A Review of Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Markets: Enabling Models and Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A detailed analysis of different P2P market architectures as well as different market mechanisms is presented. In addition, different bidding strategies and auction models that enable effective P2P energy trading are compared and evaluated.
- Different solution methods for P2P energy trading problems such as game theory, mathematical optimisation, and machine learning-based techniques are reviewed. The analysis helps evaluate the suitability of the aforementioned solution methods towards the P2P energy trading applications.
- The challenges associated with the P2P energy trading implementation in real-life platforms are reviewed. Finally, a number of innovative solutions which can further enhance the effectiveness of P2P energy trading are proposed for future research.
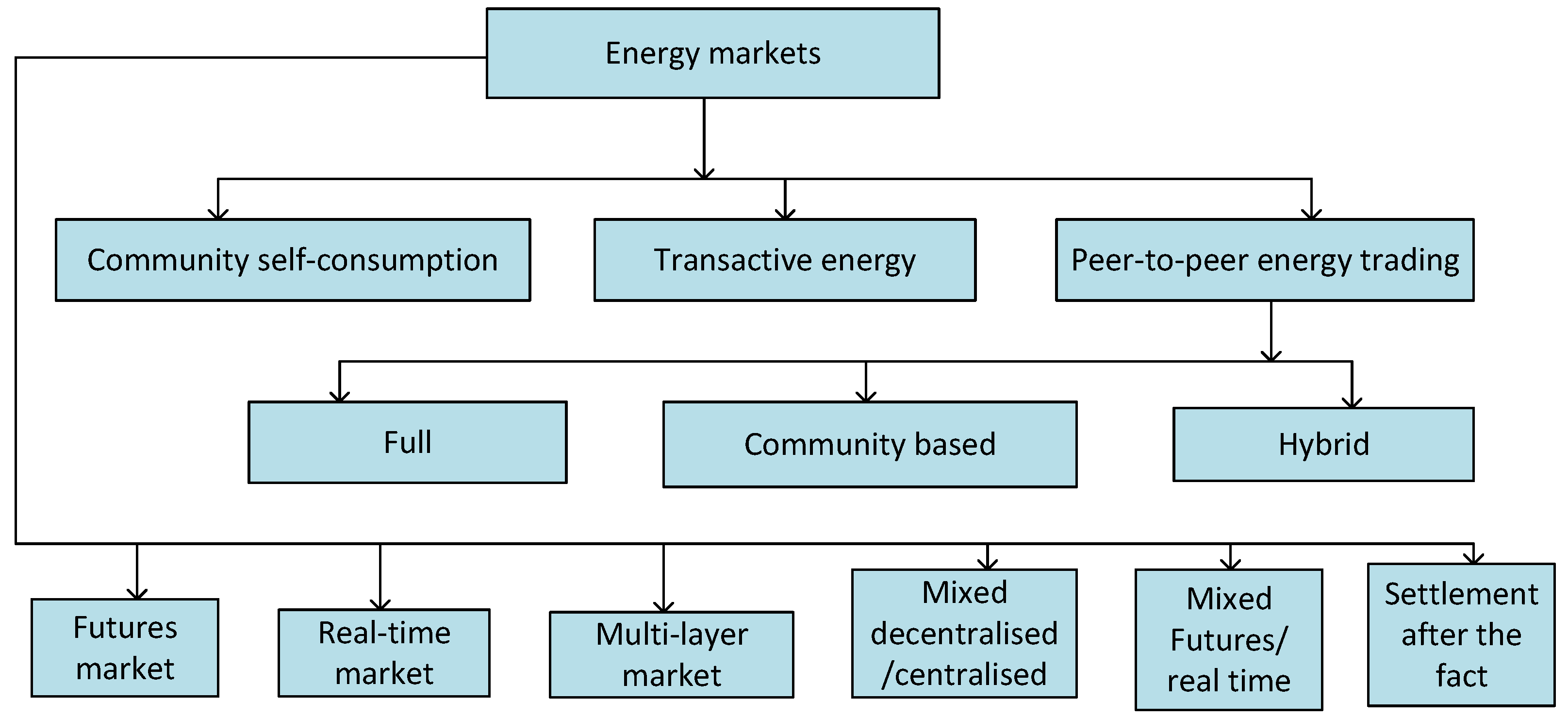
2. Overview of P2P Market Structure
3. P2P Energy Trading Platforms
4. P2P Energy Trading Techniques
4.1. Game Theoretic Approaches
4.2. Mathematical Optimisation
4.3. Auction Methods
4.4. Machine Learning Approaches
5. Challenges in P2P Energy Trading
6. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capper, T.; Gorbatcheva, A.; Mustafa, M.A.; Bahloul, M.; Schwidtal, J.M.; Chitchyan, R.; Andoni, M.; Robu, V.; Montakhabi, M.; Scott, I.J.; et al. Peer-to-peer, community self-consumption, and transactive energy: A systematic literature review of local energy market models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 162, 112403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, M.; Long, C. Peer-to-Peer energy trading in a Microgrid. Appl. Energy 2018, 220, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Sustainable Development. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- Shah, W.U.H.; Hao, G.; Yan, H.; Yasmeen, R.; Padda, I.U.H.; Ullah, A. The impact of trade, financial development and government integrity on energy efficiency: An analysis from G7-Countries. Energy 2022, 255, 124507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvelplund, F. Renewable energy and the need for local energy markets. Energy 2006, 31, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.S.; Soares, T.; Orlandini, T.; Oliveira, C.; Sousa, T.; Pinson, P.; Matos, M. P2P market coordination methodologies with distribution grid management. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 34, 101075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xu, Q.; Li, S.; Tang, R.; Du, P. Reviewing the peer-to-peer transactive energy market: Trading environment, optimization methodology, and relevant resources. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengelkamp, E.; Gärttner, J.; Rock, K.; Kessler, S.; Orsini, L.; Weinhardt, C. Designing microgrid energy markets: A case study: The Brooklyn Microgrid. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, T.; Soares, T.; Pinson, P.; Moret, F.; Baroche, T.; Sorin, E. Peer-to-peer and community-based markets: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 104, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Thomas, L.; Cheng, M.; Jenkins, N. Peer-to-peer energy trading in a community microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 16–20 July 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Long, C. Evaluation of peer-to-peer energy sharing mechanisms based on a multiagent simulation framework. Appl. Energy 2018, 222, 993–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yu, X.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Ma, L.; Lei, J. Energy-sharing model with price-based demand response for microgrids of peer-to-peer prosumers. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 3569–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Jenkins, N. Peer-to-peer energy sharing through a two-stage aggregated battery control in a community Microgrid. Appl. Energy 2018, 226, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Dang, W.; Peng, F.; Mahesuti, R.; Zhang, L.; Sun, K. A decentralized peer-to-peer energy trading strategy considering flexible resource involvement and renewable energy uncertainty. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 152, 109275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, W.; Han, Z.; Poor, H.V.; Basar, T. Game-theoretic methods for the smart grid: An overview of microgrid systems, demand-side management, and smart grid communications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, C.; Tsimopoulos, E.; Georgiadis, M. A Review on the Complementarity Modelling in Competitive Electricity Markets. Energies 2021, 14, 7133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Cho, K.S.; Son, S.Y. Voltage Management Method of Distribution System in P2P Energy Transaction Environment. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Tan, X.; Sun, B.; Wu, Y.; Tsang, D.H. Energy management of cooperative microgrids: A distributed optimization approach. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 96, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, N.K.; Yang, J.; Zacharis, E. Optimisation framework for the design and operation of open-market urban and remote community microgrids. Appl. Energy 2019, 252, 113399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Su, W. Local Energy Trading Behavior Modeling With Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 62806–62814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Lee, B. Automatic P2P Energy Trading Model Based on Reinforcement Learning Using Long Short-Term Delayed Reward. Energies 2020, 13, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebi, H.; Khodoomi, M.; Seif, M.; Pishvaee, M.; Hanne, T. The benefits of peer-to-peer renewable energy trading and battery storage backup for local grid. J. Energy Storage 2023, 63, 106970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Wei, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Q.; Mei, S. A peer-to-peer energy trading market embedded with residential shared energy storage units. Appl. Energy 2022, 308, 118400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, C.N.; Tsimopoulos, E.G.; Georgiadis, M.C. Strategic bidding of an energy storage agent in a joint energy and reserve market under stochastic generation. Energy 2022, 242, 123026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwidtal, J.; Piccini, P.; Troncia, M.; Chitchyan, R.; Montakhabi, M.; Francis, C.; Gorbatcheva, A.; Capper, T.; Mustafa, M.; Andoni, M.; et al. Emerging business models in local energy markets: A systematic review of peer-to-peer, community self-consumption, and transactive energy models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 179, 113273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faia, R.; Lezama, F.; Soares, J.; Pinto, T.; Vale, Z. Local electricity markets: A review on benefits, barriers, current trends and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 190, 114006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaousoglou, G.; Giraldo, J.S.; Paterakis, N.G. Market Mechanisms for Local Electricity Markets: A review of models, solution concepts and algorithmic techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 156, 111890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Chung, Y.S.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, H.T.; Jin, Y.G.; Yoon, Y.T. Pricing mechanisms for peer-to-peer energy trading: Towards an integrated understanding of energy and network service pricing mechanisms. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 183, 113435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.; Gebbran, D.; Mhanna, S.; Chapman, A.C.; Verbič, G. Towards a transactive energy system for integration of distributed energy resources: Home energy management, distributed optimal power flow, and peer-to-peer energy trading. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 132, 110000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.I.; Tushar, W.; Saha, T.K.; Yuen, C.; Smith, D. Peer-to-peer kilowatt and negawatt trading: A review of challenges and recent advances in distribution networks. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 169, 112908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, S.; Cherukuri, S.H.C.; Pindoriya, N.M. Peer-to-peer energy trading in smart grid: Frameworks, implementation methodologies, and demonstration projects. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 214, 108907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhsen, H.; Allahham, A.; Al-Halhouli, A.; Al-Mahmodi, M.; Alkhraibat, A.; Hamdan, M. Business Model of Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading: A Review of Literature. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parliament, E. Council of the European Union Directive (EU) 2018/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 December 2018 on the promotion of the use of energy from renewable sources. Off. J. Eur. Union 2018, 328, 1–128. [Google Scholar]
- NIST. Transactive Energy: An Overview. 2017. Available online: https://www.nist.gov/el/smart-grid-menu/hot-topics/transactive-energy-overview (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Chen, S.; Liu, C. From demand response to transactive energy: State of the art. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2017, 5, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorin, E.; Bobo, L.; Pinson, P. Consensus-Based Approach to Peer-to-Peer Electricity Markets with Product Differentiation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moret, F.; Pinson, P. Energy Collectives: A Community and Fairness Based Approach to Future Electricity Markets. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 3994–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tushar, W.; Chai, B.; Yuen, C.; Huang, S.; Smith, D.B.; Poor, H.V.; Yang, Z. Energy Storage Sharing in Smart Grid: A Modified Auction-Based Approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 1462–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasany, M.; Mishra, Y.; Ledwich, G. A Decentralized Bilateral Energy Trading System for Peer-to-Peer Electricity Markets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 4646–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, M.; Al-Wakeel, A. Feasibility of Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading in Low Voltage Electrical Distribution Networks. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 2227–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepter, J.M.; Lüth, A.; Crespo del Granado, P.; Egging, R. Prosumer integration in wholesale electricity markets: Synergies of peer-to-peer trade and residential storage. Energy Build. 2019, 184, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Baarslag, T.; Kaisers, M. Automated peer-to-peer negotiation for energy contract settlements in residential cooperatives. Appl. Energy 2020, 259, 114173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.N. A New Pricing Scheme for Intra-Microgrid and Inter-Microgrid Local Energy Trading. Energies 2019, 8, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüth, A.; Zepter, J.M.; Crespo del Granado, P.; Egging, R. Local electricity market designs for peer-to-peer trading: The role of battery flexibility. Appl. Energy 2018, 229, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Taha, A.F.; Wang, J.; Kvaternik, K.; Hahn, A. Energy Crowdsourcing and Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading in Blockchain-Enabled Smart Grids. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 49, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cali, U.; Çakir, O. Energy Policy Instruments for Distributed Ledger Technology Empowered Peer-to-Peer Local Energy Markets. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 82888–82900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shahidehpour, M.; Alabdulwahab, A.; Al-Turki, Y. Valuation of distributed energy resources in active distribution networks. Electr. J. 2019, 32, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behboodi, S.; Chassin, D.P.; Djilali, N.; Crawford, C. Transactive control of fast-acting demand response based on thermostatic loads in real-time retail electricity markets. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, T.; Faia, R.; Ghazvini, M.A.F.; Soares, J.; Corchado, J.M.; Vale, Z. Decision Support for Small Players Negotiations Under a Transactive Energy Framework. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 4015–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires Klein, L.; Krivoglazova, A.; Matos, L.; Landeck, J.; de Azevedo, M. A novel peer-to-peer energy sharing business model for the portuguese energy market. Energies 2019, 13, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tushar, W.; Saha, T.K.; Yuen, C.; Morstyn, T.; McCulloch, M.D.; Poor, H.V.; Wood, K.L. A motivational game-theoretic approach for peer-to-peer energy trading in the smart grid. Appl. Energy 2019, 243, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Lin, J.; Song, Y. Trading strategy optimization for a prosumer in continuous double auction-based peer-to-peer market: A prediction-integration model. Appl. Energy 2019, 242, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.; Chapman, A.C.; Verbič, G. Decentralized P2P Energy Trading Under Network Constraints in a Low-Voltage Network. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 5163–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, N.; Chi, Y. A novel electricity transaction mode of microgrids based on blockchain and continuous double auction. Energies 2017, 10, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Kim, J. Reinforcement learning based peer-to-peer energy trade management using community energy storage in local energy market. Energies 2021, 14, 4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Pipattanasomporn, M.; Rahman, S. Comparative analysis of auction mechanisms and bidding strategies for P2P solar transactive energy markets. Appl. Energy 2019, 255, 113687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piclo Flex. Piclo. Available online: https://picloflex.com/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Long, C.; Cheng, M. Review of Existing Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Projects. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 2563–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandherm, B.; Baus, J.; Frey, J. Peer energy cloud–civil marketplace for trading renewable energies. In Proceedings of the 2012 Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Environments, Guanajuato, Mexico, 26–29 June 2012; pp. 375–378. [Google Scholar]
- Pebbles. Peer to Peer Energy Trading Based on Blockchain Infrastructure. Available online: https://pebbles-projekt.de/en/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Lichtblick. Now for the Solar System with Storage for More Independence. Available online: https://www.lichtblick.de/zuhause/solar/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Jemma Green, P.N.; Forse, N. RENeW Nexus: Enabling Resilient, Low Cost & Localised Electricity Markets through Blockchain P2P & VPP Trading. 2020. Available online: https://assets.website-files.com/5fc9b61246966c23f17d2601/607e724f8dfb1a2d5928bbc0_renew-nexus-project-report.pdf (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Enapter. Solar-Battery-Hydrogen Microgrid. Available online: https://www.enapter.com/application/solar-battery-hydrogen-microgrid#21491 (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Danmarks Tekniske Universitet (DTU). The Energy Collective. 2016. Available online: https://energiforskning.dk/en/node/15513 (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Verma, P.; O’Regan, B.; Hayes, B.; Thakur, S.; Breslin, J.G. EnerPort: Irish Blockchain project for peer-to-peer energy trading. Energy Inform. 2018, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partz, H. Japan’s Kanto Region to Track Surplus Solar Energy with Power Ledger. 2019. Available online: https://cointelegraph.com/news/japans-kanto-region-to-track-surplus-solar-energy-with-power-ledger (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- NRGcoin. What is NRGcoin? 2023. Available online: https://nrgcoin.org/about/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- SEDA. Malaysia’s 1st Pilot Run of Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Energy Trading. 2020. Available online: https://www.seda.gov.my/malaysias-1st-pilot-run-of-peer-to-peer-p2p-energy-trading/ (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Gunarathna, C.L.; Yang, R.J.; Jayasuriya, S.; Wang, K. Reviewing global peer-to-peer distributed renewable energy trading projects. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2022, 89, 102655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooklyn Microgrid. Available online: https://www.brooklyn.energy/about (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Powerledger. Uttar Pradesh Power Corporation Limited Launches First P2P Solar Power Trading in South Asia. 2020. Available online: https://www.powerledger.io/media/uttar-pradesh-power-corporation-limited-launches-first-p2p-solar-power-trading-in-south-asia (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Başar, T.; Olsder, G.J. Dynamic Noncooperative Game Theory; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Soto, E.A.; Bosman, L.B.; Wollega, E.; Leon-Salas, W.D. Peer-to-peer energy trading: A review of the literature. Appl. Energy 2021, 283, 116268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wang, Y.W.; Liu, N. Distributed game-based pricing strategy for energy sharing in microgrid with PV prosumers. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2018, 12, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.; Lee, H.W. A real-time framework for matching prosumers with minimum risk in the cluster of microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 2832–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cadre, H.; Jacquot, P.; Wan, C.; Alasseur, C. Peer-to-peer electricity market analysis: From variational to generalized Nash equilibrium. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 282, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tushar, W.; Yuen, C.; Mohsenian-Rad, H.; Saha, T.; Poor, H.V.; Wood, K.L. Transforming energy networks via peer-to-peer energy trading: The potential of game-theoretic approaches. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Morstyn, T.; McCulloch, M. Incentivizing prosumer coalitions with energy management using cooperative game theory. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 34, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenschein, J.S. Understanding Mechanism Design—Part 2 of 3: The Vickrey-Clarke-Groves Mechanism. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 80–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Morstyn, T.; McCulloch, M. Estimation of the shapley value of a peer-to-peer energy sharing game using multi-step coalitional stratified sampling. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2021, 19, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Morstyn, T.; McCulloch, M.D. Scaling up cooperative game theory-based energy management using prosumer clustering. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 12, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Li, Q.; Song, W.; Li, G. Robust distributed optimization for energy dispatch of multi-stakeholder multiple microgrids under uncertainty. Appl. Energy 2019, 255, 113845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoratti, D.; Matamoros, J. Distributed Energy Trading: The Multiple-Microgrid Case. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2551–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, S.; He, J.; Yang, B.; Guan, X. Credit rating based real-time energy trading in microgrids. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morstyn, T.; McCulloch, M.D. Multiclass Energy Management for Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Driven by Prosumer Preferences. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 4005–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex Optimization; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hiriart-Urruty, J.B.; Lemaréchal, C. Fundamentals of Convex Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lobo, M.S.; Vandenberghe, L.; Boyd, S.; Lebret, H. Applications of second-order cone programming. Linear Algebra Appl. 1998, 284, 193–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterov, Y.; Nemirovskii, A. Interior-Point Polynomial Algorithms in Convex Programming; Studies in Applied and Numerical Mathematics; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Chatterjee, R. Understanding Auctions; Routledge: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, A.K.; Nalebuff, B.J. The Art of Strategy: A Game Theorist’s Guide to Success in Business and Life; Norton: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, D. The Double Auction Market: Institutions, Theories, and Evidence; Routledge: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Shah, S.B.H.; Usman, S.; Mahfoudh, S.; KS, F.S.; Shukla, P.K. Resource allocation and network pricing based on double auction in mobile edge computing. J. Cloud Comput. 2023, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roughgarden, T.; Nisan, N. Algorithmic Game Theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, D.; Zeng, S. A Discounted Trade Reduction Mechanism for Dynamic Ridesharing Pricing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAfee, R. A dominant strategy double auction. J. Econ. Theory 1992, 56, 434–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellman, M.P. Continuous Double Auctions; Synthesis Lectures on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liaquat, S.; Hussain, T.; Celik, B.; Fourney, R.; Hansen, T.M. Day-ahead continuous double auction-based peer-to-peer energy trading platform incorporating trading losses and network utilisation fee. IET Smart Grid 2023, 6, 312–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokkisam, H.R.; Singh, S.; Acharya, R.M.; Selvan, M. Blockchain-based peer-to-peer transactive energy system for community microgrid with demand response management. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 8, 198–211. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.M.P.; Kiekintveld, C.; Tran, S.; Yeoh, W. Bidding in Periodic Double Auctions Using Heuristics and Dynamic Monte Carlo Tree Search. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Satterthwaite, M.A.; Williams, S.R. The Bayesian theory of the k-double auction. In The Double Auction Market; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; pp. 99–124. [Google Scholar]
- Angaphiwatchawal, P.; Sompoh, C.; Chaitusaney, S. A Multi-k Double Auction Pricing Mechanism for Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Market of Prosumers. In Proceedings of the 2021 18th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (ECTI-CON), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 19–22 May 2021; pp. 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, S.; Hayes, B.P.; Breslin, J.G. Distributed double auction for peer to peer energy trade using blockchains. In Proceedings of the 2018 5th International Symposium on Environment-Friendly Energies and Applications (EFEA), Rome, Italy, 24–26 September 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bandara, K.Y.; Thakur, S.; Breslin, J. Flocking-based decentralised double auction for P2P energy trading within neighbourhoods. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 129, 106766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. Deep reinforcement learning for energy trading and load scheduling in residential peer-to-peer energy trading market. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 147, 108885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Ye, Y.; Papadaskalopoulos, D.; Strbac, G. Scalable coordinated management of peer-to-peer energy trading: A multi-cluster deep reinforcement learning approach. Appl. Energy 2021, 292, 116940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Wang, J.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Strbac, G. Mean-Field Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Peer-to-Peer Multi-Energy Trading. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2023, 38, 4853–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Xue, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Sun, M. Federated reinforcement learning for smart building joint peer-to-peer energy and carbon allowance trading. Appl. Energy 2023, 333, 120526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Wu, H. Uncertainty energy planning of net-zero energy communities with peer-to-peer energy trading and green vehicle storage considering climate changes by 2050 with machine learning methods. Appl. Energy 2022, 321, 119394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, S.; Pishvaee, M.S.; Dashti, R. Privacy-preserving energy trading management in networked microgrids via data-driven robust optimization assisted by machine learning. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 34, 101011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Ouyang, T.; Wu, J. A Sentiment-Aware Trading Volume Prediction Model for P2P Market Using LSTM. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 81934–81944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Eliassen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jacobsen, H.A. Detecting False Data Injection Attacks in Peer to Peer Energy Trading Using Machine Learning. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2022, 19, 3417–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukar, A.L.; Hamza, M.F.; Ayub, S.; Abobaker, A.K.; Modu, B.; Mohseni, S.; Brent, A.C.; Ogbonnaya, C.; Mustapha, K.; Idakwo, H.O. Peer-to-peer electricity trading: A systematic review on current developments and perspectives. Renew. Energy Focus 2023, 44, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochupurackal, A.; Pancholi, K.P.; Islam, S.N.; Anwar, A.; Oo, A.M.T. Rolling horizon optimisation based peer-to-peer energy trading under real-time variations in demand and generation. Energy Syst. 2023, 14, 541–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Paper | Market Structure | Game Theory | Optimisation Algorithms | Machine Learning | Bidding Strategies | Auction Models |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [9] | ✓ | × | × | × | × | × |
| [25] | ✓ | × | ✓ | × | ✓ | × |
| [26] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | ✓ |
| [27] | × | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ |
| [28] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | ✓ |
| [29] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ |
| [30] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ |
| [7] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | × |
| [31] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ |
| [32] | ✓ | ✓ | × | × | ✓ | ✓ |
| This paper | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Optimisation Algorithm | Distinct Features |
|---|---|
| Linear programming | Linear objective function with linear constraints |
| Mixed integer linear programming | Variables can be a combination of integer and floating point numbers |
| Convex programming | Objective function and constraints should be convex |
| Second-order cone programming | Linear objective minimised over a second-order quadratic cone |
| Quadratically constrained quadratic programming | Quadratic objective function with quadratic constraints |
| Non-convex programming | Non-convex objective and/or non-convex constraints |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, S.N. A Review of Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Markets: Enabling Models and Technologies. Energies 2024, 17, 1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071702
Islam SN. A Review of Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Markets: Enabling Models and Technologies. Energies. 2024; 17(7):1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071702
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Shama Naz. 2024. "A Review of Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Markets: Enabling Models and Technologies" Energies 17, no. 7: 1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071702
APA StyleIslam, S. N. (2024). A Review of Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Markets: Enabling Models and Technologies. Energies, 17(7), 1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071702






