Abstract
This study focuses on optimizing the thermal pyrolysis process to maximize pyrolysis oil yield using marine biomass or seaweed. The process, conducted in a batch reactor, was optimized using response surface methodology and Box–Behnken design. Variables like temperature, residence time, and stirring speed were adjusted to maximize bio-oil yield. The optimal conditions yielded 42.94% bio-oil at 463.13 °C, with a residence time of 65.75 min and stirring speed of 9.74 rpm. The analysis showed that temperature is the most critical factor for maximizing yield. The bio-oil produced contains 11 functional groups, primarily phenol, aromatics, and alcohol. Its high viscosity and water content make it unsuitable for engines but suitable for other applications like boilers and chemical additives. It is recommended to explore the potential of refining the bio-oil to reduce its viscosity and water content, making it more suitable for broader applications, including in engine fuels. Further research could also investigate the environmental impact and economic feasibility of scaling up this process.
1. Introduction
The importance of energy in our everyday lives and in the advancement of technology has led many to consider it a fundamental element. Undoubtedly, it is an essential need for human survival and progress. The clear upward trend in GDP and the rising profile of industrialization are driving up the world’s energy consumption [1]. The exponential growth of the world’s population and the precipitous depletion of fossil fuel supplies have combined to create an unprecedented energy catastrophe. A major contributor to the present energy issues globally is this exponential population expansion, which is occurring while fossil fuel resources are declining [2,3]. One of the factors that leads to the phenomena of climate change is the widespread use of fossil fuels, which not only causes enormous damage to the environment but also adds to the problem. The quantity of carbon dioxide (CO2) that was released into the atmosphere as a result of the burning of fossil fuels was 36.8 billion tonnes in 2022 [4]. A substantial amount of damage is caused to the environment because of the intensive use of fossil fuels, which also plays a role in the phenomena of climate change. Before the middle of the 20th century, this subject received very little attention, and the study of renewable energy sources was mostly reserved for circumstances that were regarded to be of an urgent nature [5]. The use of energy derived from renewable sources is a potential solution to the problem of environmental deterioration and the dwindling supply of fossil fuels. In 2022, renewable sources contributed a remarkable 14.21% of the world’s total energy consumption, which represents a big step towards tackling these concerns [6]. So, reducing emissions and meeting energy demands while reducing dependency on petroleum oil requires the use of environmentally acceptable energy alternatives.
As a potential source of renewable energy, the use of marine biomass represents a promising avenue. There is the possibility that the processing of marine biomass might fulfil a fraction of the future energy requirements. This could be accomplished via the utilization of cutting-edge technologies such as pyrolysis [7]. The process of pyrolysis is a thermal degradation method that involves the breakdown of carbon-rich materials, such as biomass, in the absence or restricted presence of air. This method results in the production of three principal energy products, namely bio-oil, biochar, and syngas. Bio-oil is one of these, and it shows a great deal of potential in terms of tackling issues related to energy and the environment. It is possible to use bio-oil as a fuel for furnaces, boilers, and engines, which contributes to the creation of both heat and electricity. Bio-oil is composed of a mixture of different organic compounds that are present in variable proportions. Moreover, it is a useful source for a wide variety of chemical applications, which is another application [8].
Pyrolysis is a process that may be broken down into three distinct types: slow pyrolysis, fast pyrolysis, and flash pyrolysis. In particular, the rapid pyrolysis approach has attracted a great deal of interest from researchers. This is due to the fact that it is recognized for its capacity to produce a bigger quantity of bio-oil in comparison to the other two methods [9]. Considering that pyrolysis primarily results in the production of a liquid product, the process of storing and transferring it is simplified. In addition, when it comes to conducting pyrolysis on seaweed or marine biomass, there are a variety of reactors that are available. An investigation of the various reactors that are utilized in fast pyrolysis was carried out by Campuzano et al. [10]. The researchers took into consideration a variety of criteria, including bio-oil output, process complexity, feedstock particle size standards, inert gas needs, and scalability levels. According to the results of their investigation, they suggested that auger reactors and fluidized bed reactors placed at the top in the evaluation. The experiments on fast pyrolysis that were conducted by Bae et al. [11] were carried out at a temperature of 500 degrees Celsius and utilised batch and auger reactors. For the purpose of providing feedstock, a number of different macroalgae, such as Undaria pinnatifida, Laminaria japonica, and Porphyra, appeared. After conducting the investigation, it was discovered that the species Undaria pinnatifida (40.4 wt.%), Laminaria japonica (37.6 wt.%), and Porphyra tenera (47.4 wt.%) produced the highest yields of bio-oil. The studies that Nam et al. carried out involved the use of rice straw as their principal material [12]. These experiments were quite similar to the ones that are described in this discussion. Their findings revealed that several extraction techniques, such as auger, batch, and fluidized bed procedures, were able to rovide a bio-oil yield that was equivalent to that of other methods. The fluidized bed reactor, on the other hand, has significant operational hurdles in comparison to other types of reactors. It requires a significant supply of inert gas in order to assist the fluidization of the bed material. Furthermore, as the reactors are developed, the procedure of delivering the necessary enthalpy for the pyrolysis process via heat transfer becomes progressively more difficult [13]. The batch reactor and the auger reactor are both considered to be extremely promising reactor designs for the thermal pyrolysis process. This is because of the qualities previously mentioned [13,14]. As a result of this, a batch pyrolysis reactor was utilised in the course of this research.
Macroalgae, commonly known as seaweeds, are marine plants that can be found in oceans and other aquatic environments around the world. They have various uses, including as food, feed, fertilizers, biofuels, and industrial products [15]. The use of seaweeds, also known as macroalgae, as a resource for the generation of biofuels in a sustainable manner is becoming an increasingly popular topic in the modern period. Contrary to conventional oil crops grown on land, seaweeds provide a number of advantages. It is not necessary for them to transfer water or nutrients inside, which results in a reduction in energy consumption. Further, as compared to terrestrial biomass, the mass productivity of several different types of seaweed is significantly higher [16]. Furthermore, they are utilized as a source of nourishment for human beings, components in cosmetic items, fertilizers for agricultural purposes, and as raw materials for the creation of chemicals that are utilised in the medical field and a variety of other sectors [17]. The production of seaweed for economic reasons has a long and illustrious history, notably in Asia. Seaweed that has been dried provides a possibility to be used as a raw material for a variety of applications, such as co-firing for the generation of electricity, thermochemical conversion for the manufacture of liquid fuel (bio-oil), and fermentation for the creation of biomethane. In spite of the fact that a significant amount of study has been conducted on the production of bio-oil from microalgae, there is still a research gap concerning the production of bio-oil from seaweeds. As a result of the high amount of carbohydrates that they contain, seaweeds have the potential to be the most suitable raw materials for the production of bio-oil.
The gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) technique was utilized by Ross et al. in order to evaluate the pyrolysis properties of five different macroalgae [17]. Pyrolysis led to the production of a wide variety of pentosans as well as a significant quantity of nitrogen-containing compounds, which ultimately culminated in the production of a significant amount of char. The thermal investigation was carried out by Wang et al. [18] on three different kinds of macroalgae as well as firewood. During the process of thermolysis, their analysis found that there was a considerable difference in the transfer of heat between seaweeds and firewood. According to the findings of the study, seaweeds typically participate in exothermic processes at relatively lower temperature ranges. On the other hand, wood has a pronounced endothermic reaction at relatively higher temperatures, which is then followed by a noticeable exothermic peak. The synthesis of bio-oil by the pyrolysis process applied to seaweeds or macroalgae has only been well established in a few studies that have been published in the academic literature [19,20]. The experiment focused on the thermal degradation process, also known as pyrolysis, of three different forms of macroalgae: two varieties of brown macroalgae, namely Undaria pinnatida and Laminaria japonica, and one type of red macroalgae, Porphyratenera. For the purpose of the study, temperatures ranging from 300 to 600 degrees Celsius were considered [19]. The bio-oil production was at its peak at 500 degrees Celsius, with a yield ranging from 37.5 to 47.4 wt.%. In the event that extra processing is performed, the bio-oils that are produced have the potential to be utilized as a chemical feedstock. However, because of the high nitrogen concentration, their usage as fuel is restricted to a certain extent.
In a similar manner, the pyrolysis of seaweed (Gracilaria) with the assistance of microwaves led to the generation of bio-oils that contained a substantial amount of aromatics, sugars, and other important compounds [20]. Via the utilization of pyrolysis technology, the production of bio-oil from seaweed may be enhanced, hence increasing the efficacy of seaweed in a variety of applications. As a consequence of this, engineers are confronted with a significant challenge: they must maximize the amount and quality of bio-oil while simultaneously minimizing costs and worries about the environment. The yield of bio-oil produced by the pyrolysis process is collectively influenced by a number of parameters, including the temperature of the pyrolysis process [21], the particle size of the feedstock [22], the stirring speed [23], the heating rate [24], and the amount of time the feedstock is allowed to remain inside the pyrolysis reactor [25]. Prior research on batch and continuous pyrolysis procedures has focused mostly on the variables and their impacts. However, some process parameters were continuously kept at values that were not stated in these experiments. Due to the fact that this approach does not take into account the total effect of all of the process factors, it is not recommended. The process of determining the optimal values takes a considerable amount of time and involves a number of trials, which may result in findings that are not accurate. In order to overcome these constraints of traditional methodologies, statistical experimental design techniques such as response surface methodology (RSM) may be utilized to simultaneously optimize all of the process parameters [26,27]. Attaining the largest possible yield of bio-oil via the process of pyrolysis is the major purpose of this inquiry into possible optimizations. To the best of our knowledge, there is a dearth of research in the current body of literature that has particularly engaged in an optimization study for the purpose of producing bio-oil by the thermal pyrolysis of seaweed.
Additionally, the use of a batch reactor for the pyrolysis of seaweed constitutes a unique contribution to the current body of literature. As a result, the purpose of this research is to investigate the combined impacts of three operational factors—temperature, residence time, and stirring speed—on the production yield of bio-oil that is the result of seaweed. Within the context of response surface methodology (RSM), the inquiry makes use of a batch reactor and applies the Box–Behnken design, also known as the BBD. It is then subjected to characterization via a variety of analytical techniques, such as FTIR (Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy), GC–MS (gas chromatography–mass spectrometry), as well as physicochemical and properties analysis. This is carried out after the bio-oil has been obtained under the maximum possible operational conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Raw Materials
The seaweed species Ascophyllum nodosum was collected from 22 Countryview Dr, Atherton QLD 4887 via Seaweed Enterprise Australia. They are the largest seaweed supplier company in Australia and import seaweed from Norway. Our sample was collected on 22 September 2022. It was initially dried in sunlight for eight days to remove excess moisture. The dried seaweed was then shredded into 1 mm pieces using a shredder, followed by further sun-drying to ensure optimal moisture reduction. Before use in experiments, the shredded biomass was thoroughly mixed to ensure uniformity in the feedstock.
2.2. Experimental Setup and Method
The experiments at CQUniversity’s Waste to Energy Laboratory in North Rockhampton involved the use of a batch reactor for conducting pyrolysis studies. The whole reactor configuration is seen in Figure 1. This reactor had its outer shell electrically insulated and heated by a ring furnace. The use of K-type thermocouples allowed for continuous temperature monitoring throughout the reactor. The pace at which the reactor heated and its temperature were both controlled by a PID Automatic Controller. To establish an inert atmosphere, a nitrogen gas bottle equipped with a pressure regulator/control valve was employed, with pressure adjusted to 30 kPa to eliminate oxygen presence. This ensured that all procedures were conducted at or around atmospheric pressure and temperature. Monitoring the reactor’s internal pressure was facilitated by a pressure gauge, and a relief valve was incorporated for safety measures. Gaseous condensate processing into bio-oil involved chilling equipment set at 5 °C. To maintain the water in the condenser below 0 °C, it was initially mixed with a polyethylene glycol solution.
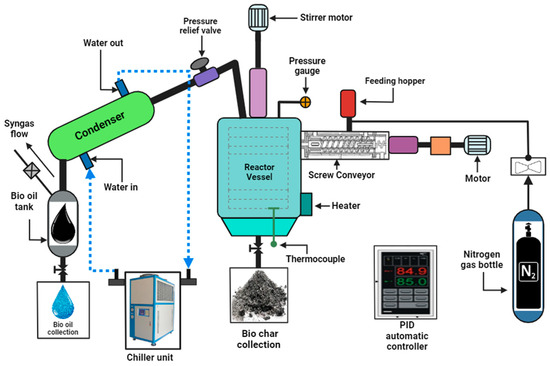
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram illustrating the pyrolysis batch reactor system employed in the present study.
The feeding hopper was used to introduce two kilograms of material. The reactor was kept oxygen-free by flushing it with nitrogen gas. During the 15 min purging operation, the reactor vessel, bio-oil tank, and syngas exhaust valves were kept open, while the feeding hopper lid remained closed. Subsequently, we initiated the data logging systems and activated the chiller. Then, we adjusted the temperature settings on each thermostat. The screw conveyor motor started up as the electric heater brought the reactor up to temperature at the study kept a fixed temperature for a predetermined amount of time, called “residence time”. The experiment had a residence time of around one hour. Because of this, the pyrolysis reaction began, and the feedstock was converted into biochar and vapour. The vapour then travelled through a water-cooled condenser, where the vapour’s condensable gases were extracted to produce bio-oil. A gas exhaust valve was used to expel any residual syngas or non-condensable gas. In the event that the syngas exhaust encountered an obstacle that caused the reactor pressure to rise over 40 kPa, a pressure relief valve would open to return the pressure to a safe level, below 40 kPa but above atmospheric pressure. Following the conclusion of the experiment, the heaters were deactivated to allow the temperature within the reactor to revert to its normal state. Subsequently, the biochar and bio-oil were gathered through their respective outlet valves.
The formula used to calculate the yields of different products from seaweed pyrolysis is outlined below.
To calculate the yield of bio-oil (Yo), the formula used is
Here, Yo represents the yield percentage of bio-oil, mo is the mass of bio-oil produced, and mf is the total mass of the feedstock used in the experiment.
In this equation, Yc is the biochar yield percentage, and mc is the mass of biochar produced.
This calculation is based on the principle of mass balance. Since the mass of syngas Yg cannot be measured directly in the absence of a mass flowmeter in the reactor, it is deduced by subtracting the combined yields of bio-oil and biochar from 100%. In this study, the mass balance analysis is performed using these equations. While biochar and syngas, two significant by-products of macroalgae pyrolysis, have various applications like soil improvement and energy production, this study focuses primarily on bio-oil. Hence, biochar and syngas are not analyzed in detail.
2.3. RSM Experimental Design
In this study, response surface methodology (RSM) was employed to optimize key operating parameters in seaweed pyrolysis, aiming to achieve the highest possible bio-oil yield. RSM is a widely recognized experimental strategy used for process optimization across various industries [28,29]. It involves developing a conceptual model to predict a specific response, followed by constructing equations and visualizations from this model to optimize the response.
The initial step in RSM is selecting an appropriate experimental design, which depends on the number of factors to be investigated and available resources. Preliminary experiments and literature reviews identified temperature, residence time, and stirring speed as the most significant factors affecting seaweed pyrolysis. The inert gas flow rate and the feedstock mass flow rate are two factors that were left out of this investigation. Since the inert gas flow rate was only used to cleanse the reactor before experimentation, it was considered to be of little consequence. Furthermore, the residence time was regulated by the motor speed, which in turn determined the feedstock mass flow rate, demonstrating a dependency between the two factors.
For this study, a Box–Behnken design (BBD) was chosen over other experimental designs like the 2n factorial or the 3n factorial [29]. The BBD is preferred for its efficiency in reducing the number of experiments required, making it less complex, costly, and time-consuming. When comparing the number of experiments to the coefficients, Ferreira et al. [30] demonstrated that the BBD performs marginally better than other designs in terms of efficiency. In addition to this, the BBD has the advantage of avoiding extreme factor combinations, which might potentially result in unfavourable effects. The BBD that was utilised in this investigation allocated three levels to three different factors: high (+1), low (−1), and centre (0). These levels were determined by the temperature, residence time, and stirring speed. The total number of experiments (N) in a BBD can be calculated using Equation (4):
where N is the total number of runs in the experiment, k is the number of factors, and r is the number of times the centre point trials are repeated. The result is fifteen experimental runs when there are three factors, three levels, and three repeats of the centre point (r = 3).
The levels for each factor were determined based on a balance between the capabilities of the experimental equipment and the need to create an effective response surface. To understand the relationship between the selected independent variables and the response (bio-oil yield), a second-order polynomial equation is typically used in BBD, as represented by Equation (5):
In this equation, Y represents the response (percentage of bio-oil); is the constant regression coefficient; , , and are the coefficients for linear, quadratic, and interaction effects [31,32]; and , , and represent the coded independent factors.
2.4. Methods for Characterization and Quantitative Analysis
2.4.1. Characterization of Seaweed
In order to determine the amount of moisture, volatile matter, fixed carbon, and ash that were present in seaweed samples, a proximate analysis was performed on them. Under a nitrogen environment, samples of A. nodosum weighing between 5 and 15 mg were analyzed using a Thermogravimetric Analyzer (TGA) in accordance with the Australian standard AS 1038.3-2000 [33]. An examination was performed. In order to determine the amount of volatile matter, the temperature was gradually increased to 550 °C at a rate of 5 °C per minute, and the amount of weight loss was tracked. Burning the leftover material after it had been decomposed allowed for the determination of the ash content.
Furthermore, a Vario Micro Cube CHNS analyzer was utilized in order to carry out the final analysis, which was carried out in accordance with the Australian standard AS1038.6.4 [34]. Quantification of the quantities of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulphur that were found in the seaweed samples was the purpose of this analysis. Using an oxygen-bomb calorimeter and according to the ASTM standard D4809 [35], the higher heating value (HHV) was accurately established.
2.4.2. Analytical Statistics
The study employed Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) to statistically analyze the results from the response surface methodology (RSM) optimization. This analysis helped identify the most effective treatments. The bio-oil yield’s actual and predicted values were derived from experiments and Minitab software (version 21.1.0), respectively. In order to determine whether or not the model was statistically suitable, ANOVA utilized a number of different factors. For the purpose of determining the significance of the F and p values, which played an important part in determining the link between bio-oil yield and a variety of independent variables, a p value that was less than 0.05 indicated that the association was statistically significant. Additional verification of the model’s dependability was carried out by employing correlation coefficients such as R2, R2(R2pred), R2(R2adj), and degrees of freedom. The generation of three-dimensional surface and contour plots was conducted in order to highlight the interaction impacts of separate process parameters on the production of bio-oil.
2.4.3. Bio-Oil Characterization
Utilizing Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), we conducted a detailed analysis of pyrolysis oil samples to identify various functional groups. In order to make use of the Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) approach, a Perkin Elmer FTIR/ATR spectrum analyzer with a resolution of 1 cm−1 was utilized. The matrix material that was utilised was Potassium Bromide. The investigation covered a wave number range from 4000 to 400 cm−1, and spectroscopic information was obtained by measuring the transmission of infrared photons via the sample chamber.
To quantitatively analyze oils obtained from the pyrolysis of various wastes, a Varian CP3800 mass spectrometry detector was used in conjunction with GC-MS. Each waste type necessitated a distinct oil sample, which was filtered and diluted with a methanol solvent solution (v/v ratio of 1:5). The GC-MS instrument was then supplied with a microliter of the diluted sample, and compound identification was achieved by matching peaks in the spectra to those in the NIST database. This comprehensive investigation enabled the precise determination of the chemical composition of the obtained pyrolysis oils.
The chemical makeup of the pyrolysis oil was further identified using a Flash 2000 Elemental Analyzer, providing accurate results. This equipment was sourced from the manufacturer company thermo fisher scientific, Waltham, MA, USA. Following the ASTM D5291 standard [36], percentages of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur, and oxygen were estimated by placing a small quantity of oil in a quartz reactor filled with helium and oxygen. Rapid combustion occurred due to high temperatures, leading to the creation of various substances. Via separation on a chromatographic column and examination using a conductivity detector, the proportions of each component were determined with precision using a specialized program.
To gauge the viability of the produced oil as a potential fuel source, its physicochemical attributes were meticulously analyzed. The study adhered to the ASTM D7052 [37] and D4052 [38] standards to assess kinematic viscosity and density, respectively. The oil’s pH was ascertained following the ASTM E70 protocol [39], utilizing an Omega DP24-pH meter. Water content determination hinged on the centrifuge sigma method, in alignment with the ASTM D2709 standard [40]. Lastly, the calorific value of the procured pyrolysis oil was gauged using an oxygen-bomb calorimeter, adhering to the ASTM D4809 method [35]. These properties, along with the standards and measuring tools, are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Physicochemical characteristics, ASTM specifications, and analytical instruments employed in the assessment of bio-oil.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Seaweed
In the study, the seaweed’s suitability as a feedstock for bio-oil production via pyrolysis was assessed via proximate and ultimate analyses. These analyses are critical in evaluating a solid material’s potential as a fuel source, where materials with high volatile matter and low ash and sulphur content are deemed ideal [41].
The proximate analysis revealed that the seaweed (Ascophyllum nodosum) had a high volatile matter content of 64.00%, suggesting its strong potential for bio-oil production. Volatile matter is crucial as it decomposes and evaporates at high temperatures, forming a range of chemicals, some of which can be condensed into liquid energy products [42]. The seaweed also exhibited low moisture content (<13%), which is favourable as high moisture levels can reduce energy content and accelerate feedstock degradation during pyrolysis [43].
The ultimate analysis showed that the seaweed had a carbon content of 45.8%, hydrogen of 7.30%, nitrogen of 0.92%, sulphur of 1.54%, and oxygen of 44.44%. The high carbon and hydrogen content indicates a higher potential heating value for the produced bio-oil. In contrast, lower nitrogen and sulphur levels are beneficial as they reduce the risk of NOx and SOx emissions, common pollutants associated with burning fuels [44]. The higher heating value (HHV) of the seaweed was found to be 18.90 MJ/kg, comparable to similar biomass types like Microalgae (Cladophora sp.) [45] and Macroalgae (Sargassum tenerrimum) [46].
Additionally, the seaweed’s ash content (12.8%) suggests a lower potential for acid formation in the resulting bio-oil, which can lead to reduced production of syngas and biochar. This ash content, along with the fixed carbon content (10.8%), further supports the suitability of seaweed as a pyrolysis feedstock. The proximate analysis data for seaweed align well with results obtained for similar algal feedstocks like Cladophora (Microalgae), Ulva prolifera (Macroalgae), Sargassum tenerrimum (Macroalgae), and Isochrysis (Microalgae) [47,48]. A comparison between the properties of seaweed and the properties of other microalgae and macroalgae found in the literature is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Dried seaweed properties compared to the literature.
3.2. Statistical Analysis of Developed Model
The purpose of this study was to conduct a statistical analysis on a model that was developed with the intention of increasing the amount of bio-oil that can be extracted from seaweed via the process of thermal pyrolysis. In the research project, the response surface methodology (RSM) was utilised in conjunction with the Box–Behnken design (BBD), and there was a total of fifteen experimental passes. Temperature (A), residence time (B), and stirring speed (C) were the three elements that were the primary focus of the experiments. The yield of bio-oil was the outcome that was assessed as a result of these investigations. The experiments and their corresponding yields of pyrolysis products are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Actual bio-oil yield, experimental design matrix, and prediction.
From Table 3, it is seen that the third run of these experiments resulted in the highest bio-oil production, which was 42.93 wt.%, while the tenth run generated the lowest yield, which was 35.71 wt.%. A graphical representation in Figure 2 compares the predicted and experimental bio-oil yields with a 45-degree line depicting predicted values and discrete data points showing actual yields. This comparison demonstrates a close match between predicted and actual values, suggesting the model’s accuracy in forecasting bio-oil yields.
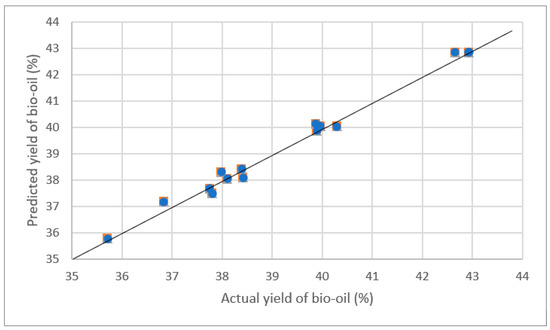
Figure 2.
Predicted and actual bio-oil (%) yield.
The correlation between the variables and the bio-oil yield is represented by the polynomial equation (Equation (6)):
To evaluate the statistical fit of the model, Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) was conducted. The ANOVA results, shown in Table 4, revealed a p-value of less than 0.0000 and a high F-value of 58.29, both indicating strong statistical support for the model. Model terms with a p-value below 0.05, including A, B, C, A2, B2, C2, AB, and BC, are considered significant in this context.

Table 4.
Quadratic model (ANOVA) for the production of bio-oil.
The agreement between the predicted R2pred and R2adj coefficients of determination was found to be satisfactory, with values of 0.8609 and 0.9736, respectively. This agreement is important as it indicates that the model reliably predicts the experimental outcomes. According to the literature, a difference of less than 0.2 between these two values is indicative of a reasonable agreement [51]. This close alignment between the predicted and adjusted R2 values further validates the model’s effectiveness in optimizing the bio-oil yield from seaweed via thermal pyrolysis. Predicted and actual yield of bio-oil (%) is shown in Figure 2.
3.3. Process Parameter Interactions on Bio-Oil Yield
Firstly, the interaction between temperature and residence time was analyzed at a fixed stirring speed of 10 rpm (as shown in Figure 3). It was observed that as both residence time and temperature increased, the bio-oil yield initially rose to a peak before eventually decreasing. Higher temperatures enhance the formation of volatiles, but beyond a certain point, these volatiles start to crack into gases like H2, CH4, and CO [52]. Similarly, an extended residence time promotes crosslinking and repolymerization reactions, favouring biochar formation over bio-oil [53].
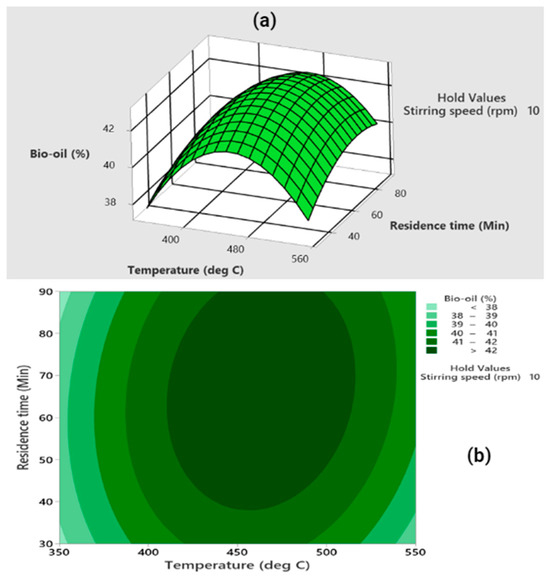
Figure 3.
(a) The interactive three-dimensional (3D) surface, and (b) the contour plot representing the synergistic impact of temperature and residence time on bio-oil yield, with a fixed stirring speed set at 10 revolutions per minute (rpm).
Statistical analysis using ANOVA (detailed in Table 4) revealed significant effects for both temperature and residence time. This was evident from the F-values of 39.33 for temperature and 9.37 for residence time and their squared terms having F-values of 332.80 and 32.44, respectively. The p-values for these terms were all found to be under 0.05, indicating their statistical significance in maximizing bio-oil yield. However, the interaction term between temperature and stirring speed (AC) was found to be insignificant, with a p-value of 0.101.
Following that, an evaluation was conducted to determine the impact that temperature and stirring rate have on the amount of bio-oil that is produced, all the while ensuring that the residence duration remains constant at 60 min. (shown in Figure 4). The findings indicated an increase in bio-oil yield with temperature until a specific point, after which secondary cracking of volatiles reduced bio-oil yield. Additionally, an increase in stirring speed positively influenced bio-oil yield due to improved heat transfer [54]. ANOVA results confirmed the significance of both temperature and stirring speed, with F-values of 39.33 and 7.17, respectively, and p-values below 0.05 indicate statistical significance. Consequently, the pyrolysis process is significantly more influenced by temperature than by stirring speed. Again, the interaction term (AC) between the two variables was found to be non-significant.
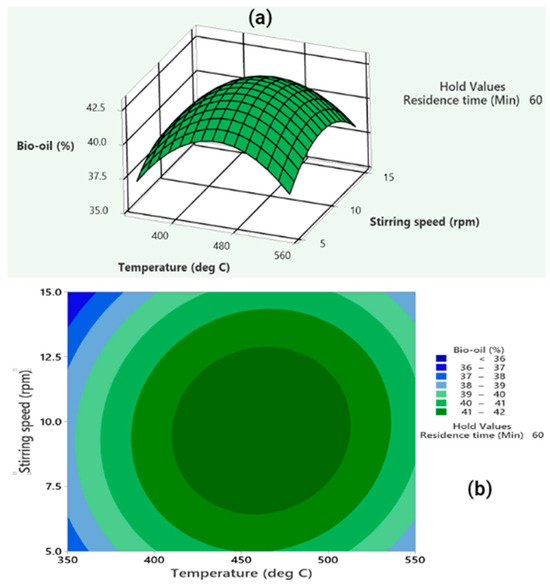
Figure 4.
(a) The three-dimensional surface and (b) contour plot depict the interactive influence of temperature and stirring speed on bio-oil yield, with a fixed residence time of 60 min.
Finally, the effect of residence time and stirring speed was examined at a constant temperature of 450 °C (as depicted in Figure 5). The optimal bio-oil yield was achieved at a stirring speed of 10 rpm and a moderate residence time range (40–90 min). Statistical analysis validated the significance of both the individual and squared terms related to residence time and stirring speed, as well as their interaction, in achieving maximum bio-oil yield.
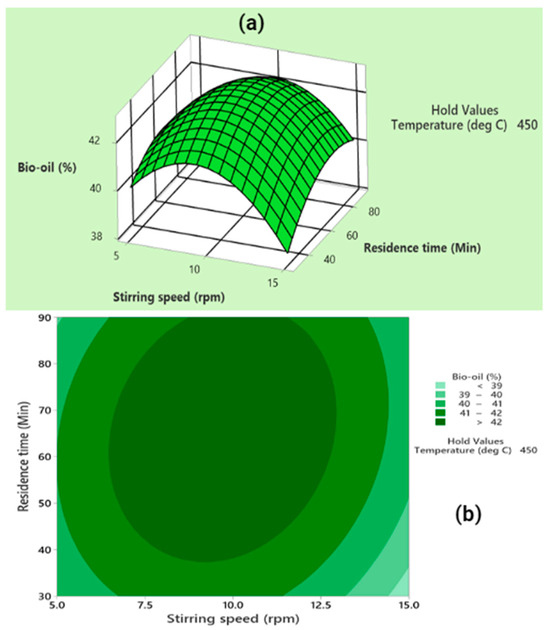
Figure 5.
(a) Generating a three-dimensional surface and (b) creating a contour plot to illustrate the interactive impact of residence time and stirring speed on bio-oil yield at a consistent temperature of 450 °C.
3.4. Bio-Oil Yield Process Parameter Validation
Using the Design Expert software (version 12) over a hundred potential settings were evaluated based on the criteria outlined in the study (in Table 5). Among these, the optimal conditions were identified: a temperature of 463.13 °C, a residence time of 65.7576 min, and a stirring speed of 9.7474 rpm, projected to yield 42.947 wt.% bio-oil.

Table 5.
Optimization independent/dependent parameter range.
However, due to the practical limitations of the laboratory equipment, slight adjustments were made to these settings for the actual experiments. The implemented conditions were a temperature of 463 °C, a residence time of 66 min, and a stirring speed of 9.80 rpm. Despite these minor deviations, the experimental results closely matched the software’s predictions, as detailed in Table 6. The observed error margin between the experimental and predicted bio-oil yields was minimal, at just 0.93%. This low error rate affirmed the reliability of the model used for the optimization.

Table 6.
Optimized bio-oil yields from experiments and predictions.
To ensure the validity of these findings, the experiments were replicated three times, averaging a bio-oil yield of 42.98%. This consistency in results further supports the effectiveness of the identified optimal conditions for producing bio-oil via the thermal pyrolysis of marine biomass. The close alignment of the experimental outcomes with the predictive model highlights the precision and reliability of the optimization process employed in this study.
3.5. Optimal Bio-Oil Production Characteristics
3.5.1. Physicochemical and Elemental Properties Analysis
From Table 7 in the study, the bio-oil obtained from seaweed exhibits a carbon content of 59.45%, as noted in the observation., which falls within the typical range of 55% to 60% for bio-oils produced from seaweed pyrolysis, as reported in previous studies [55]. This alignment with established ranges indicates the effectiveness of the pyrolysis process used in this study.
Although it is a bit lower than the normal range of 35–40% for pyrolysis oil obtained from waste biomass, the oxygen content of the bio-oil was measured at 32.17%. This figure is still rather close to the standard range [56]. For the purpose of determining the calorific value of bio-oil, the oxygen concentration is an extremely important factor. In spite of the fact that there has been an increase in the oxygen content in comparison to the original seaweed, it is absolutely necessary to perform additional reductions in the oxygen content in order for the bio-oil to become a viable source of fuel sources.
Furthermore, the bio-oil comprises 7.63% hydrogen and 0.73% nitrogen. It is important to highlight that, according to the elemental analysis, no sulphur was identified in the bio-oil. The existence of nitrogen and sulphur in bio-oil is typically deemed undesirable due to the potential emission of NOX and SOX gases during combustion, posing environmental hazards [57]. The nitrogen and sulphur levels present in bio-oil are primarily influenced by their concentrations in the initial feedstock. The enhanced elemental characteristics observed in the bio-oil, as opposed to the feedstock, indicate substantial chemical reactions taking place during the seaweed pyrolysis process.
These findings are consistent with the literature on bio-oils derived from similar types of waste materials, such as microalgae [58], macadamia nutshells [59], and cashew nutshells [60]. This comparison not only validates the results of this study but also provides a broader context within the field of bio-oil production from various biomasses.


Table 7.
The elemental composition of bio-oil derived from seaweed under optimal conditions was compared with information available in the literature.
Table 7.
The elemental composition of bio-oil derived from seaweed under optimal conditions was compared with information available in the literature.
| Elements | Seaweed | Microalgae [58] | Macadamia Nutshell [59] | Cashew Nutshell [60] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon (wt.%) | 59.45 | 74.66 | 59.27 | 69.5 |
| Hydrogen (wt.%) | 7.63 | 10.57 | 7.31 | 8.3 |
| Nitrogen (wt.%) | 0.73 | 7.13 | 0.21 | 0.6 |
| Sulphur (wt.%) | 0.01 | 0.81 | - | 0.03 |
| Oxygen a (wt.%) | 32.17 | 6.81 | 33.21 | 21.57 |
a By difference.
The quality of bio-oil derived from seaweed (A. nodosum) via optimized pyrolysis was assessed by analyzing its physicochemical properties. These properties were compared to those reported in the literature for similar feedstocks, as well as to the standards set for various types of industrial and engine fuels, such as ASTM-Grade G oil used in industrial burners [61], ASTM-Grade D oil for small commercial boilers [62], heavy fuel oil for marine diesel engines [63], and light fuel oil for different internal combustion engines [64]. This comparison is crucial to determine if the bio-oil produced aligns with previous findings and meets the standards for use as engine fuel. The physicochemical characteristics of bio-oil derived from seaweed (A. nodosum) is shown in Table 8.

Table 8.
The physicochemical characteristics of bio-oil derived from seaweed (A. nodosum) when compared to bio-oil produced from similar raw materials and conventional fuels.
Two crucial characteristics of engine fuel, namely kinematic viscosity and density, play a substantial role in impacting the performance of the engine. Kinematic viscosity affects the atomization and spray characteristics of the fuel, with high viscosity potentially impairing fuel injector performance. Density influences engine efficiency and combustion characteristics. The bio-oil obtained in this study showed a kinematic viscosity of 12.01 Cst and a density of 1.19 g/cc, aligning with findings from studies on bio-oils derived from macadamia nutshells [59] and microalgae [65]. These values are comparable to standard engine fuels, but further improvement is needed for practical applications.
Another vital characteristic of engine fuel is its pH level. Ideally, fuel should have a neutral pH for safe storage and transport. However, the bio-oil produced in this study exhibited a low pH value, indicating its acidic nature, which poses a challenge for its use in engines. This result corroborates with the findings of DeSisto et al. [66], Thangalazhy-Gopakumar et al. [67], and Salehi et al. [68], where similar feedstocks were used for bio-oil production. Despite the consistency with the existing literature, the acidic nature of the bio-oil derived in this study renders it unsuitable for use as an engine fuel.
The moisture that is present in the feedstock and the water that is produced during the pyrolysis process are the two key sources that contribute to the water content of bio-oil, which is an essential component that plays a significant role in determining its qualities [69]. In this research, the bio-oil obtained from seaweed was determined to have a water content of 23.72%. This percentage of water content corresponds with the oxygen concentration identified in elemental analysis, consistent with the results reported in previous literature [70,71,72].
The calorific value of bio-oil is notably influenced by the presence of water. In this investigation, the bio-oil generated displayed a moderate calorific value measuring 29.11 MJ/kg, a value that is comparatively lower than that of traditional commercial fuels. The calorific value aligns with the carbon concentration and moisture levels found in the bio-oil. Typically, an elevated carbon content and reduced water content in bio-oil lead to an increased calorific value, given that less energy is needed to vaporize the water [73]. Additionally, the temperature at which pyrolysis takes place is a significant factor in determining the amount of water that is present. Because of the secondary breaking of bio-oil, increased pyrolysis temperatures lead to the generation of additional water. This increases the amount of water that is produced. The calorific value of the bio-oil is eventually decreased as a consequence of this particular outcome [22].
The seaweed (A. nodosum)-derived bio-oil that was created under optimal conditions for the purpose of this inquiry is now inappropriate for use in engines due to the physicochemical properties that were discovered. In spite of this, it is demonstrated to be a feasible solution for heating applications in boilers or furnaces. There is a variety of enhancing techniques that may be performed in order to make this bio-oil suitable for engine applications. One of the processes involved is hydrodeoxygenation, which enhances the stability of bio-oil by eliminating compounds containing oxygen [74]; catalytic cracking, which is a process that involves the use of a catalyst in order to turn heavy fractions of bio-oil into lighter fractions [75]; distillation, which, in order to produce fuel products such as petrol, kerosene, and diesel, is a technique that separates various components by making use of the distinctive boiling temperatures of those components [76]; esterification, which reduces viscosity and acidity by reacting bio-oil with acid catalysts and alcohol [77]; and emulsification, which improves bio-oil quality by blending it with an emulsifier and engine fuel to reduce viscosity and increase calorific value [78]. These upgrading processes are crucial for enhancing the bio-oil’s properties, making it a more versatile and applicable energy source.
3.5.2. FTIR Analysis
The FTIR (Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy) analysis of the bio-oil sample, obtained under optimized conditions, provides critical insights into its chemical composition by identifying various functional groups of the compounds present. This analysis is depicted in Figure 6, with the corresponding data presented in Table 9.
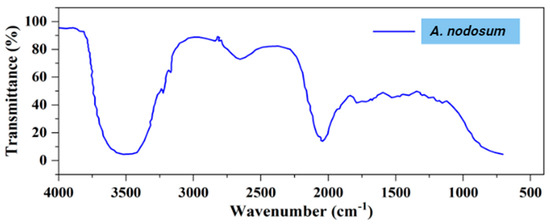
Figure 6.
FTIR spectra of bio-oil derived from A. nodosum under optimal conditions.

Table 9.
The list of functional groups present in spectra obtained from seaweed (A. nodosum).
The FTIR spectrum shows O−H stretching vibrations in the range of 3200 to 3400 cm−1, confirming the presence of phenols and alcohols. These compounds are crucial for the bio-oil’s stability, as they prevent oxidation when exposed to air. This characteristic is especially relevant for preserving the quality of bio-oil during storage and handling [79]. Stretching vibrations of C=O, observed between 1350 and 1650 cm−1, indicate the presence of ketones and aldehydes [26]. The existence of aldehydes, however, may negatively impact the stability of bio-oil, as they tend to reduce its preservation capabilities [80]. The C−H stretching vibrations between 2900 and 3000 cm−1, along with C−H deformation vibrations in the range of 1450 to 1550 cm−1, suggest the presence of alkane groups in the bio-oil [81]. Peaks between 1800 and 2000 cm−1 are indicative of C=C stretching vibrations, confirming the presence of alkenes. Additionally, absorption peaks between 1240 and 1340 cm−1 are characteristic of aromatic groups [51]. The presence of these groups suggests that bio-oil has the potential to form liquid hydrocarbons, which is significant for various applications [82].
The FTIR analysis effectively demonstrates that while the intensity of absorption bands may vary, their locations remain consistent. This consistency is crucial for the quick classification of different chemical compounds present in the bio-oil. For a more detailed and quantitative analysis of these compounds, techniques like GC−MS can be employed [83]. The combination of FTIR and GC−MS analyses provides a comprehensive understanding of the bio-oil’s composition, which is essential for determining its suitability for various applications.
3.5.3. GC–MS Analysis
The GC−MS analysis is a crucial technique employed in this study to identify the chemical composition of bio-oil produced from seaweed (A. nodosum) under optimal pyrolysis conditions. In GC-MS, each chemical compound detected in the bio-oil sample is represented by a peak in the GC−MS spectra. These peaks are quantified based on their area, expressed as a percentage of the total peak area, which sums to 100%. However, due to the extensive range of compounds detected (over a thousand peaks), this study focuses on compounds with large peak areas (greater than 0.2%) and with more than 80% similarity in their spectral profiles.
To ensure reliability, the experiments were replicated, and the peak areas were averaged. This approach confirms the consistency of the detected compounds across different runs. The key findings from the GC−MS analysis are summarized in Table 10 of the study. Notably, due to the limitation of the GC−MS apparatus, which operates at a maximum oven temperature of 200 °C, some heavier compounds that boil at temperatures up to 463 °C (the pyrolysis temperature) went undetected.

Table 10.
Under ideal conditions, the following is a list of chemical components that can be found in bio-oil that is generated from seaweed (A. nodosum).
Significant findings include the detection of benzene and toluene, with peak areas of 1.76% and 1.58%, respectively, identified at specific retention times (7.17 and 9.87 min). These compounds are crucial in gasoline production, indicating the potential of bio-oil in generating liquid hydrocarbons. Phenolic compounds like phenol and 4-methoxyphenol, likely derived from the decomposition of lignin in seaweed, were also prominent, noted at 16.39 and 19.27 min. Their high concentration in bio-oil contributes to its stability and resistance to oxidation.
Furthermore, the bio-oil contains acidic compounds such as acetic acid and methyl 2-oxopropanoate, with peak areas of 1.09% and 0.69%, respectively, found at 13.49 and 29.39 min. These acids are valuable in producing various chemicals, including esters, vinyl acetate monomers, and vinegar. Additionally, the presence of alkanes and alkenes, key components in gasoline and the chemical industry, was noted. However, extracting these valuable components from bio-oil requires highly effective separation and purification techniques to transform them into value-added products.
These findings, particularly the identification of key compounds like benzene, toluene, and phenolic compounds, emphasize the potential of bio-oil from seaweed pyrolysis as a source of valuable chemicals and fuel components. The study suggests the need for further research into refining and purifying these compounds to enhance the commercial viability of bio-oil.
The GC–MS analysis of the bio-oil produced from seaweed (A. nodosum) revealed a diverse range of chemical compounds categorized into 11 functional groups (in Table 10). This analysis highlights the presence of a wide array of phenolic, aromatic (including single-ring, polycyclic, and oxygenated), and oxygenated compounds, as well as hydrocarbons in the bio-oil.
A significant finding is the abundance of aromatic compounds in the bio-oil. These compounds are economically and environmentally valuable due to their potential applications in various industries, making the aromatic functional group a key component of the bio-oil [84]. The presence of moderate amounts of oxygenated compounds in the bio-oil, however, poses certain challenges. High concentrations of these compounds can lead to issues like poor storage stability, increased acidity, and a decrease in energy density and calorific value of the fuel [85]. This is because oxygenated compounds tend to be less energy-dense compared to hydrocarbons.
Furthermore, the bio-oil contains acidic compounds which can catalyze polymerization reactions during condensation. These reactions are driven by volatile functional groups and free oligomer radicals present in the bio-oil, leading to severe aging issues and limiting its suitability as engine fuel [86]. Additionally, these acidic compounds can degrade storage tanks and transportation lines, posing challenges for the long-term storage and transport of bio-oil [55]. The presence of nitrogen and oxygenated compounds in the bio-oil indicates a need for refining to remove these undesirable elements. This refining process is crucial to enhance the quality of the bio-oils, making them suitable as replacements for engine fuels.
Lastly, the bio-oil also contains hydrocarbons, but their quantity tends to decrease at higher pyrolysis temperatures (above 450 °C). This reduction is attributed to the breaking of weak C–H bonds at these higher temperatures, which adversely affects the relative quality of hydrocarbon materials in the bio-oil [87]. This underscores the importance of optimizing the pyrolysis temperature to balance the yield and quality of the desired compounds in the bio-oil.
4. Conclusions
This study successfully employed a batch reactor for seaweed pyrolysis in a nitrogen atmosphere, optimizing the process to enhance bio-oil production. Key variables, including temperature, residence time, and stirring speed, were systematically varied using response surface methodology (RSM) combined with the Box–Behnken design (BBD). The BBD proved effective in mapping the relationship between these variables and bio-oil yield, with high reliability indicated by an R2 value of 0.9926. The analysis revealed that temperature is the most significant factor influencing bio-oil production. The optimal conditions for maximum bio-oil yield were identified as a temperature of 463.13 °C, a residence time of 65.75 min, and a stirring speed of 9.74 rpm. Under these conditions, a bio-oil yield of 42.94 wt% was achieved, closely aligning with the experimental results. The characterization of the bio-oil derived from seaweed at these optimum conditions showed a diverse range of compounds, including phenolics, aromatics, oxygenates, and hydrocarbons, with phenolics being the most prevalent. The bio-oil’s high viscosity (12.01 Cst) and water content (23.72%) limit its direct use in engines but make it suitable for heating applications in boilers and furnaces. Moreover, it shows promise as a source of valuable chemicals, particularly when used as an additive. The potential for upgrading the bio-oil to broaden its application scope, especially in engines, is an area for future exploration.
Author Contributions
Z.I.R. was responsible for conducting the experiments, performing data analysis, interpreting the data scientifically by constructing logical arguments, and drafting the manuscript. M.G.R. acted as the supervisor and corresponding author. M.I.J. and M.M.H. supervised the project and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
I declare that this study was carried out for my Master of Research program at CQUniversity.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sikder, M.; Wang, C.; Yao, X.; Huai, X.; Wu, L.; KwameYeboah, F.; Wood, J.; Zhao, Y.; Dou, X. The integrated impact of GDP growth, industrialization, energy use, and urbanization on CO2 emissions in developing countries: Evidence from the panel ARDL approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.S.; Pudza, M.Y.; Yihdego, Y. Harnessing the energy transition from total dependence on fossil to renewable energy in the Arabian Gulf region, considering population, climate change impacts, ecological and carbon footprints, and United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals. Sustain. Earth Rev. 2023, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.A.S. The 50th Anniversary of the Limits to Growth: Does It Have Relevance for Today’s Energy Issues? Energies 2022, 15, 4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. CO2 Emissions in 2022; IEA: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, M.; Muneer, T. Energy supply, its demand and security issues for developed and emerging economies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 1388–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Review of World Energy. Share of Primary Energy Consumption That Comes from Renewables—Using the Substitution Method. 2023. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/renewable-share-energy (accessed on 5 January 2024).
- Islam Rony, Z.; Rasul, M.G.; Jahirul, M.I.; Mofijur, M. Harnessing marine biomass for sustainable fuel production through pyrolysis to support United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals. Fuel 2024, 358, 130099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, H.; Cristino, A.F.; Orišková, S.; Galhano dos Santos, R. Bio-Oil: The Next-Generation Source of Chemicals. Reactions 2022, 3, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Rasul, M.G.; Khan, M.M.K.; Ashwath, N.; Jahirul, M.I. Energy recovery from municipal solid waste using pyrolysis technology: A review on current status and developments. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 145, 111073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, F.; Brown, R.C.; Martínez, J.D. Auger reactors for pyrolysis of biomass and wastes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 102, 372–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, H.J.; Ko, J.H.; Heo, H.S.; Park, H.J.; Park, Y.K. Influence of Reaction Conditions on Fast Pyrolysis of Macroalge. 2010. Available online: https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:42089814 (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Nam, H.; Capareda, S.C.; Ashwath, N.; Kongkasawan, J. Experimental investigation of pyrolysis of rice straw using bench-scale auger, batch and fluidized bed reactors. Energy 2015, 93, 2384–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, P.; Godbout, S.; Raghavan, V. Pyrolysis in auger reactors for biochar and bio-oil production: A review. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 161, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Shyam, S.; Reddy, B.R.; Govindaraju, K.; Vinu, R. Microwave-assisted pyrolysis and analytical fast pyrolysis of macroalgae: Product analysis and effect of heating mechanism. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 3009–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Zavaglia, A.; Prieto Lage, M.A.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Mejuto, J.C.; Simal-Gandara, J. The potential of seaweeds as a source of functional ingredients of prebiotic and antioxidant value. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanik, J.; Stahl, R.; Troeger, N.; Sinag, A. Pyrolysis of algal biomass. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 103, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.; Jones, J.; Kubacki, M.; Bridgeman, T. Classification of macroalgae as fuel and its thermochemical behaviour. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6494–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, M.; Chen, M.; Li, D.; Min, F.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Ren, Z.; Yan, Y. A comparative study of thermolysis characteristics and kinetics of seaweeds and fir wood. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1883–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.J.; Ryu, C.; Jeon, J.-K.; Park, J.; Suh, D.J.; Suh, Y.-W.; Chang, D.; Park, Y.-K. The characteristics of bio-oil produced from the pyrolysis of three marine macroalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3512–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budarin, V.L.; Zhao, Y.; Gronnow, M.J.; Shuttleworth, P.S.; Breeden, S.W.; Macquarrie, D.J.; Clark, J.H. Microwave-mediated pyrolysis of macro-algae. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2330–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, N.; Banks, S.W.; Nowakowski, D.J.; Rosas, J.G.; Cara, J.; Sánchez, M.E.; Bridgwater, A.V. Effect of temperature on product performance of a high ash biomass during fast pyrolysis and its bio-oil storage evaluation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 172, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, X.-S.; Garcia-Perez, M.; Mourant, D.; Rhodes, M.J.; Li, C.-Z. Effects of particle size on the fast pyrolysis of oil mallee woody biomass. Fuel 2009, 88, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, Z.; Salema, A.A.; Ani, F.N. A new technique to pyrolyse biomass in a microwave system: Effect of stirrer speed. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 128, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Syed-Hassan, S.S.A.; Hu, X.; Han, H.; Su, S.; Xu, K.; Jiang, L.; Guo, J.; Berthold, E.E.S.; et al. Effects of heating rate on the evolution of bio-oil during its pyrolysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 163, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohaib, Q.; Habib, M.; Fawad Ali Shah, S.; Habib, U.; Ullah, S. Fast pyrolysis of locally available green waste at different residence time and temperatures. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2017, 39, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.K.; Mondal, M.K. Bio-energy generation from sagwan sawdust via pyrolysis: Product distributions, characterizations and optimization using response surface methodology. Energy 2019, 170, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Investigation of waste biomass co-pyrolysis with petroleum sludge using a response surface methodology. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, P.; Trutna, L. NIST/SEMATECH e-Handbook of Statistical Methods. Available online: https://www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/ (accessed on 30 December 2023).
- Kuehl, R.O. Design of Experiments: Statistical Principles of Research Design and Analysis, 2nd ed.; Brooks/Cole: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; Bruns, R.E.; Ferreira, H.S.; Matos, G.D.; David, J.M.; Brandão, G.C.; da Silva, E.G.P.; Portugal, L.A.; dos Reis, P.S.; Souza, A.S.; et al. Box-Behnken design: An alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charusiri, W.; Numcharoenpinij, N. Characterization of the optimal catalytic pyrolysis conditions for bio-oil production from brown salwood (Acacia mangium Willd) residues. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 106, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, F.; Erginel, N. Optimization of bio-oil production using response surface methodology and formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) at elevated pressures. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 142, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australia, S. Coal and Coke-Analysis and Testing Part 3: Proximate Analysis of Higher Rank Coal (AS 1038.3-2000); SAI Global: Chicago, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- AS1038.6.4; Higher Rank Coal and Coke—Ultimate Analysis—Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen—Instrumental Method 2005. Standards Australia: Canberra, Australia, 2005.
- D4809-2013, A; Standard Test Method for Heat of Combustion of Liquid Hydrocarbon Fuels by Bomb Calorimeter (Precision Method). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- D5291-21, A; Standard Test Methods for Instrumental Determination of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen in Petroleum Products and Lubricants. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- D7052, A; Standard Test Method for Determining Impact Resistance of New Low Slope Roof Membranes Using Steel Balls (Z8295Z). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- D4052-18a, A; Standard Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- E70-19, A; Standard Test Method for pH of Aqueous Solutions with the Glass Electrode. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- D2709-22, A; Standard Test Method for Water and Sediment in Middle Distillate Fuels by Centrifuge. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Hasan, M.M.; Rasul, M.G.; Ashwath, N.; Jahirul, M.I.; Khan, M.M.K. Effect of Temperature on the Characteristics of Bio-oil Produced from Slow Pyrolysis of Beauty Leaf Fruit Shell. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Applied Energy, Bangkok, Thailand, 1–10 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Bakar, M.S.; Ahmed, A.; Jeffery, D.M.; Hidayat, S.; Sukri, R.S.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Jamil, F.; Khurrum, M.S.; Inayat, A.; Moogi, S.; et al. Pyrolysis of solid waste residues from Lemon Myrtle essential oils extraction for bio-oil production. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 123913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routa, J.; Brännström, H.; Laitila, J. Effects of storage on dry matter, energy content and amount of extractives in Norway spruce bark. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 143, 105821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, C.W.; Reyes Molina, E.A.; André, N.; Hamilton, C.; Park, S.; Fasina, O.; Adhikari, S.; Kelley, S.S.; Tumuluru, J.S.; Rials, T.G.; et al. Blended Feedstocks for Thermochemical Conversion: Biomass Characterization and Bio-Oil Production From Switchgrass-Pine Residues Blends. Front. Energy Res. 2018, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, F.; Norouzi, O.; Tavasoli, A. Hydrothermal gasification of Cladophora glomerata macroalgae over its hydrochar as a catalyst for hydrogen-rich gas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Fernandes, A.C.; Kumar, J.; Muraleedharan, U.D.; Bhaskar, T. Valorization of Sargassum tenerrimum: Value addition using hydrothermal liquefaction. Fuel 2018, 222, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Fu, F.; Chen, B.; Liu, H. Hydrothermal liquefaction of Ulva prolifera macroalgae and the influence of base catalysts on products. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 121286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Kumar, A.; Fernandes, A.C.; Saini, K.; Negi, S.; Muraleedharan, U.D.; Bhaskar, T. Solid base catalytic hydrothermal liquefaction of macroalgae: Effects of process parameter on product yield and characterization. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Moreno, J.; Callejón-Ferre, A.; Pérez-Alonso, J.; Velázquez-Martí, B. A review of the mathematical models for predicting the heating value of biomass materials. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 3065–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, G.D.; Everard, C.D.; Fagan, C.C.; McDonnell, K.P. Prediction of quality parameters of biomass pellets from proximate and ultimate analysis. Fuel 2013, 111, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Chakraborty, J.P.; Mondal, M.K. Pyrolysis of torrefied biomass: Optimization of process parameters using response surface methodology, characterization, and comparison of properties of pyrolysis oil from raw biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Rasul, M.G.; Ashwath, N.; Khan, M.M.K.; Jahirul, M.I. Fast pyrolysis of Beauty Leaf Fruit Husk (BLFH) in an auger reactor: Effect of temperature on the yield and physicochemical properties of BLFH oil. Renew. Energy 2022, 194, 1098–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Sahu, J.N.; Ganesan, P. Effect of process parameters on production of biochar from biomass waste through pyrolysis: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.M. Effect of particle size and temperature on evolution rate of volatiles from coal. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1993, 27, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, S.; Uzoejinwa, B.B.; Zheng, A.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Abomohra, A.E.-F. A state-of-the-art review on dual purpose seaweeds utilization for wastewater treatment and crude bio-oil production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 222, 113253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echresh Zadeh, Z.; Abdulkhani, A.; Saha, B. A comparative production and characterisation of fast pyrolysis bio-oil from Populus and Spruce woods. Energy 2021, 214, 118930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djandja, O.S.; Yin, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Duan, P. Progress in thermochemical conversion of duckweed and upgrading of the bio-oil: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, U.; Das, K. Comparative evaluation of thermochemical liquefaction and pyrolysis for bio-oil production from microalgae. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 5472–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Rasul, M.; Jahirul, M.; Khan, M. Fast pyrolysis of macadamia nutshell in an auger reactor: Process optimization using response surface methodology (RSM) and oil characterization. Fuel 2023, 333, 126490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.; dos Reis Orsini, R.; Vaz, J.M.; Penteado, J.C.; Spinacé, E.V. Production of Biochar, Bio-Oil and Synthesis Gas from Cashew Nut Shell by Slow Pyrolysis. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Liu, R.; He, Y.; Chai, M.; Cai, J. Bio-oil production from fast pyrolysis of rice husk in a commercial-scale plant with a downdraft circulating fluidized bed reactor. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 171, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.; Binder, S.; Apfelbacher, A.; Gasson, J.R.; Ramírez García, P.; Hornung, A. Production and characterization of a new quality pyrolysis oil, char and syngas from digestate—Introducing the thermo-catalytic reforming process. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 113, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoulis, P.; Kazangas, D.; Doss, T.P.; Kaiktsis, L. Development and CFD validation of an integrated model for marine heavy fuel oil thermophysical properties. J. Energy Eng. 2018, 144, 04018059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhyani, V.; Bhaskar, T. A comprehensive review on the pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 695–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, S.S.M.; El-Gendy, N.S. Evaluation of fuel properties for microalgae Spirulina platensis bio-diesel and its blends with Egyptian petro-diesel. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S2040–S2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSisto, W.J.; Hill, N.; Beis, S.H.; Mukkamala, S.; Joseph, J.; Baker, C.; Ong, T.-H.; Stemmler, E.A.; Wheeler, M.C.; Frederick, B.G.; et al. Fast Pyrolysis of Pine Sawdust in a Fluidized-Bed Reactor. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 2642–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangalazhy-Gopakumar, S.; Adhikari, S.; Ravindran, H.; Gupta, R.B.; Fasina, O.; Tu, M.; Fernando, S.D. Physiochemical properties of bio-oil produced at various temperatures from pine wood using an auger reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8389–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, E.; Abedi, J.; Harding, T. Bio-oil from Sawdust: Effect of Operating Parameters on the Yield and Quality of Pyrolysis Products. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 4145–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, M.; de la Puente, G.; Sedran, U. Fuels from bio-oils: Bio-oil production from different residual sources, characterization and thermal conditioning. Fuel 2012, 95, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.J.; Lin, J.; Alviso, D.; Rolón, J.C. Effect of temperature and particle size on the yield of bio-oil, produced from conventional coconut core pyrolysis. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2016, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shumeiko, B.; Auersvald, M.; Vrtiška, D.; Šimáček, P.; Straka, P.; Kubička, D. Improved bio-oil upgrading due to optimized reactor temperature profile. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 222, 106977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onay, O. Influence of pyrolysis temperature and heating rate on the production of bio-oil and char from safflower seed by pyrolysis, using a well-swept fixed-bed reactor. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budarin, V.L.; Clark, J.H.; Lanigan, B.A.; Shuttleworth, P.; Breeden, S.W.; Wilson, A.J.; Macquarrie, D.J.; Milkowski, K.; Jones, J.; Bridgeman, T.; et al. The preparation of high-grade bio-oils through the controlled, low temperature microwave activation of wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6064–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafaghat, H.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, I.-G.; Jae, J.; Jung, S.-C.; Park, Y.-K. Catalytic hydrodeoxygenation of crude bio-oil in supercritical methanol using supported nickel catalysts. Renew. Energy 2019, 144, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, Á.; Hita, I.; Arandes, J.M.; Bilbao, J. Influence of the Composition of Raw Bio-Oils on Their Valorization in Fluid Catalytic Cracking Conditions. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 7458–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, D.A.R.; da Silva Ribeiro, H.J.; Ferreira, C.C.; de Andrade Cordeiro, M.; Guerreiro, L.H.H.; Pereira, A.M.; dos Santos, W.; Santos, M.C.; de Carvalho, F.B.; Junior, J.O.C.S. Fractional Distillation of Bio-Oil Produced by Pyrolysis of Açaí (Euterpe oleracea) Seeds. In Fractionation; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; p. 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondakh, R.C.; Hambali, E.; Indrasti, N.S. Improving characteristic of bio-oil by esterification method. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 230, 012071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Ellis, N. Upgrading Bio-oil through Emulsification with Biodiesel: Mixture Production. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Ye, X.P. Stability of crude bio-oil and its water-extracted fractions. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 132, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Moore, A.; Tilotta, D.; Kelley, S.; Park, S. Toward Understanding of Bio-Oil Aging: Accelerated Aging of Bio-Oil Fractions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2011–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Bhattacharya, T.K.; Verma, A.K.; Haydary, J. Optimization of process parameters for bio-oil synthesis from pine needles (Pinus roxburghii) using response surface methodology. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtyari, A.; Makarem, M.A.; Rahimpour, M.R. Light olefins/bio-gasoline production from biomass. In Bioenergy Systems for the Future; Dalena, F., Basile, A., Rossi, C., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 87–148. [Google Scholar]
- Isa, K.M.; Daud, S.; Hamidin, N.; Ismail, K.; Saad, S.A.; Kasim, F.H. Thermogravimetric analysis and the optimisation of bio-oil yield from fixed-bed pyrolysis of rice husk using response surface methodology (RSM). Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 33, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.T.; Horne, P.A. Analysis of aromatic hydrocarbons in pyrolytic oil derived from biomass. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1995, 31, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chang, J.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y. Review of biomass pyrolysis oil properties and upgrading research. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thring, R.W.; Katikaneni, S.P.R.; Bakhshi, N.N. The production of gasoline range hydrocarbons from Alcell® lignin using HZSM-5 catalyst. Fuel Process. Technol. 2000, 62, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Fan, T.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, M. Investigation on chemical structure and hydrocarbon generation potential of lignite in the different pretreatment process. Fuel 2021, 291, 120205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).