A Novel LCLC Parallel Resonant Circuit for High-Frequency Induction Heating Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
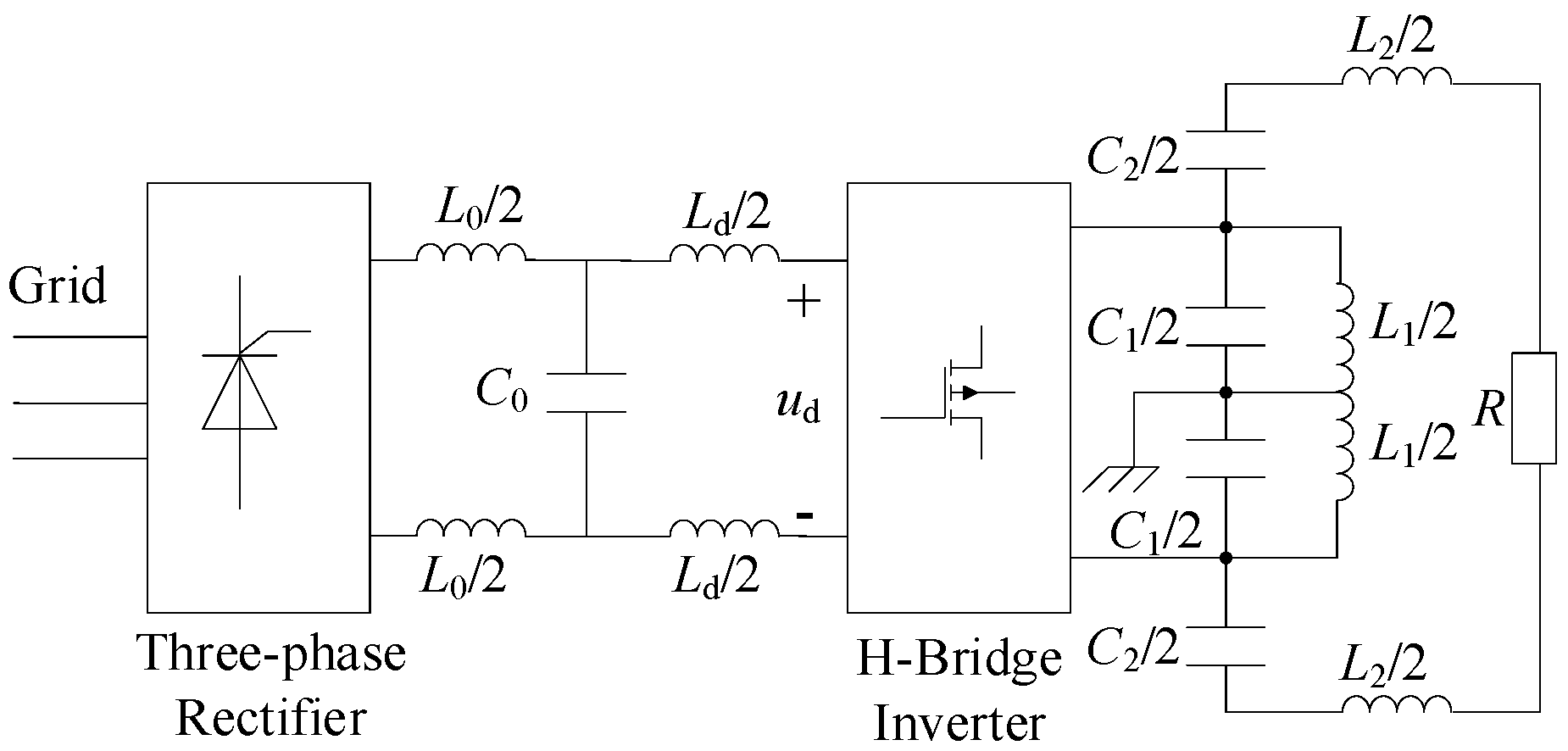
2.1. Main Circuit of the LCLC-Based High-Frequency Induction Heating System
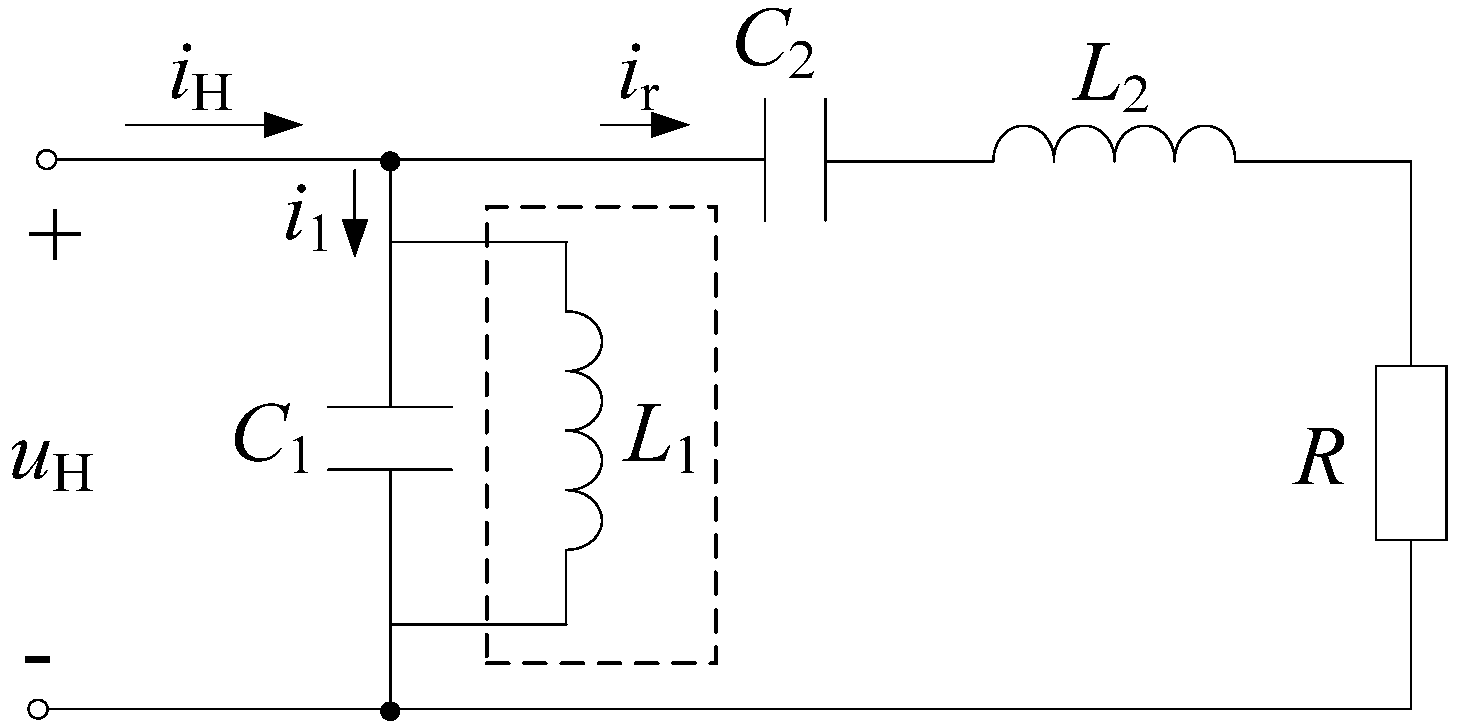
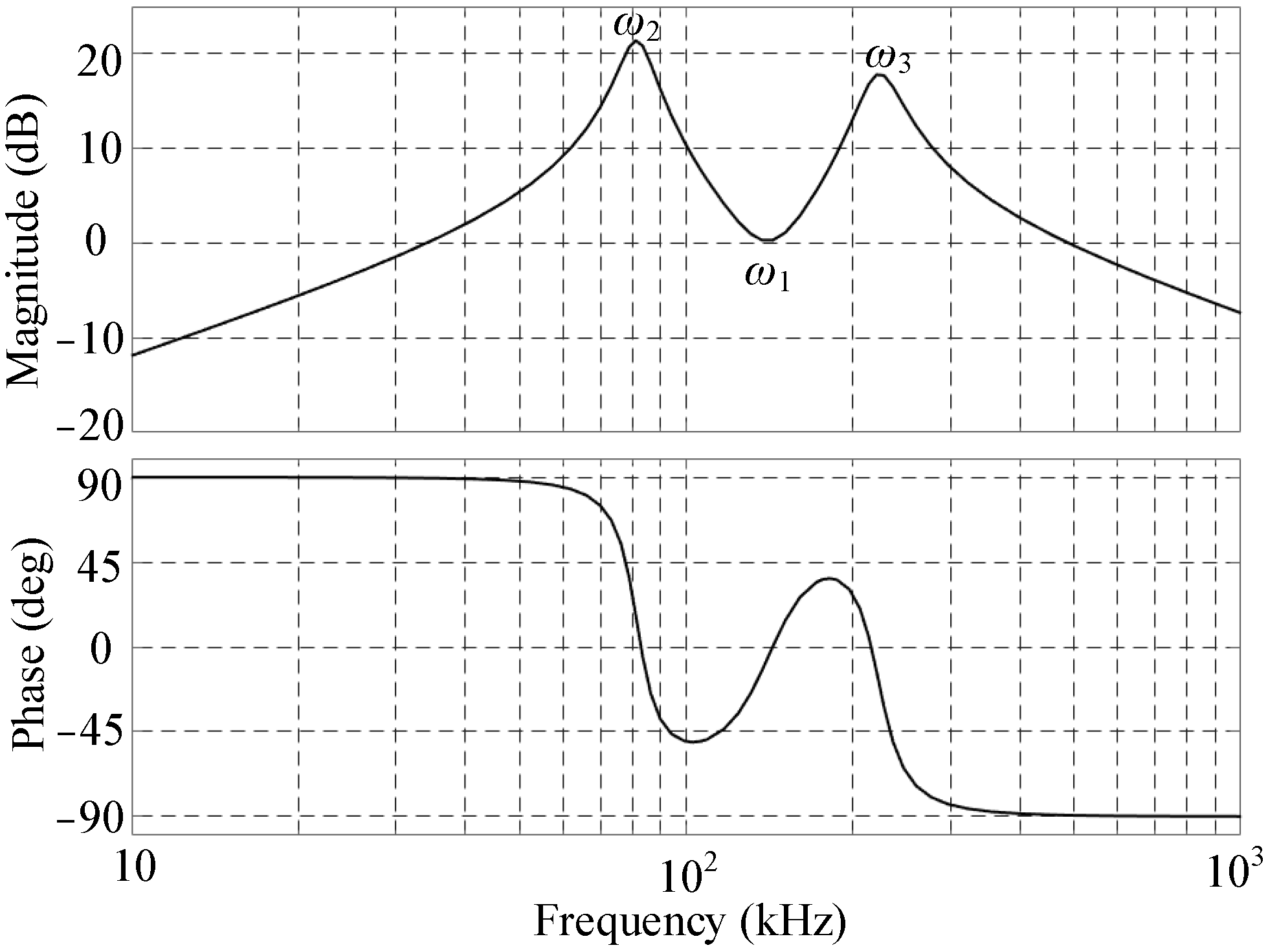
2.2. Frequency Characteristic of the LCLC Resonant Circuit
2.3. Resonant Characteristic of the LCLC Circuit
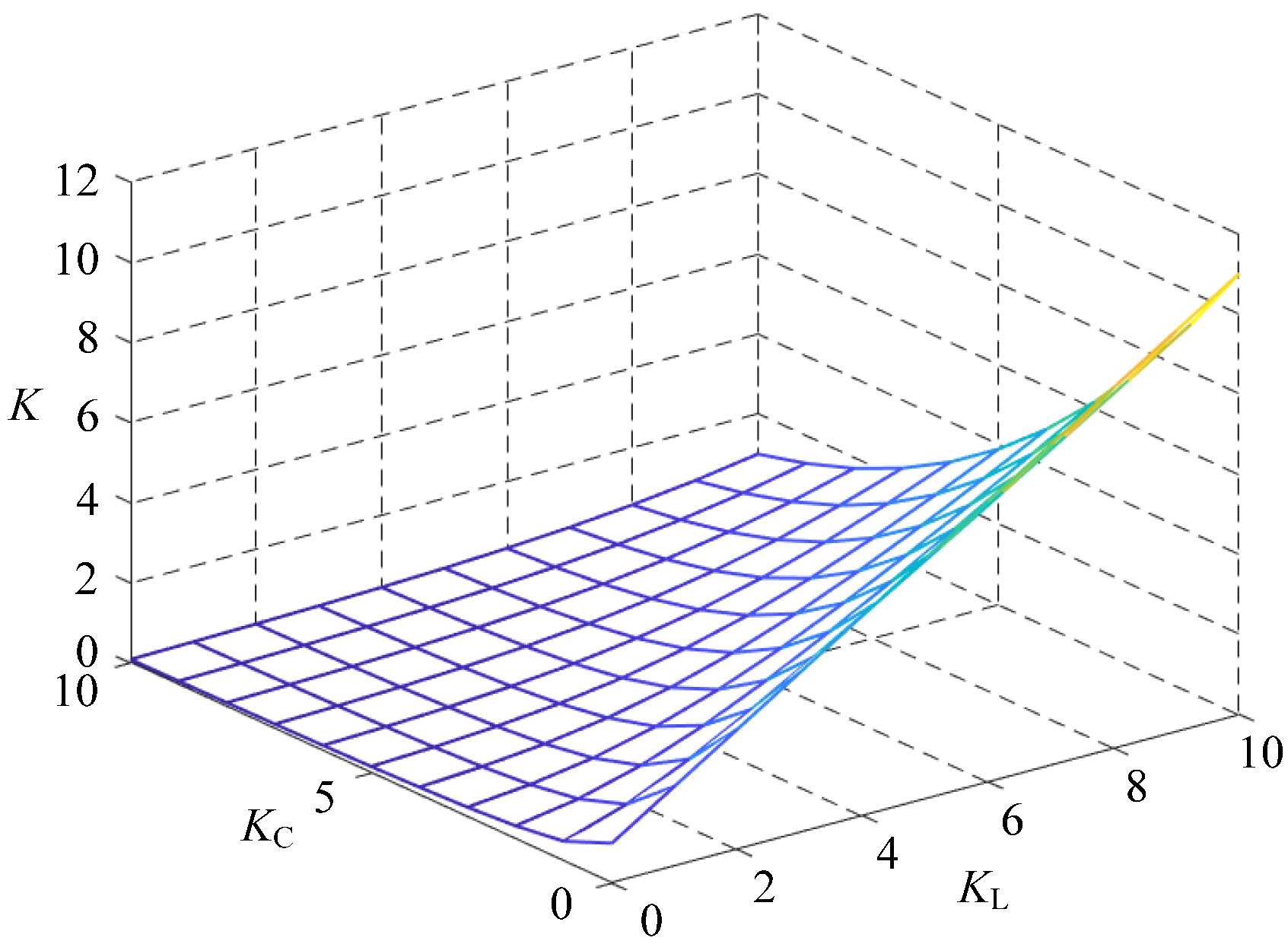
2.3.1. Quality Factor
2.3.2. Resonant Impedance
2.3.3. Resonant Current
2.3.4. Voltage Regulation Feature
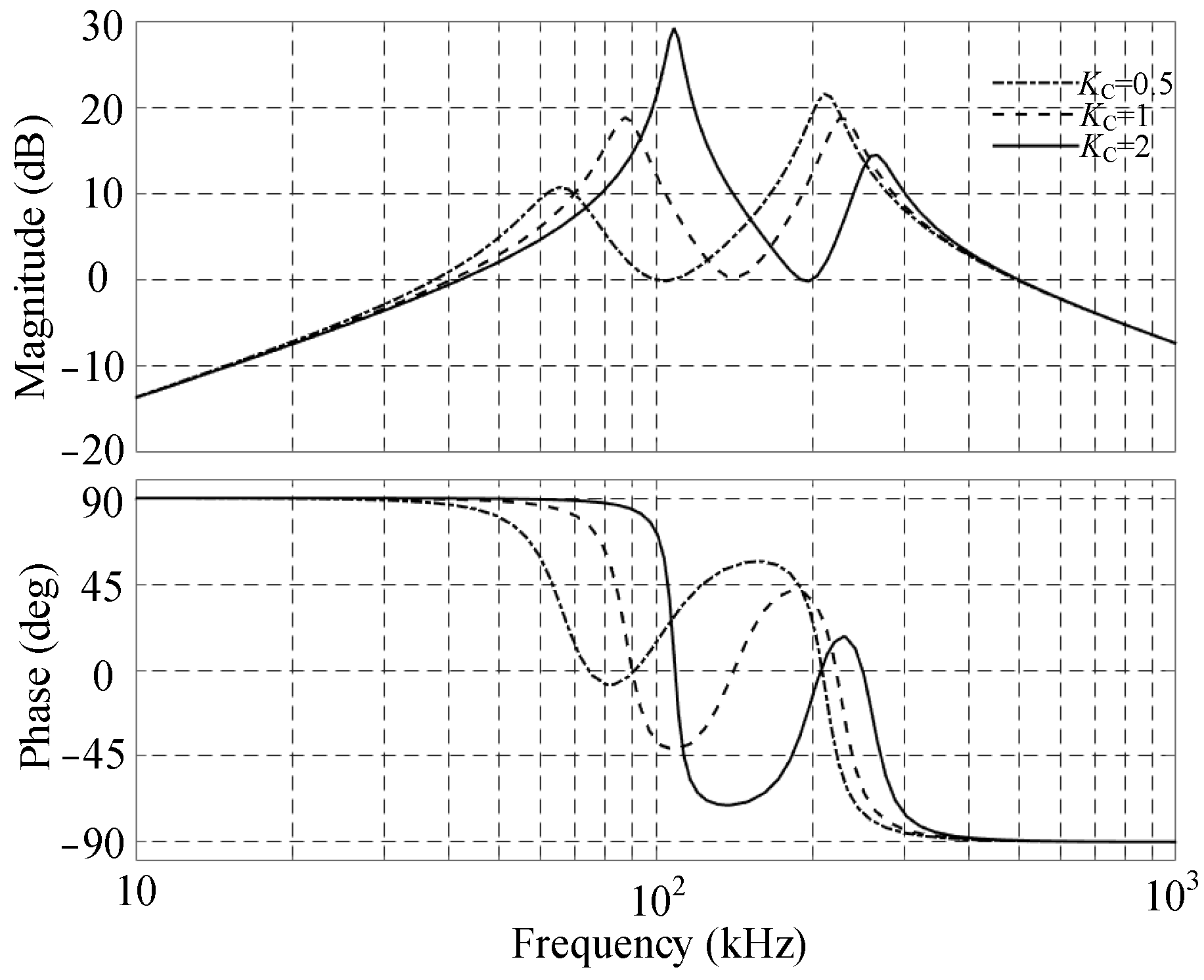
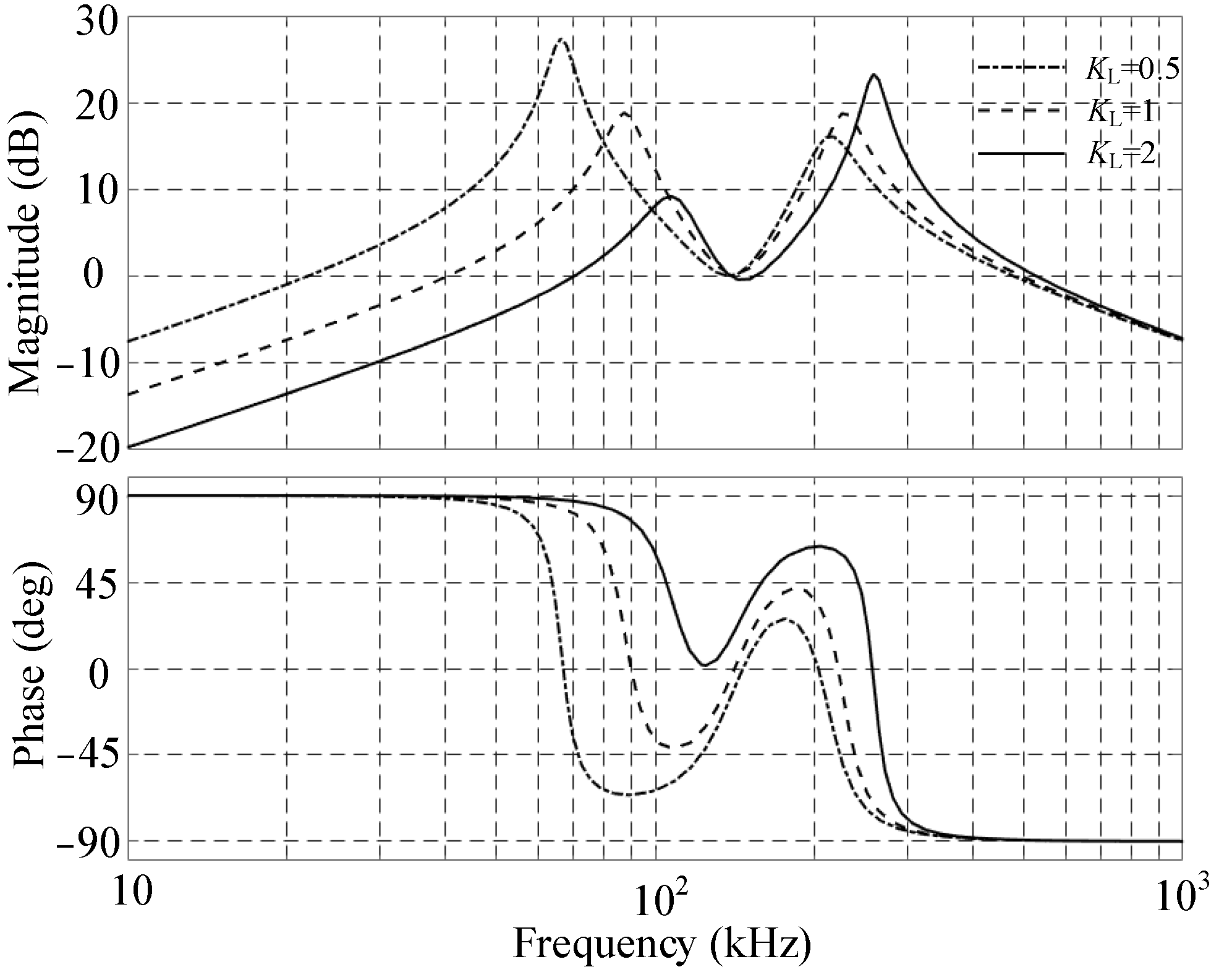
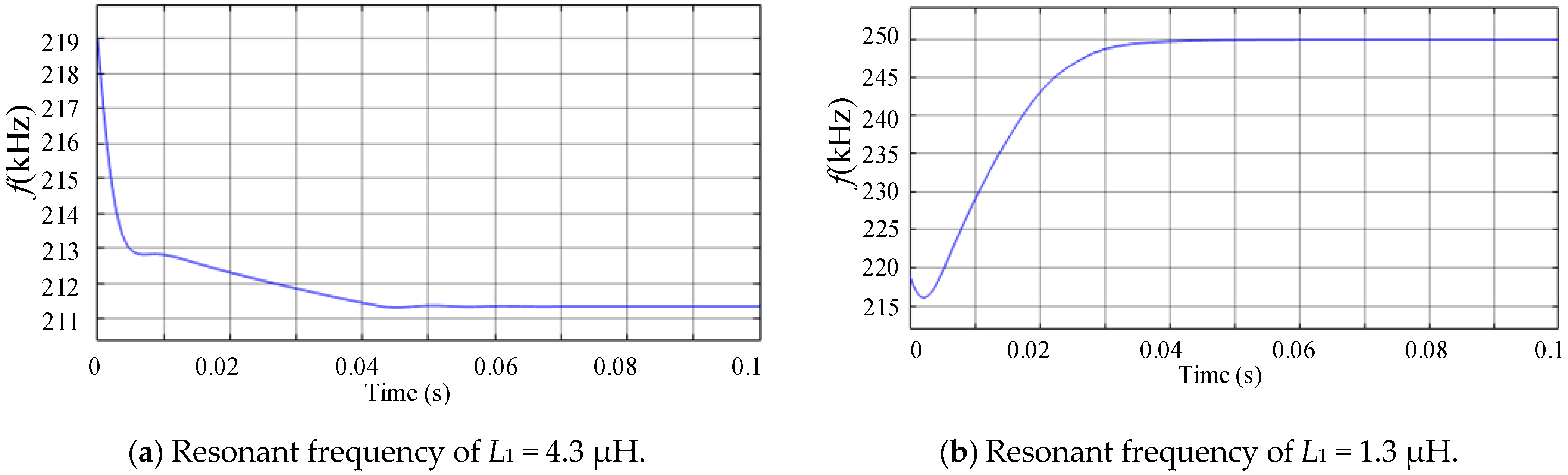
2.3.5. Influence of C2 and L1
3. Results and Discussion
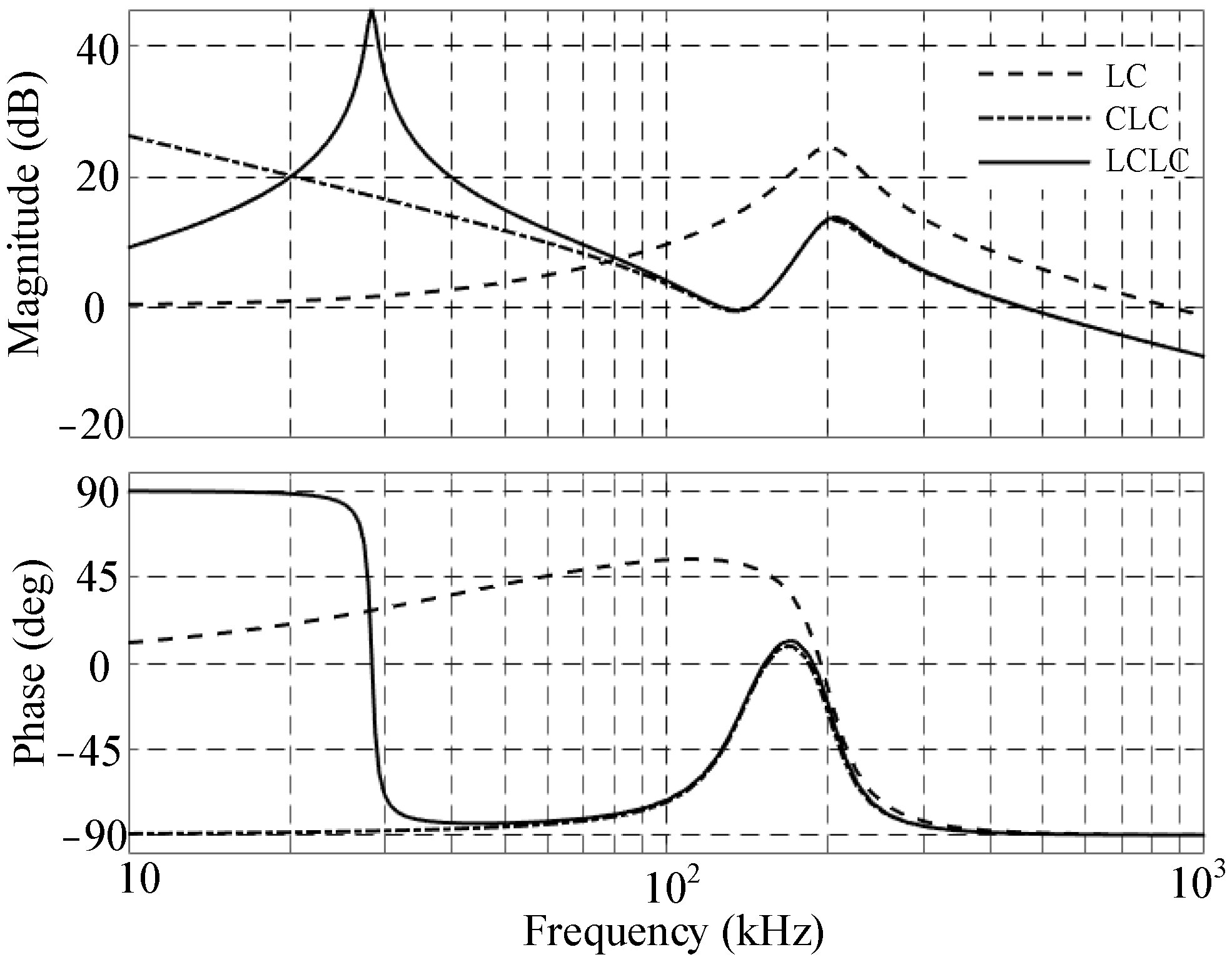
3.1. Comparative Analysis of LC, CLC, and LCLC Resonant Characteristics
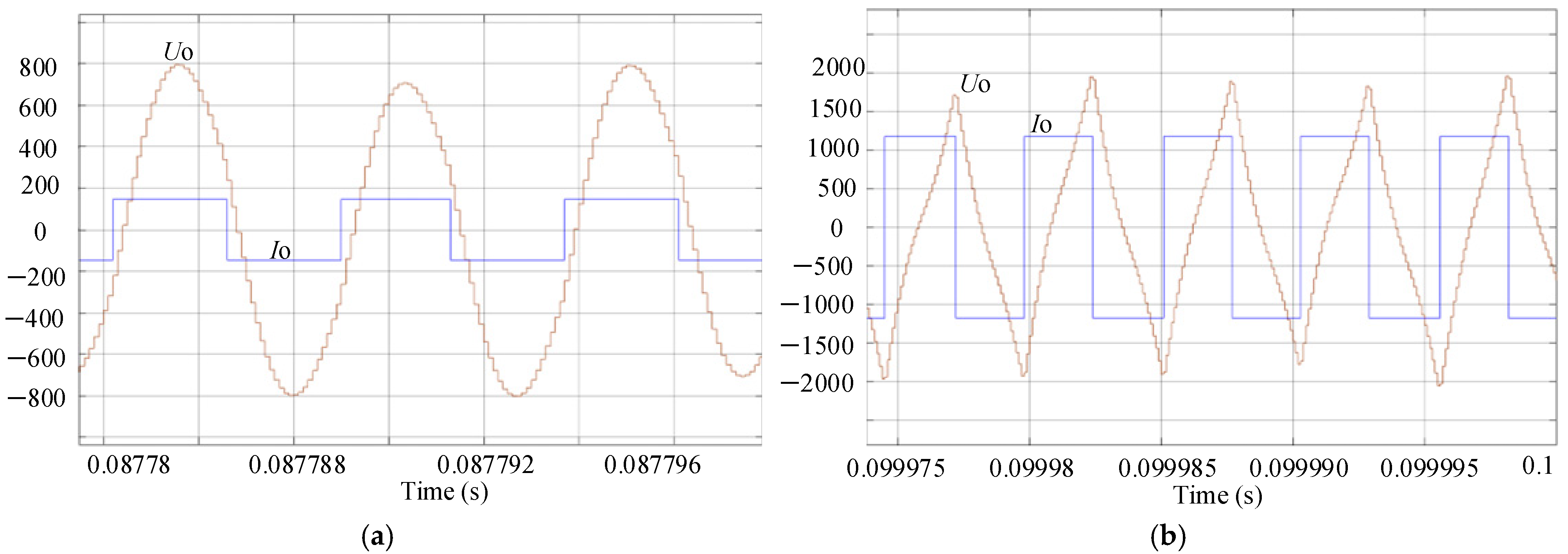
3.2. Characteristic Analysis of Induction Heating System Based on LCLC Load
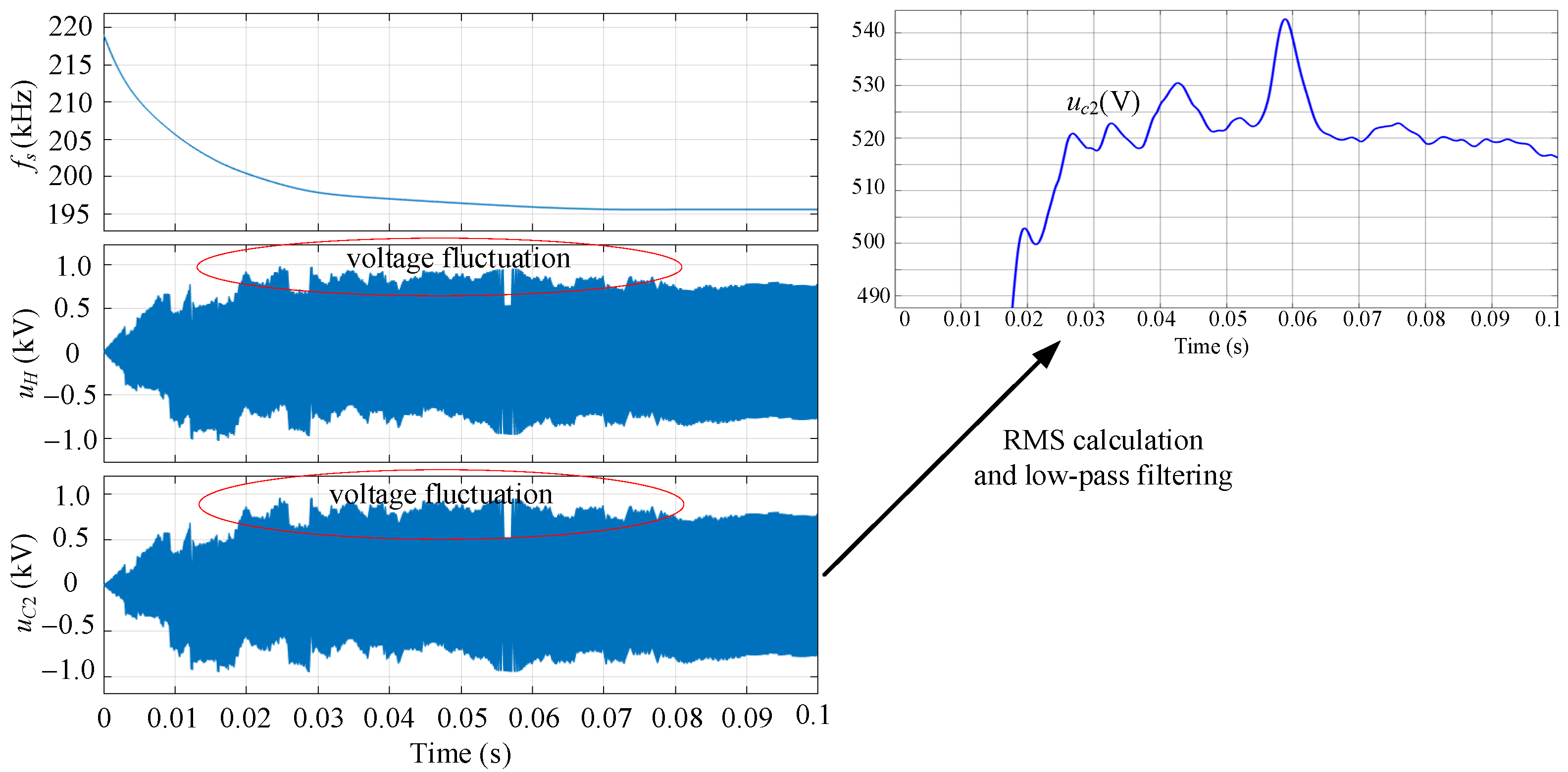
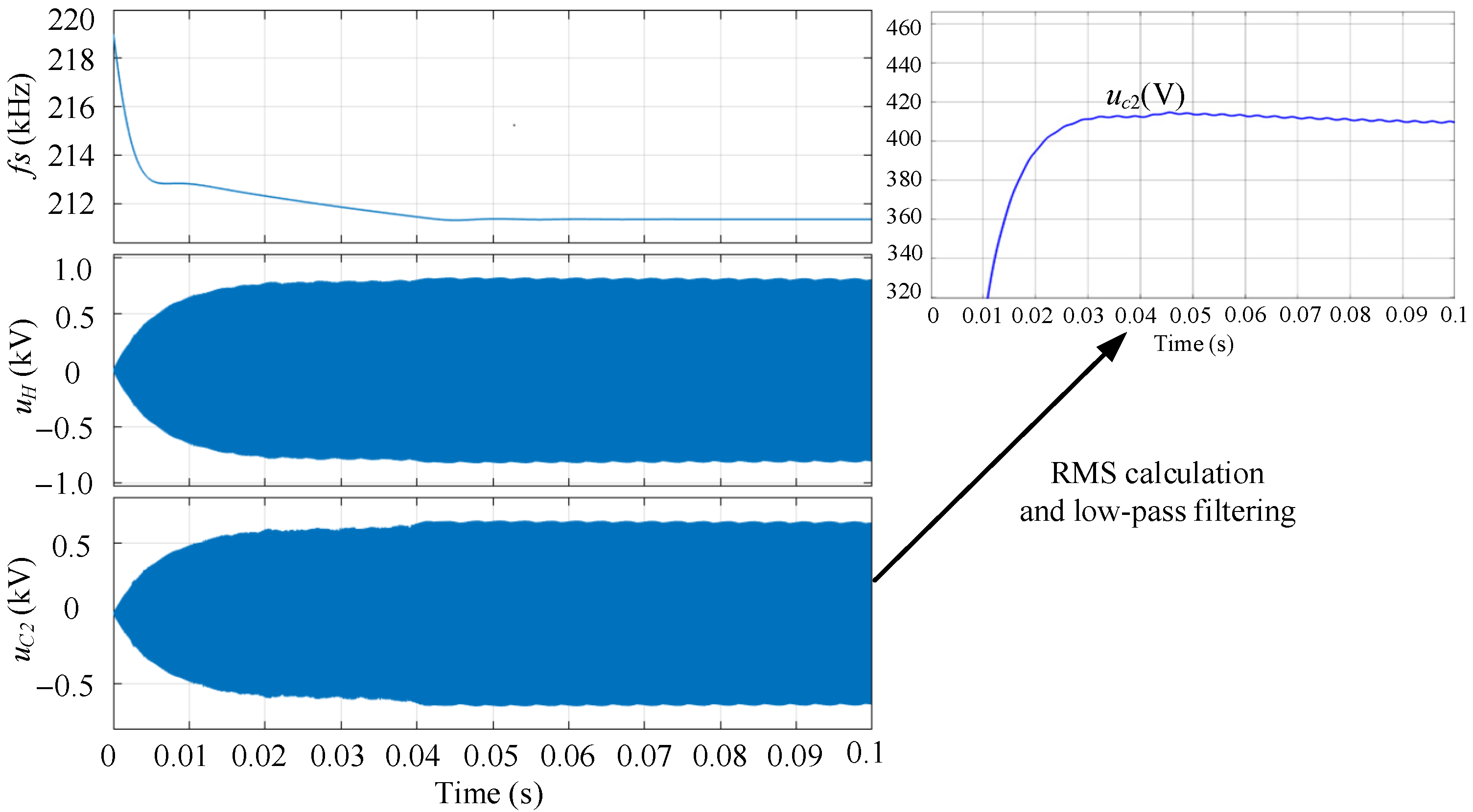
3.2.1. Frequency Tracking Control
3.2.2. Comparison and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lampa, M.; Mokrošová, L. Optimisation of the Thermal Process in Ladle Metallurgy in Terms of the Impact on Energy Consumption and the Environmental Burden During Steel Production. Rocz. Ochr. Sr. 2022, 24, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polushin, A.A.; Kamantsev, S.V.; Gryzunov, V.I.; Minakov, M.Y. Heat Treatment of Steel Rolls for Cold Rolling. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2011, 53, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gołaszewski, A.; Szawłowski, J.; Świątnicki, W.A. Multiphase Steel Microstructure and Properties Optimisation through a New Heat Treatment Process. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 37, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Nishi, T.; Yanagimoto, J. Continuous Heating System Using Electric Resistance Heating for the Hot Rolling of Stainless Steels. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käsemann, C.-P.; van Lieshout, L.; Huart, M.; Sihler, C. Thyristor Crowbar System for the High Current Power Supplies of ASDEX Upgrade. Fusion Eng. Des. 2005, 75–79, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Li, M.; Shi, B.; Yu, X.; Liu, X. A Variable Frequency Injection Method for Modular Multilevel Converters in Variable Speed Drives. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Shi, C.; Liu, T.; He, J. Analysis of Power Supply Heating Effect during High Temperature Experiments Based on the Electromagnetic Steel Teeming Technology. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2017, 36, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-M.; Chen, Y.-C. Rapid Welding of Stainless Steel Wires Using Ultra-High Frequency Induction Heating. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2013, 36, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, I.; Durna, E.; Ermis, M. Design and Implementation of a Hybrid System for the Mitigation of PQ Problems of Medium-Frequency Induction Steel-Melting Furnaces. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 2700–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolenko, D.; Iuferev, L.; Roshchin, O. The Resonant Induction Heating Method. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 54, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shami, U.T.; Shami, T.A. An Adaptive Load-matching Method for the Induction Heating Coil with DC Power Supply. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2024, 52, 5025–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aunsborg, T.S.; Duun, S.B.; Munk-Nielsen, S.; Uhrenfeldt, C. Development of a Current Source Resonant Inverter for High Current MHz Induction Heating. IET Power Electron. 2022, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khati, A.; Kansab, A.; Taleb, R.; Khouidmi, H. Current Predictive Controller for High Frequency Resonant Inverter in Induction Heating. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namadmalan, A.; Moghani, J.; Abdi, B. Improved Modification of the Current Source Parallel Resonant Push-Pull Inverter for Induction Heating Applications. Int. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2010, 5, 390–396. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.-F. A Passive-Impedance-Matching Technology to Achieve Automatic Current Sharing for a Multiphase Resonant Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 9191–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.-F.; Ouyang, X.; Alù, A. Digital Non-Foster-Inspired Electronics for Broadband Impedance Matching. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Q.; Gao, B. A Hybrid Impedance Matching Network for Underwater Acoustic Transducers. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 7622–7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudjuarjeen, S.; Sangswang, A.; Koompai, C. An Improved LLC Resonant Inverter for Induction-Heating Applications with Asymmetrical Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 2915–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppusamy, S.; Sunandhitha, V.; Suraj, R.; Roja, T.S.; Sundararaman, K. Design and Implementation of High Frequency Induction Heating with LLC Resonant Load Matching Using ELTA. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2020, 11, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, O.; Maussion, P.; Dede, E.J.; Burdio, J.M. Induction Heating Technology and Its Applications: Past Developments, Current Technology, and Future Challenges. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Jang, E.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, J.-H.; Lee, B.K. Optimal Design of High-Frequency Induction Heating Apparatus for Wafer Cleaning Equipment Using Superheated Steam. Energies 2020, 13, 6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espi-Huerta, J.M.; Dede Garcia Santamaria, E.J.; Garcia Gil, R.; Castello-Moreno, J. Design of the L-LC Resonant Inverter for Induction Heating Based on Its Equivalent SRI. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 3178–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Sengupta, M. A Commutation Strategy for IGBT-Based CSI-Fed Parallel Resonant Circuit for Induction Heating Application. Sādhanā 2017, 42, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szychta, E. The Results of the Rail Induction Heating by the Current Inverter with the Parallel Resonant Circuit. Prz. Elektrotech. 2016, 1, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zgraja, J. Dual-Frequency Induction Heating Generator with Adjustable Impedance Matching. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 8308–8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Xu, Z.; Xia, H. A Novel LCLC Parallel Resonant Circuit for High-Frequency Induction Heating Application. Energies 2024, 17, 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17235892
Xu S, Xu Z, Xia H. A Novel LCLC Parallel Resonant Circuit for High-Frequency Induction Heating Application. Energies. 2024; 17(23):5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17235892
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Sheng, Zuping Xu, and Huafeng Xia. 2024. "A Novel LCLC Parallel Resonant Circuit for High-Frequency Induction Heating Application" Energies 17, no. 23: 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17235892
APA StyleXu, S., Xu, Z., & Xia, H. (2024). A Novel LCLC Parallel Resonant Circuit for High-Frequency Induction Heating Application. Energies, 17(23), 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17235892




