) | Voltage (V) | Volume (L) | Kobs (min−1) | EE/O (kWh m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMX | 0.3 | 11.6 | 0.16 | 0.026 | 32.3 |
| CBZ | 0.3 | 11.8 | 0.16 | 0.041 | 20.6 |
| NB | 0.3 | 11.5 | 0.16 | 0.027 | 30.5 |
| MNZ | 0.3 | 11.7 | 0.16 | 0.111 | 7.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, H.; Fang, J.; Wang, J.; Long, X.; Zhang, I.Y.; Huang, R. Effective Degradation of Metronidazole through Electrochemical Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: Mechanistic Insights and Implications. Energies 2024, 17, 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071750
Liao H, Fang J, Wang J, Long X, Zhang IY, Huang R. Effective Degradation of Metronidazole through Electrochemical Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: Mechanistic Insights and Implications. Energies. 2024; 17(7):1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071750
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Haicen, Jingkai Fang, Jiahao Wang, Xianhu Long, Igor Ying Zhang, and Rongfu Huang. 2024. "Effective Degradation of Metronidazole through Electrochemical Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: Mechanistic Insights and Implications" Energies 17, no. 7: 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071750
APA StyleLiao, H., Fang, J., Wang, J., Long, X., Zhang, I. Y., & Huang, R. (2024). Effective Degradation of Metronidazole through Electrochemical Activation of Peroxymonosulfate: Mechanistic Insights and Implications. Energies, 17(7), 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071750





