Integrated Optimal Energy Management of Multi-Microgrid Network Considering Energy Performance Index: Global Chance-Constrained Programming Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Contributions and Research Gaps
- Proposing the multi-microgrid network infrastructure to provide more flexibility for the distribution network. The interconnected MGs can receive/inject the power from/into the corresponding bus;
- Proposing the chance-constrained programming approach to guarantee the confidence level of the system’s operation with high reliability. A model identifies the uncertainty of wind, PV, as well as load demand. Unlike scenario generation-based methods, the CCP guarantees the safety performance of the whole system with a lower burden of calculations;
- Developing the demand response program in individual MG to smooth the load curve, besides improving the flexibility of MMG;
- Introducing a new index named “UPC” for individual MG yields a more efficient energy management strategy at the microgrid and distribution network levels.
1.4. Paper Organization
2. Multi-Microgrid Structure
3. Problem Formulation
3.1. Problem Constraints
- Diesel generator constraints
- Demand response modeling
- Battery storage constraints
- Network Constraints
- Wind power modeling
- PV power modeling
- UPC index
3.2. Chance-Constrained Programming
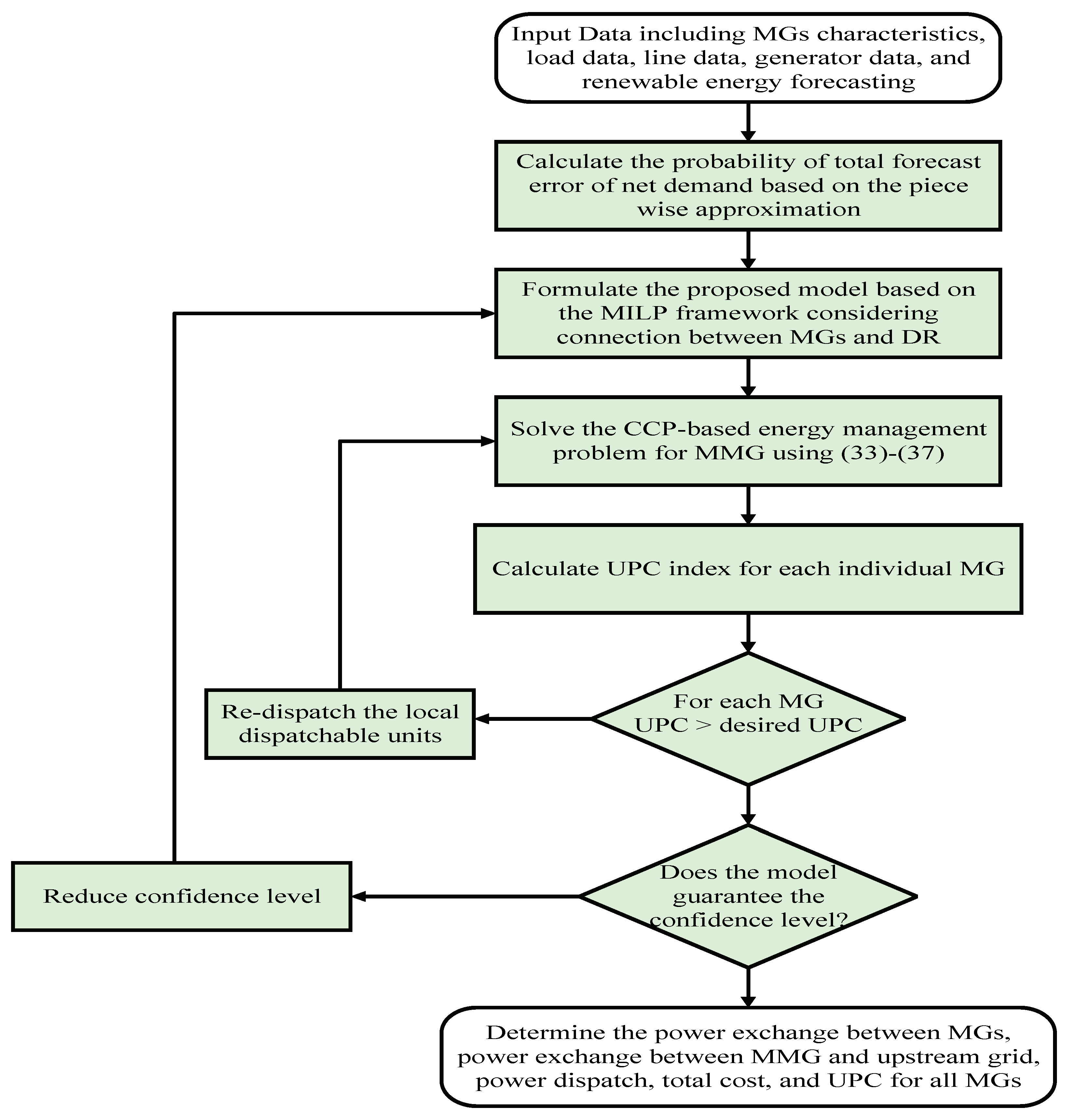
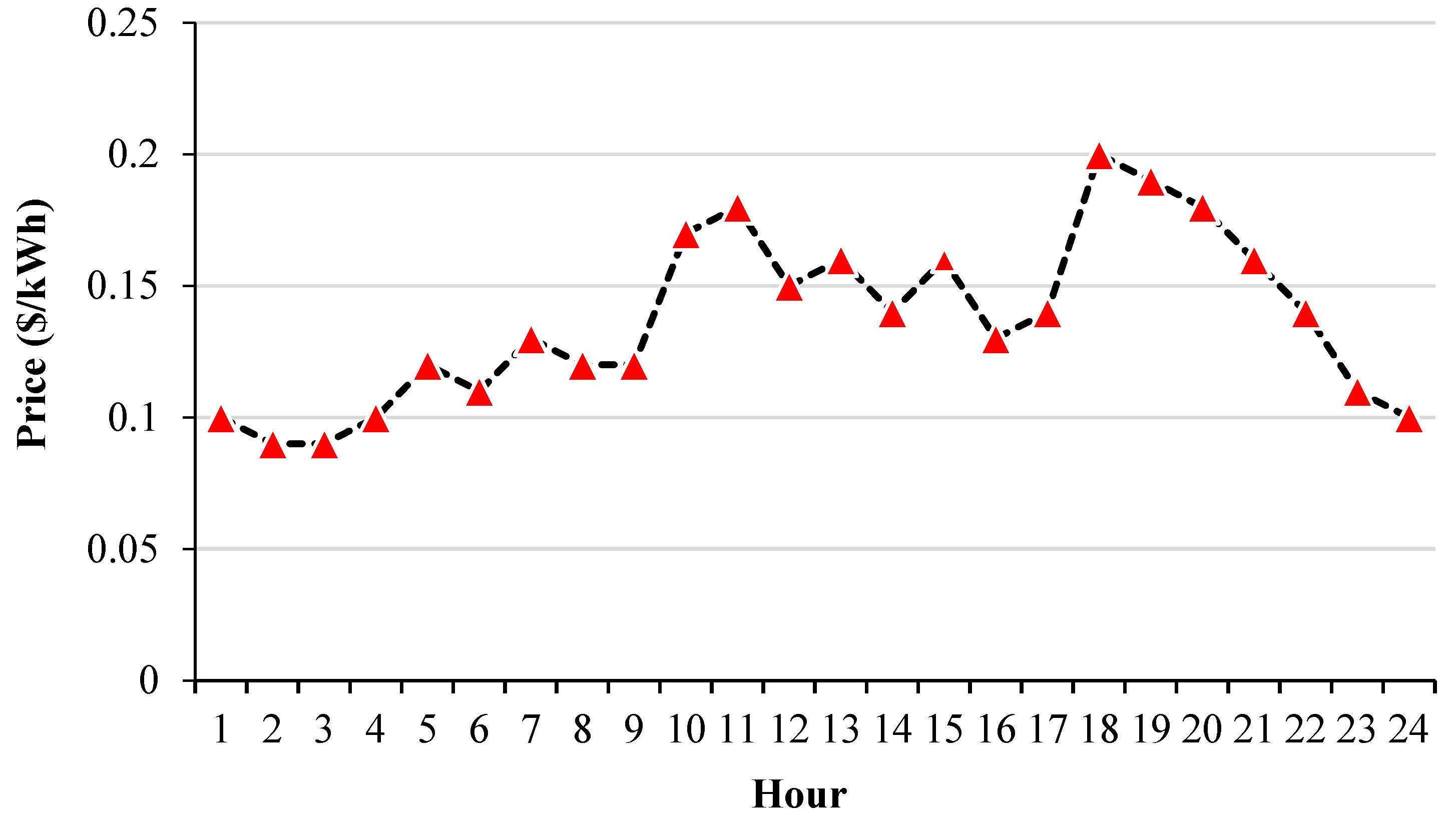
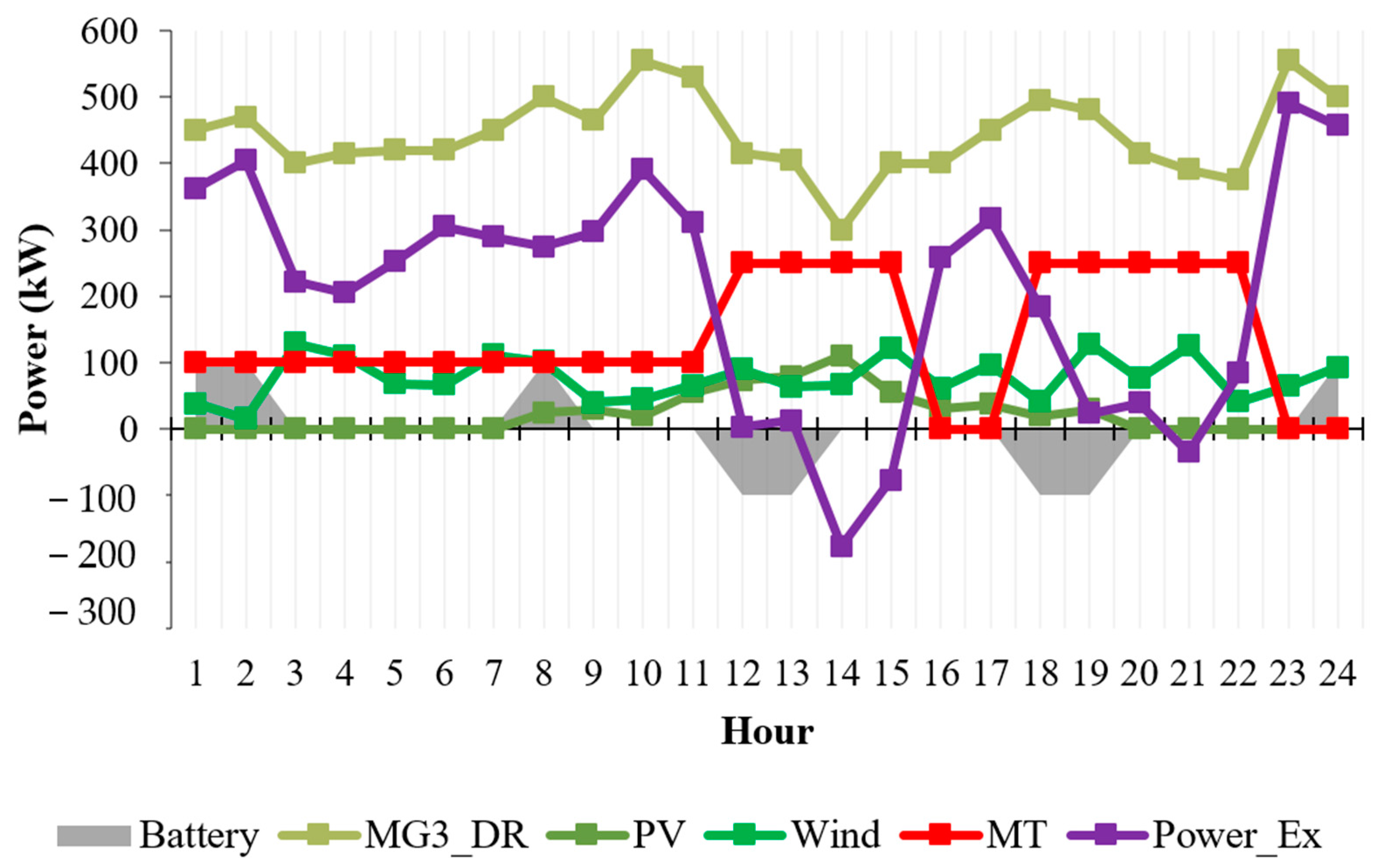
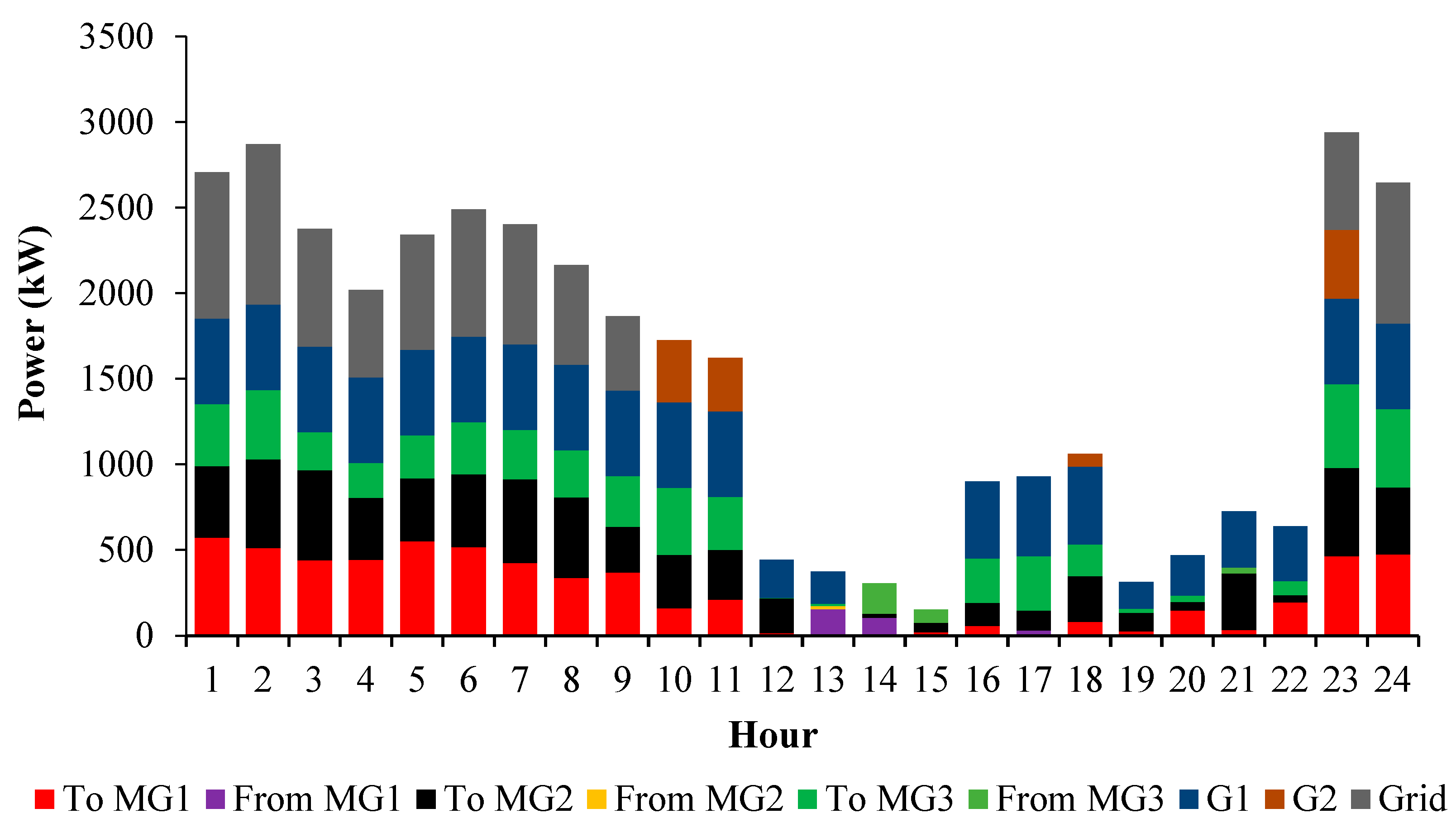
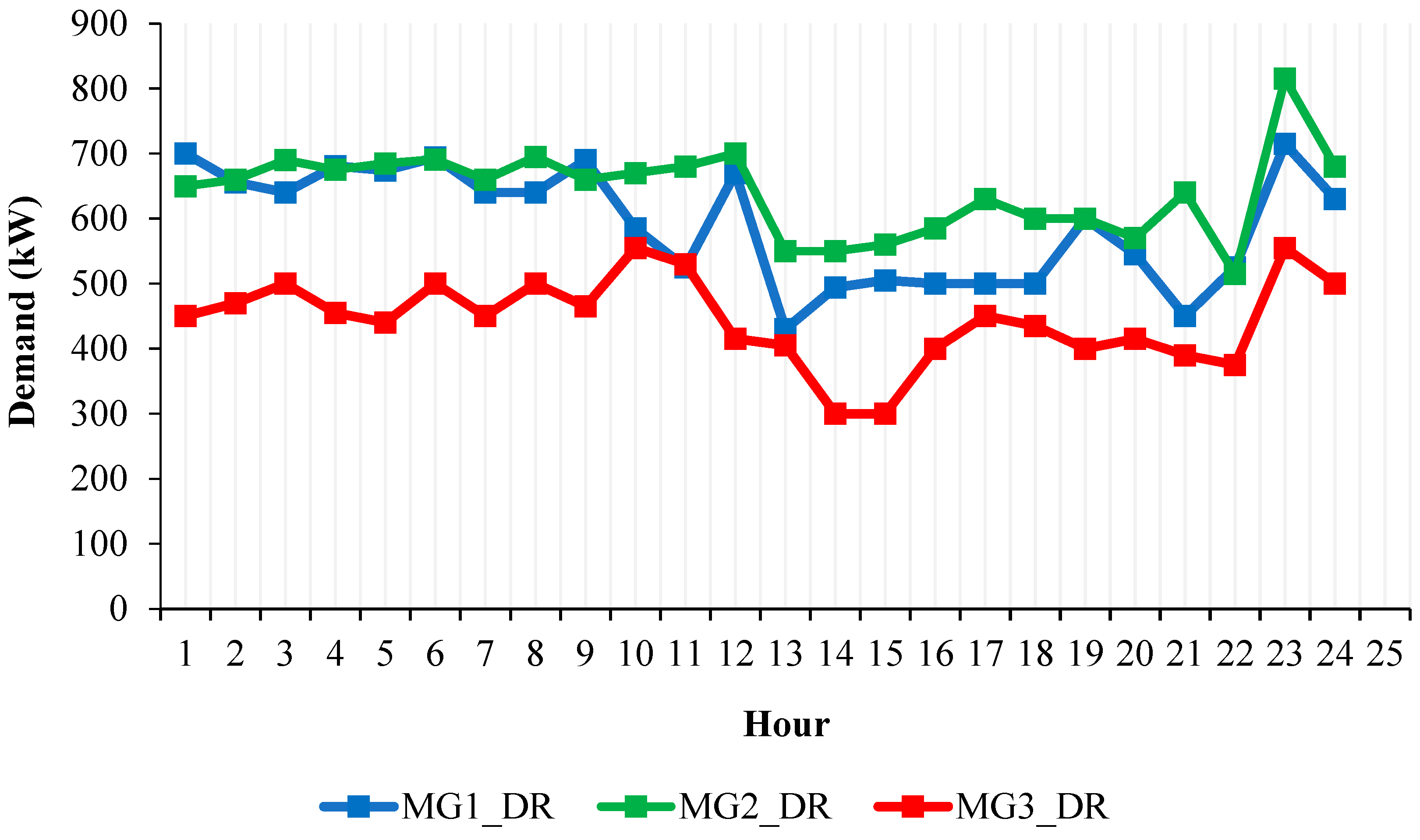
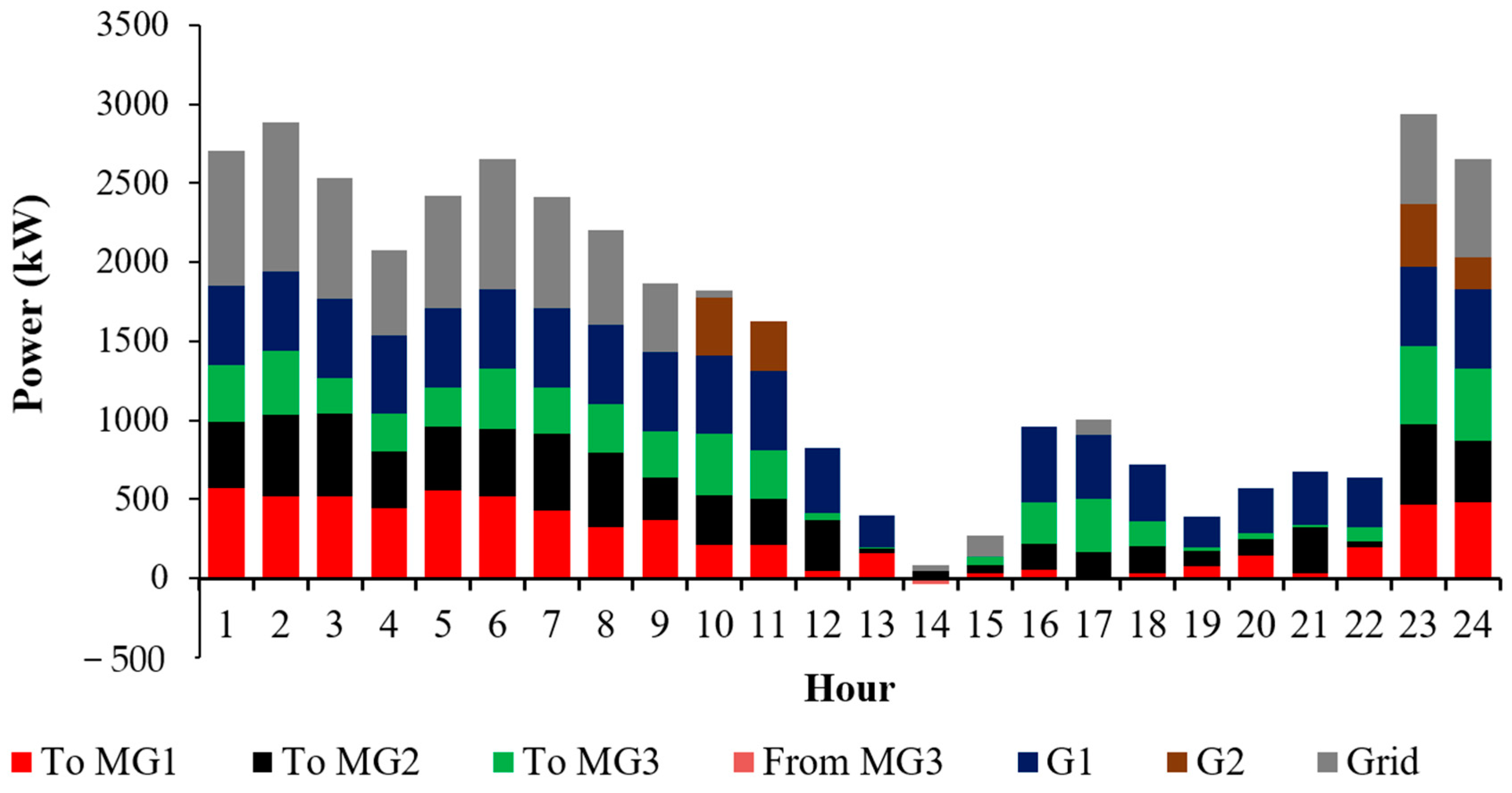
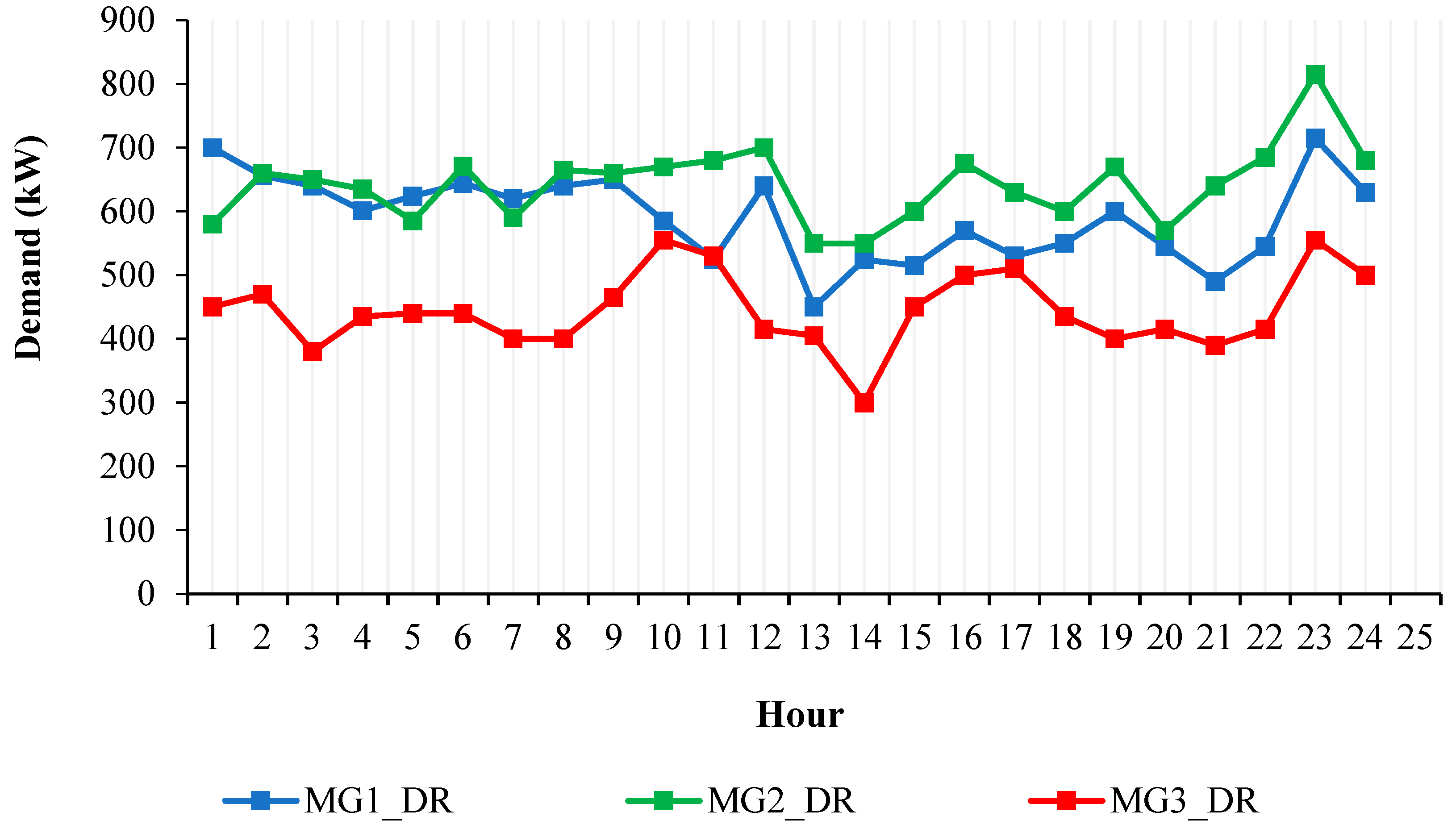
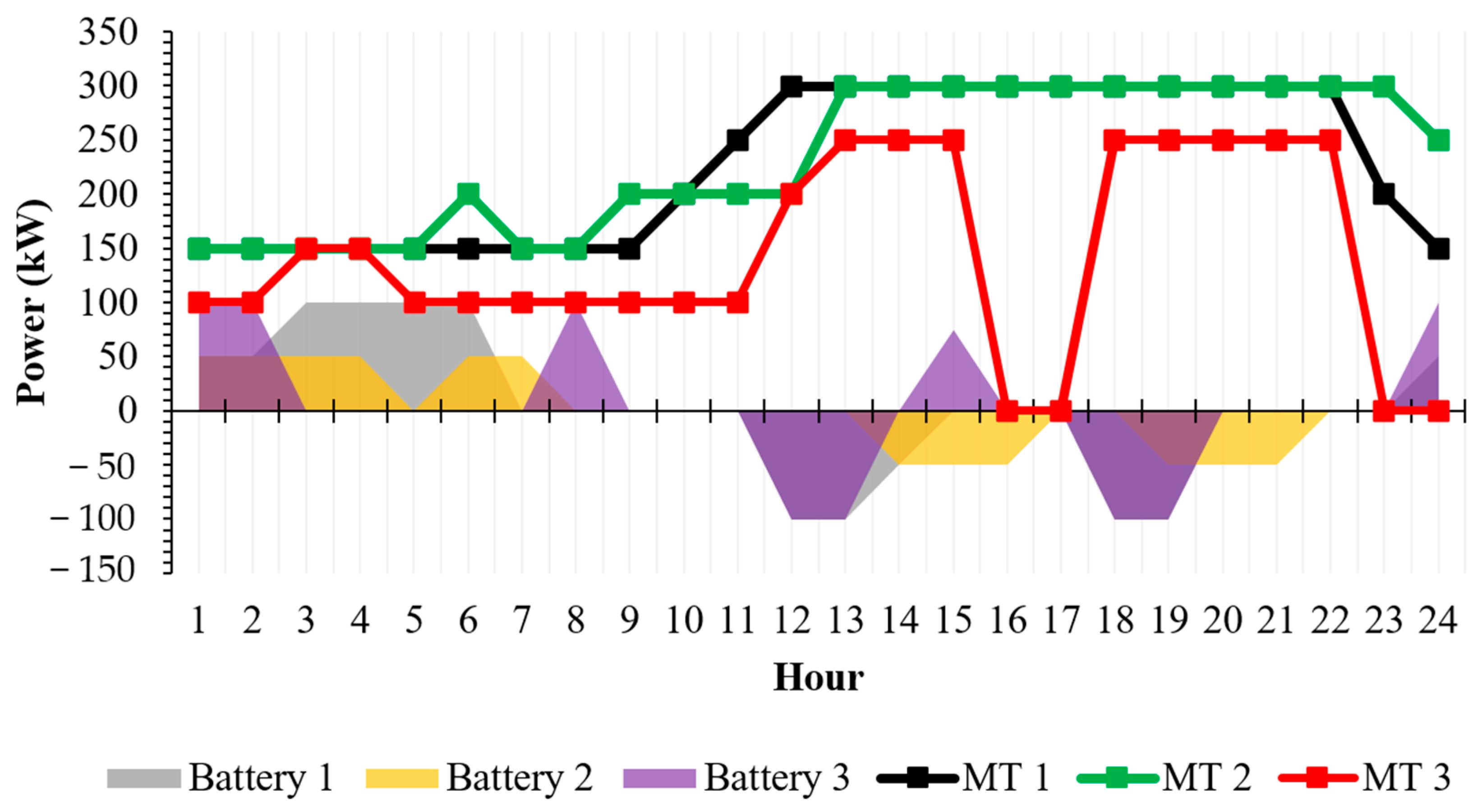
4. Simulation and Results
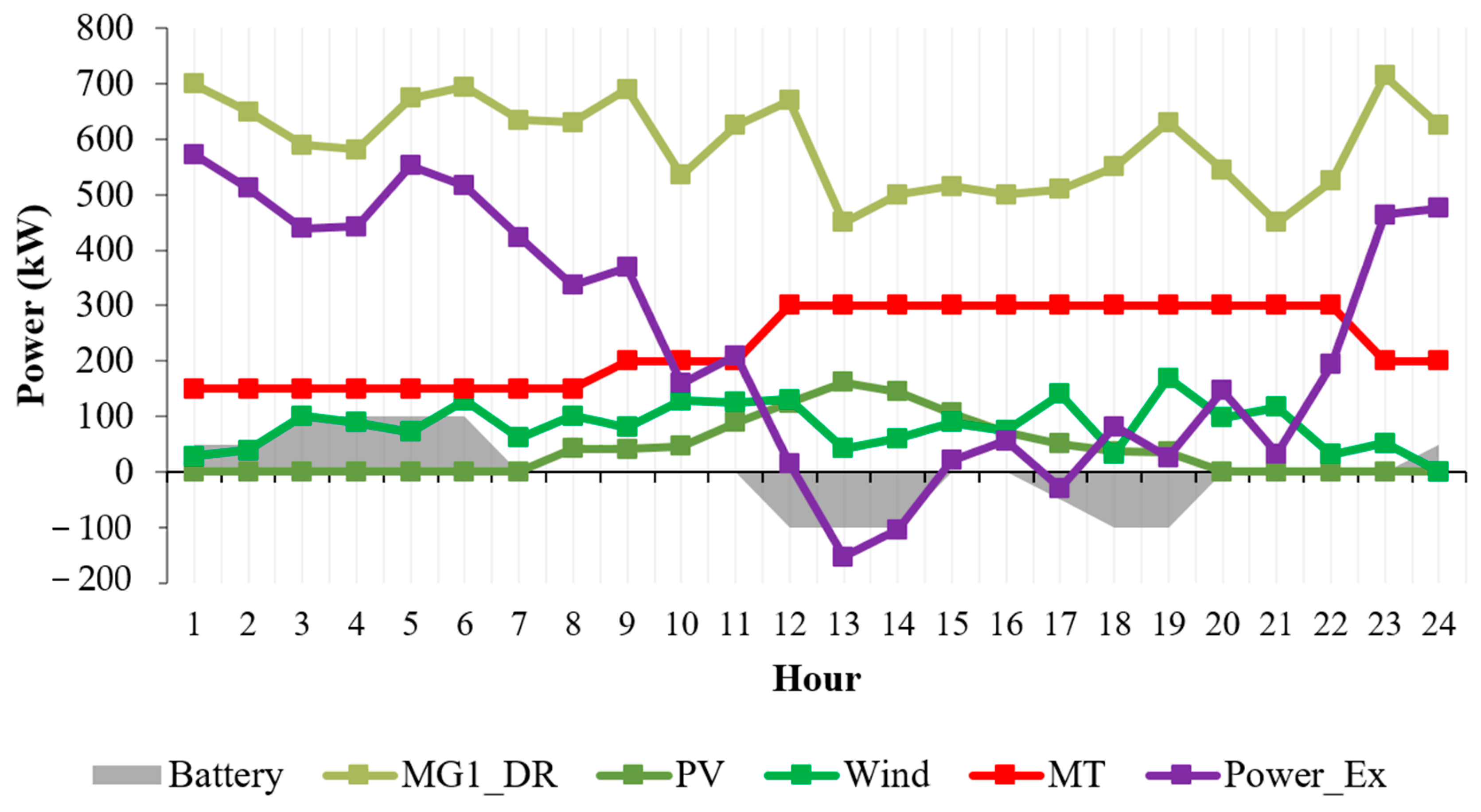
4.1. Case 1
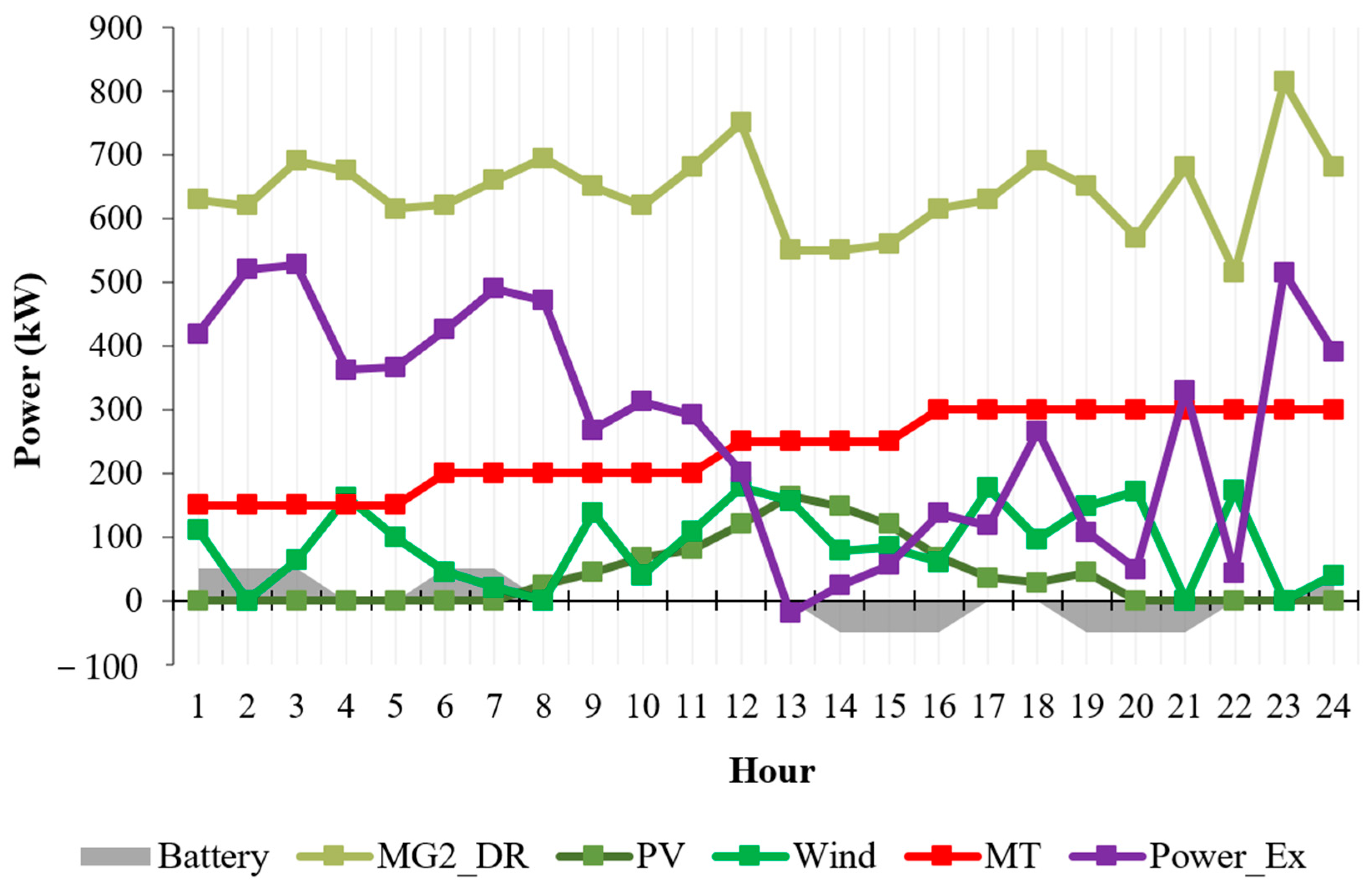
4.2. Case 2
4.3. Case 3
5. Conclusions
Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Index | |
| Index of time | |
| Index for microgrid | |
| Index for generator | |
| Index for line | |
| Index of minimum on/off time limits from 1 to | |
| Index for battery | |
| Index for load | |
| Bus nodes | |
| Index for wind turbine | |
| Parameter | |
| Number of time span | |
| Number of microgrids | |
| Set of buses | |
| Market price | |
| Objective function | |
| Minimum down time of generator | |
| Minimum up time of generator | |
| Ramp down of generator | |
| Ramp up of generator | |
| Load shedding cost | |
| Wind spillage cost | |
| PV spillage cost | |
| Susceptance of line | |
| PV panel efficiency | |
| Surface of PV panel | |
| Solar irradiation | |
| Air temperature | |
| Standard temperature | |
| Target UPC index | |
| Charging/discharging efficiency | |
| Time period (1 hour in this work) | |
| Minimum/maximum capacity of battery | |
| Maximum power flows in line | |
| Maximum power charged of battery | |
| Maximum power discharged of battery | |
| Min/max power output of generator | |
| Load factor for participating in DR | |
| Variable | |
| Power exchange with upstream grid | |
| Power output of generator in microgrid m | |
| Start-up cost | |
| Number of continuous times that the generator must be turned off | |
| Number of continuous times that the generator must be turned on | |
| Value of load participate in DR | |
| Load shedding value | |
| Value of wind spillage in microgrid m | |
| Value of PV power output in microgrid m | |
| , | Power discharging, charging of battery in microgrid m |
| Value of load demand in microgrid m | |
| Power output of wind turbine in microgrid m | |
| Value of demand response in microgrid m | |
| Power flow in line | |
| Magnitude of bus angel | |
| Binary variable for charging/discharging mode | |
| Energy capacity of battery in microgrid m | |
| Value of PV power spillage | |
| Unused power capacity in microgrid m | |
| Net load demand | |
| Binary variable for generator operation |
References
- Dahane, A.S.; Sharma, R.B. Hybrid AC-DC microgrid coordinated control strategies: A systematic review and future prospect. Renew. Energy Focus 2024, 49, 100553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Insight Partners. Microgrid Technology Market. Trends and Outlook for 2031. 2024. Available online: https://www.theinsightpartners.com/reports/microgrid-technology-market (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Wang, H.; Xing, H.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, W. Optimal scheduling of micro-energy grid with integrated demand response based on chance-constrained programming. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 144, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmethodzic, L.; Music, M. Comprehensive review of trends in microgrid control. Renew. Energy Focus 2021, 38, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.B.; e Silva, T.L.; Morais, L.B.; Bonatto, B.D.; Zambroni, A.C.; Guedes, P.A.; Ribeiro, P.F. Economic analysis of industrial energy storage systems in Brazil: A stochastic optimization approach. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 33, 100968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abisoye, B.O.; Sun, Y.; Zenghui, W. A survey of artificial intelligence methods for renewable energy forecasting: Methodologies and insights. Renew. Energy Focus 2023, 48, 100529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.; Arcos-Aviles, D.; Guinjoan, F. Simple fuzzy logic-based energy management for power exchange in isolated multi-microgrid systems: A case study in a remote community in the Amazon region of Ecuador. Appl. Energy 2024, 357, 122522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, M.; Liao, M.; Liu, F.; Xu, C. Risk assessment of renewable energy-based island microgrid using the HFLTS-cloud model method. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 284, 125362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzband, M.; Parhizi, N.; Adabi, J. Optimal energy management for stand-alone microgrids based on multi-period imperialist competition algorithm considering uncertainties: Experimental validation. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2016, 26, 1358–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaish, J.; Tiwari, A.K.; Siddiqui, K.M. Optimization of micro grid with distributed energy resources using physics based meta heuristic techniques. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Jirdehi, M.A.; Tabar, V.S.; Hemmati, R.; Siano, P. Multi objective stochasticmicrogrid scheduling incorporating dynamic voltage restorer. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2017, 93, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhorn, E.; Xie, L.; Butler-Purry, K. Multi-time scale coordination of dis-tributed energy resources in isolated power systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 8, 998–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Şengör, İ.; Erenoğlu, A.K.; Erdinç, O.; Taşcıkaraoğlu, A.; Catalão, J.P. Day-ahead charging operation of electric vehicles with on-site renewable energy resources in a mixed integer linear programming framework. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papari, B.; Edrington, C.S.; Bhattacharya, I.; Radman, G. Effective energymanagement of hybrid ac–dc microgrids with storage devices. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 10, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, Y.; Ni, C.; Wang, S.; Nimmegeers, P. Decentralized coordination between active distribution network and multi-microgrids through a fast decentralized adjustable robust operation framework. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 34, 101068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, C.; Deng, K.; Yu, X.; Huang, T. Data-driven charging strategy ofpevs under transformer aging risk. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2017, 26, 1386–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, A.; Mahdavinia, A.; Khaloie, H.; Mohammadnejad, M. Energy man-agement of a microgrid with emission limitations under uncertainty. In Proceedings of the CIRED 2018Ljubljana Workshop on Microgrids and Local Energy Communities, CIRED, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 7–8 June 2018; p. 0426. [Google Scholar]
- Papari, B.; Edrington, C.S.; Gonsoulin, D. Optimal energy-emission managementin hybrid ac-dc microgrids with vehicle-2-grid technology. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2019, 11, 015902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoon, F.A.; Hussain, I.; Iqbal, S.J. Multi-objective optimal control of renewable energy based autonomous AC microgrid using dandelion optimisation. Renew. Energy Focus 2024, 49, 100563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žnidarec, M.; Šljivac, D.; Knežević, G.; Pandžić, H. Double-layer microgrid energy management system for strategic short-term operation scheduling. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 157, 109816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Mei, X. Microgrids energy management considering net-zero energy concept: The role of renewable energy landscaping design and IoT modeling in digital twin realistic simulator. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2024, 63, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Ray, S. Economic and environmental factors based multi-objective approach for optimizing energy management in a microgrid. Renew. Energy 2024, 222, 119920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, B.; Hu, Z. Chance-constrained two-stage unit commitment under uncertain load and wind power output using bilinear benders decomposition. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 3637–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Khaparde, S.A.; Agalgaonkar, A.P.; Kulkarni, S.V.; Srivastava, A.K.; Perera, S. Chance-Constrained Pre-Contingency Joint Self- Scheduling of Energy and Reserve in VPP. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2023, 39, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; He, C.; Nan, L.; Wu, L.; Su, X.; Zhang, J. A Wasserstein Distance-Based Distributionally Robust Chance-Constrained Clustered Generation Expansion Planning Considering Flexible Resource Investments. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2022, 38, 5635–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Smaisim, G.F. Joint chance-constrained multi-objective optimal function of multi-energy microgrid containing energy storages and carbon recycling system. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, T.; Xu, W.; Xiang, Y.; Su, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, F. Chance-constrained energy-reserve co-optimization scheduling of wind-photovoltaic-hydrogen integrated energy systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 6892–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Han, C.; Kang, S.; Jang, G. Chance-constrained optimization for active distribution networks with virtual power lines. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 221, 109449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Lei, H.; Ansari, I.S.; Du, J.; Chu, X. Distributionally robust optimization based chance-constrained energy management for hybrid energy powered cellular networks. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2023, 9, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liang, H.; Lai, Y. A distributionally robust energy management of microgrid problem with ambiguous chance constraints and its tractable approximation method. Renew. Energy Focus 2024, 48, 100542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelos, S.; Borozan, S.; Aunedi, M.; Zhang, X.; Ameli, H.; Pudjianto, D.; Konstantelos, I.; Strbac, G. Modelling smart grid technologies in optimisation problems for electricity grids. Energies 2023, 16, 5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, M.; Ghasemzadeh, S.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B. Optimal scheduling of smart reconfigurable neighbour micro-grids. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2019, 13, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Deng, H. Distributed robust operation strategy of multi-microgrid based on peer-to-peer multi-energy trading. IET Energy Syst. Integr. 2023, 5, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaghian, M.S.; Saffari, M.; Kia, M.; Nazar, M.S.; Heidari, A.; Shafie-khah, M.; Catalão, J.P. Hierarchical framework for optimal operation of multiple micro-grids considering demand response programs. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 165, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, F.H.; Salehi, J.; Ghaemi, S. Contingency based energy managementof multi-microgrid based distribution network. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadian, H.; Noroozian, R. Multi-microgrid-based operation of active dis-tribution networks considering demand response programs. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2018, 10, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefifar, S.A.; Ordonez, M.; Mohamed, Y.A.R.I. Energy management in multi-microgrid systems—Development and assessment. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 910–922. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Zhou, B.; Chan, K.W.; Li, C.; Wu, Q.; Chen, B.; Xia, S. Distributed multi energy coordination of multimicrogrids with biogas-solar-wind renewables. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2018, 15, 3254–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyednouri, S.; Safari, A.; Quteishat, A.; Younis, M.; Salehi, J.; Najafi, S.; Taghizadegan, N. Stochastic energy management of a multi-microgrid system with battery/ supercapacitor energy storages considering demand response and transactive energy. Renew. Energy Focus 2024, 48, 100531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelos, S.; Bellizio, F.; Strbac, G.; Zhang, T. Machine learning approaches for predictions of CO2 emissions in the building sector. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 235, 110735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. A microgrid energy management systemand risk management under an electricity market environment. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 2349–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhu, W.; Bao, X.; Liu, C. Robust model predictive controlfor optimal energy management of island microgrids with uncertainties. Energy 2018, 164, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Liang, H.; Huang, S.; Dinavahi, V. Distributionally robust chance-constrained energy management for islanded microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 10, 2234–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papari, B.; Edrington, C.; Vu, T. Stochastic operation of interconnected microgrids. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Chicago, IL, USA, 16–20 July 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kavousi-Fard, A.; Khodaei, A. Efficient integration of plug-in electric vehicles via reconfigurable microgrids. Energy 2016, 111, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali, N.; Hakimi, S.M.; Hasankhani, A.; Derakhshan, G.; Abdi, B. Stochastic energy management for a renewable energy based microgrid considering battery, hydrogen storage, and demand response. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2022, 30, 100652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, M.; Mansour-Saatloo, A.; Ahrabi, M.; Mirzaei, M.A.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Zare, K. Evaluating the advantages of electric vehicle parking lots in day-ahead scheduling of wind-based power systems. In Energy Storage in Energy Markets; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 251–263. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho, A.; Iria, J.; Soares, F.; Lopes, J.P. Real-time management of distributed multi-energy resources in multi-energy networks. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 34, 101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, M.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Abapour, M.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A. Day-ahead profit-based reconfigurable microgrid scheduling considering uncertain renewable generation and load demand in the presence of energy storage. J. Energy Storage 2020, 28, 101161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, F.H.; Kalantari, N.T.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B. A stochastic optimal scheduling of multi-microgrid systems considering emissions: A chance constrained model. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 122965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, M.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Abapour, M.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A. Optimal Chance-Constrained Scheduling of Reconfigurable Microgrids Considering Islanding Operation Constraints. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 14, 5340–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Starke, M.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, X.; Tomsovic, K. Microgrid optimal scheduling with chance-constrained islanding capability. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 145, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odetayo, B.; Kazemi, M.; MacCormack, J.; Rosehart, W.D.; Zareipour, H.; Seifi, A.R. A Chance constrained programming approach to the integrated planning of electric power generation, natural gas network and storage. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 6883–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, F.H.; Kalantari, N.T.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B. A chance-constrained energy management in multi-microgrid systems considering degradation cost of energy storage elements. J. Energy Storage 2020, 29, 101416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, H.; Jadid, S. Optimal energy management for multi-microgrid considering demand response programs: A stochastic multi-objective framework. Energy 2020, 195, 116992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, M.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Ghasemzadeh, S.; Reihani, E. Risk-based optimal scheduling of reconfigurable smart renewable energy based microgrids. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 101, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Ref. | Uncertain Parameter | Power Flow | Demand Response | Single/Multi MG | Uncertainty Modelling | Confidence Level and Reliability Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load | PV | Wind | ||||||
| [17] | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | Single MG | Scenario-based | - |
| [29] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Single MG | CCP | Confidence level |
| [30] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | Single MG | Robust/CCP | - |
| [33] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | MMG | Robust | Confidence level |
| [35] | - | - | - | ✓ | - | MMG | - | - |
| [38] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | ✓ | MMG | Robust | - |
| [39] | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | ✓ | MMG | Stochastic | - |
| [41] | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | Single MG | Scenario-based | - |
| [42] | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | Single MG | Scenario-based | - |
| [43] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | Single MG | CCP | - |
| [44] | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | MMG | Scenario-based | - |
| This work | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | MMG | CCP | Confidence level and reliability index |
| MG 1 | MG 2 | MG 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0/300 | 0/300 | 0/200 | |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| 40 | 40 | 30 | |
| 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.1 | |
| 10 | 10 | 8 | |
| 100 | 50 | 100 | |
| 200 | 200 | 150 |
| Cost (USD) | UPC1 | UPC2 | UPC3 | Time-Solving (S) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MG1 | MG2 | MG3 | Distribution Network | |||||
| Case 1 | 1700.45 | 1158.63 | 1215.09 | 1720.5 | 0.613 | 0.759 | 0.766 | 38 |
| Case 2 | 1918.37 | 1294.11 | 1377.24 | 1930.33 | 0.802 | 0.794 | 0.809 | 79 |
| Case 3 | 1875.61 | 1194.07 | 1288.64 | 1797.26 | 0.783 | 0.77 | 0.703 | 75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hemmati, M.; Bayati, N.; Ebel, T. Integrated Optimal Energy Management of Multi-Microgrid Network Considering Energy Performance Index: Global Chance-Constrained Programming Framework. Energies 2024, 17, 4367. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174367
Hemmati M, Bayati N, Ebel T. Integrated Optimal Energy Management of Multi-Microgrid Network Considering Energy Performance Index: Global Chance-Constrained Programming Framework. Energies. 2024; 17(17):4367. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174367
Chicago/Turabian StyleHemmati, Mohammad, Navid Bayati, and Thomas Ebel. 2024. "Integrated Optimal Energy Management of Multi-Microgrid Network Considering Energy Performance Index: Global Chance-Constrained Programming Framework" Energies 17, no. 17: 4367. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174367
APA StyleHemmati, M., Bayati, N., & Ebel, T. (2024). Integrated Optimal Energy Management of Multi-Microgrid Network Considering Energy Performance Index: Global Chance-Constrained Programming Framework. Energies, 17(17), 4367. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17174367







