Low Vibration Control Scheme for Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Resonance Controllers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Electromagnetic Force Analysis
2.1. Analysis of Low-Order Harmonic Current
2.2. Electromagnetic Force Calculation
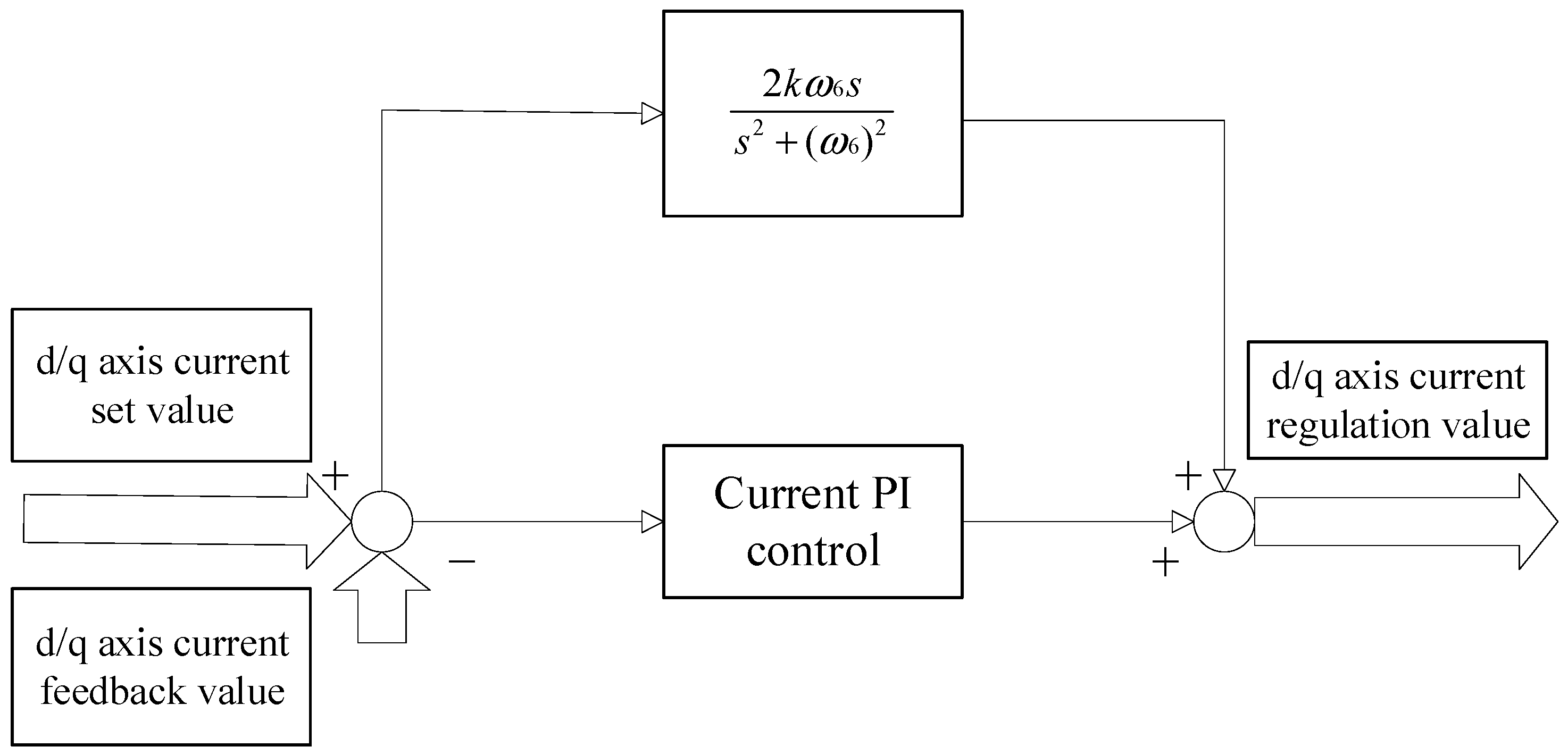
3. Basic Principle of Resonance Controller
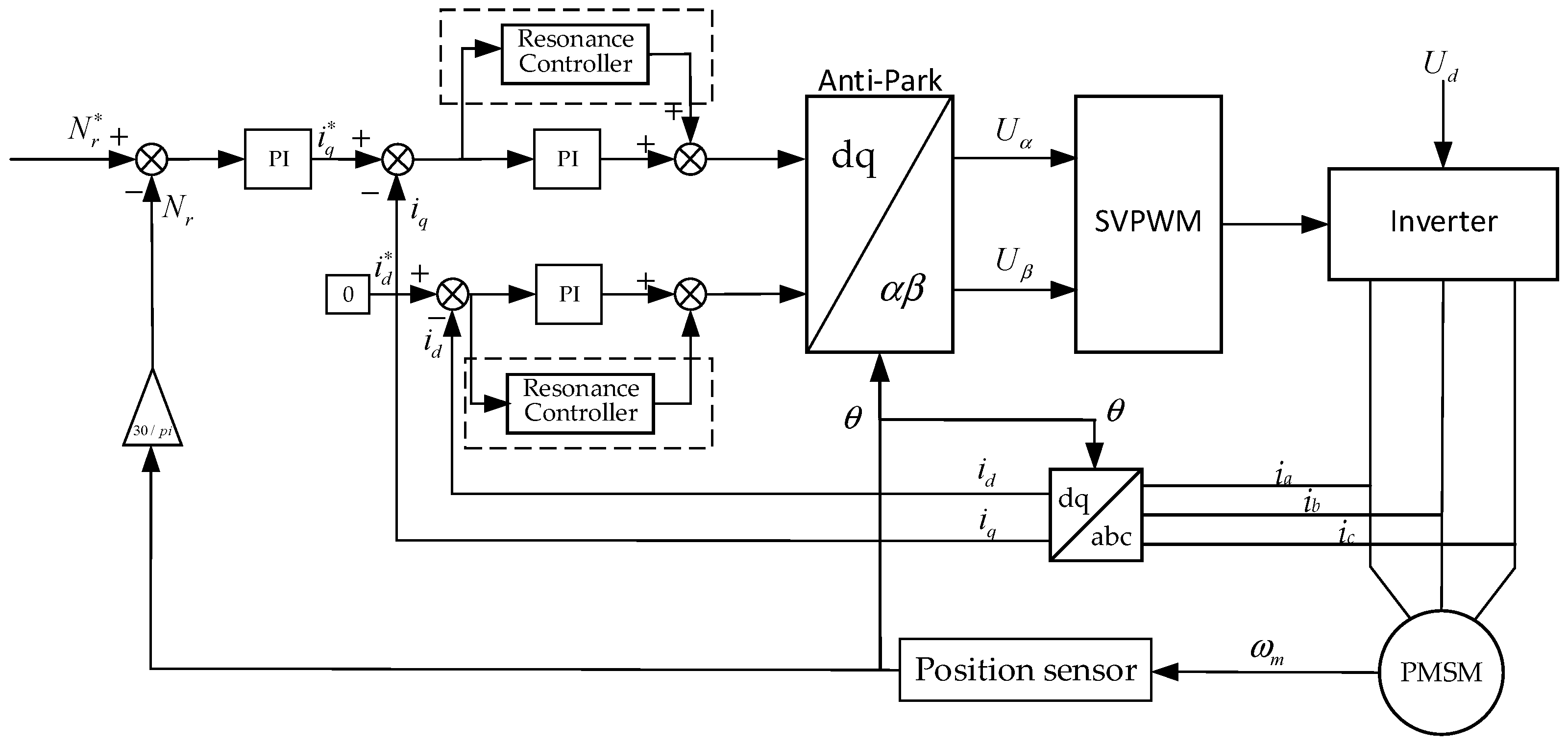
4. Verification of Resonance Controller
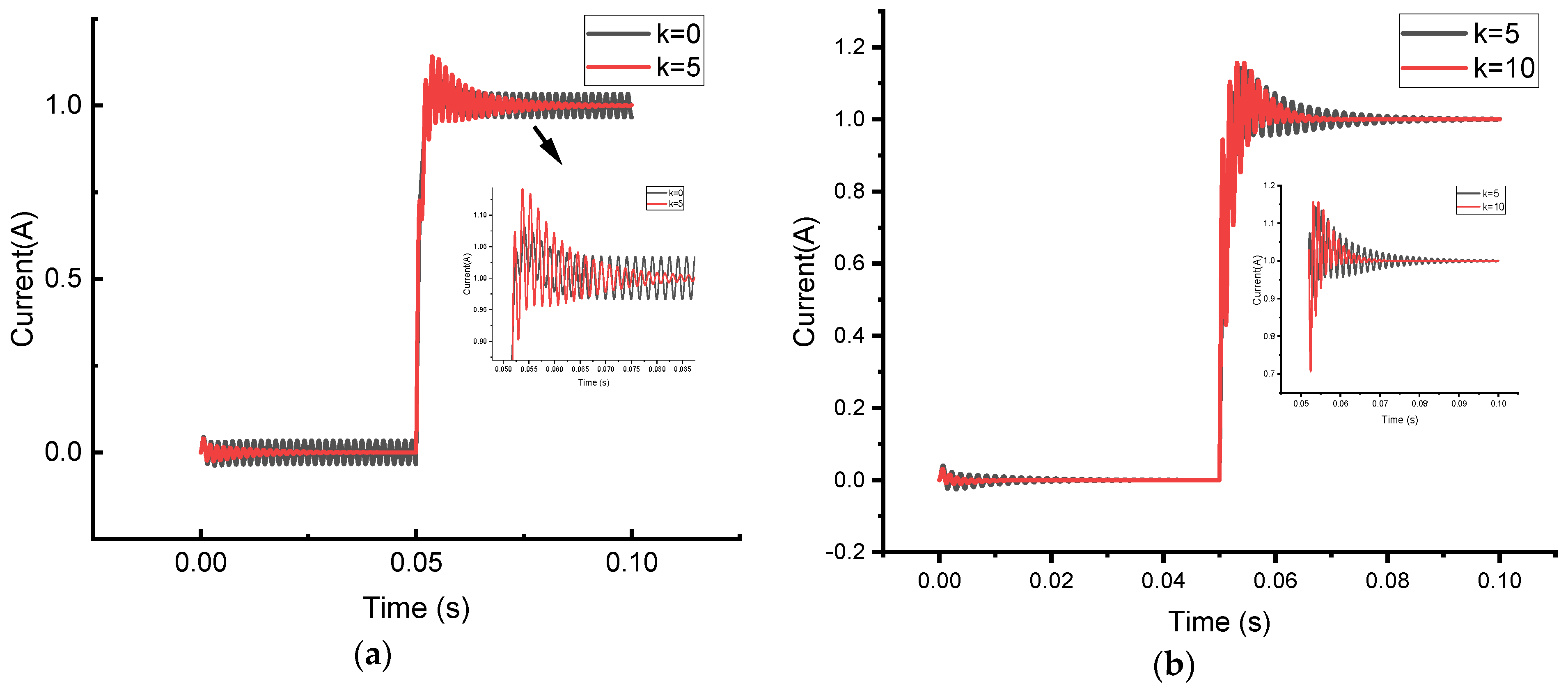
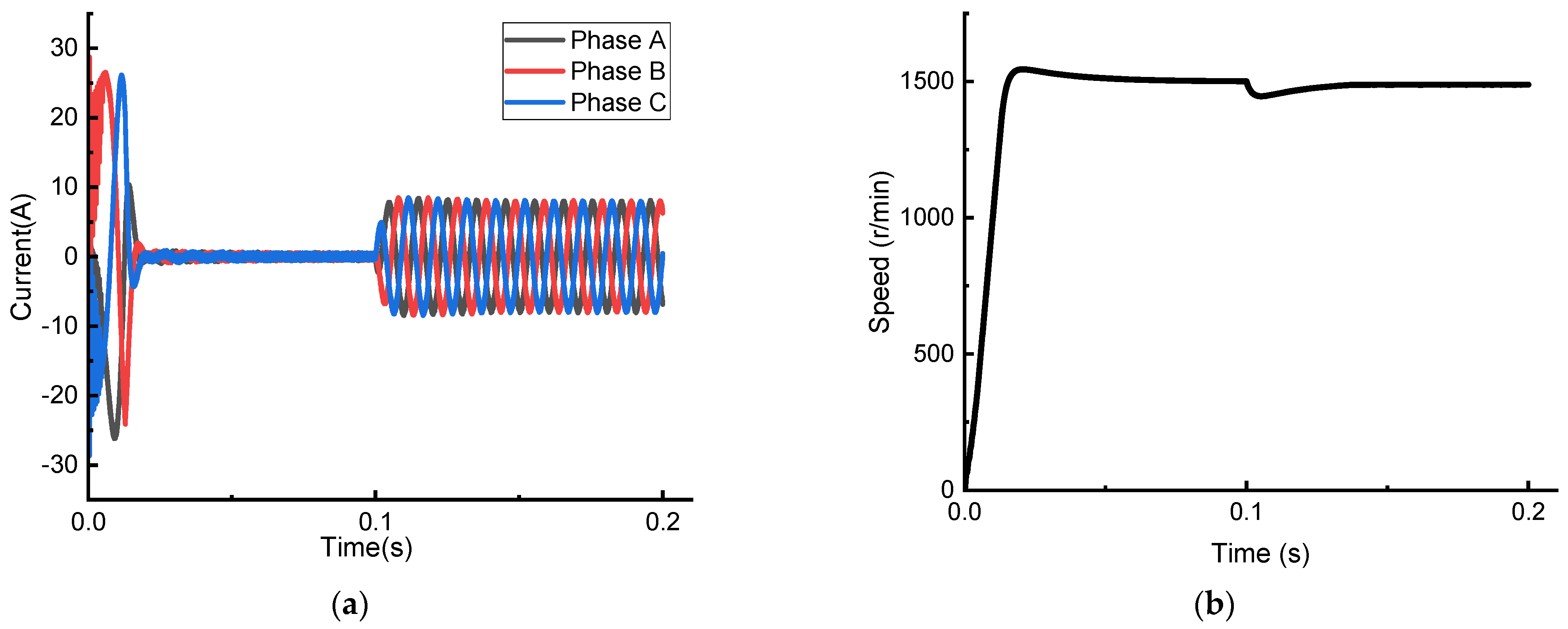
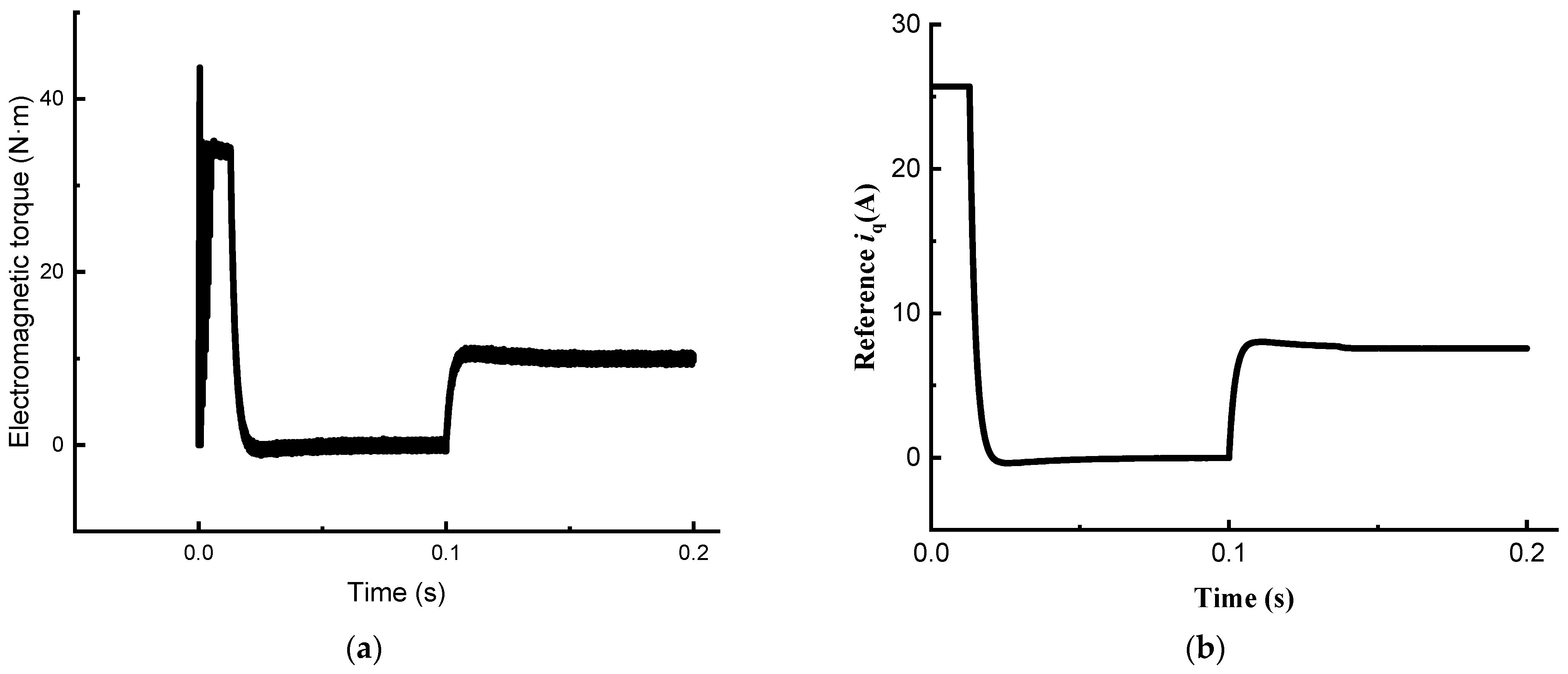
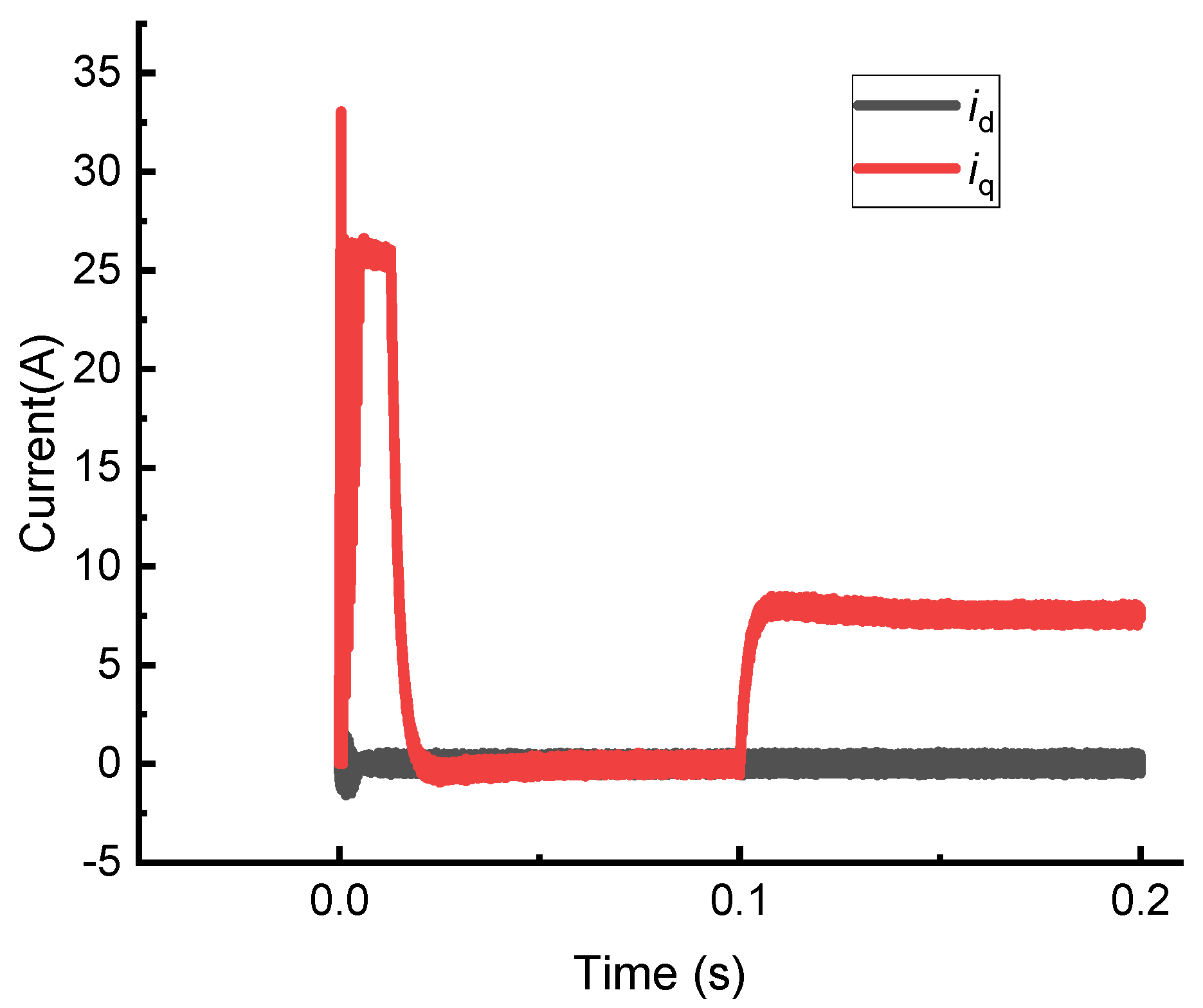
4.1. Simulation Verification
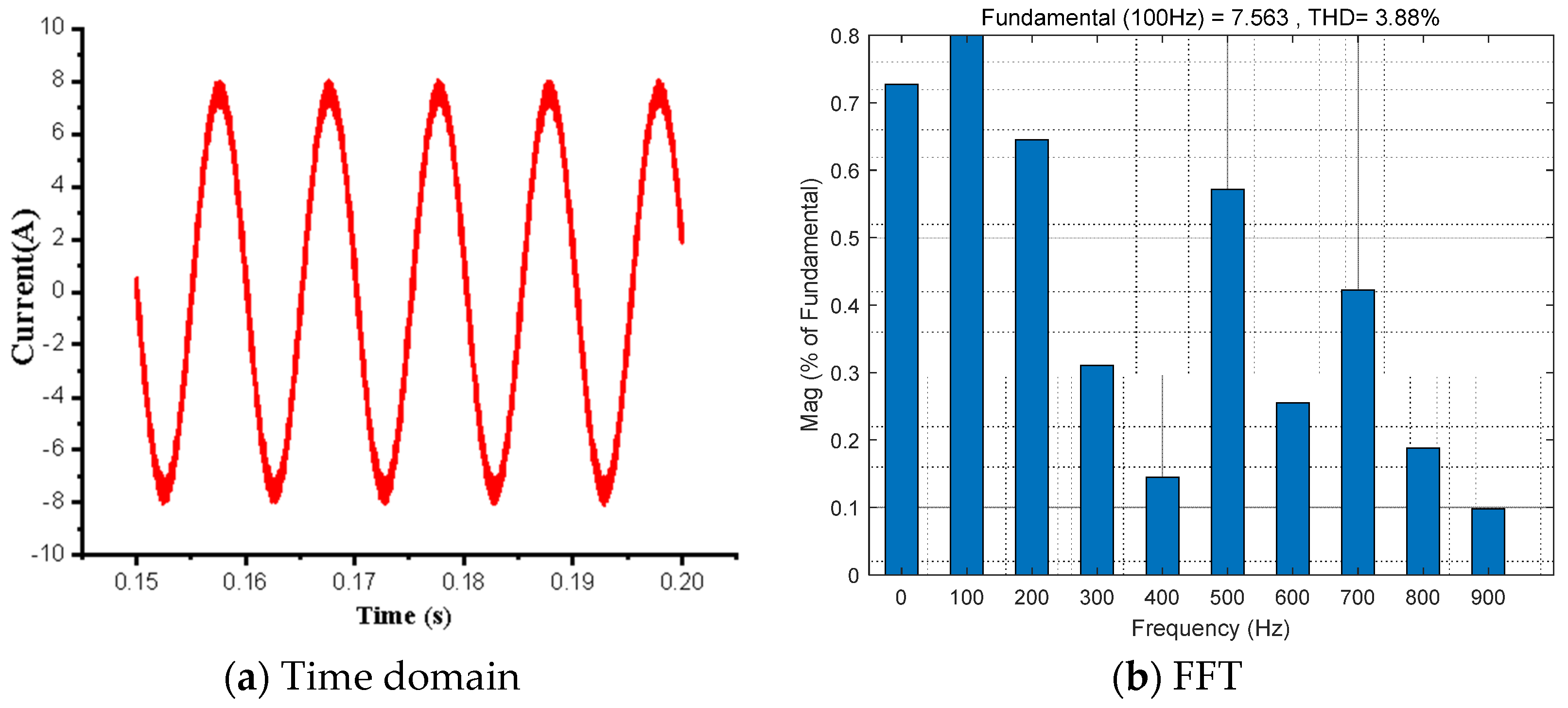
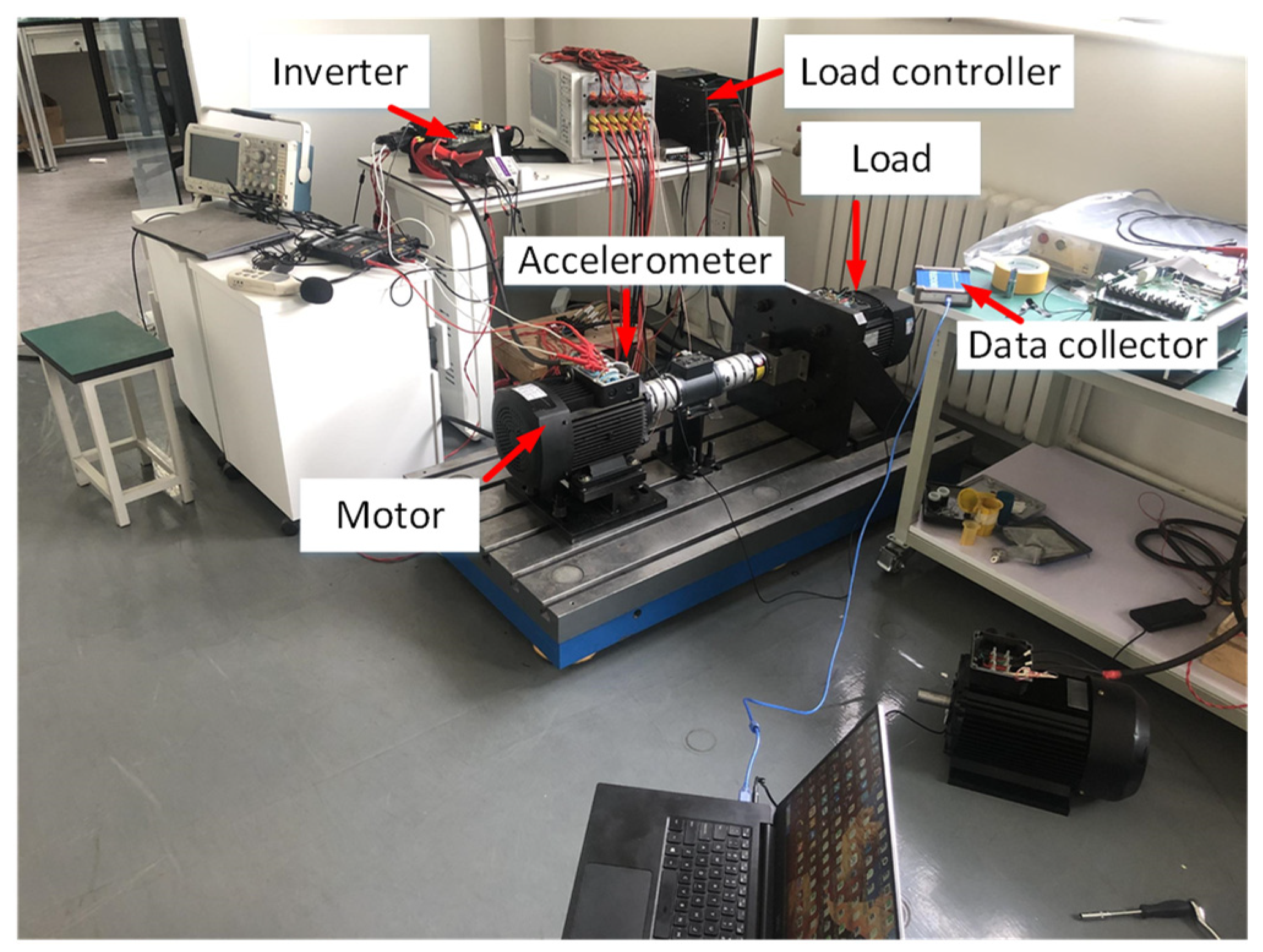
4.2. Test Verification
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The resonant regulator has almost no effect on the fundamental current, speed, and other parameters in the motor control system.
- (2)
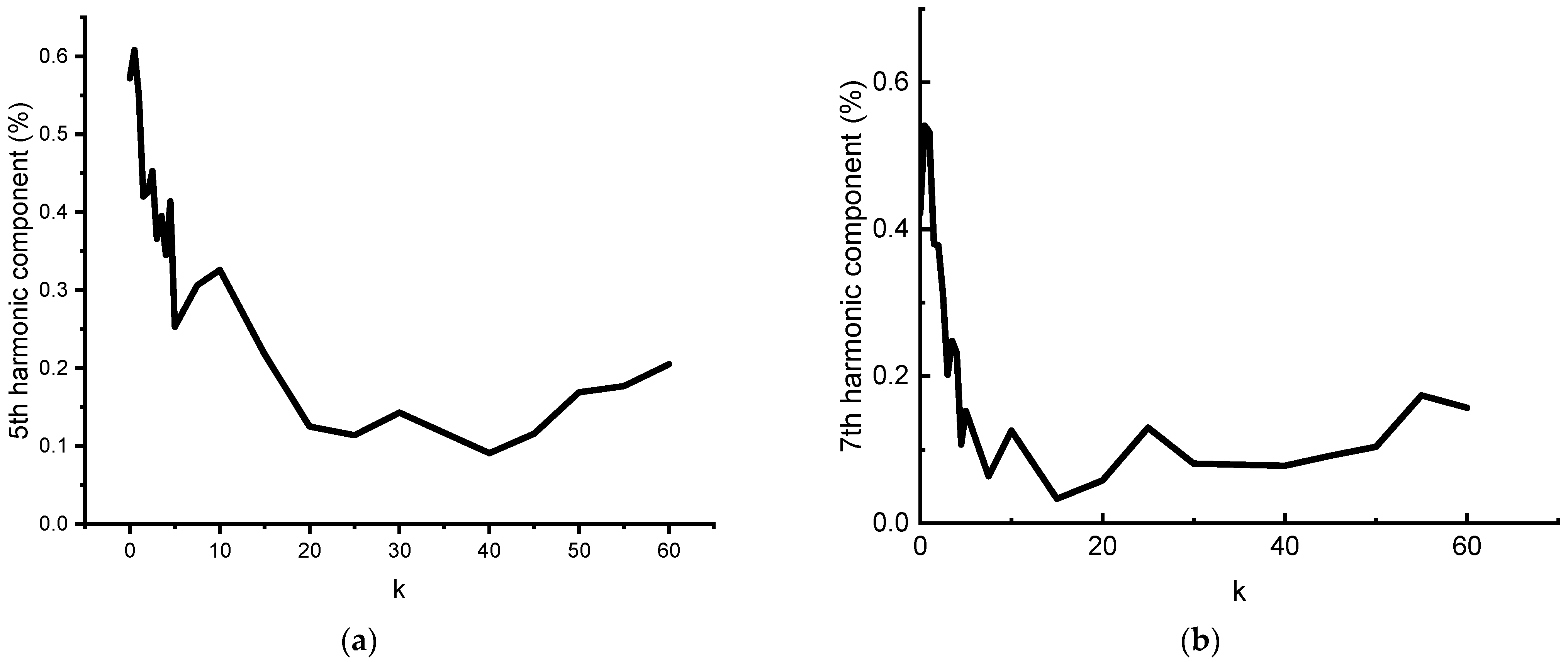
- The parameter k in the resonant regulator affects the suppression effect of low-order harmonic currents. As the parameter k increases, the suppression effect of the resonant regulator on the fifth and seventh harmonics increases. When k changes from 0 to 5, the fifth harmonic of the current decreases from 0.575 A to 0.248 A, a decrease of 56.87%, and the seventh harmonic decreases from 0.422 A to 0.147 A, a decrease of 65.17%.
- (3)
- The introduction of resonant regulators can effectively suppress low-frequency vibration components of the motor, with a 29.3% reduction in amplitude at 200 Hz, a 24.53% reduction in amplitude at 300 Hz, a 16.53% reduction in amplitude at 500 Hz, and a 16.67% reduction in amplitude at 600 Hz.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEC 60349.4-2012; Electric Traction-Rotating Electric Machines for Rail and Road Vehicles—Part 4: Permanent Magnet Synchronous Electrical Machines Connected to an Electronic Converter. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Fang, H.; Li, D.; Qu, R.; Yan, P. Modulation Effect of Slotted Structure on Vibration Response in Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 2998–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Y. Influence of Radial Force Harmonics with Low Mode Number on Electromagnetic Vibration of PMSM. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2014, 29, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60034.9-2007; Rotating Electrical Machines—Part 9: Noise Limits. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Alan, K.; Wallace, R.S.; Larry, G.M. Current harmonics and acoustic noise in ac adjust ab.-speed drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1990, 26, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Mitcham, A.J.; Antonopoulos, G.; Cullen, J.J. Favourable slot and pole number combinations forfault-tolerant PM machines. IEEE Proc. Power Appl. 2004, 151, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.D.; Chen, Y.S. Electromagnetic Vibration Analysis and Suppression of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor with Fractional Slot Combination. Proc. CSEE 2011, 31, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.M.; Hong, J.F.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Cao, H. Filling Force Valley with Interpoles for Pole-Frequency Vibration Reduction in Surface-Mounted PM Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 6709–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Z.; Han, J.W.; Wang, Y.; Ali, M.; Tang, H. High-Frequency SiC Three-Phase VSIs with Common-Mode Voltage Reduction and Improved Performance Using Novel Tri-State PWM Method. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 1809–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Lai, C.; Tian, J.; Kar, N.C. Multiple reference frame based torque ripple minimization for PMSM drive under both steady-state and transient conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 6685–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Han, Y.; Lee, K.; Bhattacharya, S. A sinusoidal current control strategy based on harmonic voltage injection for harmonic loss reduction of PMSMs with non-sinusoidal back-EMF. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 7032–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Liang, J.; Lee, Z.G.; Ahn, J.-W. A simple nonlinear logical torque sharing function for low-torque ripple SR drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 3021–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Lai, C.; Mukherjee, K.; Kar, N.C. Online PMSM magnet flux-linkage estimation for rotor magnet condition monitoring using measured speed harmonics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 2786–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, M.; Ževžikov, P.; Stosiak, M.; Skačkauskas, P.; Borucka, A.; Delembovskyi, M. Vibration Research on Centrifugal Loop Dryer Machines Used in Plastic Recycling Processes. Machines 2024, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Shao, B.; Qi, J.; Ren, Y.; Gan, C.; Brockway, S.; Hilton, C. Arbitrary current harmonic decomposition and regulation for permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 4392–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccue, P.; Neely, J.; Pekarek, S.; Stutts, D. Measurement and control of torque ripple-induced frame torsional vibration in a surface-mount permanent magnet machine. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 128–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.S.; Chang, Y.T.; Chen, B.Y. Novel Random-Switching PWM Technique with Constant Sampling Frequency and Constant Inductor Average Current for Digitally Controlled Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3126–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.F.; Gui, L.; Cao, J.C. Analysis and Experimental Verification of the Tangential Force effect on Electromagnetic Vibration of PM Motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
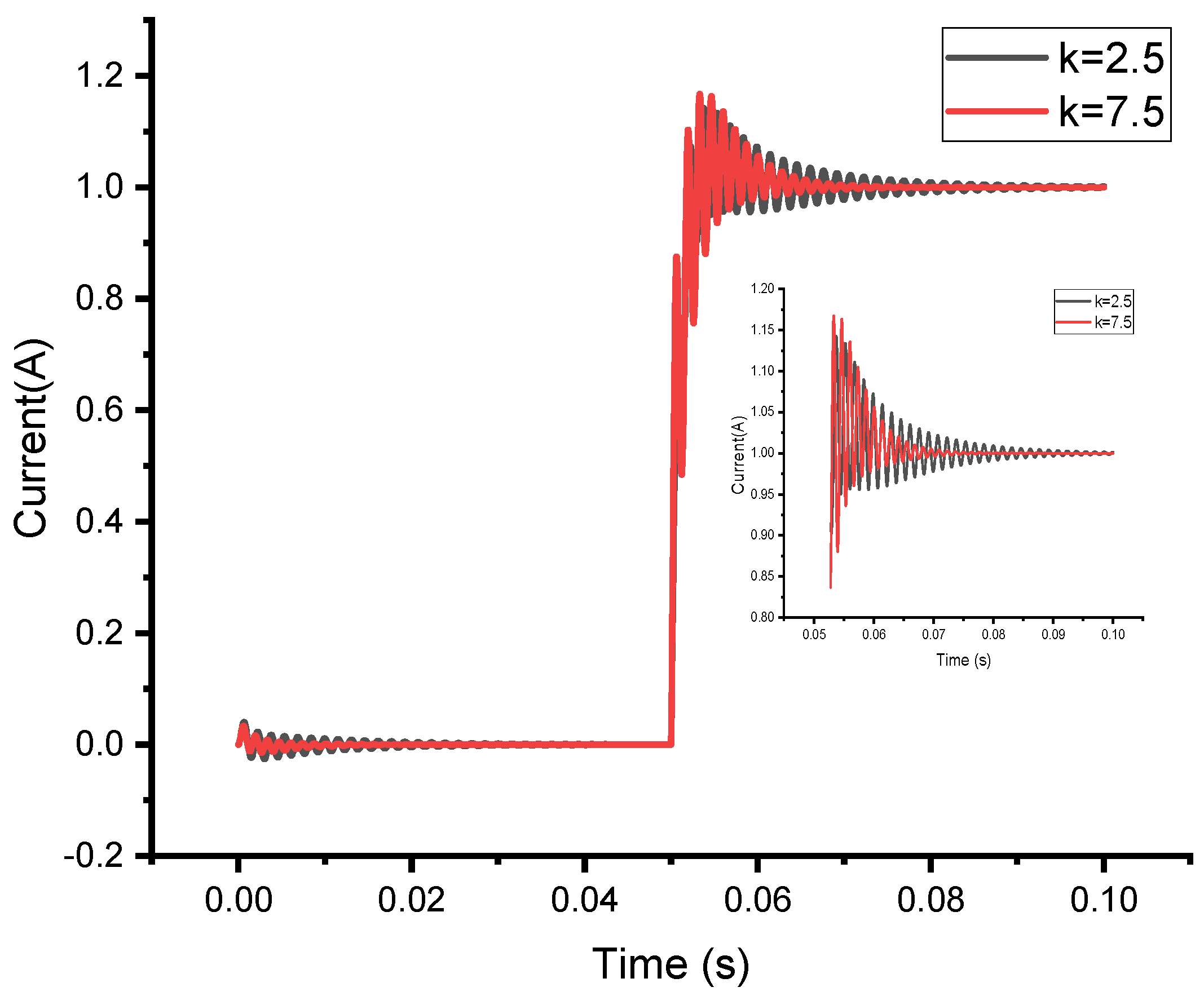
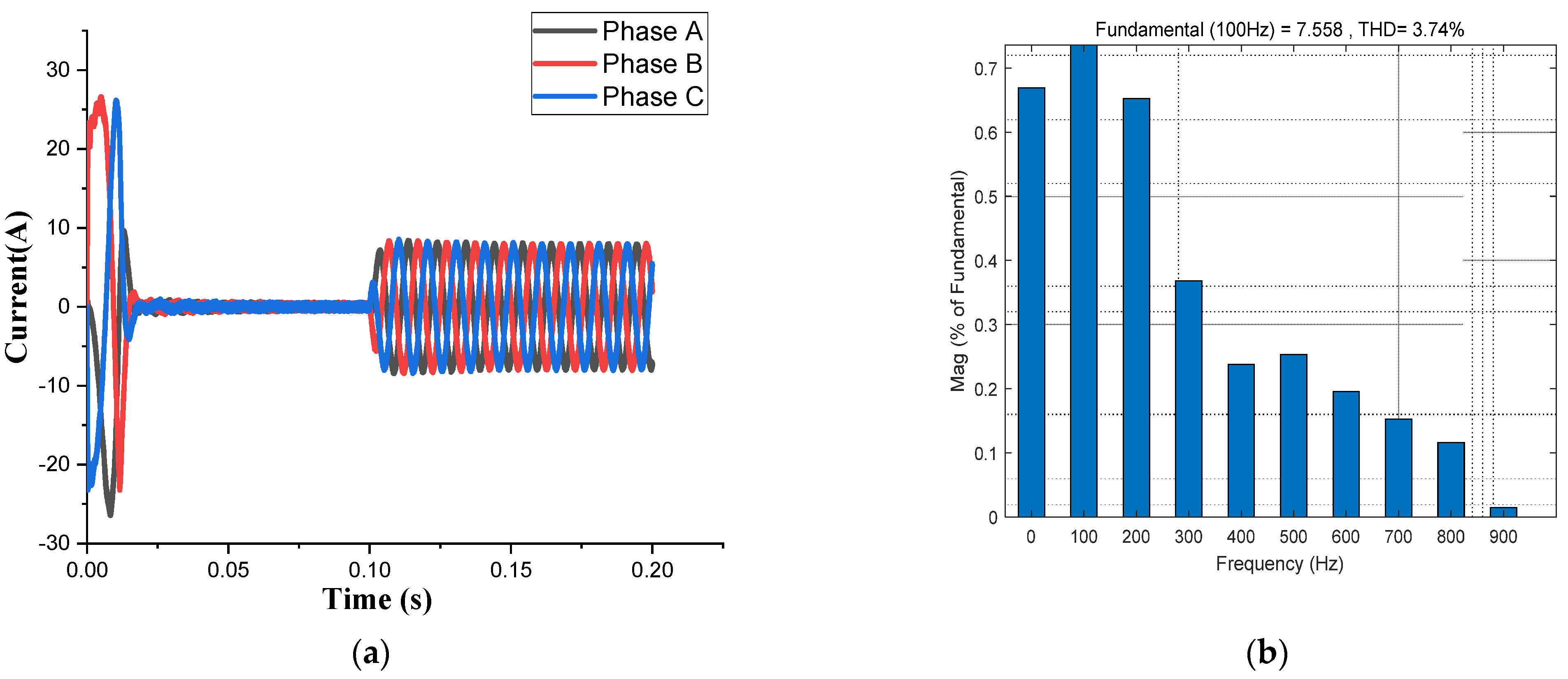
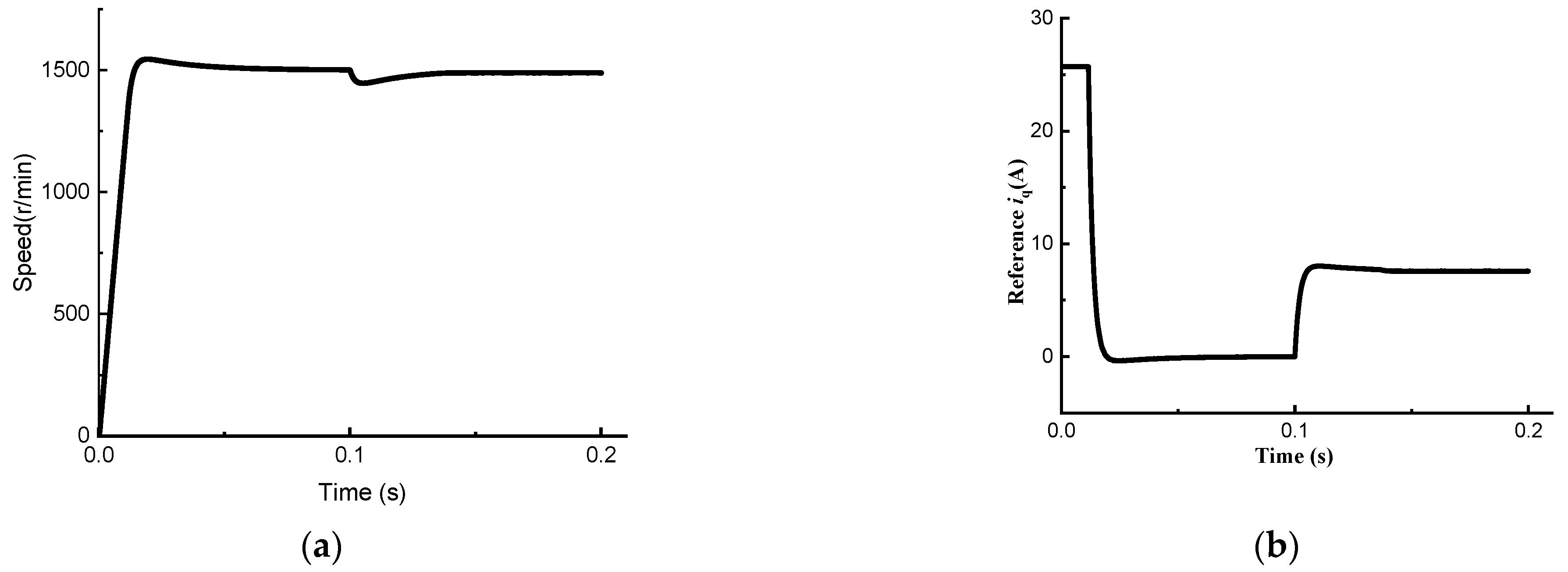
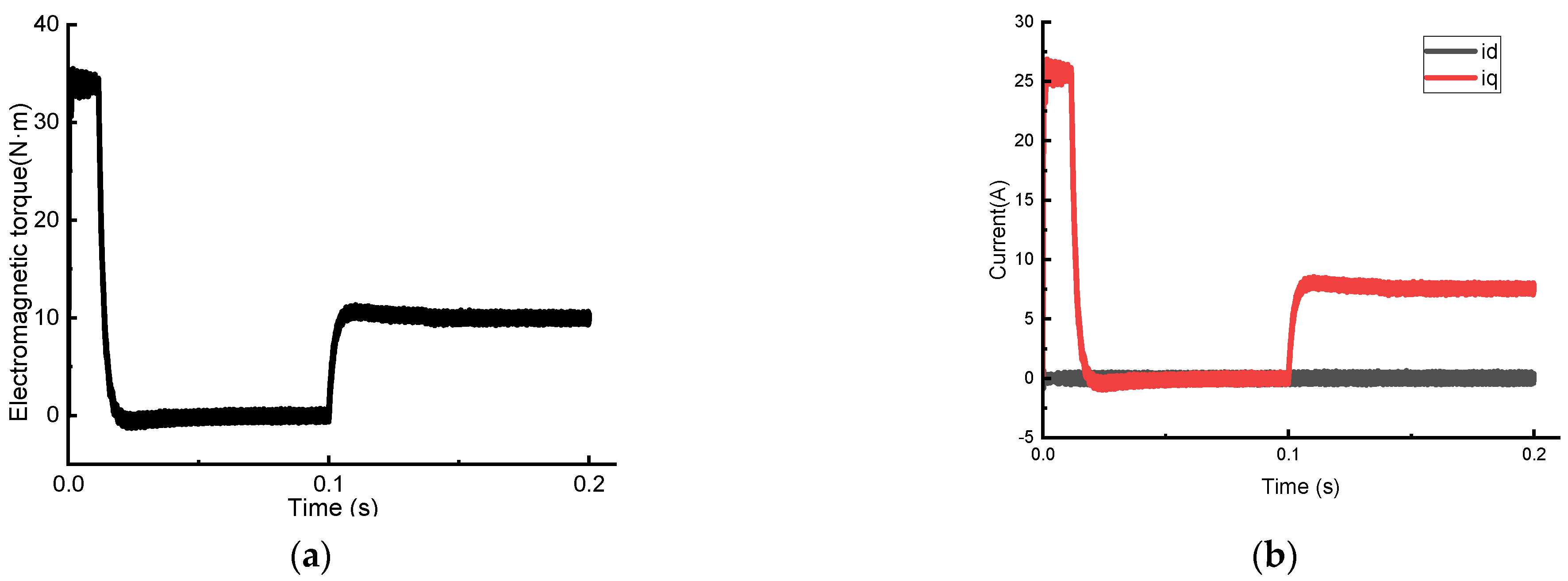
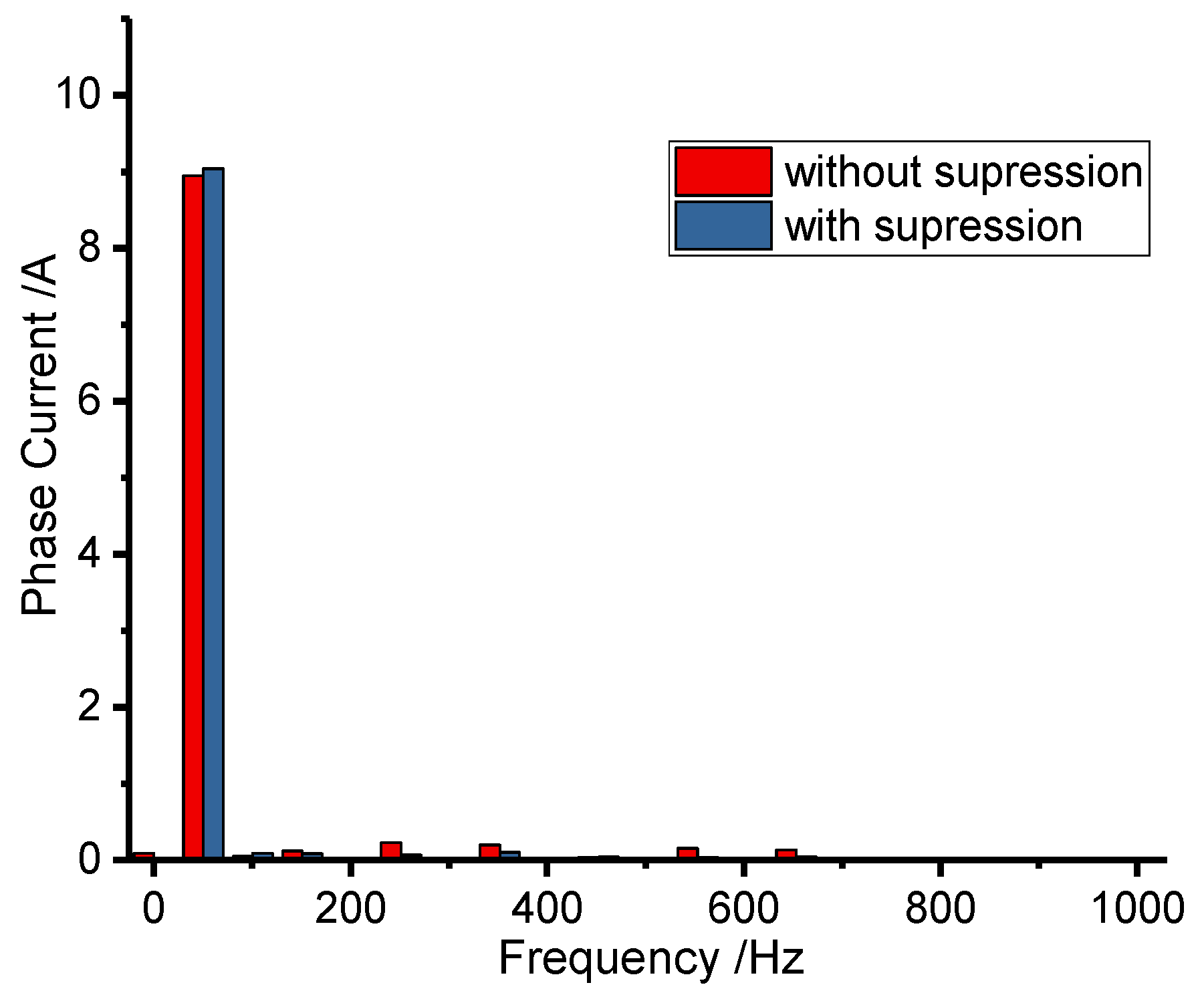

| Speed (rpm) | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 2500 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fundamental current (A) | without | 8.95 | 9.24 | 9.62 | 9.69 |
| with | 9.04 | 9.35 | 9.68 | 9.77 | |
| Fifth harmonic (A) | without | 0.095 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.229 |
| with | 0.043 | 0.046 | 0.03 | 0.068 | |
| Seventh harmonic (A) | without | 0.09 | 0.072 | 0.118 | 0.199 |
| with | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.085 | 0.101 |
| Speed (rpm) | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 2500 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 Hz | Without (g) | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.019 | 0.021 |
| With (g) | 0.009 | 0.01 | 0.012 | 0.014 | |
| 500 Hz | Without (g) | 0.0127 | 0.0142 | 0.0182 | 0.022 |
| With (g) | 0.0106 | 0.012 | 0.0133 | 0.016 | |
| 700 Hz | Without (g) | 0.0186 | 0.0211 | 0.032 | 0.041 |
| With (g) | 0.0155 | 0.0177 | 0.021 | 0.029 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, C.; Xu, W.; Liu, M.; Hong, J. Low Vibration Control Scheme for Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Resonance Controllers. Energies 2024, 17, 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184666
Ma C, Xu W, Liu M, Hong J. Low Vibration Control Scheme for Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Resonance Controllers. Energies. 2024; 17(18):4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184666
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Chi, Wenzhong Xu, Mingtian Liu, and Jianfeng Hong. 2024. "Low Vibration Control Scheme for Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Resonance Controllers" Energies 17, no. 18: 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184666
APA StyleMa, C., Xu, W., Liu, M., & Hong, J. (2024). Low Vibration Control Scheme for Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Resonance Controllers. Energies, 17(18), 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17184666







