A Review of Biomass-to-Bioenergy Supply Chain Research Using Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Background
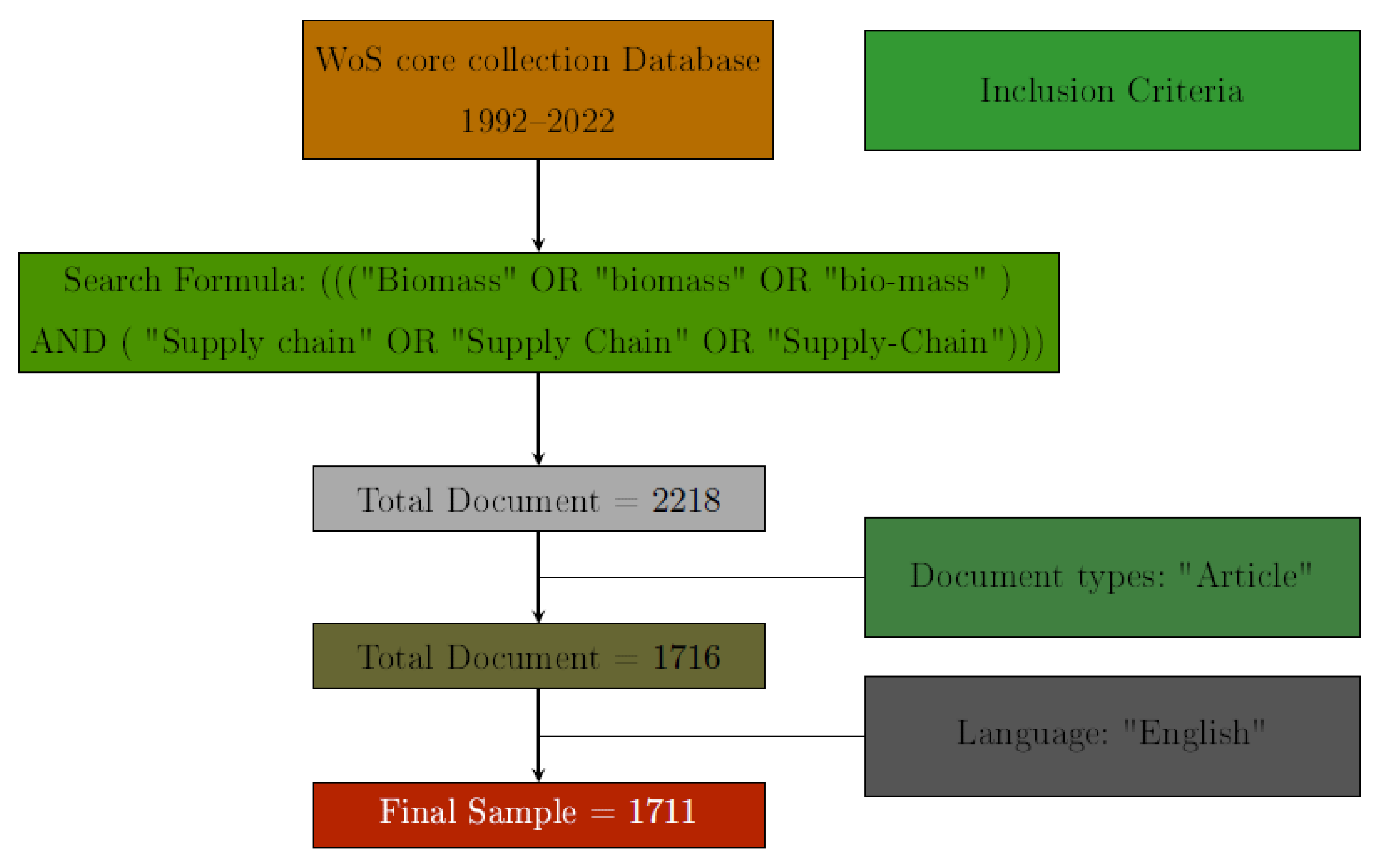
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Analysis
3. Results
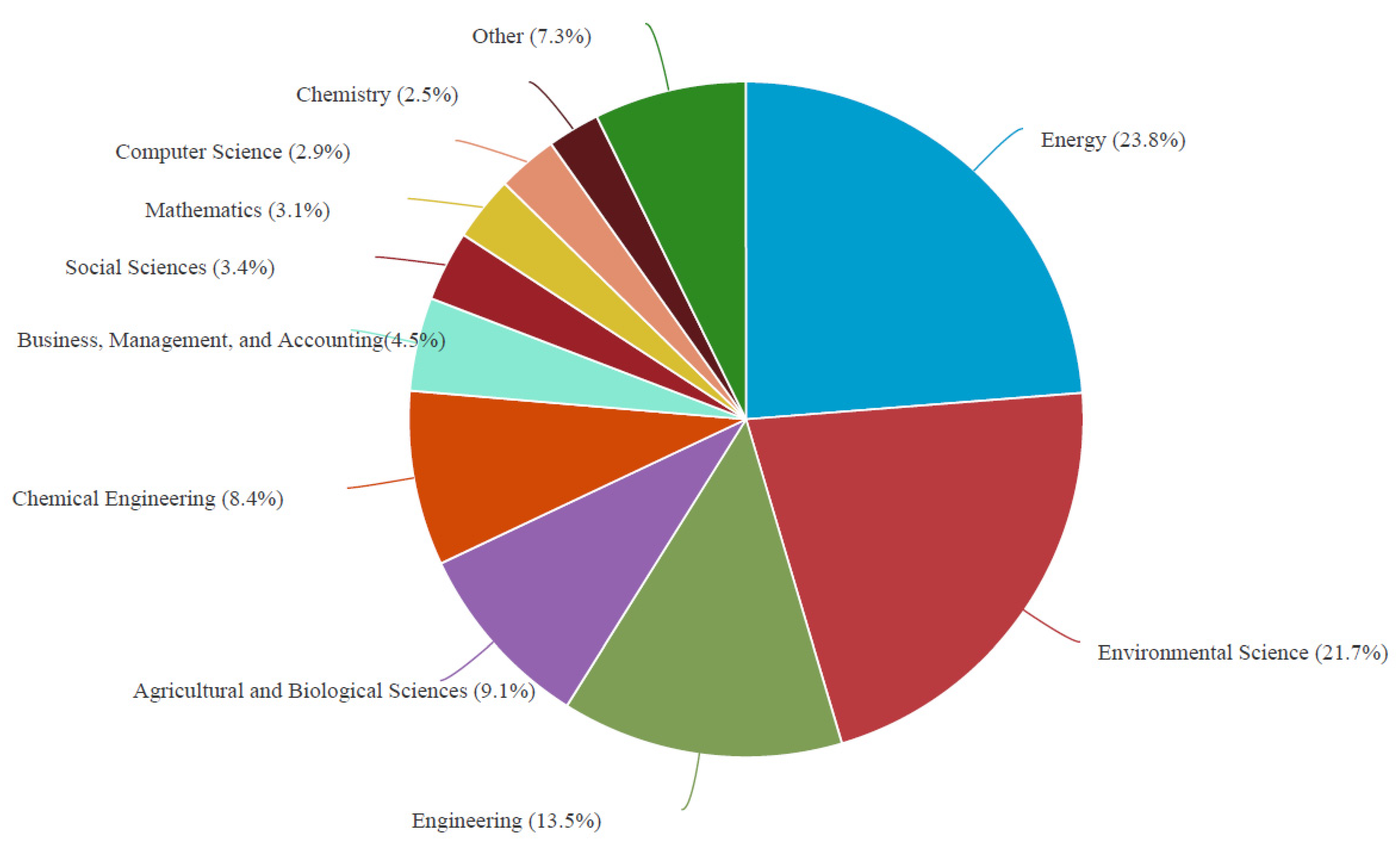
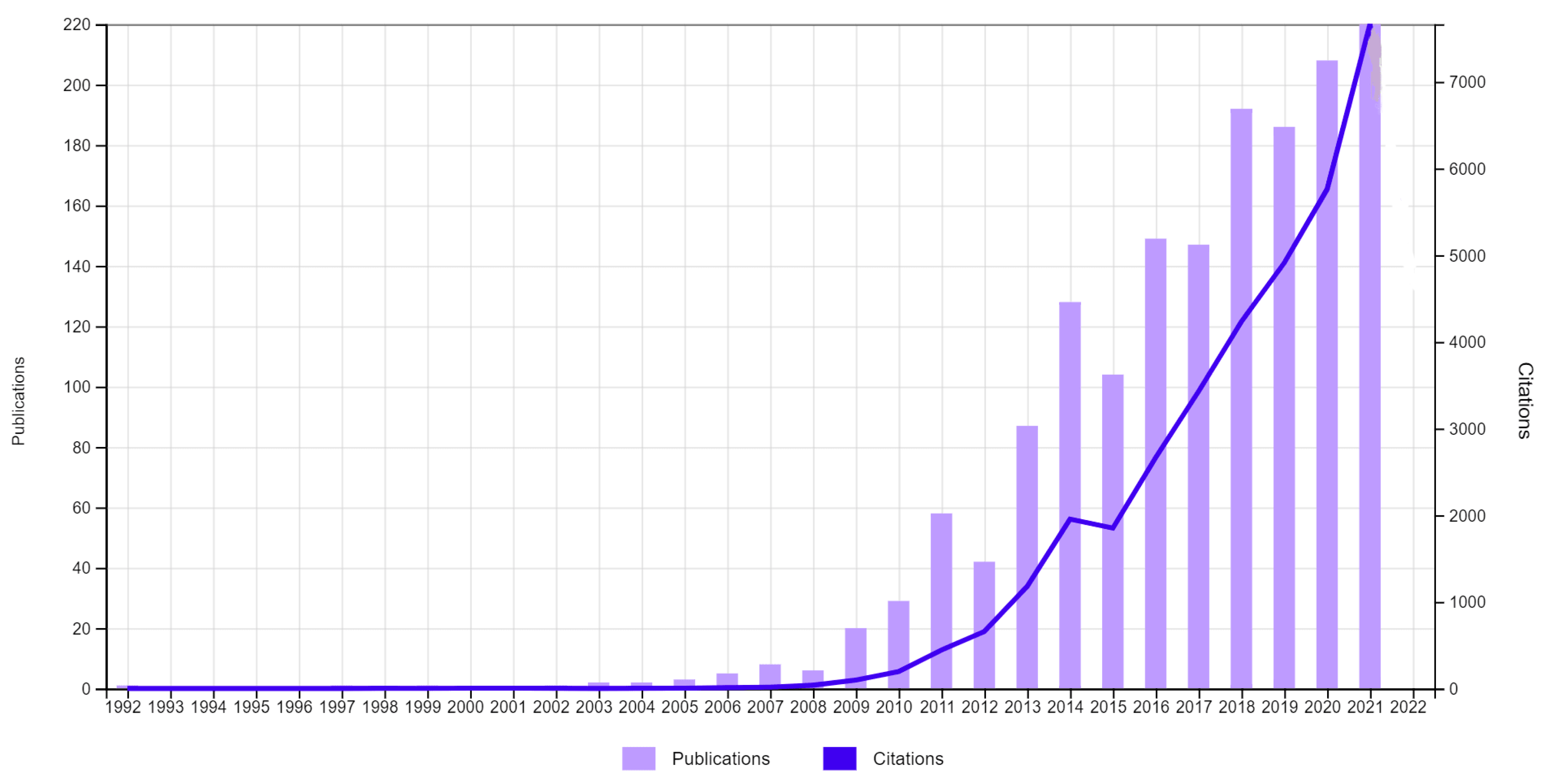
3.1. Overview
3.2. Productivity
3.3. Impact of Source
3.4. High-Impact Publications
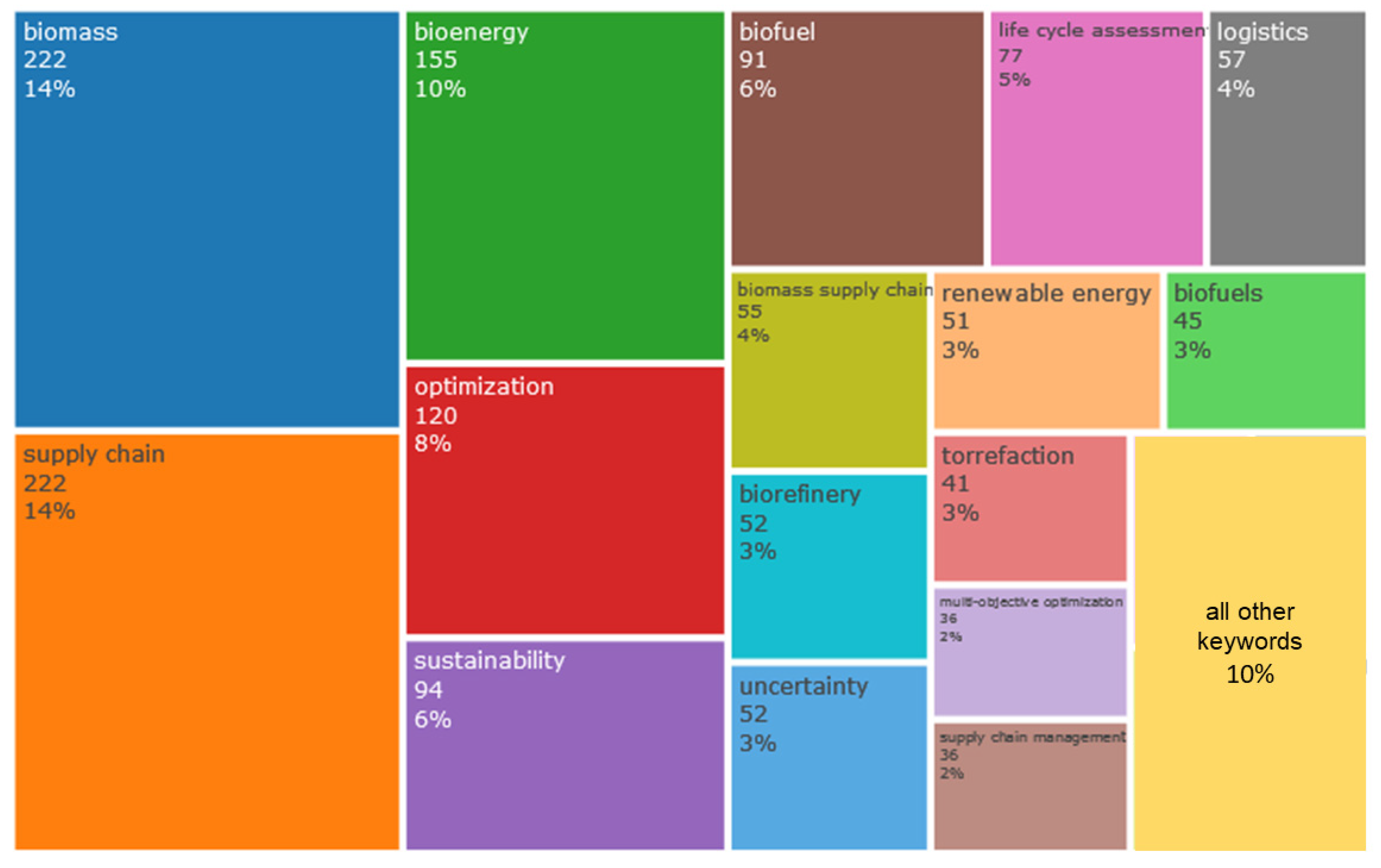
3.5. Keyword Analysis
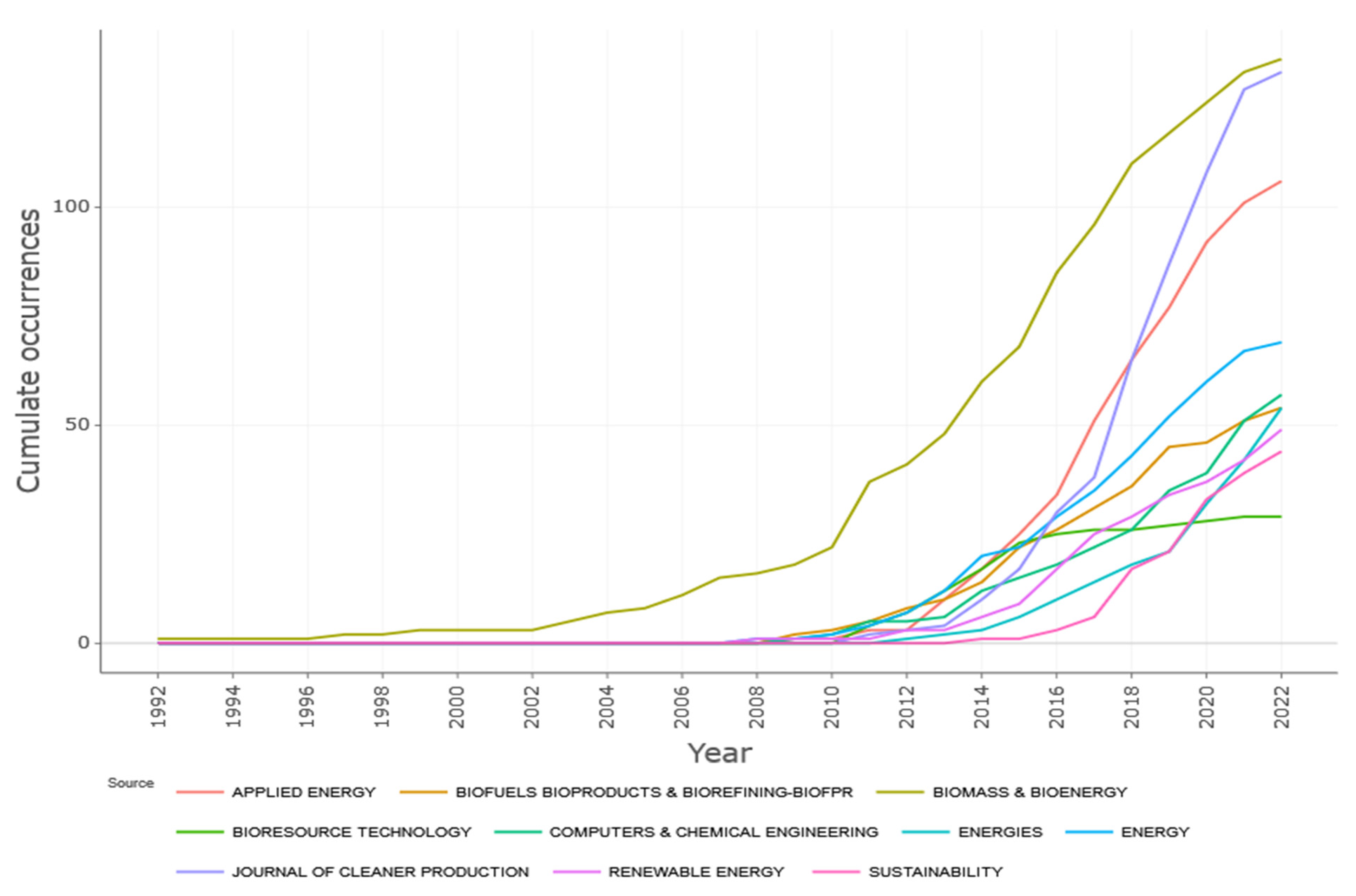
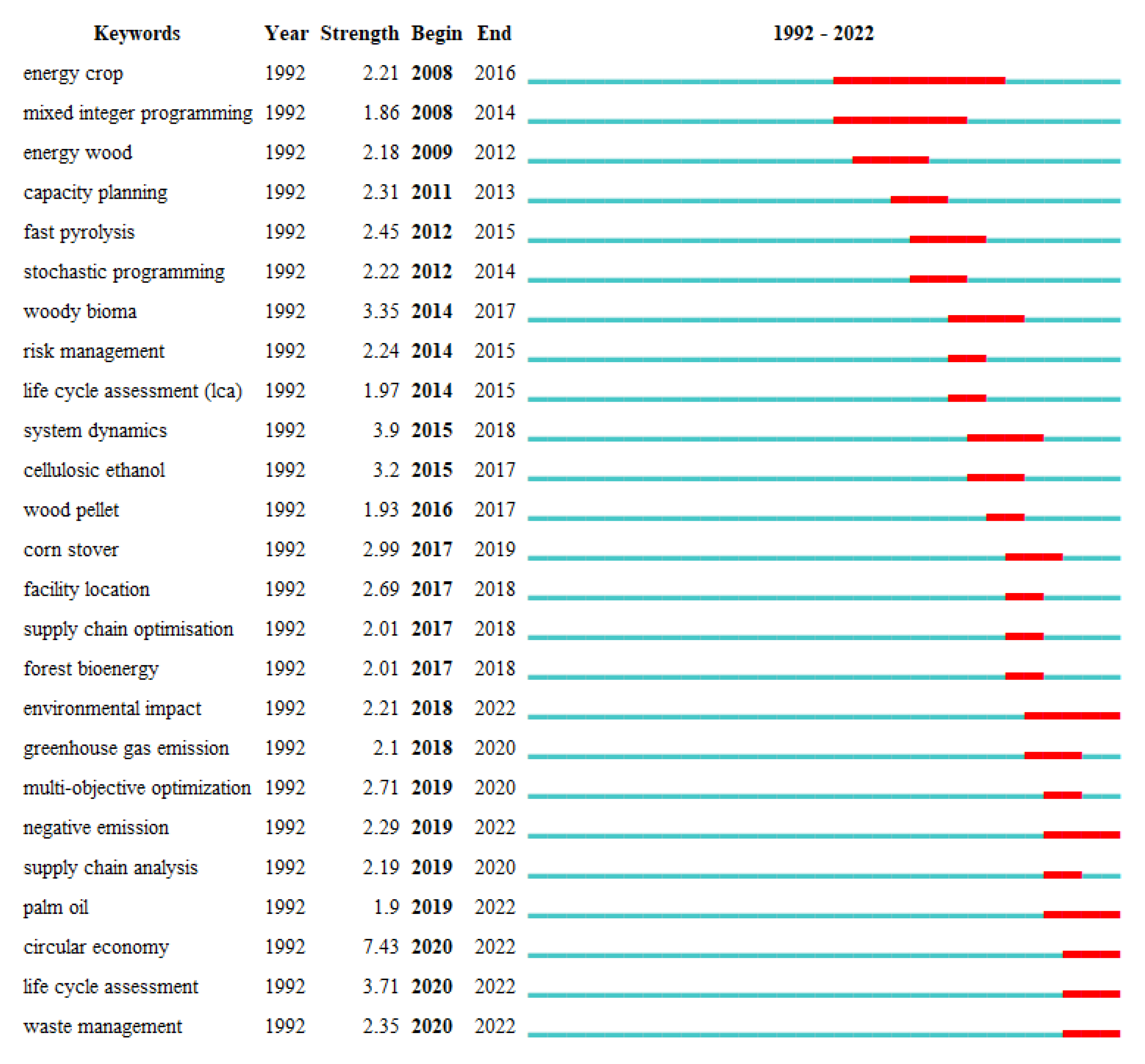
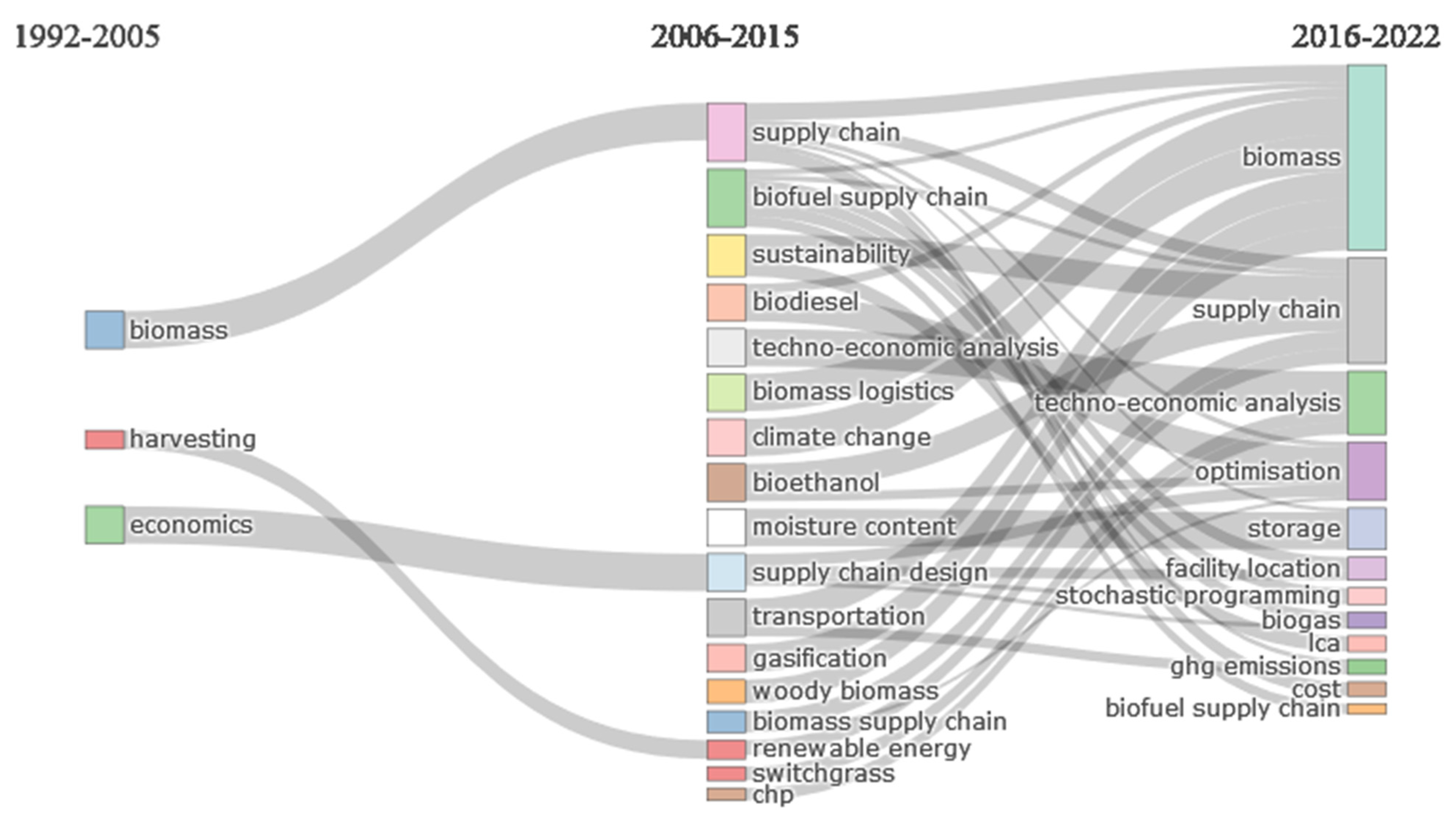
3.6. Keyword Evolution
3.7. Global Impact and Collaboration
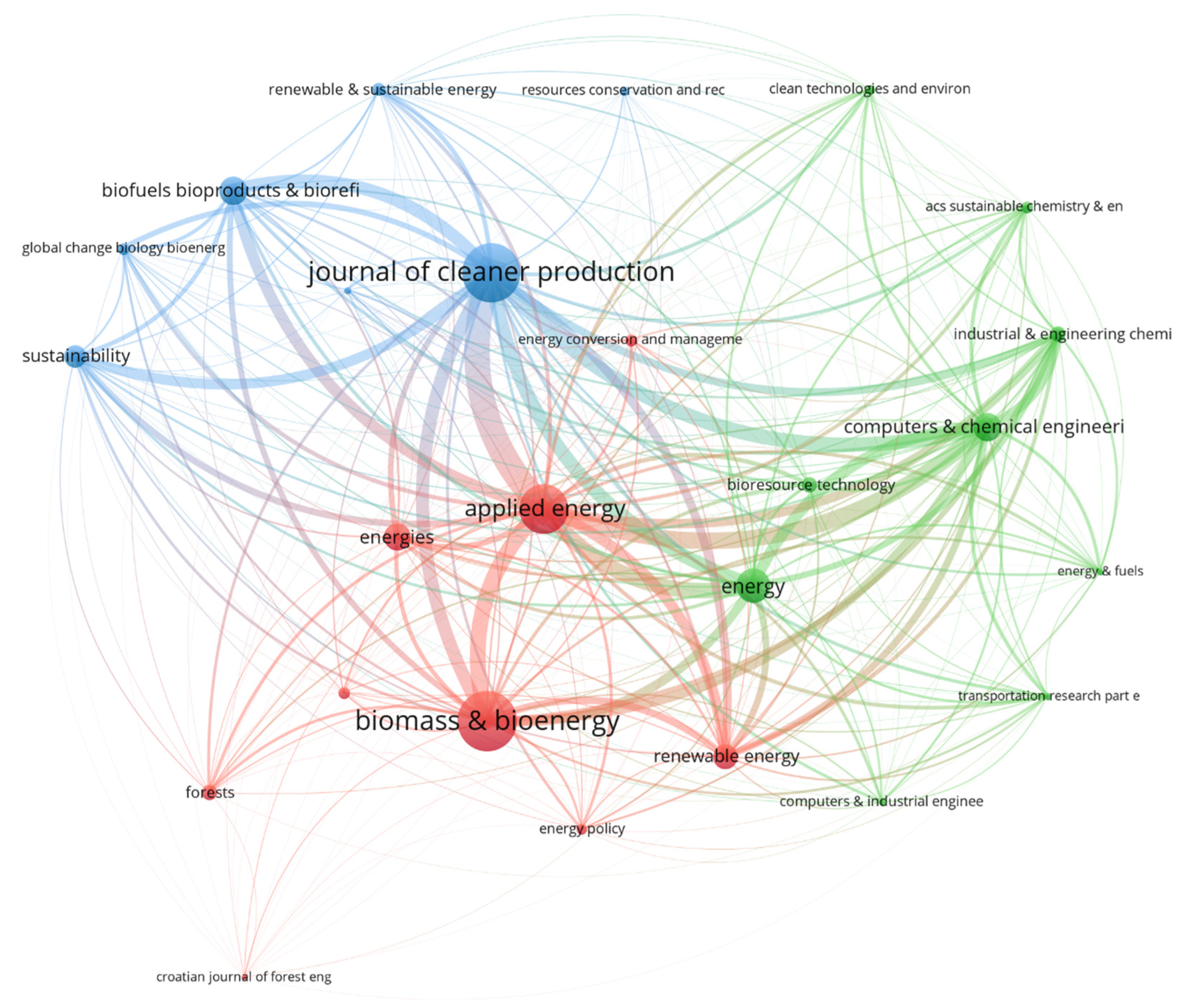
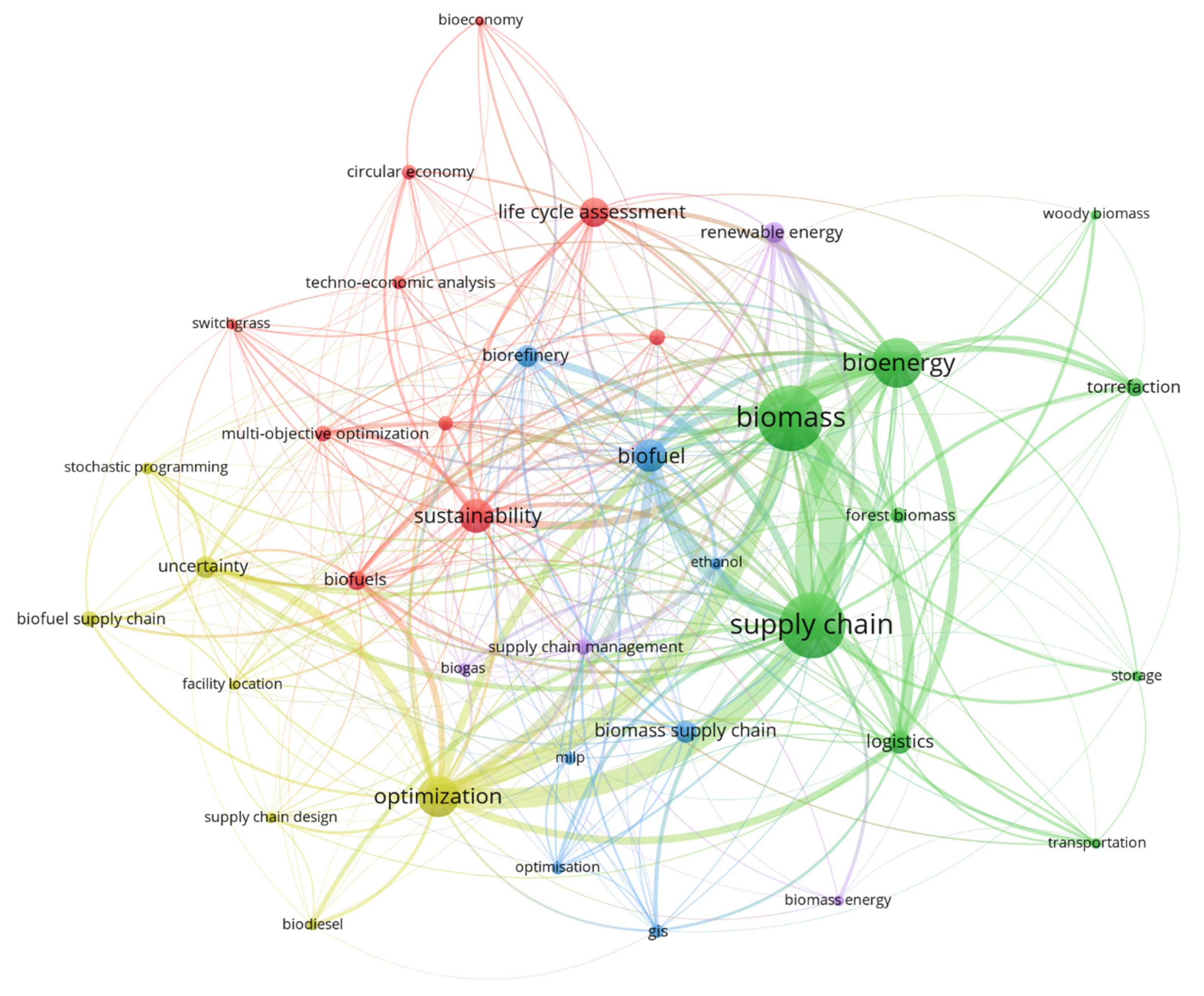
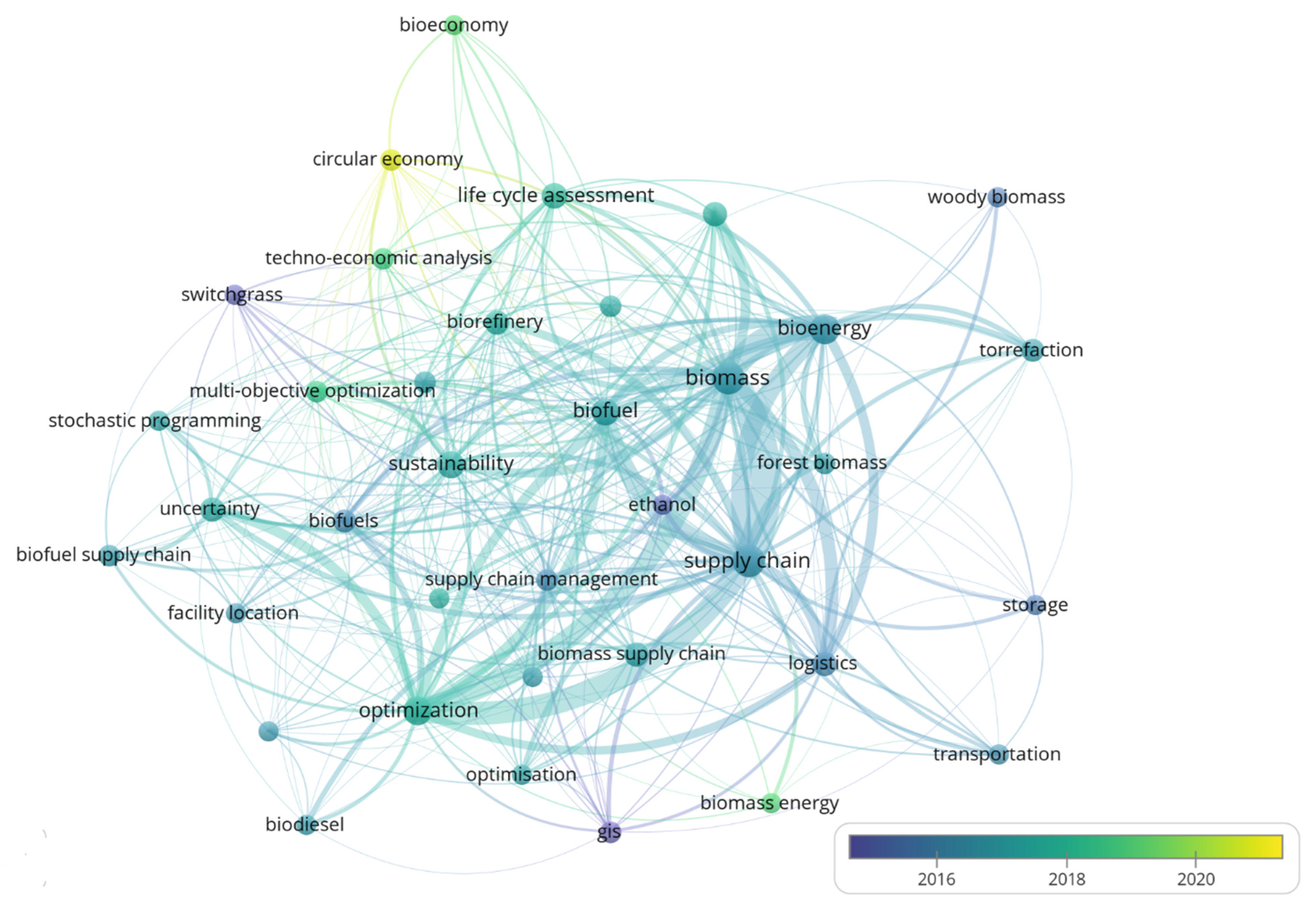
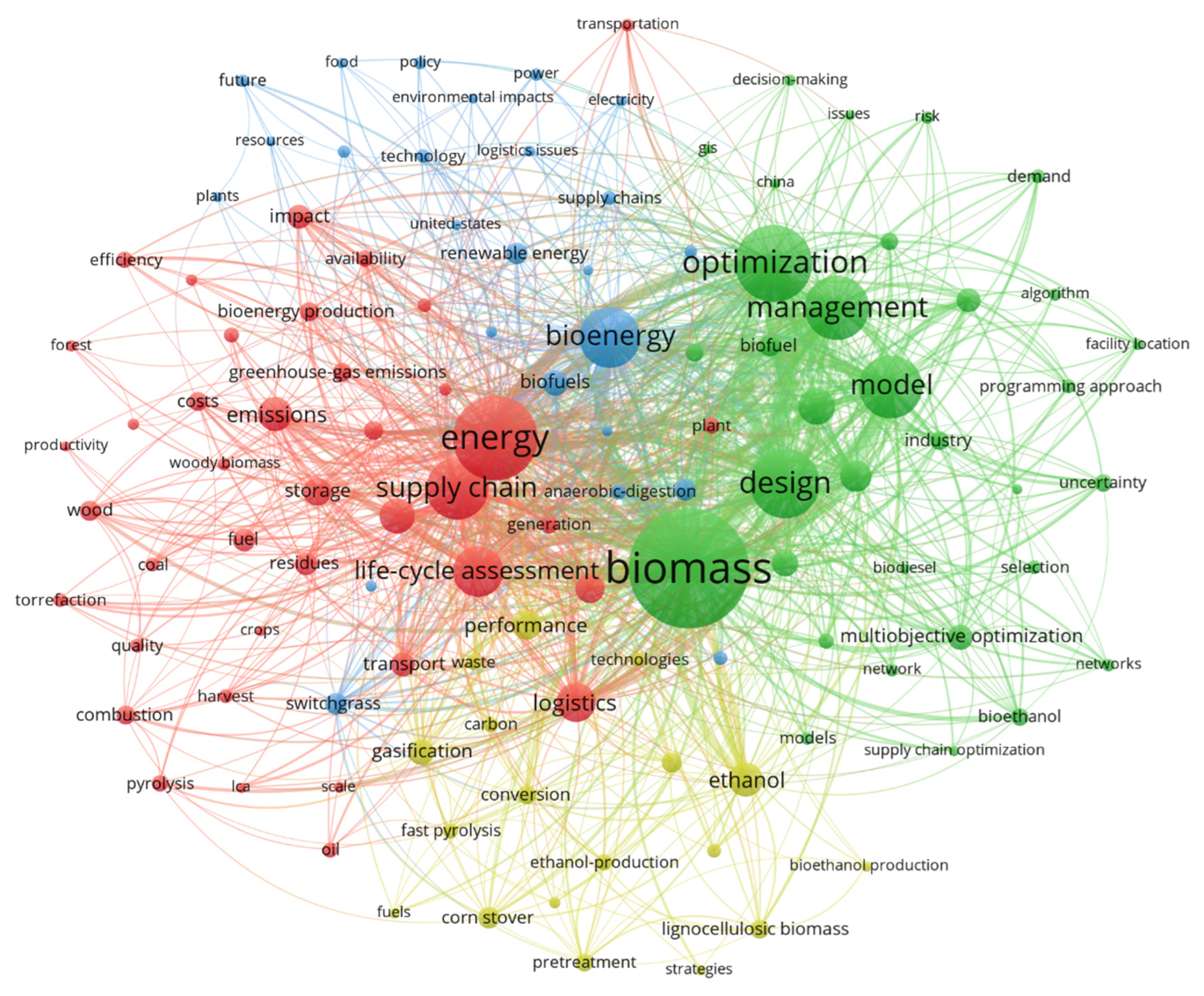
3.8. Keyword Mapping
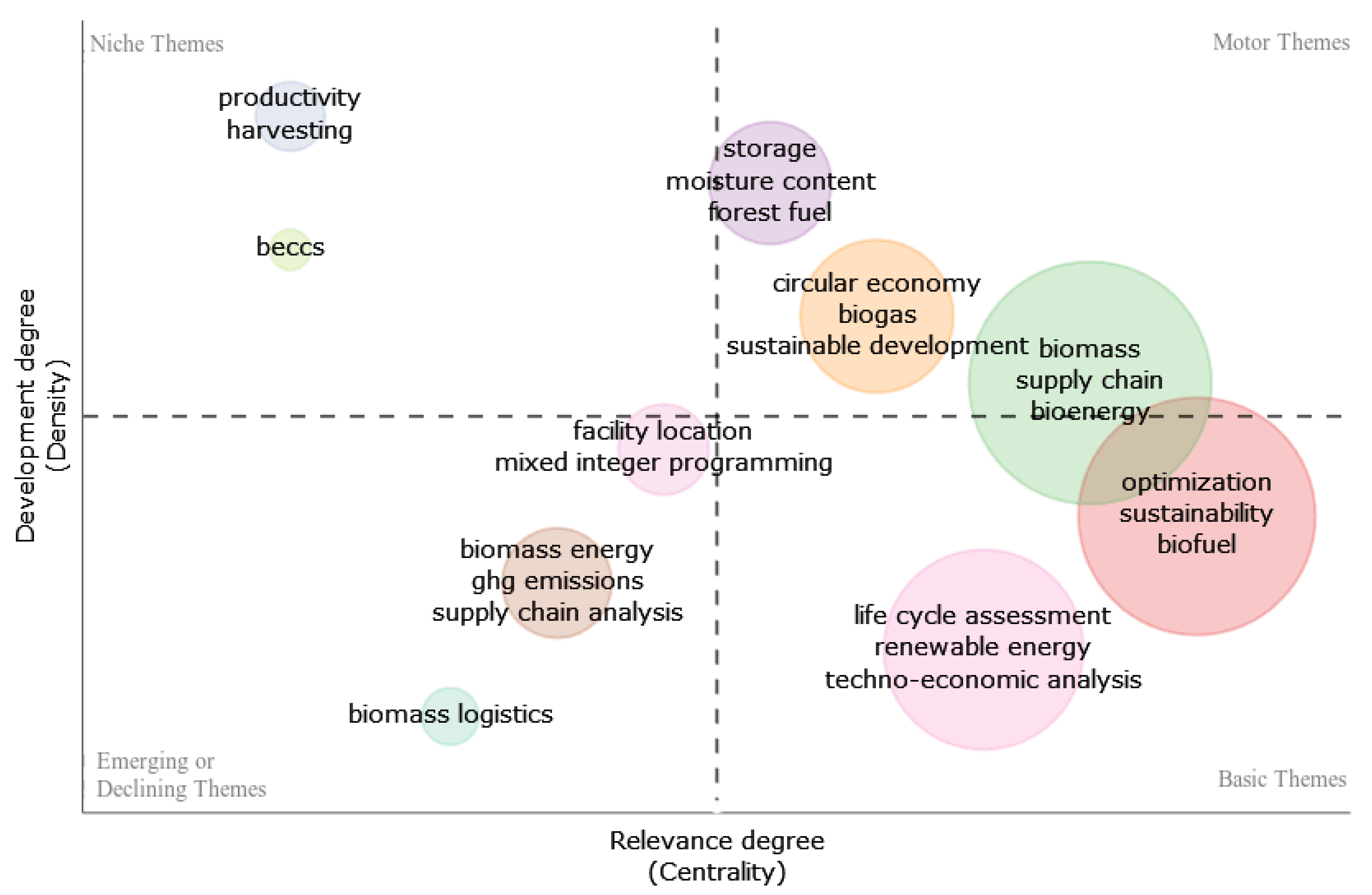
3.9. Strategic Diagram
3.10. Limitations of This Study
4. Discussion: Constraints, Gaps, and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Additional Authorship Analysis
Appendix A.1. Impactful Authors and Citation Bursts
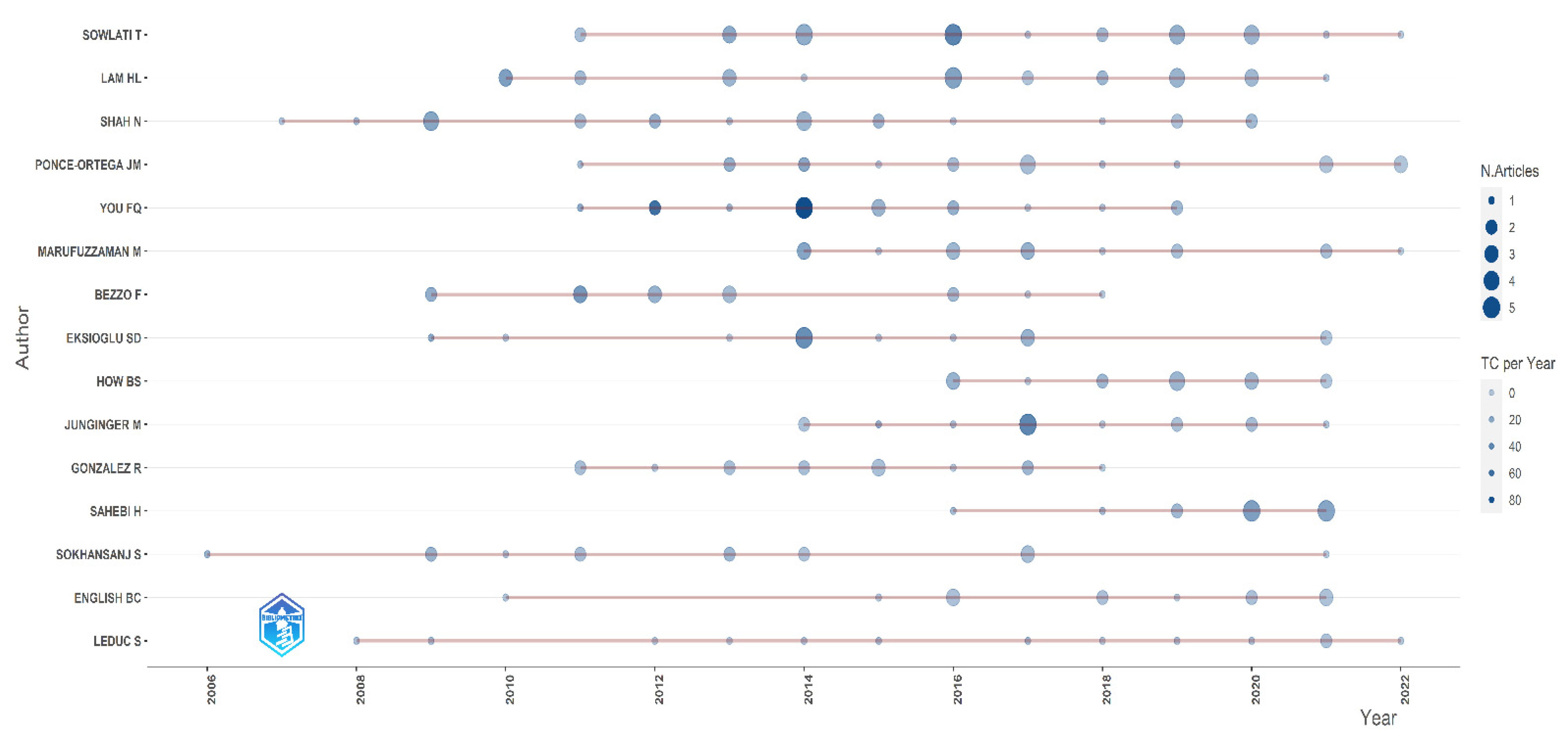
| Name | h-Index | g-Index | m-Index | Citations (Count) | Papers (Count) | First Year of Publication |
| Lam HL | 18 | 26 | 1.385 | 1003 | 26 | 2010 |
| Shah N | 18 | 23 | 1.125 | 1167 | 23 | 2007 |
| Sowlati T | 16 | 27 | 1.333 | 958 | 27 | 2011 |
| You F | 15 | 18 | 1.250 | 2085 | 18 | 2011 |
| Bezzo F | 13 | 15 | 0.929 | 993 | 15 | 2009 |
| Eksioglu SD | 12 | 15 | 0.857 | 841 | 15 | 2009 |
| Marufuzzaman M | 12 | 15 | 1.333 | 469 | 15 | 2014 |
| Ponce-Ortega JM | 12 | 18 | 1.000 | 671 | 18 | 2011 |
| Gonzalez R | 11 | 14 | 0.917 | 420 | 14 | 2011 |
| Sokhansanj S | 11 | 14 | 0.647 | 798 | 14 | 2006 |
| How BS | 10 | 14 | 1.429 | 272 | 14 | 2016 |
| Leduc S | 10 | 13 | 0.667 | 467 | 13 | 2008 |
| Giarola S | 9 | 11 | 0.7750 | 632 | 11 | 2011 |
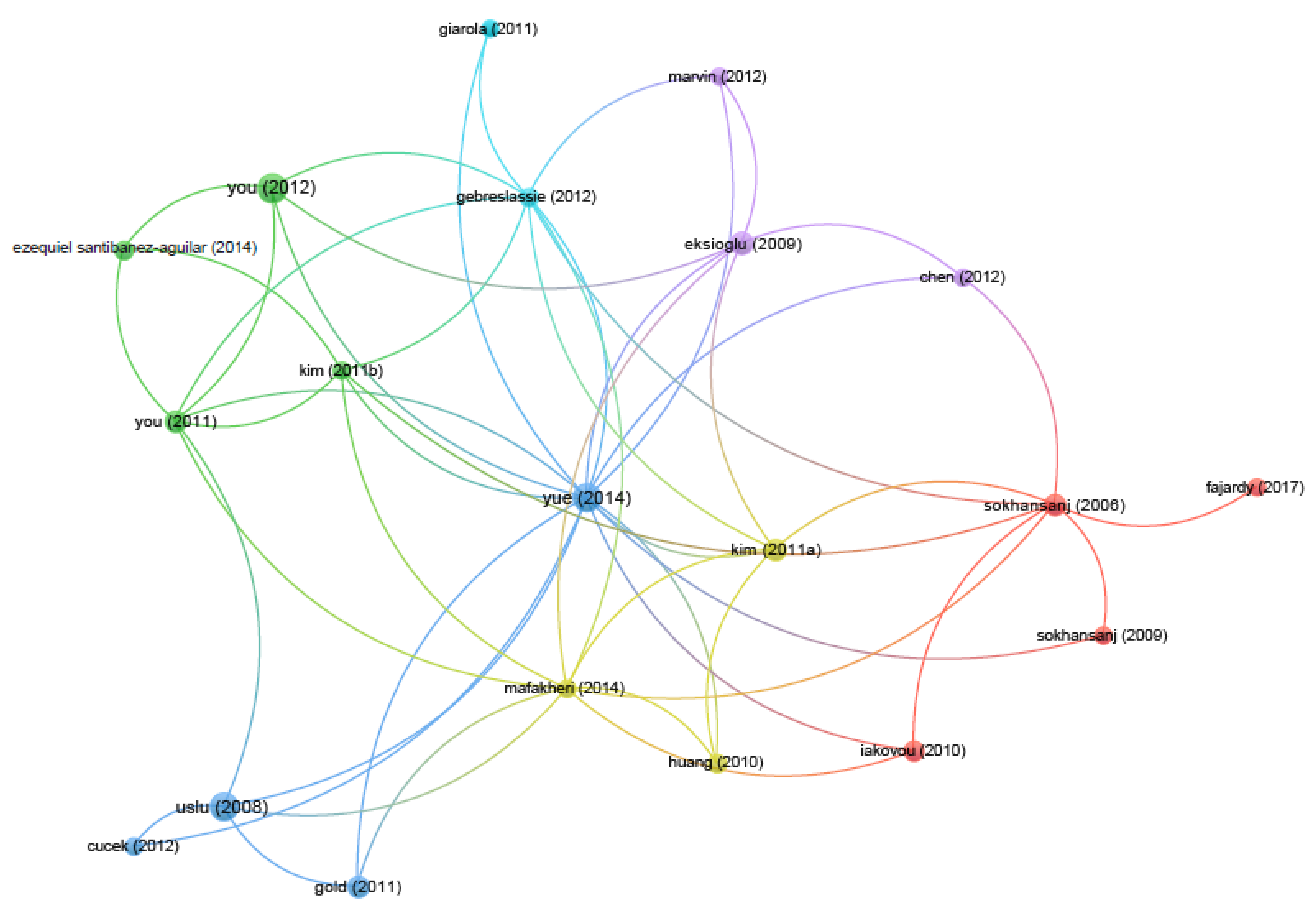
Appendix A.2. Bibliographic Coupling between Documents
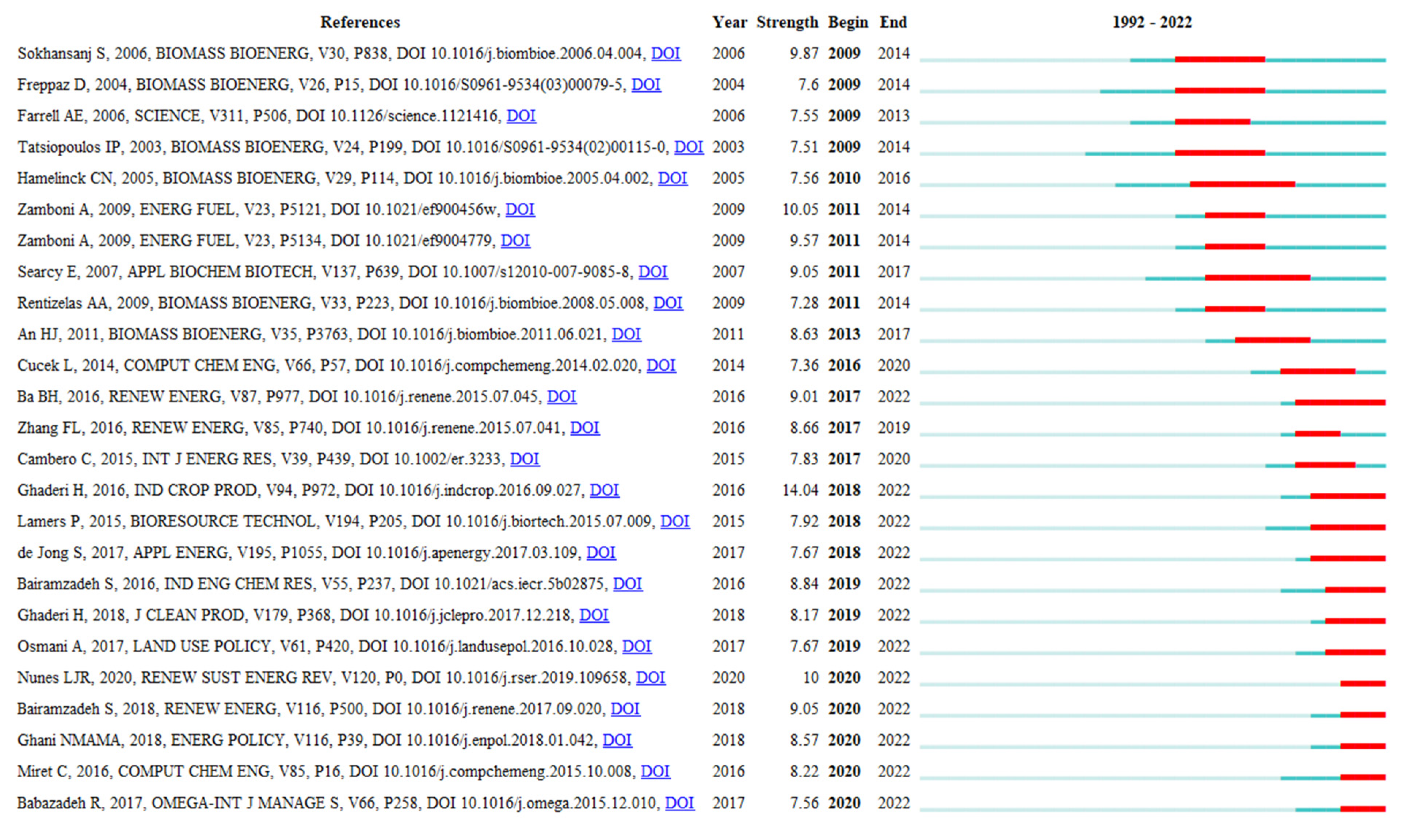
References
- Edenhofer, O.; Pichs-Madruga, R.; Sokona, Y.; Seyboth, K.; Kadner, S.; Zwickel, T.; Eickemeier, P.; Hansen, G.; Schlömer, S.; von Stechow, C.; et al. (Eds.) Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation: Special Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; p. 112. [Google Scholar]
- Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, Glossary of Statistical Terms. Available online: https://stats.oecd.org/glossary/about.asp (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Yue, D.; You, F.; Snyder, S.W. Biomass-to-bioenergy and biofuel supply chain optimization: Overview, key issues and challenges. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2014, 66, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Rjeily, M.; Gennequin, C.; Pron, H. Pyrolysis-catalytic upgrading of bio-oil and pyrolysis-catalytic steam reforming of biogas: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2825–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Fu, D.; Chu, H. Biofuel production from microalgae: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, I.; Clifton-Brown, J.C.; Scurlock, J.M.O.; Huisman, W. Miscanthus: European experience with a novel energy crop. Biomass Bioenergy 2000, 19, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnero, C.S.; Urrutia, M.V.; Ibaceta, S.V. Bioenergy from perennial grasses. Adv. Biofuels Bioenergy 2018, 1, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Grushecky, S.; Mcneel, J. Biomass Resources, Uses, and Opportunities in West Virginia. Working Report; Biomaterials Center, Division of Forestry and Natural Resources, West Virginia University: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Volk, T.A.; Berguson, B.; Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.D.; Miller, R.; Rials, T.G.; Abrahamson, L.P.; Buchman, D.; Buford, M.; Cunningham, M.W.; et al. Poplar and shrub willow energy crops in the United States: Field trial results from the multiyear regional feedstock partnership and yield potential maps based on the PRISM-ELM model. GCB Bioenergy 2018, 10, 735–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Richard, T.L.; Hartley, D.S.; Spatari, S.; Volk, T.A. Economic and life cycle assessments of biomass utilization for bioenergy products. Biofuels. Bioprod. Biorefining 2017, 11, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuxi, W.; Wang, J.; Jamie, S.; Hartley, D.; Volk, T.A.; Mark, E. Optimization of harvest and logistics for multiple lignocellulosic biomass feedstocks in the northeastern United States. Energy 2020, 197, 117260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautala, P.T.; Hilliard, M.R.; Webb, E. Opportunities and Challenges in the Design and Analysis of Biomass Supply Chains. Environ. Manag. 2015, 56, 1397–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, J.G.G.; Junginger, H.M.; Verstegen, J.A.; Lin, T.; Rodriguez, L.F.; Ting, K.C.; Faaji, A.P.C.; Van der Hilst, F. Sup-ply chain optimization of sugarcane first generation and Eucalyptus second generation ethanol production in Brazil. Appl. Energy 2016, 173, 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottaghi, M.; Bairamzadeh, S.; Pishyaee, M.S. A taxonomic review and analysis on bio-mass supply chain design and planning: New trends, methodologies and applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 180, 114747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Valencia, L.; Camenzind, D.; Wigmosta, M.; Garcia-Perez, M.; Wolcott, M. Biomass supply chain equipment for renewable fuels production: A review. Biomass Bioenergy 2021, 148, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.L.Y.; How, B.S.; Leong, W.D.; Teng, S.Y.; Rhamdhani, M.A.; Sunarso, J. Techno-economic analysis for biomass supply chain: A state-of-the-art review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalimov, V.V.; Mul’chenko, Z.M. Measurement of Science. Study of the Development of Science as an information process (No. FTD-MT-24-835-71). Foreign Technol. Div. Wright-Patterson AFB Ohio 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Ellegaard, O.; Wallin, J.A. The bibliometric analysis of scholarly production: How great is the impact? Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1809–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupic, I.; Čater, T. Bibliometric Methods in Management and Organization. Organ. Res. Methods 2015, 18, 429–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingers, J.; Leydesdorff, L. A review of theory and practice in scientometrics. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 246, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizzi, F.T.; Proto, M.; Potenza, M.R. The Basilicata Region (Southern Italy): A Natural and ‘Human-Built’ Open-Air Laboratory for Manifold Studies. Research Trends over the Last 24 Years (1994–2017). Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 433–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albort-Morant, G.; Henseler, J.; Leal-Millán, A.; Cepeda-Carrión, G. Mapping the Field: A Bibliometric Analysis of Green Innovation. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Lu, X. Selecting publication keywords for domain analysis in bibliometrics: A comparison of three methods. J. Informetr. 2016, 10, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dima, A.; Bugheanu, A.-M.; Dinulescu, R.; Potcovaru, A.-M.; Stefanescu, C.A.; Marin, I. Exploring the Research Re-garding Frugal Innovation and Business Sustainability through Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toorajipour, R.; Sohrabpour, V.; Nazarpour, A.; Oghazi, P.; Fischl, M. Artficial intelligence in supply chain management: A systematic literature review. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 122, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koberg, E.; Longoni, A. A Systematic Review of Sustainable Supply Chain Management in Global Supply Chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Sadeghieh, T.; Adeli, K. Peer review in scientific publications: Benefits, critiques, & A survival guide. EJIFCC 2014, 25, 227–243. [Google Scholar]
- Clarivate Analytics Web of Science Core Collection Help. Available online: https://www.bibliometrix.org/documents/Field_Tags_bibliometrix.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Robles, J.R.; Guallar, J.; Otegi-Olaso, J.R.; Gamboa-Rosales, N.K. El profesional de la información (EPI): Bib-liometric and thematic analysis (2006-2017). El Prof. De La Inf. 2019, 28, e280417. [Google Scholar]
- Cobo, M.J.; Jürgens, B.; Herrero-Solana, V.; Martínez, M.A.; Herrera-Viedma, E. Industry 4.0: A perspective based on bibliometric analysis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 139, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahlik, T. Comparison of the maps of science. Scientometrics 2000, 49, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. An approach for detecting, quantifying, and vis-ualizing the evolution of a research field: A practical application to the Fuzzy Sets Theory field. J. Informetr. 2011, 5, 146–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; Martínez, M.A.; Gutiérrez-Salcedo, M.; Fujita, H.; Herrera-Viedmae, E. 25 years at knowledge-based systems: A bibliometric analysis. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2015, 80, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, B.; Rajendran, D. Authorship trends and collaboration pattern in the marine sciences literature: A scientometric study. Int. J. Inf. Dissem. Technol. 2012, 2, 166–169. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, M.; Kumar, S.; Sonker, S.K.; Babbar, P. Occurrence of author keywords and keywords plus in social sciences and humanities research: A preliminary study. COLLNET J. Scientometr. Inf. Manag. 2018, 12, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biomass Research and Development Initiative. Available online: https://biomassboard.gov/brd-initiative (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Kessler, M.M. Bibliographic coupling between scientific papers. Am. Doc. 1963, 14(1), 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Han, R.; Wolfram, D.; Zhao, Y. Visualizing the intellectual structure of information science (2006–2015): Introducing author keyword coupling analysis. J. Informetr. 2016, 10, 132–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimo, A.; Corrado, C. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekşioğlu, S.D.; Acharya, A.; Leightley, L.E.; Arora, S. Analyzing the design and management of biomass-to-biorefinery supply chain. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2009, 57, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, F.; Tao, L.; Graziano, D.J.; Snyder, S.W. Optimal design of sustainable cellulosic biofuel supply chains: Multi-objective optimization coupled with life cycle assessment and input–output analysis. Process Syst. Eng. 2011, 58, 1157–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Realff, M.J.; Lee, J.H. Optimal design and global sensitivity analysis of biomass supply chain net-works for biofuels under uncertainty. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2011, 35, 1738–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, C.W.; Fan, Y. Multistage optimization of the supply chains of biofuels. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2010, 46, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, F.; Wang, B. Life cycle optimization of biomass-to-liquid supply chains with distributed–centralized processing networks. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10102–10127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokhansanj, S.; Kumar, A.; Turhollow, A.F. Development and implementation of integrated biomass supply analysis and logistics model (IBSAL). Biomass Bioenergy 2006, 30, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, S.; Seuring, S. Supply chain and logistics issues of bio-energy production. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Fan, Y. Bioethanol supply chain system planning under supply and demand uncertain-ties. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2012, 48, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Realff, M.J.; Lee, J.H.; Whittaker, C.; Furtner, L. Design of biomass processing network for biofuel production using an MILP model. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 853–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, A.; Bezzo, F.; Shah, N. Spatially Explicit Static Model for the Strategic Design of Future Bioethanol Production Systems. 2. Multi-Objective Environmental Optimization. Energy Fuels 2009, 10, 5134–5143. Available online: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ef9004779 (accessed on 12 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Bairamzadeh, S.; Saidi-Mehrabad, M.; Pishvaee, M.S. Modelling different types of uncertainty in biofuel supply network design and planning: A robust optimization approach. Renew. Energy 2018, 116, 500–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.-F.; Huang, Y.-W.; Yu, H.-C.; Wu, C.-S. Mapping knowledge structure by keyword co-occurrence and social network analysis: Evidence from library hi tech between 2006 and 2017. Libr. Hi Tech 2018, 36, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Erbis, S.; Isaacs, J.A.; Kamarthi, S. Correction: Novel keyword co-occurrence net-work-based methods to foster systematic reviews of scientific literature. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, E.; Waltman, L. Manual for VOSviewer Version 1.6.8. 2018. Available online: https://www.vosviewer.com/documentation/Manual_VOSviewer_1.6.8.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Bai, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. Visualizing research trends and research theme evolution in E-learning field: 1999–2018. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 1389–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Collins, A.M.; Coughlin, D.; Kirk, S. The role of Google Scholar in evidence reviews and its applicability to grey literature searching. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, D.V.; Dima, A.; Radu, E.; Dobrotă, E.M.; Dumitrache, V.M. Bibliometric analysis of the Green Deal policies in the food chain. Amfiteatru. Econ. 2022, 24, 410–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidhandi, H.M.; Yusuff, R.M. Integrated supply chain planning under uncertainty using an improved stochastic approach. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 2618–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, R.D.; Wade, J.P. A definition of systems thinking: A systems approach. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 44, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, B.A. Benefits of scenario planning applied to energy development. Energy Procedia 2017, 107, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prateek, M.; Sugandha, S.; Yogendra, S. Resiliency optimization of biomass to biofuel supply chain incorporating regional biomass pre-processing depots. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 97, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashish, S.; Yogendra, S. Resilient design of biomass to energy system considering uncertainty in biomass supply. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 131, 106593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, N.; Fengqi, Y. Data-driven Wasserstein distributionally robust optimization for biomass with agricultural waste-to-energy network design under uncertainty. Appl. Energy 2019, 255, 113857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laith, A.; Ghaith, R.; Andres, S.P. Supply Chain Inventory Control: A Comparison Among JIT, MRP, and MRP With Information Sharing Using Simulation. Eng. Manag. J. 2006, 18, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, D.; Whitin, T.M. The Theory of Inventory Management. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1954, 49, 667. [Google Scholar]
- Hult, G.T.M.; Ketchen Jr, D.J.; Slater, S.F. Information processing, knowledge development, and strategic supply chain performance. Acad. Manag. Manag. J. 2004, 47, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrow, K.J.; Harris, T.; Marschak, J. Optimal inventory policy. Econometrica 1951, 19, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensoussan, A.; Helal, M.A.; Ramakrishna, V.; Sethi, S. Optimal Policies for Inventory Systems with Piece-wise-Linear Concave Ordering Costs. SSRN 2020, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, M.A.; Bensoussan, A.; Ramakrishna, V.; Sethi, S.P. A mathematical method for optimal inventor policies with backlog sales. Int. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2021, 11, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensoussan, A. Dynamic programming and inventory control. Studies in Probability. Optim. Stat. 2011, 322, 891–921. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, R.; Dayron, A.; Julio, E.N.R.; Rodolfo, C.C.F. Model Predictive Control for Inventory Management in Biomass Manufacturing Supply Chains. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 3596–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grado, S.C.; Strauss, C.H. An inventory control model for supplying biomass to a processing facility. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1993, 39, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtari, S.; Sowlati, T.; Siller-Benitez, D.G.; Roeser, D. Impact of inventory management on demand fulfilment, cost and emission of forest-based biomass supply chains using simulation modelling. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 178, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, M.; Shubham, S.; Paritosh, K.; Pareek, N.; Vivekanand, V. Production of biofuels from biomass: Predicting the energy employing artificial intelligence modelling. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchu, S.P.; Hernandez, B.; Malhotra, A.; Fang, H.; Ierapetritou, M.; Vlachos, D.G. Accelerating Manufacturing for Biomass Conversion via Integrated Process and Bench Digitalization: A Perspective. React. Chem. Eng. 2022, 7, 813–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Yao, Y. Applications of artificial intelligence-based modeling for bioenergy systems: A review. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 774–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazemi, F.K.A.O.H.; Ariffin, M.K.A.B.M.; Mustapha, F.B. A New Fuzzy TOPSIS-Based Machine Learning Framework for Minimizing Completion Time in Supply Chains. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 24, 1669–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freppaz, D.; Minciardi, R.; Robba, M.; Rovatti, M.; Sacile, R.; Taramasso, A. Optimizing forest biomass exploitation for energy supply at a regional level. Biomass Bioenergy 2004, 26(1), 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, A.E.; Plevin, R.J.; Turner, B.T.; Jones, A.D.; O’Hare, M.; Kammen, D.M. Ethanol can contribute to energy and environmental goals. Science 2006, 311(5760), 506–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsiopoulos, I.P.; Tolis, A.J. Economic aspects of the cotton-stalk biomass logistics and comparison of supply chain methods. Biomass Bioenergy 2003, 24, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamelinck, C.N.; Suurs, R.A.A.; André, P.C.; Faaij, A.P.C. International bioenergy transport costs and energy balance. Biomass Bioenergy 2005, 29, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, A.; Shah, N.; Bezzo, F. Spatially Explicit Static Model for the Strategic Design of Future Bioethanol Production Systems. 1. Cost Minimization. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 5121–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searcy, E.; Flynn, P.; Ghafoori, E.; Kumar, A. The relative cost of biomass energy transport. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 137, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentizelas, A.A.; Tatsiopoulos, I.P.; Tolis, A. An optimization model for multi-biomass tri-generation energy supply. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Wilhelm, W.E.; Searcy, S.W. Biofuel and petroleum-based fuel supply chain research: A literature review. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 3763–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čuček, L.; Martín, M.; Grossmann, I.E.; Kravanja, Z. Multi-period synthesis of optimally integrated biomass and bioenergy supply network. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2014, 66, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, B.H.; Prins, C.; Prodhon, C. Models for optimization and performance evaluation of biomass supply chains: An Operations Research perspective. Renew. Energy 2016, 87, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Johnson, D.; Johnson, M.; Watkins, D.; Froese, R.; Wang, J. Decision support system integrating GIS with simulation and optimisation for a biofuel supply chain. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambero, C.; Sowlati, T.; Marinescu, M.; Roser, D. Strategic optimization of forest residues to bioenergy and biofuel supply chain. Int. J. Energy Res. 2015, 39, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, H.; Pishvaee, M.S.; Moini, A. Biomass supply chain network design: An optimization-oriented review and analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 94, 972–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, P.; Roni, M.S.; Tumuluru, J.S.; Jacobson, J.J.; Cafferty, K.G.; Hansen, J.K.; Kenney, K.; Teymouri, F.; Bals, B. Techno-economic analysis of decentralized biomass processing depots. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 194, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, S.; Hoefnagels, R.; Wetterlund, E.; Pettersson, K.; Faaij, A.; Junginger, M. Cost optimization of biofuel production – The impact of scale, integration, transport and supply chain configurations. Appl. Energy 2017, 195, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairamzadeh, S.; Pishvaee, M.S.; Saidi-Mehrabad, M. Multiobjective Robust Possibilistic Programming Approach to Sustainable Bioethanol Supply Chain Design under Multiple Uncertainties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, H.; Moini, A.; Pishvaee, M.S. A multi-objective robust possibilistic programming approach to sustainable switchgrass-based bioethanol supply chain network design. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 179, 368–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmani, A.; Zhang, J. Multi-period stochastic optimization of a sustainable multi-feedstock second generation bioethanol supply chain − A logistic case study in Midwestern United States. Land Use Policy 2016, 61, 420–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.J.R.; Causer, T.P.; Ciolkosz, D. Biomass for energy: A review on supply chain management models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 120, 109658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, N.M.A.M.A.; Vogiatzis, C.; Szmerekovsky, J. Biomass feedstock supply chain network design with biomass conversion incentives. Energy Policy 2018, 116, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miret, C.; Chazara, P.; Montastruc, L.; Negny, S.; Domenech, S. Design of bioethanol green supply chain: Comparison between first and second generation biomass concerning economic, environmental and social criteria. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2016, 85, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, R.; Razmi, J.; Pishvaee, M.S.; Rabbani, M. A sustainable second-generation biodiesel supply chain network design problem under risk. Omega 2017, 66, 258–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giarola, S.; Zamboni, A.; Bezzo, F. Spatially explicit multi-objective optimisation for design and planning of hybrid first and second generation biorefineries. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2011, 35, 1782–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvin, W.A.; Schmidt, L.D.; Benjaafar, S.; Tiffany, D.G.; Daoutidis, P. Economic Optimization of a Lignocellulosic Biomass-to-Ethanol Supply Chain. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 67, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebreslassie, B.H.; Yao, Y.; You, F. Design under uncertainty of hydrocarbon biorefinery supply chains: Multiobjective stochastic programming models, decomposition algorithm, and a Comparison between CVaR and downside risk. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 2155–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibañez-Aguilar, J.E.; González-Campos, J.B.; Ponce-Ortega, J.M.; Serna-González, M.; Mahmoud, M.; El-Halwagi, M.M. Optimal planning and site selection for distributed multiproduct biorefineries involving economic, environmental and social objectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 270–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardy, M.; Dowell, N.M. Can BECCS deliver sustainable and resource efficient negative emissions? Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1389–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokhansanj, S.; Mani, S.; Turhollow, A.; Kumar, A.; Bransby, D.; Lynd, L.; Laser, M. Large-scale production, harvest and logistics of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.)–current technology and envisioning a mature technology. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2009, 3, 124–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafakheri, F.; Nasiri, F. Modeling of biomass-to-energy supply chain operations: Applications, challenges and research directions. Energy Policy 2014, 67, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovou, E.; Karagiannidis, A.; Vlachos, D.; Toka, A.; Malamakis, A. Waste biomass-to-energy supply chain management: A critical synthesis. Waste Manage. 2010, 30, 1860–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, A.; Faaij, A.P.C.; Bergman, P.C.A. Pre-treatment technologies, and their effect on international bioenergy supply chain logistics. Techno-economic evaluation of torrefaction, fast pyrolysis and pelletisation. Energy 2008, 33, 1206–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čuček, L.; Varbanov, P.S.; Klemeš, J.J.; Kravanja, Z. Total footprints-based multi-criteria optimisation of regional biomass energy supply chains. Energy 2012, 44, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Field Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| AU | Authors |
| TI | Document Title |
| SO | Sources |
| DT | Document type |
| DE | Authors’ keywords |
| ID | Database keywords |
| PY | Year |
| SC | Subject category |
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Timespan (years) | 1992–2022 |
| Sources (count) | 365 |
| Documents (count) | 1711 |
| Peer-reviewed articles (count) | 1597 |
| Average annual growth rate (annual % change) | 17.4 |
| Average citations (# per document in literature cited) | 23.35 |
| References (count) | 60,281 |
| “KeyWords Plus”, ID (count) 1 | 2689 |
| Author keywords, DE (count) 2 | 4200 |
| Authors, total (count) | 4758 |
| Single-authored documents (count) | 53 |
| Authors of single-authored documents (count) | 49 |
| Co-Authors per doc | 4.2 |
| Collaboration index | 2.83 |
| International co-authorship (%) 3 | 29.81 |
| Journal Title | h-Index 1 | g-Index 2 | m-Index 3 | Citations (Count) | Papers (Count) | First Year of Publication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applied Energy | 37 | 53 | 2.643 | 3488 | 106 | 2009 |
| Biomass and Bioenergy | 35 | 58 | 1.129 | 4322 | 133 | 1992 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | 31 | 49 | 2.583 | 3287 | 128 | 2011 |
| Energy | 26 | 47 | 1.733 | 2341 | 69 | 2008 |
| Bioresource Technology | 21 | 29 | 1.750 | 1295 | 29 | 2011 |
| Computers and Chemical Engineering | 21 | 43 | 1.500 | 1924 | 52 | 2009 |
| Renewable Energy | 21 | 39 | 1.400 | 1574 | 46 | 2008 |
| Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining | 19 | 34 | 1.357 | 1247 | 47 | 2009 |
| Energy Policy | 14 | 19 | 0.824 | 714 | 19 | 2006 |
| Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research | 14 | 26 | 1.167 | 1095 | 26 | 2011 |
| Energies | 12 | 18 | 1.091 | 423 | 41 | 2012 |
| Energy Conversion and Management | 12 | 19 | 0.857 | 538 | 19 | 2009 |
| GCB Bioenergy | 12 | 19 | 1.000 | 392 | 19 | 2011 |
| Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews | 12 | 17 | 2.400 | 318 | 23 | 2018 |
| Bioenergy Research | 11 | 15 | 1.000 | 255 | 19 | 2012 |
| Energy & Fuels | 11 | 12 | 0.786 | 667 | 12 | 2009 |
| ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering | 10 | 18 | 1.000 | 426 | 18 | 2013 |
| Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy | 10 | 15 | 0.769 | 349 | 15 | 2010 |
| International Journal of Hydrogen Energy | 9 | 9 | 0.818 | 270 | 9 | 2012 |
| Sustainability | 9 | 14 | 1.000 | 312 | 36 | 2014 |
| Author | Title | DOI | Year | Local Citations 1 | Global Citations 2 | Normalized Local Citations 3 | Normalized Global Citations 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [42] Ekşioğlu et al. (2009) | Analyzing the design and management of bio-mass-to-biorefinery supply chain | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2009.07.003 | 2009 | 167 | 292 | 6.49 | 3.97 |
| [43] You et al. (2011) | Optimal design of sustainable cellulosic biofuel supply chains: Multi-objective optimization coupled with life cycle assessment and input–output analysis | https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.12637 | 2012 | 151 | 471 | 8.52 | 8.06 |
| [3] Yue et al. (2014) | Biomass-to-bioenergy and biofuel supply chain optimization: Overview, key issues and challenges | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2013.11.016 | 2014 | 139 | 423 | 14.94 | 12.06 |
| [44] Kim et al. (2011) | Optimal design and global sensitivity analysis of biomass supply chain networks for biofuels under uncertainty | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2011.02.008 | 2011 | 119 | 242 | 5.74 | 3.77 |
| [45] Huang et al. (2010) | Multistage optimization of the supply chains of biofuels | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2010.03.002 | 2010 | 108 | 194 | 6.09 | 3.15 |
| [46] You and Wang (2011) | Life cycle optimization of biomass-to-liquid supply chains with distributed–centralized processing networks | https://doi.org/10.1021/ie200850t | 2011 | 102 | 248 | 4.92 | 3.87 |
| [47] Sokhansanj (2006) | Development and implementation of integrated biomass supply analysis and logistics model (IBSAL) | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2006.04.004 | 2006 | 97 | 243 | 4.37 | 3.52 |
| [48] Gold and Seuring (2011) | Supply chain and logistics issues of bio-energy production | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2010.08.009 | 2011 | 94 | 259 | 4.54 | 4.04 |
| [49] Chen and Fan (2012) | Bioethanol supply chain system planning under supply and demand uncertainties | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2011.08.004 | 2012 | 83 | 157 | 4.69 | 2.69 |
| [50] Kim J et al. (2011) | Design of biomass processing network for biofuel production using an MILP model | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2010.11.008 | 2011 | 82 | 160 | 3.96 | 2.49 |
| Keyword | Cluster # | Links | Total Link Strength | Occurrences |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass | 2 | 31 | 285 | 222 |
| Supply chain | 2 | 31 | 308 | 222 |
| Bioenergy | 2 | 31 | 199 | 154 |
| Optimization | 4 | 31 | 221 | 120 |
| Sustainability | 1 | 28 | 109 | 94 |
| Life cycle assessment | 1 | 26 | 67 | 77 |
| Biofuel | 3 | 30 | 144 | 91 |
| Biorefinery | 3 | 21 | 69 | 52 |
| Logistics | 2 | 24 | 107 | 57 |
| Renewable energy | 5 | 16 | 59 | 51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Helal, M.A.; Anderson, N.; Wei, Y.; Thompson, M. A Review of Biomass-to-Bioenergy Supply Chain Research Using Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization. Energies 2023, 16, 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031187
Helal MA, Anderson N, Wei Y, Thompson M. A Review of Biomass-to-Bioenergy Supply Chain Research Using Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization. Energies. 2023; 16(3):1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031187
Chicago/Turabian StyleHelal, Md Abu, Nathaniel Anderson, Yu Wei, and Matthew Thompson. 2023. "A Review of Biomass-to-Bioenergy Supply Chain Research Using Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization" Energies 16, no. 3: 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031187
APA StyleHelal, M. A., Anderson, N., Wei, Y., & Thompson, M. (2023). A Review of Biomass-to-Bioenergy Supply Chain Research Using Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization. Energies, 16(3), 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031187