Review on Plasma-Assisted Ignition Systems for Internal Combustion Engine Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Plasma-Assisted Combustion
2.1. Thermal Plasma
2.1.1. Plasma Jet Ignition
2.1.2. Laser Ignition
2.2. Non-Thermal Plasma
2.2.1. Corona Ignition
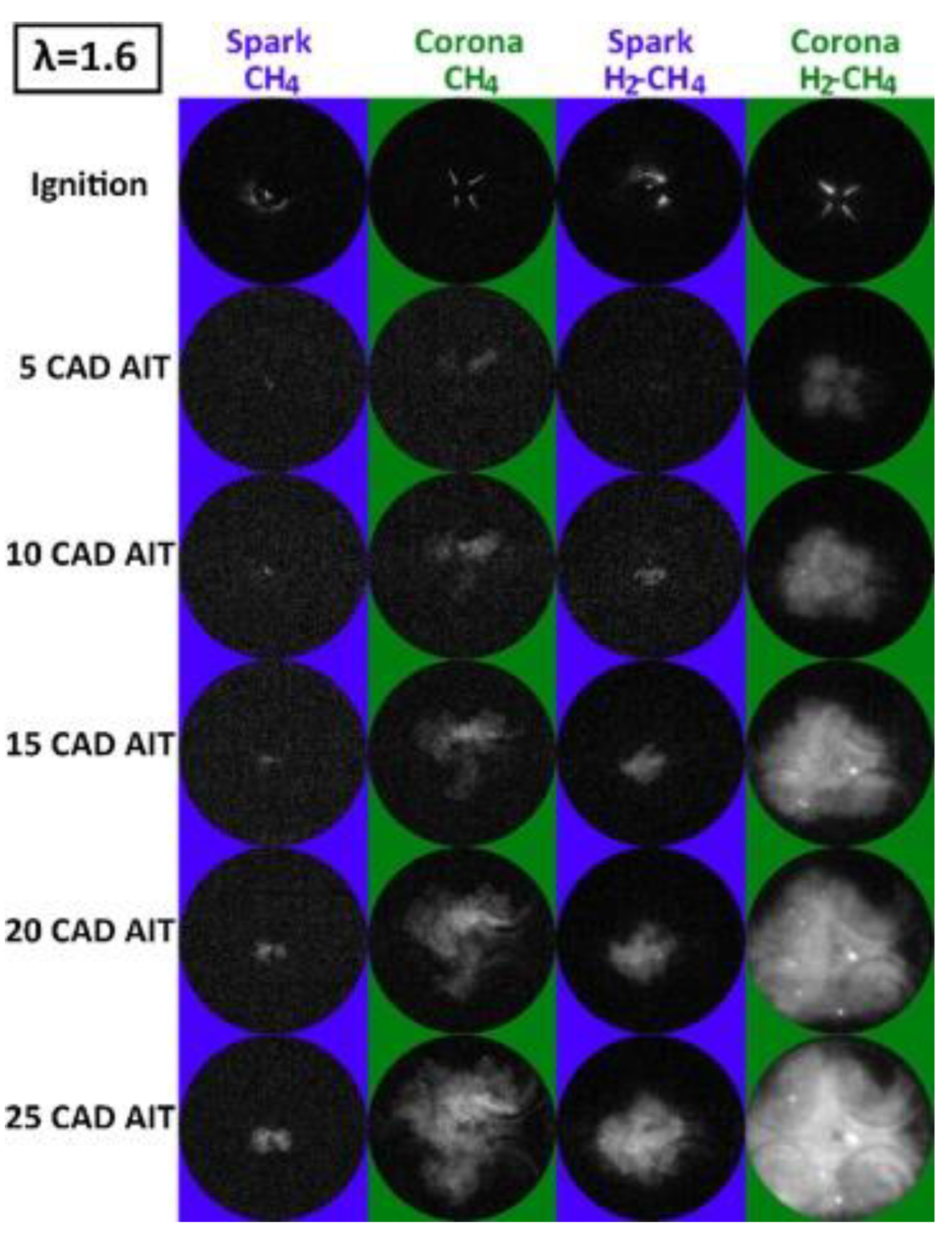
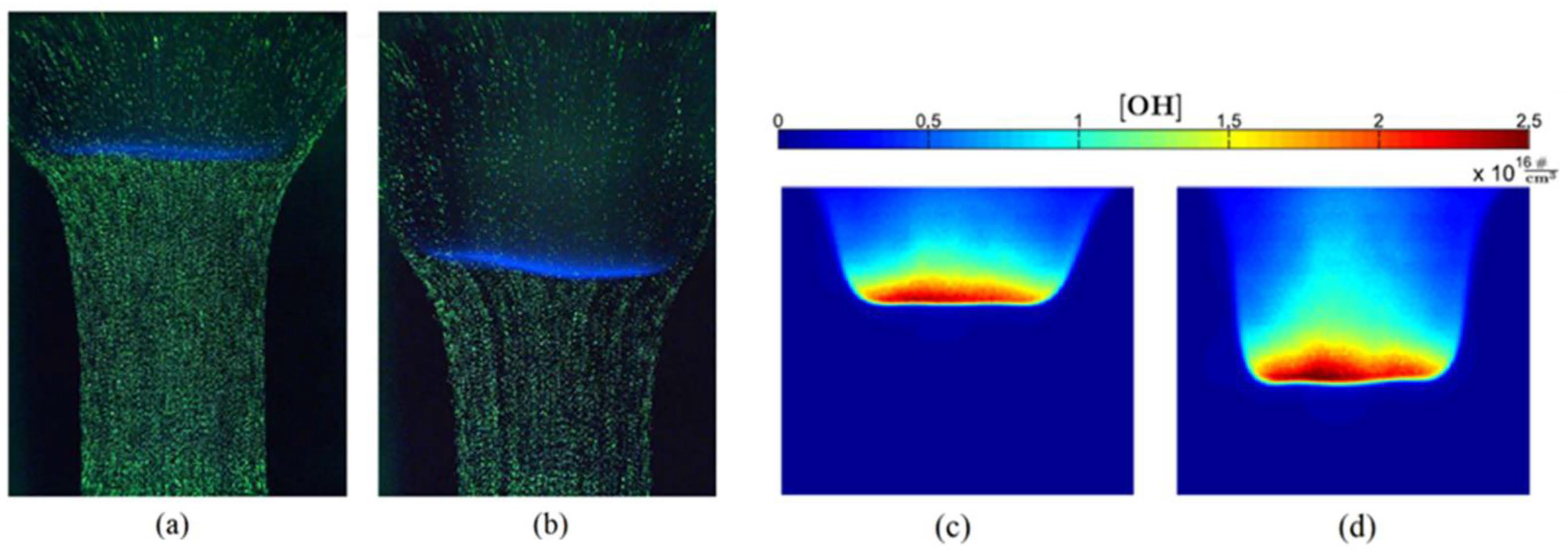
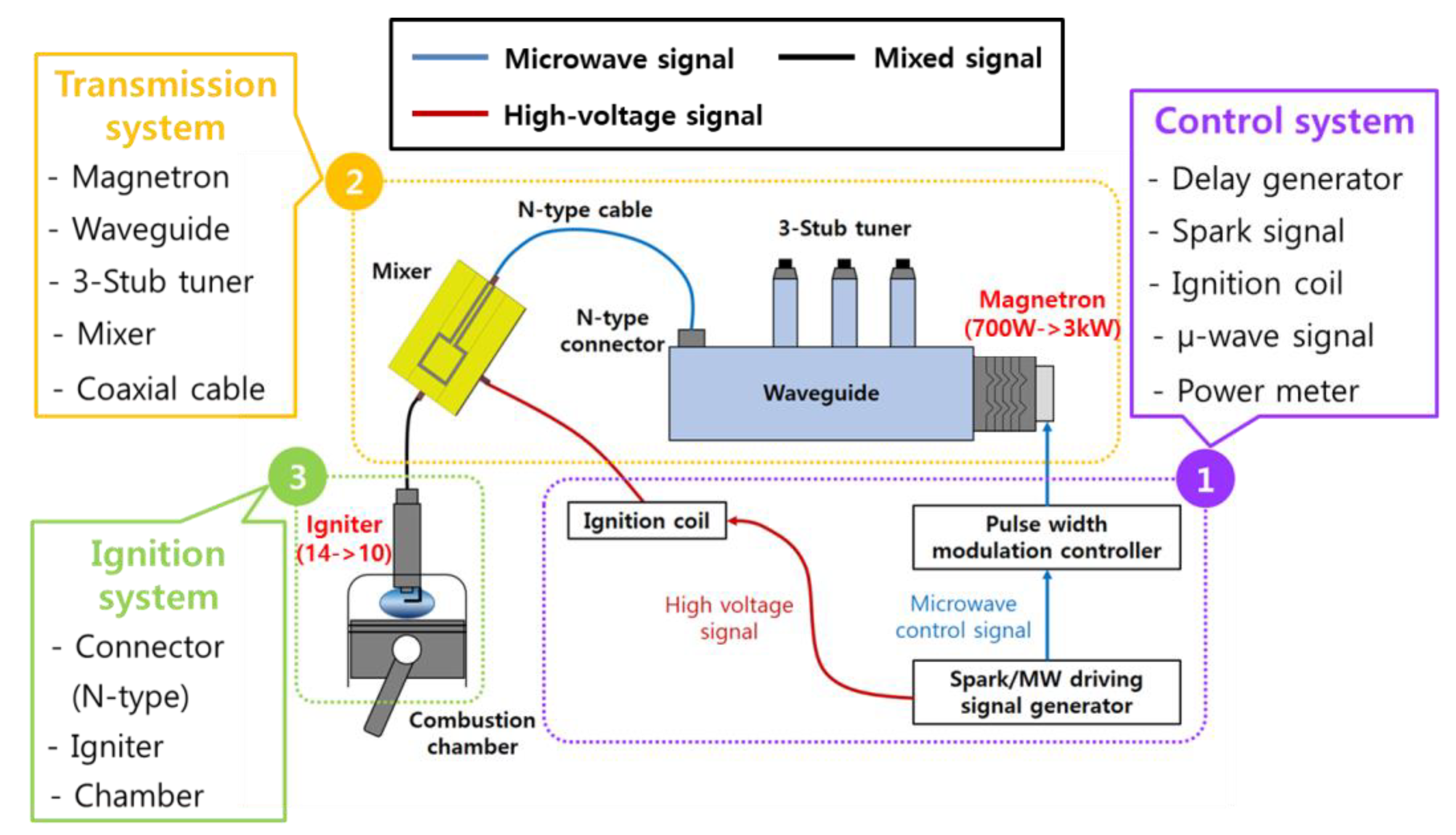
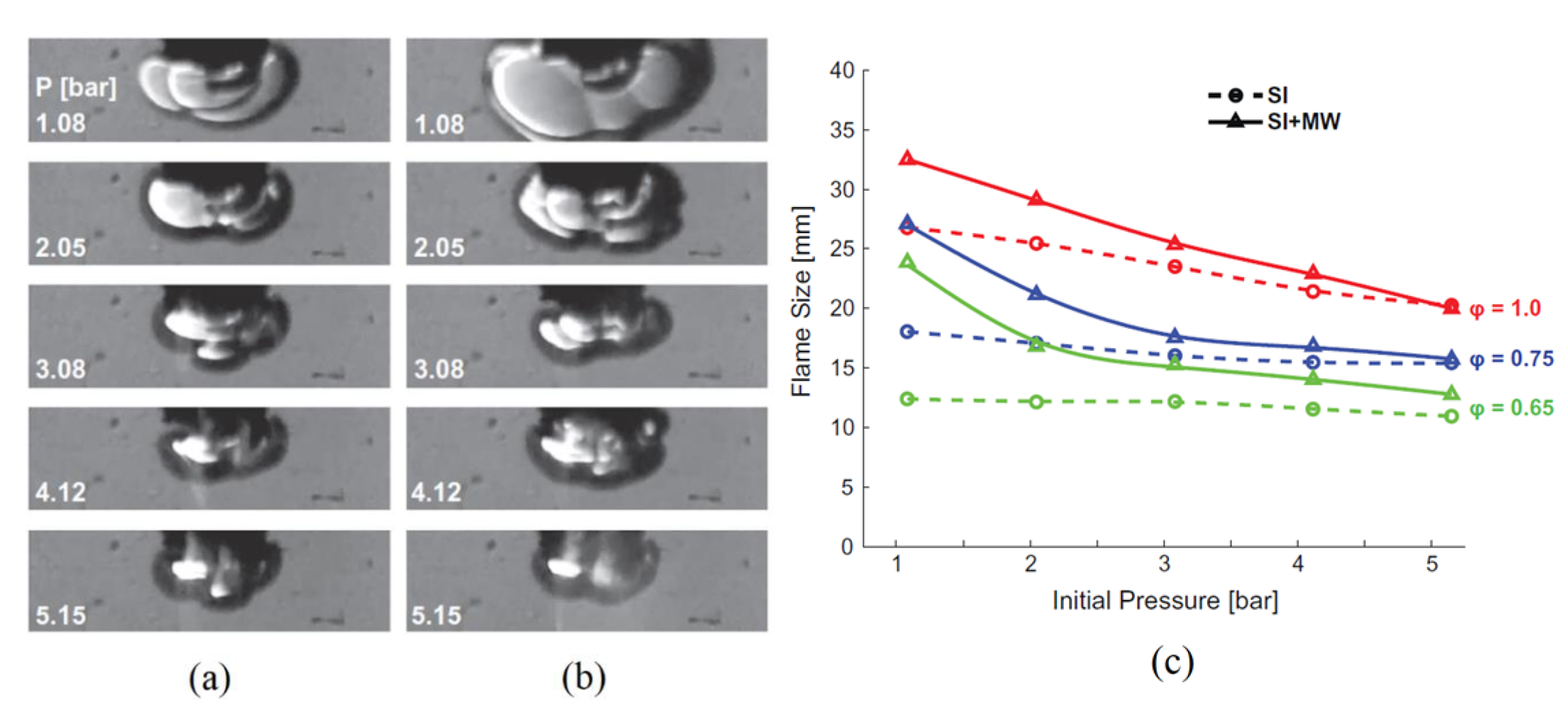
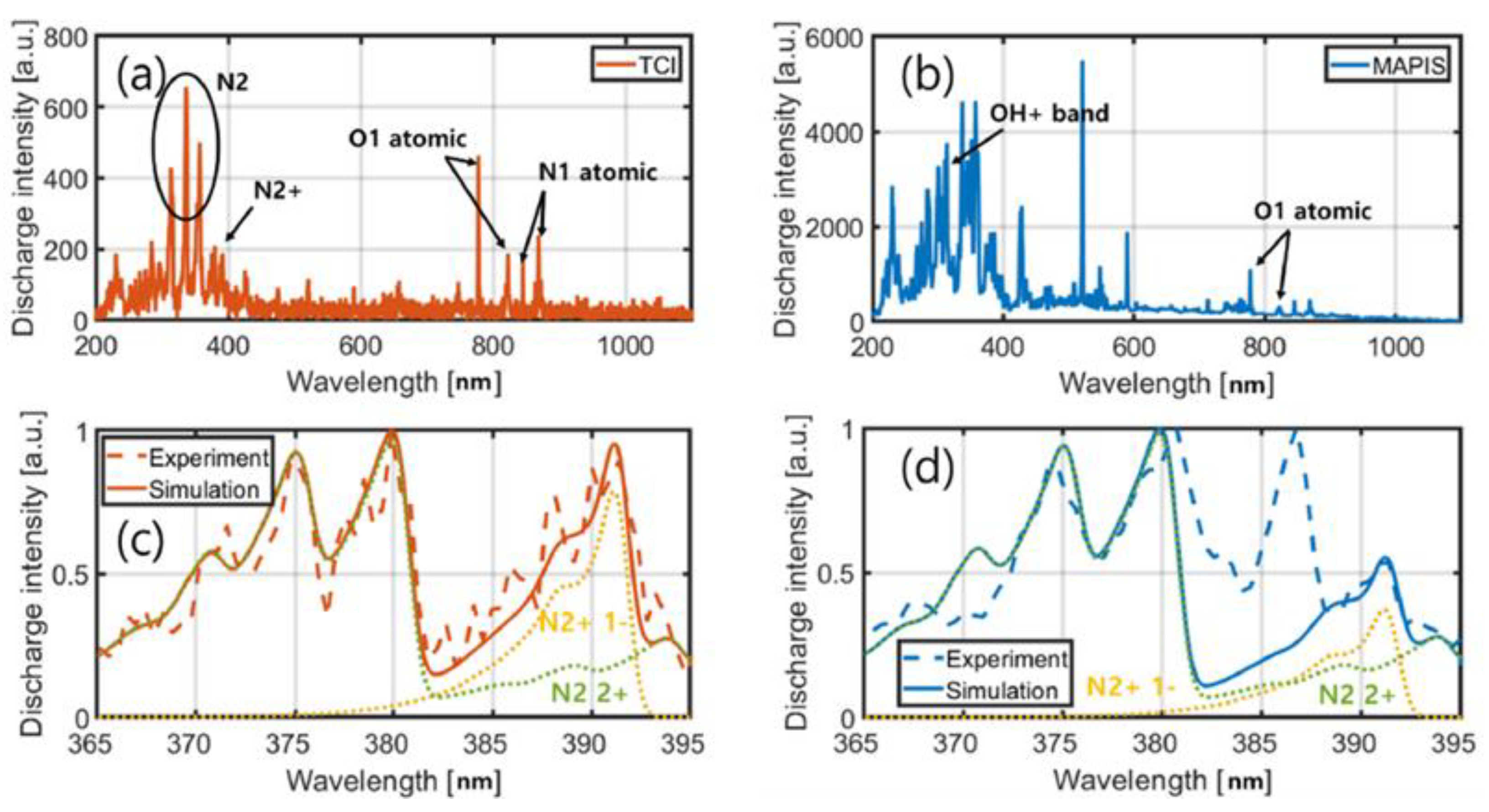
2.2.2. Microwave-Assisted Ignition
3. Other Ignition Systems
3.1. Multi-Spark Ignition
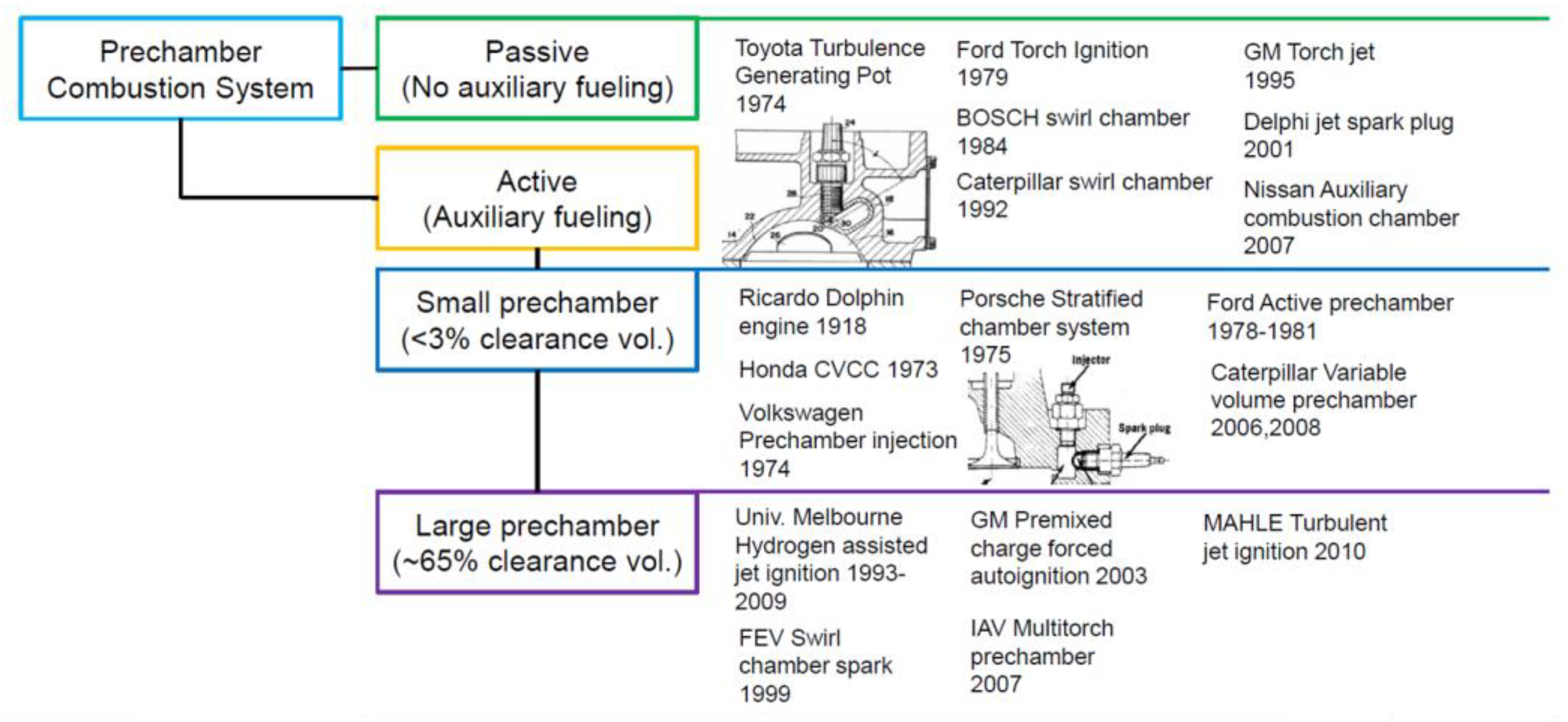
3.2. Pre-Chamber Ignition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSFC | Brake-specific fuel consumption |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| CI | Compression ignition |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| CO | Coefficient of variation |
| CVCC | Constant volume combustion chamber |
| DISI | Direct injection spark ignition |
| EGR | Exhaust gas recirculation |
| FRS | Filtered Rayleigh scattering |
| HC | Hydrocarbons |
| IC | Internal combustion |
| IMEP | Indicated mean effective pressure |
| MAI | Microwave assisted spark ignition |
| MFB | Mass fraction burn |
| MSD | Multi-channel spark discharge |
| Nd:YAG | Neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet |
| NOX | Nitrogen oxide |
| OES | Optical emission spectroscopy |
| PFI | Port fuel injection |
| PIV | Particle image velocimetry |
| PLIF | Planar laser-induced fluorescence |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| SG | Spray-guided |
| SI | Spark ignition |
| WOT | Wide open throttle |
References
- US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/greenvehicles/fast-facts-transportation-greenhouse-gas-emissions (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Heywood, J. Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals 2E; McGraw-Hill Education: Boston, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Duronio, F.; De Vita, A.; Montanaro, A.; Villante, C. Gasoline Direct Injection Engines–A Review of Latest Technologies and Trends. Part 2. Fuel 2020, 265, 116947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Bae, C. Effects of the Injection Timing on Spray and Combustion Characteristics in a Spray-Guided DISI Engine under Lean-Stratified Operation. Fuel 2013, 107, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.H.; Park, K.W.; Han, S.K.; Kim, W.T. Development of Theta II 2.4L GDI Engine for High Power & Low Emission; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Hu, J.; Bao, X.; He, L.; Zu, L. Effects of Aromatics, Olefins and Distillation Temperatures (T50 & T90) on Particle Mass and Number Emissions from Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) Vehicles. Energy Policy 2017, 101, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, B.T.; Knothe, G.; Mueller, C.J. Liquid-Phase Penetration under Unsteady in-Cylinder Conditions: Soy-and Cuphea-Derived Biodiesel Fuels versus Conventional Diesel. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 5163–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smocha, R.; Vuilleumier, D.; Christison, K.; Loeper, P.; Ketterer, N.; Pickett, L.; Hwang, J.; Kim, N.; Strickland, T. Gasoline Direct Injector Deposits: Impacts of Fouling Mechanism on Composition and Performance. SAE Tech. Pap. 2022, 4, 1413–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicher, U.; Magar, M.; Hadler, J. High Pressure Gasoline Direct Injection in Spark Ignition Engines-Efficiency Optimization through Detailed Process Analyses. SAE Int. J. Engines 2016, 9, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Moriyoshi, Y. Stratified Lean Combustion Characteristics of a Spray-Guided Combustion System in a Gasoline Direct Injection Engine. Energy 2012, 41, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jono, M.; Taguchi, M.; Shonohara, T.; Narihiro, S. Development of a New 2.0L I4 Turbocharged Gasoline Direct Injection Engine. SAE Tech. Pap. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.; Reuss, D.L.; Sick, V. High-Speed Imaging Analysis of Misfires in a Spray-Guided Direct Injection Engine. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 3089–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, J. Fundamentals of Plasma Physics, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Starikovskiy, A.; Aleksandrov, N. Plasma-Assisted Ignition and Combustion. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2013, 39, 61–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, T.; Kakuho, A.; Urushihara, T.; Cathey, C.; Tang, T.; Gundersen, M. A Study of Volumetric Ignition Using High-Speed Plasma for Improving Lean Combustion Performance in Internal Combustion Engines. SAE Int. J. Engines 2009, 1, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Shoji, H.; Tanaka, H. Performance of Newly Developed Plasma Jet Igniter. SAE Tech. Pap. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Matthews, R.D.; Hall, M.J.; Hari, S. From Spark Plugs to Railplugs—The Characteristics of a New Ignition System. SAE Tech. Pap. 2004, 1, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Ezekoye, O.A.; Hall, M.J.; Matthews, R.D. PAPER SERIES A New Ignitior for Large-Bore Natural Gas Engines–Railplug Design Improvement and Optimization Reprinted from: SI Combustion and Direct Injection SI Engine Technology; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, M.J.; Tajima, H.; Matthews, R.D.; Koeroghlian, M.M.; Weldon, W.F.; Nichols, S.P. Initial Studies of a New Type of Ignitor: The Railplug. SAE Tech. Pap. 1991, 100, 1730–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Im, S.; Choe, M.; Yoon, T.; Kang, D.; Choi, D. Relationship between Flame Thickness and Velocity Based on Thermodynamic Three Kernels in a Constant Volume Combustion Chamber. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 2459–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Sasaki, H.; Yoshida, K.; Shoji, H.; Tanaka, H. A Study on the Plasma Jet Diffusive Combustion; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, R.; Iijima, A.; Shoji, H.; Yoshida, K. The Influence of Hot Gas Jet on Combustion Enhancement for Lean Mixture in Plasma Jet Ignition. SAE Int. J. Engines 2012, 5, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinrotter, M.; Ast, G.; Kopecek, H.; Wintner, E. An Extensive Comparison of Laser-Induced Plasma Ignition and Conventional Spark Plug Ignition of Lean Methane-Air Mixtures under Engine-like Conditions; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Groß, V.; Kubach, H.; Spicher, U.; Schießl, R.; Maas, U. nfluence of Laser-Induced Ignition on Spray-Guided Combustion—Experimental Results and Numerical Simulation of Ignition Processes; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Genzale, C.L.; Pickett, L.M.; Hoops, A.A.; Headrick, J.M. Laser Ignition of Multi-Injection Gasoline Sprays; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tsunekane, M.; Inohara, T.; Ando, A.; Kido, N.; Kanehara, K.; Taira, T. High Peak Power, Passively. Quantum 2010, 46, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Pavel, N.; Chiriac, R.; Birtas, A.; Draghici, F.; Dinca, M. On the Improvement by Laser Ignition of the Performances of a Passenger Car Gasoline Engine. Opt. Express 2019, 27, A385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Yamaki, Y.; Lee, J.; Nakaya, S.; Tsue, M. Effects of Microwave Radiation on Laser Induced Plasma Ignition of N-Butane/Air Mixture under Atmospheric Conditions. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2021, 38, 6593–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, J.V.; García-Oliver, J.M.; García, A.; Pinotti, M. Effect of Laser Induced Plasma Ignition Timing and Location on Diesel Spray Combustion. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 133, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuoc, T.X.; White, F.P. Laser-Induced Spark Ignition of CH4/Air Mixtures. Combust. Flame 1999, 119, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinrotter, M.; Wintner, E.; Iskra, K.; Neger, T.; Olofsson, J.; Seyfried, H.; Dén, M.; Lackner, M.; Winter, F.; Vressner, A.; et al. Optical Diagnostics of Laser-Induced and Spark Plug-Assisted Hcci Combustion. SAE Tech. Pap. 2005, 2005, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, T.; Urushihara, T.; Gundersen, M. A Trial of Ignition Innovation of Gasoline Engine by Nanosecond Pulsed Low Temperature Plasma Ignition. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 135208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, T.; Urushihara, T. Fundamental Analysis of Combustion Initiation Characteristics of Low Temperature Plasma Ignition for Internal Combustion Gasoline Engine; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hampe, C.; Bertsch, M.; Beck, K.W.; Spicher, U.; Bohne, S.; Rixecker, G. Influence of High Frequency Ignition on the Combustion and Emission Behaviour of Small Two-Stroke Spark Ignition Engines. SAE Tech. Pap. 2013, 2013, 9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampe, C.; Kubach, H.; Spicher, U.; Rixecker, G.; Bohne, S. Investigations of Ignition Processes Using High Frequency Ignition. SAE Tech. Pap. 2013, 2, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, A.; Foucher, F. Radio Frequency Spark Plug: An Ignition System for Modern Internal Combustion Engines. Appl. Energy 2014, 122, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, D.I.; Wolk, B.; Chen, J.Y.; Dibble, R.W. Application of Corona Discharge Ignition in a Boosted Direct-Injection Single Cylinder Gasoline Engine: Effects on Combustion Phasing, Fuel Consumption, and Emissions. SAE Int. J. Engines 2016, 9, 1970–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembi, J.; Cruccolini, V.; Mariani, F.; Scarcelli, R.; Battistoni, M. Modeling of Thermal and Kinetic Processes in Non-Equilibrium Plasma Ignition Applied to a Lean Combustion Engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 197, 117377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggiani, C.; Cimarello, A.; Battistoni, M.; Grimaldi, C.N.; Dal Re, M.A.; De Cesare, M. Optical Investigations on a Multiple Spark Ignition System for Lean Engine Operation. SAE Tech. Pap. 2016, 2016, 7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruccolini, V.; Discepoli, G.; Cimarello, A.; Battistoni, M.; Mariani, F.; Grimaldi, C.N.; Dal Re, M. Lean Combustion Analysis Using a Corona Discharge Igniter in an Optical Engine Fueled with Methane and a Hydrogen-Methane Blend. Fuel 2020, 259, 116290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serizawa, T.; Oi, H.; Uchida, K.; Shima, Y.; Okumura, F. Experimental Study of the Performance of HF Electric Field Applied-Type Ignition System in SI EngineIn the 8th International Conference on Modeling and Diagnostics for Advanced Engine Systems; COMODIA: Tokyo, Japan, 2012; pp. 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Y.; Sun, W. Plasma Assisted Combustion: Dynamics and Chemistry. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2015, 48, 21–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclatchy, C.S. Langmuir Probe Measurements of Ion Density in an Atmosphereic-Pressure Air-Propane Flame. Combust. Flame 1979, 36, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclatchy, C.S.; Clements, R.M.; Smy, P.R. An Experimental Investigation of the Effect of Microwave Radiation on a Propane-Air Flame. Combust. Flame 1982, 45, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockman, E.S.; Zaidi, S.H.; Miles, R.B.; Carter, C.D.; Ryan, M.D. Measurements of Combustion Properties in a Microwave Enhanced Flame. Combust. Flame 2009, 156, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Nishiyama, A.; Kaneko, M. Microwave Enhanced Ignition Process for Fuel Mixture at Elevated Pressure of 1MPa. In Proceedings of the 47th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–8 January 2009; 2009; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolk, B.; DeFilippo, A.; Chen, J.Y.; Dibble, R.; Nishiyama, A.; Ikeda, Y. Enhancement of Flame Development by Microwave-Assisted Spark Ignition in Constant Volume Combustion Chamber. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Bae, C.; Park, J.; Choe, W.; Cha, J.; Woo, S. Microwave-Assisted Plasma Ignition in a Constant Volume Combustion Chamber. Combust. Flame 2016, 167, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, W.; Bae, C.; Choe, W.; Cha, J.; Woo, S. Application of a Novel Microwave-Assisted Plasma Ignition System in a Direct Injection Gasoline Engine. Appl. Energy 2017, 205, 562–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, W.; Bae, C. Influence of Plasma-Assisted Ignition on Flame Propagation and Performance in a Spark-Ignition Engine. Appl. Energy Combust. Sci. 2021, 6, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, H.; Liu, C.; Cheng, X.; Chen, J.Y. Propulsive Effect of Microwave-Induced Plasma Jet on Spark Ignition of CO2-Diluted CH4-Air Mixture. Combust. Flame 2021, 229, 111400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. Effect of Microwave Pulse Parameters on Energy Coupling and Enhancement of Microwave Assisted Ignition. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2022, 000, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Nishiyama, A.; Katano, H.; Kaneko, M.; Jeong, H. Research and Development of Microwave Plasma Combustion Engine (Part II: Engine Performance of Plasma Combustion Engine); SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama, A.; Ikeda, Y. Improvement of Lean Limit and Fuel Consumption Using Microwave Plasma Ignition Technology; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Defilippo, A.; Saxena, S.; Rapp, V.; Dibble, R.; Chen, J.Y.; Nishiyama, A.; Ikeda, Y. Extending the Lean Stability Limits of Gasoline Using a Microwave-Assisted Spark Plug; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hammack, S.; Rao, X.; Lee, T.; Carter, C. Direct-Coupled Plasma-Assisted Combustion Using a Microwave Waveguide Torch. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2011, 39, 3300–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, J.B.; Chng, T.L.; Miles, R.B. Sustained Propagation of Ultra-Lean Methane/Air Flames with Pulsed Microwave Energy Deposition. Combust. Flame 2013, 160, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, M.; Wang, H.; Cai, Z. Ignition and Combustion Enhancement in a Cavity-Based Supersonic Combustor by a Multi-Channel Gliding Arc Plasma. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2021, 120, 110248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Bian, D.; Jin, D. Ignition Enhancement of Lean Propane/Air Mixture by Multi-Channel Discharge Plasma under Low Pressure. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 148, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, T.; Wu, S.; Ma, G.; Yan, C.; Ju, Y. Studies of Multi-Channel Spark Ignition of Lean n-Pentane/Air Mixtures in a Spherical Chamber. Combust. Flame 2020, 212, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, M.; Sanda, S.; Nakamura, N. Development of Toyota Lean Burn Engine; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, T.G. Torch Ignition for Combustion Control of Lean Mixtures; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Latsch, R. The Swirl-Chamber Spark Plug: A Means of Faster, More Uniform Energy Conversion in the Spark-Ignition Engine; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Date, T.; Yagi, S.; Ishizuya, A.; Fujii, I. Research and Development of the Honda CVCC Engine; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Attard, W.P.; Kohn, J.; Parsons, P. Ignition Energy Development for a Spark Initiated Combustion System Capable of High Load, High Efficiency and near Zero NOx Emissions. SAE Tech. Pap. 2010, 3, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boretti, A.A.; Watson, H.C. Enhanced Combustion by Jet Ignition in a Turbocharged Cryogenic Port Fuel Injected Hydrogen Engine. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 2511–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulson, E.; Schock, H.J.; Attard, W.P. A Review of Pre-Chamber Initiated Jet Ignition Combustion Systems; SAE Tech. Pap. SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Attard, W.P.; Blaxill, H. A Single Fuel Pre-Chamber Jet Ignition Powertrain Achieving High Load, High Efficiency and near Zero NOx Emissions. SAE Tech. Pap. 2011, 5, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benajes, J.; Novella, R.; Gomez-Soriano, J.; Barbery, I.; Libert, C. Advantages of Hydrogen Addition in a Passive Pre-Chamber Ignited SI Engine for Passenger Car Applications. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 13219–13237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
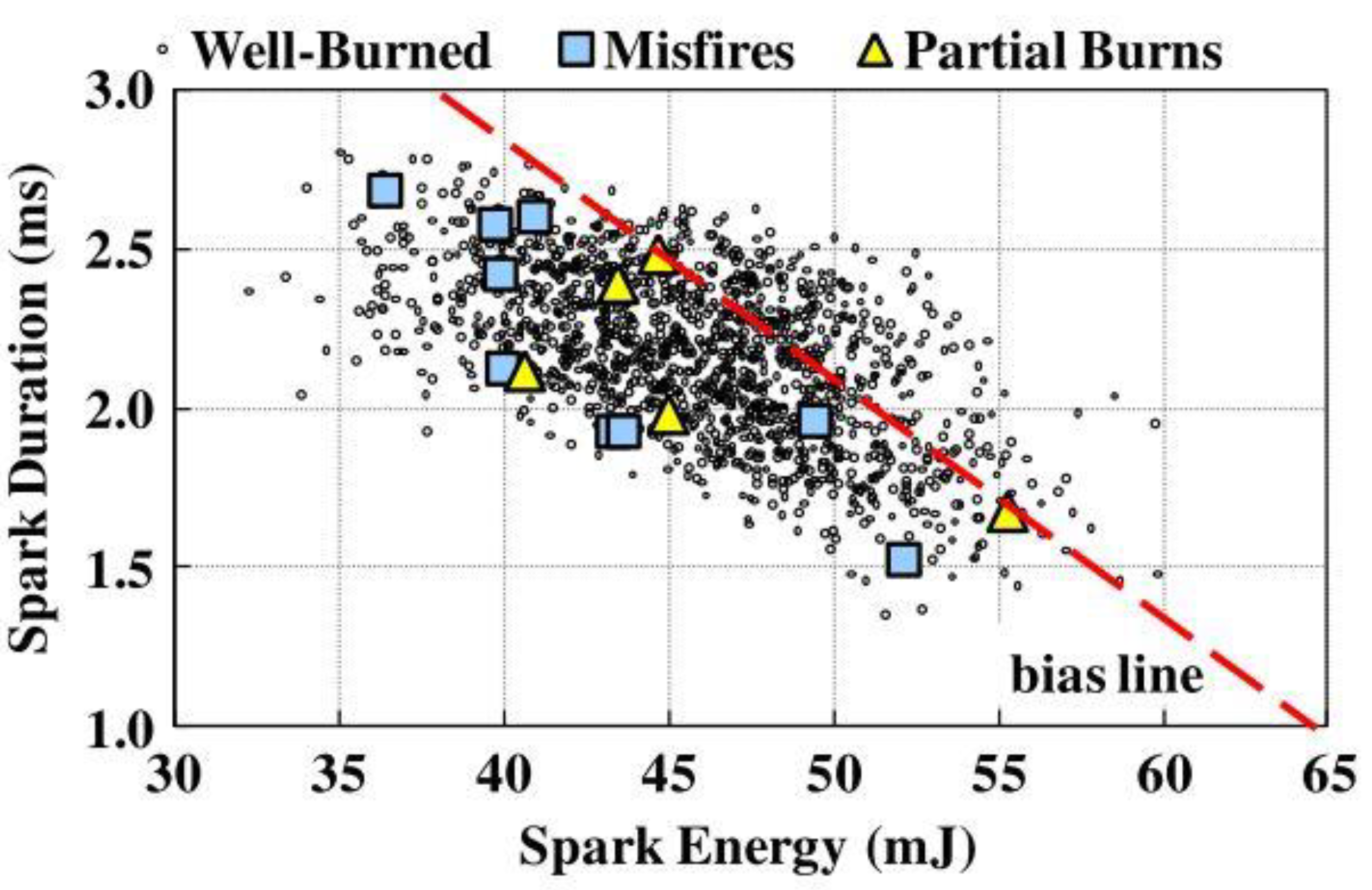
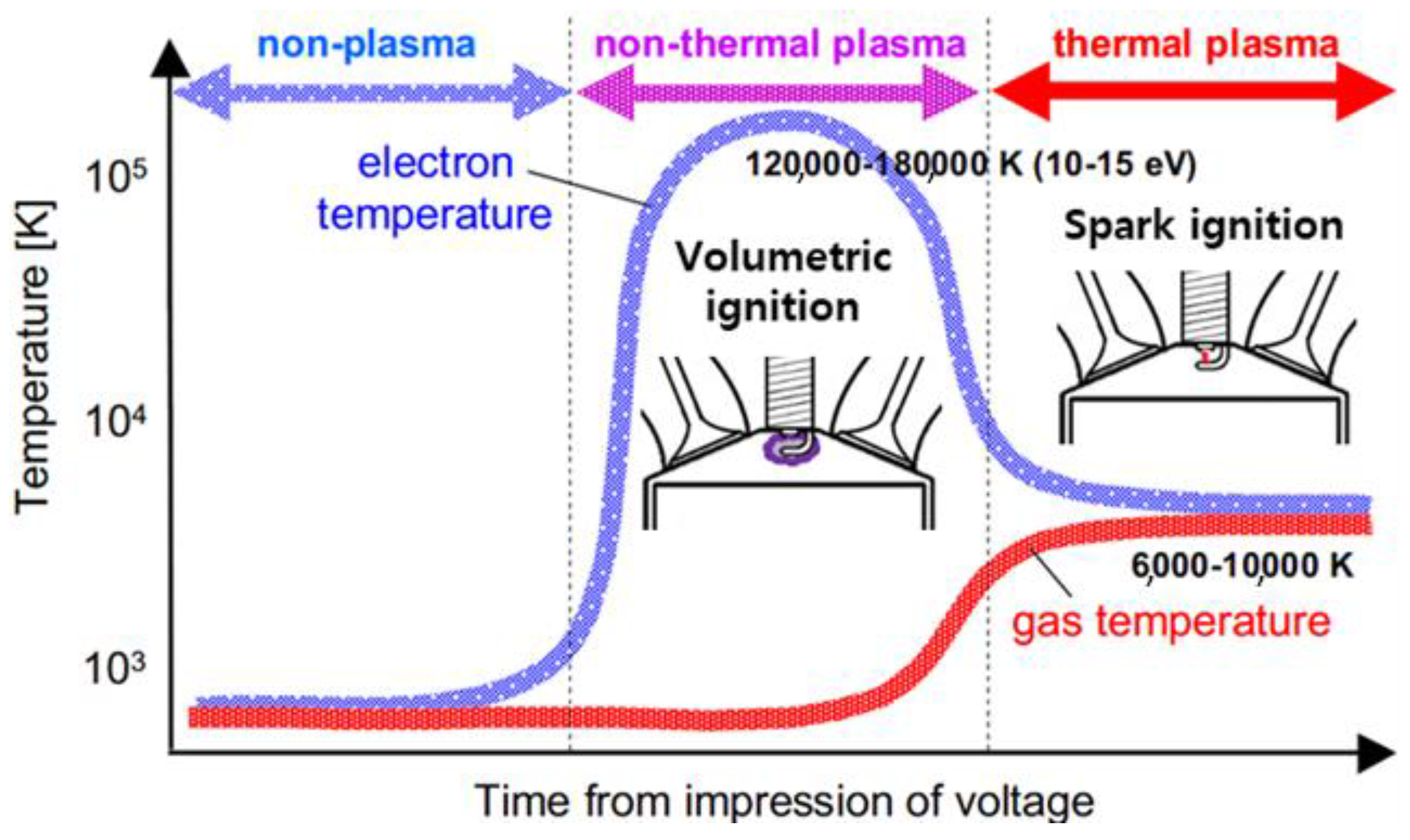
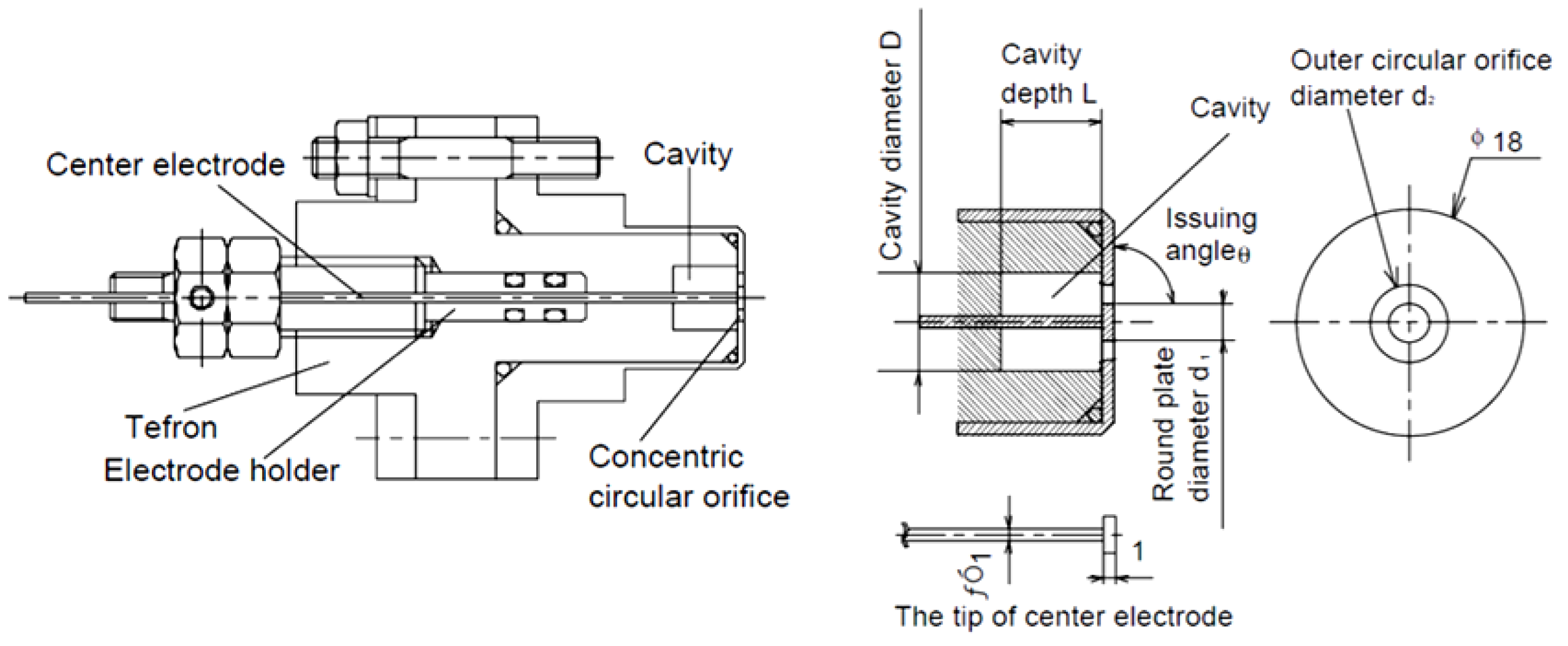
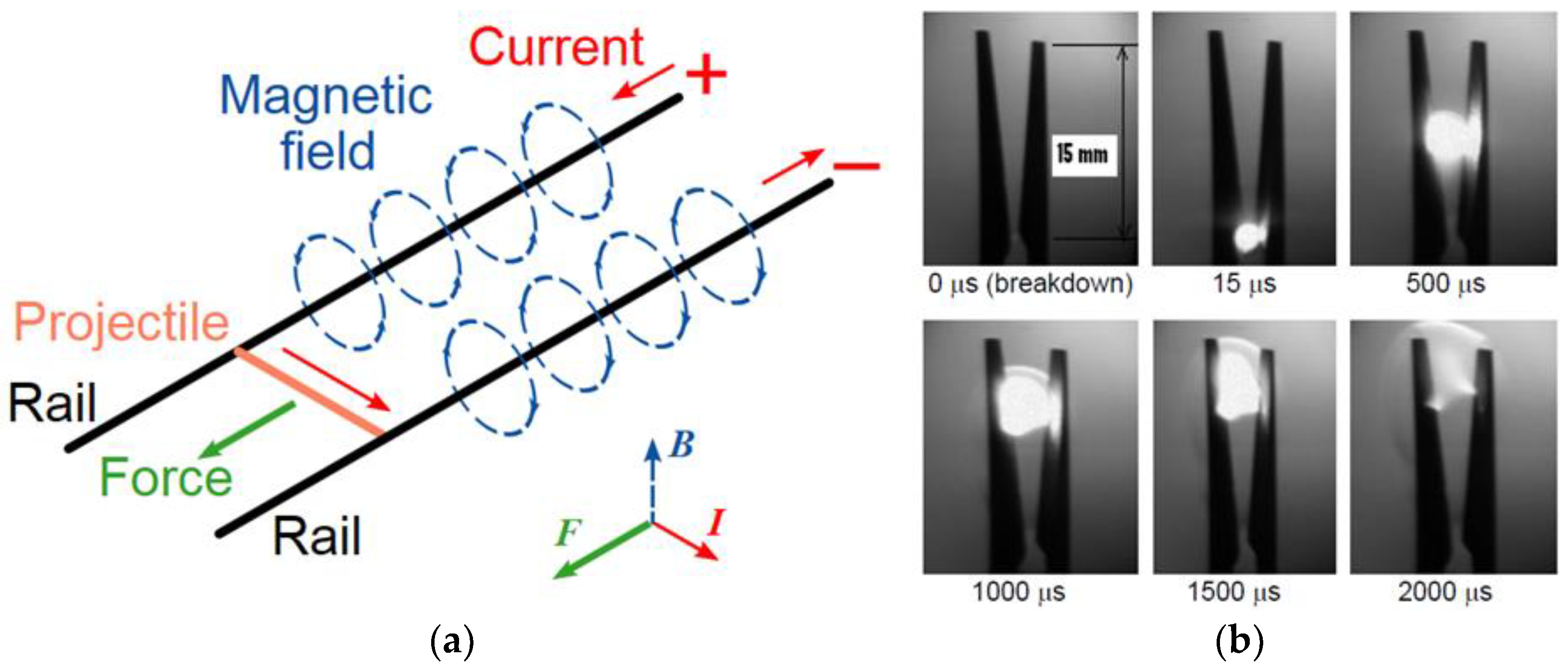
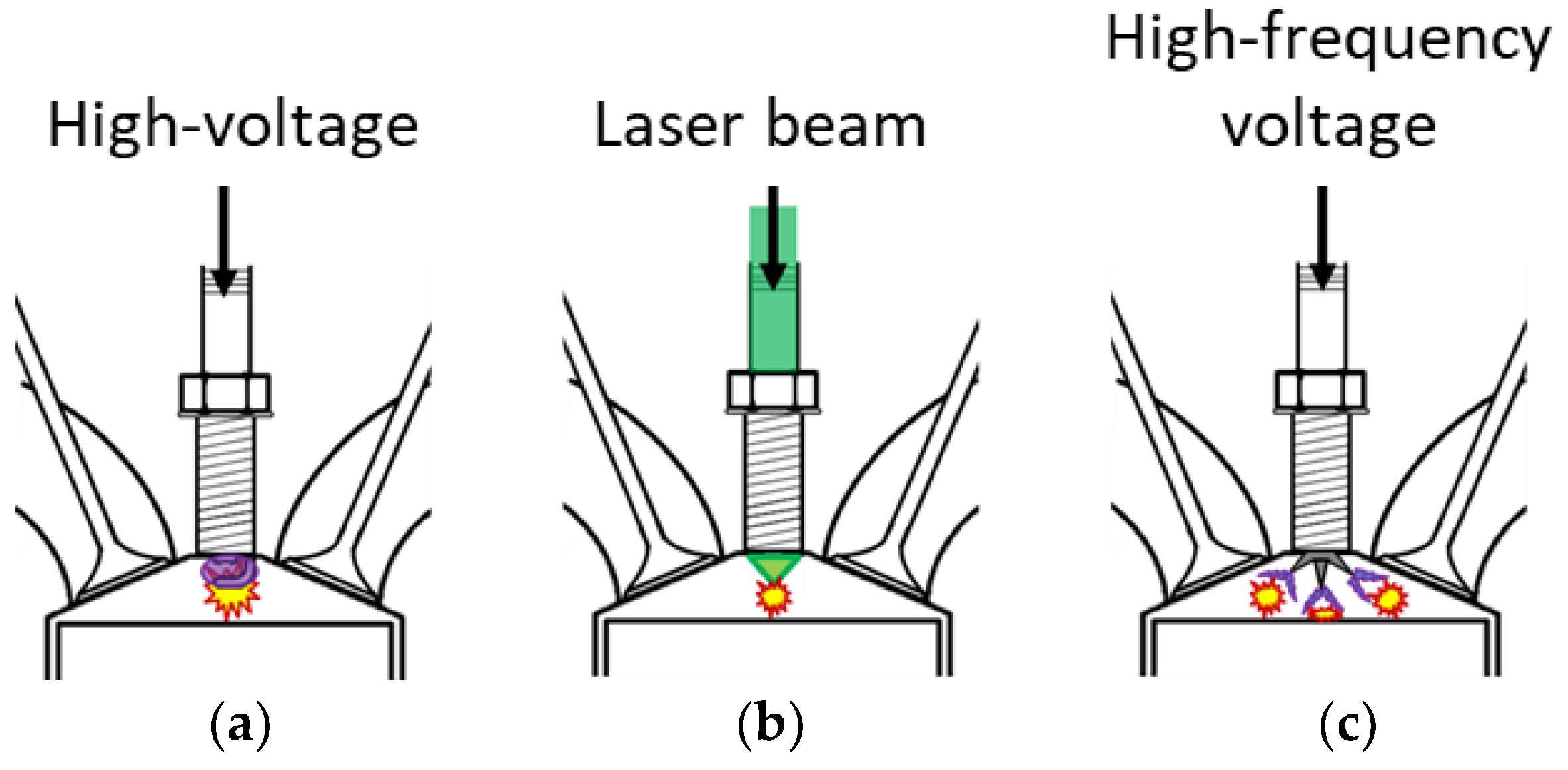
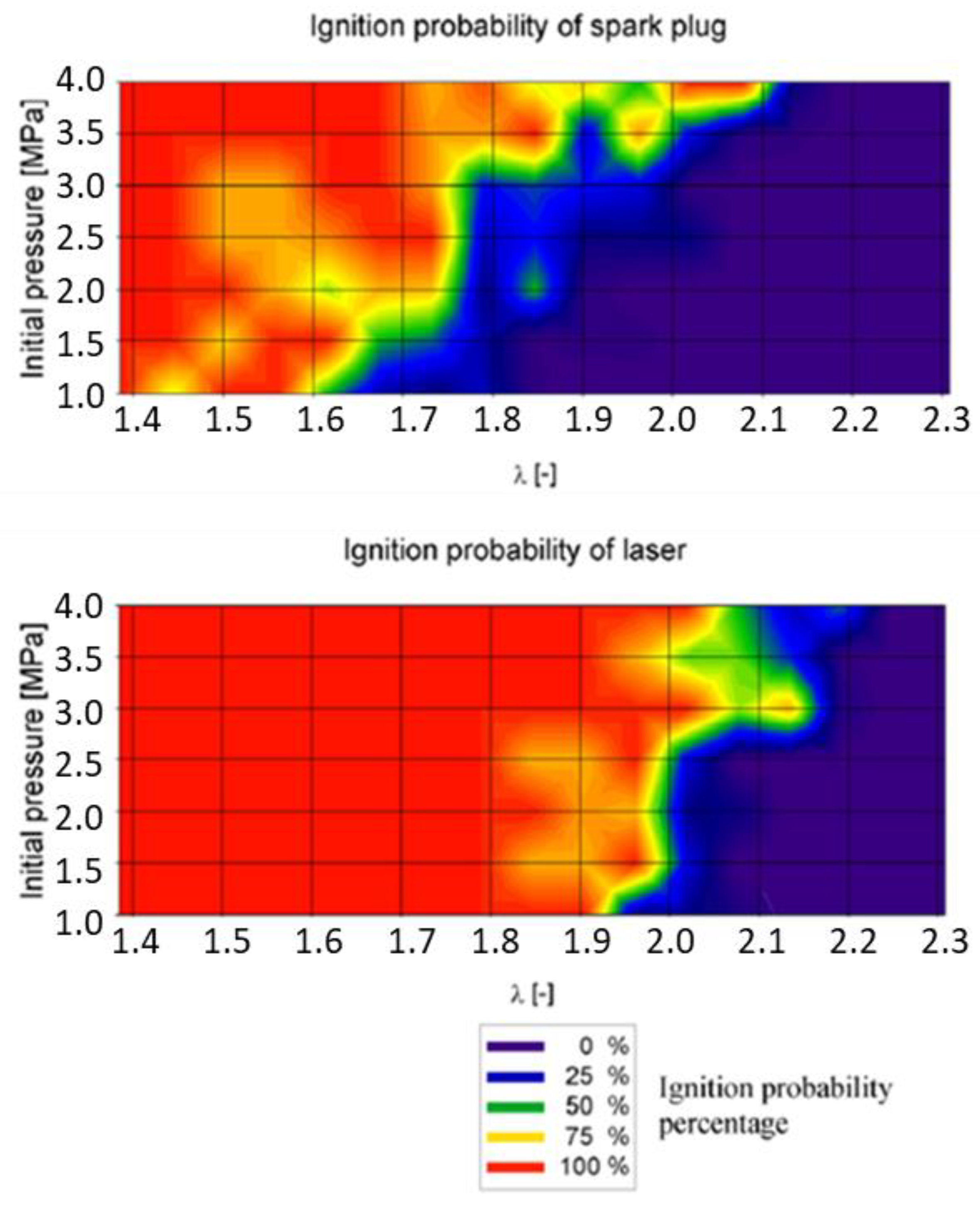
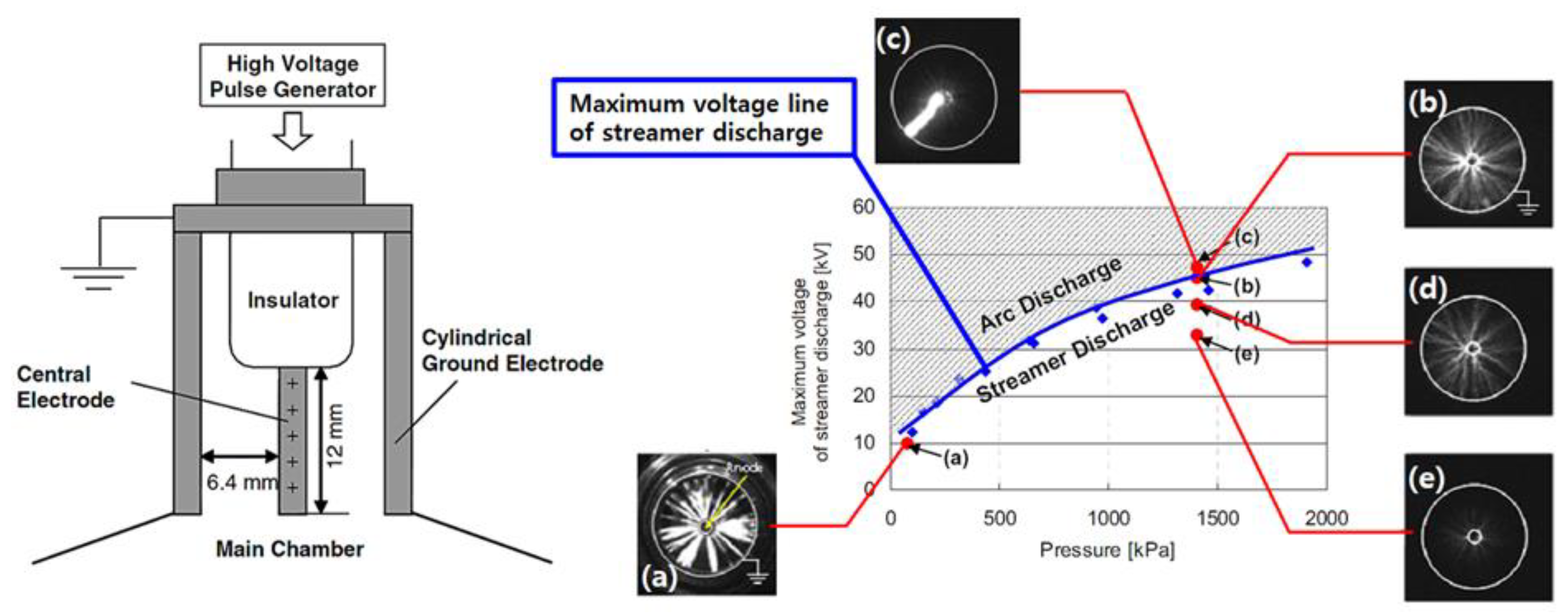
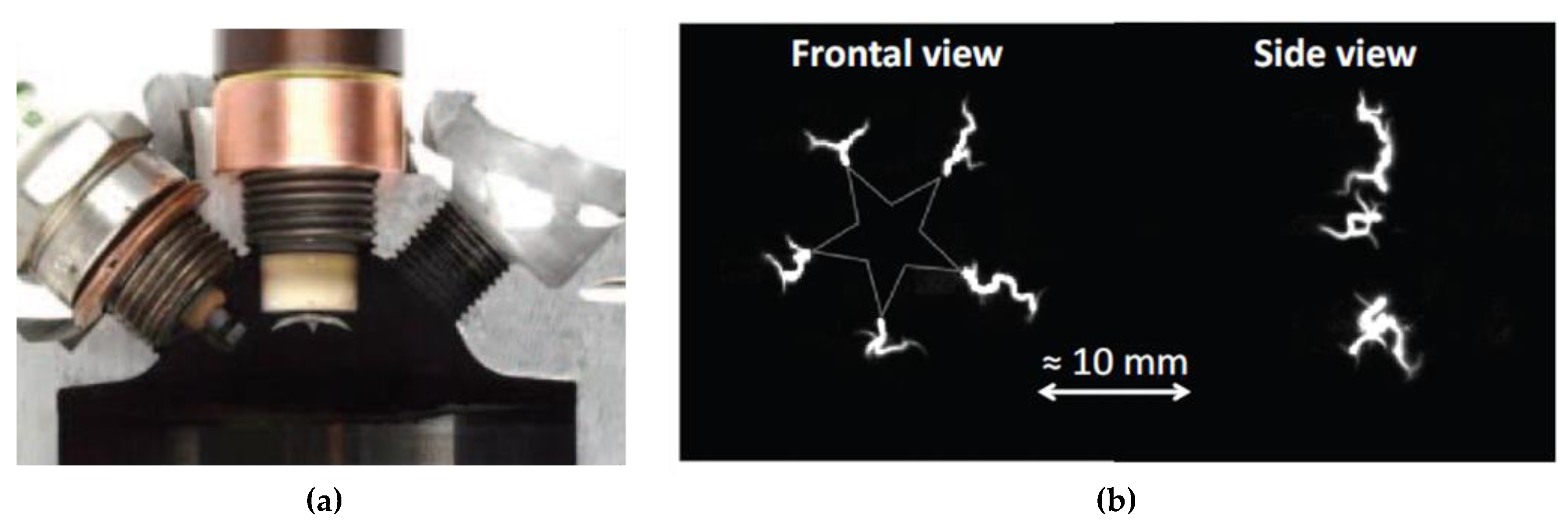
| Author | Affiliation | Main Parameter | Main Results | Energy Per event | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yoshida | Nihon Univ. | Orifice area↑ (Chamber exp.) | Peak pressure↑ Combustion duration↓ | 5.0 J | [16] |
| Gao | Univ. Texas at Austin | Rail plug application (Engine exp.) | Lean limit↑ Combustion stability↑ | [18] | |
| Kim | Mississippi state Univ | A/f ratio↑ Ignition energy↑ (Chamber exp.) | Lean limit↑ Flame speed↑ | 2.03 J | [20] |
| Ogawa | Nihon Univ. | Cavity volume↑ (Chamber exp.) | Luminous area ↑ Penetration depth ↑ | 5.0 J | [21] |
| Gao | Univ. Texas at Austin | Discharge duration↑ Ignition energy↑ (Engine exp.) | Combustion stability↑ Combustion duration↓ | 0.3–1.5 J | [17] |
| Sasaki | Nihon Univ. | Cavity depth↑ Orifice diameter↑ Ignition energy↑ (Chamber exp.) | Peak pressure↑ Plasma jet velocity↑ | 2.5–10 J | [22] |
| Author | Affiliation | Main Parameter | Main Results | Energy Per Event | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weinrotter | Vienna Univ. Tech. | H2 addition Multi-ignition (Chamber exp.) | Peak pressure↑ Combustion duration↓ | 8–24 mJ | [23] |
| Groß | KIT | Laser energy↑ (Engine exp.) | - Homogeneous Combustion stability↑ Ignition delay↓ - Stratified Combustion opposite trend | 10—50 mJ | [24] |
| Genzale | Georgia Inst. Tech. | Ignition timing (Chamber exp.) | Optimized ignition timing | 2–15 mJ | [25] |
| Tsunekane | JST | # of ignition↑ (Chamber exp.) | Flame area↑ Ignition limit↑ | 2.7–11.7 mJ | [26] |
| Pavel | National Institute for Laser, Romania | Laser-induced plasma ignition | Engine brake power↑ BSFC↓ | 4 mJ | [27] |
| Kumar | Univ. of Tokyo | Pulse width and pulse repetition frequency | Ignition success rate and ignition delay | 14.3 mJ | [28] |
| Pastor | CMT, Valencia | Ignition location (Chamber exp.) | Optimized ignition location | 800 mJ | [29] |
| Phuod | U.S. DOE | Laser energy↑ | Ignition limit↑ | 15–200 mJ | [30] |
| Weinrotter | Vienna Univ. Tech. | Laser-induced plasma ignition (Chamber exp.) | Ignition limit↑ Peak pressure↑ Ignition delay↓ | 25 mJ | [31] |
| Author | Affiliation | Main Parameter | Main Results | Energy Per Event | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shiraishi | Nissan Motor | Streamer discharge (Engine exp.) | Peak pressure↑ Ignition delay↓ Flame speed↑ | 60 mJ | [32] |
| Shiraishi | Nissan Motor | Streamer discharge (Engine exp.) | Flame area↑ Flame speed↑ O radical↑ | 60 mJ | [33] |
| Hampe | MOT GmbH | RFSI application (Engine exp.) | Peak pressure↑ IMEP↑ Fuel consumption↓ CO, HC, and NOx ↓ Combustion duration↓ | >55 mJ | [34] |
| Mariani | Uni. Orléans | RFSI application Equivalence ratio↓ (Engine exp.) | Combustion stability↑ Lean limit↑ Fuel consumption↓ CO and HC↓ NOx↑ | - | [36] |
| Pineda | Uni. California | RF corona discharge ignition application (Engine exp.) | Combustion stability↑ Fuel consumption↓ Knock↓ | 265–670 mJ | [37] |
| Zembi | Università degli Studi di Perugia | RF corona discharge ignition application Equivalence ratio (Engine exp.) | Active radicals↑ Flame speed↑ | 35–120 mJ | [38] |
| Poggiani | Università degli Studi di Perugia | A/f ratio | Flame speed↑ Lean limit↑ NOx↑ | 50 mJ | [39] |
| Cruccolini | Università degli Studi di Perugia | Fuel, A/f ratio | Flame speed↑ Lean limit↑ | 10–20 mJ | [40] |
| Serizawa | Daihatsu Motor | HF electric field application | O radical↑ NOx↑ | 120 mJ | [41] |
| Author | Affiliation | Main Parameter | Main Results | Energy Per Event | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groff | GM | Microwave (Waveguide exp.) | Flame deflection↑ Flame speed↑ | 250 W (CW) | [43] |
| Maclatchy | Acadia Univ. | Microwave (Waveguide exp.) | Flame speed↑ Flame temperature↑ | 500 W (CW) Continuous wave | [44] |
| Stockman | Univ. Princeton | A/F ratio↑ (Waveguide exp.) | Flame temperature↑ OH number density↑ Flame speed↑ Lean limit↑ | 1.3 kW (CW) | [45] |
| Wolk | UC Berkeley | Initial pressure↑ (Chamber exp.) | Flame speed↓ Flame deflection↓ | 225 mJ | [47] |
| Hwang | KAIST | Microwave (Chamber exp.) | Lean limit↑ Flame speed↑ | 700 W | [48] |
| Hwang | KAIST | Microwave (Chamber, engine exp.) | Combustion pressure↑ Combustion stability↑ Fuel consumption↓ | 3 kW | [49] |
| Hwang | KAIST | Microwave (Chamber, engine exp.) | Electron temperature↑ Flame speed↑ | 3 kW | [50] |
| Zhang | Huazhong Univ. | EGR condition (Chamber exp.) | Lean limit↑ | 150 mJ | [51] |
| Wu | Huazhong Univ. | uw energy↑ | Coupled energy↑ | 400–1000 W | [52] |
| Ikeda | Imagineering | Microwave (Bench exp.) | OH radical↑ Discharge intensity↑ | - | [53] |
| Ikeda | Imagineering | A/F ratio↑ (Engine exp.) | Lean limit↑ Combustion stability↑ CO↓ NOx↑ | - | [54] |
| Defilippo | UC Berkeley | uw energy↑ (Engine exp.) | Combustion stability↑ Fuel consumption↓ | 130–1640 mJ | [55] |
| Hammack | Michigan state Univ. | uw energy↑ (Waveguide exp.) | Flame temperature↑ OH number density↑ | 200–1000 W (CW) | [56] |
| Michael | Univ. Princeton | uw energy↑ | Flame temperature↑ Flame speed↑ Flame luminosity↑ Lean limit↑ | 25–50 mJ | [57] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.H.; Hwang, J. Review on Plasma-Assisted Ignition Systems for Internal Combustion Engine Application. Energies 2023, 16, 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041604
Choi YH, Hwang J. Review on Plasma-Assisted Ignition Systems for Internal Combustion Engine Application. Energies. 2023; 16(4):1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041604
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Yong Hyun, and Joonsik Hwang. 2023. "Review on Plasma-Assisted Ignition Systems for Internal Combustion Engine Application" Energies 16, no. 4: 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041604
APA StyleChoi, Y. H., & Hwang, J. (2023). Review on Plasma-Assisted Ignition Systems for Internal Combustion Engine Application. Energies, 16(4), 1604. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041604





