Optimal Electrification Using Renewable Energies: Microgrid Installation Model with Combined Mixture k-Means Clustering Algorithm, Mixed Integer Linear Programming, and Onsset Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Scientific Models of Microgrid Technologies
2.2. Scientific Methods for Microgrid Deployment
2.2.1. Clustering Techniques
k-Means Clustering Model
Elbow Method
2.2.2. Haversine Method
2.2.3. Open-Source Spatial Planning for Electrification Method: Onsset
2.3. Bibliographical Reviews
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
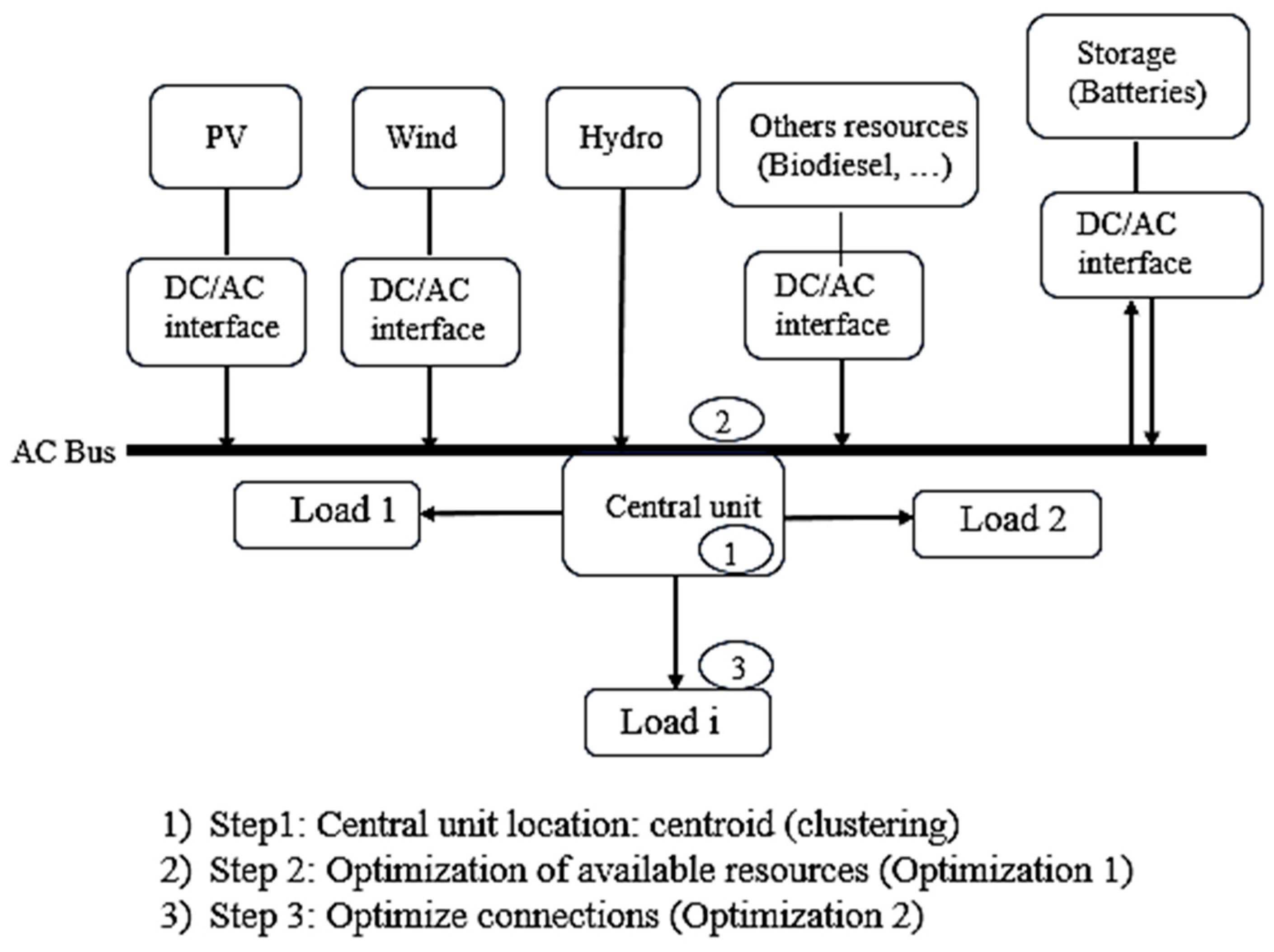
3.2.1. Microgrid System Model
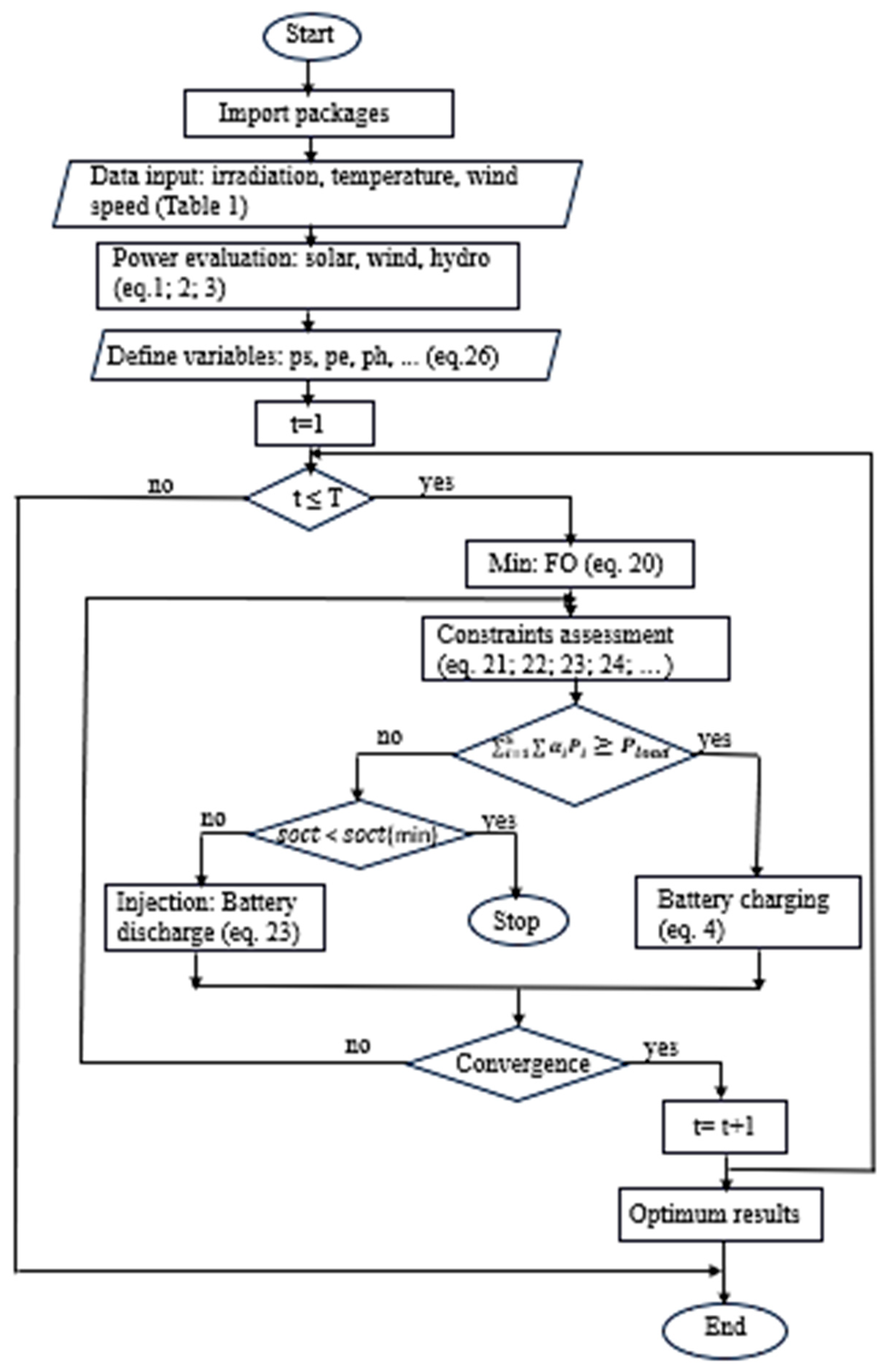
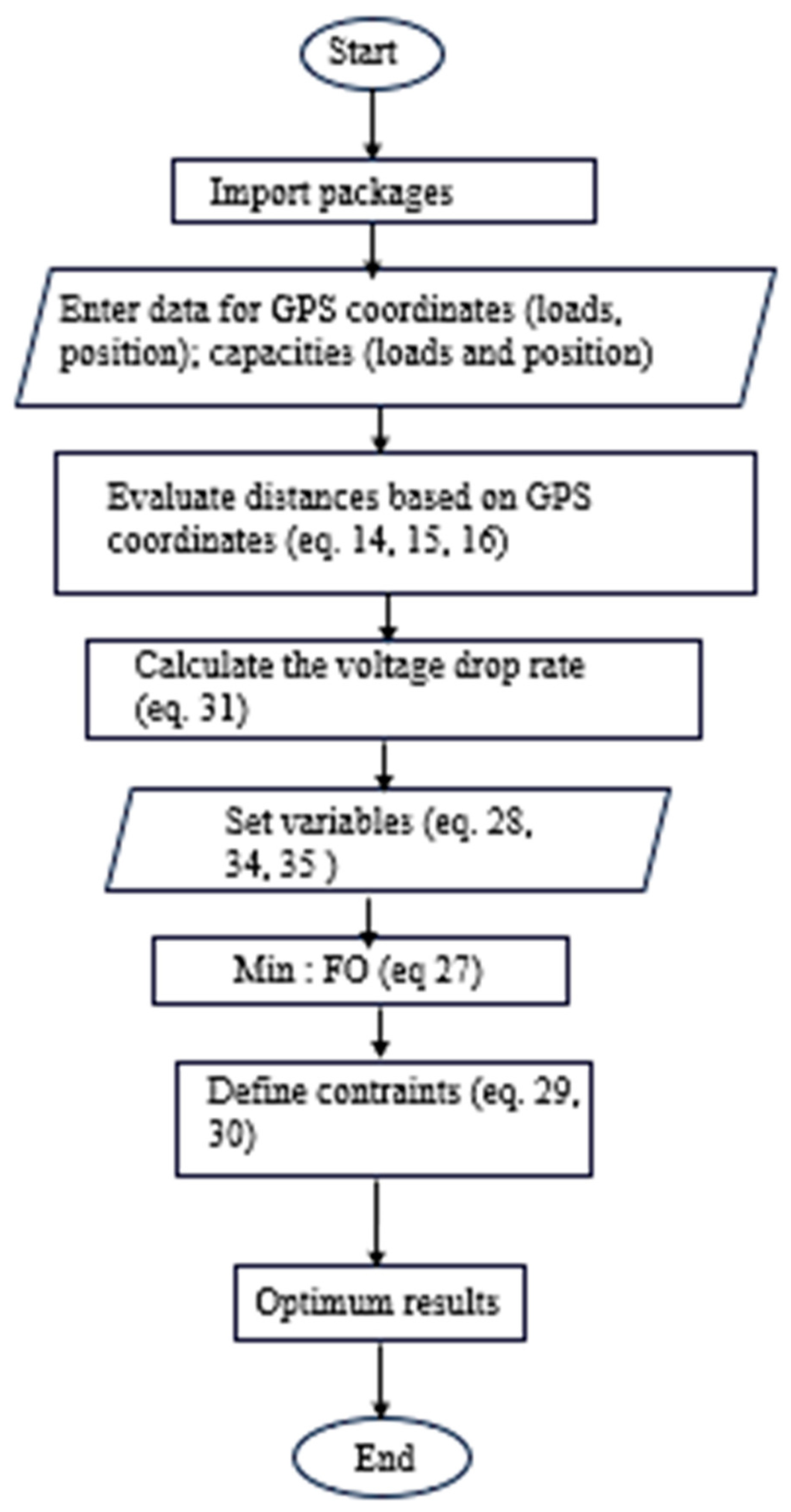
3.2.2. Optimizations Problem Formulation
- Enter data for each vector
- Initialize the position of the centers:
- Calculate mk averages of vectors in cluster k
- -
- Until there are no more changes in the mk
- -
- Assign each Vi point to the nearest cluster
- -
- Calculate new mk
- -
- End As long as
3.2.3. Data
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Optimization Results
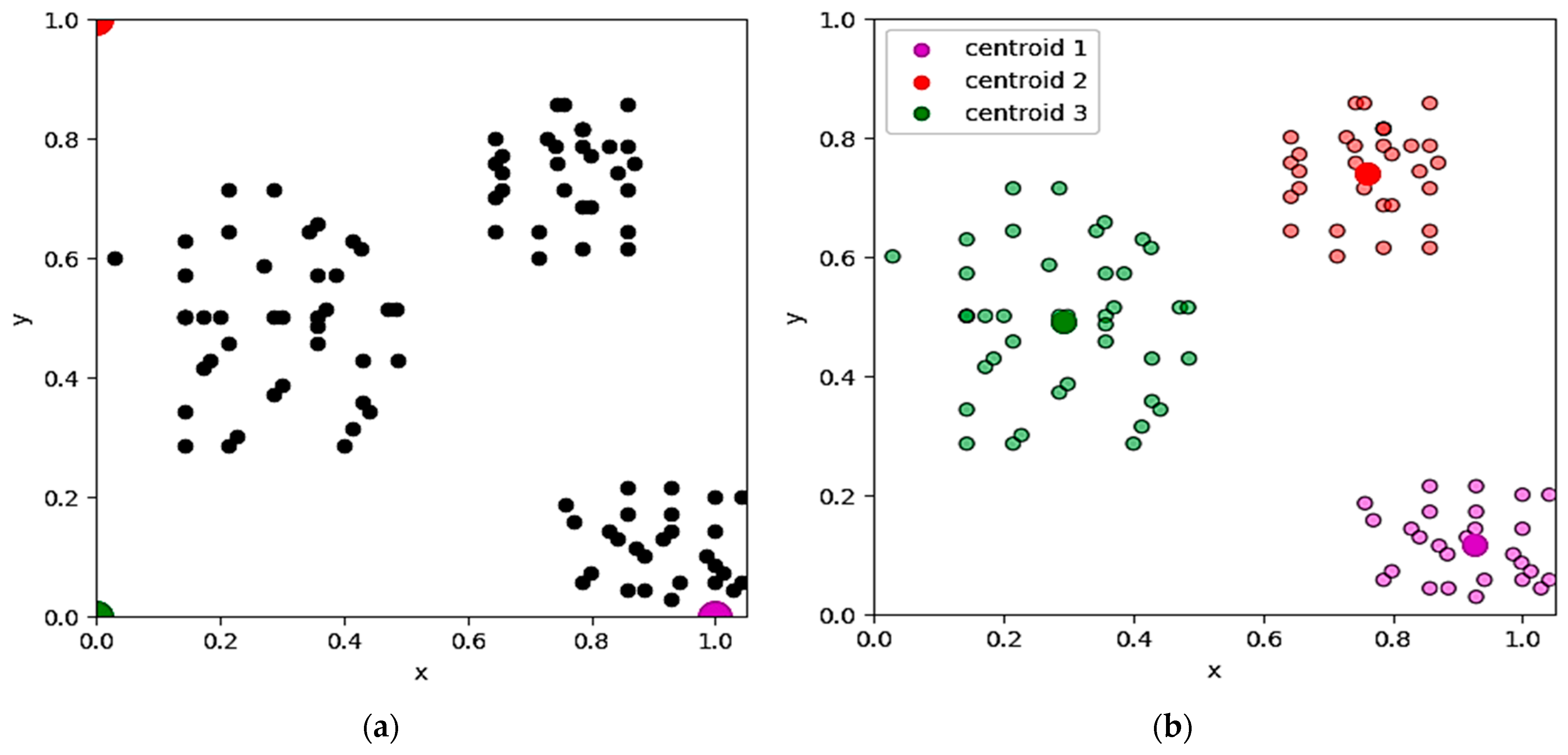
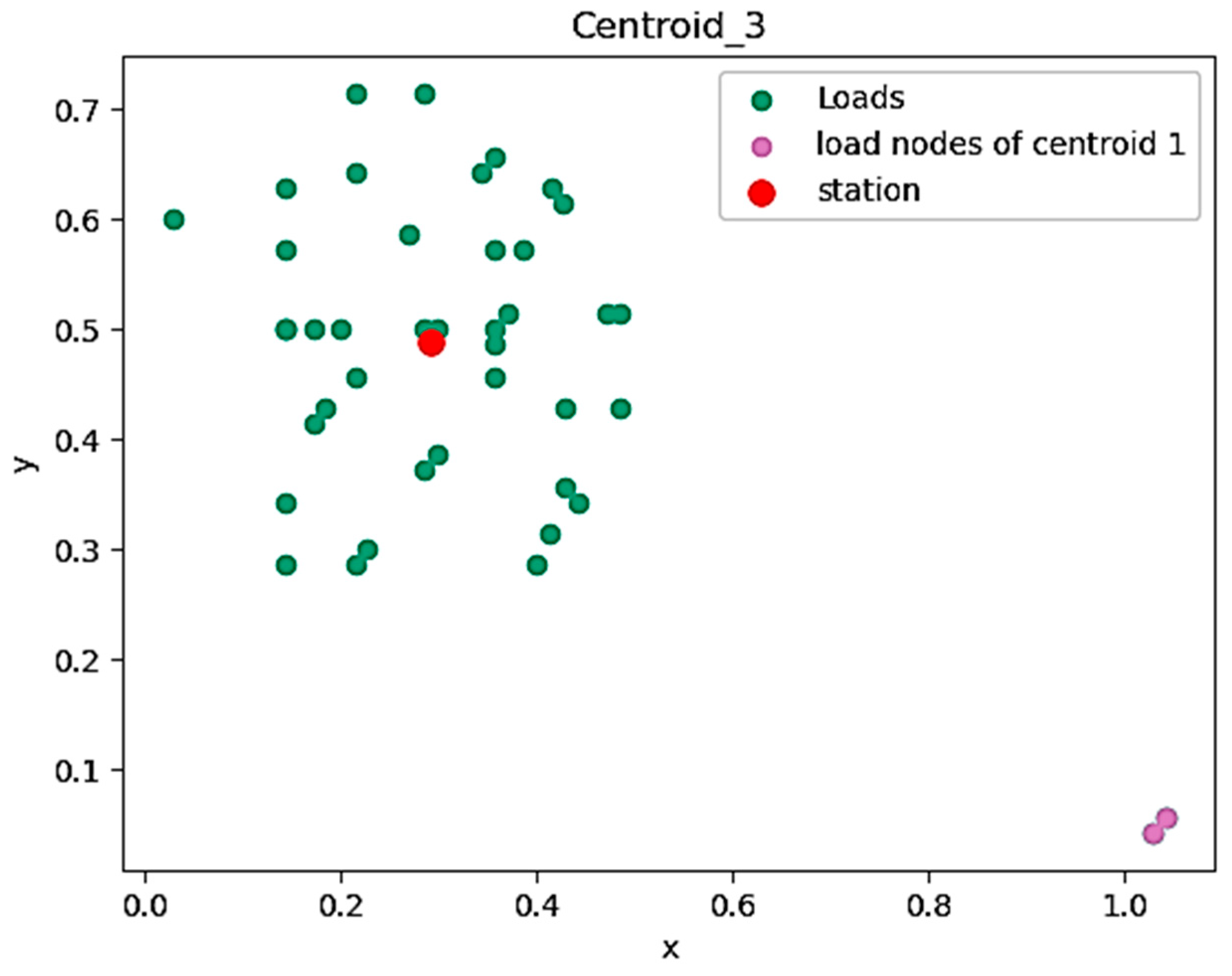
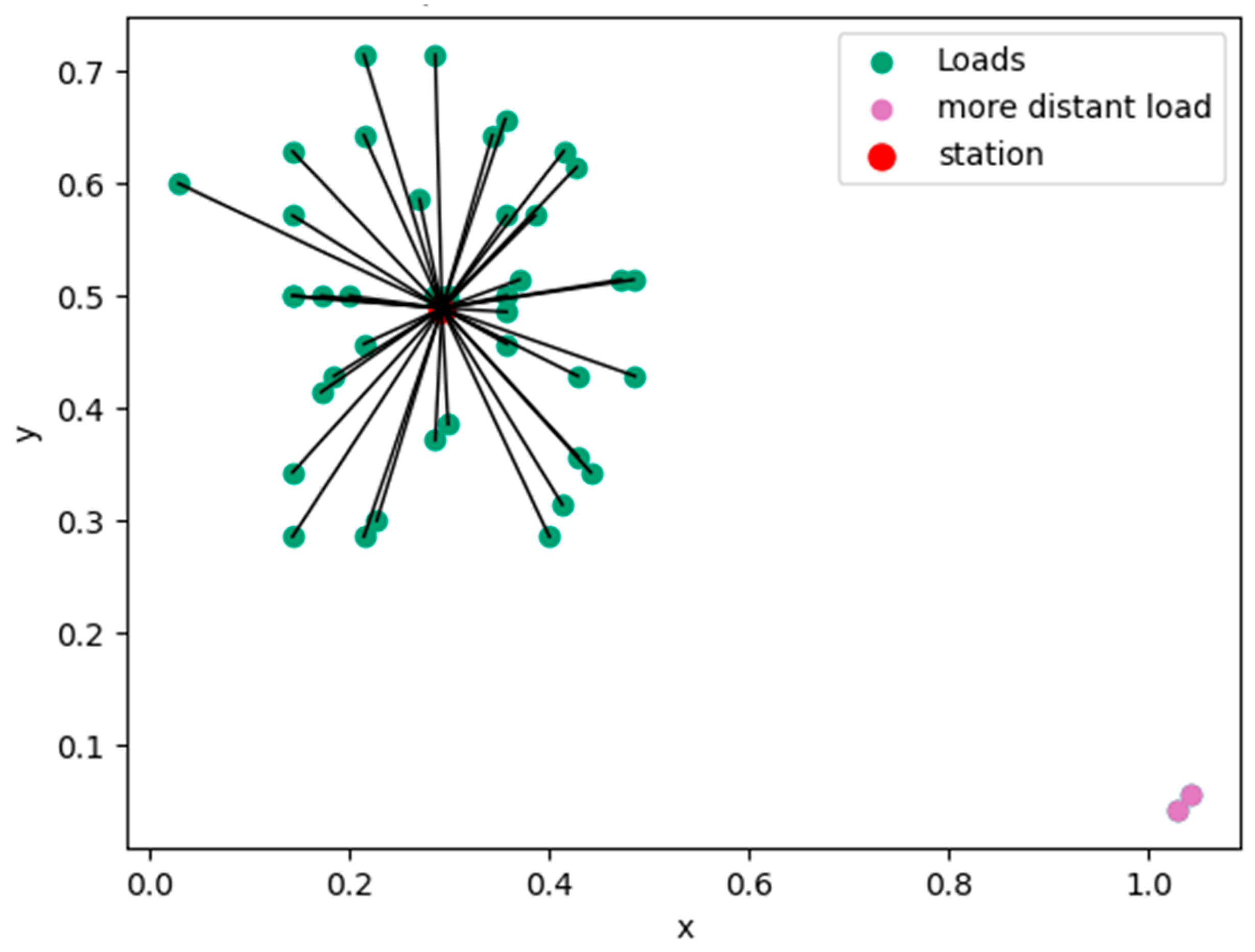
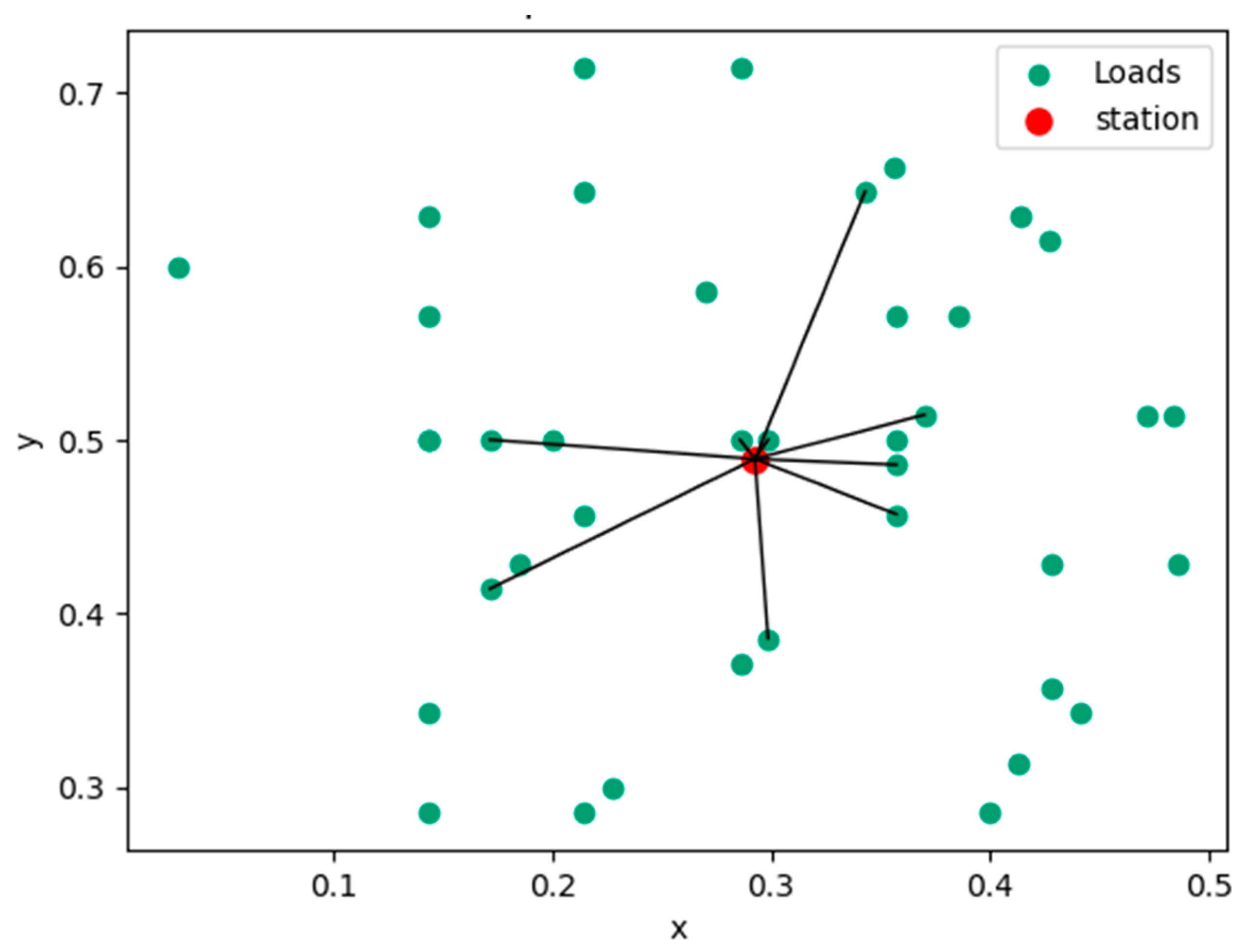
4.1.1. Results for Cluster Formation: Physical Allocation of Microgrid Centers
4.1.2. Renewable Energy Resource Availability Results
4.1.3. Optimization Results for Technology Selection
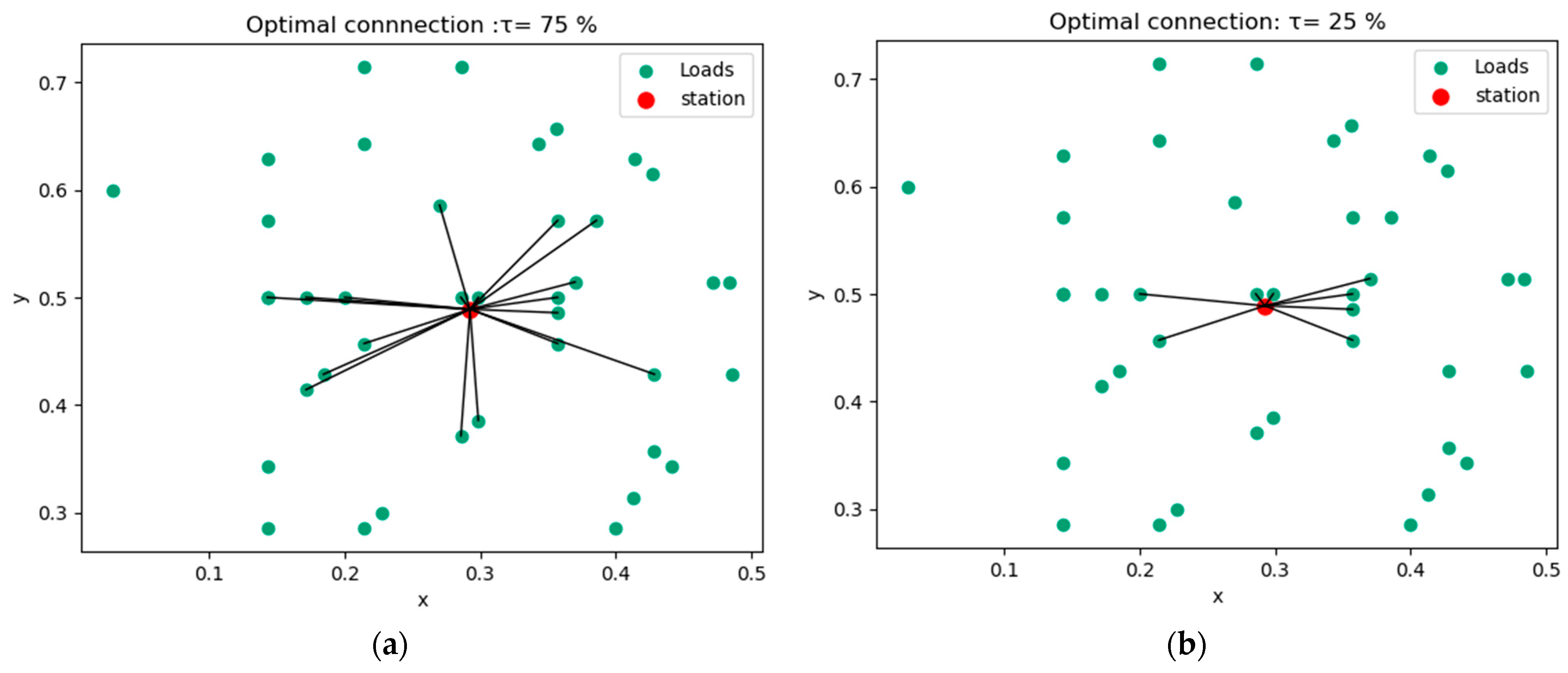
4.1.4. Capacity and Connection Optimization Results
- (a)
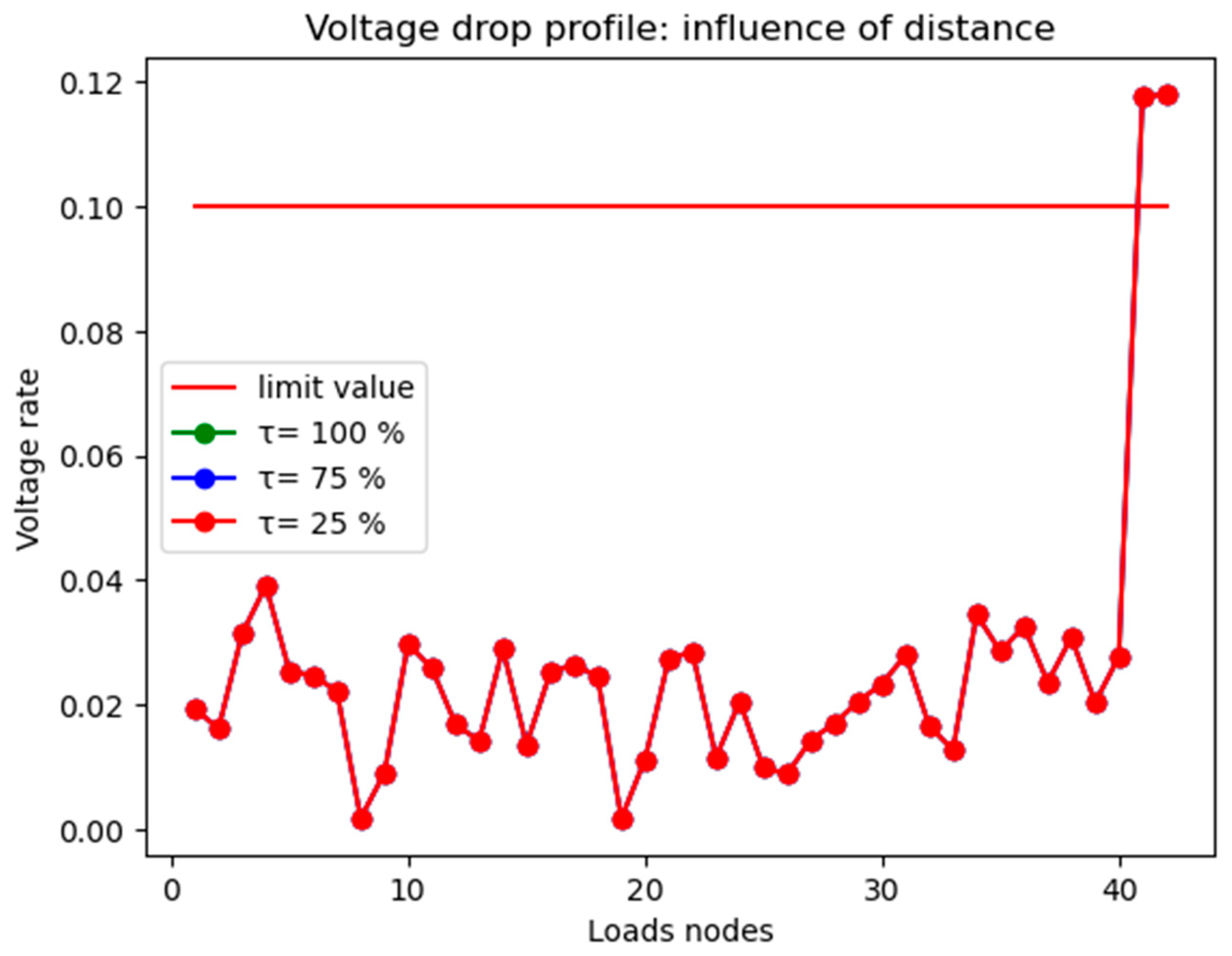
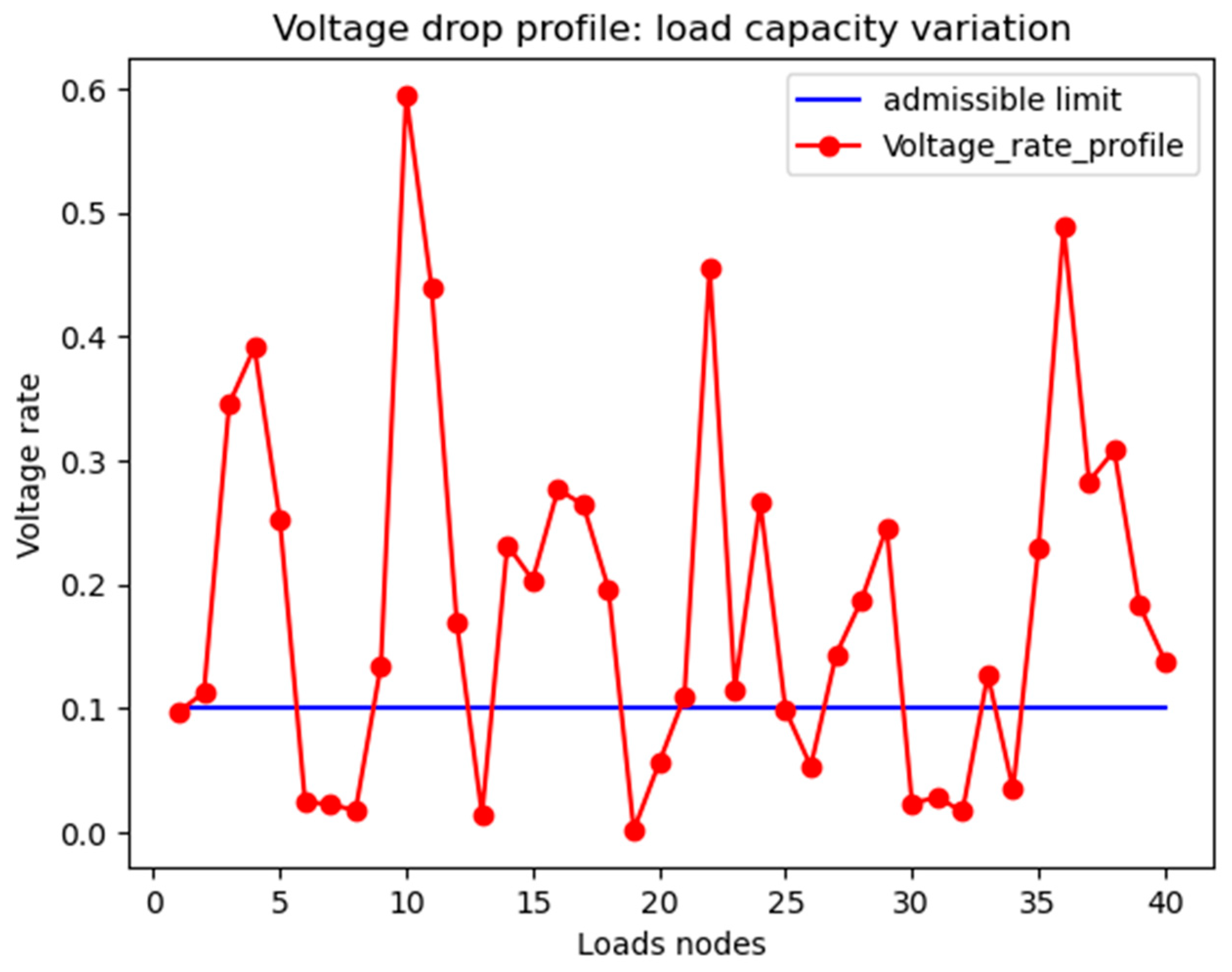
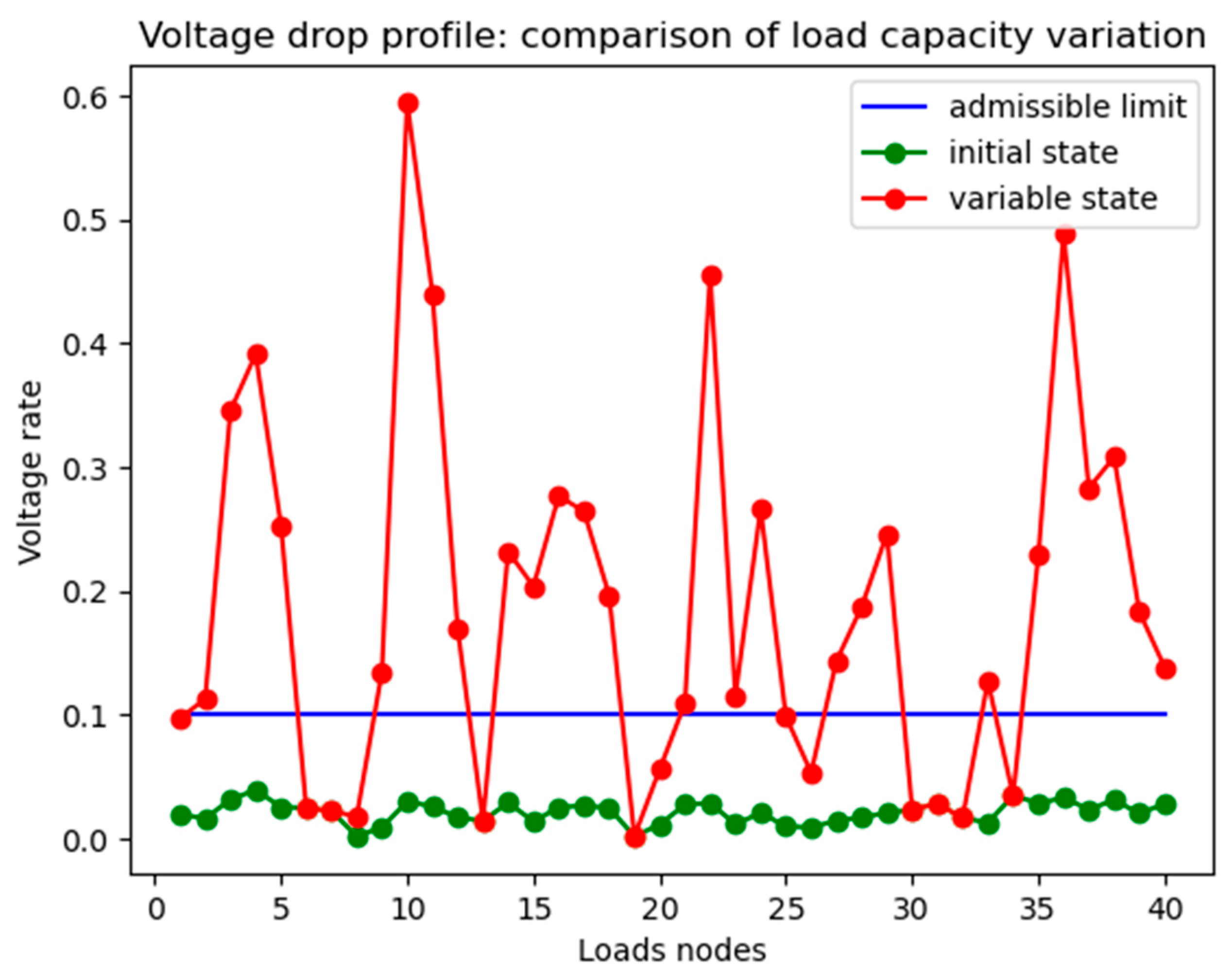
- Scenario 1: results for voltage rate profile/distance
- (b)
- Scenario 2: influence of load capacity
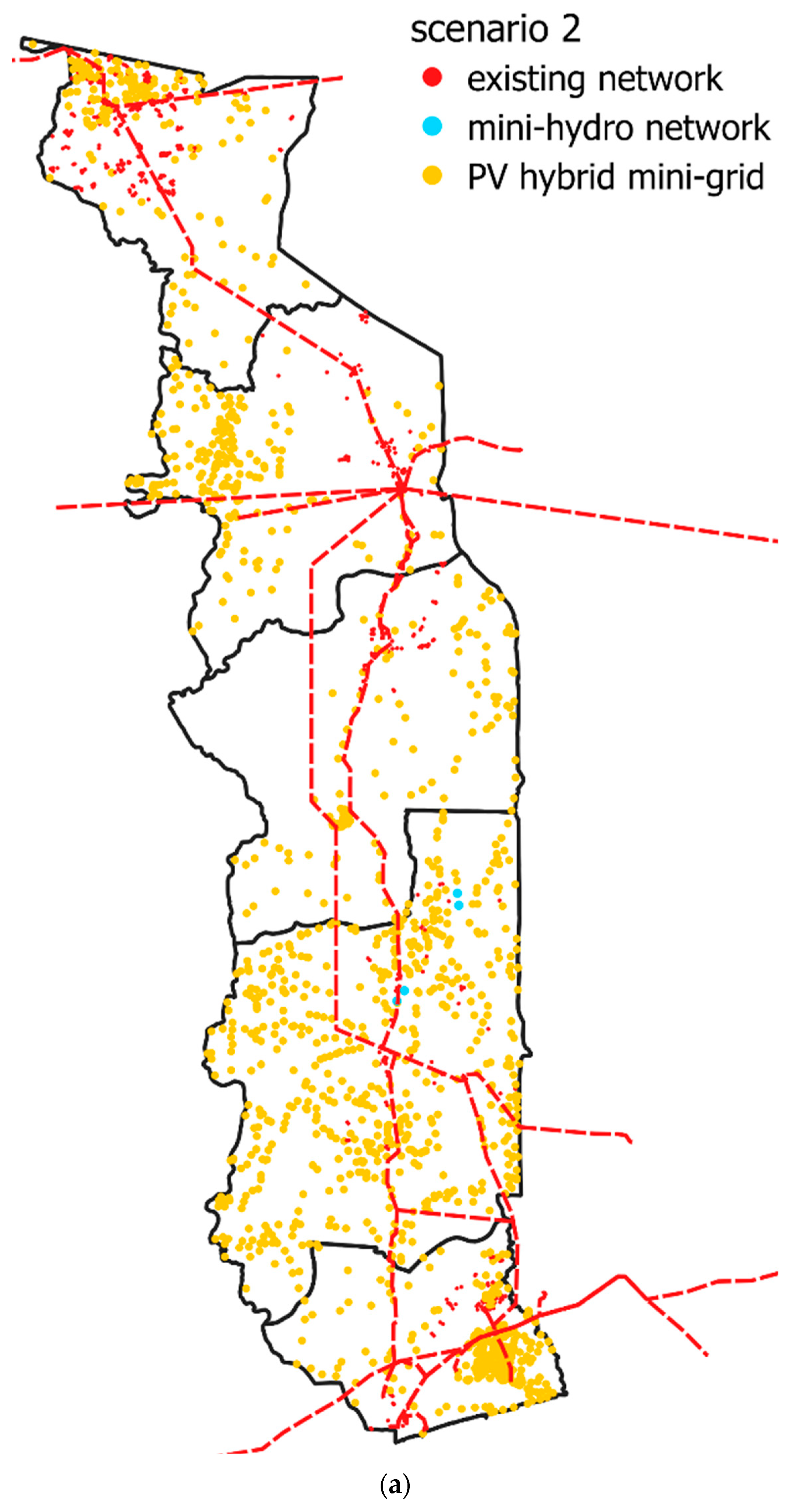
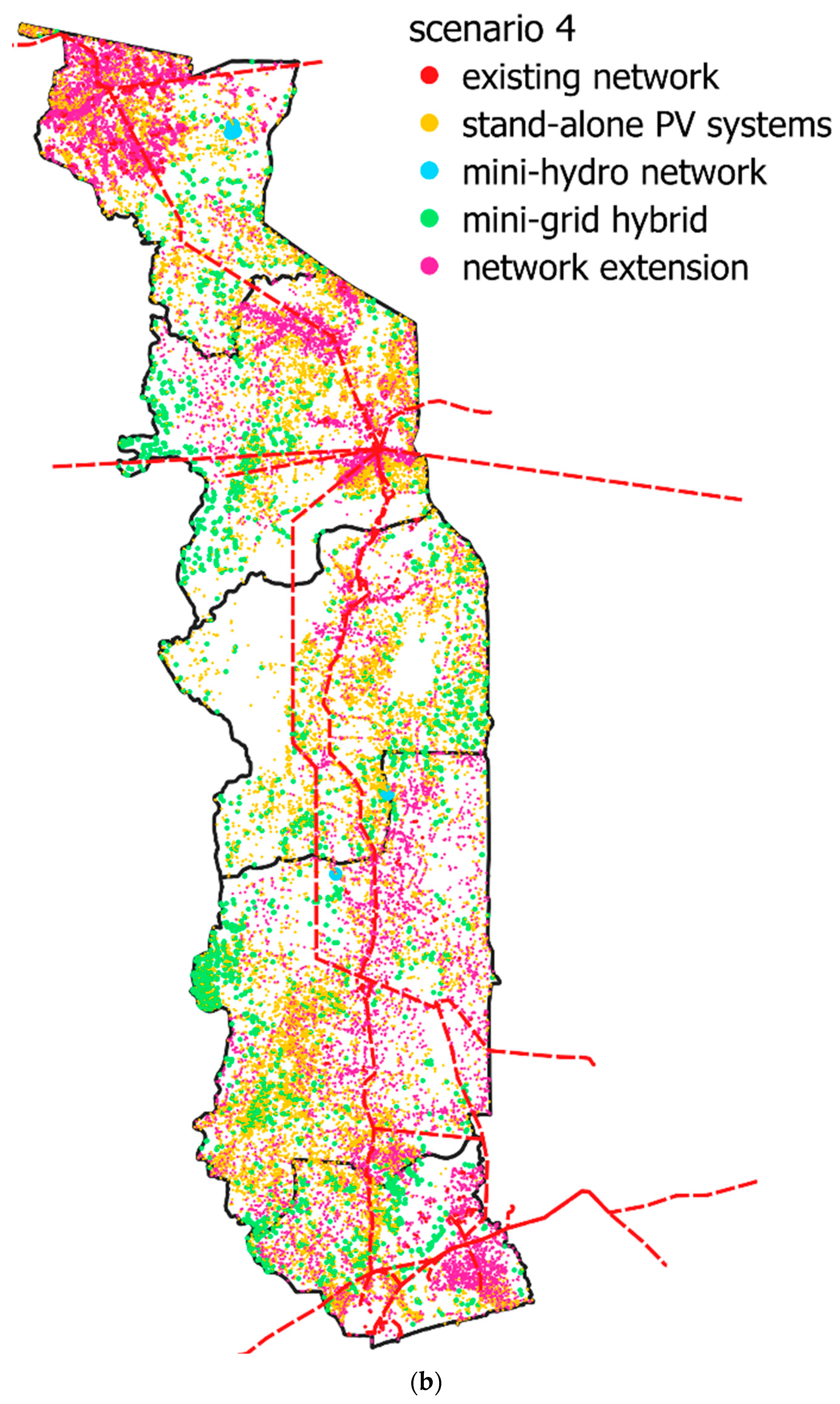
4.1.5. Results of Microgrid Formation Evaluation Studies in Togo
4.2. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| solar power variable | |
| charging (80%) and discharging (20%) rates | |
| performance | |
| performance rate | |
| area | |
| temperature differential | |
| decision variable | |
| standard temperature | |
| battery storage at t + 1 | |
| battery storage at t | |
| battery power | |
| number of batteries | |
| battery capacity | |
| battery volatge | |
| battery efficiency | |
| wind power | |
| air density | |
| area swept by the turbine | |
| wind power efficiency | |
| wind decision variable | |
| probability density | |
| scale factor | |
| wind speed | |
| standard deviation | |
| average speed | |
| average power | |
| gamma function | |
| hydroelectric power | |
| density of water | |
| acceleration | |
| water flow rate | |
| waterfall height | |
| hydroelectric efficiency | |
| i | index |
| load vector matrix | |
| vector i | |
| , | latitudes |
| , | longitudes |
| j | substation index |
References
- Antonanzas-Torres, F.; Antonanzas, J.; Blanco-Fernandez, J. State-of-the-Art of Mini Grids for Rural Electrification in West Africa. Energies 2021, 14, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, P.; Châtaigner, J.M. Un Défi pour la Planète: Les Objectifs de Développement Durable en Débat; Casalini Libri: Fiesole, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, R.B.; Karimu, A. Renewable electricity and sustainable development goals in the EU. World Dev. 2020, 125, 104693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhana, K.; Kadirgama, K.; Mahamude, A.S.F.; Mica, M.T. Energy consumption, environmental impact, and implementation of renewable energy resources in global textile industries: An overview towards circularity and sustainability Nano-fluid Technology View project NASA HUNCH-Sleeping Rack for Astronauts View pro. Mater. Circ. Econ. 2022, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.S.; Ali, Z.M.; Bilal, M.; Sohail, H.M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Environmental impacts and risk factors of renewable energy paradigm—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 33516–33526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedzro, K.S.A.; Lamadrid, A.J.; Zuluaga, L.F. Allocation of resources using a microgrid formation approach for resilient electric grids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 33, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muqeet, H.A.; Javed, H.; Akhter, M.N.; Shahzad, M.; Munir, H.M.; Nadeem, M.U.; Sabir, S.; Bukhari, H.; Huba, M. Sustainable Solutions for Advanced Energy Management System of Campus Microgrids: Model Opportunities and Future Challenges. Sensors 2022, 22, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Naeem, M.; Iqbal, M.; Qaisar, S.; Anpalagan, A. A compendium of optimization objectives, constraints, tools and algorithms for energy management in microgrids. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1664–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariam, L.; Basu, M.; Conlon, M.F. A Review of Existing Microgrid Architectures. J. Eng. 2013, 2013, 937614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ismail, F.S. DC Microgrid Planning, Operation, and Control: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 36154–36172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diego, S. Office of Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability Smart Grid R&D Program DOE Microgrid Workshop Report; U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Electricity: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Premadasa, P.N.D.; Silva, C.M.M.R.S.; Chandima, D.P.; Karunadasa, J.P. A multi-objective optimization model for sizing an off-grid hybrid energy microgrid with optimal dispatching of a diesel generator. J. Energy Storage 2023, 68, 107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viteri, J.P.; Henao, F.; Cherni, J.; Dyner, I. Optimizing the insertion of renewable energy in the off-grid regions of Colombia. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedzro, K.S.A.; Salami, A.A.; Agbessi, P.A.; Kodjo, M.K. Comparative Study of Wind Energy Potential Estimation Methods for Wind Sites in Togo and Benin (West Sub-Saharan Africa). Energies 2022, 15, 8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, S. Optimised model for community-based hybrid energy system. Renew. Energy 2007, 32, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Das, B.K.; Hasan, M. Integrated off-grid hybrid renewable energy system optimization based on economic, environmental, and social indicators for sustainable development. Energy 2022, 250, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.R.; Li, J.Q.; Han, Y.; Niu, B.; Liu, L.; Zhang, B. An improved brain storm optimization for a hybrid renewable energy system. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 49513–49526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, M.; Wang, R.; Zha, Y.; Zhang, T. Multi-objective optimization of hybrid renewable energy system using an enhanced multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. Energies 2017, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, L.; Zhou, W. A novel optimization sizing model for hybrid solar-wind power generation system. Sol. Energy 2007, 81, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaked, D.K.; Gopal, Y.; Birla, D. Battery Charging Optimization of Solar Energy based Telecom Sites in India. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2019, 9, 5041–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash Kumar, K.; Saravanan, B. Recent techniques to model uncertainties in power generation from renewable energy sources and loads in microgrids-A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 71, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talari, S.; Yazdaninejad, M.; Haghifam, M.R. Stochastic-based scheduling of the microgrid operation including wind turbines, photovoltaic cells, energy storages and responsive loads. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2015, 9, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakariazadeh, A.; Jadid, S.; Siano, P. Smart microgrid energy and reserve scheduling with demand response using stochastic optimization. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 63, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labeeuw, W.; Deconinck, G. Residential Electrical Load Model based on Mixture Model Clustering and Markov Models. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syakur, M.A.; Khotimah, B.K.; Rochman, E.M.S.; Satoto, B.D. Integration K-Means Clustering Method and Elbow Method For Identification of The Best Customer Profile Cluster. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 336, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umargono, E.; Suseno, J.E.; Gunawan, S.V. K-Means Clustering Optimization using the Elbow Method and Early Centroid Determination Based-on Mean and Median. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Seminar on Science and Technology (ISSTEC 2019), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 25 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gunawan, W.; Kaburuan, E.R.; Rudianto, B.; Puspitasari, A.; Sudrajat, B.; Erri, D.; Hidayah, A.N.; Chowanda, A.; Sudha, S. Design and build of searching system for the nearest fish shop on an ornamental fish market website using the haversine. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2023, 101, 6257–6263. [Google Scholar]
- Jaya, N.; Asst, S.; Professor, A. Pragmatic investigations to smart dusts location appraisal precisely using machine learning. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2023, 31, 6301–6309. [Google Scholar]
- Peña Balderrama, J.G.; Balderrama Subieta, S.; Lombardi, F.; Stevanato, N.; Sahlberg, A.; Howells, M.; Colombo, E.; Quoilin, S. Incorporating high-resolution demand and techno-economic optimization to evaluate micro-grids into the Open Source Spatial Electrification Tool (OnSSET). Energy Sustain. Dev. 2020, 56, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyème, K.; Yao, B.; Sedzro, K.S.; Aragah, M.; Pidéname, T.; Yendoubé, L. Global atlas of renewables energies: A complementary to an optimal electrification planning method at short and long terms–Case study of togo. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Res. Technol. 2023, 12, 18–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, K.; Wang, T.; Han, C.; Xie, J.; Ma, Y.; Peng, R. A Review of Optimization of Microgrid Operation. Energies 2021, 14, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Roche, R.; Miraoui, A. Microgrid sizing with combined evolutionary algorithm and MILP unit commitment. Appl. Energy 2017, 188, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisio, A.; Rikos, E.; Glielmo, L. A Model Predictive Control Approach to Microgrid Operation Optimization. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, W.; Cai, J.; Hong, B.; Wang, C. A two-stage optimal planning and design method for combined cooling, heat and power microgrid system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 74, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Silva, D.P.; Queiroz, M.D.; Fardin, J.F.; Sales, J.L.F.; Orlando, M.T.D. Hybrid modeling of energy storage system and electrical loads in a pilot-microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Industry Applications (INDUSCON), Sao Paulo, Brazil, 12–14 November 2018; pp. 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- Mah, A.X.Y.; Ho, W.S.; Hassim, M.H.; Hashim, H.; Ling, G.H.T.; Ho, C.S.; Muis, Z.A. Optimization of a standalone photovoltaic-based microgrid with electrical and hydrogen loads. Energy 2021, 235, 121218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saadi, M.; Al-Greer, M.; Short, M.; Štreimikien, D.; Baležentis, T. Strategies for controlling microgrid networks with energy storage systems: A review. Energies 2021, 14, 7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, A.A.; Keypour, R. Participation of responsive electrical consumers in load smoothing and reserve providing to optimize the schedule of a typical microgrid. Energy Syst. 2020, 11, 885–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiswariya, L.; Imthias Ahamed, T.P.; Mohammed, S.S. Optimal Microgrid Battery Scheduling Using Simulated Annealing. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Power Electronics and Renewable Energy Applications (PEREA), Kannur, India, 27–28 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rutenbar, R.A. Simulated annealing algorithms: An overview. IEEE Circuits Devices Mag. 1989, 5, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhuang, W. Stochastic modeling and optimization in a microgrid: A survey. Energies 2014, 7, 2027–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikmehr, N.; Najafi-Ravadanegh, S.; Khodaei, A. Probabilistic optimal scheduling of networked microgrids considering time-based demand response programs under uncertainty. Appl. Energy 2017, 198, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, J. Artificial intelligence for operation and control: The case of microgrids. Electr. J. 2021, 34, 106890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonori, S.; Paschero, M.; Mascioli, F.M.F.; Rizzi, A. Optimization strategies for Microgrid energy management systems by Genetic Algorithms. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 86, 105903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, T.; Mohamed, A.; Sopian, K. Optimization of a PV/wind micro-grid for rural housing electrification using a hybrid iterative/genetic algorithm: Case study of Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia. Energy Build. 2012, 47, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Ni, Z. A computationally efficient optimization approach for battery systems in islanded microgrid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 9, 6489–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenfen, D.; Finardi, C. A mixed integer linear programming model for the energy management problem of microgrids. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 122, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigalo, M.B.; Pillai, A.C.; Das, S.; Abusara, M. An energy management system for the control of battery storage in a grid-connected microgrid using mixed integer linear programming. Energies 2021, 14, 6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawoud, S.M.; Lin, X.; Okba, M.I. Hybrid renewable microgrid optimization techniques: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2039–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, L.; Rubino, G.; Esempio, R. Linear Programming-Based Power Management for a Multi-Feeder Ultra-Fast DC Charging Station. Energies 2023, 16, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakumar, R.; Shetty, P.S.; Ashenayi, K. Linear programming approach to the design of integrated renewable energy systems for developing countries. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1986, EC-1, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakumar, R.; Abouzahr, I.; Ashenayi, K. A knowledge-based approach to the design of integrated renewable energy systems. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1992, 7, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabares, A.; Muñoz-Delgado, G.; Franco, J.F.; Arroyo, J.M.; Contreras, J. Multistage reliability-based expansion planning of AC distribution networks using a mixed-integer linear programming model. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 138, 107916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twaha, S.; Ramli, M.A.M. A review of optimization approaches for hybrid distributed energy generation systems: Off-grid and grid-connected systems. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, O.K.; Ochiegbu, C.V.; Ofosu, E.A.; Gyamfi, S. A review of hybrid renewable energies optimisation: Design, methodologies, and criteria. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2023, 42, 648–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezkallah, M.; Chandra, A.; Singh, B.; Singh, S. Microgrid: Configurations, control and applications. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 10, 1290–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badal, F.R.; Das, P.; Sarker, S.K.; Das, S.K. A survey on control issues in renewable energy integration and microgrid. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2019, 4, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.; Ferdowsi, M.; Shamsi, P.; Dagli, C.H. Modeling and simulation of microgrid. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 114, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.S.; Saif Ur Rahman, M.; AL-Sunni, F.M. Review of microgrid architectures-a system of systems perspective. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2015, 9, 1064–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.M.; Ashraf, I.; Fernandez, E. Efficient two-layer rural electrification planning and techno-economic assessment integrating renewable sources. Energy Storage 2022, 4, e314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Afif, R.; Ayed, Y.; Maaitah, O.N. Feasibility and optimal sizing analysis of hybrid renewable energy systems: A case study of Al-Karak, Jordan. Renew. Energy 2023, 204, 229–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

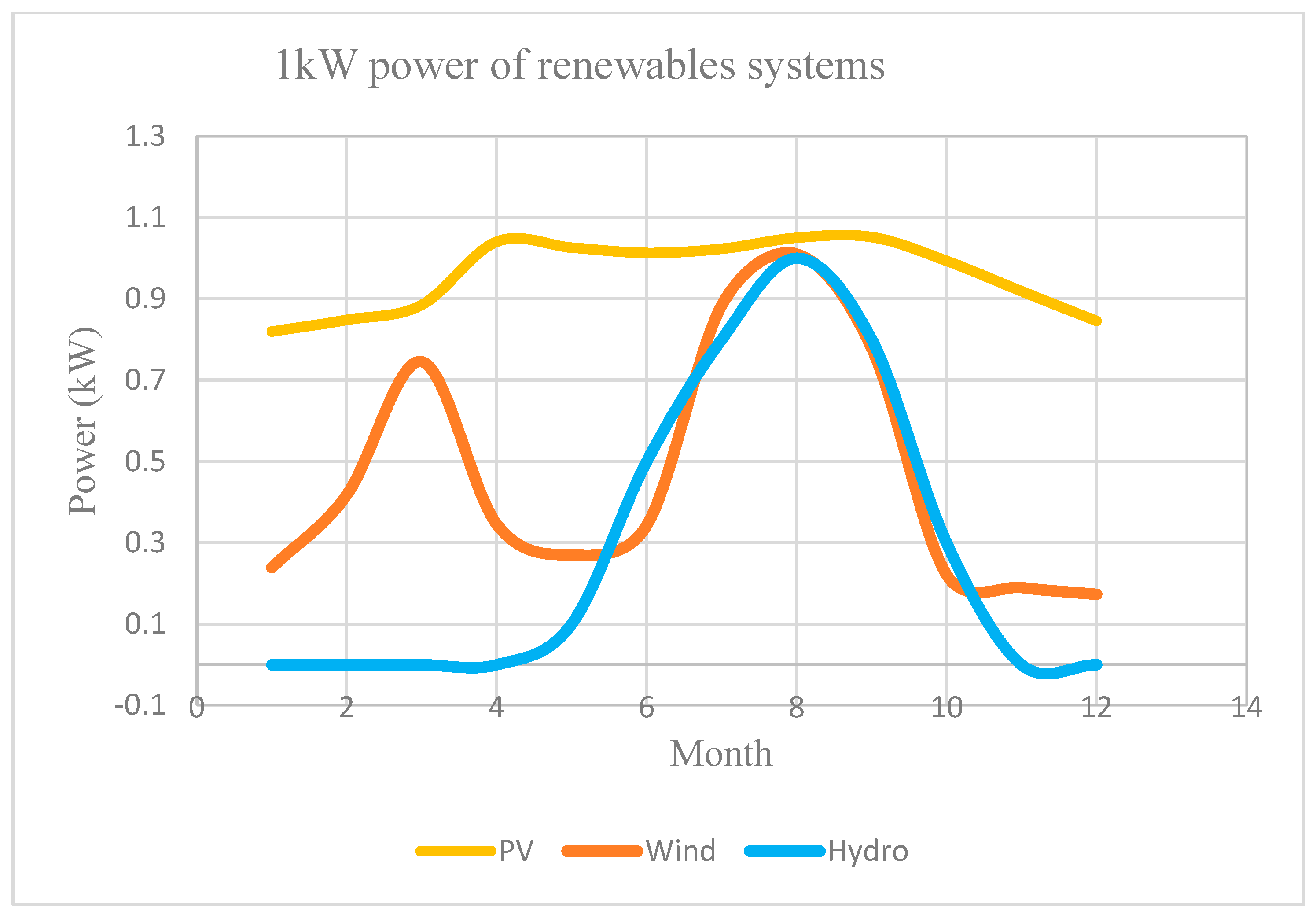
| Months | Solar Radiation (W/m2) | Temperature (Degrees) | Relative Humidity (%) | Wind Speed (m/s) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | |||||||||
| Jan | 85.46 | 115.71 | 99.01 | 5.87 | 26.12 | 28.41 | 27.59 | 0.59 | 60.56 | 85.62 | 75.25 | 6.92 | 2.04 | 4.45 | 3.27 | 0.68 |
| Fev | 85.98 | 113.63 | 103.63 | 6.95 | 27.58 | 28.57 | 28.05 | 0.23 | 69.75 | 85.19 | 80.92 | 2.97 | 2.21 | 5.17 | 3.94 | 0.76 |
| Mar | 84.98 | 122.43 | 108.85 | 9.69 | 27.83 | 28.96 | 28.38 | 0.23 | 78.44 | 86.31 | 81.99 | 1.89 | 3.99 | 6.11 | 4.78 | 0.57 |
| Apr | 109.64 | 137.14 | 127.32 | 7.0 | 26.95 | 28.38 | 27.67 | 0.46 | 78.31 | 88.31 | 83.72 | 2.35 | 1.86 | 5.49 | 3.7 | 0.91 |
| May | 108.89 | 132.91 | 126.36 | 4.72 | 26.49 | 28.11 | 27.41 | 0.41 | 76.19 | 88.62 | 85.21 | 2.59 | 1.91 | 4.47 | 3.41 | 0.56 |
| June | 112.42 | 128.5 | 121.95 | 3.63 | 25.09 | 27.42 | 26.25 | 0.73 | 79.0 | 92.88 | 87.34 | 3.28 | 1.9 | 5.6 | 3.69 | 0.85 |
| Jul | 117.48 | 129.11 | 123.56 | 2.93 | 24.44 | 25.9 | 25.10 | 0.36 | 82.19 | 90.81 | 87.35 | 2.33 | 3.42 | 6.55 | 5.06 | 0.66 |
| Aug | 117.97 | 134.07 | 127.02 | 3.74 | 23.64 | 25.35 | 24.34 | 0.46 | 82.62 | 92.31 | 87.89 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 7.82 | 5.29 | 1.36 |
| Sep | 125.77 | 140.23 | 134.24 | 3.19 | 24.95 | 25.87 | 25.45 | 0.24 | 82.88 | 91.5 | 87.28 | 2.18 | 3.26 | 6.55 | 4.85 | 0.88 |
| Oct | 113.06 | 133.61 | 125.49 | 4.72 | 25.17 | 27.4 | 26.32 | 0.63 | 84.62 | 90.69 | 87.60 | 1.55 | 2.16 | 5.55 | 3.19 | 0.89 |
| Nov | 106.05 | 122.58 | 114.64 | 4.22 | 26.64 | 27.83 | 27.24 | 0.3 | 79.44 | 87.0 | 83.24 | 1.78 | 1.65 | 4.77 | 3.03 | 0.71 |
| Dec | 90.72 | 111.33 | 103.36 | 4.46 | 25.9 | 27.8 | 27.01 | 0.35 | 61.62 | 86.62 | 78.24 | 6.64 | 1.62 | 4.3 | 2.94 | 0.61 |
| Indicators | Min | Max | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data | 100 | 0.028 | 0.9 | 0.455 | 0.25 |
| Costs/Systems | PV (USD/kW) | Batteries/6 V (USD/Unit) | Wind (USD/kW) | Hydraulic (USD/kW) | Biodiesel (USD/kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Installation cost | 800–2000 | 900–1300 | 1800 | 2000 | 650 |
| Maintenance and operating costs | 8–200 | 9–14 | 700–1000 | 100/year | 20/year |
| Replacement cost | 700 | 1300 | - | - | - |
| Centroid/Axis | x | y |
|---|---|---|
| Centroid 1 | 0.92463054 | 0.11527094 |
| Centroid 2 | 0.75952381 | 0.74047619 |
| Centroid 3 | 0.29246429 | 0.48892857 |
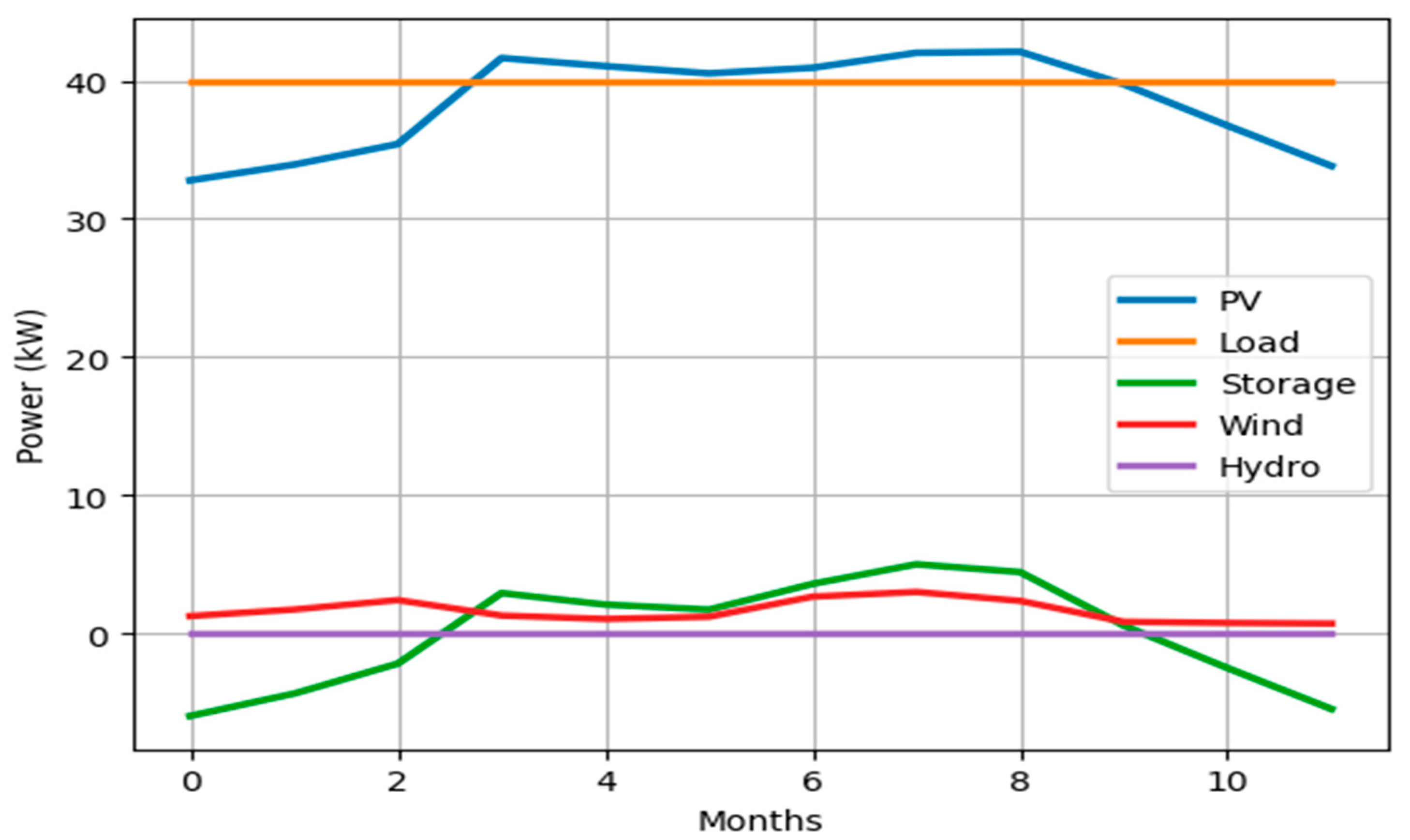
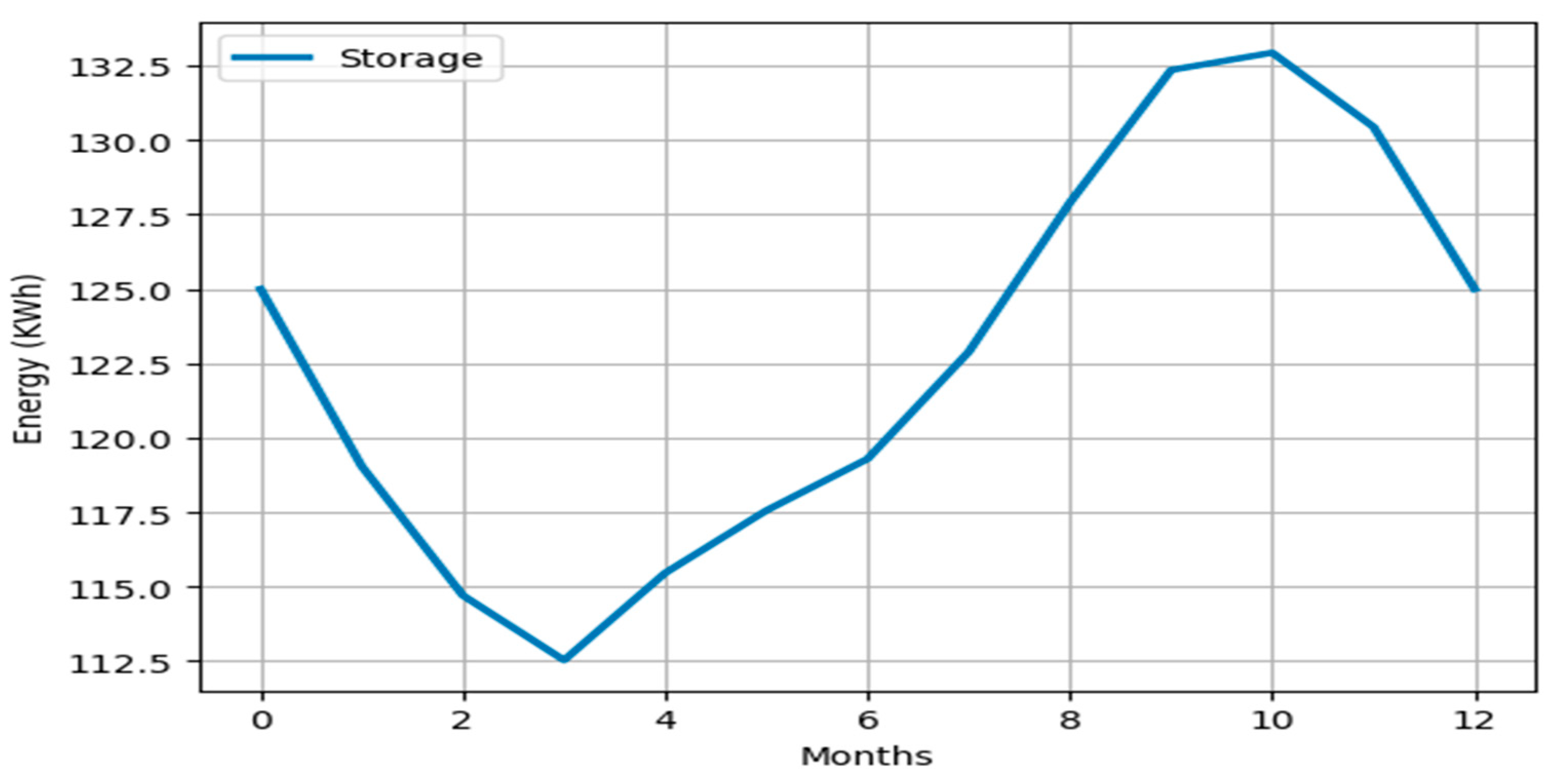
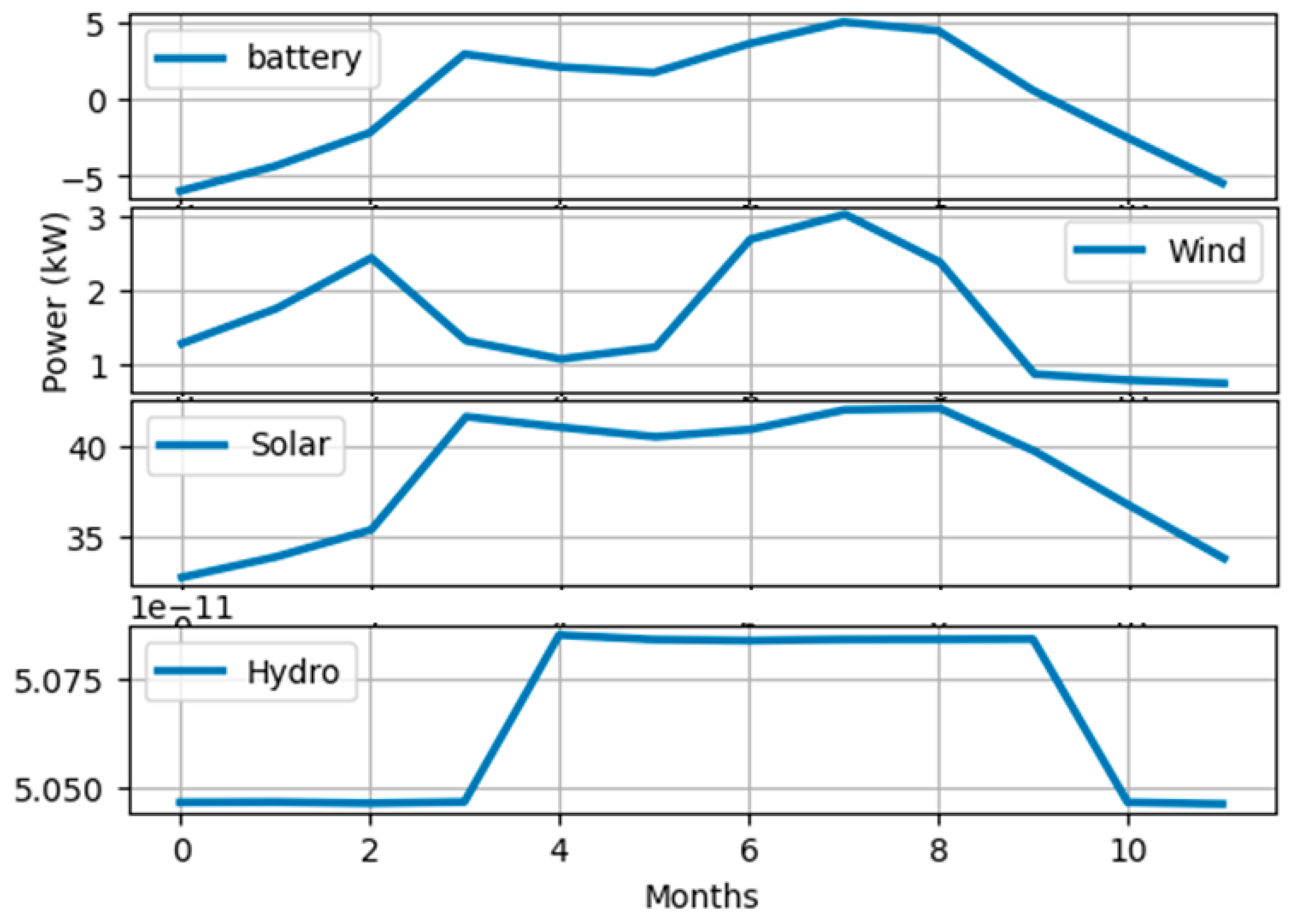
| Month/Resources | Objective Function | Batteries (Injection/Consumption) | Storage | Solar | Wind | Hydro |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost (USD) | P (kW) | E (kWh) | P (kW) | P (kW) | P (kW) | |
| January | 86,993.372 | −5.9521873 | 125 | 32.78232 | 1.2654927 | 5.05 |
| February | 107,862.57 | −4.3408207 | 119.04781 | 33.91956 | 1.7396193 | 5.05 |
| March | 137,518.88 | −2.1732186 | 114.70699 | 35.40348 | 2.4233014 | 5.05 |
| April | 113,170.6 | 2.9308321 | 112.53377 | 41.62752 | 1.3033121 | 5.05 |
| May | 102,321.29 | 2.0975483 | 115.46461 | 41.04108 | 1.0564683 | 5.05 |
| Jun | 106,827.33 | 1.7328749 | 117.56215 | 40.5162 | 1.2166749 | 5.05 |
| Jully | 162,312.84 | 3.5950199 | 119.29503 | 40.9212 | 2.6738199 | 5.05 |
| August | 177,942.34 | 5.0149667 | 122.89005 | 42.00336 | 3.0116067 | 5.05 |
| September | 154,083.06 | 4.4502273 | 127.90502 | 42.08436 | 2.3658673 | 5.05 |
| October | 91,055.383 | 0.5818162 | 132.35524 | 39.72888 | 0.8529362 | 5.05 |
| November | 79,623.893 | −2.4906887 | 132.93706 | 36.73836 | 0.7709513 | 5.05 |
| December | 69,867.2 | −5.44637 | 130.44637 | 33.8256 | 0.72803 | 5.05 |
| Horizon/Years | 2024–2030 | 2030–2050 | ||
| Population | 8,095,498 | >12,000,000 | ||
| Scenarios | Scenario 2 | Scenario 4 | ||
| Technologies/costs | Capacity (MW) | Investment (In million USD) | Capacity (MW) | Investment (In million USD) |
| Mini-grid PV hybrid | 320 | 564 | 720 | 1371 |
| Mini-grid hydraulic | <1 | 1.12 | 1 | 4.42 |
| Mini-grid wind, biodiesel | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Extension | - | - | 274 | 964 |
| Stand-alone PV systems | - | - | 62 | 280 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabe, M.; Bokovi, Y.; Sedzro, K.S.; Takouda, P.; Lare, Y. Optimal Electrification Using Renewable Energies: Microgrid Installation Model with Combined Mixture k-Means Clustering Algorithm, Mixed Integer Linear Programming, and Onsset Method. Energies 2024, 17, 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17123022
Kabe M, Bokovi Y, Sedzro KS, Takouda P, Lare Y. Optimal Electrification Using Renewable Energies: Microgrid Installation Model with Combined Mixture k-Means Clustering Algorithm, Mixed Integer Linear Programming, and Onsset Method. Energies. 2024; 17(12):3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17123022
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabe, Moyème, Yao Bokovi, Kwami Senam Sedzro, Pidéname Takouda, and Yendoubé Lare. 2024. "Optimal Electrification Using Renewable Energies: Microgrid Installation Model with Combined Mixture k-Means Clustering Algorithm, Mixed Integer Linear Programming, and Onsset Method" Energies 17, no. 12: 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17123022
APA StyleKabe, M., Bokovi, Y., Sedzro, K. S., Takouda, P., & Lare, Y. (2024). Optimal Electrification Using Renewable Energies: Microgrid Installation Model with Combined Mixture k-Means Clustering Algorithm, Mixed Integer Linear Programming, and Onsset Method. Energies, 17(12), 3022. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17123022






