Performance Improvement of a Limaçon Gas Expander Using an Inlet Control Valve: Two Case Studies
Abstract
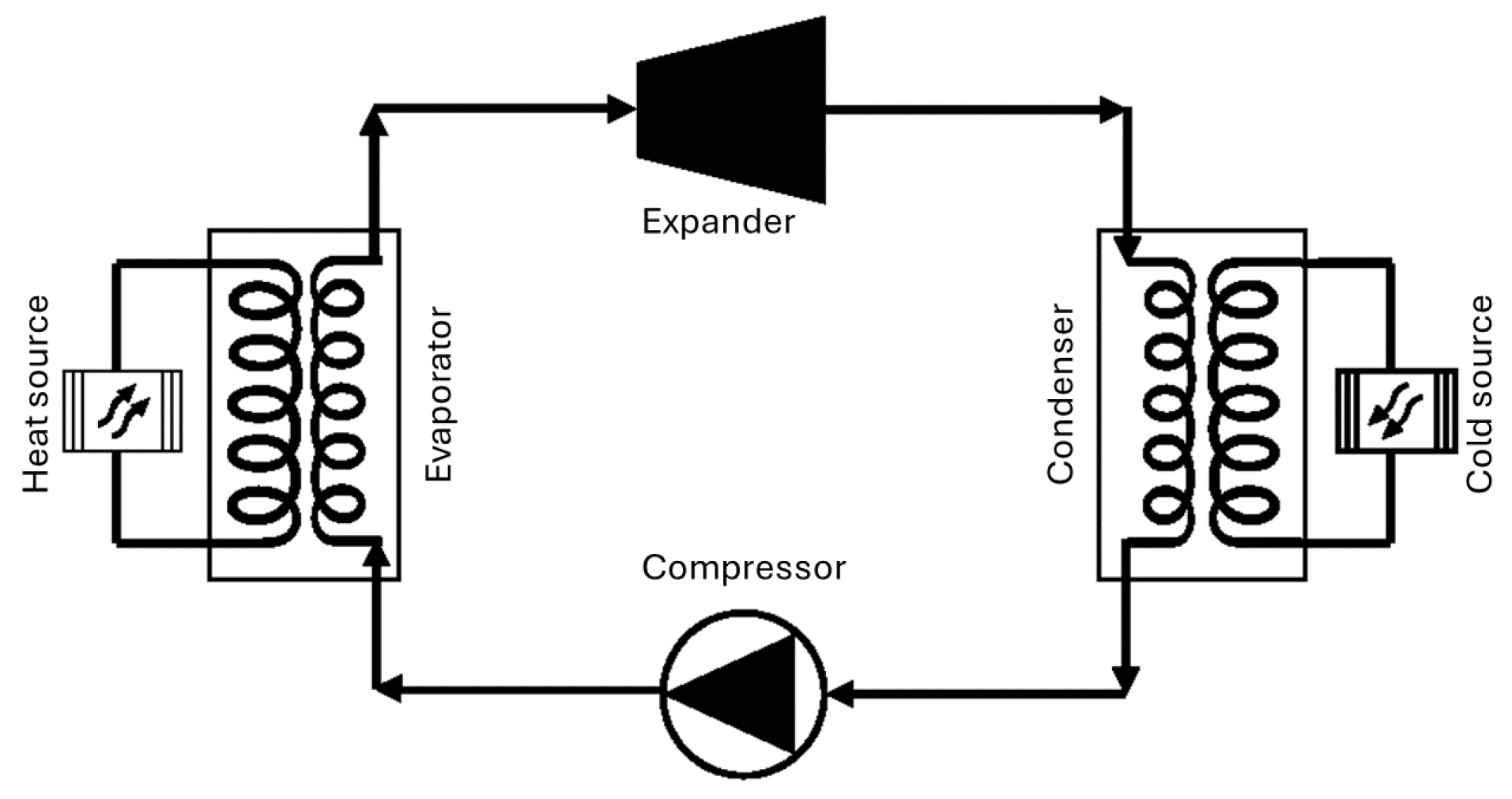
1. Introduction
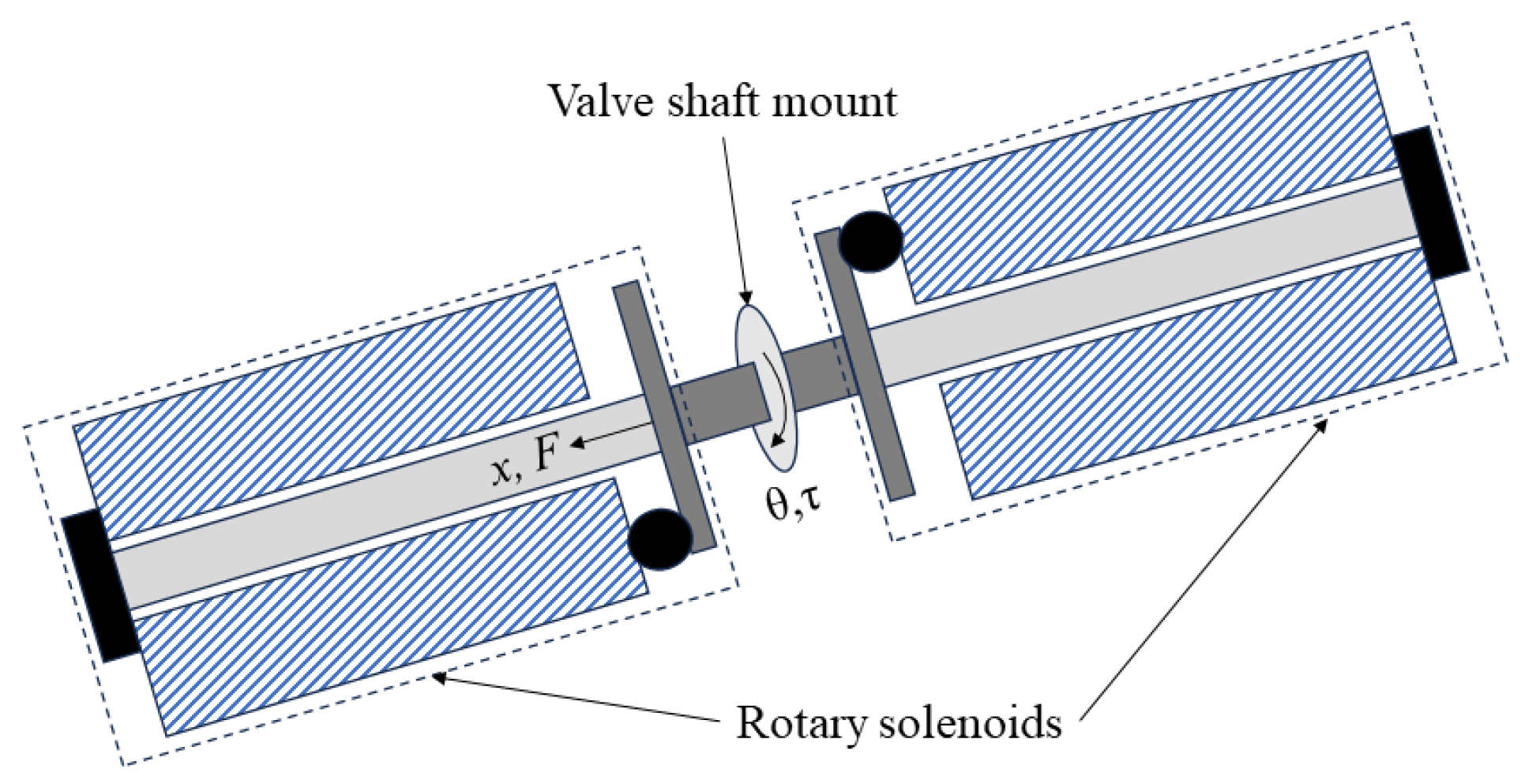
2. Outline of the Proposed Valve
3. Mathematical Modeling
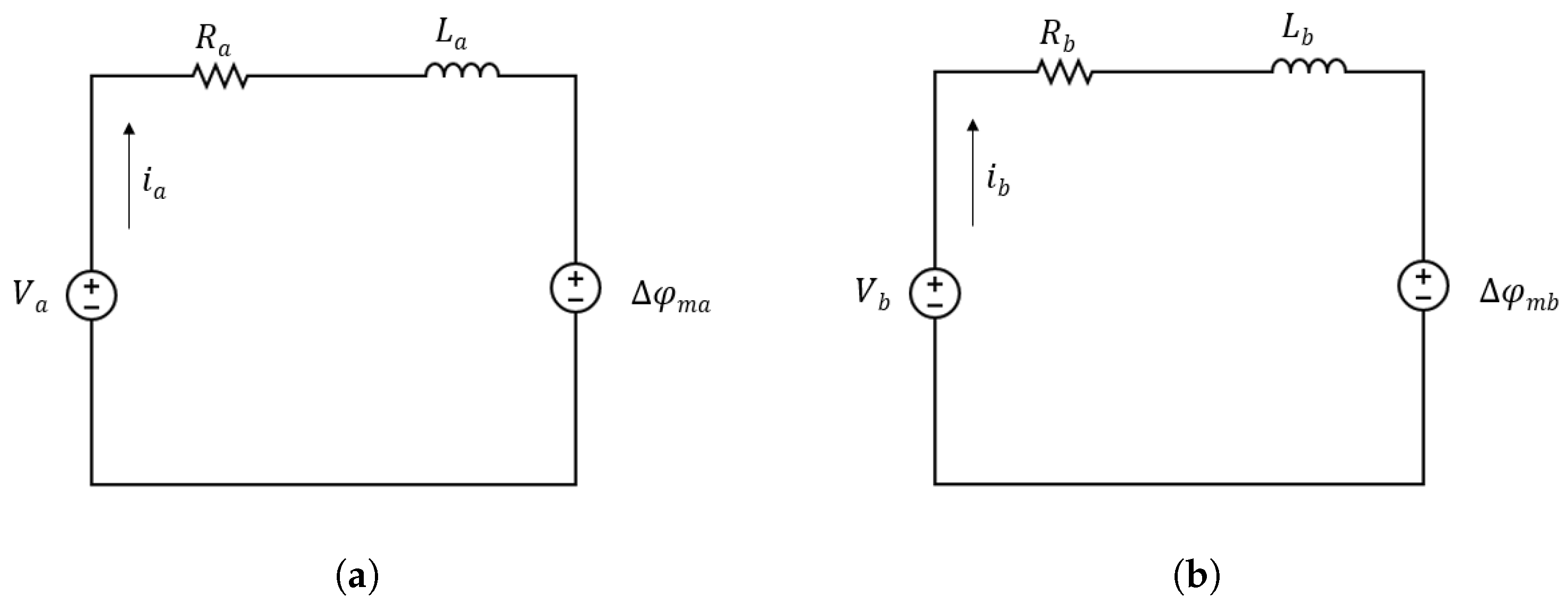
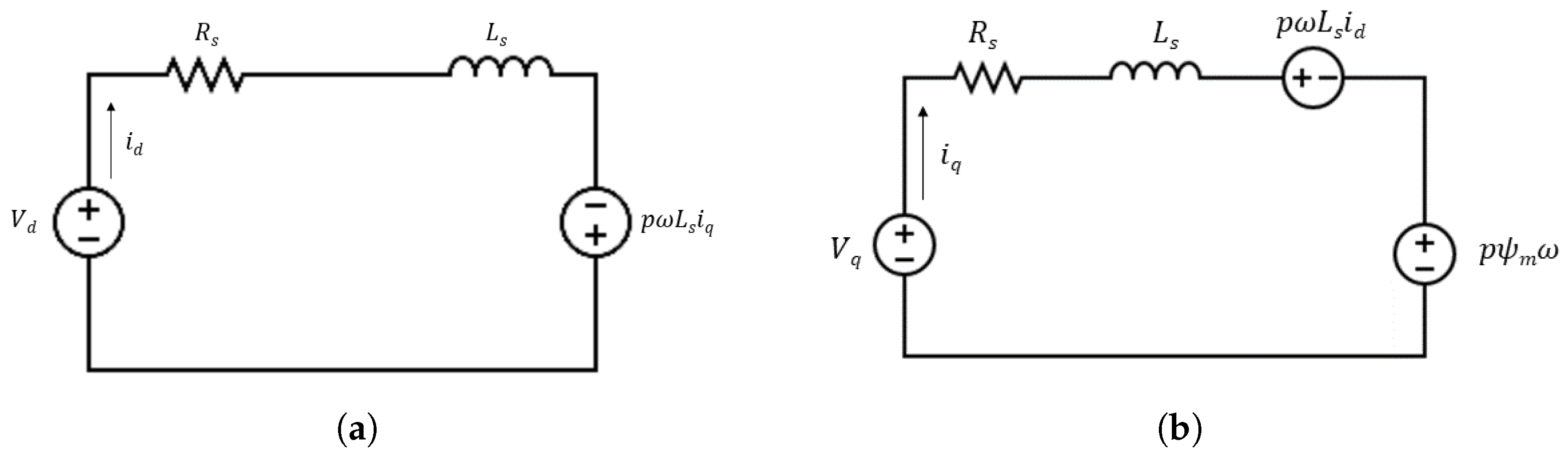
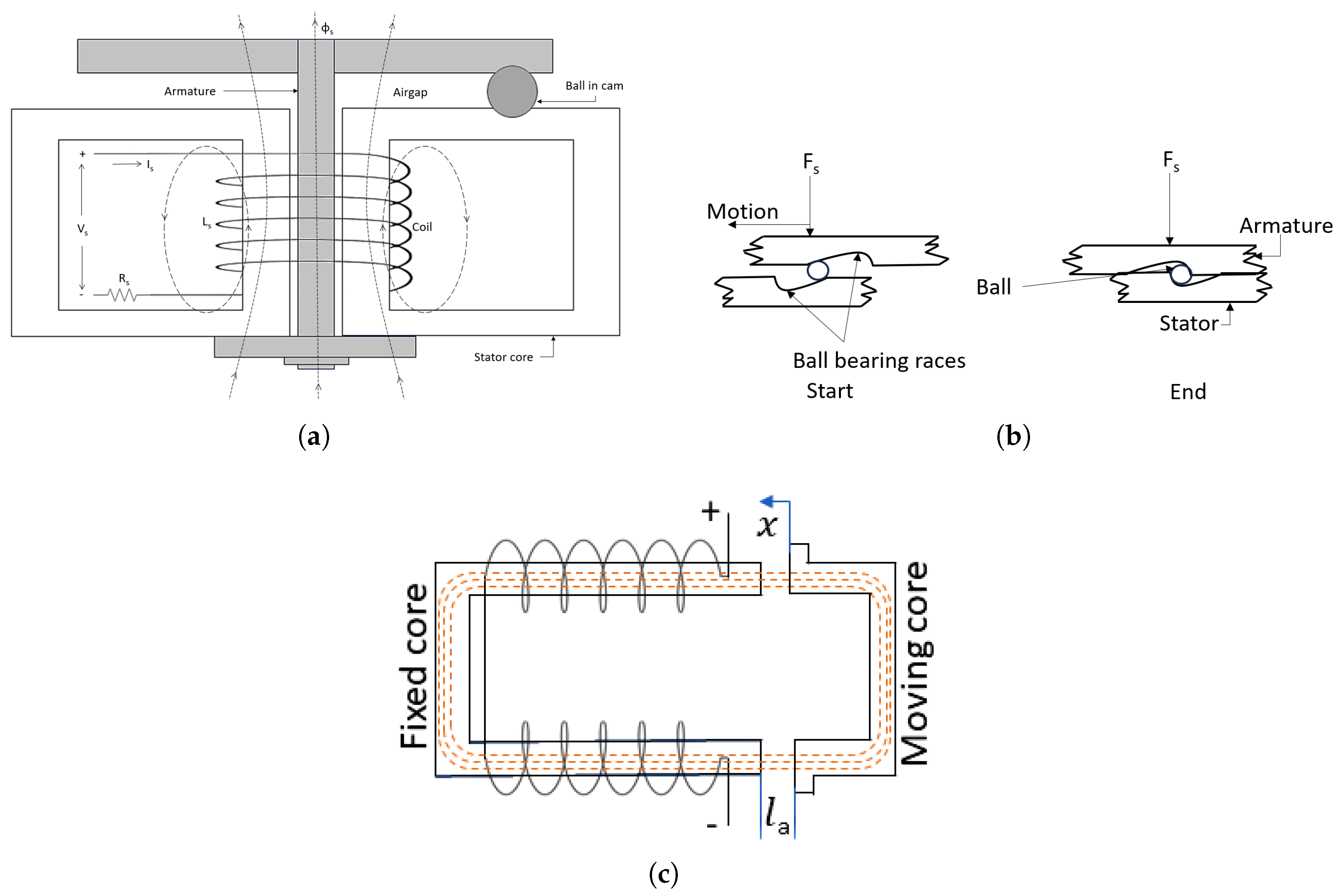
3.1. Stepper Motor
3.2. Rotary Solenoid
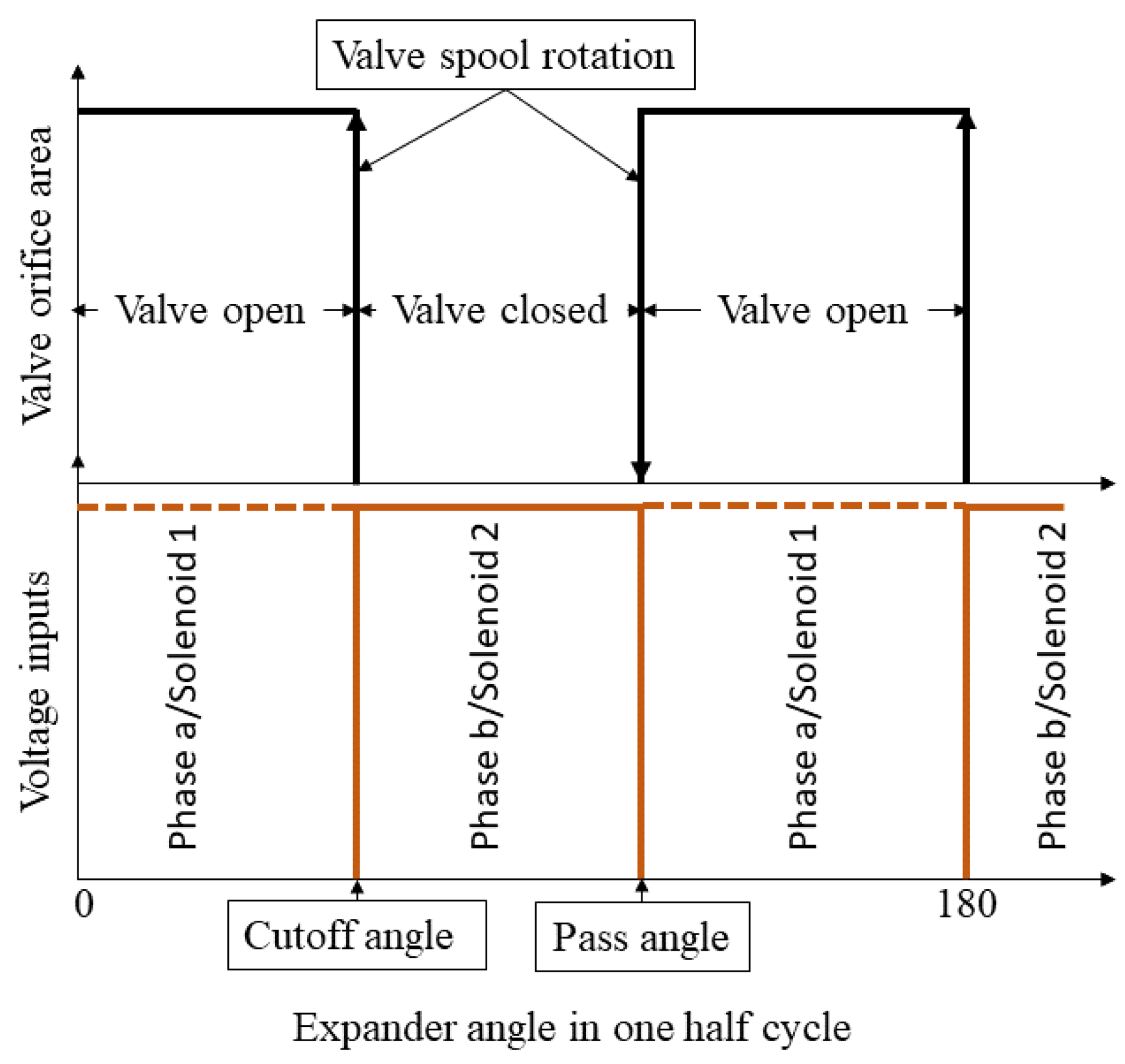
3.3. Valve Dynamics
3.4. System Equations
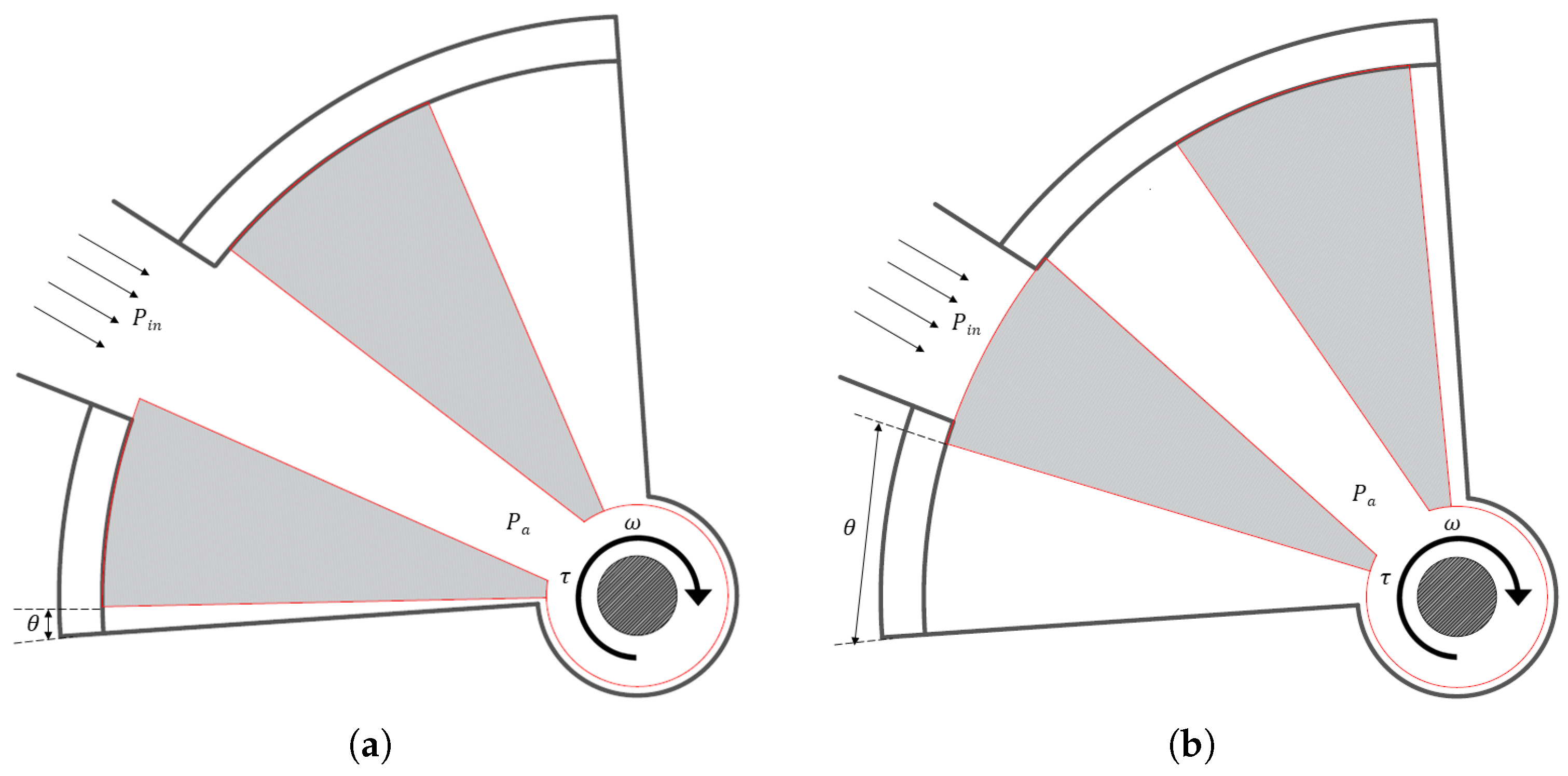
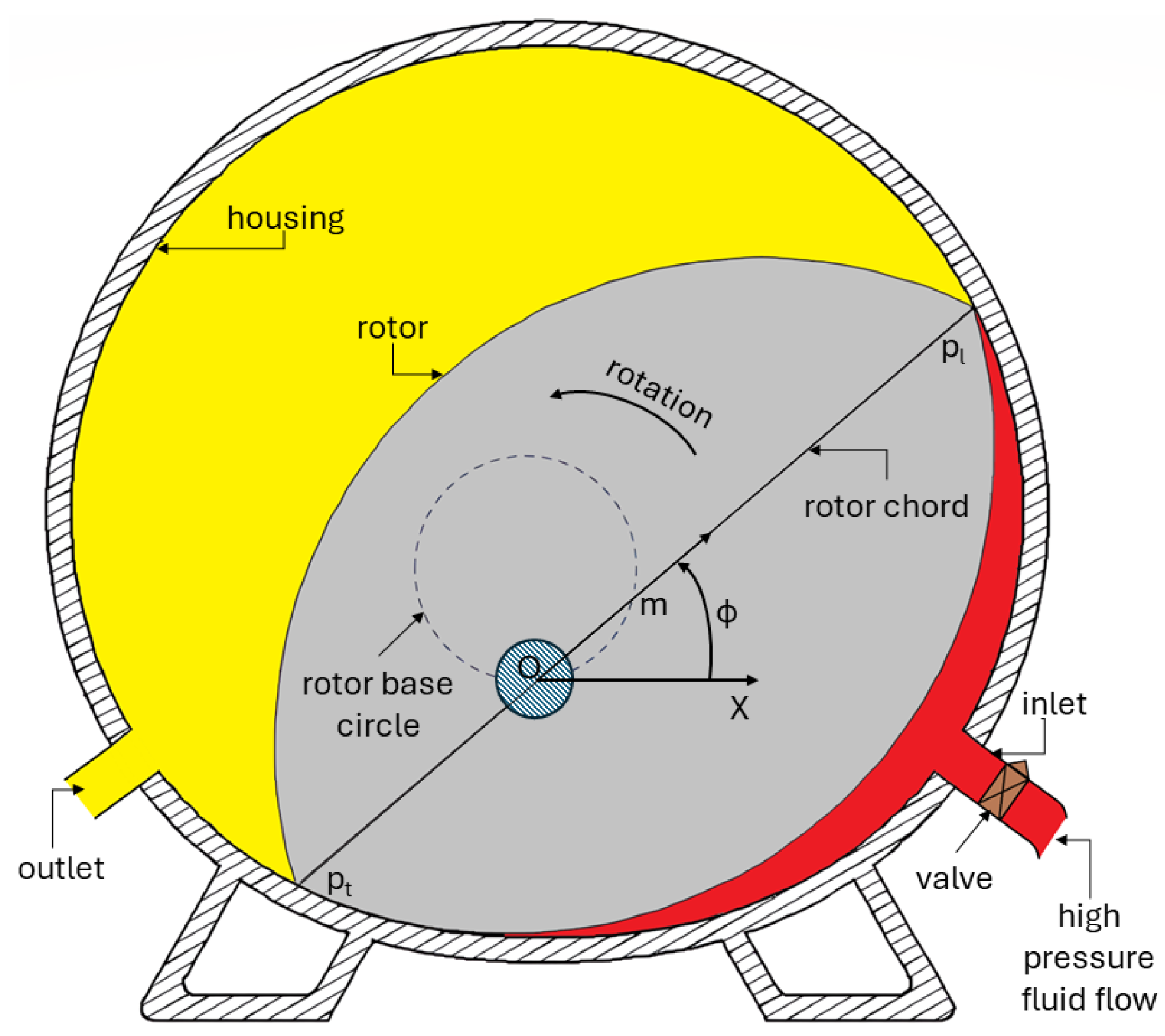
3.5. Limaçon Positive Displacement Gas Expander
4. Simulation of Actuators
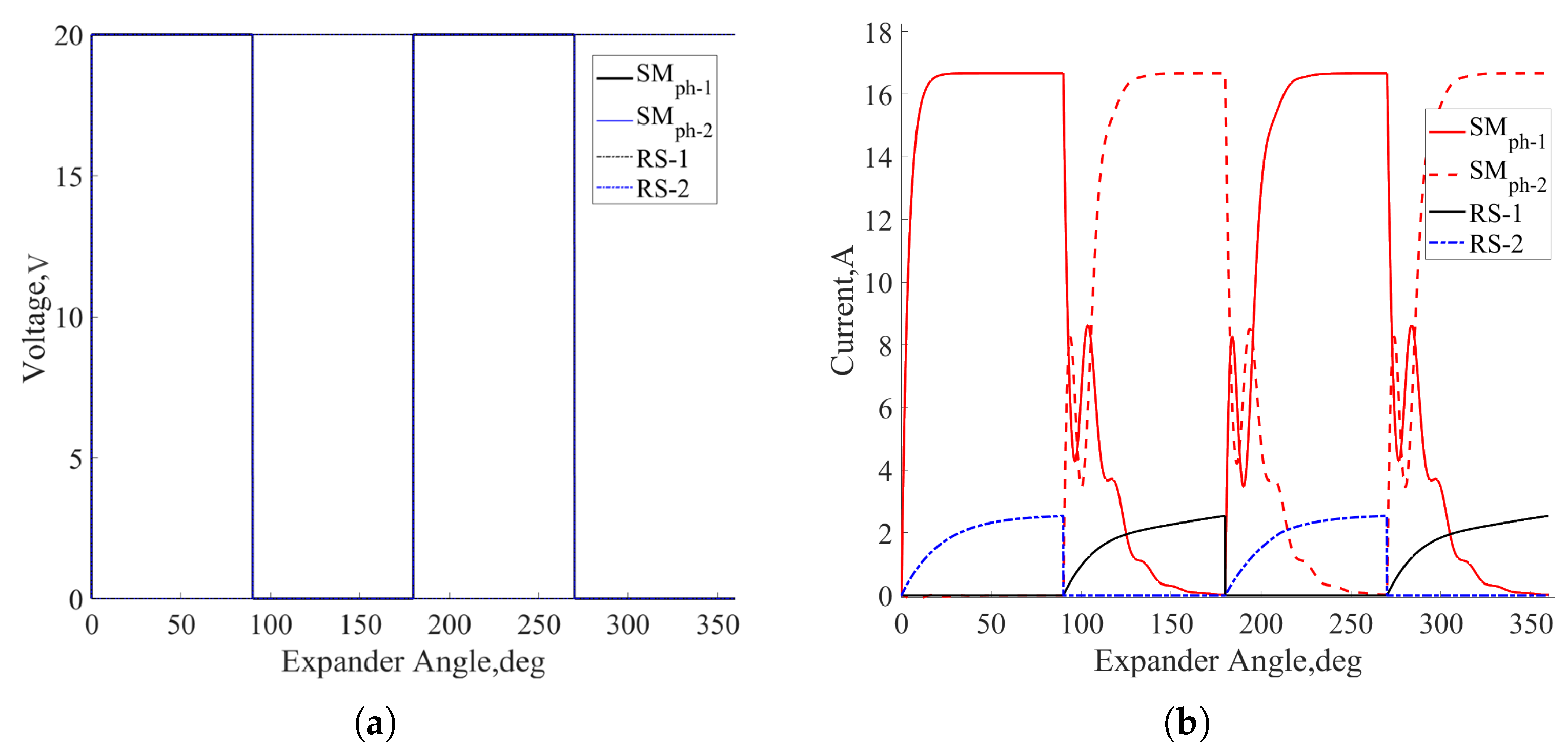
4.1. Dynamic Response of the Valve
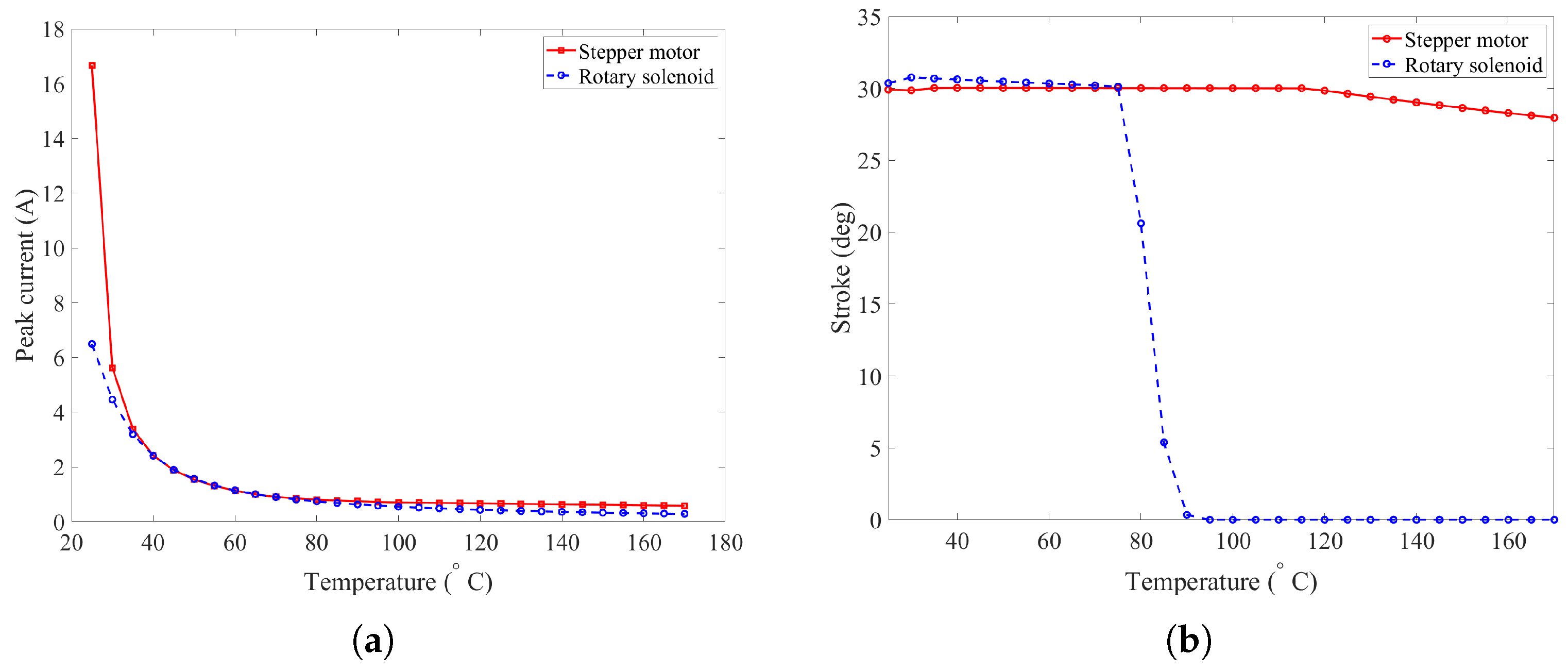
Effect of Temperature and Friction
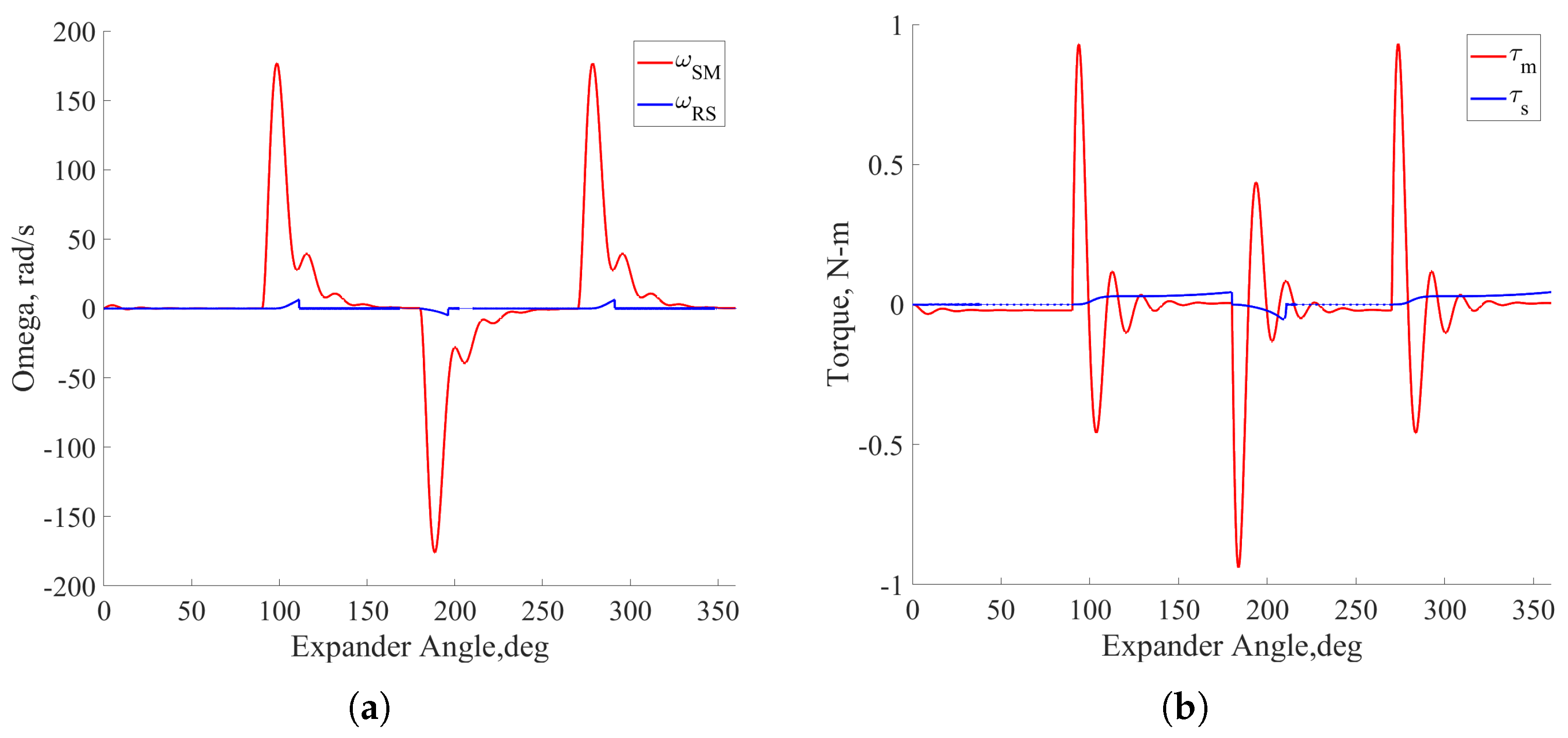
4.2. Application of Proposed DDRVs to the Limaçon Expander
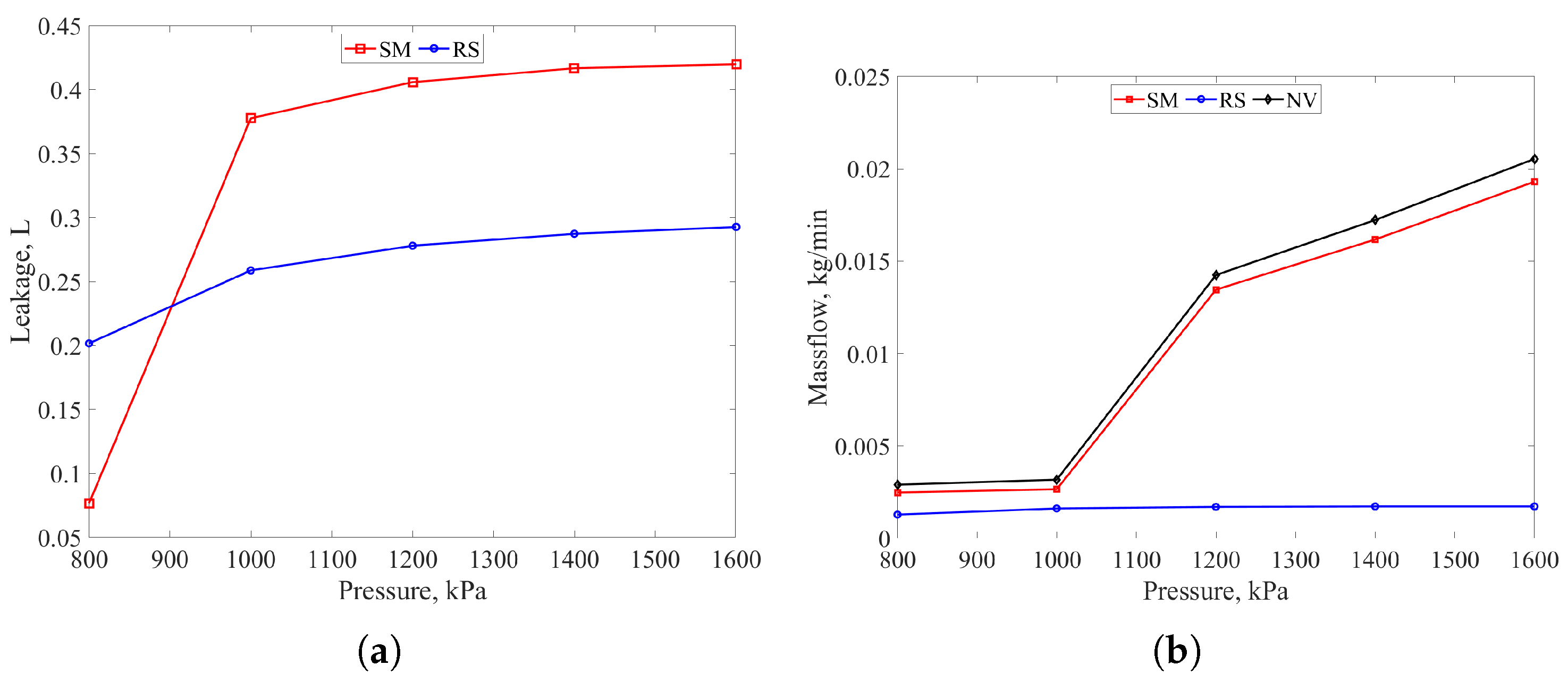
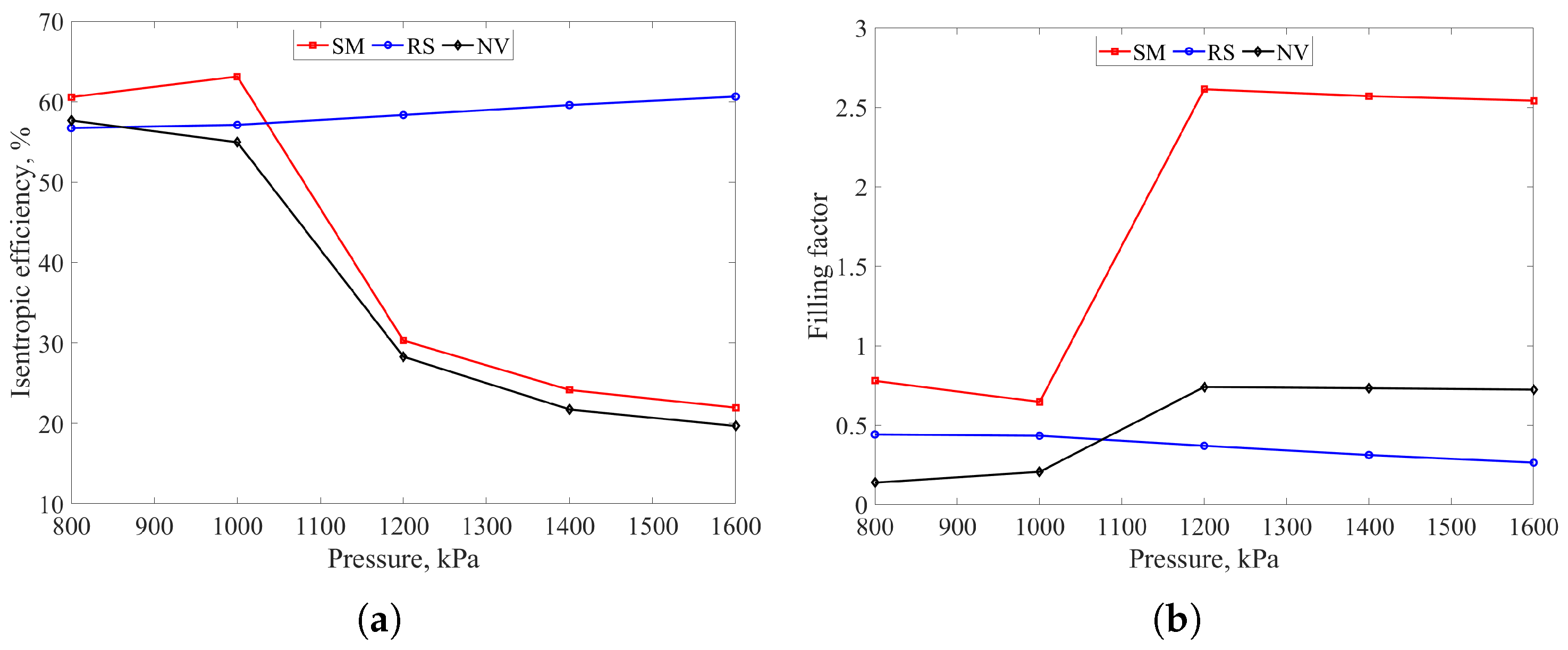
4.3. Sensitivity to Inlet Pressure
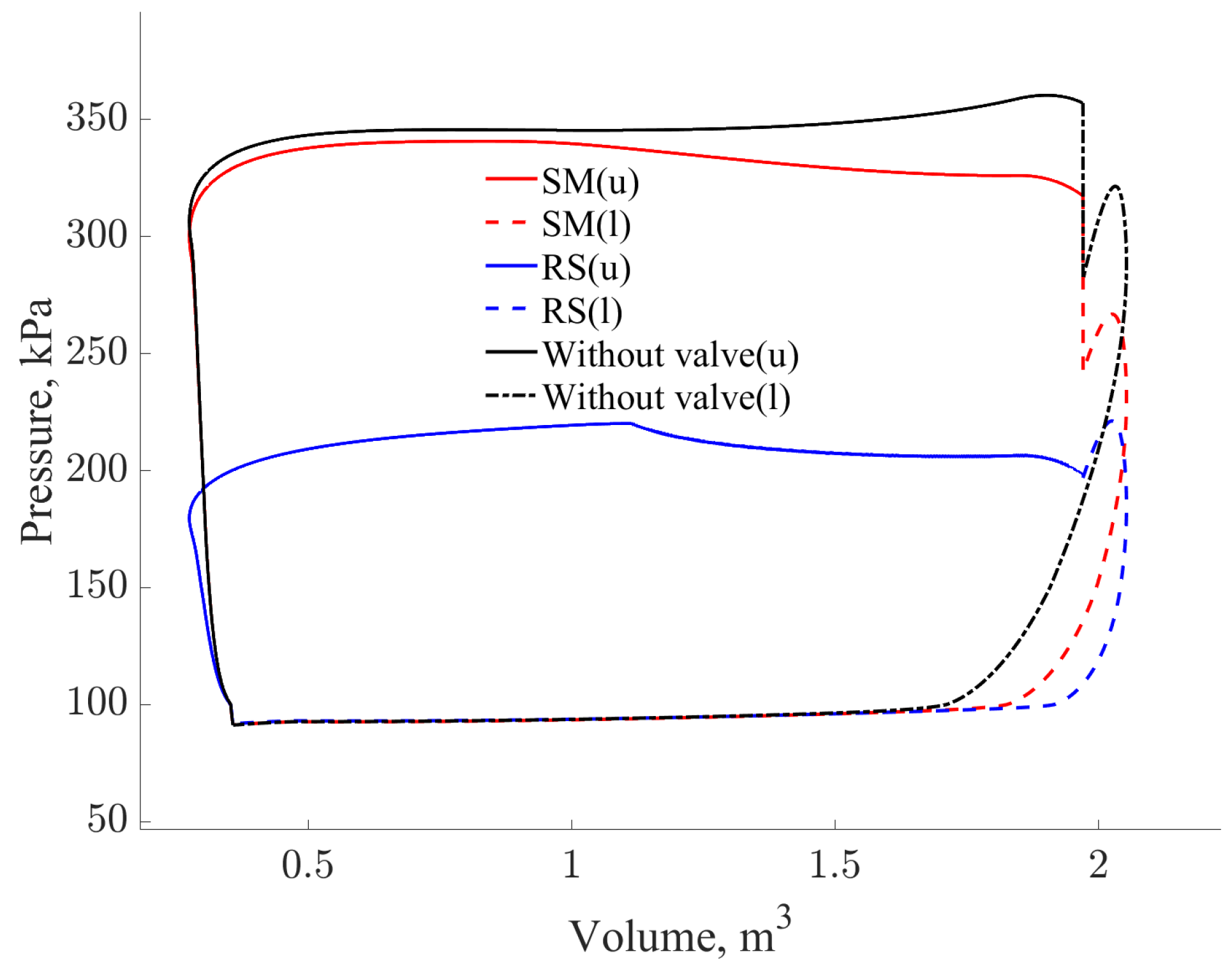
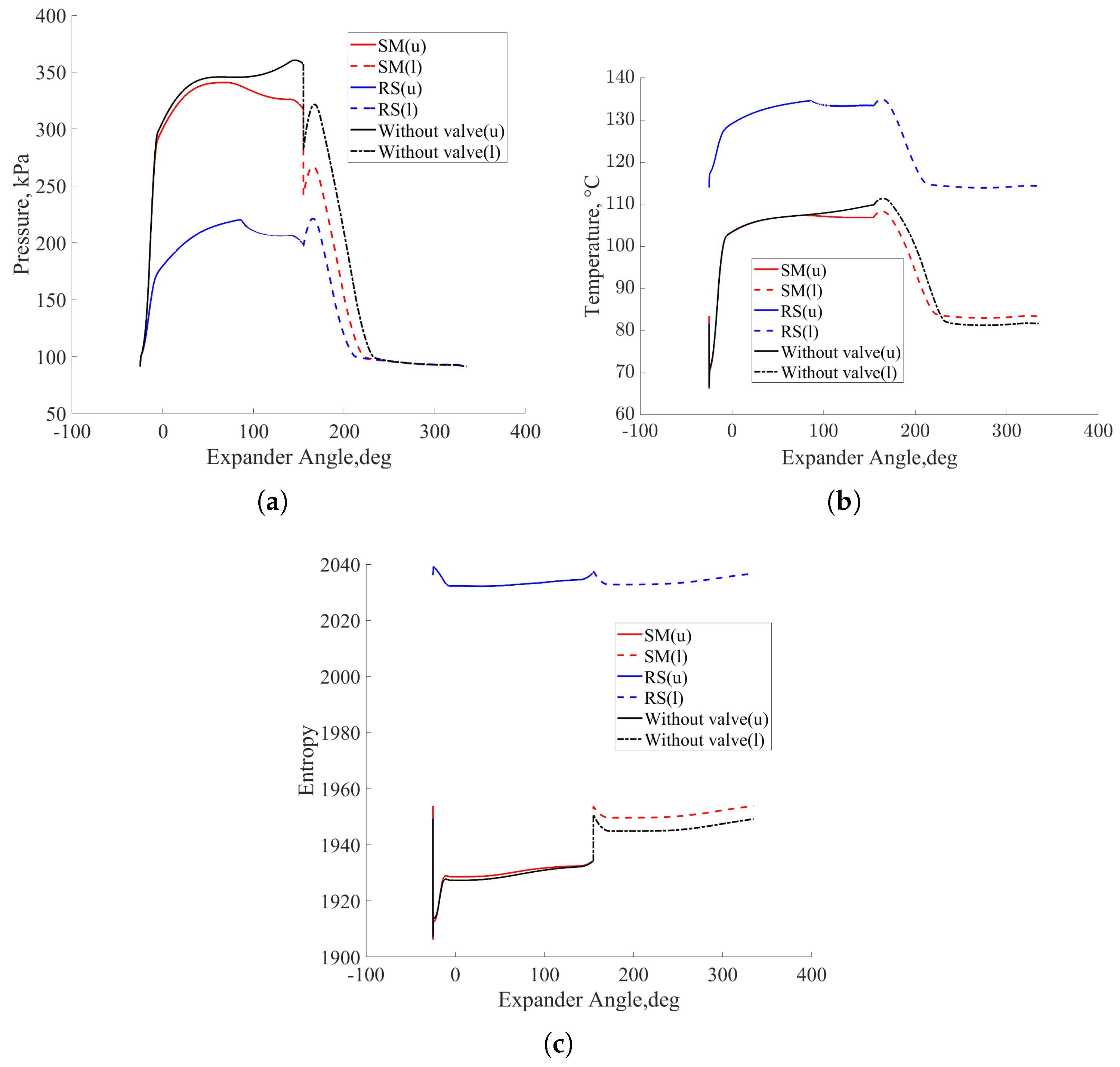
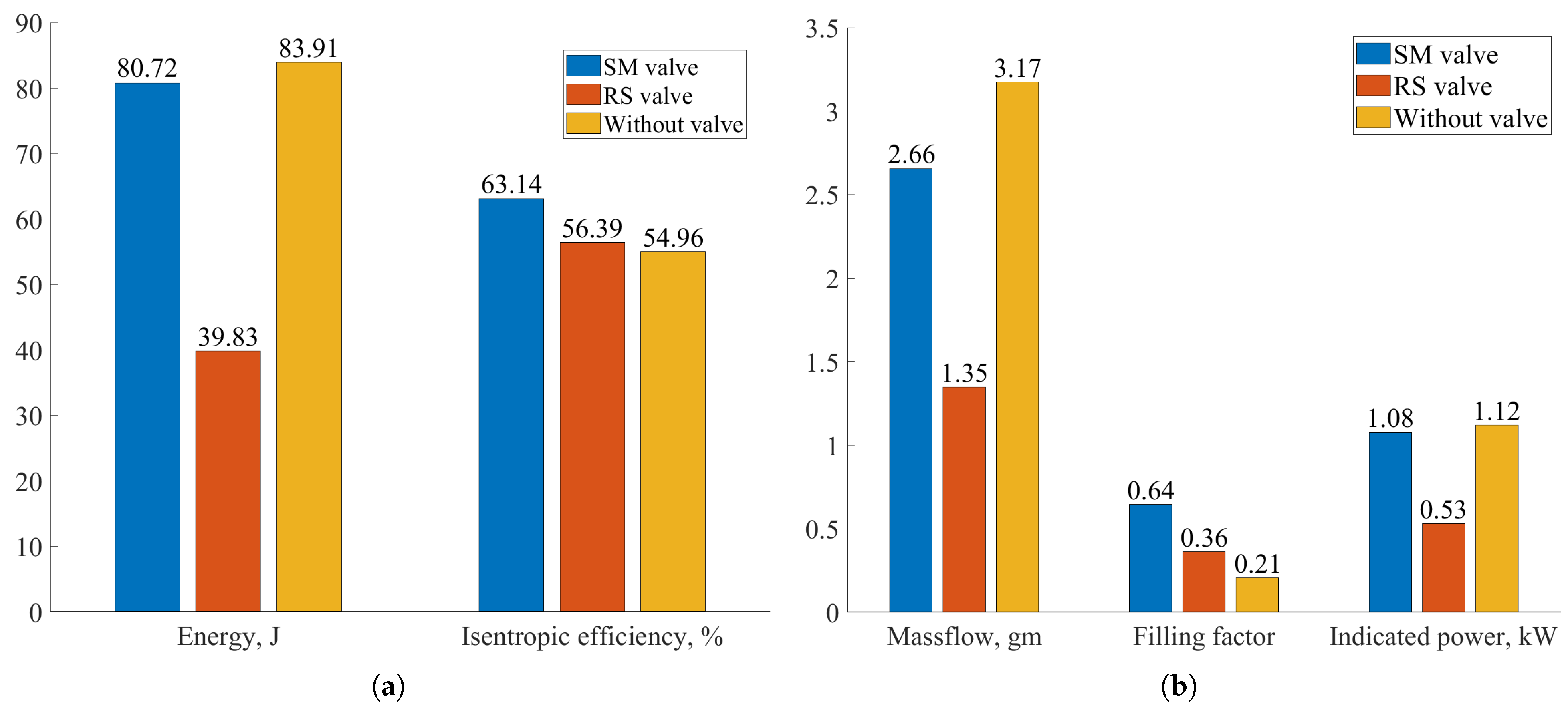
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ORC | organic Rankine cycle |
| DDRV | direct-drive rotary valve |
| SM-DDRV | stepper motor DDRV |
| RS-DDRV | rotary solenoid DDRV |
| WHR | waste heat recovery |
| CHP | combined heat and power |
| GWP | Global Warming Potential |
| ODP | Ozone Depletion Potential |
References
- Putrus, G.; Bentley, E. 20-Integration of distributed renewable energy systems into the smart grid. In Electric Renewable Energy Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 487–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchanche, B.; Quoilin, S.; Declaye, S.; Papadakis, G.; Lemort, V. Economic Optimization of Small Scale Organic Rankine Cycles. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Efficiency, Cost, Optimization, Simulation and Environmental Impact of Energy Systems, Lausanne, Switzerland, 14–17 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Lu, X.; Lu, Z.; Gu, J. Performance analysis and optimization of organic Rankine cycle (ORC) for waste heat recovery. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lasala, S. Waste heat recovery from fossil-fired power plants by organic rankine cycles. In Organic Rankine Cycles for Waste Heat Recovery-Analysis and Applications; Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Gundersen, T.; Feng, X. Process integration of organic Rankine cycle (ORC) and heat pump for low temperature waste heat recovery. Energy 2018, 160, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.; Mohamad, M.N.A.; Kien, T.T. Study on thermal efficiency of low- to medium-temperature organic Rankine cycles using HFO1234yf. Renew. Energy 2012, 41, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ge, Y.; Tassou, S. Experimental Study on a Small-scale R245fa Organic Rankine Cycle System for Low-grade Thermal Energy Recovery. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Goswami, D.Y.; Stefanakos, E.K. A review of thermodynamic cycles and working fluids for the conversion of low-grade heat. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 3059–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Shi, L.; Qian, W. Thermal stability of hexamethyldisiloxane (MM) as a working fluid for organic Rankine cycle. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvish, K.; Ehyaei, M.A.; Atabi, F.; Rosen, M.A. Selection of Optimum Working Fluid for Organic Rankine Cycles by Exergy and Exergy-Economic Analyses. Sustainability 2015, 7, 15362–15383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Q.; Li, M.J.; Xu, J.L.; Yan, J.J.; Wang, K. Thermodynamic performance analysis of different supercritical Brayton cycles using CO2-based binary mixtures in the molten salt solar power tower systems. Energy 2019, 173, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, M.; Voicu, I.; Tiffonnet, A.L. Study and optimization of a solar subcritical organic Rankine cycle. Renew. Energy 2012, 48, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyerer, S.; Dawo, F.; Kaindl, J.; Wieland, C.; Spliethoff, H. Experimental investigation of modern ORC working fluids R1224yd(Z) and R1233zd(E) as replacements for R245fa. Appl. Energy 2019, 240, 946–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Shu, G. 17-Organic Rankine Cycle systems for large-scale waste heat recovery to produce electricity. In Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) Power Systems; Woodhead Publishing: Shaston, UK, 2017; pp. 613–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auld, A.; Berson, A.; Hogg, S. Organic Rankine cycles in waste heat recovery: A comparative study. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2013, 8, i9–i18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdmann, G. The Chena Hot Springs 400kW Geothermal Power Plant: Experience Gained During the First Year of Operation. Trans. Geotherm. Resour. Counc. 2008, 31, 515–519. [Google Scholar]
- Rentizelas, A.; Karellas, S.; Kakaras, E.; Tatsiopoulos, I. Comparative techno-economic analysis of ORC and gasification for bioenergy applications. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quoilin, S.; Orosz, M.S.; Lemort, V. Modeling and experimental investigation of an Organic Rankine Cycle using scroll expander for small scale solar applications. In Proceedings of the 1st International Congress on Heating, Cooling, and Buildings, Lisbon, Portugal, 7–10 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kane, M.; Larrain, D.; Favrat, D.; Allani, Y. Small hybrid solar power system. Energy 2003, 28, 1427–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Wu, W. Performance evaluation of a low-temperature solar Rankine cycle system utilizing R245fa. Sol. Energy 2010, 84, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksayer, E.B.L. Design of an ORC system operating with solar heat and producing sanitary hot water. Energy Procedia 2011, 6, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bademlioglu, A.; Canbolat, A.; Yamankaradeniz, N.; Kaynakli, O. Investigation of parameters affecting Organic Rankine Cycle efficiency by using Taguchi and ANOVA methods. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 145, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, I.A. Optimum design of limaçon gas expanders based on thermodynamic performance. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 39, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, I.A.; Phung, T.H.; Alhelal, A. Improving Process Efficiency by Waste Heat Recuperation: An Application of the Limaçon Technology. In Sustainability in the Mineral and Energy Sectors; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 475–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.K.; Lin, B.W.; Lai, H.Y.; Chen, G.Y. FPGA-Based Hybrid Stepper Motor Drive System Design by Variable Structure Control. Actuators 2021, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Shen, J.; Lai, J.; Wu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. Research on stepper motor motion control based on MCU. In Proceedings of the 2017 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Jinan, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 3122–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Taj, T.A.; Ijaz, I. Hybrid stepper motor and its controlling techniques a survey. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE NW Russia Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering Conference, St. Petersburg, Russia, 3–5 February 2014; pp. 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojati, M.; Baktash, A. Design and fabrication of a new hybrid stepper motor with significant improvements in torque density. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acarnley, P.P. Stepping Motors: A Guide to Theory and Practice; IET: London, UK, 2002; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, N.; Nakamura, M.; Kosaka, T. Instantaneous torque analysis of hybrid stepping motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1996, 32, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqteit, N.A.; Yahya, K.; Makahleh, F.M.; Attar, H.; Amer, A.; Solyman, A.A.A.; Qudaimat, A.; Tamizi, K. Simple Mathematical and Simulink Model of Stepper Motor. Energies 2022, 15, 6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, A.; Charles Kingsley, J.; Umans, S.D. Electric Machinery; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bolden, B.O. Hybrid Computer Simulation of the Dynamic Performance of a Rotary Solenoid. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Okhotnikov, I.; Noroozi, S.; Sewell, P.; Godfrey, P. Evaluation of steady flow torques and pressure losses in a rotary flow control valve by means of computational fluid dynamics. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2017, 64, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watton, J. Fundamentals of Fluid Power Control; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, T.; Sultan, I.; Boretti, A. Design of Limaçon Gas Expanders. In Nonlinear Approaches in Engineering Applications: Advanced Analysis of Vehicle Related Technologies; Jazar, R.N., Dai, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of phases | 2 |
| Phase voltages ( and ) | |
| Step angle | |
| Winding self-inductance () | |
| Winding resistance () | |
| Maximum flux linkage () |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Applied voltage () | 20 |
| Number of turns () | 500 |
| Coil resistance () | |
| Spring constant (k) | |
| Effective air gap () | m2 |
| Radius of ball bearing races (r) | m |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Total mass (M) | |
| Total moment of inertia (J) | 2 |
| Total friction (B) | kgm/ |
| Supply pressure () | 1000 |
| Supply temperature () | 120 °C |
| Valve ante-chamber pressure () | 600 |
| Expander speed | 800 rpm |
| Diameter of orifice () | 25 |
| Diameter of valve shaft () | 15 |
| Discharge velocity coefficient () | 0.98 |
| Discharge coefficient () | 0.65 |
| Jet angle () | 69° |
| Cutoff angle () | 90° |
| Pass angle () | 180° |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Half of rotor chord length (L) | mm |
| Base circle radius (r) | mm |
| Limaçon aspect ratio () | 0.171 |
| Housing–rotor clearance (C) | mm |
| Clearance ratio () | 0.0153 |
| Design coefficient (a) | 1.73 |
| Depth of rotor housing (H) | mm |
| Fluid type | R245fa |
| Outlet pressure () | 100 |
| Inlet port start angle | ° |
| Inlet port end angle | ° |
| Inlet port length | mm |
| Outlet port start angle | 140° |
| Outlet port end angle | 175° |
| Outlet port length | mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hossain, M.S.; Sultan, I.; Phung, T.; Kumar, A. Performance Improvement of a Limaçon Gas Expander Using an Inlet Control Valve: Two Case Studies. Energies 2024, 17, 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102427
Hossain MS, Sultan I, Phung T, Kumar A. Performance Improvement of a Limaçon Gas Expander Using an Inlet Control Valve: Two Case Studies. Energies. 2024; 17(10):2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102427
Chicago/Turabian StyleHossain, Md Shazzad, Ibrahim Sultan, Truong Phung, and Apurv Kumar. 2024. "Performance Improvement of a Limaçon Gas Expander Using an Inlet Control Valve: Two Case Studies" Energies 17, no. 10: 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102427
APA StyleHossain, M. S., Sultan, I., Phung, T., & Kumar, A. (2024). Performance Improvement of a Limaçon Gas Expander Using an Inlet Control Valve: Two Case Studies. Energies, 17(10), 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102427








