Recent Trends and Issues of Energy Management Systems Using Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- In this paper, a comprehensive analysis is provided on the construction of ML-based EMS, encompassing a variety of key component systems.
- Enhancements in stability, efficiency, and reliability within EMS are attributed to the integration of ML technologies, highlighting their pivotal role in optimizing energy flow and efficient system operations.
- An in-depth comparison of EMS framework characteristics is presented, along with suggestions for promising ML candidates tailored to specific frameworks.
- The EMS frameworks, recent trends, operational constraints, and challenging issues of ML-based EMS are discussed to provide insights into future developments and enhancements.
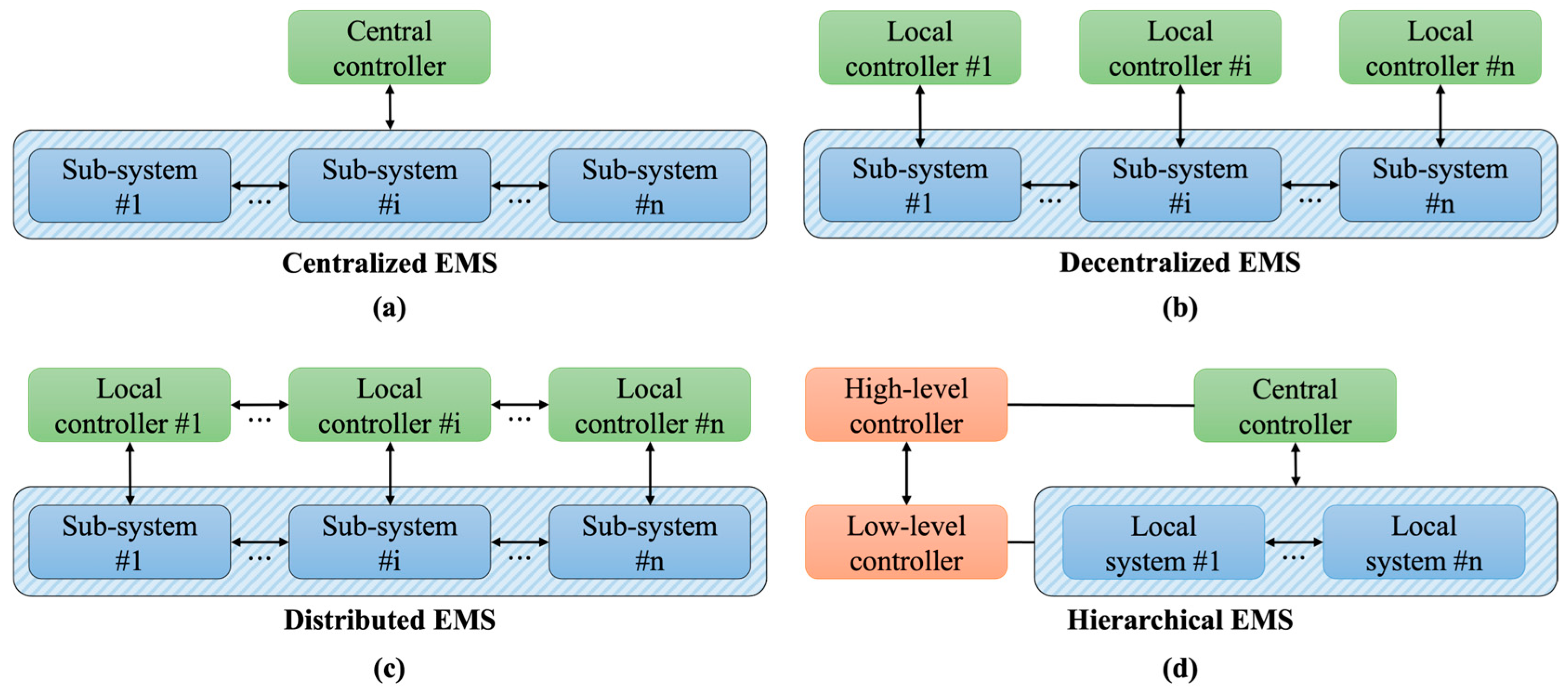
2. Architectural Frameworks of EMS
2.1. Centralized EMS Framework
2.2. Decentralized EMS Framework
2.3. Distributed EMS Framework
2.4. Hierarchical EMS Framework
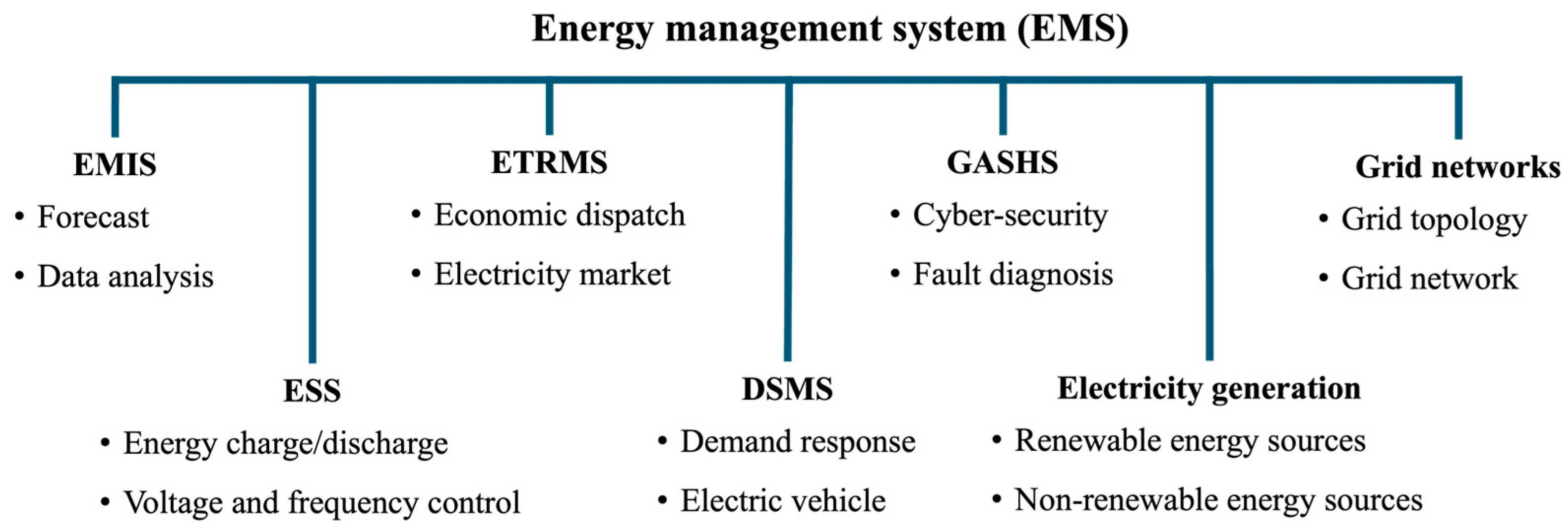
3. ML-Based EMS Approaches
3.1. ML-Based EMIS
3.2. ML-Based GASHS
3.3. ML-Based ESS
3.4. ML-Based ETRMS
3.5. ML-Based DSMS
4. Operational Constraints and Challenging Issues
4.1. Operational Constraints in ML-Based EMS
4.2. Operational Challenging Issues in ML-Based EMS
4.3. Technical Challenging Issues in ML-Based EMS
4.4. Challenges of Case Studies in ML-Based EMS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMI | Advanced Metering Infrastructure | IEA | International Energy Agency |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network | IEC | International Electromechanical Commission |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network | ILM | Intrusive Load Monitoring |
| DER | Distributed Energy Resource | LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network | ML | Machine Learning |
| DR | Demand Response | NILM | Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring |
| DSMS | Demand-Side Management System | PAR | Peak-to-Average Ratio |
| EMIS | Energy Management Information System | RDFC | Response-Driven Frequency Control |
| EMS | Energy Management System | RES | Renewable Energy Source |
| ESS | Energy Storage System | RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| ETRMS | Energy Trading Risk Management System | RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| EV | Electric Vehicle | SCADA | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition |
| GASHS | Grid Autonomation and Self-Healing System | SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit | V2G | Vehicle-to-Grid |
References
- Advance Market Analytics. Smart Grid IT Systems Comprehensive Study by Application, Services, Software, Hardware Players and Region—Global Market Outlook to 2026. Available online: https://www.advancemarketanalytics.com/reports/7385-global-smart-grid-it-systems-market-1 (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Energy Transitions Require Innovation in Power System Planning. Available online: https://www.iea.org/articles/energy-transitions-require-innovation-in-power-system-planning (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). 2020 Smart Grid System Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/oe/articles/2020-smart-grid-system-report (accessed on 22 December 2023).
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Electricity Grids and Secure Energy Transitions. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/electricity-grids-and-secure-energy-transitions (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Souza Junior, M.E.T.; Freitas, L.C.G. Power electronics for modern sustainable power systems: Distributed generation, microgrids and smart grids—A review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, A.F.; Mokhlis, H.; Mansor, N.N.; Jamian, J.J.; Wang, L.; Muhammad, M.A. Power distribution system outage management using improved resilience metrics for smart grid applications. Energies 2023, 16, 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joinup. IEC 61970-1:2005—Energy Management System Application Program Interface (EMS-API)—Part 1: Guidelines and General Requirements. Available online: https://joinup.ec.europa.eu/solution/iec-61970-12005-energy-management-system-application-program-interface-ems-api-part-1-guidelines-and (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- Sharma, P.; Dutt Mathur, H.; Mishra, P.; Bansal, R.C. A critical and comparative review of energy management strategies for microgrids. Appl. Energy 2022, 327, 120028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathor, S.K.; Saxena, D. Energy management system for smart grid: An overview and key issues. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 4067–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliani, M.; Barkany, A.E.; Abbassi, I.E.; Darcherif, A.M.; Mahmoudi, M. Energy management in the smart grid: State-of-the-art and future trends. Int. J. Eng. Bus. Manag. 2021, 13, 184797902110329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakran, S.; Chanana, S. Smart operations of smart grids integrated with distributed generation: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukkarasu, G.S.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Jamei, E.; Horan, B.; Mekhilef, S.; Stojcevski, A. Role of optimization techniques in microgrid energy management systems—A review. Energy Strategy Rev. 2022, 43, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, Y.; El Kamoun, N.; Lakrami, F. A survey: Centralized, decentralized, and distributed control scheme in smart grid systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 7th Mediterranean Congress of Telecommunications (CMT), Fez, Morocco, 24–25 October 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; El-Bayeh, C.Z.; Lai, C.; Eicker, U. Multi-level energy management systems toward a smarter grid: A review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 71994–72016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Choi, B.J. State-of-the-art artificial intelligence techniques for distributed smart grids: A review. Electronics 2020, 9, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omitaomu, O.A.; Niu, H. Artificial intelligence techniques in smart grid: A survey. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 548–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, A.; Balachandra, P. Smart grid to energy internet: A systematic review of transitioning electricity systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 215787–215805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketter, W.; Collins, J.; Saar-Tsechansky, M.; Marom, O. Information systems for a smart electricity grid: Emerging challenges and opportunities. ACM Trans. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2018, 9, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Khalid, A.; Javaid, N. Towards efficient energy management in smart grids considering microgrids with day-ahead energy forecasting. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 182, 106232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalci, Y. A survey on smart metering and smart grid communication. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, A.; Conti, M. Key management systems for smart grid advanced metering infrastructure: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2831–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Qin, Y.; Hao, C.; Cao, J. Optimal energy management strategies for energy internet via deep reinforcement learning approach. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeimozafar, M.; Monaghan, R.F.D.; Barrett, E.; Duffy, M. A review of behind-the-meter energy storage systems in smart grids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 164, 112573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, R.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Thilak, K.R.; Balaji, A.N.V.S.S. A review on demand side management: Definition, scope, challenges and benefits. In Proceedings of the 2022 8th International Conference on Smart Structures and Systems (ICSSS), Chennai, India, 21–22 April 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Honarmand, M.E.; Hosseinnezhad, V.; Hayes, B.; Shafie-Khah, M.; Siano, P. An overview of demand response: From its origins to the smart energy community. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 96851–96876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morstyn, T.; Hredzak, B.; Agelidis, V.G. Control strategies for microgrids with distributed energy storage systems: An overview. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 3652–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Sanseverino, E.R.; Luna, A.; Dragicevic, T.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M. Microgrid supervisory controllers and energy management systems: A literature review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, E.; Badri, A.; Ebrahimpour, R. Decentralized multi-agent based energy management of microgrid using reinforcement learning. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 122, 106211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zou, J.; Yung Chung, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, N.; Voropai, N.; Xu, D. Multi-microgrid energy management systems: Architecture, communication, and scheduling strategies. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 9, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavas, C.-S.; Kyriakarakos, G.; Arvanitis, K.G.; Papadakis, G. A multi-agent decentralized energy management system based on distributed intelligence for the design and control of autonomous polygeneration microgrids. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 103, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, R.; Dotoli, M. Decentralized control for residential energy management of a smart users microgrid with renewable energy exchange. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sinica 2019, 6, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torreglosa, J.P.; García-Triviño, P.; Fernández-Ramirez, L.M.; Jurado, F. Decentralized energy management strategy based on predictive controllers for a medium voltage direct current photovoltaic electric vehicle charging station. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 108, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, S.; Javaid, N.; Khan, R.D.; Nawaz, N.; Iqbal, M. A convex optimization based decentralized real-time energy management model with the optimal integration of microgrid in smart grid. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananduta, W.; Pippia, T.; Ocampo-Martinez, C.; Sijs, J.; De Schutter, B. Online partitioning method for decentralized control of linear switching large-scale systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 3290–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Liang, H. Hierarchical and decentralized stochastic energy management for smart distribution systems with high BESS penetration. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 6516–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.M.; Patne, N.R. Priority-based energy scheduling in a smart distributed network with multiple microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2017, 13, 3134–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.; Gebbran, D.; Mhanna, S.; Chapman, A.C.; Verbič, G. Towards a transactive energy system for integration of distributed energy resources: Home energy management, distributed optimal power flow, and peer-to-peer energy trading. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 132, 110000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, R.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Shah, N.; Zhao, Y. Distributed or centralized? designing district-level urban energy systems by a hierarchical approach considering demand uncertainties. Appl. Energy 2019, 252, 113424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jayaweera, S.K. Distributed smart-home decision-making in a hierarchical interactive smart grid architecture. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2015, 26, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.M.; Chandorkar, M.; Lee, T.-L.; Loh, P.C. Advanced control architectures for intelligent microgrids—Part I: Decentralized and hierarchical control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoei, T.T.; Slimane, H.O.; Kaabouch, N. Cyber-security of smart grids: Attacks, detection, countermeasure techniques, and future directions. Commun. Netw. 2022, 14, 119–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Tang, H.; Huang, T.; Yu, F.R.; Xie, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. A survey of blockchain technology applied to smart cities: Research issues and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2794–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Lee, Y.; Hyun, S.H.; Koo, I. Unsupervised machine learning-based detection of covert data integrity assault in smart grid networks utilizing isolation forest. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 14, 2765–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghnegahdar, L.; Wang, Y. A whale optimization algorithm-trained artificial neural network for smart grid cyber intrusion detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 9427–9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowah, R.A.; Ofori-Amanfo, K.B.; Mills, G.A.; Koumadi, K.M. Detection and prevention of man-in-the-middle spoofing attacks in MANETs using predictive techniques in artificial neural networks (ANN). J. Comput. Netw. Commun. 2019, 2019, 4683982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abassi, A.; Karimipour, H.; Dehghantanha, A.; Parizi, R.M. An ensemble deep learning-based cyber-attack detection in industrial control system. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 83965–83973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foba, V.J.; Boum, A.T.; Mbey, C.F. Optimal reliability of a smart grid. Int. J. Smart Grid 2021, 5, 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Liu, C. Soft computing based smart grid fault detection using computerised data analysis with fuzzy machine learning model. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2024, 41, 100945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhanaf, A.S.; Balik, H.H.; Farsadi, M. Intelligent fault detection and classification schemes for smart grids based on deep neural networks. Energies 2023, 16, 7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.L.; Mesbah, W.; Al-Awami, A.T. An algorithm for accurate detection and correction of technical and nontechnical losses using smart metering. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 8809–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenza, G.; Gallo, M.; Loia, V. Drift-aware methodology for anomaly detection in smart grid. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 9645–9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, N.; Aurangzeb, K.; Awais, M.; Ali, U. Electricity theft detection using CNN-GRU and Manta Ray foraging optimization algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 23rd International Multitopic Conference (INMIC), Bahawalpur, Pakistan, 5–7 November 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Gao, Y.; Gu, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, K. A novel approach to detect electricity theft based on conv-attentional transformer neural network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 145, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Seon, J.; Lee, S.; Kyeong, C.; Kim, J. Energy theft detection model based on VAE-GAN for imbalanced dataset. Energies 2023, 16, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Wang, J. A semi-supervised learning method for electricity theft detection based on CT-GAN. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Power Systems and Electrical Technology (PSET), Aalborg, Denmark, 13–15 October 2022; pp. 335–340. [Google Scholar]
- Tokam, L.W.; Ouro-Djobo, S.S. Comparative study on load monitoring approaches. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Cho, H.S.; Lee, D. Appliance recognition from electric current signals for information-energy integrated network in home environments. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Smart Homes and Health Telematics, Tours, France, 7–8 July 2009; Volume 5597, pp. 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Guedes, J.D.S.; Ferreira, D.D.; Barbosa, B.H.G. A non-intrusive approach to classify electrical appliances based on higher-order statistics and genetic algorithm: A smart grid perspective. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 140, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seon, J.; Sun, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, J. Time-lapse image method for classifying appliances in nonintrusive load monitoring. Energies 2021, 14, 7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mao, S.; Nelms, R.M. Transformer for nonintrusive load monitoring: Complexity reduction and transferability. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 18987–18997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, D.; Boshell, F.; Saygin, D.; Bazilian, M.D.; Wagner, N.; Gorini, R. The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 24, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, M.F.; Dabiri, J.O. Wind farm modeling with interpretable physics-informed machine learning. Energies 2019, 12, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, M.; Focken, U. New developments in wind energy forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting—Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 20–24 July 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, C.; Alaíz, C.M.; Dorronsoro, J.R. Multitask support vector regression for solar and wind energy prediction. Energies 2020, 13, 6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannizzaro, D.; Aliberti, A.; Bottaccioli, L.; Macii, E.; Acquaviva, A.; Patti, E. Solar radiation forecasting based on convolutional neural network and ensemble learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 181, 115167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Liu, G.; Tai, Y. Hourly stepwise forecasting for solar irradiance using integrated hybrid models CNN-LSTM-MLP combined with error correction and VMD. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 280, 116804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, J.B.; Mantovani, J.R.S. Development of a self-healing strategy with multiagent systems for distribution networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2198–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Karim, M.; Currie, J.; Lie, T.-T. Dynamic event detection using a distributed feature selection based machine learning approach in a self-healing microgrid. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 4706–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shen, J.; Lin, D.; Jiang, Y. Evaluation of power grid social risk early warning system based on deep learning. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Syst. Approach 2023, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, M.; Maldonado, J.; Bergmann, W.; Jung, F.; Weber, M.; Büskens, C. Self-learning data-based models as basis of a universally applicable energy management system. Energies 2020, 13, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.; Zhou, R.; Feng, W.; Quinsey, P. Estimating energy forecasting uncertainty for reliable AI autonomous smart grid design. Energies 2021, 14, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.A.; Currie, J.; Lie, T.-T. Distributed machine learning on dynamic power system data features to improve resiliency for the purpose of self-healing. Energies 2020, 13, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.; Bae, J. Deep-learning- and reinforcement-learning-based profitable strategy of a grid-level energy storage system for the smart grid. J. Energy Storage 2021, 41, 102868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banguero, E.; Correcher, A.; Pérez-Navarro, Á.; García, E.; Aristizabal, A. Diagnosis of a battery energy storage system based on principal component analysis. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 2438–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodan, I.; Zio, E. A model predictive control framework for reliable microgrid energy management. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 61, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffonneau, Y.; Bacha, S.; Barruel, F.; Ploix, S. Optimal power flow management for grid connected PV systems with batteries. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2011, 2, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuwir, B.; Ruelens, F.; Spiessens, F.; Deconinck, G. Battery energy management in a microgrid using batch reinforcement learning. Energies 2017, 10, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brabandere, K.; Bolsens, B.; Van den Keybus, J.; Woyte, A.; Driesen, J.; Belmans, R. A voltage and frequency droop control method for parallel inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Fozdar, M. Event-driven frequency and voltage stability predictive assessment and unified load shedding. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2019, 13, 4410–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouammi, A.; Dagdougui, H.; Sacile, R. Optimal control of power flows and energy local storages in a network of microgrids modeled as a system of systems. IEEE Trans. Contr. Syst. Technol. 2015, 23, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Saad, W.; Han, Z.; Poor, H.V.; Basar, T. A Game-theoretic approach to energy trading in the smart grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dehghanpour, K.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Q. A learning-based power management method for networked microgrids under incomplete information. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Han, S.; Zhu, S. Reinforcement learning-based energy trading and management of regional interconnected microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 14, 2047–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twaisan, K.; Barışçı, N. Integrated distributed energy resources (DER) and microgrids: Modeling and optimization of DERs. Electronics 2022, 11, 2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlqvist, V.; Holmberg, P.; Tangerås, T. A survey comparing centralized and decentralized electricity markets. Energy Strategy Rev. 2022, 40, 100812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Chowdhury, S.; Shorfuzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.K.; Hammoudeh, M. Peer-to-peer power energy trading in blockchain using efficient machine learning model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, B.A.; Broadwater, R. Energy trading in the distribution system using a non-model based game theoretic approach. Appl. Energy 2019, 253, 113532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrad, Y.; Habaebi, M.H.; Islam, M.R.; Gunawan, T.S.; Elsheikh, E.A.A.; Suliman, F.M.; Mesri, M. Machine learning-blockchain based autonomic peer-to-peer energy trading system. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Seon, J.; Kyeong, C.; Kim, S.; Sun, Y.; Kim, J. Novel energy trading system based on deep-reinforcement learning in microgrids. Energies 2021, 14, 5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrold, D.J.B.; Cao, J.; Fan, Z. Renewable energy integration and microgrid energy trading using multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. Appl. Energy 2022, 318, 119151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Hong, S.H.; Yu, M. Demand response for home energy management using reinforcement learning and artificial neural network. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 6629–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Hafeez, G.; Khan, I.; Jan, K.U.; Li, H.; Khan, S.A.; Wadud, Z. An intelligent integrated approach for efficient demand side management with forecaster and advanced metering infrastructure frameworks in smart grid. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132551–132581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.N.F.; Sulaima, M.F.; Razak, I.A.W.A.; Kadir, A.F.A.; Mokhlis, H. Artificial intelligence application in demand response: Advantages, issues, status, and challenges. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 16907–16922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, I.; Robu, V.; Couraud, B.; Kirli, D.; Norbu, S.; Kiprakis, A.; Flynn, D.; Elizondo-Gonzalez, S.; Wattam, S. Artificial intelligence and machine learning approaches to energy demand-side response: A systematic review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 130, 109899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, D.-H. Federated reinforcement learning for energy management of multiple smart homes with distributed energy resources. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2022, 18, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, Z.; Hafeez, K.; Sabir, D.; Ijaz, B.; Bukhari, S.S.H.; Ro, J.-S. RECLAIM: Renewable energy based demand-side management using machine learning models. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 3846–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Canteli, J.R.; Nagy, Z. Reinforcement learning for demand response: A review of algorithms and modeling techniques. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 1072–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, C.-S.; Hong, J.-H.; Hong, D.-Y.; Fu, L.-C. A real-time demand-side management system considering user preference with adaptive deep Q learning in home area network. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2022, 29, 100572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, F. Intelligent multi-microgrid energy management based on deep neural network and model-free reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Liu, D.; Hua, H.; Cao, J. Privacy preserving load control of residential microgrid via deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 4079–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reka, S.S.; Venugopal, P.; Ravi, V.; Dragicevic, T. Privacy-based demand response modeling for residential consumers using machine learning with a cloud–fog-based smart grid environment. Energies 2023, 16, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, B.; Li, K.; Ge, X.; Lu, H.; Lai, J.; Dehghanian, P. Smart households’ aggregated capacity forecasting for load aggregators under incentive-based demand response programs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S. Load demand forecasting of residential buildings using a deep learning model. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 179, 106073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S.; Lu, X. Optimal load dispatch of community microgrid with deep learning based solar power and load forecasting. Energy 2019, 171, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almani, A.A.; Han, X. Real-time pricing-enabled demand response using long short-time memory deep learning. Energies 2023, 16, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Lin, R.; Wu, B.; Zhao, X.; Zou, H. Pre-attention mechanism and convolutional neural network based multivariate load prediction for demand response. Energies 2023, 16, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Hong, S.H. Incentive-based demand response for smart grid with reinforcement learning and deep neural network. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Wang, S. Modified deep learning and reinforcement learning for an incentive-based demand response model. Energy 2020, 205, 118019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Qiu, D.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y.; Strbac, G. Real-time autonomous residential demand response management based on twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient learning. Energies 2021, 14, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Seon, J.; Sun, Y.G.; Kim, S.H.; Kyeong, C.; Kim, D.I.; Kim, J.Y. Novel architecture of energy management systems based on deep reinforcement learning in microgrid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid, 2023; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Khan, A.; Naeem, M.; Iqbal, M.; Qaisar, S.; Anpalagan, A. A compendium of optimization objectives, constraints, tools and algorithms for energy management in microgrids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1664–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Arefifar, S.A. Energy management in power distribution systems: Review, classification, limitations and challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 92979–93001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.H.; Abedini, M.; Hosseinian, S.M. Improving operation constraints of microgrid using PHEVs and renewable energy sources. Renew. Energy 2015, 83, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, F.; Ishchenko, D.; Almaleck, P. Network constraints consideration for grid-edge energy management system. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition (T&D), New Orleans, LA, USA, 25–28 April 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fontenot, H.; Dong, B. Modeling and control of building-integrated microgrids for optimal energy management—A review. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamulapati, T.; Cavus, M.; Odigwe, I.; Allahham, A.; Walker, S.; Giaouris, D. A review of microgrid energy management strategies from the energy trilemma perspective. Energies 2022, 16, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Tobar, A.; Massi Pavan, A.; Petrone, G.; Spagnuolo, G. A review of the optimization and control techniques in the presence of uncertainties for the energy management of microgrids. Energies 2022, 15, 9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, K.; Iqbal, S.; Mukhtar, H. Optimal fuzzy energy trading system in a fog-enabled smart grid. Energies 2021, 14, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji Mirzaee, P.; Shojafar, M.; Cruickshank, H.; Tafazolli, R. Smart grid security and privacy: From conventional to machine learning issues (threats and countermeasures). IEEE Access 2022, 10, 52922–52954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, N.; Marinelli, M.; Heussen, K.; Ziras, C. On the trade-off between profitability, complexity and security of forecasting-based optimization in residential energy management systems. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 34, 101033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridha, E.; Nolting, L.; Praktiknjo, A. Complexity profiles: A large-scale review of energy system models in terms of complexity. Energy Strategy Rev. 2020, 30, 100515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iringan Iii, R.A.; Janer, A.M.S.; Tria, L.A.R. A machine-learning based energy management system for microgrids with distributed energy resources and storage. In Proceedings of the 2022 25th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 29 November–2 December 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
| Framework | Characteristic | Promising ML Candidate |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized EMS |
|
|
| Decentralized EMS |
|
|
| Distributed EMS |
|
|
| Hierarchical EMS |
|
|
| Component Systems | EMS Framework | Key Technology | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMIS |
|
|
|
| GASHS |
|
|
|
| Component Systems | EMS Framework | Key Technology | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| ESS |
|
|
|
| ETRMS |
|
|
|
| DSMS |
|
|
|
| Constraints | Primary Issues | Implications for EMS Design |
|---|---|---|
| Architectural Framework |
|
|
| Cybersecurity |
|
|
| Economics |
|
|
| Energy Storage |
|
|
| Environment |
|
|
| Grid Connection |
|
|
| Human Factors |
|
|
| Interoperability |
|
|
| Regulation |
|
|
| Power Balance |
|
|
| Technology |
|
|
| Operational Index | Challenging Issue |
|---|---|
| Scalability |
|
| Security |
|
| Storage |
|
| Technical Index | Challenging Issue |
|---|---|
| Performance Measure |
|
| Reliability and Robustness |
|
| Integration and Interoperability |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Seon, J.; Hwang, B.; Kim, S.; Sun, Y.; Kim, J. Recent Trends and Issues of Energy Management Systems Using Machine Learning. Energies 2024, 17, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030624
Lee S, Seon J, Hwang B, Kim S, Sun Y, Kim J. Recent Trends and Issues of Energy Management Systems Using Machine Learning. Energies. 2024; 17(3):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030624
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seongwoo, Joonho Seon, Byungsun Hwang, Soohyun Kim, Youngghyu Sun, and Jinyoung Kim. 2024. "Recent Trends and Issues of Energy Management Systems Using Machine Learning" Energies 17, no. 3: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030624
APA StyleLee, S., Seon, J., Hwang, B., Kim, S., Sun, Y., & Kim, J. (2024). Recent Trends and Issues of Energy Management Systems Using Machine Learning. Energies, 17(3), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17030624






