Subdomain Analytical Modeling of a Double-Stator Spoke-Type Permanent Magnet Vernier Machine
Abstract
1. Introduction
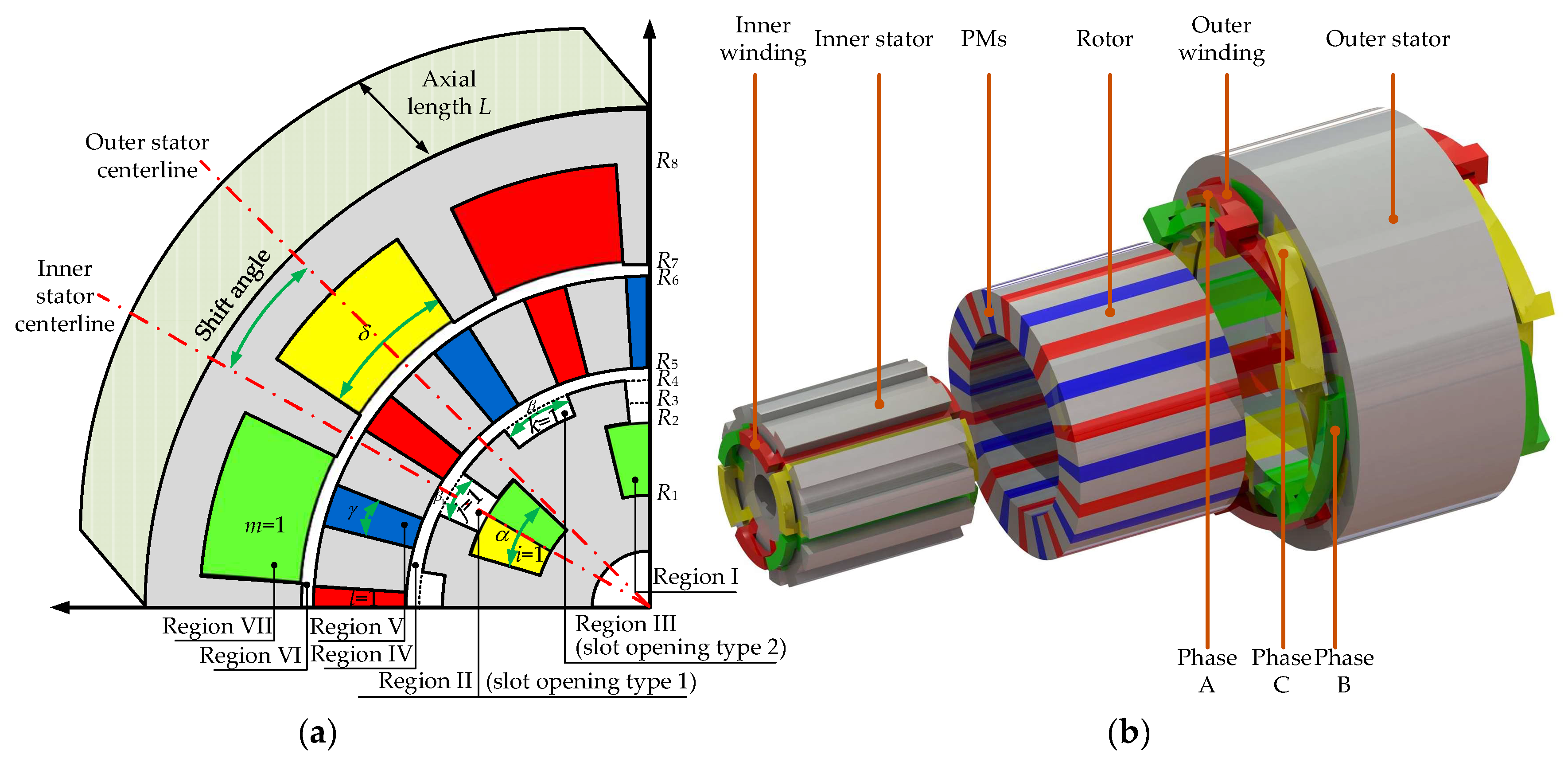
2. Machine Geometry and Methodology
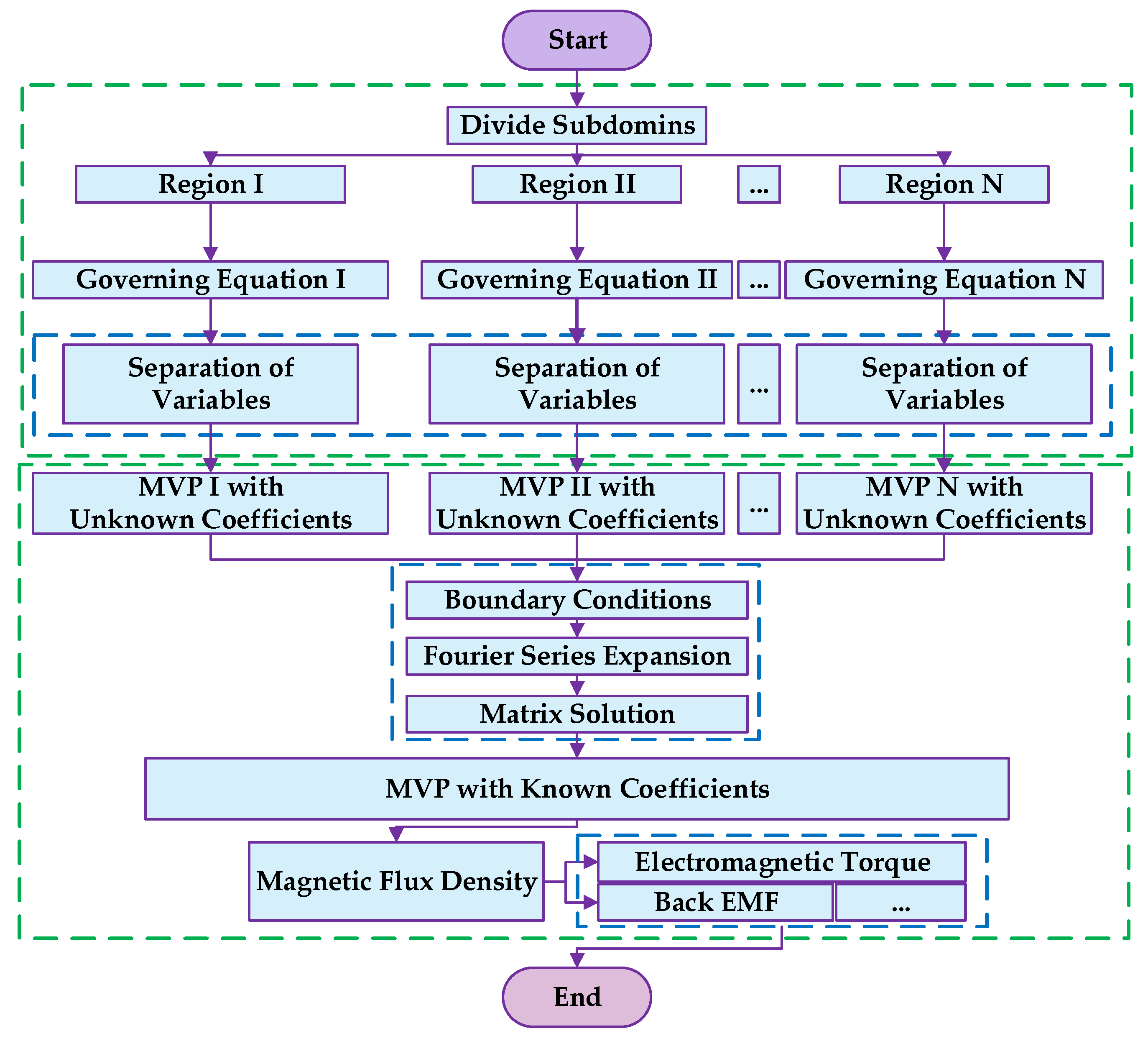
3. Analytical Modeling Process
3.1. Boundary Condition and General Solution Expressions
3.1.1. Region I
3.1.2. Region II
3.1.3. Region III
3.1.4. Region IV
3.1.5. Region V
3.1.6. Region VI
3.1.7. Region VII
3.2. Postprocessing Electromagnetic Parameters Calculation
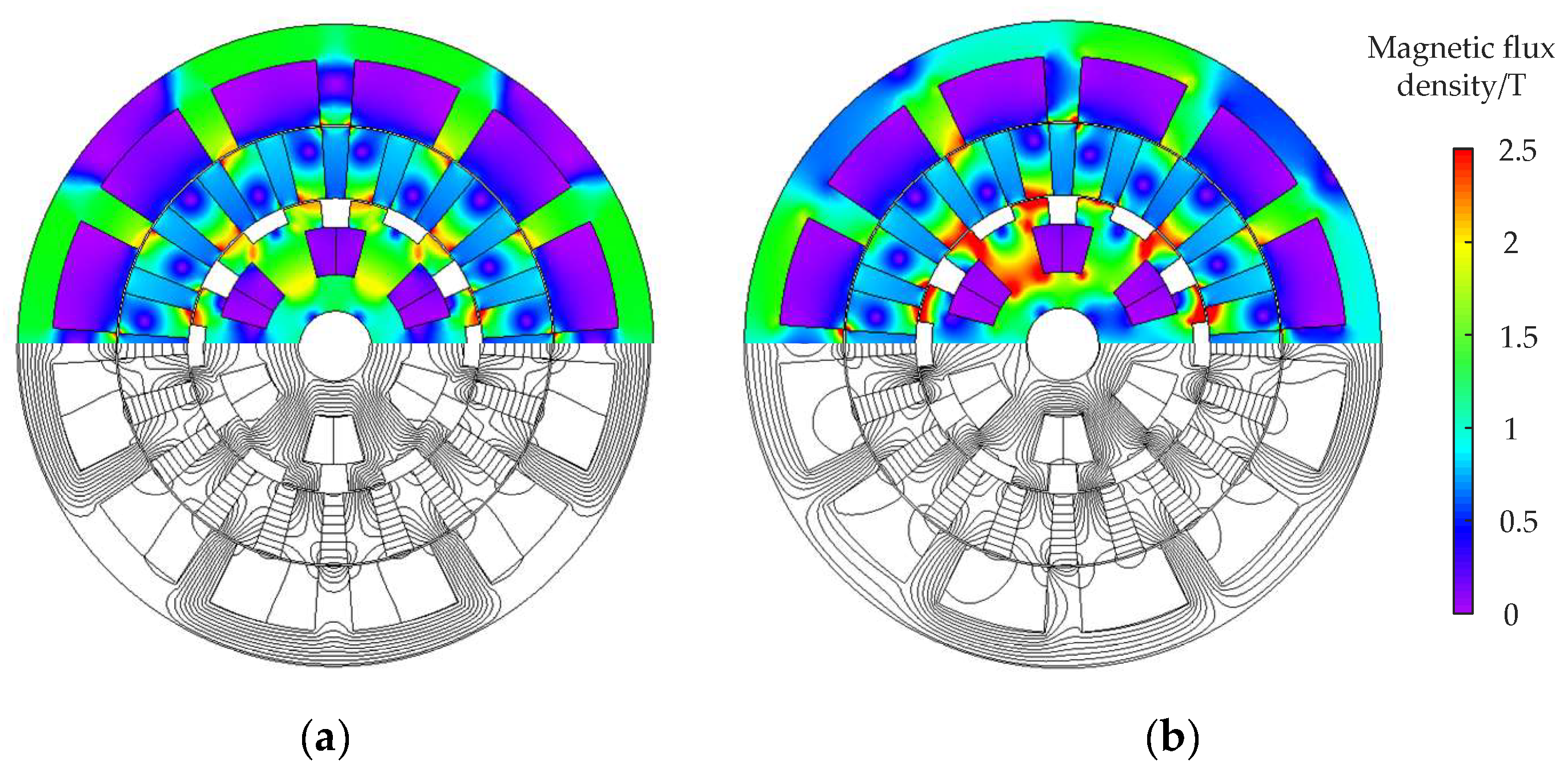
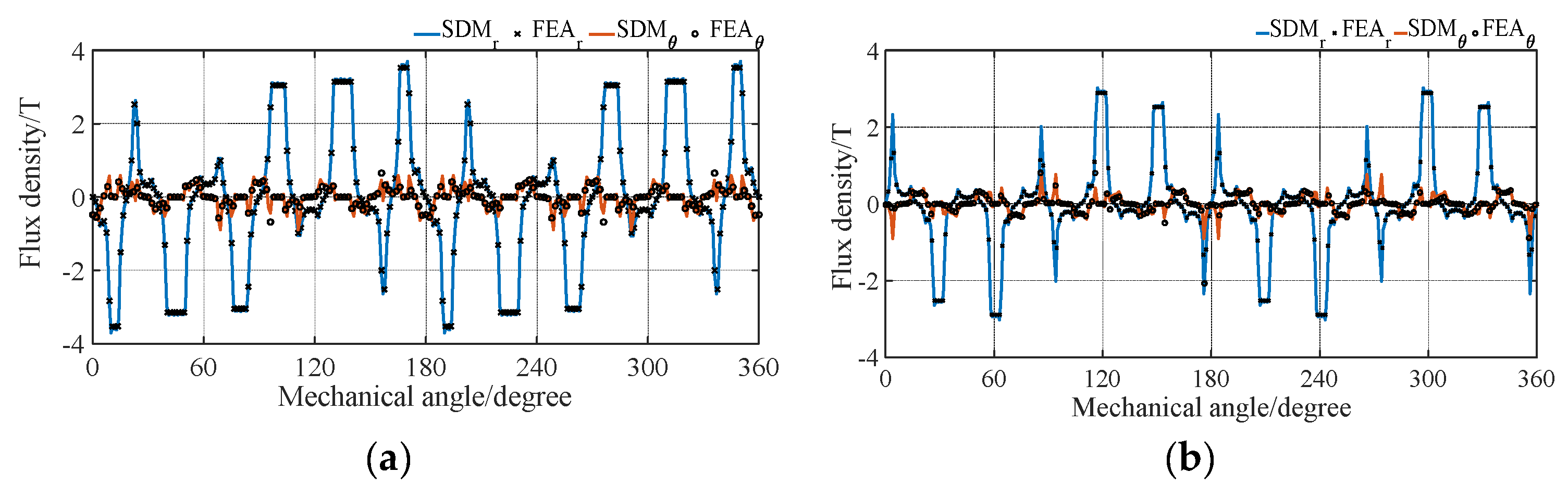
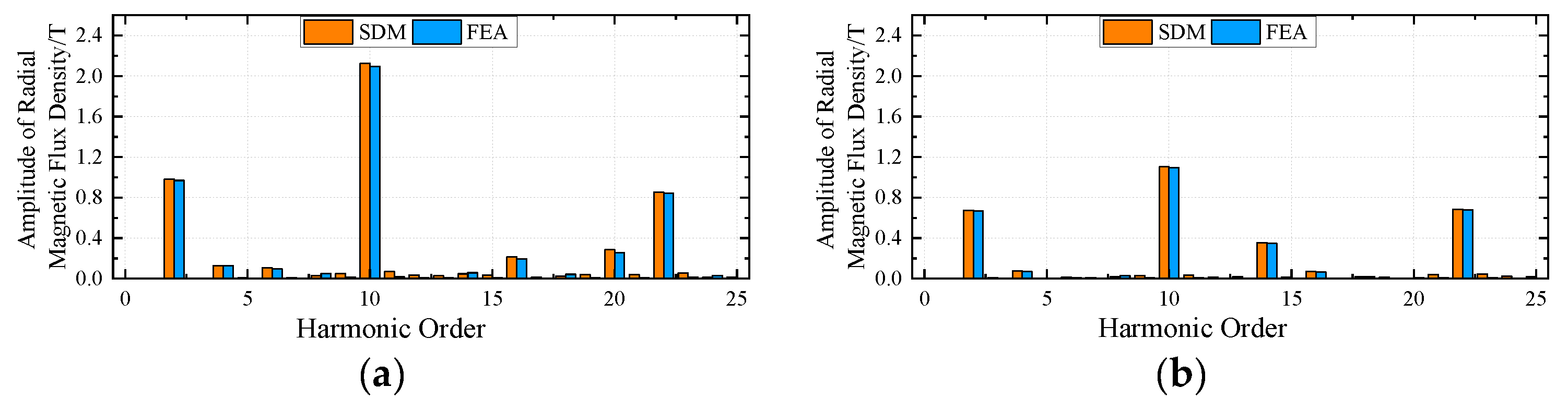
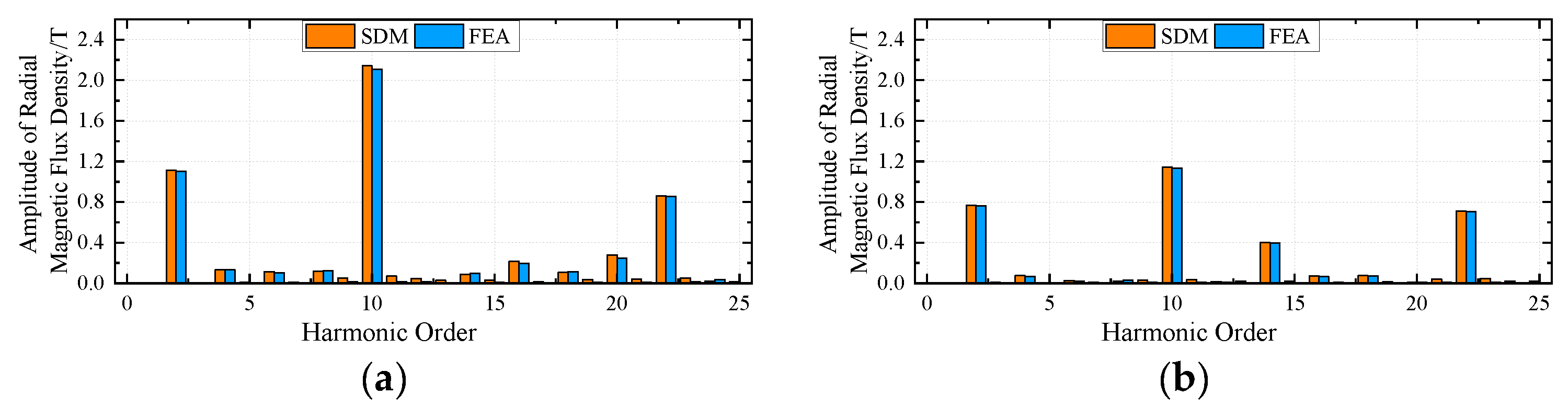
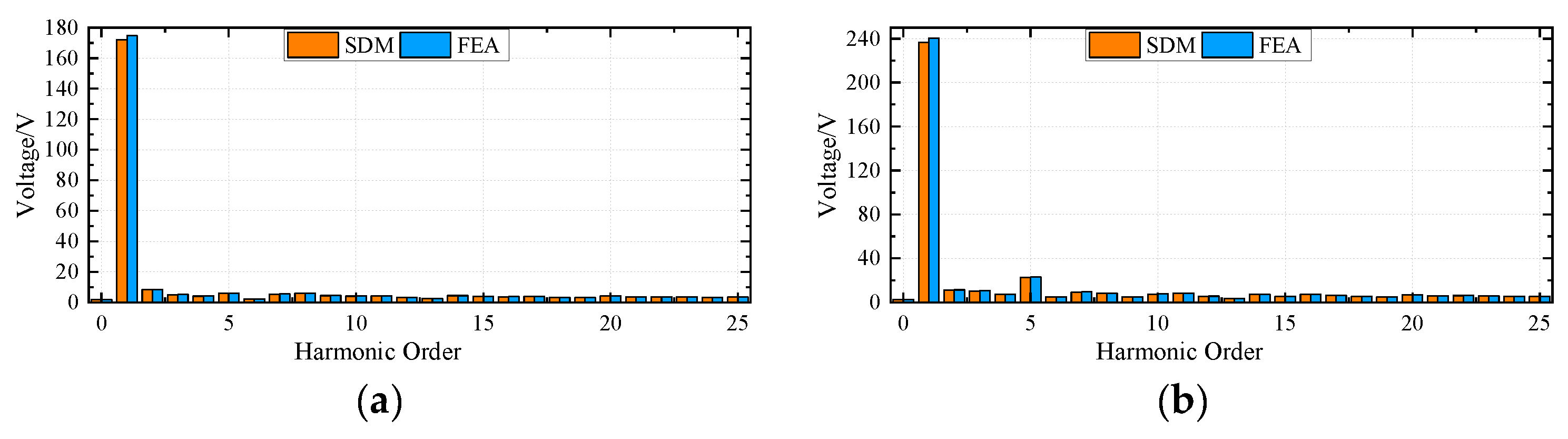
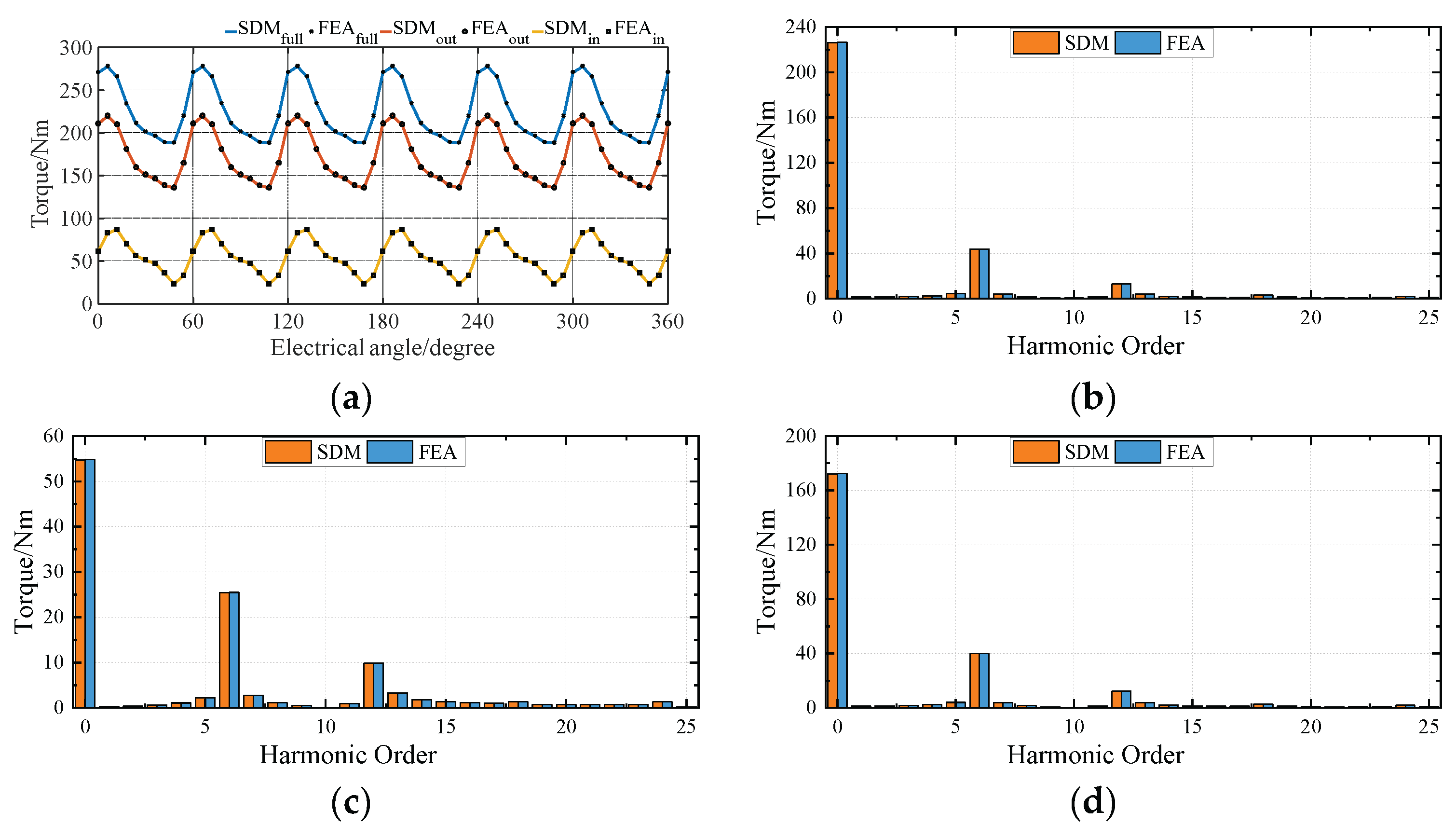
4. Finite Element Analysis Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| R1 | The inner radius of the inner stator slot |
| R2 | Inner radius of opening slot type 1 |
| R3 | Inner radius of opening slot type 2 |
| R4 | The outer radius of the inner stator |
| R5 | The inner radius of the rotor |
| R6 | The outer radius of the rotor |
| R7 | The inner radius of the outer stator |
| R8 | The inner radius of the outer stator yoke |
| N | Turns number |
| L | Stack length |
| α | The angle of the ith slot within Region I |
| β1 | The angle of the jth slot within Region II (slot-opening type 1) |
| β2 | The angle of the kth slot in Region III (slot-opening type 2) |
| γ | The angle of the lth PM within Region V |
| δ | The angle of the mth slot within Region VII |
| Pr | Pole-pair number of rotor’s permanent magnets (PMs) |
| Pw | Pole-pair numbers of the inner and outer stators’ windings |
| Z | Slot numbers of the inner and outer stators |
| Jz | Current density |
| MVP of the ith slot in Region I | |
| MVP of the jth slot within Region II | |
| MVP of the kth slot within Region III | |
| MVP within Region IV | |
| MVP of the lth slot within Region V | |
| MVP within Region VI | |
| MVP of the mth slot within Region VII | |
| The initial angle of the ith slot in Region I | |
| The initial angle of the jth slot within Region II | |
| The initial angle of the kth slot within Region III | |
| Tangential magnetization of the lth PM within Region V | |
| The initial angle of the lth PM within Region V | |
| The initial angle of the mth slot within Region VII |
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
References
- Niu, S.; Chau, K.T.; Jiang, J.Z.; Liu, C. Design and Control of a New Double-Stator Cup-Rotor Permanent-Magnet Machine for Wind Power Generation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 2501–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, W.; Gao, Q.; Lenwari, W. Optimal Design of a 5-MW Double-Stator Single-Rotor PMSG for Offshore Direct Drive Wind Turbines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Quan, L.; Zhu, X.; Xiang, Z.; Que, H. Airgap-Harmonic-Based Multilevel Design and Optimization of a Double-Stator Flux-Modulated Permanent-Magnet Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 10534–10545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Liu, C.; Song, Z.; Zhao, H. Permeance and Inductance Modeling of a Double-Stator Hybrid-Excited Flux-Switching Permanent-Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 6, 1134–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asef, P.; Perpina, R.B.; Moazami, S.; Lapthorn, A.C. Rotor Shape Multi-Level Design Optimization for Double-Stator Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, C.; Milde, F.; Trebbels, D.; Schmidt, J.; Doppelbauer, M. A Stator with Offset Segments and a Double Stator Design for the Reduction of Torque Ripple of a Switched Reluctance Motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, A.; Lipo, T.A. Generic torque-maximizing design methodology of surface permanent-magnet vernier machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2000, 36, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, C.; Song, Z.; Wang, W. Exact Modeling and Multiobjective Optimization of Vernier Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 11740–11751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qu, R.; Lipo, T.A. High-Power-Factor Vernier Permanent-Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3664–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughrara, K.; Ibtiouen, R.; Zarko, D.; Touhami, O.; Rezzoug, A. Magnetic Field Analysis of External Rotor Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors Using Conformal Mapping. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 3684–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeida, A.; Lehikoinen, A.; Rasilo, P.; Vansompel, H.; Belahcen, A.; Arkkio, A.; Sergeant, P. A Simple and Efficient Quasi-3D Magnetic Equivalent Circuit for Surface Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 8318–8333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chau, K.T.; Yang, T.; Song, Z.; Liu, C. A Novel Quasi-3D Analytical Model for Axial Flux Motors Considering Magnetic Saturation. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, C.; Song, Z.; Wang, W. Analytical Modeling of a Double-Rotor Multiwinding Machine for Hybrid Aircraft Propulsion. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 6, 1537–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oner, Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Wu, L.J.; Ge, X.; Zhan, H.; Chen, J.T. Analytical On-Load Subdomain Field Model of Permanent-Magnet Vernier Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4105–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, M.; Wang, D.; Fang, Y. A Subdomain Model for Open-Circuit Field Prediction in Dual-Stator Consequent-Pole Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Han, P.; Du, Y.; Wen, H. General Airgap Field Modulation Theory for Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr. 2017, 64, 6063–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysen, B.L.J.; Meessen, K.J.; Paulides, J.J.H.; Lomonova, E.A. General Formulation of the Electromagnetic Field Distribution in Machines and Devices Using Fourier Analysis. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, T.; Mezani, S.; Rezzoug, A. 2-D Exact Analytical Model for Surface-Mounted Permanent-Magnet Motors with Semi-Closed Slots. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, C.; Song, Z.; Liu, S.; Lubin, T. Analytical Model for Magnetic-Geared Double-Rotor Machines and Its d–q-Axis Determination. IET Electric. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Symbol | Value | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 24.8 mm | α | π/6 rad |
| R2 | 41 mm | β1 | π/9 rad |
| R3 | 45.3 mm | β2 | π/10 rad |
| R4 | 50.3 mm | γ | 37π/900 rad |
| R5 | 50.9 mm | δ | 37π/300 rad |
| R6 | 66 mm | Pr | 10 |
| R7 | 75.2 mm | Pw | 2 |
| N | 200 | Z | 12 |
| L | 100 mm | Jz | 6 A/mm2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, X.; Zhao, H.; Ou, Z.; Yu, J.; Liu, C. Subdomain Analytical Modeling of a Double-Stator Spoke-Type Permanent Magnet Vernier Machine. Energies 2024, 17, 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051114
Su X, Zhao H, Ou Z, Yu J, Liu C. Subdomain Analytical Modeling of a Double-Stator Spoke-Type Permanent Magnet Vernier Machine. Energies. 2024; 17(5):1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051114
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Xiangdong, Hang Zhao, Zhijun Ou, Jincheng Yu, and Chunhua Liu. 2024. "Subdomain Analytical Modeling of a Double-Stator Spoke-Type Permanent Magnet Vernier Machine" Energies 17, no. 5: 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051114
APA StyleSu, X., Zhao, H., Ou, Z., Yu, J., & Liu, C. (2024). Subdomain Analytical Modeling of a Double-Stator Spoke-Type Permanent Magnet Vernier Machine. Energies, 17(5), 1114. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051114









