A Hybrid Forecasting Model for Electricity Demand in Sustainable Power Systems Based on Support Vector Machine
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Contributions
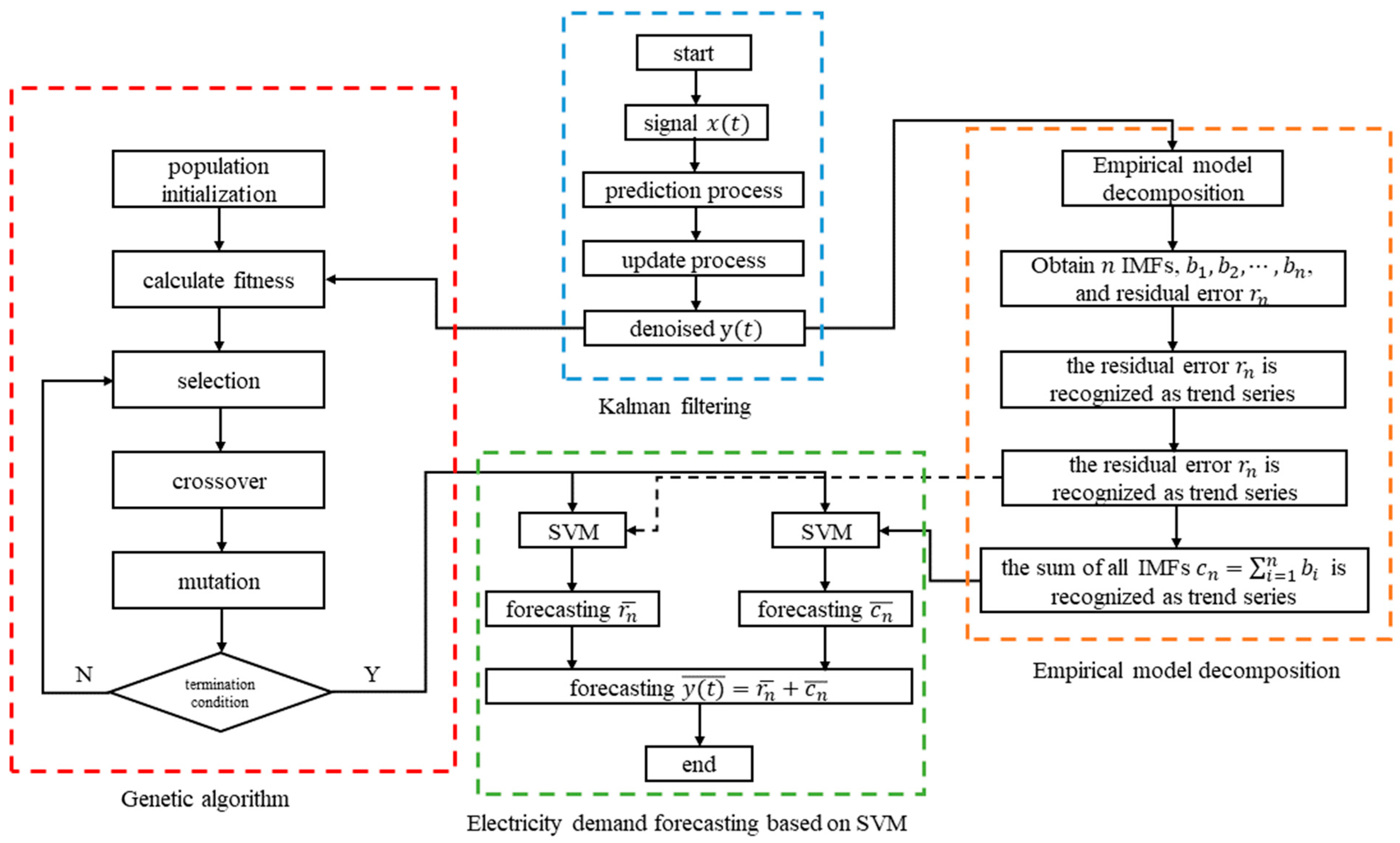
- Utilize Kalman filtering to remove noise signals from the electricity demand series.
- Develop a prediction model using the denoised electricity demand series.
- Utilize EMD to extract sub-trend series, which are residuals from the denoised electricity demand series.
- Finally, model and predict the sub-trend series of the denoised electricity demand series separately using the SVM.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Support Vector Machine
2.2. Empirical Mode Decomposition
- (1)
- Form the maxima and minima envelopes by connecting the local maxima and local minima of original signal based on the two cubic spline lines;
- (2)
- Calculate the mean value series of maxima and minima envelopes;
- (3)
- Determine whether first satisfies the two conditions of IMF;
- (4)
- If it does, will be the first IMF and the second IMF will be found using the residue signal as a new ;
- (5)
- If it doesn’t, repeat steps (1) to (2) until the is less than 0.2~0.3; then the will the first IMF, and step (4) will be repeated to discover the next IM. The screening threshold is given as follows:
2.3. Kalman Filter
3. Proposed Forecasting Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Problem Description
4.2. Statistics Measures of Forecasting Performance
4.3. The Electricity Demand Forecasting
5. Conclusions and Future Work
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dluhopolskyi, O.; Kozlovskyi, S.; Popovskyi, Y.; Lutkovska, S.; Butenko, V.; Popovskyi, T.; Mazur, H.; Kozlovskyi, A. Formation of the model of sustainable economic development of renewable energy. ECONOMICS-Innov. Econ. Res. J. 2023, 11, 51–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahabuddin, M.; Khan, I. Analysis of demand, generation, and emission for long-term sustainable power system planning using LEAP: The case of Bangladesh. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2023, 15, 035503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, J.; Xiao, X.; Goh, M. Energy demand forecasting in China: A support vector regression-compositional data second exponential smoothing model. Energy 2023, 263, 125955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Salehpour, S.Y.; Shahbaazy, F.; Behzadpoor, S.; Pirouzi, S.; Jafarpour, S. Participation of energy storage-based flexible hubs in day-ahead reserve regulation and energy markets based on a coordinated energy management strategy. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2022, 2022, 6481531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Ye, X.; Pirouzi, S. Economic energy managementof networked flexi-renewable energy hubs according to uncertainty modeling by the unscented transformation method. Energy 2023, 278, 128054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Xu, C.; Yang, F.; Ling, F.; Pirouzi, S. Market clearing price-based energy management of grid-connected renewable energy hubs including flexible sources according to thermal, hydrogen, and compressed air storage systems. J. Energy Storage 2023, 69, 107981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirouzi, S. Transmission and Distribution, Network-constrained unit commitment-based virtual power plant model in the day-ahead market according to energy management strategy. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2023, 17, 4958–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalafian, F.; Iliaee, N.; Diakina, E.; Parsa, P.; Alhaider, M.M.; Masali, M.H.; Pirouzi, S.; Zhu, M. Capabilities of compressed air energy storage in the economic design of renewable off-grid system to supply electricity and heat costumers and smart charging-based electric vehicles. J. Energy Storage 2024, 78, 109888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Pirouzi, S. Energy management system based on economic Flexi-reliable operation for the smart distribution network including integrated energy system of hydrogen storage and renewable sources. Energy 2024, 293, 130745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, M.; Aghaei, J.; Niknam, T.; Pirouzi, S.; Lehtonen, M. Bi-level fuzzy stochastic-robust model for flexibility valorizing of renewable networked microgrids. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2022, 31, 100684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, M.; Aghaei, J.; Pirouzi, S.; Niknam, T.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M. Flexibility pricing of integrated unit of electric spring and EVs parking in microgrids. Energy 2022, 239, 122080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrizi, N.; LaTouf, S.K.; Tsiropoulou, E.E.; Papavassiliou, S. Prosumer-centric self-sustained smart grid systems. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 6042–6053. [Google Scholar]
- Gebremeskel, D.H.; Ahlgren, E.O.; Beyene, G.B. Long-term evolution of energy and electricity demand forecasting: The case of Ethiopia. Energy Strategy Rev. 2021, 36, 100671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippert, H.S.; Pedreira, C.E.; Souza, R.C. Neural networks for short-term load forecasting: A review and evaluation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2001, 16, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, W. Forecasting China′s natural gas consumption based on a combination model. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2010, 19, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J. A seasonal hybrid procedure for electricity demand forecasting in China. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3807–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-C. Energy demand forecasting using a novel remnant GM (1, 1) model. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 13903–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homod, R.Z.; Togun, H.; Abd, H.J.; Sahari, K.S. A novel hybrid modelling structure fabricated by using Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy to forecast HVAC systems energy demand in real-time for Basra city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 56, 102091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Kimmig, A.; Niu, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Ovtcharova, J. A flexible potential-flow model based high resolution spatiotemporal energy demand forecasting framework. Appl. Energy 2021, 299, 117321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Choi, Y.; Kim, C.S.; Miller, J.I.; Park, J.Y. Forecasting regional long-run energy demand: A functional coefficient panel approach. Energy Econ. 2021, 96, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, D.; Atak, M. Grey prediction with rolling mechanism for electricity demand forecasting of Turkey. Energy 2007, 32, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musaylh, M.S.; Deo, R.C.; Li, Y.; Adamowski, J.F. Two-phase particle swarm optimized-support vector regression hybrid model integrated with improved empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise for multiple-horizon electricity demand forecasting. Appl. Energy 2018, 217, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, J.; Toshniwal, D. Deep learning framework to forecast electricity demand. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Shang, D.; Zhao, E. Using multi-output feedforward neural network with empirical mode decomposition based signal filtering for electricity demand forecasting. Energy 2013, 49, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Ren, Y.; Suganthan, P.N.; Amaratunga, G.A. Empirical Mode Decomposition based ensemble deep learning for load demand time series forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 54, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Dong, Z.Y.; Jia, Y.; Hill, D.J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Short-term residential load forecasting based on LSTM recurrent neural network. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 10, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthika, S.; Margaret, V.; Balaraman, K. Hybrid short term load forecasting using ARIMA-SVM. In Proceedings of the Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies (i-PACT), Vellore, India, 21–22 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Barman, M.; Choudhury, N.B. A similarity based hybrid GWO-SVM method of power system load forecasting for regional special event days in anomalous load situations in Assam, India. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaouane, M.; Chennaif, M.; Zouggar, S.; Krajačić, G.; Duić, N.; Zahboune, H.; ElMiad, A.K. Using neural network modelling for estimation and forecasting of transport sector energy demand in developing countries. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 258, 115556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Rajasekar, E.; Natarajan, S.; McCullen, N. A comparative assessment of SARIMA, LSTM RNN and Fb Prophet models to forecast total and peak monthly energy demand for India. Energy Policy 2022, 168, 113097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemzadeh, M.-R.; Amjadian, A.; Amraee, T. A hybrid data mining driven algorithm for long term electric peak load and energy demand forecasting. Energy 2020, 204, 117948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağbulut, Ü. Forecasting of transportation-related energy demand and CO2 emissions in Turkey with different machine learning algorithms. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 29, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liao, S. Kernel selection with spectral perturbation stability of kernel matrix. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2014, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liao, S. Granularity selection for cross-validation of SVM. Inf. Sci. 2017, 378, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Tzeng, G.H.; Goo, Y.J.; Fang, W.C. A real-valued genetic algorithm to optimize the parameters of support vector machine for predicting bankruptcy. Expert Syst. Appl. 2007, 32, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, R.C.; Wen, X.; Qi, F. A wavelet-coupled support vector machine model for forecasting global incident solar radiation using limited meteorological dataset. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 568–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Bao, Y.; Hu, Z. Interval forecasting of electricity demand: A novel bivariate EMD-based support vector regression modeling framework. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 63, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Chao, F.; Yang, S.L.; Zhou, K.L. A review of the decomposition methodology for extracting and identifying the fluctuation characteristics in electricity demand forecasting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 75, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1971, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudraa, A.O.; Cexus, J.C. EMD-Based Signal Filtering. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 56, 2196–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.N.; Lee, C.M. Short-term load forecasting using SVR (support vector regression)-based radial basis function neural network with dual extended Kalman filter. Energy 2013, 49, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Tamura, Y.; Sato, S. Using the ensemble Kalman filter for electricity load forecasting and analysis. Energy 2016, 104, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blood, E.A.; Krogh, B.H.; Ilic, M.D. Electric power system static state estimation through Kalman filtering and load forecasting. In Proceedings of the Power and Energy Society General Meeting—Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 20–24 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bedi, J.; Toshniwal, D. Empirical mode decomposition based deep learning for electricity demand forecasting. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 49144–49156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calik, N.; Güneş, F.; Koziel, S.; Pietrenko-Dabrowska, A.; Belen, M.A.; Mahouti, P. Deep-learning-based precise characterization of microwave transistors using fully-automated regression surrogates. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.G.; Wu, J.; Hu, Z.H.; McLachlan, G.J. A new algorithm for support vector regression with automatic selection of hyperparameters. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 133, 108989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sub-Series | Input Variables | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | 156.17 | |
| IMF2 | 241.14 | |
| IMF3 | 328.84 | |
| IMF4 | 66.87 | |
| IMF5 | 12.73 | |
| IMF6 | 17.85 | |
| IMF7 | 11.09 | |
| IMF8 | 13.56 | |
| IMF9 | 74.98 | |
| IMF10 | 7.33 | |
| IMF11 | 23.06 | |
| IMF12 | 2.23 | |
| IMF13 | 1.54 | |
| IMF14 | 1.87 | |
| IMF15 | 2.01 | |
| Residue error | 0.16 | |
| Sum | / | 0.92 |
| Sub-Series | Input Variables | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|
| non-trend | 156.17 | |
| trend | 241.14 | |
| sum | / | 0.25 |
| Model | SVM | ESVM | FSVM | KESVM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAPE (%) | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.51 | 0.25 |
| RMSE | 121.86 | 104.59 | 60.26 | 30.33 |
| MAE | 58.54 | 54.04 | 30.41 | 15.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Jiang, M.; Cai, D.; Song, W.; Sun, Y. A Hybrid Forecasting Model for Electricity Demand in Sustainable Power Systems Based on Support Vector Machine. Energies 2024, 17, 4377. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174377
Li X, Jiang M, Cai D, Song W, Sun Y. A Hybrid Forecasting Model for Electricity Demand in Sustainable Power Systems Based on Support Vector Machine. Energies. 2024; 17(17):4377. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174377
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuejun, Minghua Jiang, Deyu Cai, Wenqin Song, and Yalu Sun. 2024. "A Hybrid Forecasting Model for Electricity Demand in Sustainable Power Systems Based on Support Vector Machine" Energies 17, no. 17: 4377. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174377
APA StyleLi, X., Jiang, M., Cai, D., Song, W., & Sun, Y. (2024). A Hybrid Forecasting Model for Electricity Demand in Sustainable Power Systems Based on Support Vector Machine. Energies, 17(17), 4377. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174377






