External Insulation Performance under DC Voltages of Polluted Post Insulators for Power Stations in Rainy Weather: A Brief Review and Recent Progress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Definition of the Concept of ‘Pollution Rain Flashover’
2.1. Comparison of the Concepts of PRF and PF
2.2. Characteristics and Mechanism of PRF Discharge
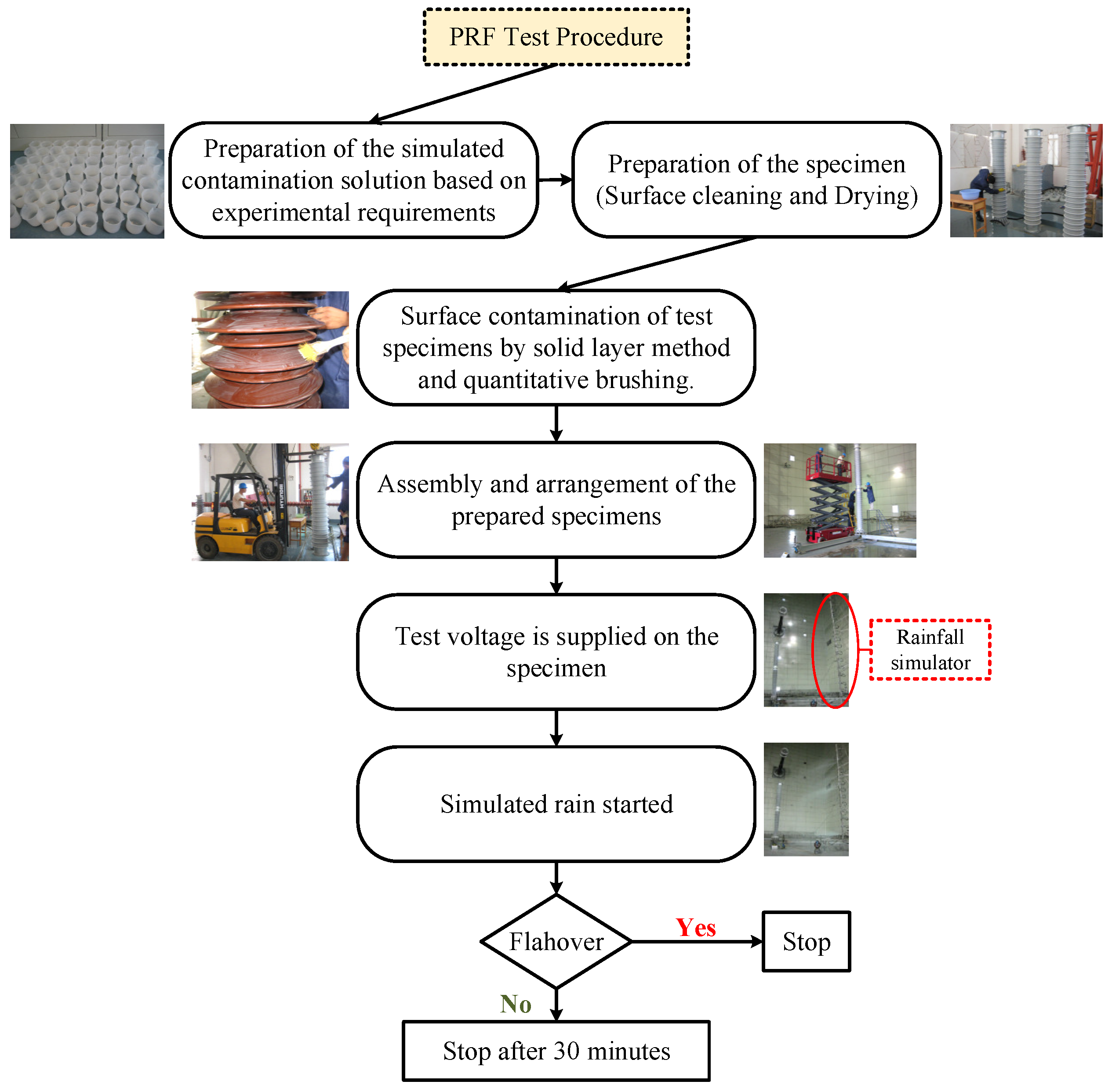
3. Available Test Results
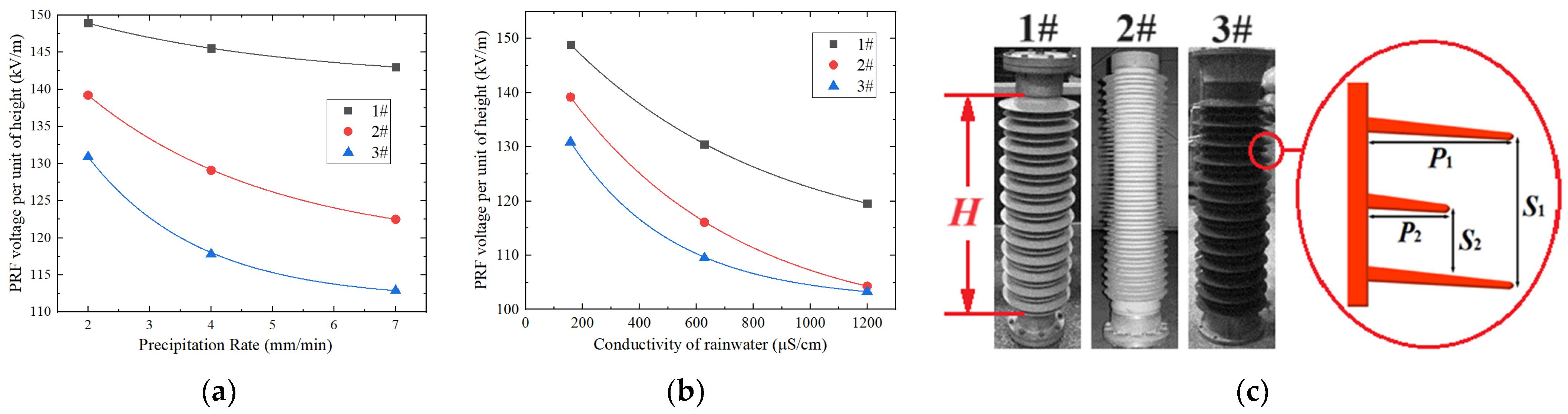
3.1. Influence of Rainfall Parameters
3.2. Influence of Other Factors
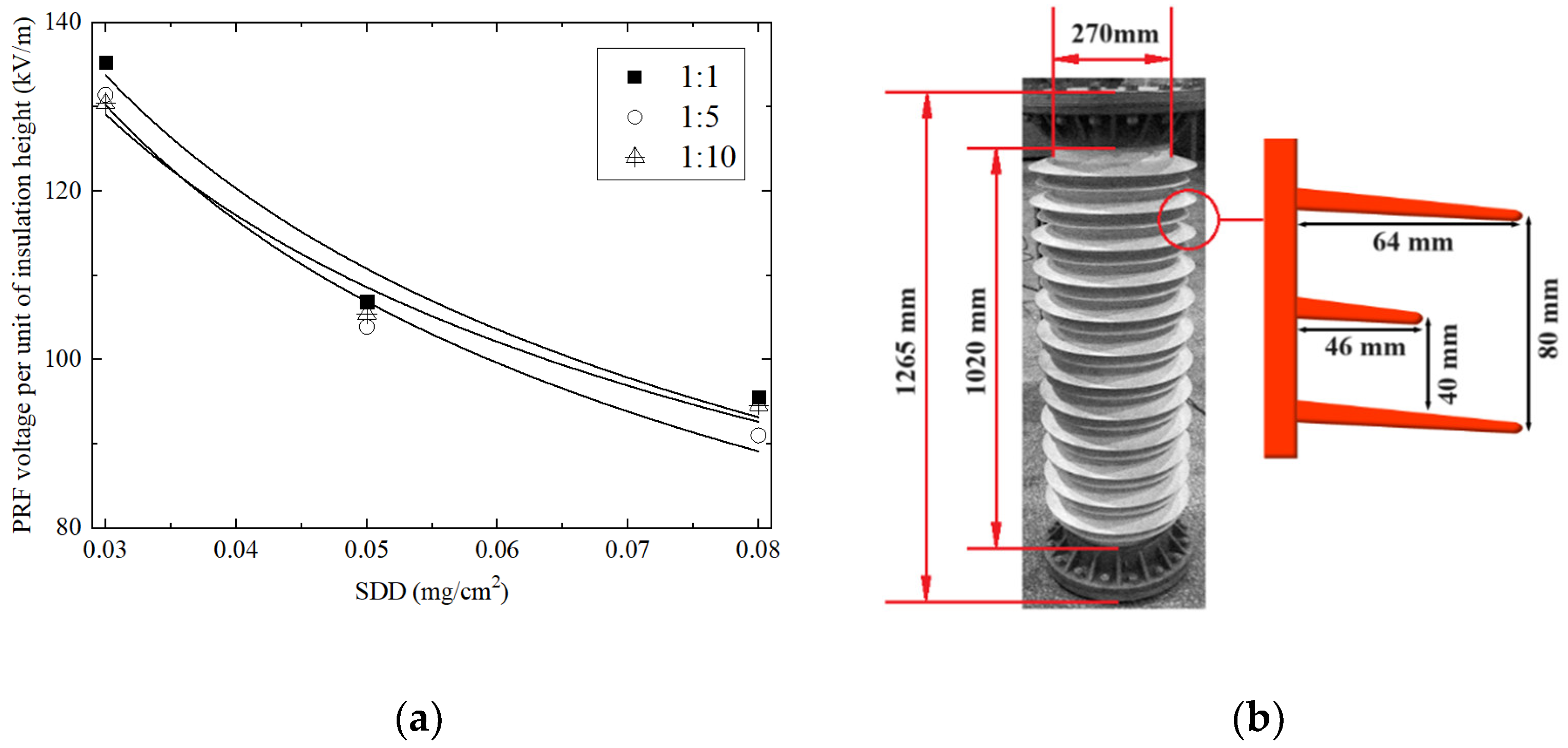
3.2.1. Surface Contamination
3.2.2. Distribution of Pollution
3.2.3. Material of the Shed
3.2.4. Shed Parameters
- Design and production of multiple molds with different parameters;
- Production of insulator specimens with different shed parameters by injection molding using the above molds;
- Tests were carried out on specimens to obtain the flashover characteristics;
- Comparison and analysis of the test results to select the specimen with the optimum external insulation characteristics.
4. Discharge Prevention and Application
4.1. Application of Rainproof Sheds
4.2. Optimized Design of Shed Parameters
4.3. Utilization of Raindrop Energy
5. Conclusions and Prospects
- Energy variation in surface raindrops on post insulators in rainy weather;
- PRF characteristics under AC voltages and a comparison of the results with those under DC voltages;
- Modification and enhancement of the shed materials of post insulators;
- Discharge mechanism of a gap between electrodes in rainy weather.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaelani, A.A.; Haya, S.N.; Lumba, L.S.; Suwarno, S. Effect of Artificial Aging on Silicone Rubber Polymeric Insulators Performance at Various Environmental Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Conference on High Voltage Engineering and Power Systems (ICHVEPS), Bandung, Indonesia, 5–6 October 2021; pp. 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, A.A.; Lau, K.Y.; Rahiman, W.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Al-Gailani, S.; Mohammed, N.; Rahman, R.A.; Al-Ameri, S.M. Pollution flashover voltage of transmission line insulators: Systematic review of experimental works. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 10416–10444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousalreza, F.P.; Sina, M.; Mohammad, M.; Amin, M. Designing an Automatic Detector Device to Diagnose Insulator State on Overhead Distribution Lines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Peng, X.; Yu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Xie, Y.; Hu, C. Simulation and analysis of charge accumulation characteristics of post insulator of transmission line for the CRAFT NNBI system. Fusion Eng. Des. 2021, 173, 112948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q. Assessment of the External Insulation Performance of Post Insulator in Rain: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 781, 042048. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, S.; Peter, K.; Pihler, P. New design of a medium voltage indoor post insulator. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, C.B.; Stephen, B.; Allen, B.R.; Glenn, A.D.; DeSantis, N.; Shawn, E.; Kevin, E.; Michael, G.; Robert, K.; Niedospial, E.; et al. High Voltage Composite Line Post Insulators Combined Load Limits. IEEE Trans. Power Deliver. 2023, 38, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Song, Y.; Huang, H.; He, Y.; Zhou, S.; Gao, Z. Meteorological Characteristics of a Continuous Ice-Covered Event on Ultra-High Voltage Transmission Lines in Yunnan Region in 2021. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.X.; Liang, H.C.; Li, J. Surface coating affecting charge distribution and flashover voltage of cone-type insulator under DC stress. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2019, 26, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hao, Y.P.; Li, L.C.; Zhao, Y.M. Comparison of pollution flashover performance of porcelain long rod, disc type, and composite UHVDC insulators at high altitudes. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2012, 19, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Das, A.K.; Dalai, S. The effects of non-standard lightning impulse on electrical insulation: A review. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 4239–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, L.S.; Chang Shen, O.; Eng Eng, N. An Integrated Lightning Risk Assessment of Outdoor Air-Insulated HV Substations. Energies 2022, 15, 7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gençoğlu, M.T.; Cebeci, M. The pollution flashover on high voltage insulators. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2008, 78, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.A.; Abd, R.R.; Al-Ameri, S. Pollution flashover characteristics of high-voltage outdoor insulators: Analytical study. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 2711–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Xu, H.; Huang, X.N.; Zhang, Z.J.; Jiang, X.L. Space Electric Field Characteristics of Silicone Rubber Insulator Pollution Flashover and Its Application in Flashover Prewarning. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2023, 30, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.A.; Abd-Rahman, R.; Rahiman, W.; Rahiman, W.; Al-Gailani, S.A.; Al-Ameri, S.M.; Ishak, M.T.; Sheikh, U.U. Pollution flashover under different contamination profiles on high voltage insulator: Numerical and experiment investigation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 37800–37812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadie, F. Investigative analysis of the impact of the climatic induced pollution upon the insulators in 500 kV HVDC transmission line. Electr Power Syst. Res. 2023, 220, 109244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hao, Y.P.; Li, L.C.; Zhang, F.Z. Artificial pollution flashover performance of porcelain long rod UHVDC insulators at high altitudes. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2014, 21, 1965–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Meng, X.B.; Wang, L.M. Influence of Shed Shape on Direct-Current Pollution Flashover Voltage and Pressure Decrease Exponent. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 51804–51813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.M.; Chen, J.Y.; Shi, X.F.; Li, X.L. Surface Flashover Characteristics of Epoxy Resin Composites in SF6/CF4 Gas Mixture with DC Voltage. Energies 2022, 15, 4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Yang, Z.D.; Yang, X.; Gao, C.J.; Lu, L.C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, C.X.; Li, C.R. Effect of Different DC Prestressed Time on Flashover Characteristics of Epoxy Resin Under Polarity Reversal Voltage. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2022, 29, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, Y.; Maeda, M.; Kondo, K. Flashover Risk-Based Probabilistic Design of Transmission Line Insulators under Contamination Conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Deliver. 2023, 38, 3611–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.B.; Mei, H.W.; Zhu, B.; Yin, F.H.; Wang, L.M. Influence of contaminated location on streamer discharge. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 218, 109243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Q.; Wang, X.F.; Zhang, R.Q.; Qi, Z.B.; Wang, W.W. Influence of Sheath Radial Crack on Flashover Arc and Leakage Current of Roof Silicon Rubber Insulator for High-Speed Train. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 19720–19731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezavar, H.R.; Fahimi, N.; Shayegani, A.A. A Dynamic Intelligent Approach Based on Gaussian Function for Prediction of the Flashover Voltage Conditions on Polluted Polymer Insulators. IEEE Trans. Power Deliver. 2022, 37, 3458–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.C.; Zhou, R.W.; Zhang, Y.; Dang, X.S.; Huang, X.B. Review on flashover risk prediction method of iced insulator based on icing monitoring technology. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2021, 185, 103252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gorur, R.S. Flashover of insulators in a wet environment. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2017, 24, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihani, T.; Mekhaldi, A.; Beroual, A.; Teguar, M.; Madjoudj, D. Model for polluted insulator flashover under AC or DC voltage. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2018, 25, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, G.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, S.Y.; Yao, D.G.; Kou, X.K.; Liu, Z.H.; Liu, C. The Movement Characteristics of Charged Haze Particles in Ionized Field and Its Influence on Contamination of Insulator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 7203304. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, F.H.; Liu, P.Y.; Mei, H.W.; Wang, L.M.; Li, L.C.; Farzaneh, M. The Shed Hole Influence on the Electrical Performance of Composite Insulator. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 217447–217455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Kuang, Z.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, C. Discharge Behavior and Morphological Characteristics of Suspended Water-Drop on Shed Edge during Rain Flashover of Polluted Large-Diameter Post Insulator. Energies 2021, 14, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezavar, H.R.; Fahimi, N.; Hasanzadeh, S.; Akmal, A.A.S. Risk assessment of contaminated composite insulators in pre-flashover conditions. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 230, 110256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad; Nekahi, A.; McMeekin, S.G.; Farzaneh, M. Effect of pollution severity and dry band location on the flashover characteristics of silicone rubber surfaces. Electr. Eng. 2017, 99, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC. Artificial Pollution Tests on High-Voltage Ceramic and Glass Insulators to Be Used on D.C. Systems; IEC TS 61245; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- IEC. Artificial Pollution Tests on High-Voltage Ceramic and Glass Insulators to Be Used on A.C. Systems; IEC 60507; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Kuang, Z.Q.; Sun, Y.J.; Liao, Y.F.; Hao, Y.P.; Li, L.C.; Zhang, F.Z. Study on Surface Rainwater and Arc Characteristics of High-Voltage Bushing with Booster Sheds Under Heavy Rainfall. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 146865–146875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Guan, Z. Investigation of DC discharge behavior of polluted porcelain post insulator in artificial rain. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.C.; Gu, Y.; Hao, Y.P.; Xue, Y.W.; Xiong, G.K.; Yang, L.; Zhang, F.Z. Shed Parameters Optimization of Composite Post Insulators for UHV DC Flashover Voltages at High Altitudes. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.J.; Yang, L.; Shang, G.F.; Kuang, Z.Q.; Liao, Y.F.; Hao, Y.P.; Li, L.C. Effects of dynamic deformation of pendant water drops on the electric field between hollow porcelain insulator sheds under extreme rainfall. High Voltage 2022, 7, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, H.W.; Wen, S.; Zhang, C. Prediction Model for the DC Flashover Voltage of a Composite Insulator Based on a BP Neural Network. Energies 2023, 16, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Cao, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. A dropl et-based electricity generator for large-scale raindrop energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Cheng, G.; Lee, S.; Pradel, K.C.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting water drop energy by a sequential contact-electrification and electrostatic-induction process. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4690–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Han, J.; Wu, F.; Rao, X.; Zhou, G.; Xu, C.; Li, P.; Song, Q. A novel retractable spring-like-electrode triboelectric nanogenerator with highly-effective energy harvesting and conversion for sensing road conditions. RSC Adv. 2017, 80, 50993–51000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, S.; Wang, W.; Xu, W.; Zheng, H.; Song, Y.; Jiao, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. A bulk effect liquid-solid generator with 3D electrodes for wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, B.; Long, J.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, X.; Hou, M.; Gao, J.; Zhou, S.; Fan, B.; He, Y.; et al. Interfacial Laser-Induced Graphene Enabling High-Performance Liquid−Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, R.G.; Khoo, B.C. Towards a larger scale energy harvesting from falling water droplets with an improved electrode configuration. Appl. Energy 2021, 285, 116428. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Wang, Z. Fusion of Slippery Interfaces and Transistor-Inspired Architecture for Water Kinetic Energy Harvesting. Joule 2020, 4, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Mendel, N.; van den Ende, D.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G.; Mugele, F. Charge Trapping-Based Electricity Generator (CTEG): An Ultrarobust and High Efficiency Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting from Water Droplets. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
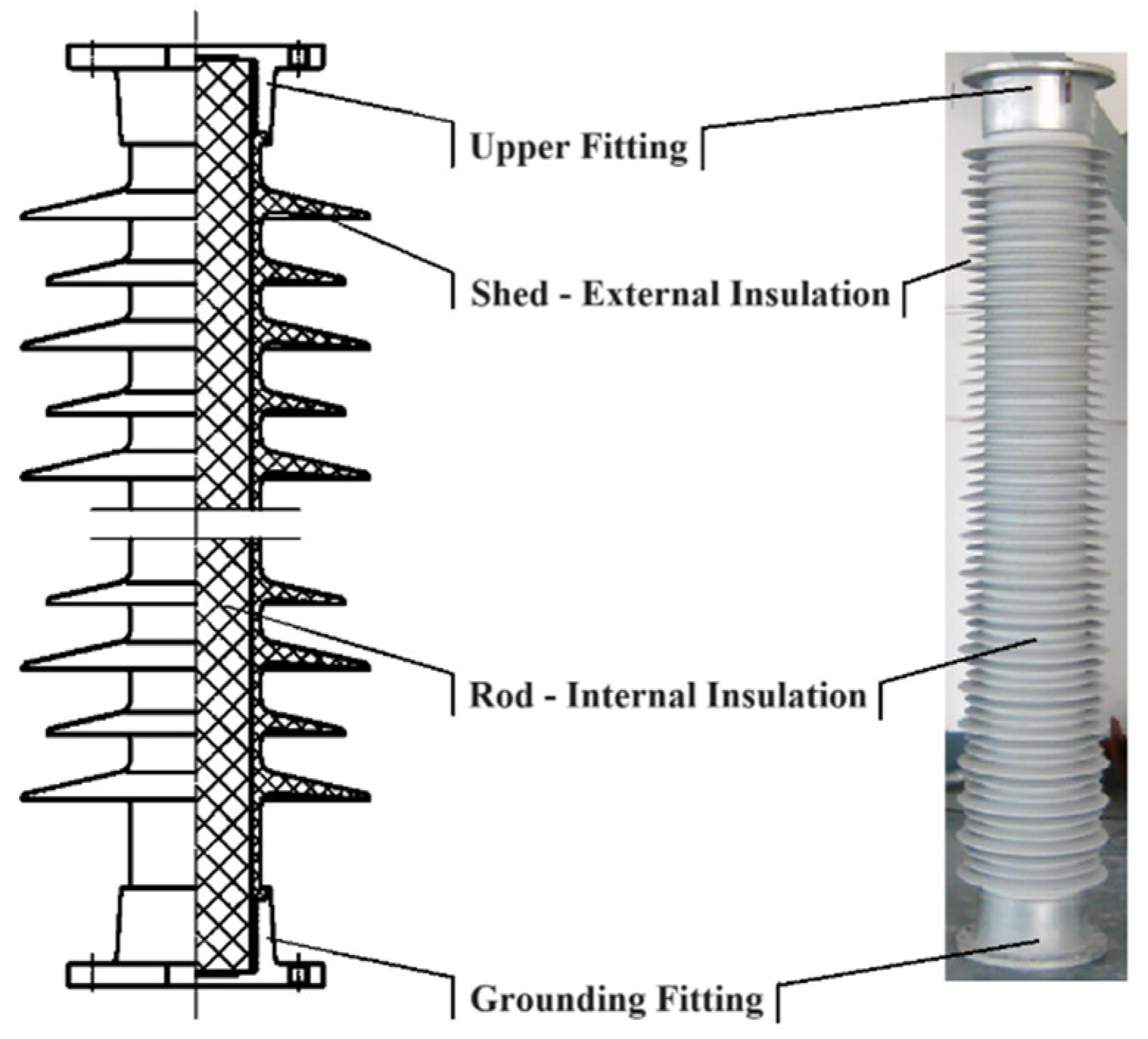
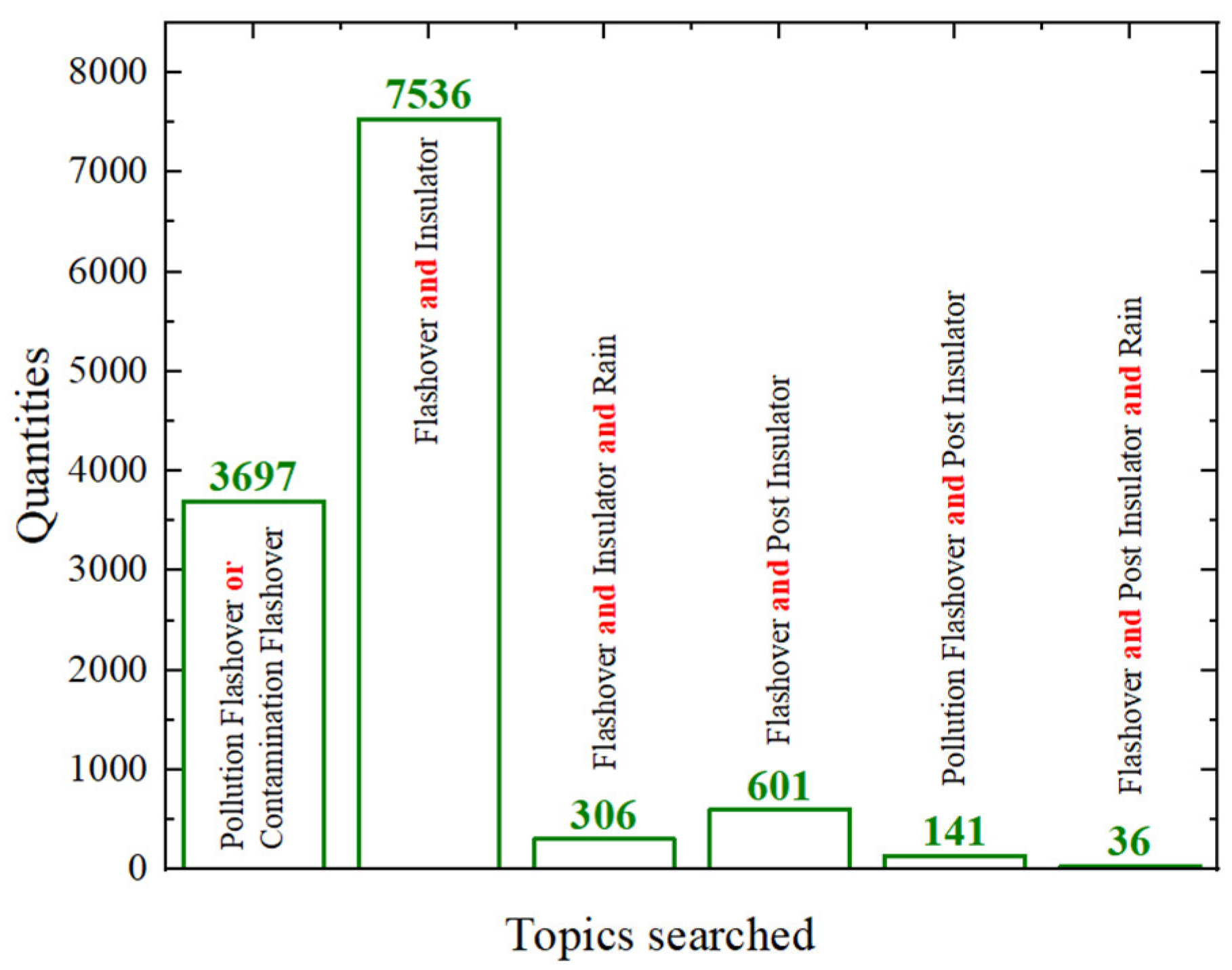
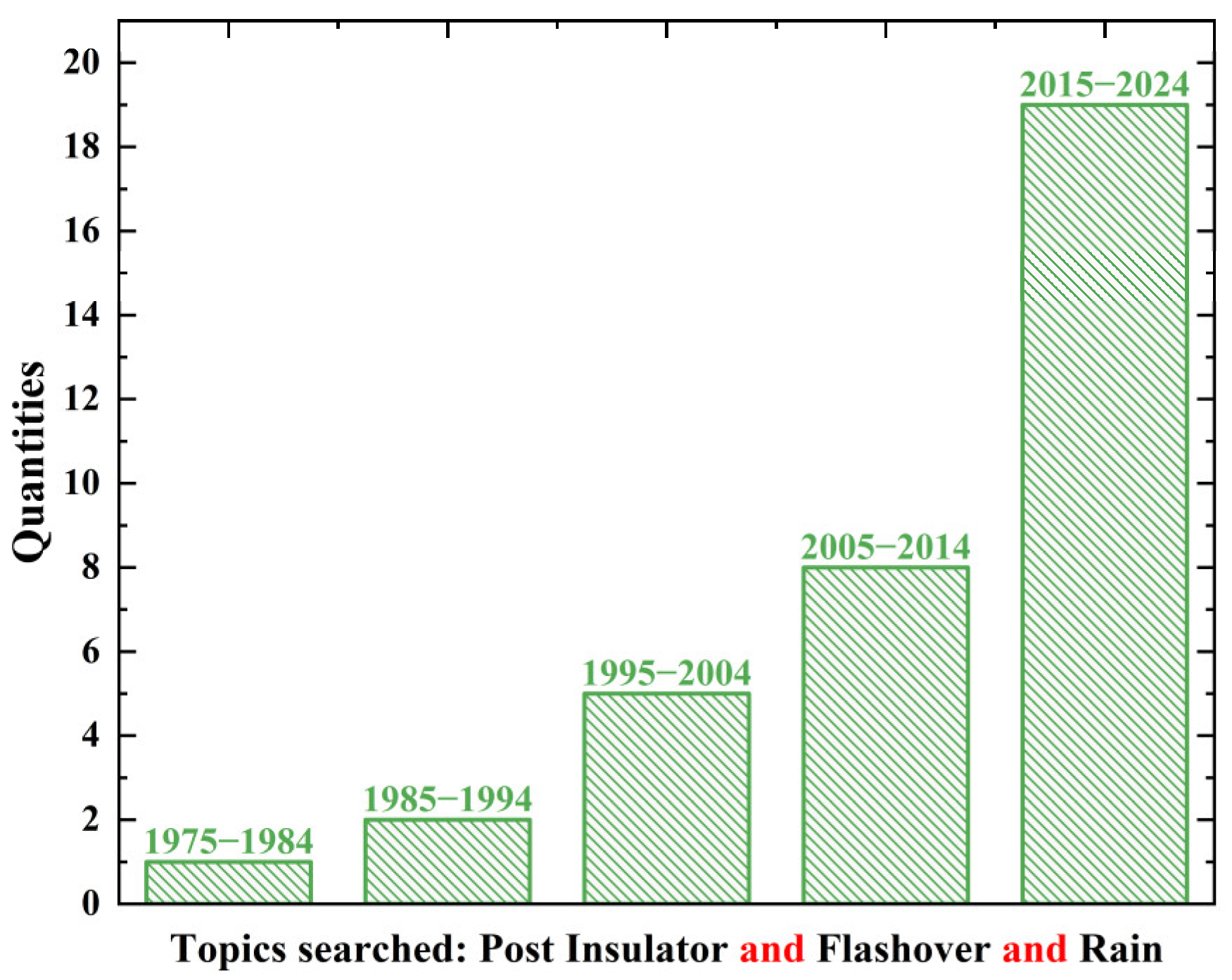
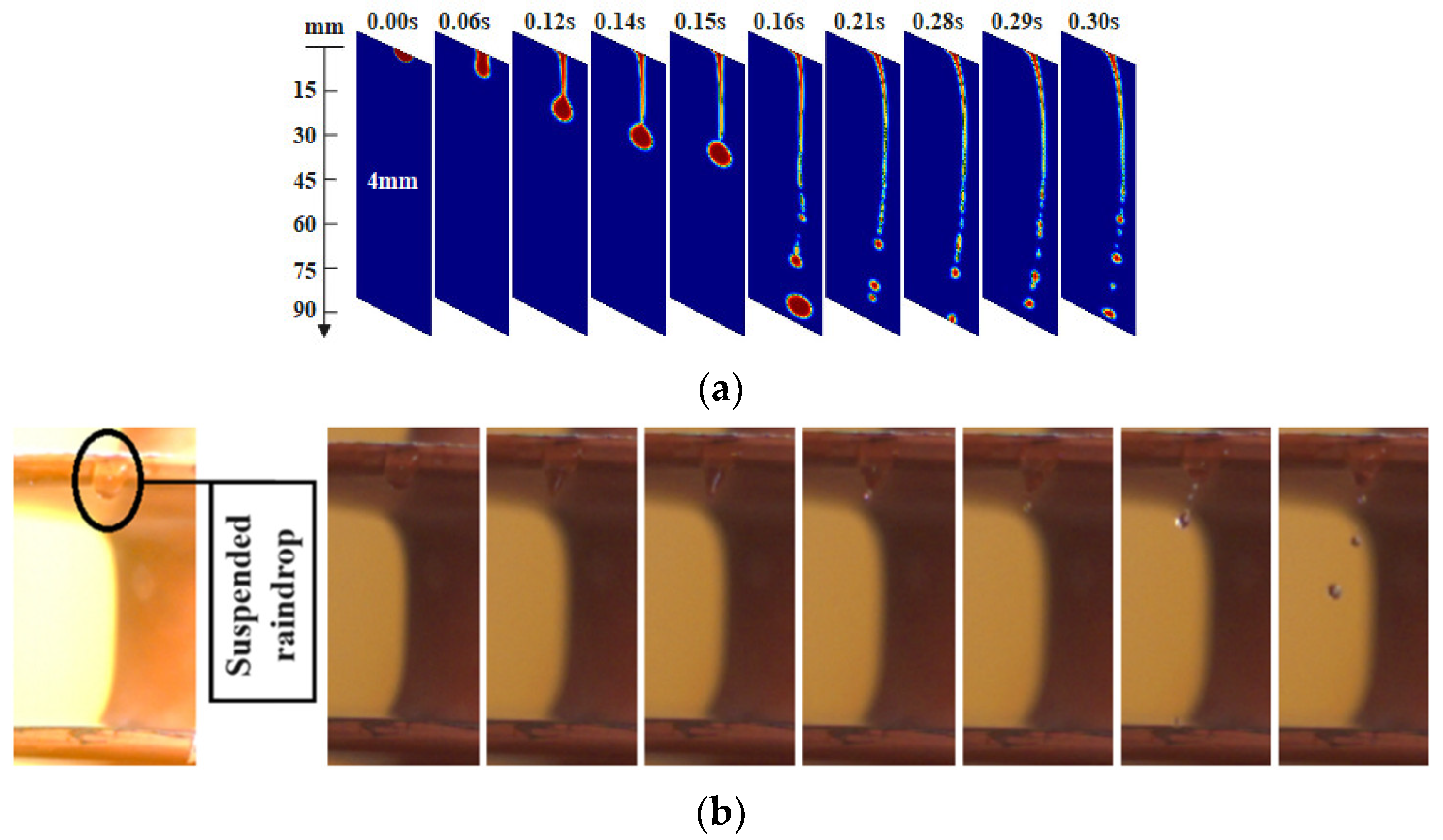
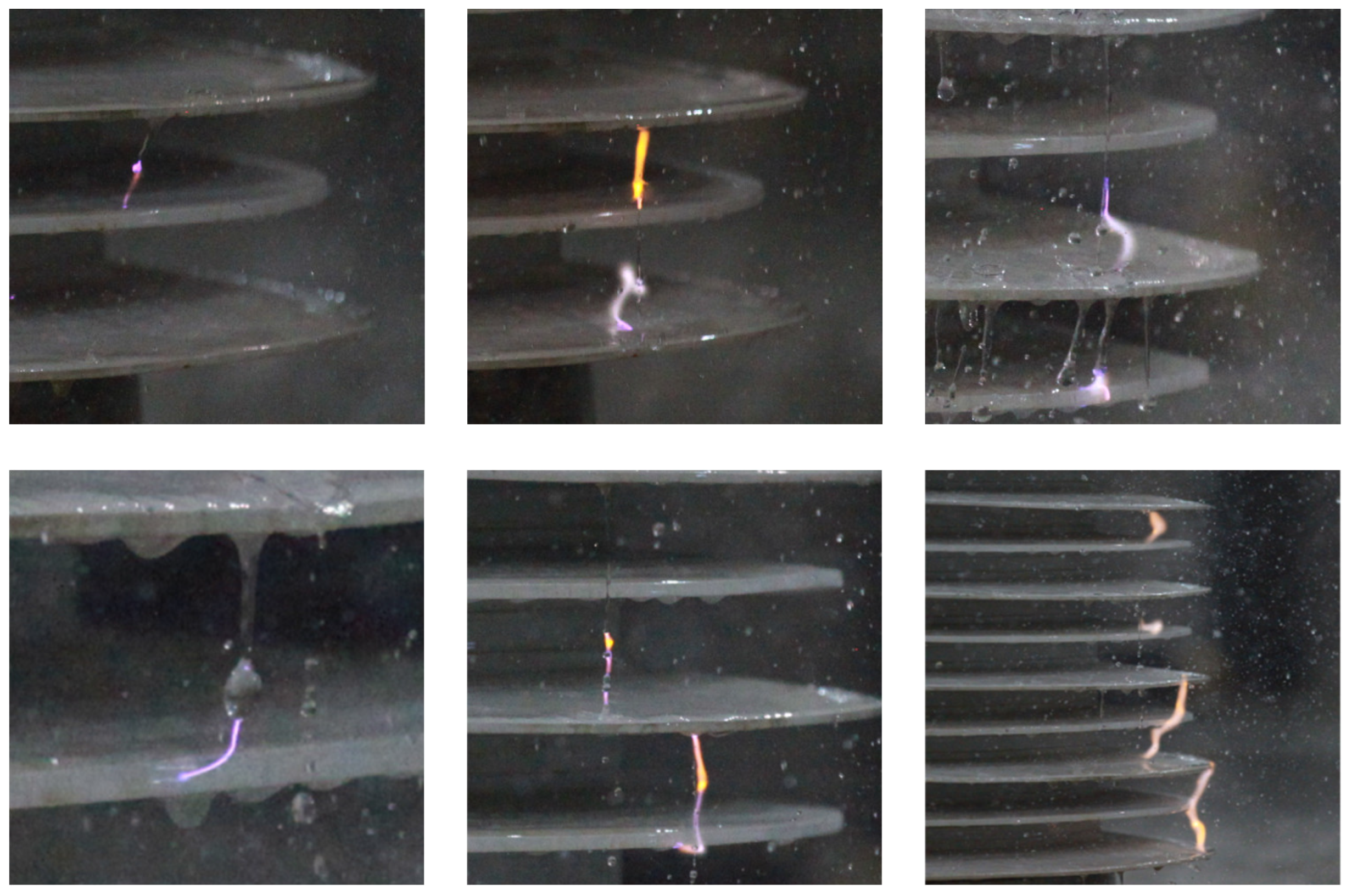
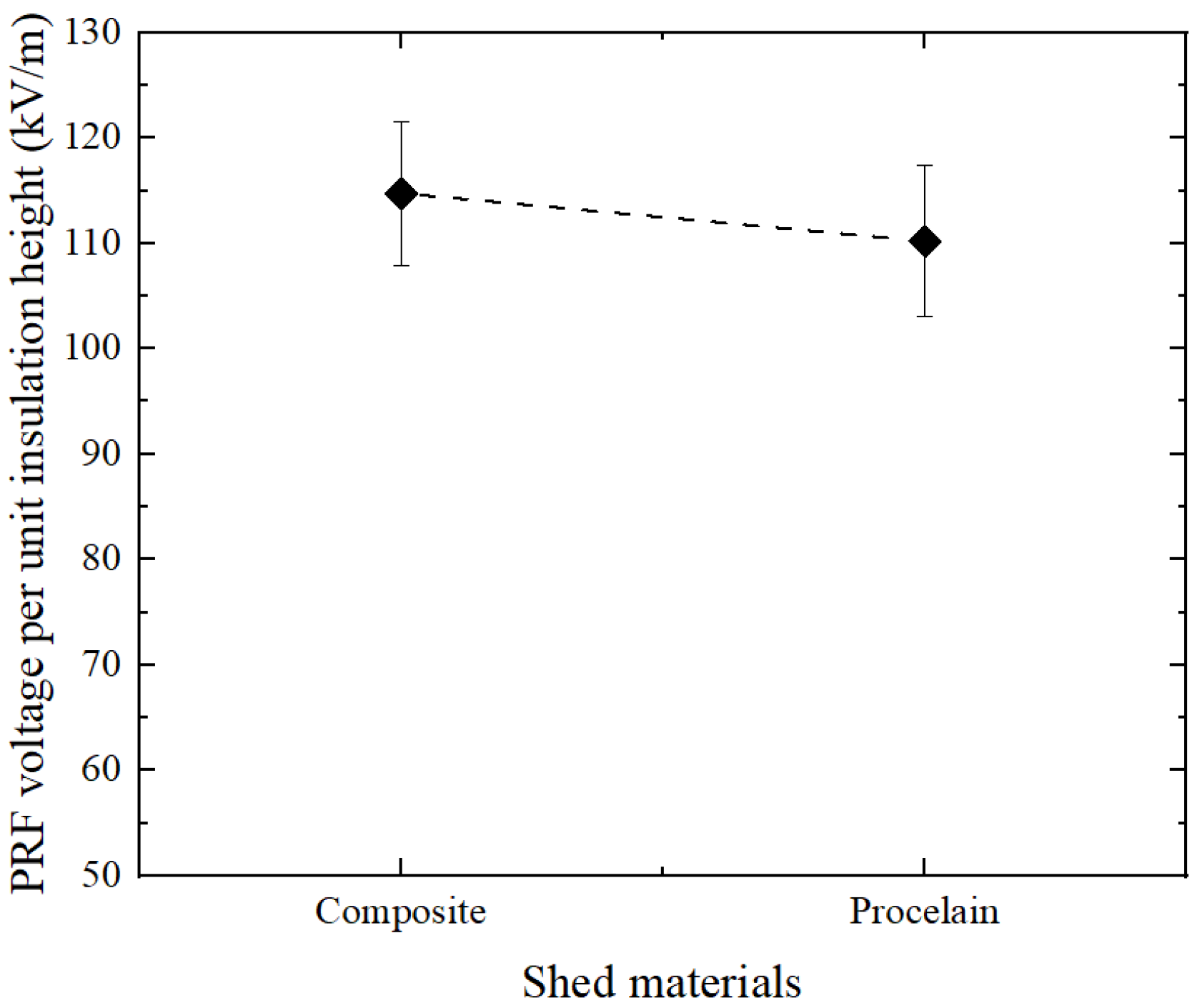
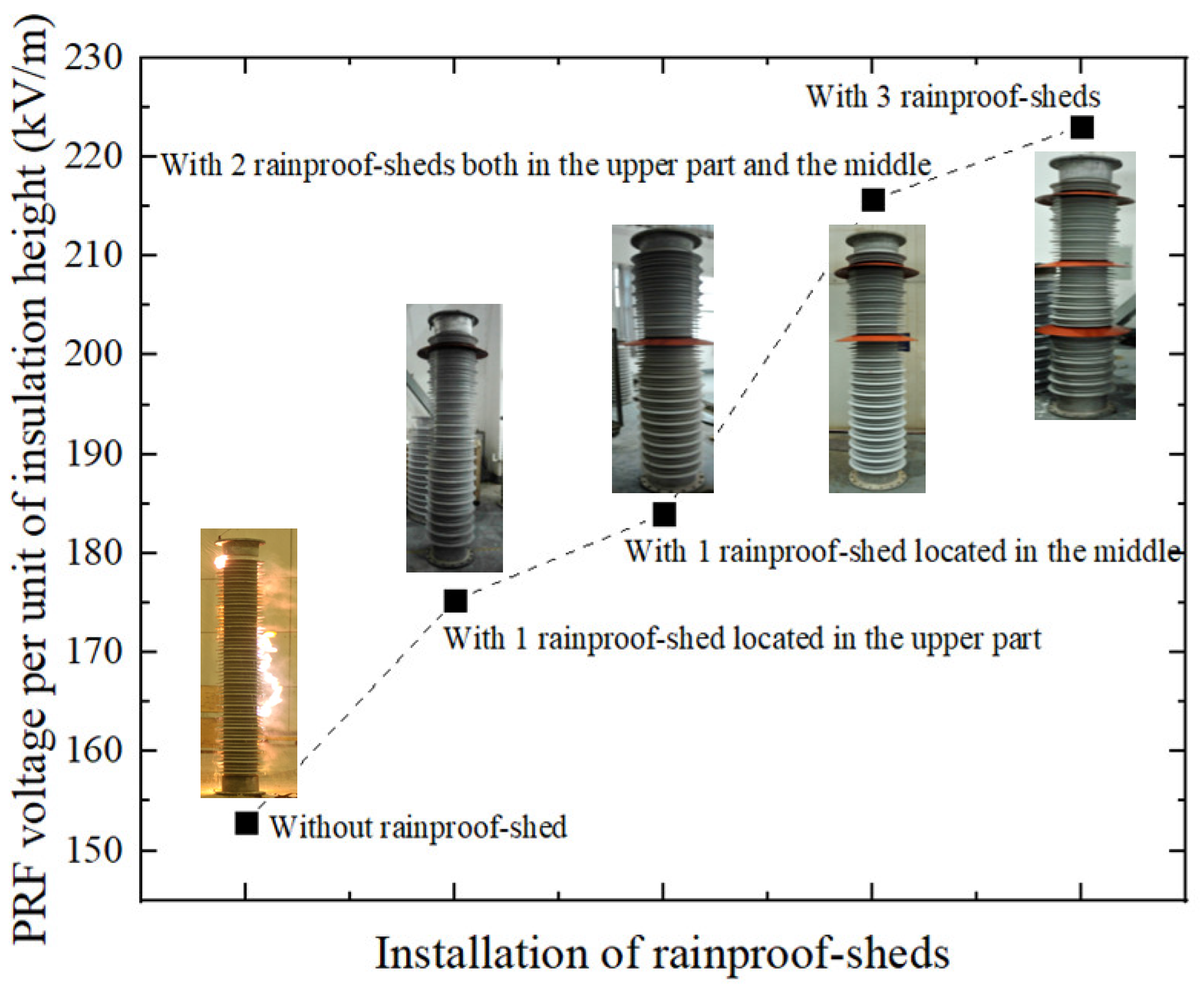
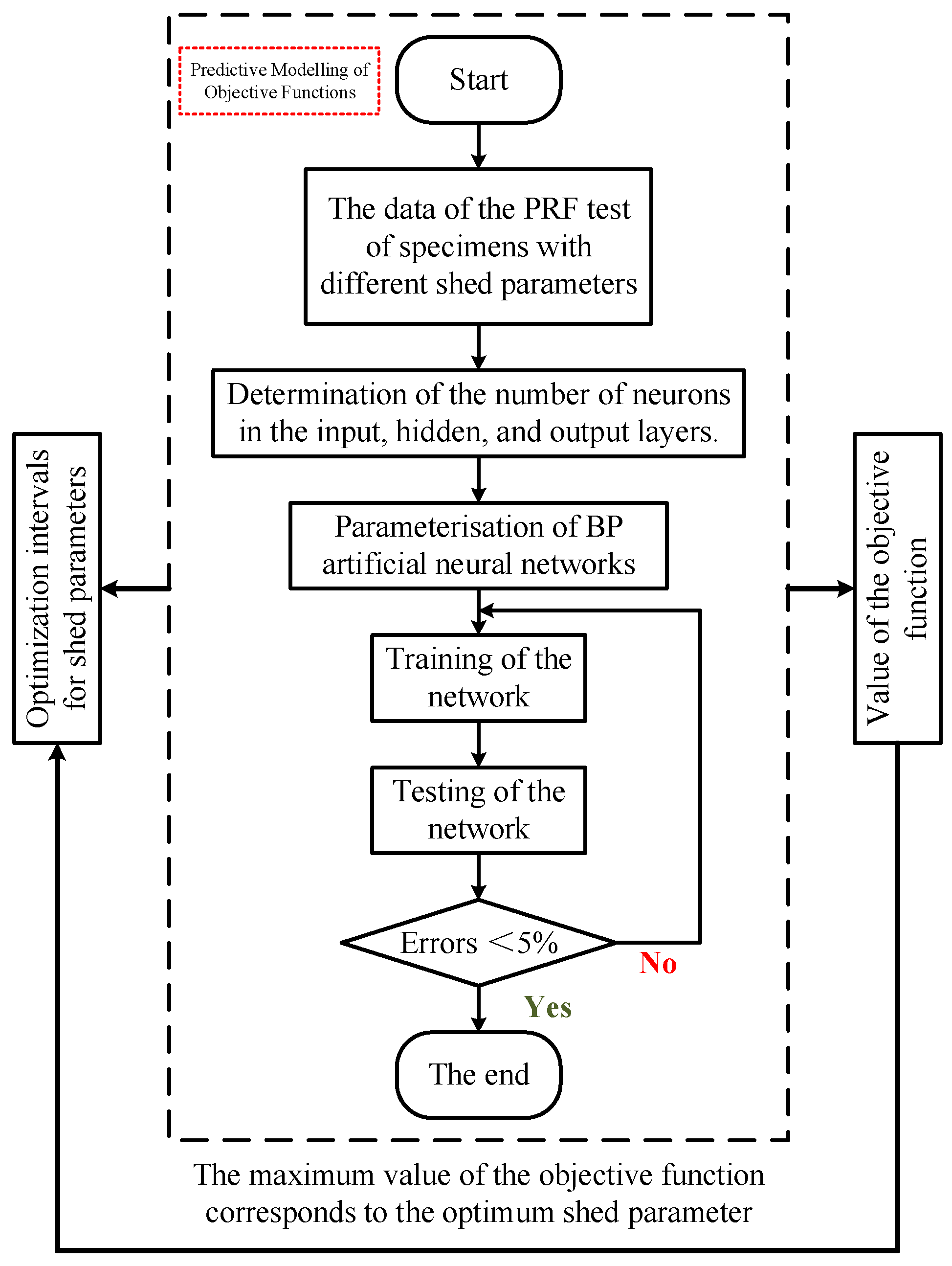
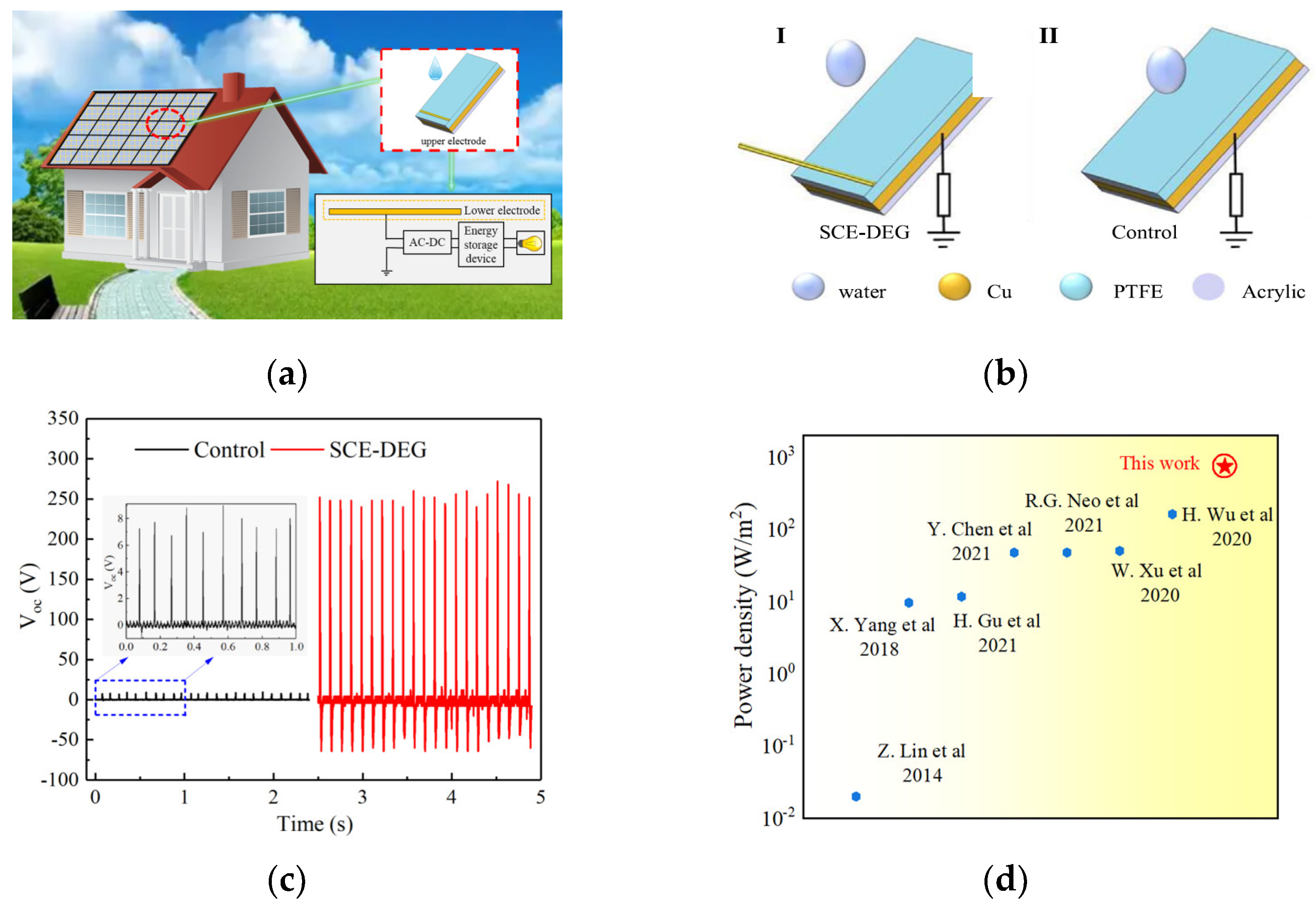
| Insulating Materials of Shed | Insulating Materials of Rod | Flashover Performance | Mechanical Properties | Aging Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain | Alumina ceramics | Depends on operating environment | High capacity to withstand longitudinal mechanical stresses | High resistance to aging |
| Silicone rubber | Fiberglass or epoxy resin | Strong resistance to pollution flashover | Capability to withstand both longitudinal and tangential stresses | Aging of composites needs attention |
| Concept | PF | RF | PRF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface condition | Contaminated surfaces | Clean surface | Contaminated surface |
| Wetting method of insulator’s surface | Mostly fog | Rain | Rain |
| Rainwater condition | \ | Clean rainwater | Rainwater of a certain conductivity |
| Discharge path | Mainly along the surface | Along water streamer + air gap | Along the surface + air gaps between sheds |
| Flashover voltage | Lowest | Highest | Middle (may be lower than PF voltage if the clearance between sheds is minimal) |
| Flashover process | Accumulation of surface contamination—wetting—leakage current—dry-band—arc-creepage—flashover | Shed bridging by water streamer—electric field distortion—flashover | Corona and streamer discharge of surface water droplets—deformation of surface raindrops—electric field distortion—breakdown of air gaps between sheds—flashover |
| Prevention and control methods | Shed optimization | Rainproof sheds | Both shed optimization and rainproof sheds |
| Specimen No. | Insulation Height: H (mm) | S1/S2 (mm) | P1/P2 (mm) | Surface Insulation Length (mm) | Rod Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 920 | 72/36 | 71/54 | 3470 | 147 |
| 2# | 1235 | 48/24 | 64/31 | 4455 | 184 |
| 3# | 1225 | 85/40 | 87/70 | 4770 | 264 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Diao, M.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Cao, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C. External Insulation Performance under DC Voltages of Polluted Post Insulators for Power Stations in Rainy Weather: A Brief Review and Recent Progress. Energies 2024, 17, 4137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17164137
Dong Y, Wang Z, Diao M, Wang X, Deng Y, Cao B, Xu Y, Zhang C. External Insulation Performance under DC Voltages of Polluted Post Insulators for Power Stations in Rainy Weather: A Brief Review and Recent Progress. Energies. 2024; 17(16):4137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17164137
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Yuxi, Zili Wang, Mingguang Diao, Xi Wang, Yu Deng, Bin Cao, Ying Xu, and Chuyan Zhang. 2024. "External Insulation Performance under DC Voltages of Polluted Post Insulators for Power Stations in Rainy Weather: A Brief Review and Recent Progress" Energies 17, no. 16: 4137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17164137
APA StyleDong, Y., Wang, Z., Diao, M., Wang, X., Deng, Y., Cao, B., Xu, Y., & Zhang, C. (2024). External Insulation Performance under DC Voltages of Polluted Post Insulators for Power Stations in Rainy Weather: A Brief Review and Recent Progress. Energies, 17(16), 4137. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17164137








