Design of Inductive Power Transfer Charging System with Weak Coupling Coefficient
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Comparison of Different Compensation Topologies
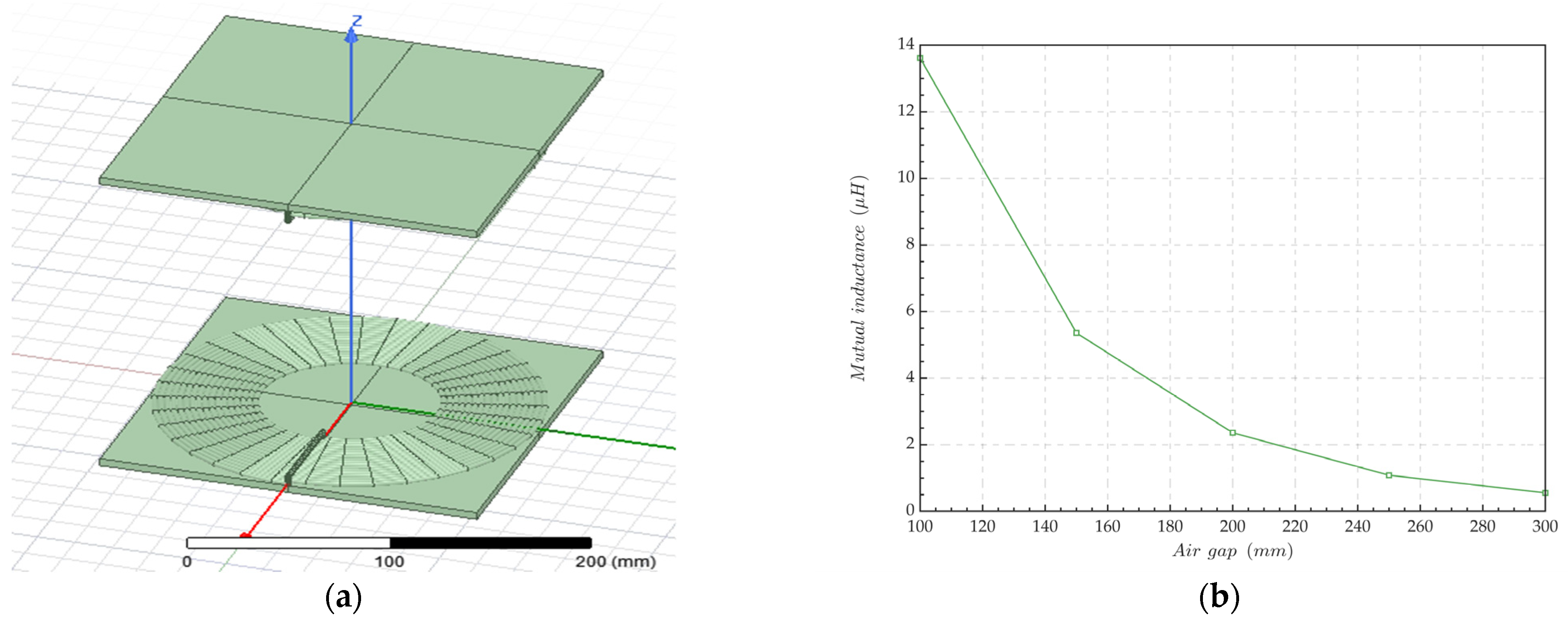
2.1. Magnetic Field Simulation of Charging Pad in Weak Coupling IPT System
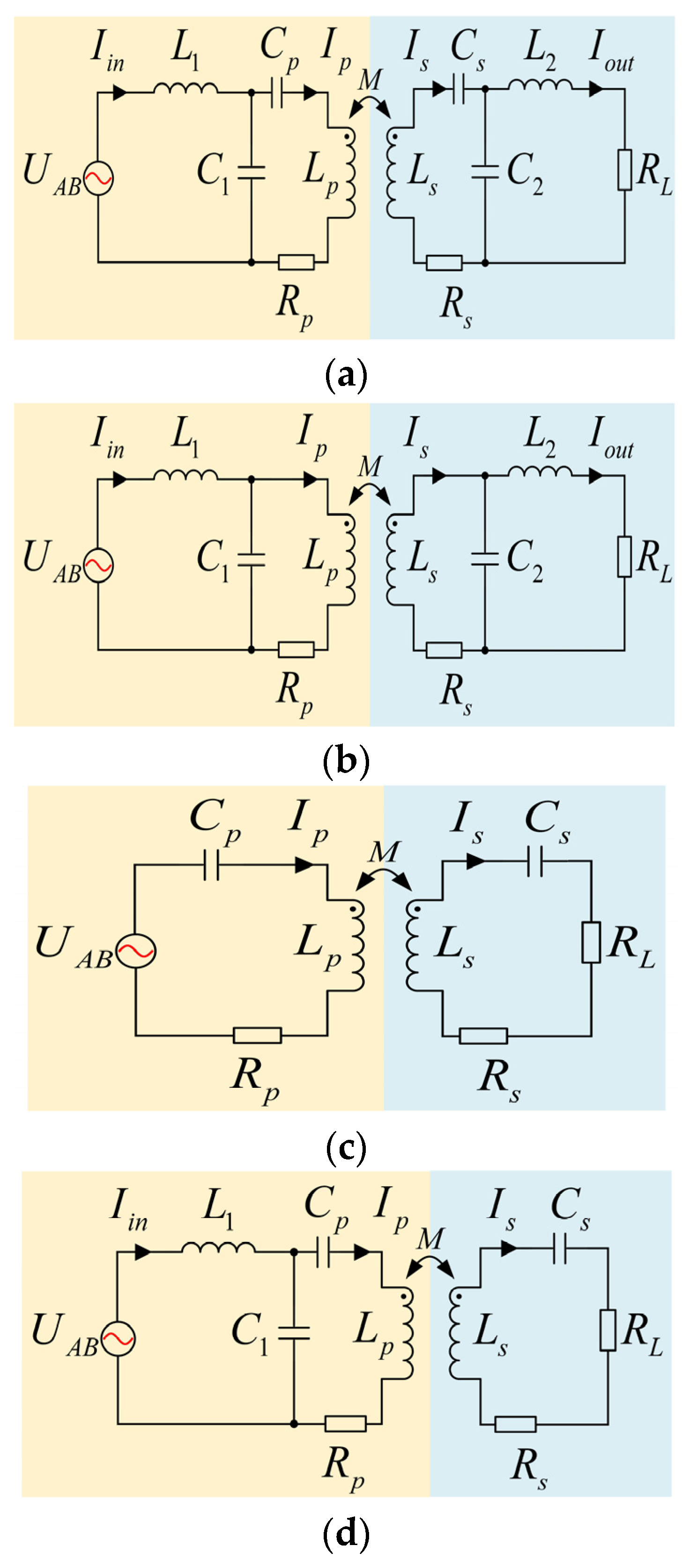
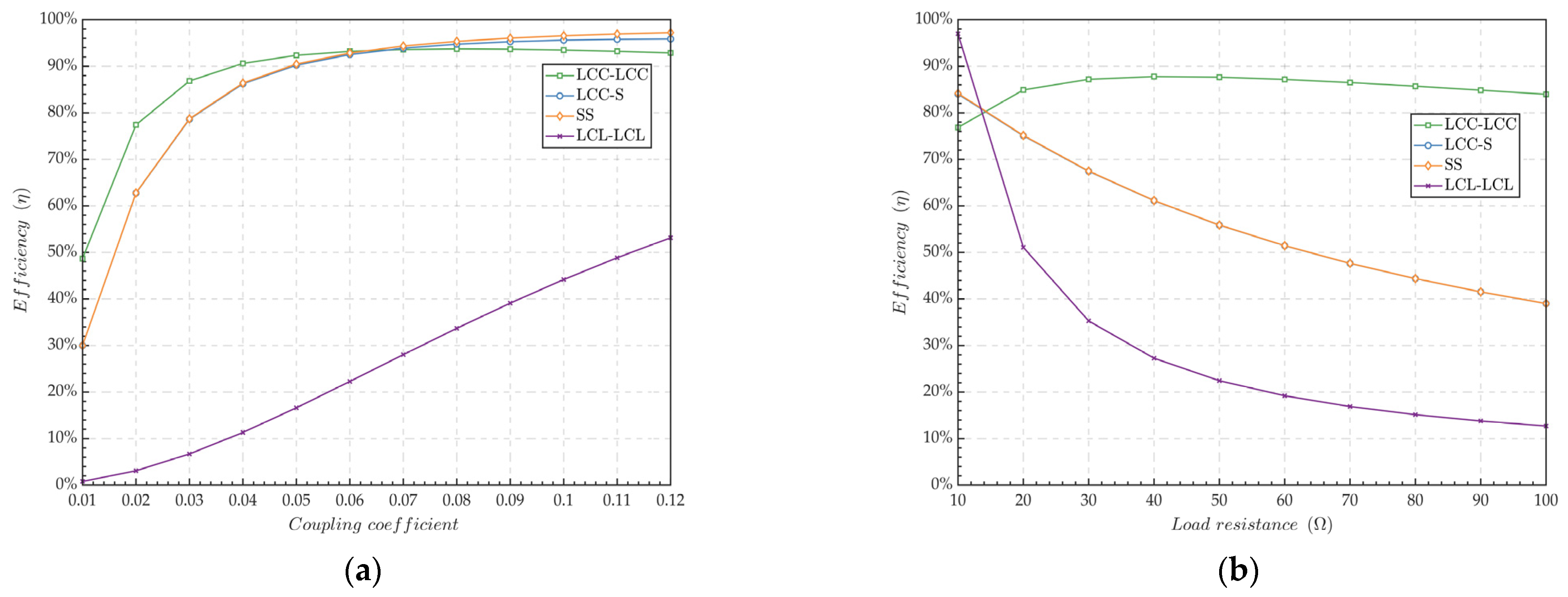
2.2. Basic Characteristics of Different Compensation Topologies
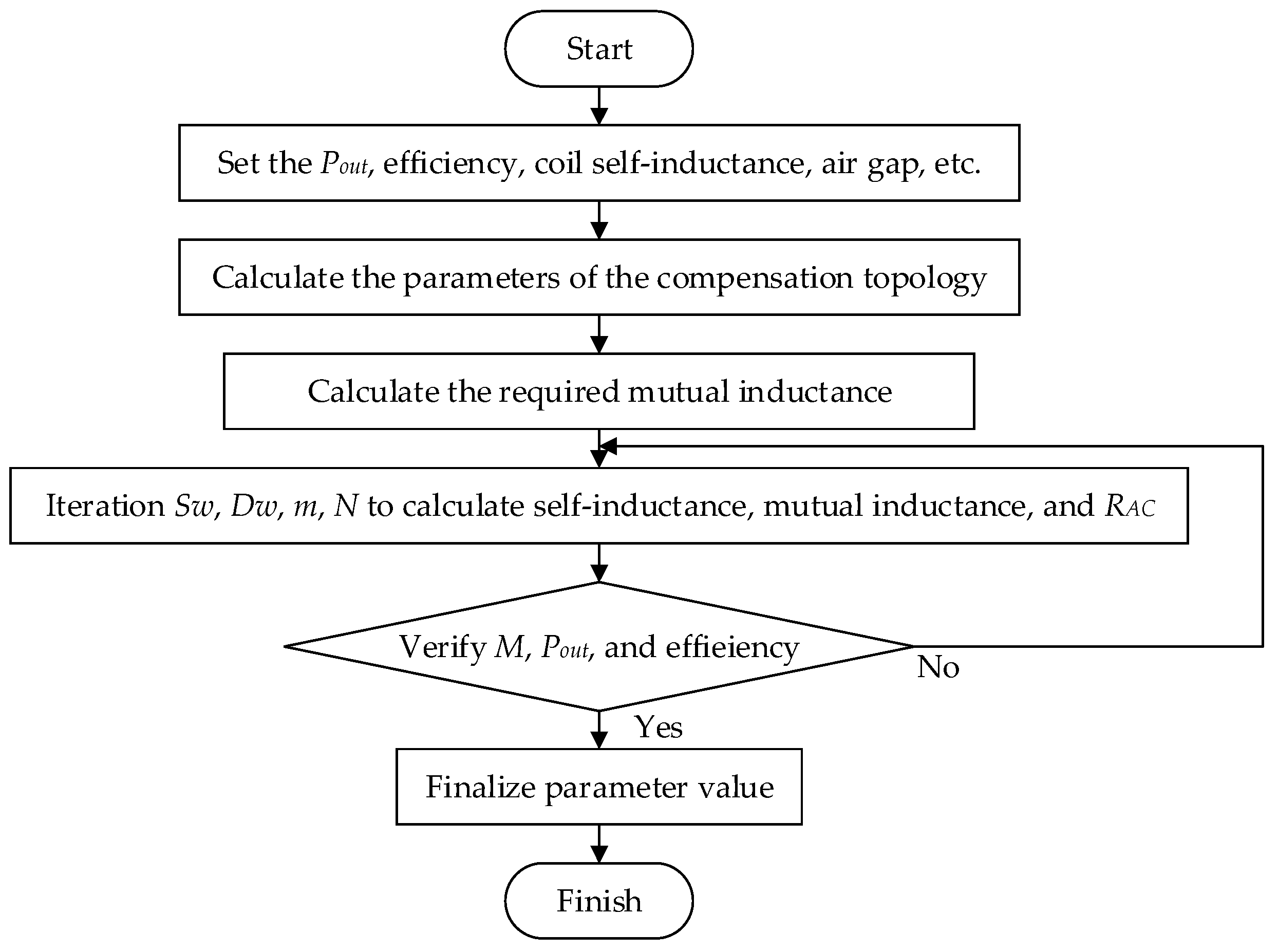
3. Modeling of Coupling Coils
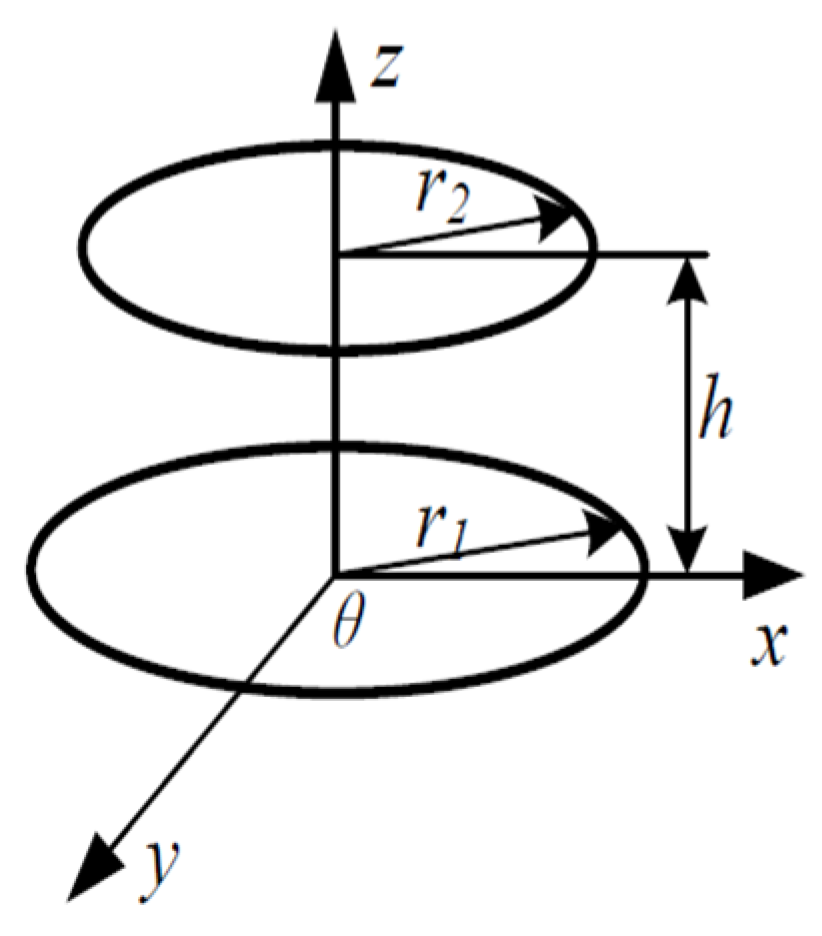
3.1. Modeling of Coreless Coils
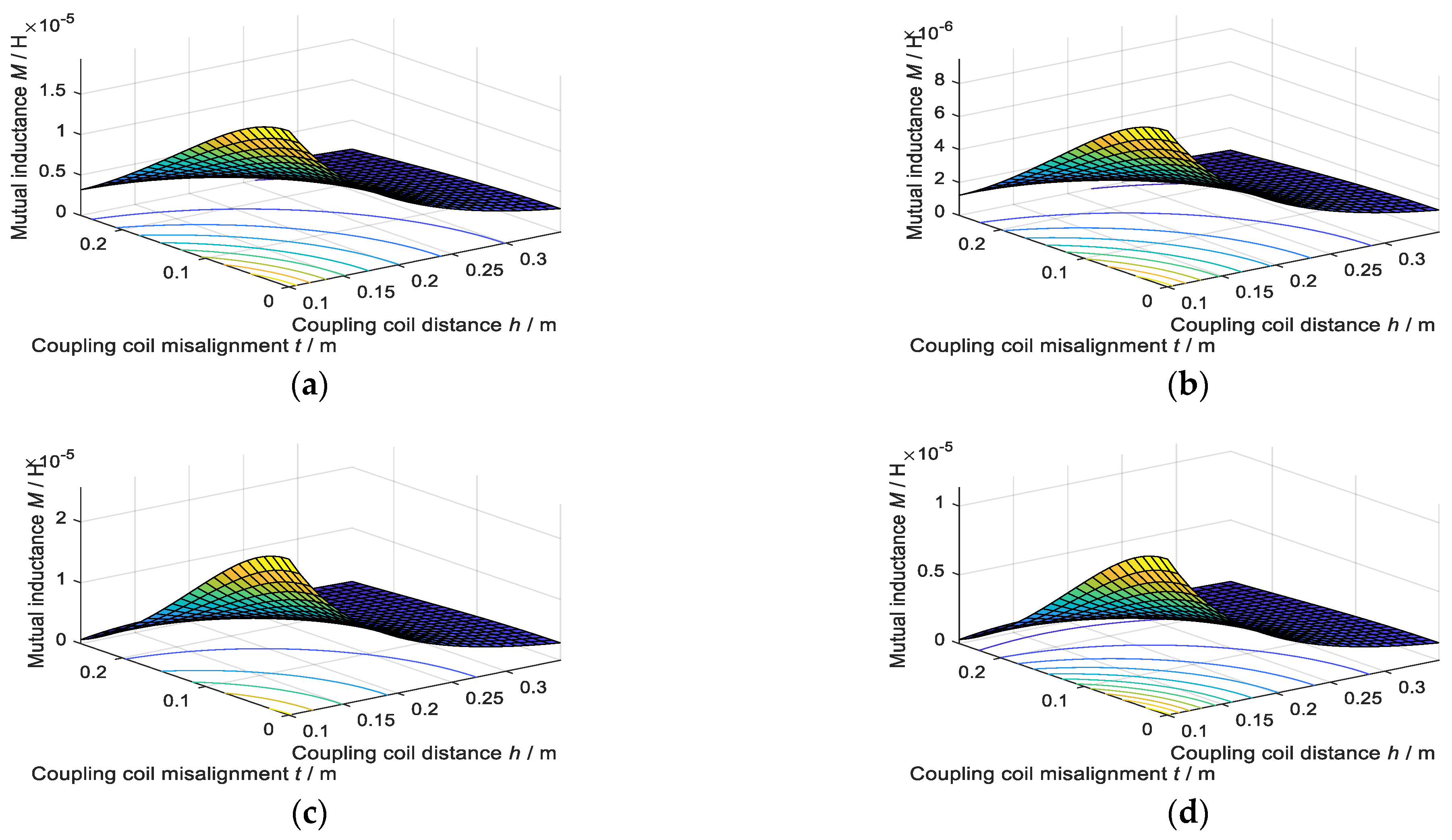
3.2. Designing Coreless Coupling Coils to Optimize Mutual Inductance
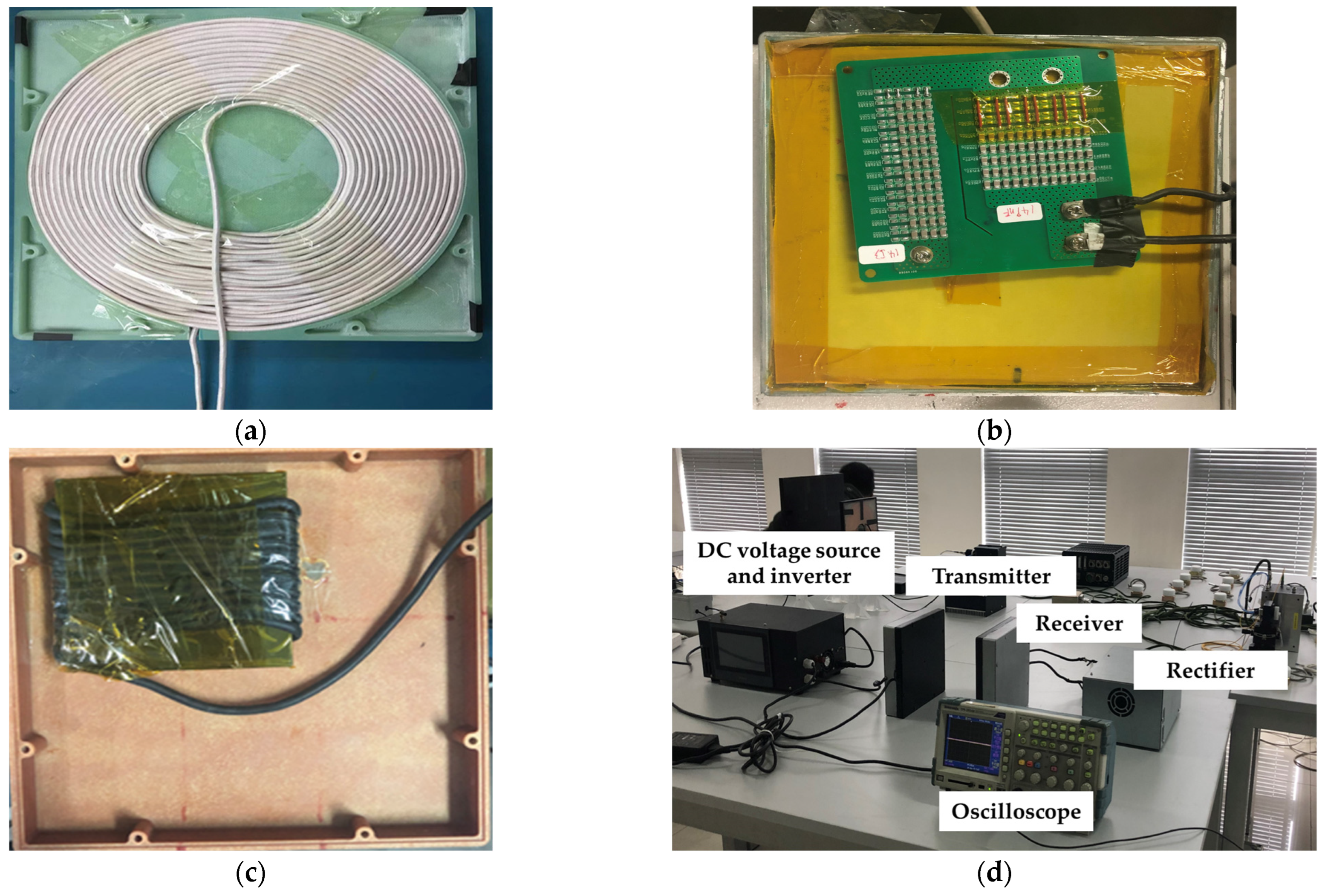
4. Experiment
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, Z.; Hu, H.; Su, Y.; Chen, F.; Xiao, J.; Tang, C.; Lin, T. Design of a 60-kW EV Dynamic Wireless Power Transfer System With Dual Transmitters and Dual Receivers. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; He, X. Orthogonal-Frequency Simultaneous Wireless Power and Data Transfer for High-Power Wireless EV Charging. Energies 2024, 17, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Lan, Y.; Wei, R.; Yang, G.; Yang, F.; Li, W.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, C.; Li, Y. A Control Strategy for Wireless EV Charging System to Improve Weak Coupling Output Based on Variable Inductor and Capacitor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 12853–12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, W.; Deng, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Mi, C.C. A Double-Sided LCC Compensation Network and Its Tuning Method for Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, M.G.S.; Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. Reduced Ferrite Double D Pad for Roadway IPT Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 5055–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Tahir, M.; Wu, X.; Hu, S. High-Performance Wireless Power and Data Transmission System for Medical Implant Devices Using ASK Modulation. Energies 2024, 17, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, J. A New Coil Structure for Implantable Wireless Charging System. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 68, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Luo, B.; Cheng, Y. Compact Curved Coupler With Novel Flexible Nanocrystalline Flake Ribbon Core for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Dai, X.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zuo, Z. A Magnetic Coupling Structure Design of Wireless Charging UAVs with Multidirectional Misalignment Improvement and Output Fluctuation Suppression. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 6th International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC), Hefei, China, 12–14 May 2023; pp. 4296–4299. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Kan, T.; Lu, F.; Zhang, K.; Song, B.; Mi, C.C. Frequency Optimization of a Loosely Coupled Underwater Wireless Power Transfer System Considering Eddy Current Loss. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 3468–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Long, M.; Hu, M.; Lin, Z. Resonant Wireless Charging System Design for 110-kV High-Voltage Transmission Line Monitoring Equipment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 4118–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-D.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Mi, C.C. Feasibility Study on Bipolar Pads for Efficient Wireless Power Chargers. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition—APEC 2014, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 16–20 March 2014; pp. 1676–1682. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-S.; Covic, G.A.; Stielau, O.H. Power Transfer Capability and Bifurcation Phenomena of Loosely Coupled Inductive Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, J.L.; Sallan, J.; Sanz Osorio, J.F.; Llombart, A. High-Misalignment Tolerant Compensation Topology For ICPT Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, Y.H.; Choi, B.H.; Lee, E.S.; Lim, G.C.; Cho, G.-H.; Rim, C.T. General Unified Analyses of Two-Capacitor Inductive Power Transfer Systems: Equivalence of Current-Source SS and SP Compensations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6030–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.; McDonough, M.K.; Miller, J.M.; Fahimi, B.; Balsara, P.T. Wireless Power Transfer for Vehicular Applications: Overview and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Transport. Electrific. 2018, 4, 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. Balanced Dual-Side LCC Compensation in IPT Systems Implementing Unity Power Factor for Wide Load Range and Misalignment Tolerance. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 7796–7809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wu, X.; Sun, P.; Deng, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhou, H. Design of Constant-Voltage and Constant-Current Output Modes of Double-Sided LCC Inductive Power Transfer System for Variable Coupling Conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 1676–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, R.; Wang, H.; Liang, J.; Fu, M. Modified LCC Compensation and Magnetic Integration for Inductive Power Transfer. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Sun, Q.; Li, X.; Hu, A.P. Robust μ-synthesis Control of Dual LCL Type IPT System Considering Load and Mutual Inductance Uncertainty. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 72770–72782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongming, G.; Dangshu, W. Research on Transmission Characteristics of Dual LCL Resonance Compensation Topology in Wireless Charging System. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 5th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Xi’an, China, 15–17 October 2021; pp. 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; Cui, X.; Jiao, C.; Yang, X. Design of LCC-S Compensation Topology and Optimization of Misalignment Tolerance for Inductive Power Transfer. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 191309–191318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Cheng, K.W.E. A Compact and Integrated Magnetic Coupler Design With Cross-Coupling Elimination Utilizing LCC-S Compensation Network for Building Attached Photovoltaic Systems. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2023, 59, 8401205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yan, X.; He, H.; Yang, P.; Peng, Z.; Cui, H. Control Strategy for Vehicle Inductive Wireless Charging Based on Load Adaptive and Frequency Adjustment. Energies 2018, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Deng, J.; Li, S.; Mi, C.C. Comparison Study on SS and Double-Sided LCC Compensation Topologies for EV/PHEV Wireless Chargers. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 4429–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Hofmann, H.; Deng, J.; Mi, C. Output Power and Efficiency Sensitivity to Circuit Parameter Variations in Double-Sided LCC-Compensated Wireless Power Transfer System. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Charlotte, NC, USA, 15–19 March 2015; pp. 597–601. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.; Woo, S.; Lee, C.; Rhee, J.; Huh, S.; Ahn, S. Determination of Current Ratio to Minimize Power Losses of Coils in Wireless Power Transfer System with Double-Sided LCC Topology. In Proceedings of the 2022 Wireless Power Week (WPW), Bordeaux, France, 5–8 July 2022; pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Budhia, M.; Covic, G.A.; Boys, J.T. Design and Optimization of Circular Magnetic Structures for Lumped Inductive Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 3096–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, R.; Kolar, J.W. Inductive Power Transfer for Electric Vehicle Charging: Technical Challenges and Tradeoffs. IEEE Power Electron. Mag. 2016, 3, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.R.; Miller, J.M.; Daga, A.; Schrafel, P.C.; Wolgemuth, J. Which Way for Wireless Power: High Q or High k? In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE PELS Workshop on Emerging Technologies: Wireless Power Transfer (WoW), Knoxville, TN, USA, 4–6 October 2016; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Li, X.; Sun, Q.; Liao, Z.; Hu, A.P. Improving Magnetic Coupling Characteristics of Square Coupler ICPT System by Round Corner Design. Electr. Eng. 2020, 102, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharani, M.; Ravi, K. An Analytical Study for the Realization of Maximum Efficiency in Wireless Charging System Using a Circular Inductive Coil. In Proceedings of the 2023 Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies (i-PACT), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–10 December 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, X.-L.; Li, Q.; Dong, W.-H.; Liu, J.-M.; Ni, X. Influences of Coil Radius on Effective Transfer Distance in WPT System. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 125960–125968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Kim, J.; Park, Y.-J. Optimization and Design of Small Circular Coils in a Magnetically Coupled Wireless Power Transfer System in the Megahertz Frequency. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuah, C.M.; Danuor, P.; Moon, J.-I.; Jung, Y.-B. Novel Coil Design and Analysis for High-Power Wireless Power Transfer with Enhanced Q-Factor. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhia, M.; Boys, J.T.; Covic, G.A.; Huang, C.-Y. Development of a Single-Sided Flux Magnetic Coupler for Electric Vehicle IPT Charging Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; White, J.C.; Abraham, A.M.; Mi, C.C. Loosely Coupled Transformer Structure and Interoperability Study for EV Wireless Charging Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6356–6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshard, R.; Iruretagoyena, U.; Kolar, J.W. Comprehensive Evaluation of Rectangular and Double-D Coil Geometry for 50 kW/85 kHz IPT System. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2016, 4, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.; Choi, S. Optimization of Ferrite Core to Reduce the Core Loss in Double-D Pad of Wireless Charging System for Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 4–8 March 2018; pp. 1350–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Li, W.; Deng, Z.; Mi, C.C. A Power Relay System With Multiple Loads Using Asymmetrical Coil Design. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, C.; Cheng, C.; Deng, Z.; Chen, X.; Mi, C.C. A High-Efficiency and Long-Distance Power-Relay System With Equal Power Distribution. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wang, J.; Jing, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, P.; Fang, Z.; Zhou, Y.-G. Universal Wireless Powered Terminals for Robust Overhead Transmission Line Monitoring. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 3739–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 19363:2020; Electrically Propelled Road Vehicles—Magnetic Field Wireless Power Transfer—Safety and Interoperability Requirements. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Mohan, S.S.; del Mar Hershenson, M.; Boyd, S.P.; Lee, T.H. Simple Accurate Expressions for Planar Spiral Inductances. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1999, 34, 1419–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, T.; Perrottet, M.; Nguyen, V.; Perriard, Y. Contactless Power and Information Transmission. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väisänen, V.; Hiltunen, J.; Nerg, J.; Silventoinen, P. AC Resistance Calculation Methods and Practical Design Considerations When Using Litz Wire. In Proceedings of the IECON 2013—39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013; pp. 368–375. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Hu, M. Optimisation Design of Real-Time Wireless Power Supply System Overhead High-Voltage Power Line. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 13, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Symbol | Parameter | LCC-LCC | LCL-LCL | SS | LCC-S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UAB | First-order rms value of input voltage | ≤250 V | |||
| f | Resonance frequency | 83 kHz | |||
| P | Designed power | ~640 W | |||
| Lp | Self-inductance of the transmitting coil | ||||
| Ls | Self-inductance of the receiving coil | ||||
| Rp | AC resistance of the transmitting coil | ||||
| Rs | AC resistance of the receiving coil | ||||
| Cp | Primary-side series compensation capacitor | 14.1 nF | / | 12.9 nF | 14.1 nF |
| Cs | Secondary-side series compensation capacitor | 14.1 nF | / | 12.9 nF | 12.9 nF |
| L1 | Primary-side compensation inductance | / | |||
| L2 | Secondary-side compensation inductance | / | / | ||
| R1 | AC resistance of L1 | / | |||
| R2 | AC resistance of L2 | / | / | ||
| C1 | Primary-side parallel compensation capacitor | 147 nF | 12.9 nF | / | 147 nF |
| C2 | Secondary-side parallel compensation capacitor | 147 nF | 12.9 nF | / | / |
| Coil Shape | c1 | c2 | c3 | c4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular coil | 1.00 | 2.46 | 0.00 | 0.20 |
| Rectangular coil | 1.27 | 2.07 | 0.18 | 0.13 |
| Parameter | f0 | Lp/Ls | Rp/Rs | Cp,s | L1,2 | C1,2 | m | N | Dw | Sw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 83 kHz | 14.1 nF | 147 nF | 2 | 17 | 2 mm | 2 mm |
| Reference | Year | Compensation Topology | Frequency | Air Gap or k | Efficiency (%) | Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [11] | 2019 | LCL-S | 547.7 kHz | 700~1600 mm | 15~32.5 | 16.7 W (1500 mm) |
| [42] | 2019 | SS | 450 kHz | 1175 mm | 37 | 60 W |
| [47] | 2019 | S-S-S-S | 4.02 MHz | 900~1100 mm | 22~46 | 30.5 W (900 mm) |
| [22] | 2020 | LCC-S | 60 kHz | 0.293~0.5 | 73~86 | 100 W |
| [3] | 2022 | LCC-LCC | 85 kHz | 0.08~0.18 | 83~87.55 | 3.3 kW |
| [23] | 2023 | LCC-S | 200 kHz | 34 mm | 83.4 | 160 W |
| [19] | 2024 | LCC-LCC | 100 kHz | 100 mm | 93.4~91 | 100 W |
| This paper | 2024 | LCC-S | 83 kHz | 200 mm | 79~86.6 | 640 W |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Zheng, M.; Yan, X. Design of Inductive Power Transfer Charging System with Weak Coupling Coefficient. Energies 2024, 17, 3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17153836
Chen Y, Yang S, Zheng M, Yan X. Design of Inductive Power Transfer Charging System with Weak Coupling Coefficient. Energies. 2024; 17(15):3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17153836
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuhang, Shichun Yang, Mengchao Zheng, and Xiaoyu Yan. 2024. "Design of Inductive Power Transfer Charging System with Weak Coupling Coefficient" Energies 17, no. 15: 3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17153836
APA StyleChen, Y., Yang, S., Zheng, M., & Yan, X. (2024). Design of Inductive Power Transfer Charging System with Weak Coupling Coefficient. Energies, 17(15), 3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17153836






