Harvesting Losses for a Cut-and-Chip Harvesting System Operating in Willow Short-Rotation Coppice
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Willow Systems
1.2. Losses and Efficiency
1.3. Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
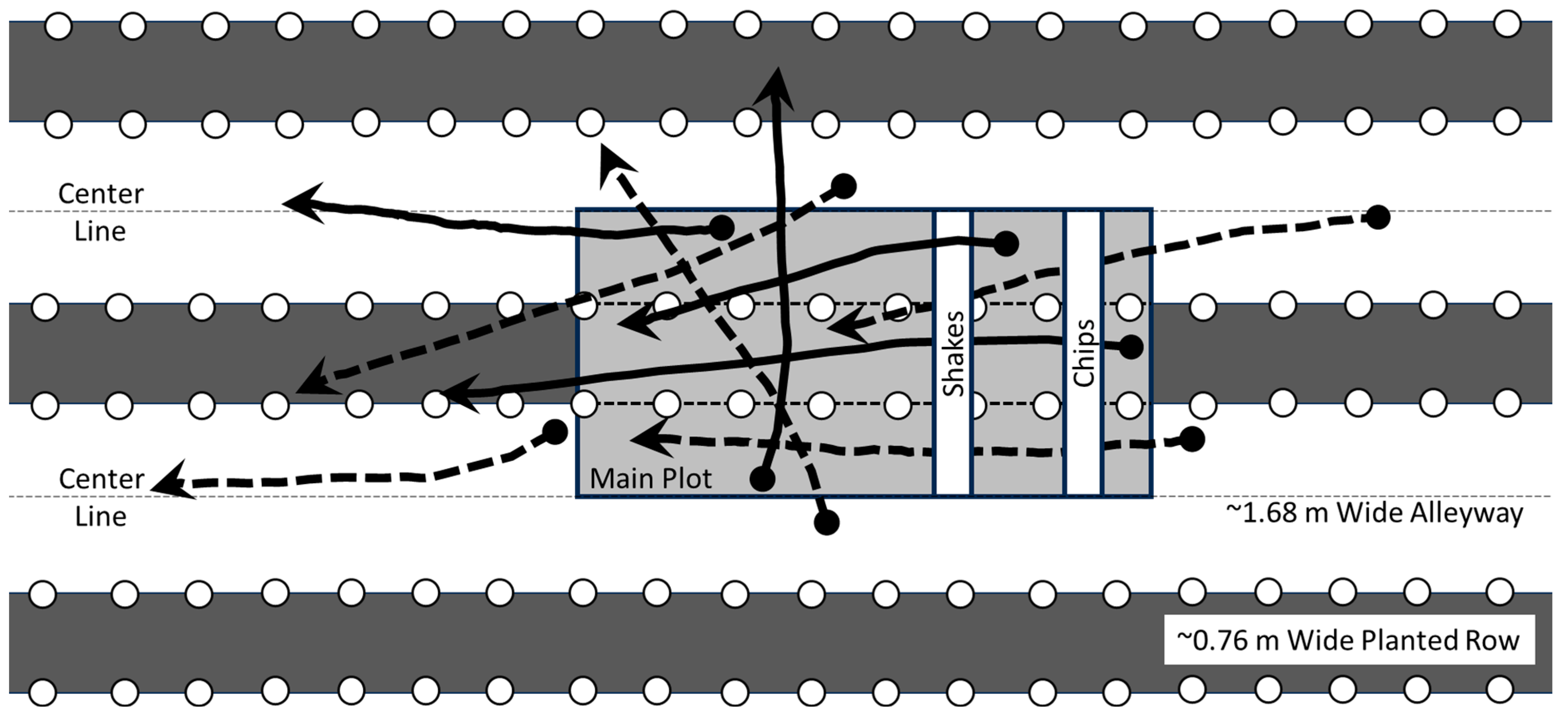
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Site Descriptions
2.3. Harvesting Operations
2.4. Collection of Harvesting Losses
2.5. Statistical Methods
- SB = adjusted standing biomass Mgdry ha−1 (Table 2)
- L = season (leaf-on = 1, leaf-off = 0)
- HP = harvester performance metric
- ε = error
3. Results and Discussion
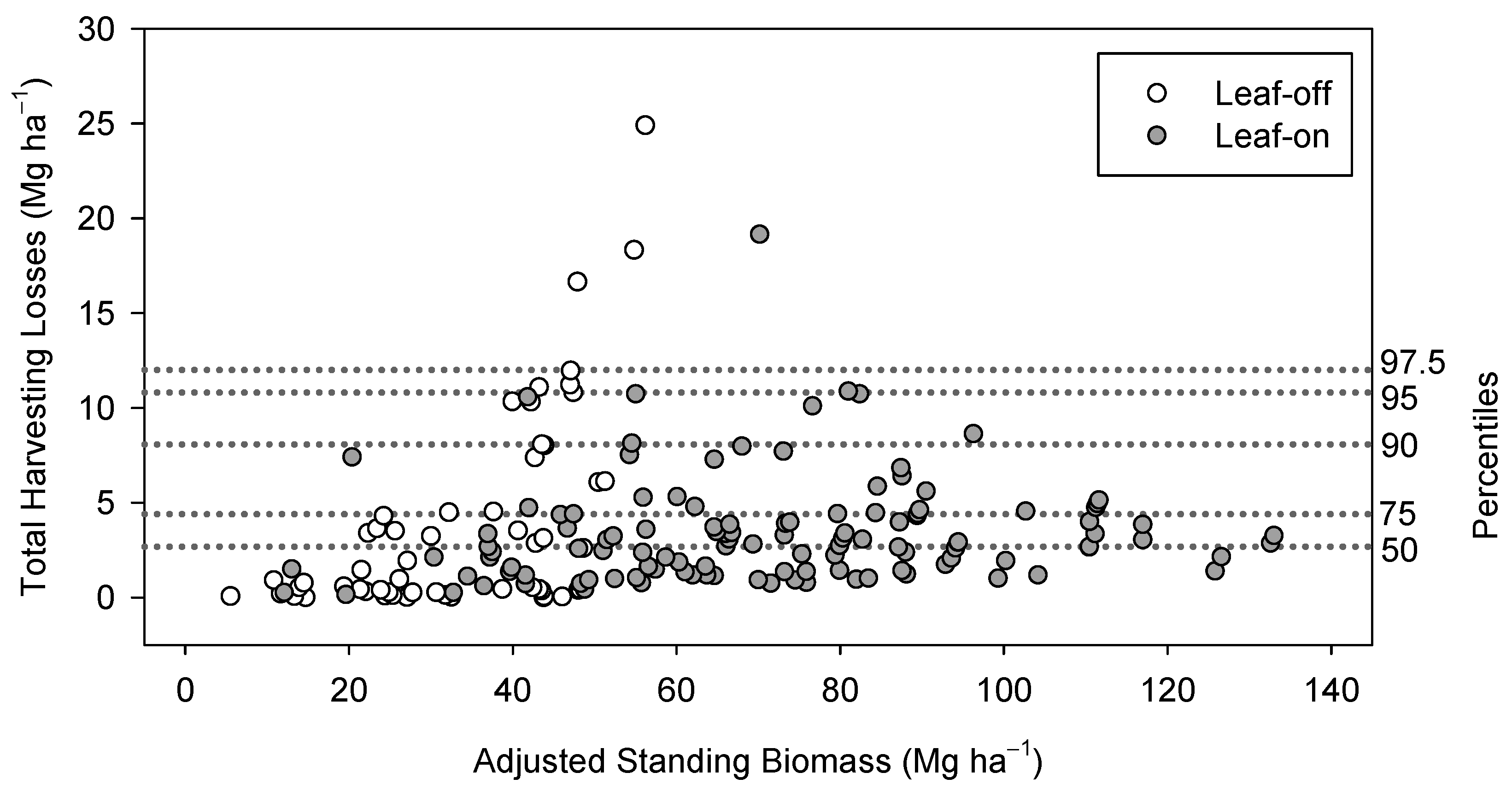
3.1. Total Harvesting Losses
3.2. Partitioning of Harvesting Losses
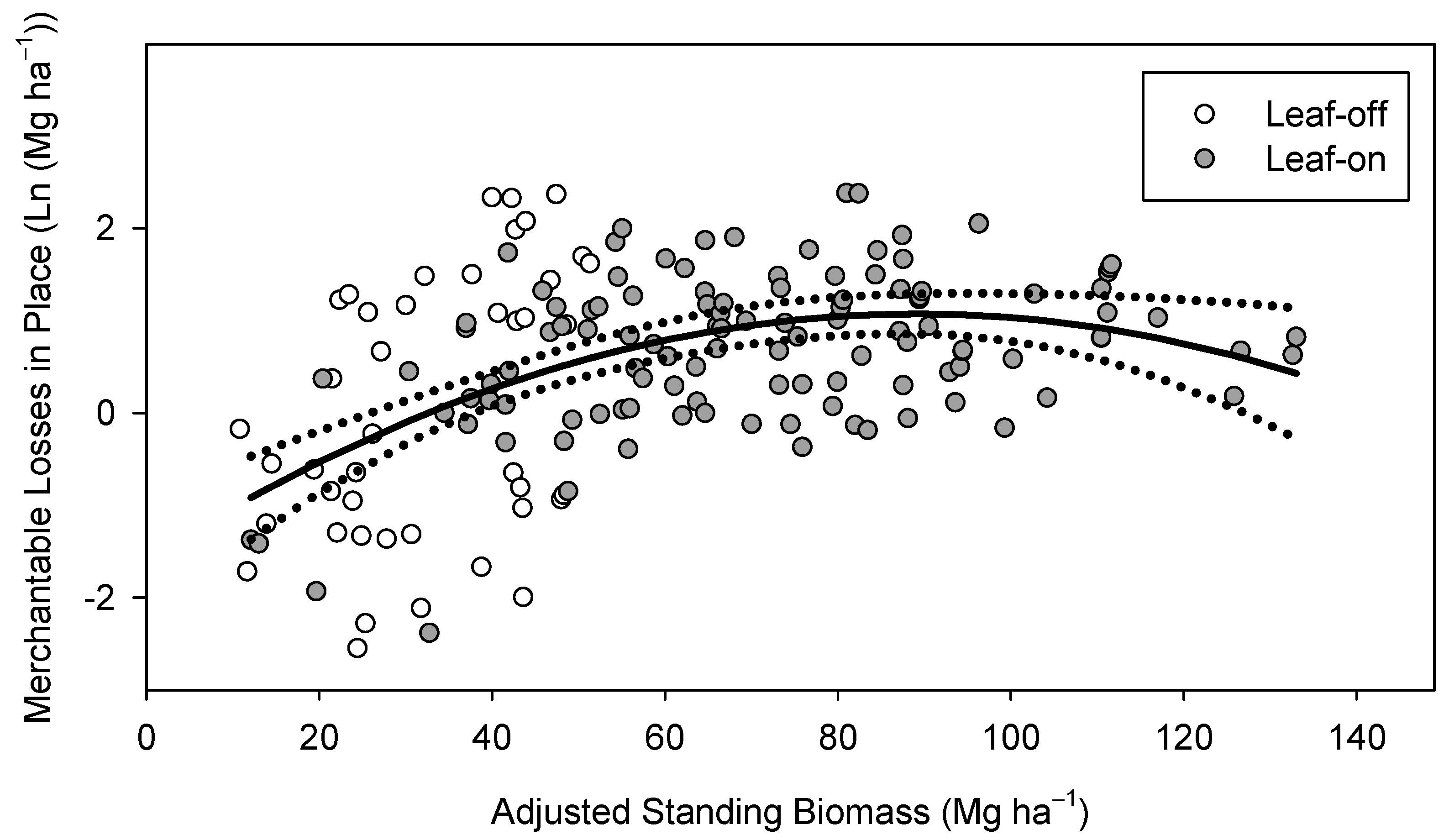
3.3. Regression Modeling
- M = merchantable harvesting losses in place (Mgdry ha−1) (Table 2)
- SB = adjusted standing biomass (Mgdry ha−1)
- ε = error
3.4. Harvest Losses during Field Transitions
3.5. Ratios of Live to Dead Stems
3.6. Implications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Department of Energy. 2016 Billion-Ton Report: Advancing Domestic Resources for a Thriving Bioeconomy, Volume 1: Economic Availability of Feedstocks; Langholtz, M.H., Stokes, B.J., Eaton, L.M., Eds.; ORNL/TM-2016/160; Oak Ridge National Laboratory: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2016; 448p. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2016/12/f34/2016_billion_ton_report_12.2.16_0.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023). [CrossRef]
- Vanbeveren, S.P.P.; Schweier, J.; Berhongaray, G.; Ceulemans, R. Operational Short Rotation Woody Crop Plantations: Manual or Mechanised Harvesting? Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 72, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, R.; Tenorio, C.; Oporto, G. Short Rotation Wood Crops in Latin American: A Review on Status and Potential Uses as Biofuel. Energies 2019, 12, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbeveren, S.P.P.; Spinelli, R.; Eisenbies, M.; Schweier, J.; Mola-Yudego, B.; Magagnotti, N.; Acuna, M.; Dimitriou, I.; Ceulemans, R. Mechanised Harvesting of Short-Rotation Coppices. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, T.A.; Heavey, J.P.; Eisenbies, M.H. Advances in Shrub-Willow Crops for Bioenergy, Renewable Products, and Environmental Benefits. Food Energy Secur. 2016, 5, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.C. Energy Plantations. In Forest Bioenergy; Gonçalves, A.C., Malico, I., Eds.; Green Energy and Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 91–119. ISBN 978-3-031-48223-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ashton, M.S.; Kelty, M.J. The Practice of Silviculture: Applied Forest Ecology, 10th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-119-27095-9. [Google Scholar]
- Dickmann, D. Silviculture and Biology of Short-Rotation Woody Crops in Temperate Regions: Then and Now. Biomass Bioenergy 2006, 30, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bassam, N. Handboook for Bioenergy Crops; Earthscan: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-1-84407-854-7. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.D.; Hannaway, D.B.; Eaton, L.M. Environmental Limitation Mapping of Potential Biomass Resources across the Conterminous U Nited S Tates. GCB Bioenergy 2018, 10, 717–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Aberle, E.; Anderson, E.K.; Anderson, W.; Baldwin, B.S.; Baltensperger, D.; Barrett, M.; Blumenthal, J.; Bonos, S.; Bouton, J.; et al. Biomass Production of Herbaceous Energy Crops in the United States: Field Trial Results and Yield Potential Maps from the Multiyear Regional Feedstock Partnership. GCB Bioenergy 2018, 10, 698–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, J.; Therasme, O.; Volk, T.A.; Brown, T.; Malmsheimer, R.W.; Fortier, M.-O.; Eisenbies, M.H.; Ha, H.; Heavey, J. Integrated Stochastic Life Cycle Assessment and Techno-Economic Analysis for Shrub Willow Production in the Northeastern United States. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, C.; Shield, I. Short Rotation Woody Energy Crop Supply Chains. In Biomass Supply Chains for Bioenergy and Biorefining; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 217–248. ISBN 978-1-78242-366-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ebadian, M.; Shedden, M.E.; Webb, E.; Sokhansanj, S.; Eisenbies, M.; Volk, T.; Heavey, J.; Hallen, K. Impact of Parcel Size, Field Shape, Crop Yield, Storage Location, and Collection Equipment on the Performance of Single-Pass Cut-and-Chip Harvest System in Commercial Shrub Willow Fields. BioEnergy Res. 2018, 11, 364–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, T.; Spinelli, R.; Eisenbies, M.; Clark, R.; Emerson, R.; Frank, J.; Hallen, K.; Therasme, O.; Webb, E. Harvesting Systems for Short Rotation Coppice and the Influence of Harvest Season and Ground Conditions on Harvester Performance and Biomass Quality. In Handbook of Biorefinery Research and Technology; Bisaria, V.S., Ed.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/378120857_Harvesting_Systems_for_Short_Rotation_Coppice_Crops_Influence_Cost_Performance_and_Biomass_Quality (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Sharma, B.; Ingalls, R.G.; Jones, C.L.; Khanchi, A. Biomass Supply Chain Design and Analysis: Basis, Overview, Modeling, Challenges, and Future. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 608–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanturf, J.A.; Perdue, J.H.; Young, T.M.; Huang, X.; Guo, Z.; Dougherty, D.; Pigott, M. A Spatially Explicit Approach to Modeling Biological Productivity and Economic Attractiveness of Short-Rotation Woody Crops in the Eastern USA. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2019, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbies, M.H.; Volk, T.A.; de Souza, D.P.L.; Hallen, K.W. Cut and Chip Harvester Material Capacity and Fuel Performance on Commercial-scale Willow Fields for Varying Ground and Crop Conditions. GCB Bioenergy 2020, 12, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, D.P.; Eisenbies, M.H.; Volk, T.A. Growing Season Harvests of Shrub Willow (Salix Spp.) Have Higher Nutrient Removals and Lower Yields Compared to Dormant-Season Harvests. Forests 2022, 13, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, D.F.; O’Connor, M.H.; Jovanovic, T.; Herr, A.; Raison, R.J.; O’Connell, D.A.; Baynes, T. A Spatial Assessment of Potential Biomass for Bioenergy in Australia in 2010, and Possible Expansion by 2030 and 2050. GCB Bioenergy 2016, 8, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.R.; Willis, H.H.; Curtright, A.E.; Samaras, C.; Skone, T. Incorporating Uncertainty Analysis into Life Cycle Estimates of Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Biomass Production. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 2619–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlert, D.; Pecenka, R. Harvesters for Short Rotation Coppice: Current Status and New Solutions. Int. J. For. Eng. 2013, 24, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoie, P.; Herbert, P.L.; Robert, F.S. Novel Willow Header Adapted to a Pull-Type Forage Harvester: Development and Field Experiments; ASABE: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2014; Volume 141831398, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meijden, G.P.M.; Gigler, J.K. Harvesting Techniques and Logistics of Short Rotation Energy Forestry—A Descriptive Study on Harvest and Transport Systems in Salix Production Currently Used in Sweden; Swedish Institute of Agricultural Engineering: Uppsala, Sweden, 1995; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbies, M.H.; Volk, T.A.; Posselius, J.; Foster, C.; Shi, S.; Karapetyan, S. Evaluation of a Single-Pass, Cut and Chip Harvest System on Commercial-Scale, Short-Rotation Shrub Willow Biomass Crops. BioEnergy Res. 2014, 7, 1506–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, S.P.S.; Oguri, G.; Spinelli, R. Harvesting Eucalyptus Energy Plantations in Brazil with a Modified New Holland Forage Harvester. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 86, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweier, J.; Becker, G. New Holland Forage Harvester’s Productivity in Short Rotation Coppice: Evaluation of Field Studies from a German Perspective. Int. J. For. Eng. 2012, 23, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garren, A.M.; Bolding, M.C.; Barrett, S.M.; Aust, W.M.; Coates, T.A. Best Management Practices, Estimated Erosion, Residual Woody Debris, and Ground Cover Characteristics Following Biomass and Conventional Clearcut Harvests in Virginia’s Mountains. For. Sci. 2022, 68, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, D. Farm Power and Machinery Management, 10th ed.; Iowa State Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2001; ISBN 0-8138-1756-0. [Google Scholar]
- ASABE. Uniform Terminology for Agricultural Machinery Management—ASABE Standards S495.1 NOV2005(R2011); American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2011; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Korboulewsky, N.; Bilger, I.; Bessaad, A. How to Evaluate Downed Fine Woody Debris Including Logging Residues? Forests 2021, 12, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldendorp, G.; Keenan, R.J.; Barry, S.; Spencer, R.D. Analysis of Sampling Methods for Coarse Woody Debris. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 198, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhongaray, G.; El Kasmioui, O.; Ceulemans, R. Comparative Analysis of Harvesting Machines on an Operational High-Density Short Rotation Woody Crop (SRWC) Culture: One-Process versus Two-Process Harvest Operation. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 58, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoie, P.; Hébert, P.-L.; Robert, F.-S.; Sidders, D. Harvest of Short-Rotation Woody Crops in Plantations with a Biobaler. EPE 2013, 5, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbies, M.H.; Burger, J.A.; Aust, W.M.; Patterson, S.C. Soil Physical Disturbance and Logging Residue Effects on Changes in Soil Productivity in Five-Year-Old Pine Plantations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbies, M.; Volk, T.; Amidon, T.; Bergey, S.; Bold-Erdene, Z.; Clark, R.; DeSouza, D.; Ebadian, M.; Emerson, R.; Gantz, C.; et al. Improved Advanced Biomass Logistics Utilizing Woody and Other Feedstocks in the Northeast and Pacific Northwest; Final Report:EE0006638; US DOE Office of Science and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/1768177 (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Berner, L.T.; Alexander, H.D.; Loranty, M.M.; Ganzlin, P.; Mack, M.C.; Davydov, S.P.; Goetz, S.J. Biomass Allometry for Alder, Dwarf Birch, and Willow in Boreal Forest and Tundra Ecosystems of Far Northeastern Siberia and North-Central Alaska. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 337, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, B.; Poudel, K.P.; Renninger, H.J.; Granger, J.J.; Leininger, T.D.; Gardiner, E.S.; Souter, R.A.; Rousseau, R.J. Aboveground Biomass Equations for Black Willow (Salix Nigra Marsh.) and Eastern Cottonwood (Populus Deltoides Bartr. Ex Marsh.). Trees For. People 2022, 7, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallows, C. Some Comments on Cp. Technometrics 1973, 15, 661–675. [Google Scholar]
- Eich, S.; Volk, T.A.; Eisenbies, M.H. Bark Content of Two Shrub Willow Cultivars Grown at Two Sites and Relationships with Centroid Bark Content and Stem Diameter. Bioenerg. Res. 2015, 8, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, D.P.L. Nutrient Removal in Willow Biomass Cover Crops Is Impacted over Multiple Rotations, Timing of Harvest, and Harvesting System. Ph.D. Thesis, State University of New York College of Environmental Science and Forestry, Syracuse, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]

| Site | Lat/Long | Date | Season | Rotation | Stem Age | Monitored Loads | Harvested Area | Total Sampling Plots |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | y | N | ha | N | ||||
| Lafayette, NY, USA | 42°58′46.0″ N 76°06′43.3″ W | June 2016 | Leaf-on | 2 or more | 5+ | 58 | 5.4 | 54 |
| Cape Vincent, NY, USA | 44°03′05.8″ N 76°16′55.6″ W | October 2016 | Leaf-on | 1 | 3 | 30 | 32 | 2 |
| Solvay, NY, USA | 43°03′57.6″ N 76°15′43.0″ W | January 2017 | Leaf-off | 1 | 4 | 16 | 0.6 | 13 |
| Solvay, NY, USA | 43°03′57.6″ N 76°15′43.0″ W | June 2017 | Leaf-on | 1 | 4 | 48 | 2.7 | 39 |
| Jacobs, NY, USA | 44°07′32.8″ N 76°18′59.7″ W | September/October 2017 | Leaf-on | 1 | 4 | 199 | 38 | 46 |
| Rockview, PA, USA | 40°51′33.1″ N 77°47′47.1″ W | March 2019 | Leaf-off | 2 | 3 | 108 | 14.2 | 22 |
| Solvay, NY, USA | 43°03′57.6″ N 76°15′43.0″ W | January 2022 | Leaf-off | 2 | 3, 5 | 67 | 3.6 | 57 |
| Total | 526 | 95.5 | 233 |
| Component | Definition | Determination | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cut | Willow stems with a diameter at the base >2.5 mm that were fully severed from stool but left on the ground | Hand collected, main plot | Mgdry ha−1 |
| Uncut | Willow stems with a diameter at the base >2.5 mm that were not fully severed from stool | Hand collected, main plot | |
| Shakes | Non-merchantable (due to shape) willow stems <2.5 mm collected from random subplot | Hand collected, shake subplot | |
| Chips | Chipped woody material that was processed by a forage harvester, but found on the ground | Hand collected, chip subplot | |
| Dead | Dead willow stems lying on the ground | Hand collected, entire plot | |
| Total harvesting losses | Sum of cut, uncut, shakes, chips, and dead material | Calculated | |
| Merchantable harvesting losses | Sum of harvesting losses including cut + uncut + chips + dead —or—total harvesting losses − shakes | Calculated | |
| Stem harvesting losses | Sum of harvesting losses including cut + uncut + dead material | Calculated | |
| Standing biomass delivered | Dry weight of biomass in the collection vehicle over the area where the material was harvested on a load basis | Time–motion study methods [18,25] | |
| Adjusted standing biomass | Standing biomass delivered plus total harvesting losses, not including chips | Calculated [34] | |
| Percent merchantable losses | Merchantable harvesting losses/adjusted standing biomass | Calculated | % |
| Merchantable losses in place | Merchantable harvesting losses minus chips | Calculated | |
| Percent merchantable losses in place | Merchantable harvesting losses in place/adjusted standing biomass | Calculated |
| Percentile Group | N | Adjusted Standing Biomass | Standing Biomass Delivered | Total Harvesting Losses | Merchantable Harvesting Losses | Stem Harvesting Losses | Cut | Uncut | Shakes | Chips | Dead |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mgdry ha−1 | |||||||||||
| Combined | |||||||||||
| All | 175 | 59.13 | 56.21 | 3.55 | 2.81 | 2.19 | 1.84 | 0.14 | 0.73 | 0.63 | 0.20 |
| Combined Season | |||||||||||
| Leaf-off | 57 | 34.11 b | 30.62 b | 3.81 a | 3.59 a | 3.28 a | 2.56 a | 0.09 a | 0.22 b | 0.32 a | 0.63 |
| Leaf-on | 118 | 71.21 a | 68.56 a | 3.42 a | 2.44 b | 1.66 b | 1.50 b | 0.17 a | 0.98 a | 0.78 a | 0.00 |
| Combined Percentile Groups | |||||||||||
| P0–5 | 8 | 28.36 B | 28.33 B | 0.03 D | 0.03 D | 0.02 E | 0.02 D | 0.00 B | 0.01 C | 0.01 C | 0.00 D |
| P5–P90 | 150 | 60.91 A | 58.70 A | 2.71 C | 2.00 C | 1.5 D | 1.32 C | 0.14 B | 0.71 B | 0.50 C | 0.04 D |
| P90–P95 | 9 | 59.60 A | 51.50 AB | 10.04 B | 8.33 B | 6.39 C | 5.49 B | 0.14 B | 1.71 A | 1.94 B | 0.76 C |
| P95–P97.5 | 4 | 54.59 AB | 43.42 AB | 11.28 B | 10.17 B | 10.05 B | 7.54 B | 0.02 B | 1.12 AB | 0.12 C | 2.50 B |
| P97.5–P100 | 4 | 57.29 AB | 41.66 AB | 19.76 A | 19.26 A | 15.14 A | 11.15 A | 0.66 A | 0.50 BC | 4.12 A | 3.32 A |
| Leaf-off Condition | |||||||||||
| P0–5 | 8 | 28.36 | 28.33 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| P5–P90 | 40 | 32.29 | 30.42 | 2.27 | 2.14 | 1.74 | 1.52 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.41 | 0.14 |
| P90–P95 | 3 | 43.21 | 32.83 | 10.49 | 10.14 | 10.04 | 7.77 | 0.00 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 2.27 |
| P95–P97.5 | 3 | 45.78 | 34.49 | 11.42 | 10.03 | 9.90 | 6.57 | 0.00 | 1.40 | 0.13 | 3.32 |
| P97.5–P100 | 3 | 52.99 | 33.32 | 19.96 | 19.40 | 19.11 | 13.88 | 0.81 | 0.55 | 0.29 | 4.42 |
| Leaf-on Condition | |||||||||||
| P0–5 | 0 | ||||||||||
| P5–P90 | 110 | 71.32 | 68.99 | 2.87 | 1.94 | 1.41 | 1.25 | 0.16 | 0.92 | 0.53 | 0.00 |
| P90–P95 | 6 | 67.79 | 60.84 | 9.82 | 7.43 | 4.56 | 4.36 | 0.21 | 2.39 | 2.86 | 0.00 |
| P95–P97.5 | 1 | 81.00 | 70.21 | 10.87 | 10.60 | 10.52 | 10.43 | 0.09 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.00 |
| P97.5–P100 | 1 | 70.19 | 66.67 | 19.15 | 18.80 | 3.21 | 2.98 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 15.62 | 0.00 |
| Group | Standing Biomass Delivered | Total Harvesting Losses | Merchantable Harvesting Losses | Stem Harvesting Losses | Cut | Uncut | Shakes | Chips | Dead |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percent of Adjusted Standing Biomass | |||||||||
| All | 94.6 | 6.6 | 5.5 | 4.3 | 3.6 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 0.4 |
| Percent of Adjusted Standing Biomass | |||||||||
| P0–5 | 99.8 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| P5–P90 | 96.0 | 5.1 | 4.1 | 3.8 | 2.6 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| P90–P95 | 84.9 | 18.7 | 15.8 | 12.3 | 10.2 | 0.3 | 2.8 | 3.6 | 1.8 |
| P95–P97.5 | 78.2 | 22.1 | 19.7 | 19.8 | 14.1 | 0.3 | 2.3 | 0.2 | 5.4 |
| P97.5–P100 | 71.0 | 34.9 | 34.0 | 28.0 | 20.4 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 6.0 | 6.4 |
| Percent of Standing Biomass Delivered | |||||||||
| P0–5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | |
| P5–P90 | 5.5 | 4.4 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.1 | |
| P90–P95 | 22.6 | 19.4 | 15.3 | 12.7 | 0.3 | 3.2 | 4.0 | 2.3 | |
| P95–P97.5 | 28.8 | 25.7 | 25.5 | 18.2 | 0.1 | 3.1 | 0.3 | 7.2 | |
| P97.5–P100 | 52.6 | 51.2 | 44.7 | 33.0 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 6.5 | 10.0 | |
| Percent of Total Harvesting Losses | |||||||||
| P0–5 | 92.4 | 85.2 | 85.2 | 0.0 | 7.6 | 7.2 | 0.0 | ||
| P5–P90 | 77.6 | 62.2 | 55.7 | 5.9 | 22.4 | 15.4 | 0.6 | ||
| P90–P95 | 82.2 | 62.2 | 53.6 | 1.4 | 17.8 | 19.9 | 7.2 | ||
| P95–P97.5 | 90.1 | 89.1 | 67.2 | 0.2 | 9.9 | 1.2 | 21.7 | ||
| P97.5–P100 | 97.3 | 75.7 | 54.0 | 3.6 | 2.7 | 22.0 | 18.1 | ||
| Percent of Merchantable Harvesting Losses | |||||||||
| P0–5 | 92.8 | 0.0 | na | 7.2 | 0.0 | ||||
| P5–P90 | 69.8 | 8.6 | na | 21.0 | 0.6 | ||||
| P90–P95 | 63.4 | 1.9 | na | 27.2 | 7.5 | ||||
| P95–P97.5 | 73.7 | 0.2 | na | 1.1 | 24.9 | ||||
| P97.5–P100 | 55.5 | 3.7 | na | 22.0 | 18.8 | ||||
| Location | N | Total | Merchantable | Stem-Only |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg ha−1 | ||||
| Interior | ||||
| Leaf-off | 26 | 4.12 (0.61) B | 3.93 (0.60) A | 2.30 (0.61) A |
| Leaf-on | 15 | 7.03 (0.78) A | 4.98 (0.69) A | 1.62 (0.66) AB |
| Transitional | ||||
| Leaf-off | 17 | 2.39 (0.33) C | 2.29 (0.33) B | 1.06 (0.27) B |
| Leaf-on | 12 | 2.88 (0.44) BC | 2.13 (0.31) B | 1.41 (0.31) AB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eisenbies, M.H.; Volk, T.A. Harvesting Losses for a Cut-and-Chip Harvesting System Operating in Willow Short-Rotation Coppice. Energies 2024, 17, 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071541
Eisenbies MH, Volk TA. Harvesting Losses for a Cut-and-Chip Harvesting System Operating in Willow Short-Rotation Coppice. Energies. 2024; 17(7):1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071541
Chicago/Turabian StyleEisenbies, Mark H., and Timothy A. Volk. 2024. "Harvesting Losses for a Cut-and-Chip Harvesting System Operating in Willow Short-Rotation Coppice" Energies 17, no. 7: 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071541
APA StyleEisenbies, M. H., & Volk, T. A. (2024). Harvesting Losses for a Cut-and-Chip Harvesting System Operating in Willow Short-Rotation Coppice. Energies, 17(7), 1541. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17071541






