DAB-Based Bidirectional Wireless Power Transfer System with LCC-S Compensation Network under Grid-Connected Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
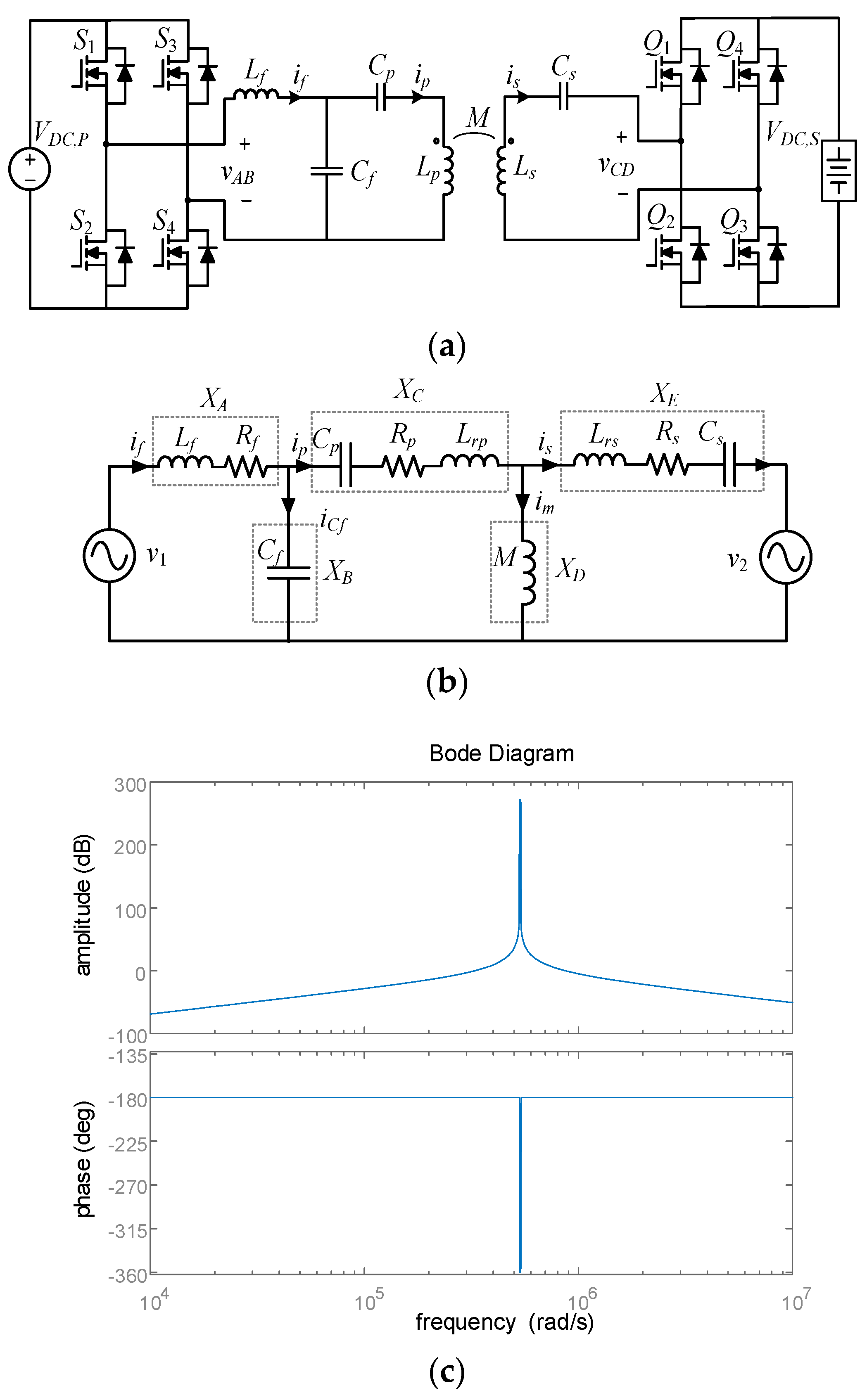
2. Operation Principles of the Proposed BDWPT System
2.1. Proposed System and Its Mathematical Model
2.2. Power Transmission Characteristics
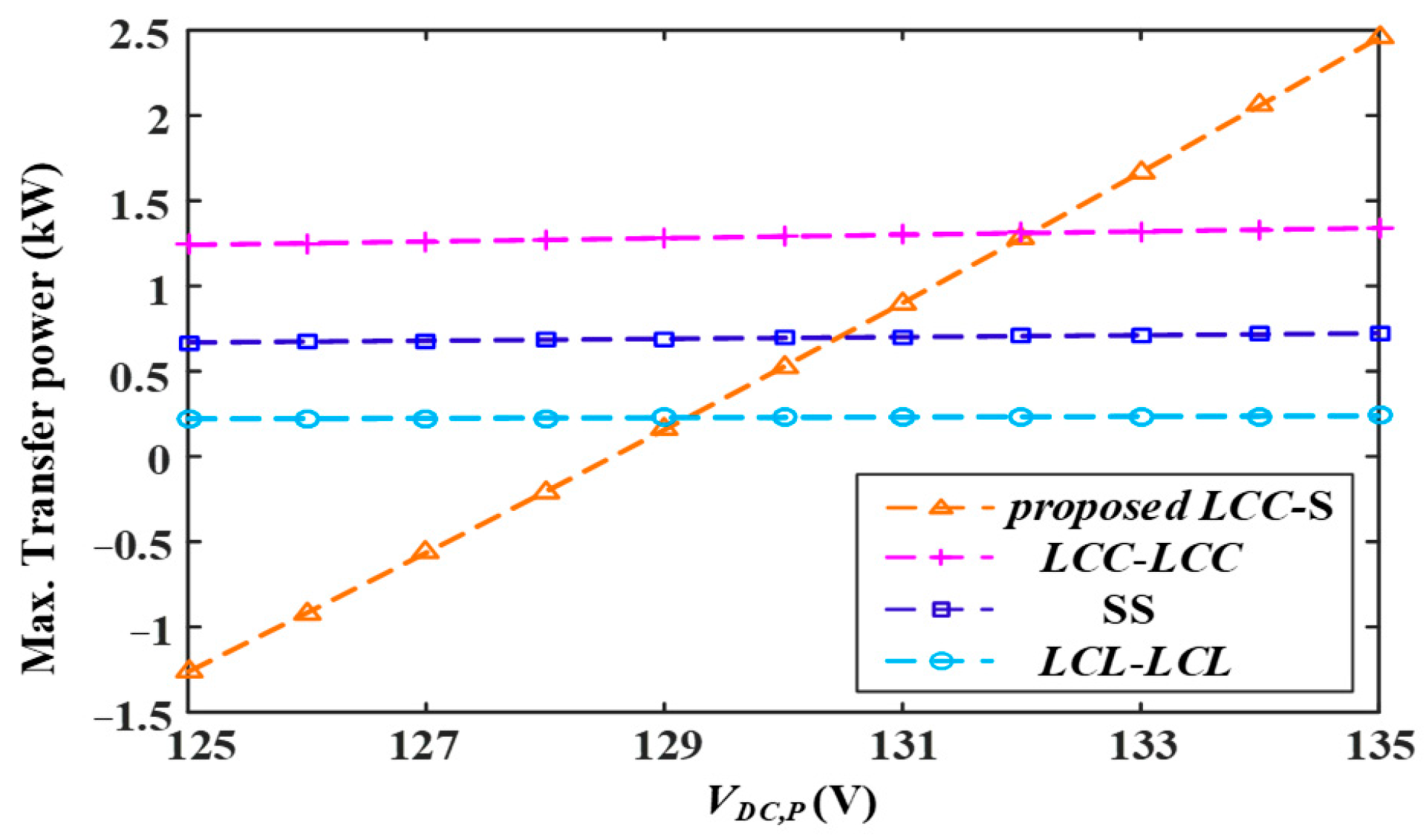
3. Performance Comparison with CC-BDWPT Systems
3.1. Better Regulation Capability of Transfer Power
3.2. Reduced Switching Losses with PSM
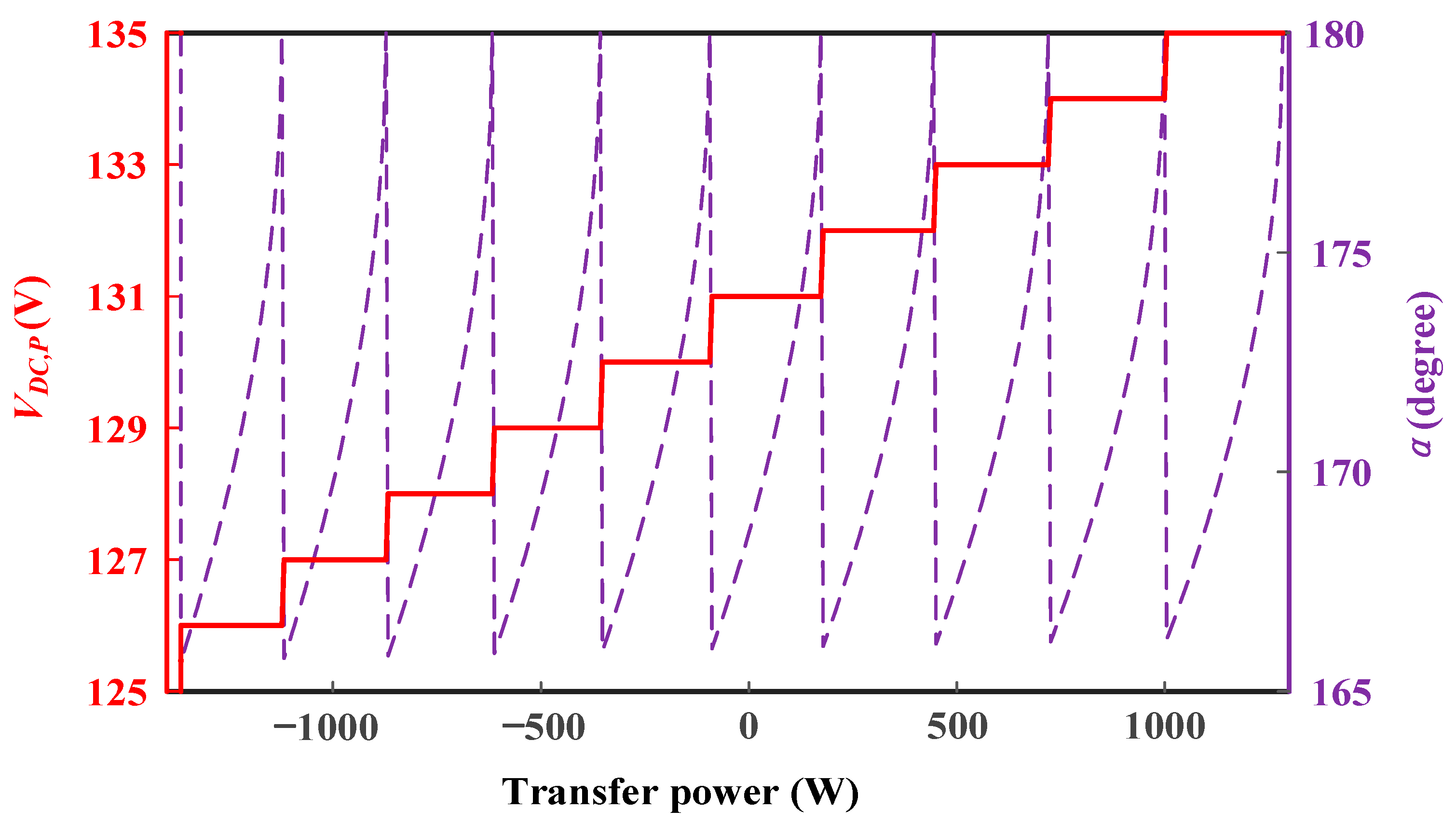
4. Hybrid Control Strategy for Proposed System
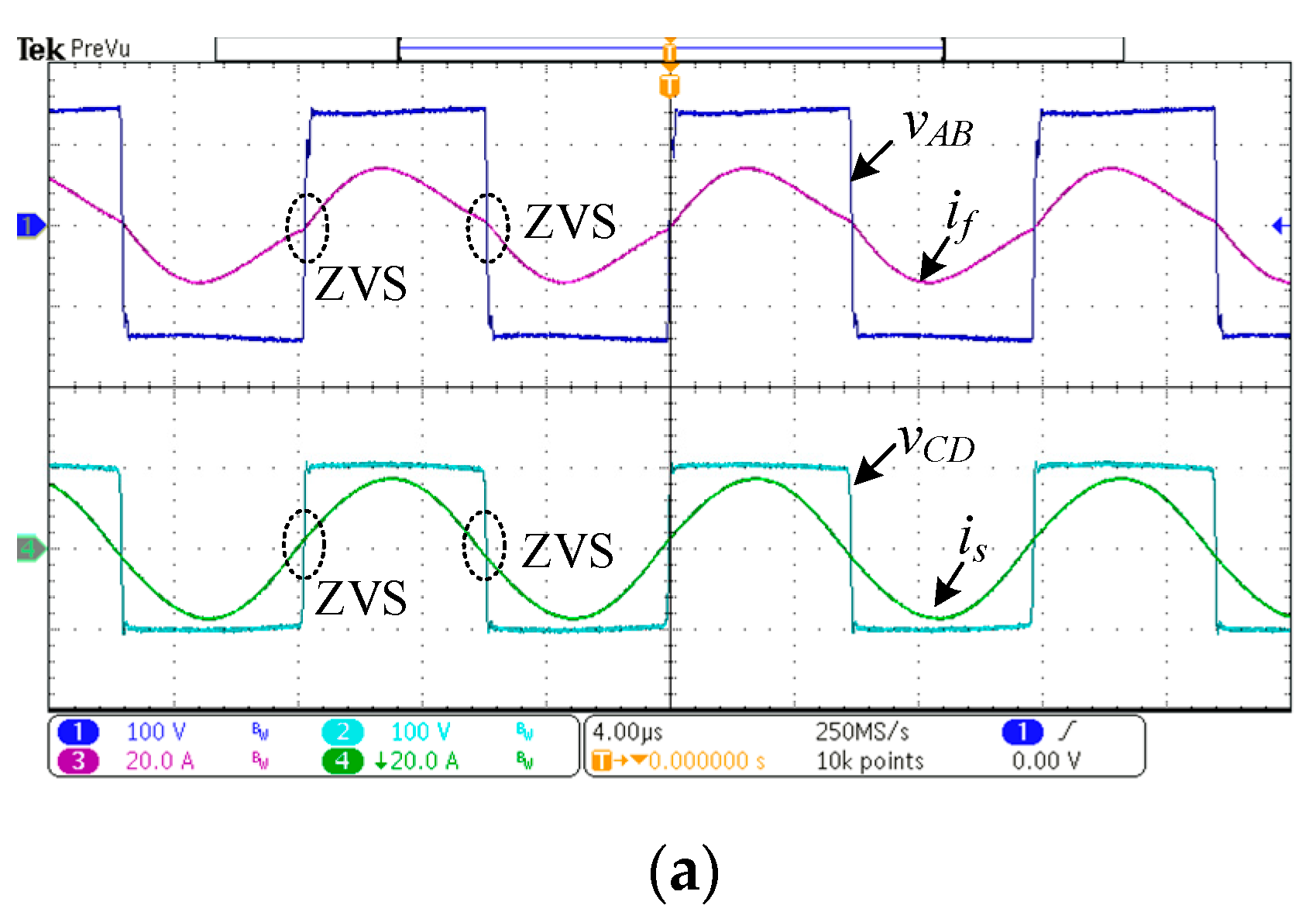
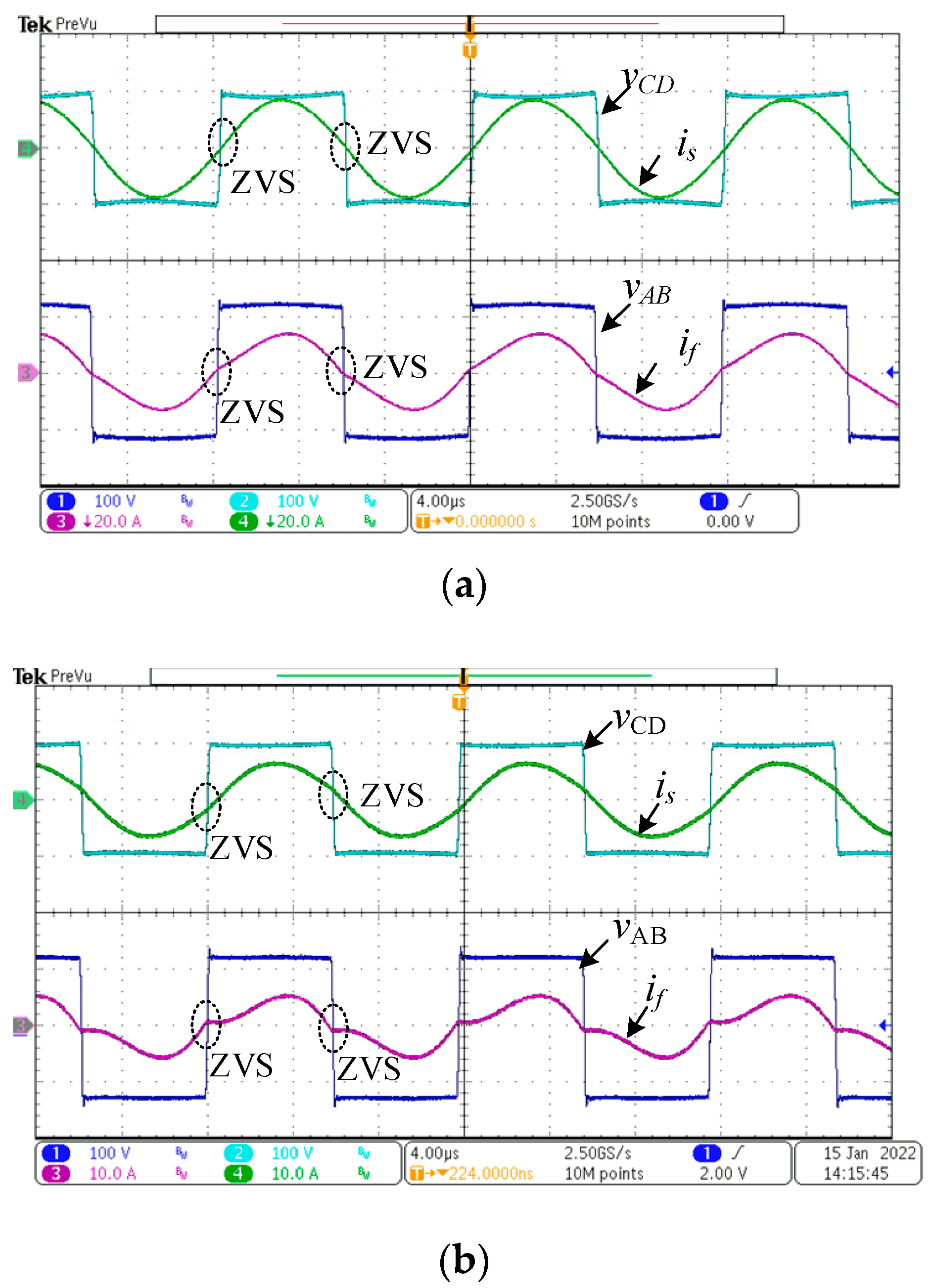
5. Experimental Verification
6. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Gu, C.; Li, C. Non-contact hand interaction with smart phones using the wireless power transfer features. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), San Diego, CA, USA, 25–28 January 2015; pp. 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Kim, H.; Penugonda, S.; Fan, J. Analysis and Modeling of the Common-Mode Conducted EMI From a Wireless Power Transfer System for Mobile Applications. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2021, 63, 2143–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wong, S.C.; Tse, C.K.; Ruan, X. Analysis, Design, and Control of a Transcutaneous Power Regulator for Artificial Hearts. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2009, 3, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci, N.; Kwan, C.H.; Yates, D.C.; Arnold, A.D.; Keene, D.; Whinnett, Z.I.; Mitcheson, P.D. Effect of Fields Generated through Wireless Power Transfer on Implantable Biomedical Devices. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE PELS Workshop on Emerging Technologies: Wireless Power Transfer (WoW), London, UK, 18–21 June 2019; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Lei, Y.; Song, K.; Zhu, C. Design and Loss Analysis of Loosely Coupled Transformer for an Underwater High-Power Inductive Power Transfer System. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, I.F.; Lacerda Valle, R.; Azevedo Fogli, G.; Ferreira, A.A.; Gomes Barbosa, P. Low-Frequency Underwater Wireless Power Transfer: Maximum Efficiency Tracking Strategy. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2020, 18, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wong, S.; Tse, C.K. Design of a Single-Stage Inductive-Power-Transfer Converter for Efficient EV Battery Charging. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 5808–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.-B.; Tran, D.-H.; Choi, W. Implementation of the Constant Current and Constant Voltage Charge of Inductive Power Transfer Systems with the Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topology for Electric Vehicle Battery Charge Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 33, 7398–7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhu, G.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Jiang, J.; Mi, C.C. Sensitivity Analysis of Inductive Power Transfer Systems with Voltage-Fed Compensation Topologies. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 4502–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, D.-H. A Switching Hybrid LCC-S Compensation Topology for Constant Current/Voltage EV Wireless Charging. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 133924–133935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhu, G.; Lin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Mi, C.C. Realizing Constant Current and Constant Voltage Outputs and Input Zero Phase Angle of Wireless Power Transfer Systems with Minimum Component Counts. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Li, G.; Lu, J.; Pan, X. Parameter Identification Method with Dynamic Impedance Modulation for the DWPT System. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 6332–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, H.-L.; Wu, J.-C.; Wu, K.-D.; Kuo, C.-Y. Bidirectional DC–DC Wireless Power Transfer Based on LCC-C Resonant Compensation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 2310–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.; Onar, O.C.; Su, G.J.; Pries, J.; Galigekere, V.P.; Anwar, S.; Asa, E.; Wilkins, J.; Wiles, R.; White, C.P.; et al. Bidirectional LCC–LCC-Compensated 20-kW Wireless Power Transfer System for Medium-Duty Vehicle Charging. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Madawala, U.K.; Mai, R.; He, Z. Zero-Phase-Angle Controlled Bidirectional Wireless EV Charging Systems for Large Coil Misalignments. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 5343–5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fang, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y. A Joint Control with Variable ZVS Angles for Dynamic Efficiency Optimization in Wireless Power Transfer System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 11064–11081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madawala, U.K.; Thrimawithana, D.J. A Bidirectional Inductive Power Interface for Electric Vehicles in V2G Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4789–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Madawala, U.K.; Thrimawithana, D.J.; Ma, H. A New Controller for Bidirectional Wireless Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 9076–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, T.; Duan, S.; Feng, H.; Hu, H.; Niu, J.; Chen, C. A Control Strategy for Efficiency Optimization and Wide ZVS Operation Range in Bidirectional Inductive Power Transfer System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 5958–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenil, V.; Cetin, S. Load Independent Constant Current and Constant Voltage Control of LCC-Series Compensated Wireless EV Charger. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 8701–8712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Deng, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. A Control Strategy for ZVS Realization in LCC-S Compensated WPT System with Semi Bridgeless Active Rectifier for Wireless EV Charging. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Vancouver, CA, USA, 10–14 October 2021; pp. 5823–5827. [Google Scholar]
- Ann, S.; Lee, B.K. Analysis of Impedance Tuning Control and Synchronous Switching Technique for a Semibridgeless Active Rectifier in Inductive Power Transfer Systems for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 8786–8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann; Son, W.-J.; Byun, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, B.K. Switch Design for a High-Speed Switching Semi—Bridgeless Active Rectifier of Inductive Power Transfer Systems Considering Reverse Recovery Phenomenon. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th International Conference on Power Electronics and ECCE Asia (ICPE 2019—ECCE Asia), Busan Exhibition & Convention Center, Busan, Republic of Korea, 27–30 May 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lawder, M.T.; Suthar, B.; Northrop, P.W.; De, S.; Hoff, C.M.; Leitermann, O.; Crow, M.L.; Santhanagopalan, S.; Subramanian, V.R. Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) and Battery Management System (BMS) for Grid-Scale Applications. Proc. IEEE 2014, 102, 1014–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiolas; Stecca, M.; Ramirez-Elizondo, L.M.; Soeiro, T.B.; Bauer, P. Optimal Battery Energy Storage Dispatch in Energy and Frequency Regulation Markets While Peak Shaving an EV Fast Charging Station. IEEE Open Access J. Power Energy 2022, 9, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Lee, F.C.; Zhang, A.J.; Huang, G. LLC resonant converter for front end DC/DC conversion. In Proceedings of the APEC. Seventeenth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (Cat. No. 02CH37335), Dallas, TX, USA, 10–14 March 2002; pp. 1108–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Ryu, M.-H.; Baek, J.-W. Design Methodology of Bidirectional CLLC Resonant Converter for High-Frequency Isolation of DC Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, C. A Reconfigurable Bidirectional Isolated LLC Resonant Converter for Ultra-Wide Voltage-Gain Range Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 5713–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Symbol | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Lp | primary-side coil inductance | 121.34 μH |
| Ls | secondary-side coil inductance | 121.56 μH |
| Lf | compensation inductance | 36.175 μH |
| M | mutual inductance | 29.0 μH |
| k | coupling coefficient | 0.24 |
| Cp | series compensation capacitor | 29.34 nF |
| Cs | series compensation capacitor | 41.71 nF |
| Cf | compensation capacitor | 95.94 nF |
| Rp | parasitic resistance of Cp | 0.179 Ω |
| Rf | parasitic resistance of Cf | 0.049 Ω |
| Rs | parasitic resistance of Cs | 0.182 Ω |
| Structures | Mathematical Expression of Transfer Power | Max Powerin Theory |
|---|---|---|
| SS | ||
| LCL-LCL | ||
| LCC-LCC | ||
| proposed S-LCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Cai, Z.; Feng, C.; Sun, Z.; Pan, X. DAB-Based Bidirectional Wireless Power Transfer System with LCC-S Compensation Network under Grid-Connected Application. Energies 2024, 17, 4519. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174519
Li G, Cai Z, Feng C, Sun Z, Pan X. DAB-Based Bidirectional Wireless Power Transfer System with LCC-S Compensation Network under Grid-Connected Application. Energies. 2024; 17(17):4519. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174519
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guocun, Zhouchi Cai, Chen Feng, Zeyu Sun, and Xuewei Pan. 2024. "DAB-Based Bidirectional Wireless Power Transfer System with LCC-S Compensation Network under Grid-Connected Application" Energies 17, no. 17: 4519. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174519
APA StyleLi, G., Cai, Z., Feng, C., Sun, Z., & Pan, X. (2024). DAB-Based Bidirectional Wireless Power Transfer System with LCC-S Compensation Network under Grid-Connected Application. Energies, 17(17), 4519. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174519






