The Influence of Temperature on Rheological Parameters and Energy Efficiency of Digestate in a Fermenter of an Agricultural Biogas Plant
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (a)
- The influence of temperature on microbiological processes:
- (b)
- The influence of temperature on mixing processes:
2. Materials and Methods
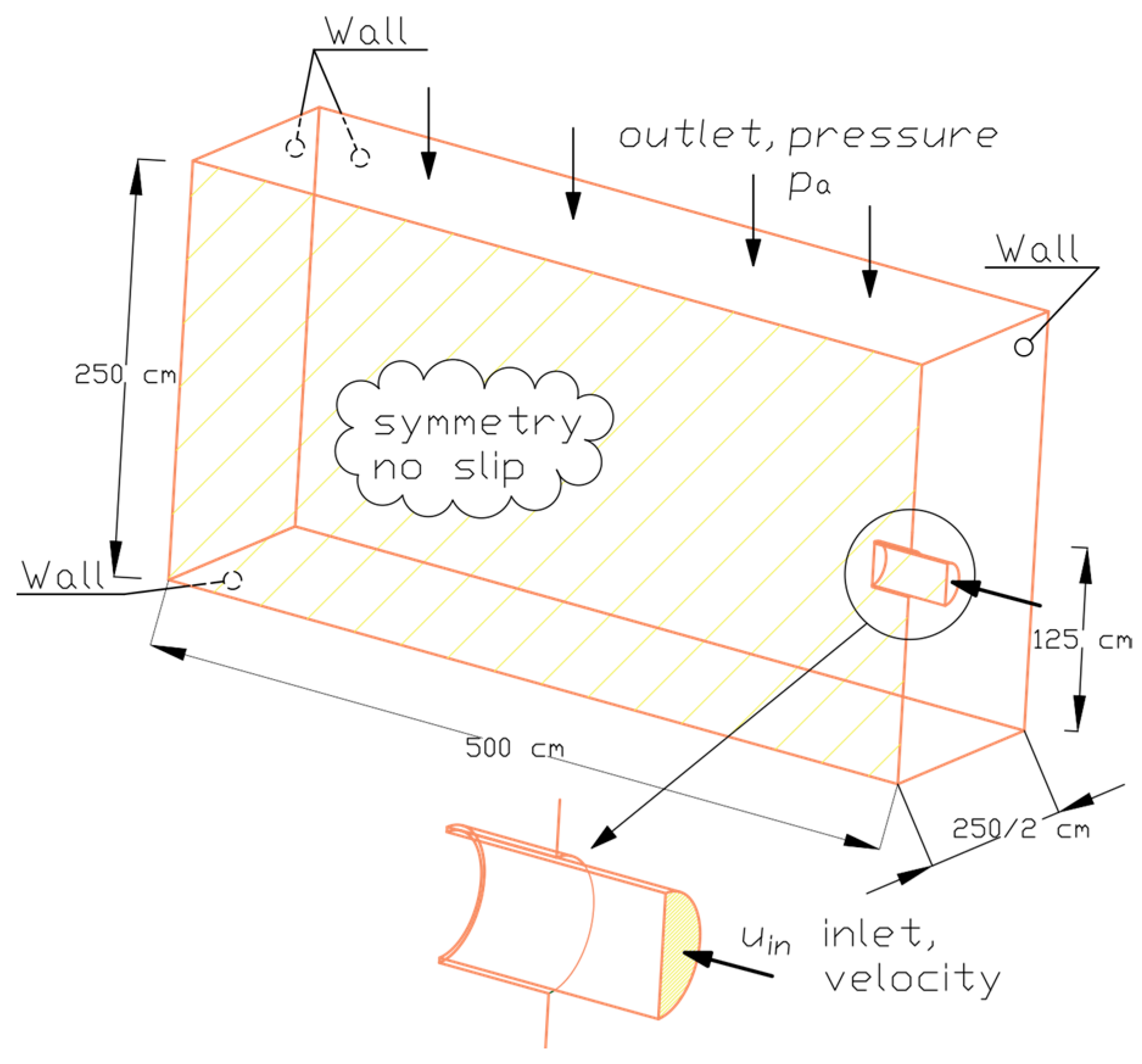
2.1. Description of the “Przybroda” Installation
2.2. Physical and Chemical Parameters of the Digestate
2.3. Determination of Rheological Parameters Taking into Account the Effect of Temperature
- —average velocity [m/s],
- D—pipe diameter [m].
- in the mixer duct—50.9 1/s,
- in the reactor chamber—0.04 1/s.
- —shear rate at the tube wall [1/s],
- Ω—angular velocity [rad/s],
- n—flow behavior index [-],
- —shear stress at the wall [Pa],
- R1—radius of inner cylinder [m],
- R2—radius of outer cylinder [m],
- N—rotational speed [rpm].
2.4. Analysis Methodology—The Influence of Fluid Temperature on Energy Consumption During Mixing
3. Results
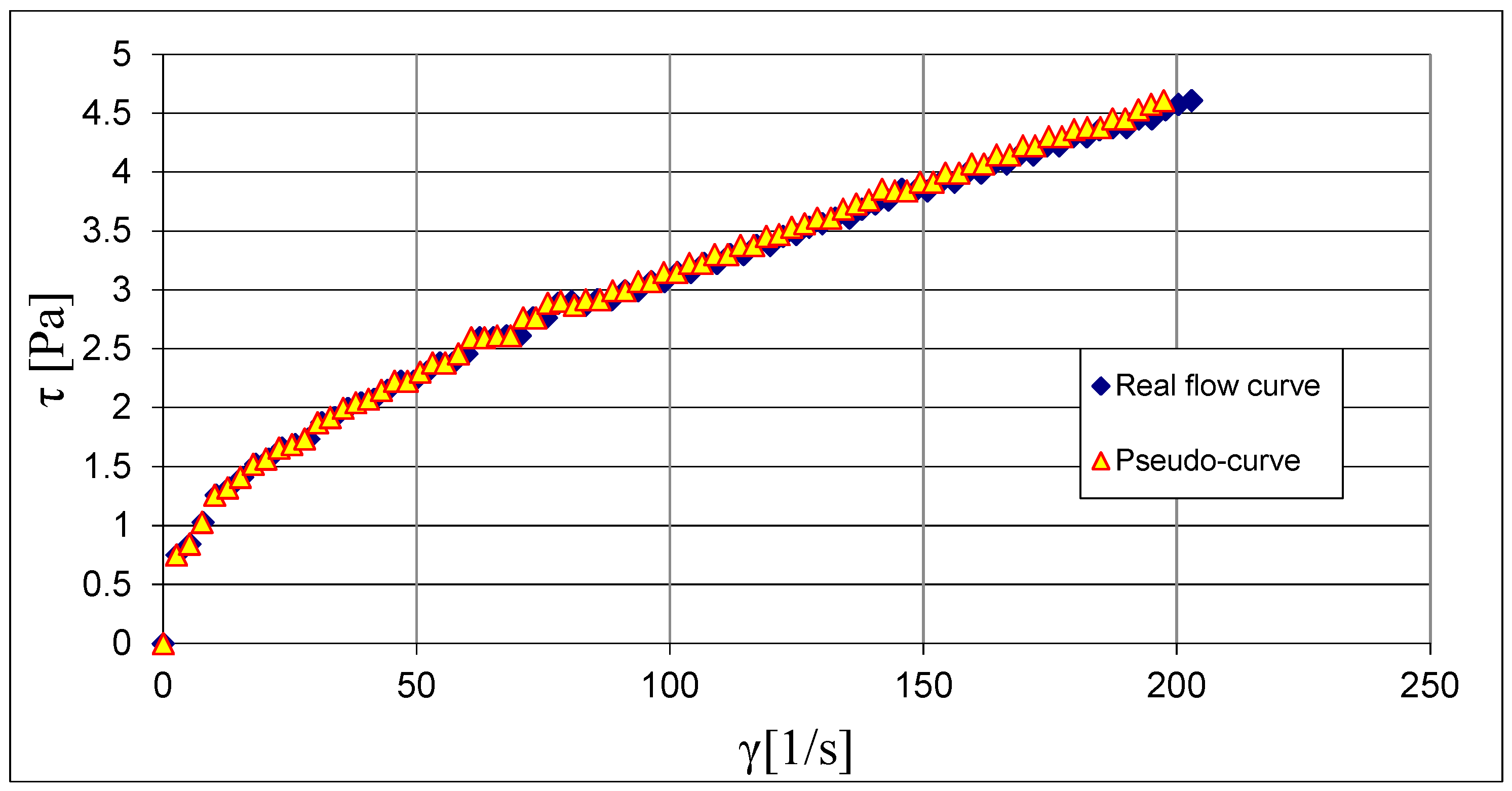
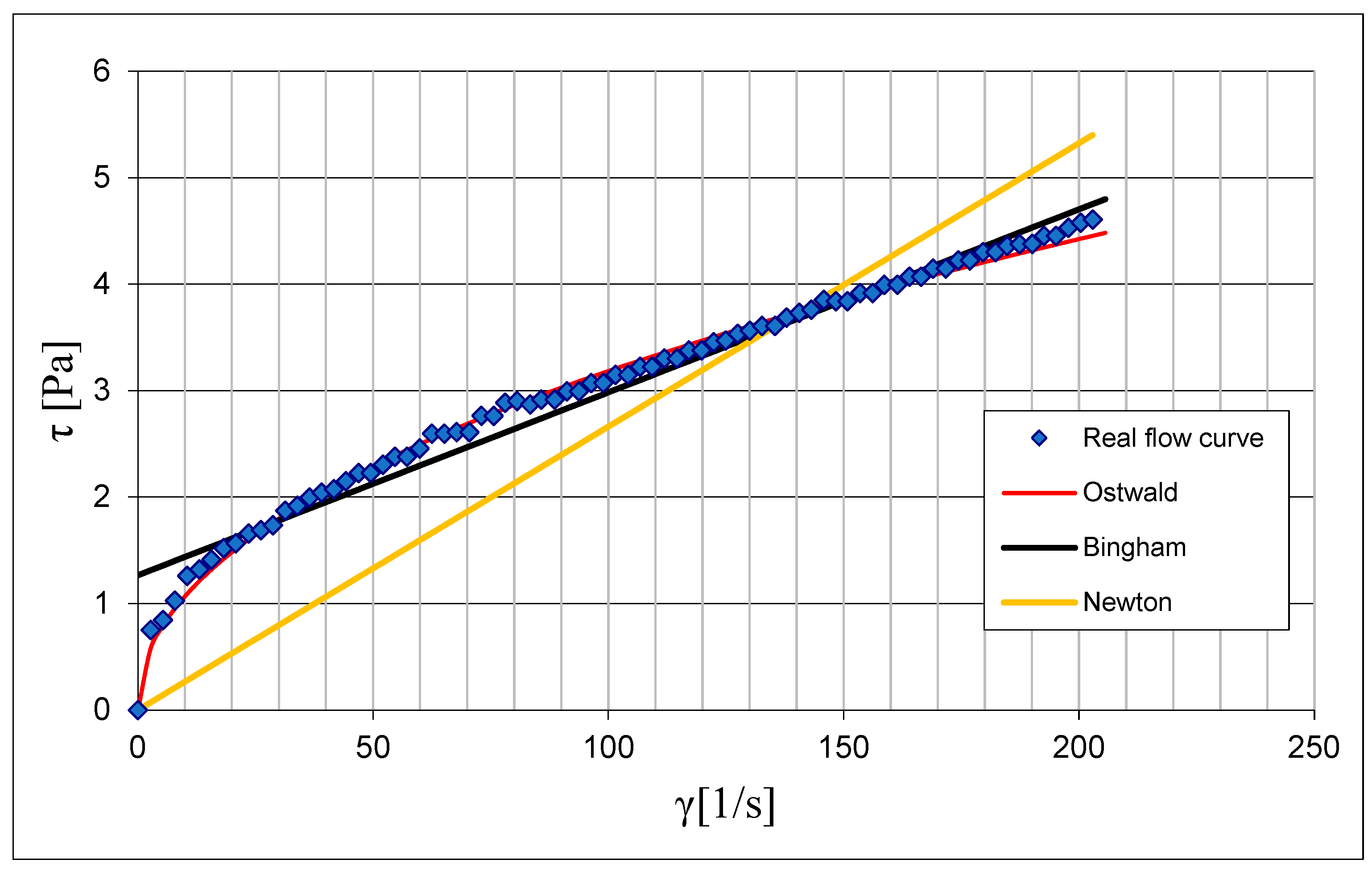
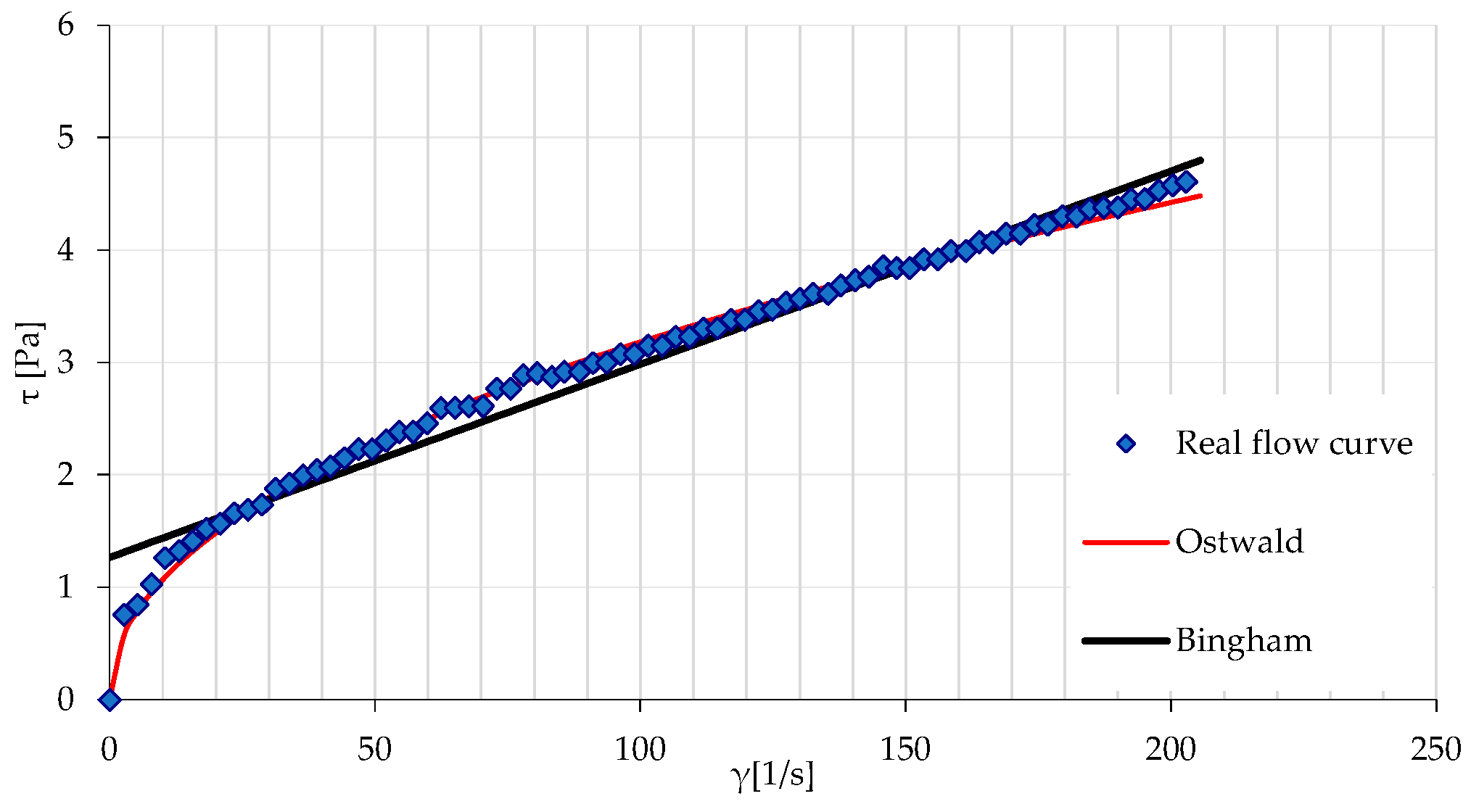
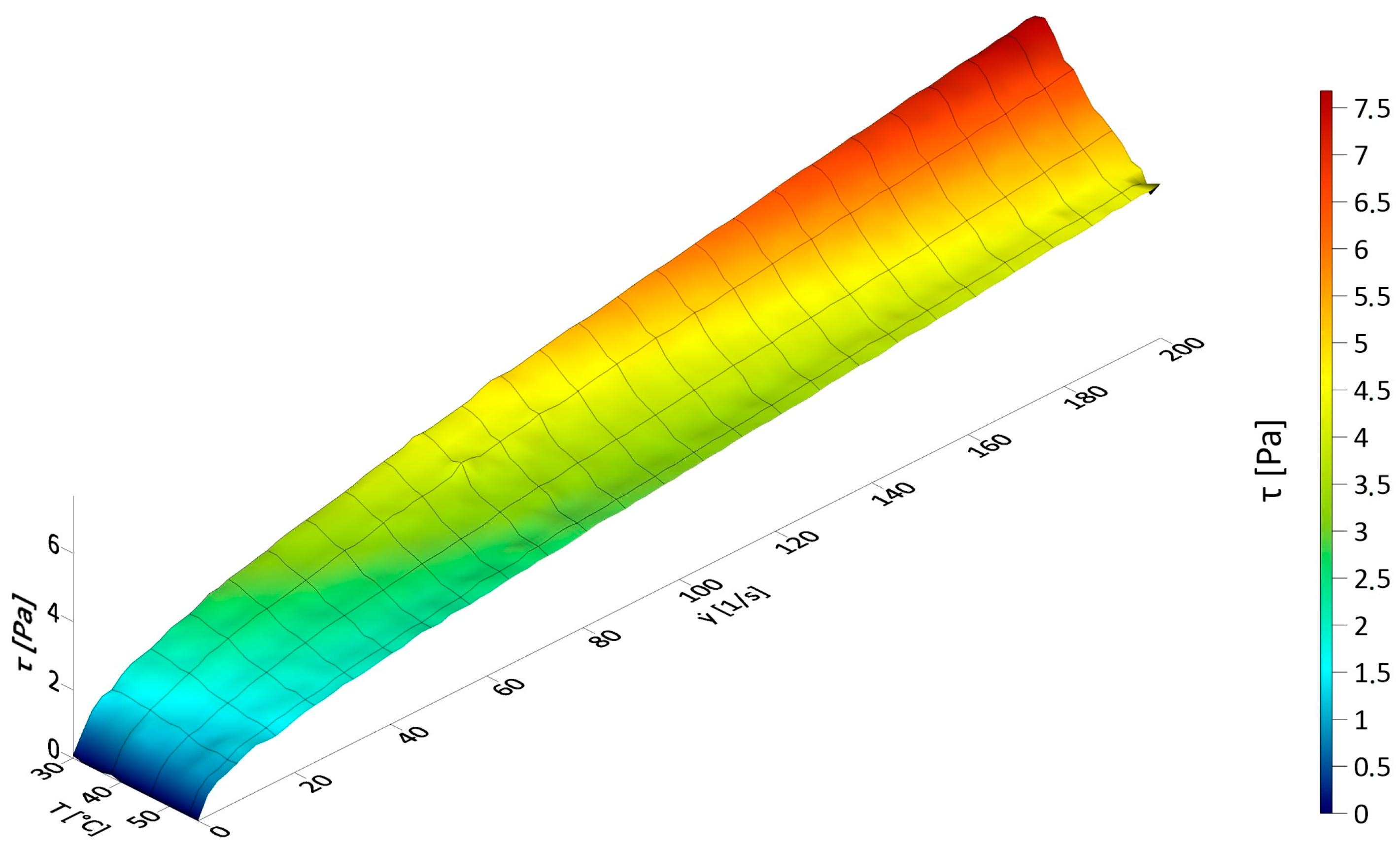
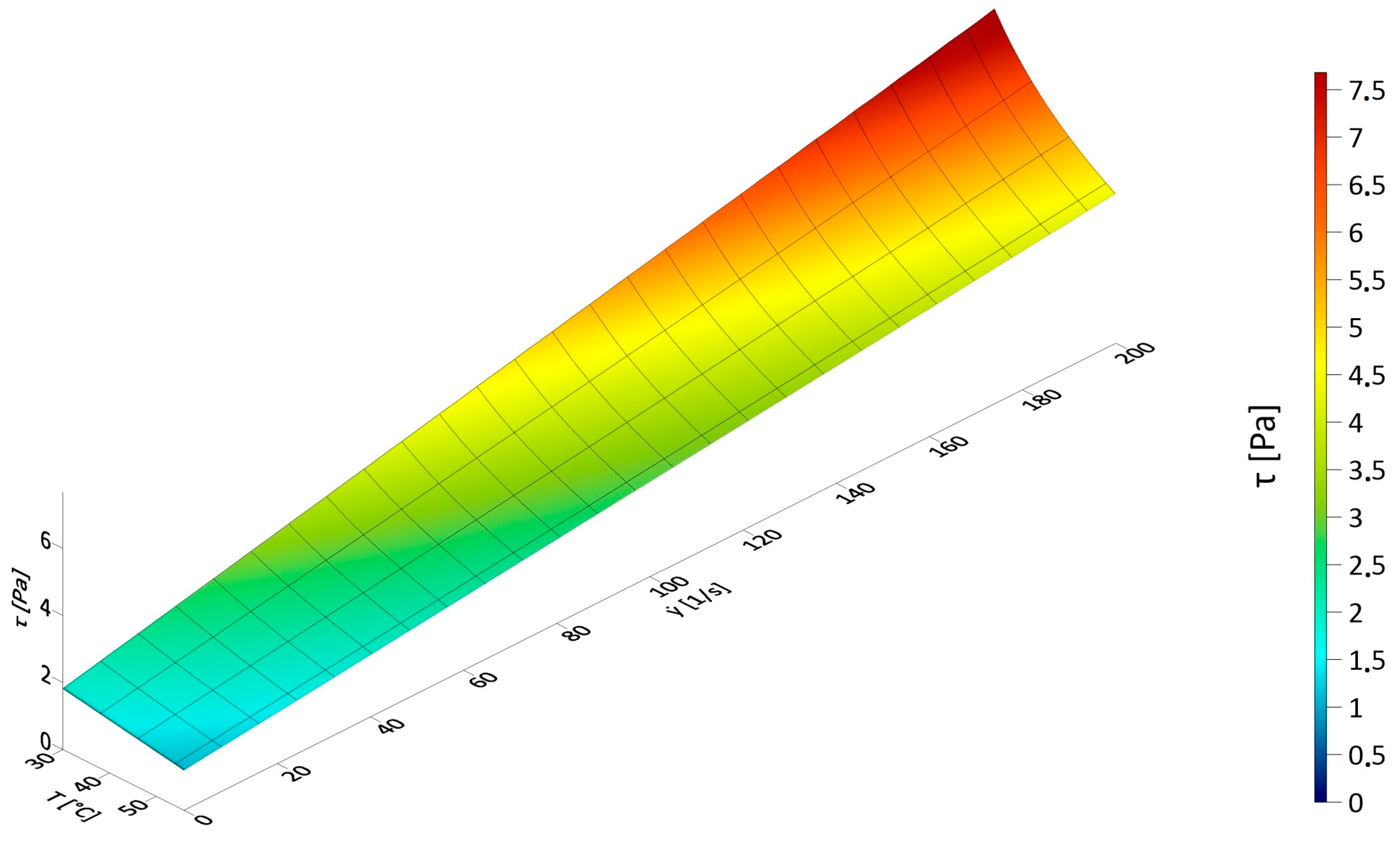
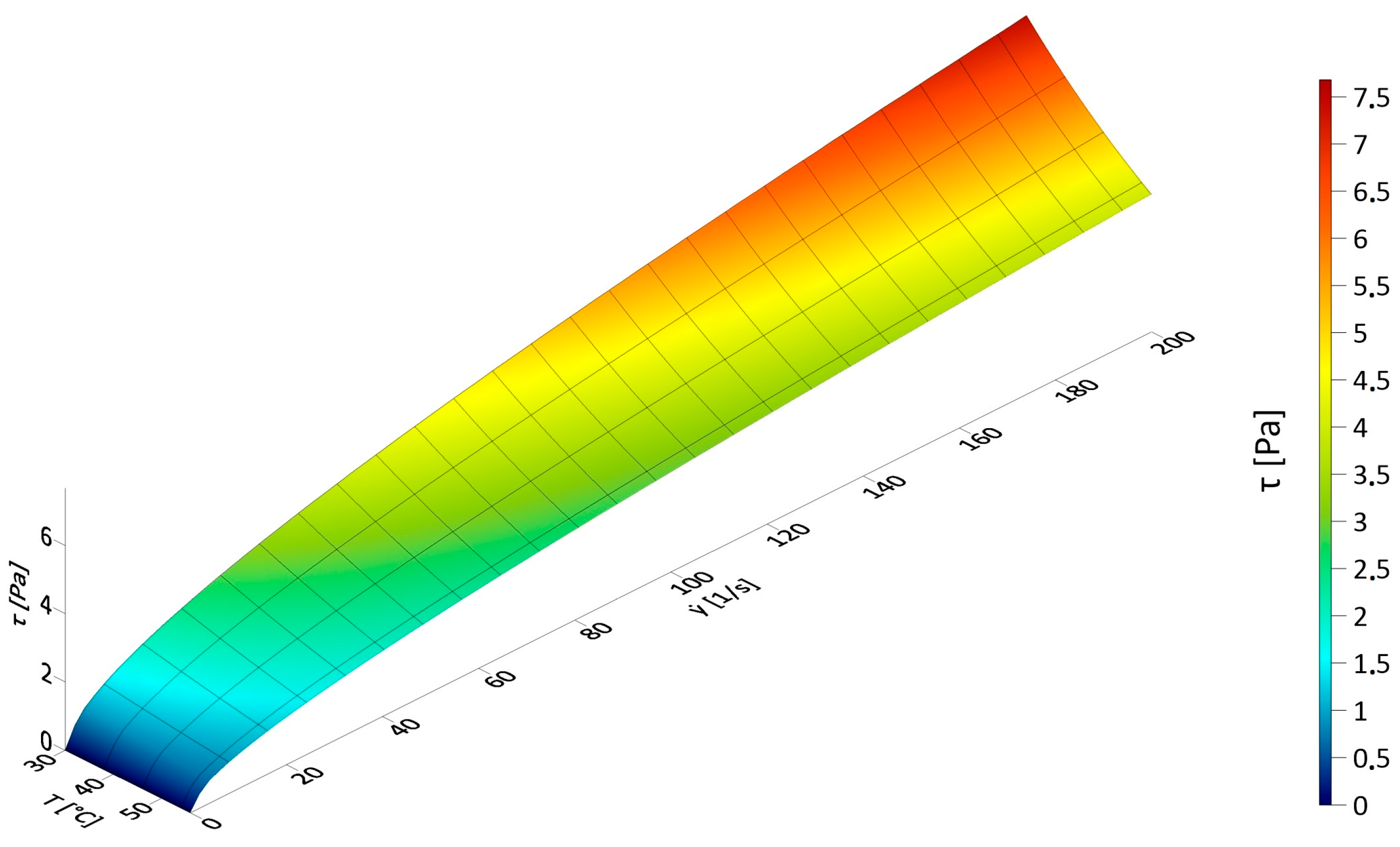
3.1. Results of Rheological Measurements
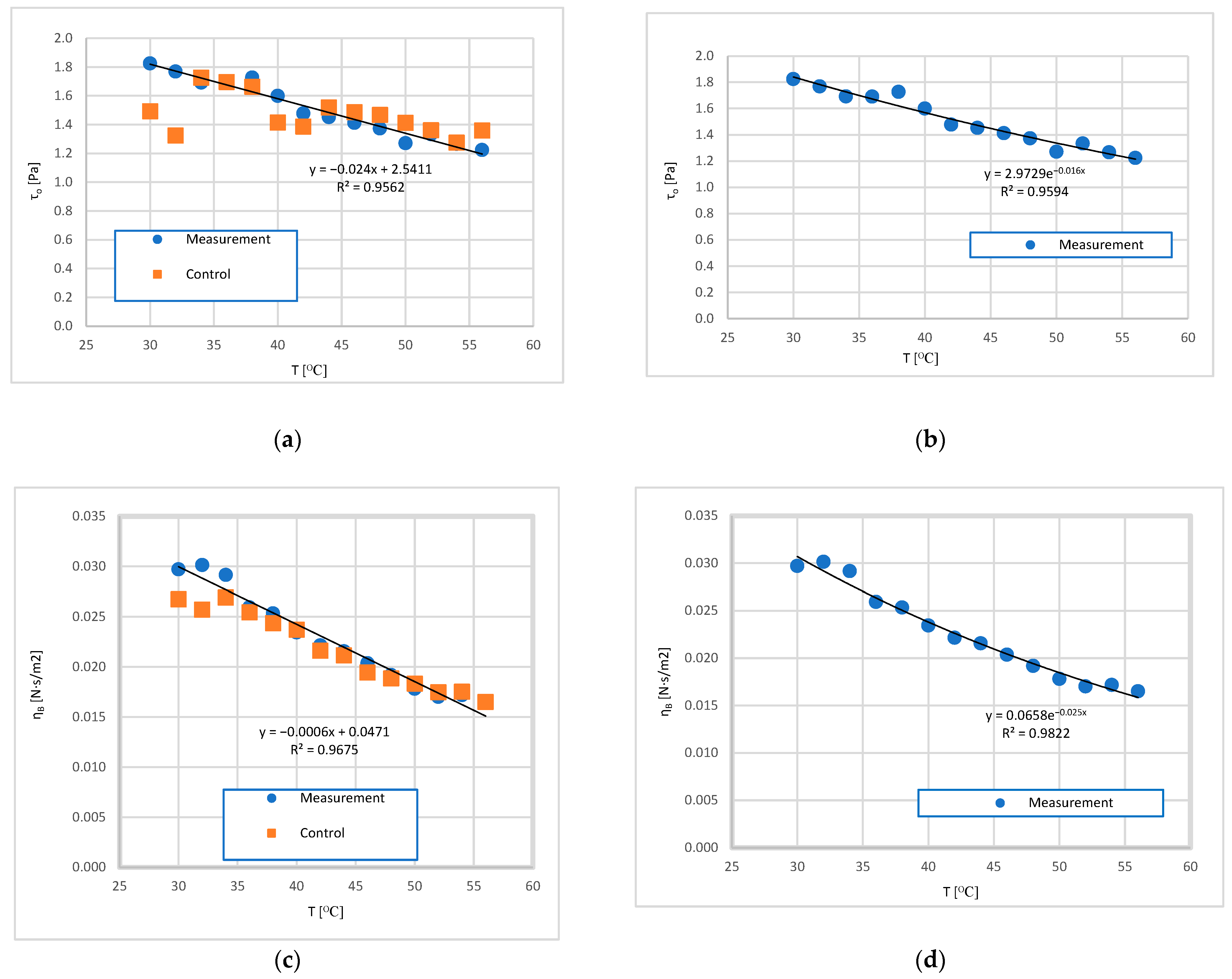
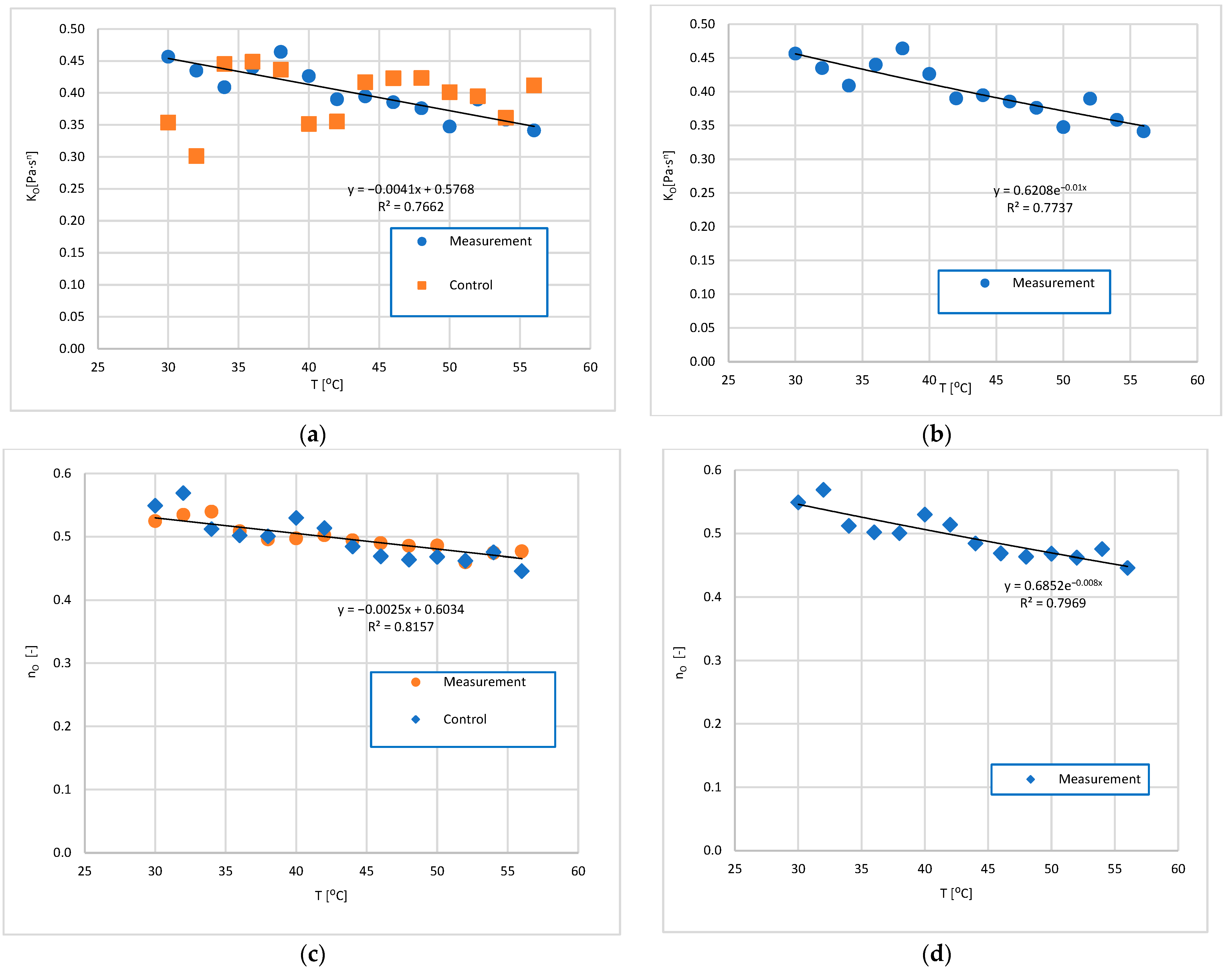
3.2. Analysis of the Influence of Mixture Temperature on the Values of the Bingham Model Parameters
- a—directional coefficient of the function [-],
- b—free expression of the function [-],
- T—fluid temperature [°C],
- and
- c—base of the exponential function [-],
- d—function parameter [-].
3.2.1. Rheological Parameters of the Bingham Model as a Function of Temperature
3.2.2. Rheological Parameters of the Ostwald Model as a Function of Temperature
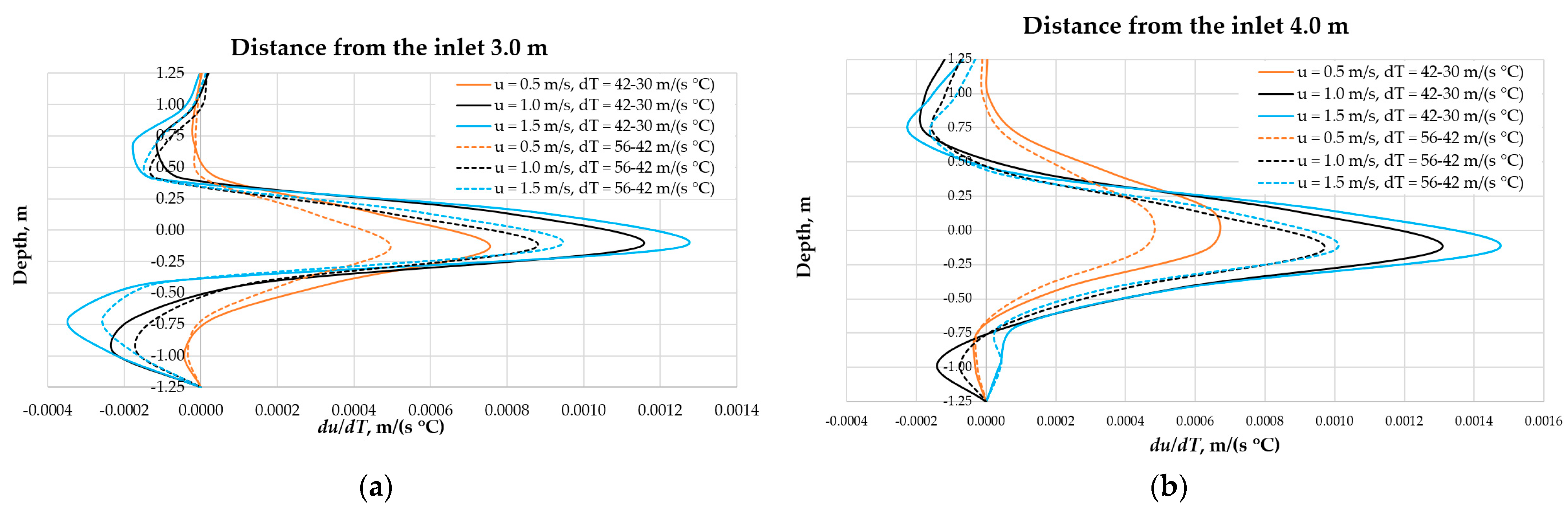
3.3. The Influence of Fluid Temperature on the Energy Intensity of Mixing in CFD Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Capua, F.; Spasiano, D.; Giordano, A.; Adani, F.; Fratino, U.; Pirozzi, F.; Esposito, G. High-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: Challenges and opportunities. Appl. Energy 2020, 278, 115608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.; Lamb, J.J.; Hjelme, D.R.; Lien, K.M. A Review of the Role of Critical Parameters in the Design and Operation of Biogas Production Plants. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneli, E.; Dragoni, F.; Adessi, A.; De Philippis, R.; Bonari, E.; Ragaglini, G. Energy conversion of biomass crops and agroindustrial residues by combined biohydrogen/biomethane system and anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harirchi, S.; Wainaina, S.; Sar, T.; Nojoumi, S.A.; Parchami, M.; Parchami, M.; Varjani, S.; Khanal, S.K.; Wong, J.; Awasthi, M.K.; et al. Microbiological insights into anaerobic digestion for biogas, hydrogen or volatile fatty acids (VFAs): A review. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 6521–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buan, N.R. Methanogens: Pushing the boundaries of biology. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2018, 2, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Shi, H. Influences of volatile solid concentration, temperature and solid retention time for the hydrolysis of waste activated sludge to recover volatile fatty acids. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 119, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rademacher, A.; Nolte, C.; Schonberg, M.; Klocke, M. Temperature increases from 55 to 75 degrees C in a two-phase biogas reactor result in fundamental alterations within the bacterial and archaeal community structure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszczyński, M.; Błotnicki, J.; Czaban, S.; Tymiński, T. The effect of solid components on the rheological properties of copper ore tailings. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Transport & Sedimentation of Solid Particles, Cape Town, South Africa, 24–27 September 2019; Sobota, J., Haklenwang, R., Eds.; pp. 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Guo, J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, W.; Dong, R. Two-phase anaerobic digestion of municipal solid wastes enhanced by hydrothermal pretreatment: Viability, performance and microbial community evaluation. Appl. Energy 2017, 189, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yuan, X.; Ren, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W.; Cui, Z. Methane production and characteristics of the microbial community in a two-stage fixed-bed anaerobic reactor using molasses. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J.L.; Rojas, P.; Morato, A.; Mendez, L.; Ballesteros, M.; González-Fernández, C. Microbial communities of biomethanization digesters fed with raw and heat pre-treated microalgae biomasses. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, F.; Ma, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, G.; Lu, X. Influence of Temperature on Biogas Production Efficiency and Microbial Community in a Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion System. Water 2019, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Qiao, W.; Zhang, J.; Dong, R. Process Performance and Functional Microbial Community in the Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure: A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Al Seadi, T. Oleskowicz-Popiel, P. The future of anaerobic digestion and biogas utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5478–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, K.J.; Jang, A.; Yim, S.K.; Kim, I.S. The effects of digestion temperature and temperature shock on the biogas yields from the mesophilic anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.J.; Hobbs, P.J.; Holliman, P.J.; Jones, D.L. Optimisation of the anaerobic digestion of agricultural resources. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7928–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannoun, H.; Othman, N.B.; Bouallagui, H.; Moktar, H. Mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of olive mill wastewaters and abattoir wastewaters in an upflow anaerobic filter. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 6737–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, G.; Pullammanappallil, P. Comparison of thermophilic and mesophilic one-stage, batch, high-solids anaerobic digestion. Environ. Technol. 2007, 28, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fezzani, B.; Cheikh, R.B. Thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of olive mill wastewater with olive mill solid wastes in a tubular digester. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 132, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parawira, W.; Murto, M.; Read, J.S.; Mattiasson, B. A study of two-stage anaerobic digestion of solid potato waste using reactors under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Environ. Technol. 2007, 28, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.H.P.; Chung, D.W.C. Anaerobic treatment of proteinaceous wastewater under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, Y.; Lichtfouse, E.; Li, Z.; Kumar, P.S.; Liu, J.; Feng, D.; Yang, Q.; Liu, F. Effect of Antibiotics on the Microbial Efficiency of Anaerobic Digestion of Wastewater: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 611613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmer, A.; Nägele, H.; Sondermann, J. How Efficient are Agitators in Biogas Digesters? Determination of the Efficiency of Submersible Motor Mixers and Incline Agitators by Measuring Nutrient Distribution in Full-Scale Agricultural Biogas Digesters. Energies 2013, 6, 6255–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slatter, P. The Engineering Hydrodynamics of Viscoplastic Suspensions. Part. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, P.; Nägele, H.J.; Lemmer, A.; Kolb, B. Flow velocities and flow profiles in a thoroughly mixed biogas fermenter. Landtechnik 2020, 75, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillet, H.; Adelard, L. A Review on the rheological behavior of organic waste for CFD modeling of flows in anaerobic reactors. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2023, 14, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Carnevale Miino, M.; Bellazzi, S.; Caccamo, F.M.; Durante, A.; Abbà, A. Review of rheological behaviour of sewage sludge and its importance in the management of wastewater treatment plants. Water Pract. Technol. 2022, 17, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudez, J.C.; Slatter, P.; Eshtiaghi, N. The impact of temperature on the rheological behaviour of anaerobic digested sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215–216, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindmark, J.; Thorin, E.; Fdhila, R.B.; Dahlquista, E. Effects of mixing on the result of anaerobic digestion: Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 1030–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maria, F.; Sisani, F.; Norouzi, O.; Mersky, R.L. The effectiveness of anaerobic digestion of bio-waste in replacing primary energies: An EU28 case study. Renew. Sustain Energy Rev. 2019, 108, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillet, H.; Bastide, A.; Adelard, L. Advances in computational fluid dynamics modeling of anaerobic digestion process for renewable energy production: A review. Clean. Waste Syst. 2023, 6, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Jiménez, P.A.; Escudero-González, J.; Martínez, T.M.; Montañana, V.F.; Gualtieri, C. Application of CFD methods to an anaerobic digester: The case of Ontinyent WWTP, Valencia, Spain. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 7, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesvikar, M.S.; Al-Dahhan, M. Flow pattern visualization in amimic anaerobic digester using CFD. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 89, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Chen, S. CFD simulation of non-Newtonian fluid flow in anaerobic digesters. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 99, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillet, H.; Bastide, A.; Adelard, L. CFD simulations in mechanically stirred tank and flow field analysis: Application to the wastewater (Sugarcane Vinasse) anaerobic digestion. In Promising Techniques for Wastewater Treatment and Water Quality Assessment; Moujdin, I.A., Summers, J.K., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; p. 93926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, D.A. The effects of mixing and volatile fatty acid concentrations on anaerobic digester performance. Biomass 1982, 2, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroot, P.G.; McMahon, K.D.; Mackie, R.I.; Raskin, L. Anaerobic codigestion of municipal solid waste and biosolids under various mixing conditions—I. Digester performance. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaparaju, P.; Buendiaa, I.; Ellegaardb, L.; Angelidakiaa, I. Effect of mixing on methane production during thermophilic anaeroboc digestion of manure: Lab-scale and pilot-scale studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 99, 4919–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Szamosi, Z.; Siménfalvi, Z. State of the art on mixing in an anaerobic digester: A review. Renew. Energy 2019, 141, 922–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostalski, K. Tauchmotorrührwerke in Biogasanlagen—Ein Beitrag zur Effizienzsteigerung. In Tagungsband zur 18. Jahrestagung des Fachverbandes Biogas e. V.—Biogas: Dezentral Erzeugen—Regional Profitieren—International Gewinnen; Fachverband Biogas e. V.: Hannover, Germany, 2009; pp. 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska, H.; Dzido, A.; Krawczyk, P. Determination of Rheological Parameters of Non-Newtonian Fluids on an Example of Biogas Plant Substrates. Energies 2023, 16, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszczyński, M.; Kałuża, T.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Zawadzki, P.; Pawlak, M.; Matz, R.; Dach, J.; Czekała, W. Preparation of Samples for the Study of Rheological Parameters of Digested Pulps in a Bioreactor of an Agricultural Biogas Plant. Energies 2024, 17, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekała, W.; Jasiński, T.; Grzelak, M.; Witaszek, K.; Dach, J. Biogas Plant Operation: Digestate as the Valuable Product. Energies 2022, 15, 8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN ISO 3219 International Standard ISO 3219-1:2021; Rheology—Part 1: Vocabulary and symbols for rotational and oscillatory rheometry. Deutsches Institut fur Normung E.V. (DIN): Berlin, Germany, 2021.
- DIN 53019 European Standards DIN 53019-1; Viscometry—Measurement of Viscosities and Flow Curves by Means of Rotational Viscometers—Part 1: Principles and Geometry of Measuring System. Deutsches Institut fur Normung E.V. (DIN): Berlin, Germany, 2008.
- Osadolor, O.A.; Jabbari, M.; Nair, R.B.; Lennartsson, P.R.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Effect of media rheology and bioreactor hydrodynamics on filamentous fungi fermentation of lignocellulosic and starch-based substrates under pseudoplastic flow conditions. Bioresour Technol. 2018, 263, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziubiński, M.; Kiljański, T.; Sęk, J. Theoretical Foundations and Measurement Methods of Rheology, 1st ed.; Lodz University of Technology Publishing: Lodz, Poland, 2014; pp. 1–295. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Leonzio, G. Study of mixing systems and geometric configurations for anaerobic digesters using CFD analysis. Renew. Energy 2018, 123, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamo, U.; Viccione, G.; Coppola, S.; Landi, A.; Meda, A.; Gualtieri, C. Analysis of anaerobic digester mixing: Comparison of long shafted paddle mixing vs gas mixing. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1406–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wątroba, J. Straightforward About Fitting Straights, or Linear Regression Analysis in Practice; StatSoft Polska: Kraków, Poland, 2011; pp. 31–44. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.K.; Ko, J.; Kim, Y.S. Rheology of Fly Ash Mixed Tailings Slurries and Applicability of Prediction Models. Minerals 2017, 7, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaban, S. Etermination of Parameters of Hydraulic Transport in Pipelines for Rheostable Diphase Mixtures; Scientific Papers of the Agricultural University No. 60; Wydawnictwo Akademii Rolniczej: Wrocław, Poland, 1987; pp. 1–76. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kozłowski, K.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Chełkowski, D.; Jeżowska, A.; Cieślik, M.; Brzoski, M.; Smurzyńska, A.; Dongmin, Y.; Wei, Q. The effect of mixing during laboratory fermentation of maize straw with thermophilic technology. J. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 19, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annas, S.; Elfering, M.; Jantzen, H.; Scholz, J.; Janoske, U. Experimental analysis of mixing-processes in biogas plants. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 258, 117767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Khan, S.; AbdulQuadir, M.; Thaher, M.; Waqas, M.; Easa, A.; Attia, E.S.M.; Al-Jabri, H. Energy recovery and nutrients recycling from municipal sewage sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 13677515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saidi, M.; Das, P.; Saadaoui, I. Circular Economy in Basic Supply: Framing the Approach for the Water and Food Sectors of the Gulf Cooperation Council Countries. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kałuża, T.; Hämmerling, M.; Zawadzki, P.; Czekała, W.; Kasperek, R.; Sojka, M.; Mokwa, M.; Ptak, M.; Szkudlarek, A.; Czechlowski, M.; et al. The hydropower sector in Poland: Historical development and current status. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 158, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kałuża, T.; Hämmerling, M.; Zawadzki, P.; Czekała, W.; Kasperek, R.; Sojka, M.; Mokwa, M.; Ptak, M.; Szkudlarek, A.; Czechlowski, M.; et al. The hydropower sector in Poland: Barriers and the outlook for the future. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 163, 112500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurkiewicz, J. Energy and Economic Balance between Manure Stored and Used as a Substrate for Biogas Production. Energies 2022, 15, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochwatka, P.; Kowalczyk-Juśko, A.; Sołowiej, P.; Wawrzyniak, A.; Dach, J. Biogas plant exploitation in a middle-sized dairy farm in Poland: Energetic and economic aspects. Energies 2020, 13, 6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurkiewicz, J. Loss of Energy and Economic Potential of a Biogas Plant Fed with Cow Manure due to Storage Time. Energies 2023, 16, 6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurkiewicz, J. The Impact of Manure Use for Energy Purposes on the Economic Balance of a Dairy Farm. Energies 2023, 16, 6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beugre, E.Y.-M.; Gnagne, T. Vane geometry for measurement of influent rheological behavior in dry anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 155, 111928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Cui, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, P. Rheological Properties of Municipal Sewage Sludge: Dependency on Solid Concentration and Temperature. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füreder, K.; Svardal, K.; Krampe, J.; Kroiss, H. Rheology and friction loss of raw and digested sewage sludge with high TSS concentrations: A case study. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 1, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhodapkar, S.; Jacob, K.; Hu, S. Fluid-solid flow in duct. In Multiphase Flow Handbook; Crowe, C.T., Ed.; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar]
- Mönch-Tegeder, M.; Lemmer, A.; Hinrichs, J.; Oechsner, H. Development of an in-line process viscometer for the full-scale biogas process. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, C.; Beccati, N. Mixing Phase Study of a Concrete Truck Mixer via CFD Multiphase Approach. J. Eng. Mech. 2022, 148, 0002042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name/Parameters | pH | Average Dry Matter, % | Average Dry Organic Matter, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole sample before sieving | 8.2 | 8.37 | 75.66 |
| Sample after 0.5 mm sieving | 8.4 | 5.93 | 66.89 |
| Measurement | Bingham Model | Ostwald de Waele’s Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Parameters | Fit | Parameters | Fit | ||||||
| T | τo | ηB | R2 | MAE | MAPE | Ko | no | R2 | MAE | MAPE |
| °C | Pa | N·s/m2 | - | Pa | % | Pa·sn | - | - | Pa | % |
| 30 | 1.8249 | 0.0297 | 0.9667 | 0.2399 | 1.8390 | 0.4565 | 0.5246 | 0.9986 | 0.0541 | 0.5157 |
| 32 | 1.7688 | 0.0301 | 0.9672 | 0.2355 | 2.3911 | 0.4349 | 0.5345 | 0.9984 | 0.0615 | 0.3602 |
| 34 | 1.6919 | 0.0292 | 0.9718 | 0.1941 | 1.3970 | 0.4089 | 0.5395 | 0.9973 | 0.0800 | 0.8707 |
| 36 | 1.6906 | 0.0259 | 0.9615 | 0.2273 | 1.7145 | 0.4401 | 0.5084 | 0.9989 | 0.0453 | 0.4300 |
| 38 | 1.7273 | 0.0253 | 0.9583 | 0.2277 | 1.6156 | 0.4641 | 0.4956 | 0.9982 | 0.0490 | 0.3741 |
| 40 | 1.6002 | 0.0234 | 0.9647 | 0.1831 | 0.8389 | 0.4263 | 0.4972 | 0.9966 | 0.0680 | 0.8123 |
| 42 | 1.4777 | 0.0222 | 0.9628 | 0.1836 | 1.2234 | 0.3901 | 0.5022 | 0.9978 | 0.0518 | 0.6435 |
| 44 | 1.4528 | 0.0216 | 0.9570 | 0.1899 | 1.1566 | 0.3947 | 0.4941 | 0.9896 | 0.0687 | 0.5828 |
| 46 | 1.4129 | 0.0204 | 0.9583 | 0.1771 | 1.1420 | 0.3853 | 0.4898 | 0.9933 | 0.0628 | 0.5918 |
| 48 | 1.3730 | 0.0192 | 0.9597 | 0.1642 | 1.1274 | 0.3760 | 0.4854 | 0.9970 | 0.0570 | 0.6008 |
| 50 | 1.2709 | 0.0178 | 0.9644 | 0.1372 | 0.6290 | 0.3475 | 0.4859 | 0.9952 | 0.0627 | 0.8735 |
| 52 | 1.3337 | 0.0170 | 0.9603 | 0.1318 | 0.3634 | 0.3897 | 0.4598 | 0.9925 | 0.0748 | 0.8741 |
| 54 | 1.2664 | 0.0172 | 0.9552 | 0.1414 | 0.8302 | 0.3582 | 0.4744 | 0.9939 | 0.0607 | 0.6535 |
| 56 | 1.2241 | 0.0165 | 0.9656 | 0.1194 | 0.3260 | 0.3413 | 0.4768 | 0.9929 | 0.0722 | 1.0031 |
| Control | Bingham Model | Ostwald de Waele’s Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Parameters | Fit | Parameters | Fit | ||||||
| T | τo | ηB | R2 | MAE | MAPE | Ko | no | R2 | MAE | MAPE |
| °C | Pa | N·s/m2 | - | Pa | % | Pa·sn | - | - | Pa | % |
| 30 | 1.4939 | 0.0267 | 0.9725 | 0.1942 | 1.4277 | 0.3539 | 0.5490 | 0.9985 | 0.0546 | 0.8379 |
| 32 | 1.3248 | 0.0257 | 0.9759 | 0.1664 | 1.8524 | 0.3015 | 0.5688 | 0.9979 | 0.0579 | 0.8508 |
| 34 | 1.7279 | 0.0269 | 0.9655 | 0.2192 | 1.3691 | 0.4455 | 0.5120 | 0.9981 | 0.0492 | 0.6466 |
| 36 | 1.6971 | 0.0254 | 0.9594 | 0.2256 | 1.9785 | 0.4491 | 0.5018 | 0.9986 | 0.0494 | 0.2950 |
| 38 | 1.6642 | 0.0244 | 0.9638 | 0.2112 | 1.8455 | 0.4365 | 0.5005 | 0.9986 | 0.0376 | 0.3938 |
| 40 | 1.4152 | 0.0237 | 0.9673 | 0.1834 | 1.7097 | 0.3517 | 0.5298 | 0.9976 | 0.0622 | 0.5836 |
| 42 | 1.3869 | 0.0216 | 0.9646 | 0.1754 | 1.5571 | 0.3555 | 0.5137 | 0.9981 | 0.0471 | 0.5659 |
| 44 | 1.5195 | 0.0212 | 0.9608 | 0.1848 | 1.0529 | 0.4171 | 0.4843 | 0.9976 | 0.0506 | 0.6203 |
| 46 | 1.4880 | 0.0194 | 0.9553 | 0.1751 | 1.1439 | 0.4233 | 0.4689 | 0.9976 | 0.0484 | 0.4961 |
| 48 | 1.4681 | 0.0188 | 0.9528 | 0.1796 | 1.2159 | 0.4235 | 0.4638 | 0.9980 | 0.0421 | 0.3916 |
| 50 | 1.4127 | 0.0183 | 0.9569 | 0.1620 | 0.7905 | 0.4015 | 0.4684 | 0.9972 | 0.0493 | 0.6389 |
| 52 | 1.3619 | 0.0175 | 0.9571 | 0.1564 | 0.8094 | 0.3951 | 0.4622 | 0.9966 | 0.0495 | 0.6117 |
| 54 | 1.2762 | 0.0175 | 0.9552 | 0.1490 | 0.9286 | 0.3617 | 0.4753 | 0.9940 | 0.0600 | 0.6030 |
| 56 | 1.3596 | 0.0165 | 0.9544 | 0.1340 | 0.4561 | 0.4121 | 0.4459 | 0.9925 | 0.0723 | 0.7092 |
| Bingham Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | MAE | MAPE | ||
| - | Pa | % | ||
| Linear model | τo | 0.9562 | 0.0328 | 2.243 |
| - | N·s/m2 | % | ||
| Linear model | ηB | 0.9675 | 0.0012 | 5.892 |
| - | Pa | % | ||
| Exponential model | τo | 0.9582 | 0.0304 | 2.015 |
| - | N·s/m2 | % | ||
| Exponential model | ηB | 0.9805 | 0.0007 | 2.973 |
| Ostwald Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | MAE | MAPE | ||
| - | Pa·sn | % | ||
| Linear model | KO | 0.9562 | 0.7662 | 0.0137 |
| - | - | % | ||
| Linear model | no | 0.9675 | 0.8157 | 0.0078 |
| - | Pa·sn | % | ||
| Exponential model | KO | 0.9582 | 0.7616 | 0.0152 |
| - | - | % | ||
| Exponential model | no | 0.9805 | 0.8221 | 0.0153 |
| d10 | d50 | d90 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | µm | ||
| Sample 1 | 4.23 | 28.36 | 144.9 |
| Sample 2 | 4.32 | 29.12 | 155.4 |
| Sample 3 | 4.41 | 29.45 | 170.1 |
| Sample 4 | 4.59 | 29.60 | 154.1 |
| Sample 5 | 4.31 | 27.50 | 125.1 |
| Average | 4.39 | 28.81 | 149.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gruszczyński, M.F.; Kałuża, T.; Czekała, W.; Zawadzki, P.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Matz, R.; Pawlak, M.; Jarzembowski, P.; Nezhad, F.S.; Dach, J. The Influence of Temperature on Rheological Parameters and Energy Efficiency of Digestate in a Fermenter of an Agricultural Biogas Plant. Energies 2024, 17, 6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17236111
Gruszczyński MF, Kałuża T, Czekała W, Zawadzki P, Mazurkiewicz J, Matz R, Pawlak M, Jarzembowski P, Nezhad FS, Dach J. The Influence of Temperature on Rheological Parameters and Energy Efficiency of Digestate in a Fermenter of an Agricultural Biogas Plant. Energies. 2024; 17(23):6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17236111
Chicago/Turabian StyleGruszczyński, Maciej Filip, Tomasz Kałuża, Wojciech Czekała, Paweł Zawadzki, Jakub Mazurkiewicz, Radosław Matz, Maciej Pawlak, Paweł Jarzembowski, Farokh Sahraei Nezhad, and Jacek Dach. 2024. "The Influence of Temperature on Rheological Parameters and Energy Efficiency of Digestate in a Fermenter of an Agricultural Biogas Plant" Energies 17, no. 23: 6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17236111
APA StyleGruszczyński, M. F., Kałuża, T., Czekała, W., Zawadzki, P., Mazurkiewicz, J., Matz, R., Pawlak, M., Jarzembowski, P., Nezhad, F. S., & Dach, J. (2024). The Influence of Temperature on Rheological Parameters and Energy Efficiency of Digestate in a Fermenter of an Agricultural Biogas Plant. Energies, 17(23), 6111. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17236111








