Energy, Exergy and Thermoeconomic Analyses on Hydrogen Production Systems Using High-Temperature Gas-Cooled and Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
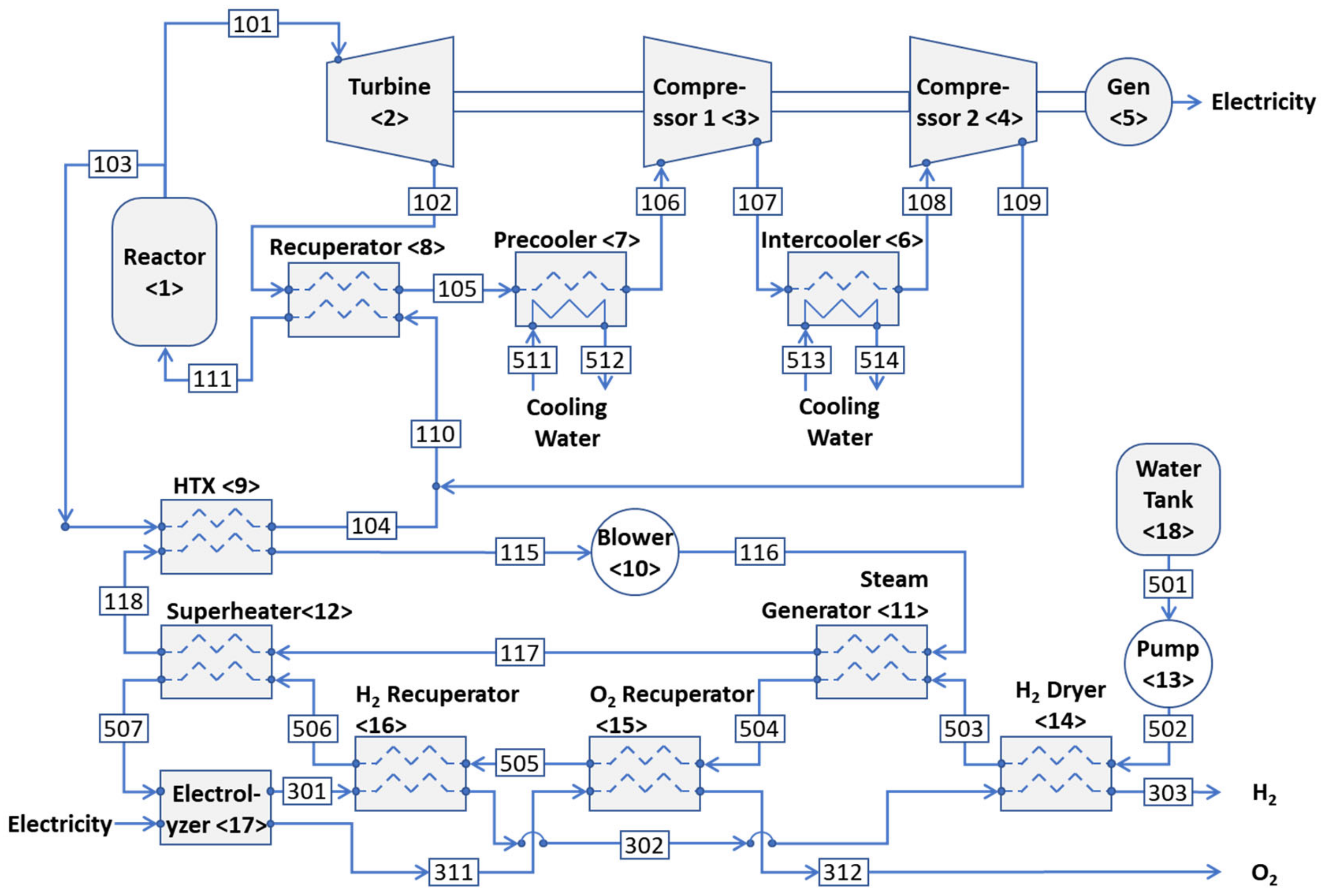
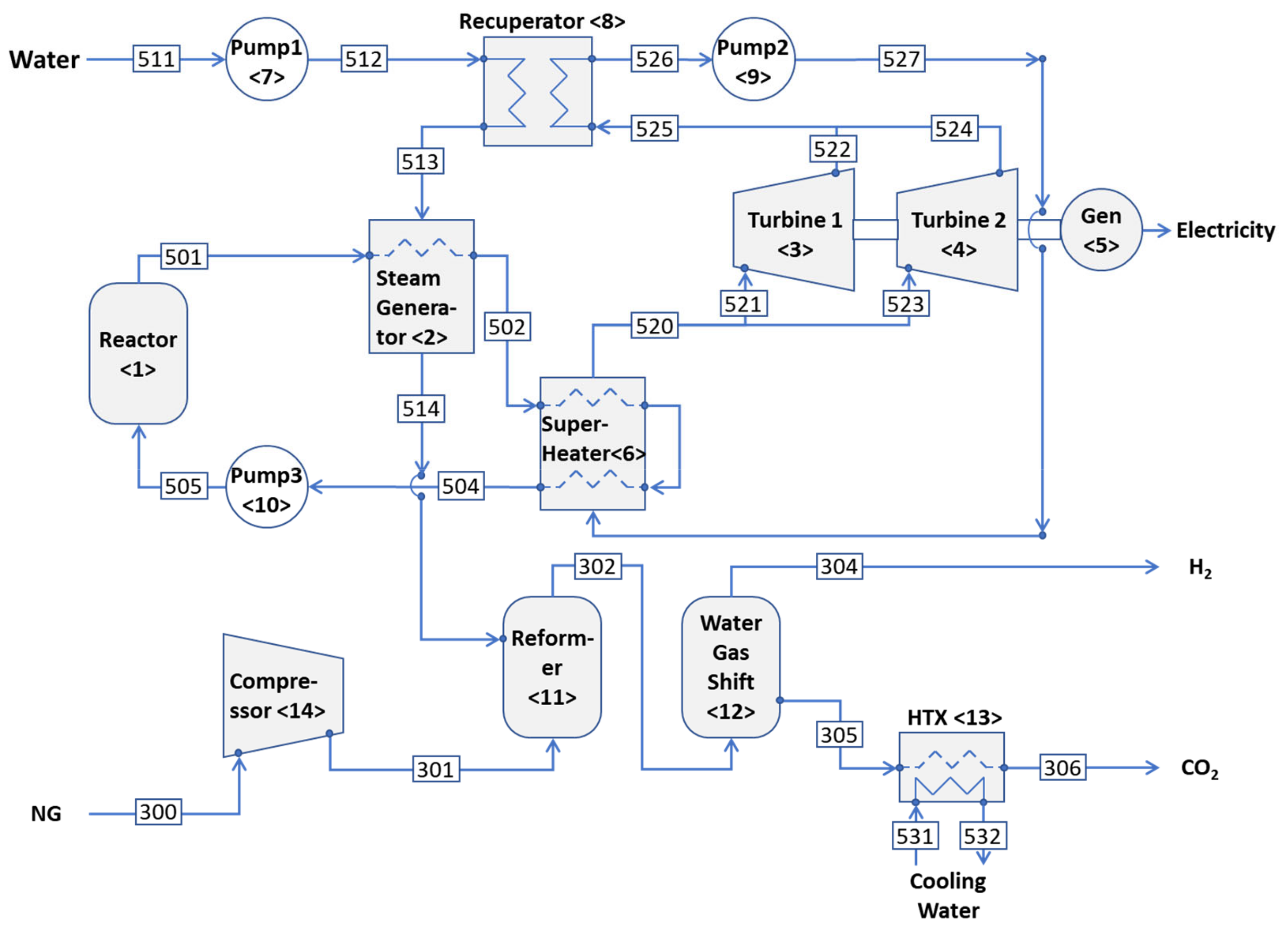
2. System Description
2.1. HTGR with the Brayton Cycle
2.2. HTWR with Steam Reforming
3. Exergy Analysis of HTGR/HTWR Systems
3.1. Mass and Energy Conservation, and the Exergy-Balance Equation
3.2. Exergy-Balance Equations for the HTGR System
- 1.
- Reactor <1>:
- 2.
- Gas Turbine <2>:
- 3.
- Compressor 1 <3>:
- 4.
- Compressor 2 <4>:
- 5.
- Generator <5>:
- 6.
- Intercooler <6>:
- 7.
- Precooler <7>:
- 8.
- Recuperator <8>:
- 9.
- Heat exchanger <9>:
- 10.
- Blower <10>:
- 11.
- Steam generator <11>:
- 12.
- Superheater <12>:
- 13.
- Pump <13>:
- 14.
- Hydrogen dryer <14>:
- 15.
- Oxygen recuperator <15>:
- 16.
- Hydrogen recuperator <16>:
- 17.
- Electrolyzer <17>:
3.3. Exergy-Balance Equations for the HTWR System
- 1.
- Reactor <1>:
- 2.
- Steam generator <2>:
- 3.
- Turbine 1<3>:
- 4.
- Turbine 2 <4>:
- 5.
- Generator <5>:
- 6.
- Superheater <6>:
- 7.
- Pump 1 <7>:
- 8.
- Recuperator <8>:
- 9.
- Pump 2 <9>:
- 10.
- Pump 3 <10>:
- 11.
- Reformer <11>:
- 12.
- Water–gas shift reactor <12>:
- 13.
- Heat exchanger <13>:
- 14.
- Compressor <14>:
4. Thermoeconomic Analysis of HTGR/HTWR Systems
4.1. Exergy Cost-Balance Equations
4.2. Exergy Cost-Balance Equations for the HTGR System
- 1.
- Reactor <1>:
- 2.
- Gas Turbine <2>:
- 3.
- Compressor 1 <3>:
- 4.
- Compressor 2 <4>:
- 5.
- Generator <5>:
- 6.
- Intercooler <6>:
- 7.
- Precooler <7>:
- 8.
- Recuperator <8>:
- 9.
- Heat exchanger <9>:
- 10.
- Blower <10>:
- 11.
- Steam generator <11>:
- 12.
- Superheater <12>:
- 13.
- Pump <13>:
- 14.
- Hydrogen dryer <14>:
- 15.
- Oxygen recuperator <15>:
- 16.
- Hydrogen recuperator <16>:
- 17.
- Electrolyzer <17>:
4.3. Exergy Cost-Balance Equations for the HTWR System
- 1.
- Reactor <1>:
- 2.
- Steam generator <2>:
- 3.
- Turbine 1 <3>:
- 4.
- Turbine 2 <4>:
- 5.
- Generator <5>:
- 6.
- Superheater <6>:
- 7.
- Pump 1 <7>:
- 8.
- Recuperator <8>:
- 9.
- Pump 2 <9>:
- 10.
- Pump 3 <10>:
- 11.
- Reformer <11>:
- 12.
- Water-gas shift reactor <12>:
- 14.
- Compressor <14>:
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. HTGR System
5.2. HTWR System
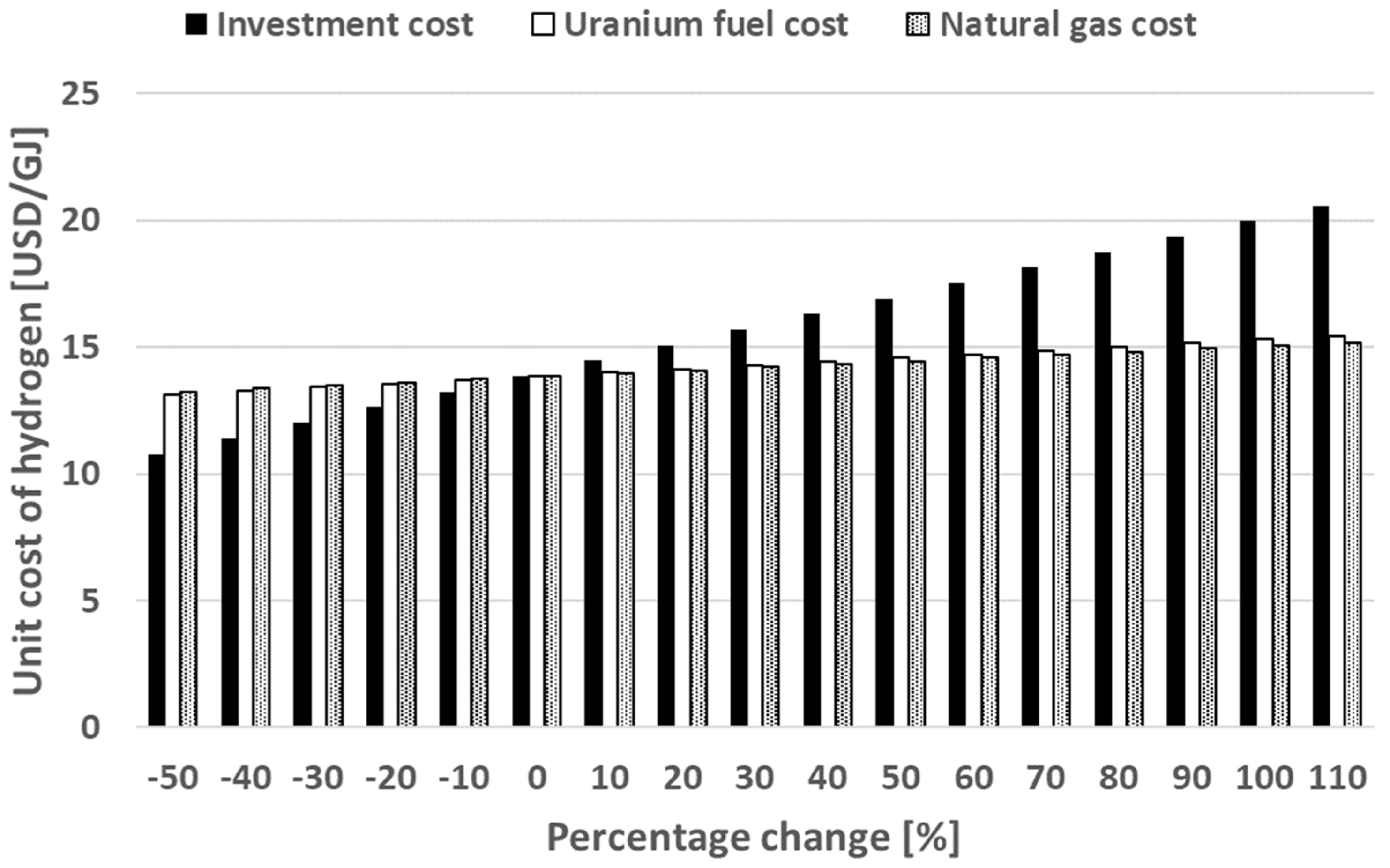
5.3. Scaled-Down of the Plant
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaszczur, M.; Rosen, M.A.; Sliwa, T.; Dudel, M. Hydrogen production using high temperature nuclear reactors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 7861–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zareer, M.; Dincer, I.; Rosen, M.A. Development and assessment of a novel integrated nuclear plant for electricity and hydrogen production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 134, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milewski, J.; Kupecki, J.; Szczesnial, A.; Uzunow, N. Hydrogen production in s. Energyolid oxide electrolyzers coupled with nuclear reactors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 35765–35776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oettingen, M.; Cetnar, J. Numerical modeling of modular high-temperature gas-cooled reactors with thorium fuel. Nukleonika 2021, 66, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvego, E.A.; Reza, S.M.M.; Richards, M.; Shenoy, A. An evaluation of reactor cooling and coupled hydrogen production using the modular helium reactor. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2006, 236, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Tachibana, T.; Ohashi, H.; Sato, H.; Tazawa, Y.; Kunitomi, K. A small modular reactor design for multiple energy applications. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2013, 45, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikazawa, Y.; Konomura, M.; Uchida, S.; Sato, H. A feasibility study of a steam methane reforming hydrogen production plant with a sodium-cooled fast reactor. Nucl. Technol. 2005, 152, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandell, L. High Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactors for the Production of Hydrogen: An Assessment in Support of the Hydrogen Economy; EPRI: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2003; p. 1007802. [Google Scholar]
- Boldon, L.; Sabharwall, P.; Rabiti, C.; Bragg-Sitton, S.M.; Liu, L. Thermodynamic exergy analysis for small modular reactor. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kwak, H. Thermoeconomic analysis of high-temperature gas-cooled reactors with steam methane reforming for hydrogen production. Nucl. Technol. 2011, 176, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenhumberg, N.; Büker, K. Ecological and economic evaluation of hydrogen production by different water electrolysis technologies. Chem. Ing. Technol. 2020, 92, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Emam, R.S.; Ozcan, H. Comprehensive review on the techno-economics of sustainable large-scale clean hydrogen production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 593–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machhammer, O.; Bode, A.; Hormuth, W. Financial and ecological evaluation of hydrogen production processes on large scale. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2016, 39, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragiacomo, P.; Genovese, M. Technical-economic analysis of a hydrogen production facility for power-to-gas and hydrogen mobility under different renewable sources in Southern Italy. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 223, 113332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai-Qahtani, A.; Parkinson, B.; Hellgardt, K.; Shah, N.; Guillen-Gosalbez, G. Uncovering the true cost of hydrogen production routes using life cycle monetization. Appl. Energy 2021, 281, 115958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Shi, M.; Wang, J. Life cycle assessment of nuclear hydrogen production processes based on high temperature gas-cooled reactor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 22302–22318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, S.; Kye, D.H.; Park, H.J.; Park, W.; Shin, J.; Park, K. Environ-economic analysis of high-temerature steam electrolysis for decentralized hydrogen production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 266, 115856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Naterer, G.F.; Gabriel, K.S.; Gravelsins, R.; Daggupati, V.N. Comparison of sulfur–iodine and copper–chlorine thermochemical hydrogen production cycles. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 4820–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbilen, A.; Dincer, I.; Rosen, M.A. Development of a four-step Cu–Cl cycle for hydrogen production—Part I: Exergoeconomic and exergoenvironmental analyses. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 11321–11327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-D.; Pang, H.-S.; Kim, S.; Kwak, H. Exergy analysis for a gas turbine cogeneration system. J. Eng. Gas Turb. Power 1996, 118, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaljani, M.; Saray, R.K.; Bahlouli, K. Comprehensive analysis of energy, exergy and exergo-economic of cogeneration of heat and power in a combined gas turbine and organic Rankine cycle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 97, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.; Kim, D.-J.; Jeon, J.-S. Exergetic and thermoeconomic analyses of power plants. Energy 2003, 28, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordesch, K.; Simader, G. Fuel Cells and Their Applications; VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.-H.; Oh, S.-D.; Park, J.; Oh, H.; Choi, Y.-Y.; Lee, W.-Y.; Kwak, H. Thermodynamic, exergetic, and thermoeconomic analyses of a 1-kW proton exchange membrane fuel cell system fueled by natural gas. Energy 2021, 217, 11962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A. Advanced Engineering Thermodynamics, 4th ed; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kotas, T.J. The Exergy Methods of Thermal Plant Analysis; Krieger Publishing, Co.: Malabar, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, J. Availability Analysis: A Guide to Efficient Energy Use; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, M.; Shenoy, A.; Schultz, K.; Brown, L.; Fukuie, M.; Harvego, E. The modular helium reactor for hydrogen production. In Proceedings of the 15th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (15PBNC), Sydney, Australia, 16 October 2006. [Google Scholar]

| Account | Cost Per Year ($M/year) | Cost Flow Rate (USD/s) | Percent of Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMR plant capital charges | 181.2 | 5.74 | 36.1 |
| SMR plant O&M costs | 37.4 | 1.19 | 7.5 |
| H2 plant capital charges | 135.3 | 4.29 | 26.9 |
| H2 plant O&M costs | 76.6 | 2.43 | 15.3 |
| Nuclear fuel cost | 71.2 | 2.26 | 14.2 |
| Total | 501.7 | 15.91 | 100. |
| States | (kmole/s) | T (°C) | P (kPa) | H (kJ/s) | S (kJ/s-K) | Ex (kJ/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | 69.493 | 850.05 | 7100.0 | 1,191,862.03 | −539.32 | 1,352,659.75 |
| 102 | 69.493 | 531.49 | 2600.0 | 731,678.16 | −400.70 | 863,073.59 |
| 103 | 9.9990 | 850.05 | 7100.0 | 171,490.94 | −77.60 | 194,627.30 |
| 104 | 9.9990 | 577.05 | 7100.0 | 114,746.47 | −135.48 | 155,139.90 |
| 105 | 69.493 | 470.00 | 2550.0 | 642,844.23 | −544.33 | 805,136.53 |
| 106 | 69.493 | 27.05 | 2500.0 | 2961.43 | −1842.34 | 552,255.01 |
| 107 | 69.493 | 109.26 | 4300.0 | 121,721.01 | −1806.04 | 660,190.72 |
| 108 | 69.493 | 27.05 | 4250.0 | 2961.43 | −2148.93 | 643,665.80 |
| 109 | 69.493 | 103.56 | 7100.0 | 113,487.96 | −2117.48 | 744,814.38 |
| 110 | 79.492 | 440.0 | 7100.0 | 685,766.34 | −1367.53 | 1,093,496.89 |
| 111 | 79.492 | 488.05 | 7100.0 | 765,166.47 | −1259.79 | 1,140,772.31 |
| 115 | 5.8244 | 800.0 | 450.0 | 93,833.64 | 54.64 | 50,523.54 |
| 116 | 5.8244 | 981.38 | 650.0 | 115,794.29 | 83.97 | 90,759.09 |
| 117 | 5.8244 | 750.35 | 600.0 | 87,822.23 | 63.20 | 6897.60 |
| 118 | 5.8244 | 566.85 | 500.0 | 64,394.09 | 46.66 | 50,482.80 |
| 301 | 1.2767 | 536.85 | 250.0 | 19,072.03 | 37.15 | 19,072.03 |
| 302 | 1.2767 | 476.85 | 200.0 | 16,801.64 | 34.24 | 16,801.64 |
| 303 | 1.2767 | 57.0 | 150.0 | 1179.74 | 3.76 | 1179.74 |
| 311 | 0.6384 | 536.85 | 250.0 | 10,396.94 | 20.07 | 10,396.94 |
| 312 | 0.6384 | 266.85 | 200.0 | 4733.97 | 11.58 | 4733.97 |
| 501 | 1.2767 | 27.05 | 101.0 | 2608.77 | 9.10 | 0.67 |
| 502 | 1.2767 | 27.07 | 600.0 | 2621.24 | 9.10 | 12.19 |
| 503 | 1.2767 | 75.0 | 550.0 | 7229.99 | 23.35 | 373.68 |
| 504 | 1.2767 | 389.85 | 500.0 | 74,771.08 | 178.55 | 21,641.04 |
| 505 | 1.2767 | 440.0 | 450.0 | 77,205.65 | 183.20 | 2268.81 |
| 506 | 1.2767 | 509.85 | 400.0 | 80,637.86 | 189.04 | 24,380.97 |
| 507 | 1.2767 | 686.85 | 350.0 | 89,627.93 | 200.79 | 29,865.72 |
| 511 | 238.69 | 25.0 | 101.20 | 450,887.36 | 1578.01 | −0.54 |
| 512 | 238.69 | 51.0 | 150. | 918,287.15 | 3080.37 | 19,470.79 |
| 513 | 44.4074 | 25.0 | 101.20 | 83,886.02 | 293.58 | −0.10 |
| 514 | 44.4074 | 53.0 | 150. | 177,534.48 | 593.67 | 4178.01 |
| Component | Work (kJ/s) | Heat (kJ/s) | Enthalpy in (kJ/s) | Enthalpy Out (kJ/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor<1> | 0.0 | −598,186.50 | −765,166.47 | 1,363,352.97 |
| Turbine<2> | 460,183.87 | 0.0 | −119,1862.03 | 731,678.16 |
| Compressor 1<3> | −118,759.58 | −2961.43 | 121,721.01 | |
| Compressor 2<4> | −110,526.54 | −2961.43 | 113,487.96 | |
| Pump<13> | −12.47 | −2608.77 | 2621.24 | |
| Blow<10> | −21,960.66 | −93,833.64 | 115,794.29 | |
| Intercooler<6> | 118,759.58 | −121,721.01 | 2961.43 | |
| recooler<7> | 639,882.81 | −642,844.23 | 2961.43 | |
| Recuperator<8> | 9433.80 | −1,417,444.50 | 1,408,010.70 | |
| HTX<9> | 27,304.93 | −235,885.03 | 208,580.10 | |
| Steam generator<11> | −39,569.02 | −123,024.28 | 162,593.31 | |
| Superheater<12> | 14,438.07 | −168,460.09 | 154,022.01 | |
| H2 Dryer<14> | 11,013.15 | −19,422.88 | 8409.73 | |
| O2 Recuperator<15> | 80,434.05 | −85,168.02 | 4733.97 | |
| H2 Recuperator<16> | −1161.82 | −96,277.68 | 97,439.50 | |
| Electrolyzer<17> | −111,355.22 | 17,1514.18 | −89,627.93 | 29,468.97 |
(kW) | (kW) | (kW) | Irreversibility Rate (kW) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor | −600,000.0 * | 406,514.75 | 193,485.25 | |
| Turbine | 460,183.87 | −316,527.62 | −173,058.54 | 29,402.30 |
| Compressor 1 | −118,759.58 | 14,510.06 | 93,425.65 | 10,823.87 |
| Compressor 2 | −110,526.54 | 12,744.32 | 88,404.27 | 9377.95 |
| Intercooler | −10,371.10 | −1975.71 | 12,346.81 | |
| Precooler | −230,209.24 | −3200.94 | 233,410.19 | |
| Recuperator | −7316.51 | −3345.13 | 10,661.64 | |
| HTX | −19,322.62 | −1521.23 | 20,843.85 | |
| Steam generator | 643.72 | −1156.84 | 513.12 | |
| Super heater | −10,377.47 | −2633.58 | 13,011.05 | |
| H2 Dryer | −15,259.25 | −1.15 | 15,260.40 | |
| O2 Recuperator | −27,294.82 | −9.19 | 27,304.02 | |
| H2 Recuperator | −577.08 | −1.15 | 578.23 | |
| Pump | −12.47 | 0.01 | 11.51 | 0.95 |
| Blow | −21,960.66 | 16,323.40 | 5309.35 | 327.92 |
| Electrolyzer | −197,379.73 | −393.02 | −5.74 | 308,734.95 |
| Component | Initial Investment Cost | Annualized Cost (USD × 106/yr) | Monetary Flow Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| (USD × 106) | (USD/s) | ||
| Reactor | 757.69 | 49.29 | 2.9026 |
| Turbine | 275.54 | 17.92 | 1.0555 |
| Compressor 1 | 92.00 | 5.98 | 0.3524 |
| Compressor 2 | 69.00 | 4.49 | 0.2643 |
| Generator | 23.00 | 1.50 | 0.0811 |
| Intercooler | 18.40 | 1.20 | 0.0705 |
| Precooler | 18.40 | 1.20 | 0.0705 |
| Recuperator | 27.60 | 1.80 | 0.1057 |
| HTX | 18.40 | 1.20 | 0.0705 |
| Blower | 13.80 | 0.90 | 0.0529 |
| Steam generator | 27.60 | 1.80 | 0.1057 |
| Superheater | 27.60 | 1.80 | 0.1057 |
| Pump | 13.80 | 0.90 | 0.0529 |
| H2 Dryer | 18.40 | 1.20 | 0.0705 |
| O2 recuperator | 18.40 | 1.20 | 0.0705 |
| H2 recuperator | 18.40 | 1.20 | 0.0705 |
| Electrolyzer | 1150.00 | 74.8 | 4.4054 |
| Total | 2588.03 | 168.38 | 9.9072 |
| Component | Thermal | Mechan | Work | Lost Cost | Investment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor | 5.0347 | −0.0321 | −5.0026 | ||
| Turbine | −2.3670 | −4.1435 | 7.5709 | −0.0049 | −1.0555 |
| Compressor 1 | 0.1085 | 2.1996 | −1.9358 | −0.0018 | −0.3524 |
| Compressor 2 | 0.0953 | 1.9890 | −1.8184 | −0.0016 | −0.2643 |
| Generator | −3.7987 | 3.8887 | −0.0019 | −0.0881 | |
| Intercooler | −0.0591 | 0.1323 | −0.0006 | −0.0021 | −0.0705 |
| Precooler | −0.7760 | 0.8887 | −0.0035 | −0.0388 | −0.0705 |
| Recuperator | 0.1876 | −0.0801 | −0.0018 | −0.1057 | |
| HTX | 0.1104 | −0.0364 | −0.0035 | −0.0705 | |
| Blower | 0.1221 | 0.2922 | −0.3613 | −0.0001 | −0.0529 |
| Steam generator | 0.1388 | −0.0330 | −0.0001 | −0.1057 | |
| Super heater | 0.1762 | −0.0683 | −0.0022 | −0.1057 | |
| Pump | 0.0531 | −0.0002 | 0.0 | −0.0529 | |
| H2 Dryer | 0.0783 | −0.0053 | −0.0025 | −0.0705 | |
| O2 recuperator | 0.1174 | −0.0424 | −0.0045 | −0.0705 | |
| H2 recuperator | 0.0759 | −0.0053 | −0.0001 | −0.0705 | |
| Electrolyzer * | −4.0878 | −0.0264 | −3.5272 | 0.0184 | −4.4054 |
| C1T | C2W | C3P | C4P | C5E | C6T | C7T | C8T |
| 12.39 | 16.45 | 23.54 | 22.50 | 17.73 | 45.23 | 14.25 | −25.64 |
| C9T | C10P | C11DT | C12DT | C13DP | C14DT | C15DT | C16T |
| −5.71 | 55.02 | 13.78 | 53.75 | 4611.3 | 538.15 | −7.39 | 54.85 |
| C17H2 | CT | CP | CDT | CDP | CW | Cs | |
| 35.65 | 7.48 | 23.94 | 144.29 | 4611.3 | 16.45 | −0.17 |
| States | (kmole/s) | T (°C) | P (kPa) | H (kJ/s) | S (kJ/s−K) | Ex (kJ/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 300 | 2.2000 | 25.05 | 101.300 | 4.19 | 7.36 | −2190.32 |
| 301 | 2.2000 | 202.56 | 600.000 | 17,127.67 | 51.96 | 1636.31 |
| 302 | 13.6103 | 426.85 | 400.000 | 179,864.52 | 503.83 | 29,648.05 |
| 304 | 8.0958 | 326.85 | 200.000 | 79,685.41 | 253.49 | 4106.74 |
| 305 | 5.5145 | 326.85 | 200.000 | 63,097.87 | 185.70 | 7732.72 |
| 306 | 2.6036 | 25.05 | 101.300 | 4.77 | 9.59 | −2855.32 |
| 501 | 37.1912 | 850.05 | 6700.000 | 2,847,520.14 | 5155.82 | 1,313,422.84 |
| 502 | 37.1912 | 646.85 | 6650.000 | 2,520,159.30 | 4849.22 | 1,077,418.12 |
| 504 | 37.1912 | 429.85 | 6450.000 | 2,175,795.72 | 4430.93 | 857,768.44 |
| 505 | 37.1912 | 426.85 | 6850.000 | 2,166,436.58 | 4400.45 | 857,495.57 |
| 511 | 7.2162 | 25.05 | 101.200 | 13,658.65 | 47.80 | −0.01 |
| 512 | 7.2162 | 25.06 | 680.000 | 13,733.69 | 47.80 | 75.44 |
| 513 | 7.2162 | 150.05 | 700.000 | 82,225.49 | 239.45 | 11,426.97 |
| 514 | 7.2162 | 726.85 | 620.000 | 518,229.92 | 1112.55 | 187,116.32 |
| 520 | 8.3264 | 599.85 | 5800.000 | 548,627.72 | 1077.47 | 228,064.92 |
| 521 | 6.6611 | 600.00 | 5800.000 | 438,944.23 | 862.02 | 182,479.62 |
| 522 | 6.6611 | 310.22 | 700.000 | 369,741.37 | 880.40 | 107,796.78 |
| 523 | 1.6653 | 600.00 | 5800.000 | 109,736.06 | 215.51 | 45,619.91 |
| 524 | 1.6653 | 310.22 | 700.000 | 92,435.34 | 220.10 | 26,949.20 |
| 525 | 8.3264 | 310.22 | 700.000 | 462,176.71 | 1100.50 | 134,745.98 |
| 526 | 8.3264 | 159.85 | 650.000 | 101,226.40 | 291.14 | 15,106.90 |
| 527 | 8.3264 | 159.86 | 6100.00 | 101,714.99 | 290.19 | 15,878.27 |
| 531 | 29.4199 | 25.05 | 101.30 | 55,685.29 | 194.87 | 0.0 |
| 532 | 29.4199 | 51.85 | 150.0 | 115,067.90 | 385.48 | 2553.24 |
| Component | Work (kJ/s) | Heat (kJ/s) | Enthalpy In (kJ/s) | Enthalpy Out (kJ/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor<1> | −681,083.56 | −2,166,436.58 | 2,847,520.14 | |
| Steam generator<2> | −108,643.58 | −2,929,745.63 | 3,038,389.22 | |
| Superheater<3> | −102,549.15 | −2,621,874.29 | 2,724,423.45 | |
| Pump 3<10> | −338.38 | 9697.53 | −2,175,795.72 | 2,166,436.58 |
| Turbine 1<3> | 69,202.86 | −438,944.23 | 369,741.37 | |
| Turbine 2<4> | 17,300.71 | −109,736.06 | 92,435.34 | |
| Pump 1<7> | −95.01 | 19.96 | −13,658.65 | 13,733.69 |
| Recuperator<8> | 292,458.51 | −475,910.40 | 183,451.89 | |
| Pump 2<9> | −1032.20 | 543.61 | −101,226.40 | 101,715.0 |
| Compressor<14> | −17,123.48 | −4.19 | 17,127.67 | |
| Reformer<11> | 596,063.09 | −535,357.59 | 179,864.52 | |
| Water-gas shift <12> | 28,528.20 | −179,864.52 | 142,783.28 | |
| HTX<13> | −26.08 | 45,997.94 | −63,097.87 | 17,126.00 |
(kW) | (kW) | (kW) | Irreversibility Rate (kW), | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor | −600,000.0 * | 455,792.28 | 135.00 | 144,072.72 |
| Steam generator | −60,035.96 | −279.41 | 60,315.37 | |
| Superheater | −7284.03 | 88.99 | 7195.04 | |
| Pump 3 | −338.38 | −540.85 | 267.98 | 611.25 |
| Turbine 1 | 69,202.86 | −74,069.96 | −612.88 | 5479.98 |
| Turbine 2 | 17,300.71 | −18,499.48 | −171.23 | 1370.00 |
| Pump 1 | −95.01 | 0.0010 | 75.45 | 19.56 |
| Recuperator | −108,282.63 | −4.91 | 108,287.54 | |
| Pump 2 | −1032.20 | −47.26 | 818.63 | 260.83 |
| Compressor | −17,123.48 | −5874.58 | 9701.21 | 13,296.85 |
| Reformer | −195,665.27 | 36,560.69 | −81,465.44 | |
| Water-gas shift | −8553.05 | 5577.55 | −23,886.14 | 26,361.64 |
| HTX | −26.07 | 4090.15 | −9269.62 | 5205.54 |
| Component | Initial Investment Cost | Annualized Cost (USD × 106/yr) | Monetary Flow Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| (USD × 106) | (USD/s) | ||
| Reactor | 747.5 | 48.63 | 2.8635 |
| Steam generator | 18.4 | 1.20 | 0.0705 |
| Turbine 1 | 138.0 | 8.98 | 0.5287 |
| Turbine 2 | 121.9 | 7.93 | 0.4670 |
| Generator | 20.7 | 1.35 | 0.0793 |
| Superheater | 12.42 | 0.81 | 0.0476 |
| Pump 1 | 8.28 | 0.54 | 0.0317 |
| Recuperator | 12.42 | 0.81 | 0.0476 |
| Pump 2 | 12.42 | 0.81 | 0.0476 |
| Pump 3 | 28.98 | 1.89 | 0.1110 |
| Reformer | 575.0 | 37.4 | 2.2027 |
| Water-gas shift | 575.0 | 37.4 | 2.2027 |
| HTX | 12.42 | 0.81 | 0.0476 |
| Compressor | 34.5 | 2.24 | 0.1322 |
| Total | 2317.94 | 150.8 | 8.880 |
| Component | Thermal | Mechan | Work | Lost Cost | Investment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor | 6.153 | 0.032 | −1.222 | −4.9635 | |
| Steam generator | 0.649 | −0.067 | −0.511 | −0.0705 | |
| Turbine 1 | −2.077 | −0.147 | 2.799 | −0.046 | −0.5287 |
| Turbine 2 | −0.519 | −0.041 | 1.038 | −0.012 | −0.4670 |
| Generator | 3.954 * | −3.838 | −0.037 | −0.0793 | |
| Superheater | 0.087 | 0.021 | −0.061 | −0.0476 | |
| Pump 1 | 0.036 | −0.004 | −0.0317 | ||
| Recuperator | 0.967 | −0.001 | −0.918 | −0.0476 | |
| Pump 2 | −0.001 | 0.097 | −0.046 | −0.002 | −0.0476 |
| Pump 3 | −0.015 | 0.146 | −0.015 | −0.005 | −0.1110 |
| Reformer | −18.016 | 24.401 | −3.129 | 0.691 | −3.9470 |
| Water-gas shift | 5.186 | −15.590 | 20.204 ** | −0.224 | −9.5773 |
| HTX | 6.283 | −6.197 | 0.001 | −0.044 | −0.0476 |
| Compressor | −5.462 | 6.467 | −0.760 | −0.113 | −0.1312 |
| C1DT | C2DT | C3W | C4W | C5E | C6DT | C7DP | C8DT |
| 13.50 | −10.81 | 40.45 | 60.02 | 48.11 | −11.97 | 478.47 | −8.93 |
| C9DP | C10DP | C11BT | C12H2 | C13BP | C14BP | C15DT | C16DP |
| 118.38 | 546.2 | 1482.2 | 13.92 | 3975.2 | 666.62 | 28.04 | 240.42 |
| CT | CP | CW | CS | ||||
| 929.85 | 666.6 | 44.36 | −8.48 |
| Plant | Hydrogen Production Rate | Unit Cost of Hydrogen |
|---|---|---|
| (kg/s) | (USD/GJ) | |
| HTGR 60-MW | 0.257 | 35.6 |
| HTWR 60-MW | 1.628 | 13.8 |
| HTGR 6-MW | 0.0258 | 35.6 |
| HTWR 6-MW | 0.159 | 13.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.; Lee, W.-Y.; Seo, S.-H.; Oh, S.-D.; Kwak, H.-Y. Energy, Exergy and Thermoeconomic Analyses on Hydrogen Production Systems Using High-Temperature Gas-Cooled and Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors. Energies 2023, 16, 8090. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248090
Kim T, Lee W-Y, Seo S-H, Oh S-D, Kwak H-Y. Energy, Exergy and Thermoeconomic Analyses on Hydrogen Production Systems Using High-Temperature Gas-Cooled and Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors. Energies. 2023; 16(24):8090. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248090
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Taehun, Won-Yong Lee, Seok-Ho Seo, Si-Doek Oh, and Ho-Young Kwak. 2023. "Energy, Exergy and Thermoeconomic Analyses on Hydrogen Production Systems Using High-Temperature Gas-Cooled and Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors" Energies 16, no. 24: 8090. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248090
APA StyleKim, T., Lee, W.-Y., Seo, S.-H., Oh, S.-D., & Kwak, H.-Y. (2023). Energy, Exergy and Thermoeconomic Analyses on Hydrogen Production Systems Using High-Temperature Gas-Cooled and Water-Cooled Nuclear Reactors. Energies, 16(24), 8090. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16248090






