The Reference Wideband Inductive Current Transformer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
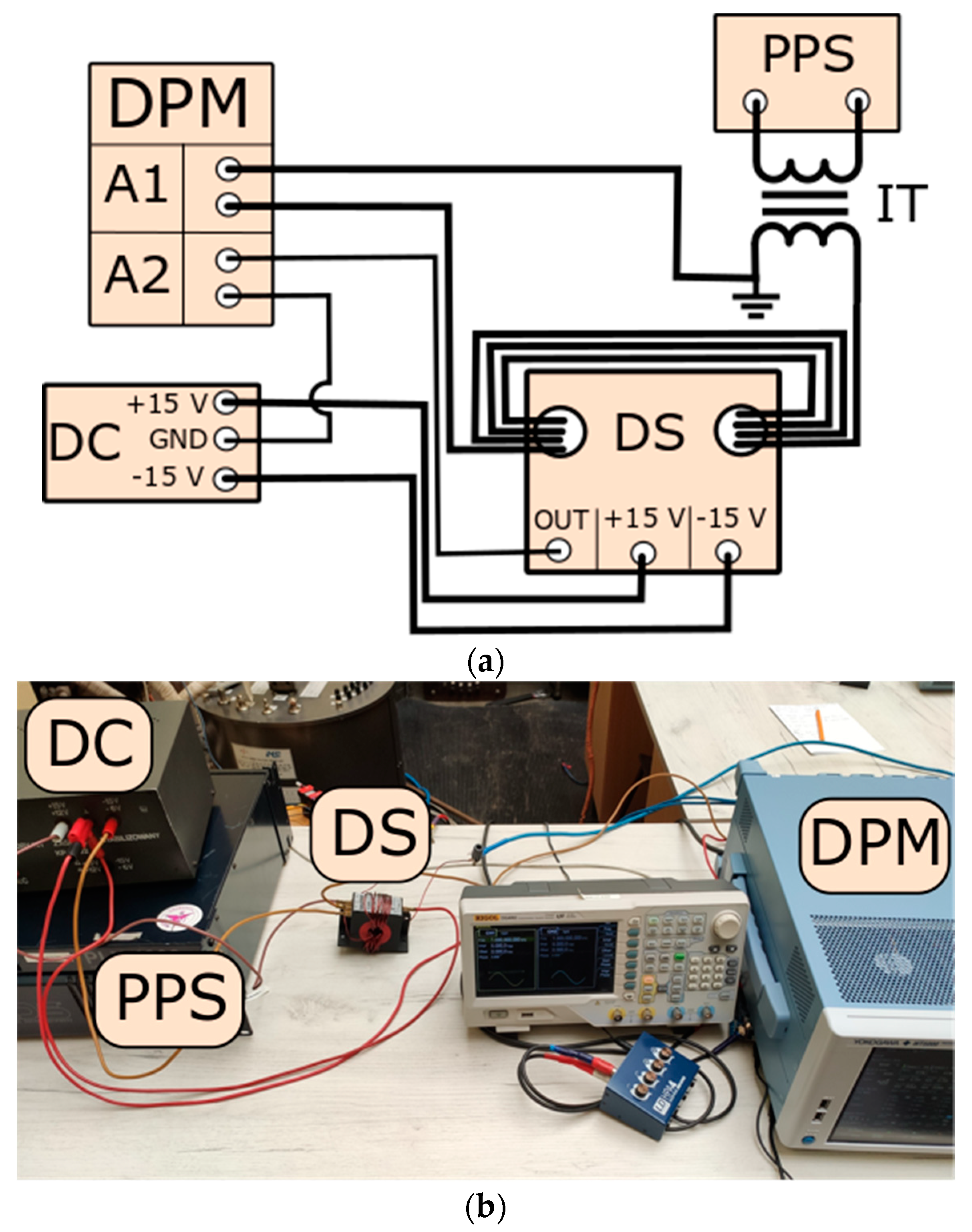
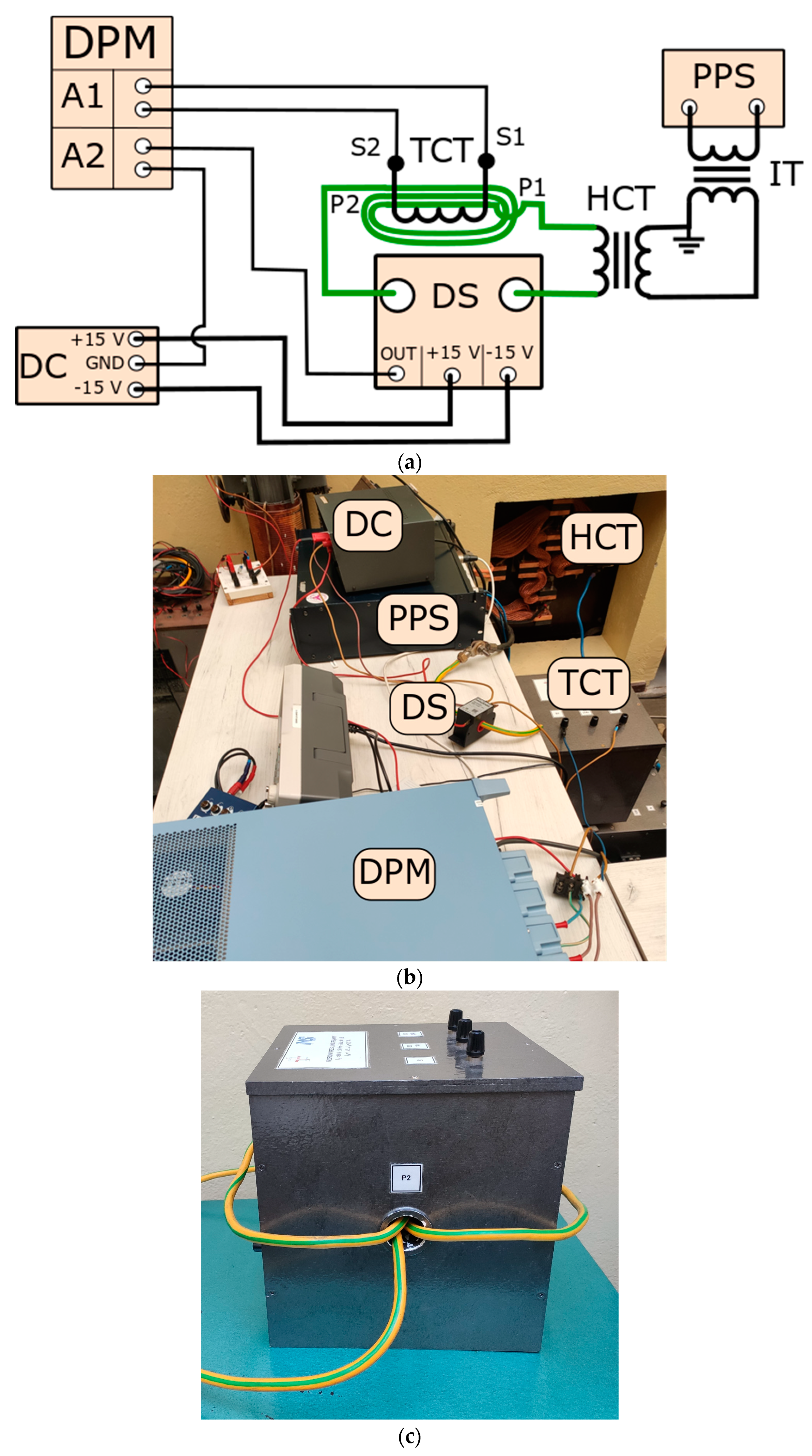
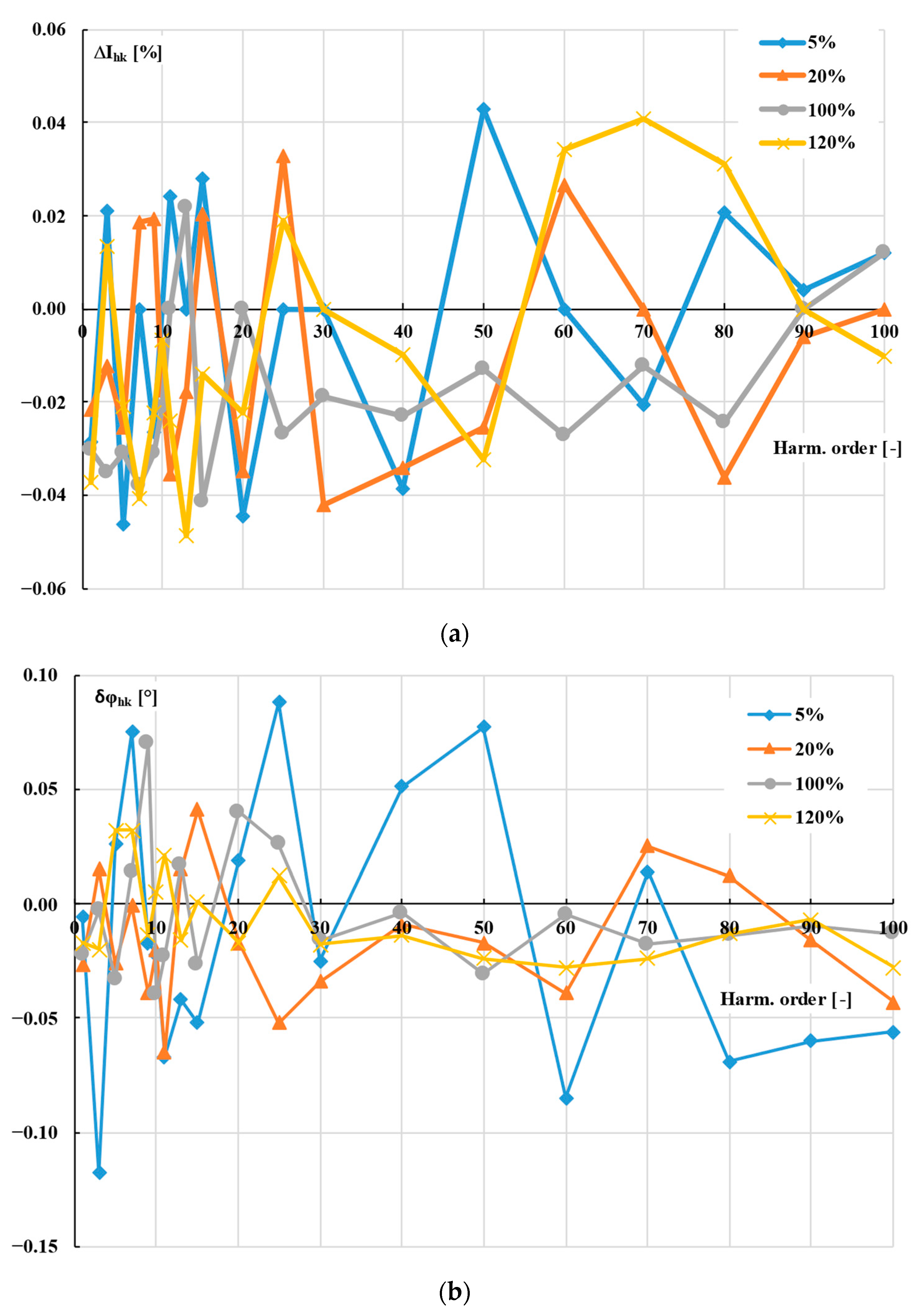
2. Measuring Systems, Methods, and Reference Inductive CT
- DPM—digital power meter Yokogawa WT5000;
- DS—Danisense DC200IF current transducer (the value of rated primary current is equal to 200 A RMS, the value of rated secondary current is equal to 200 mA RMS);
- PPS—programmable power supply composed of the audio power amplifier and arbitrary waveform generator;
- IT—insulation transformer;
- DC—DC power supply for DS (±15 V).
- kDS—rated value of current ratio of DS is 1000 A/A;
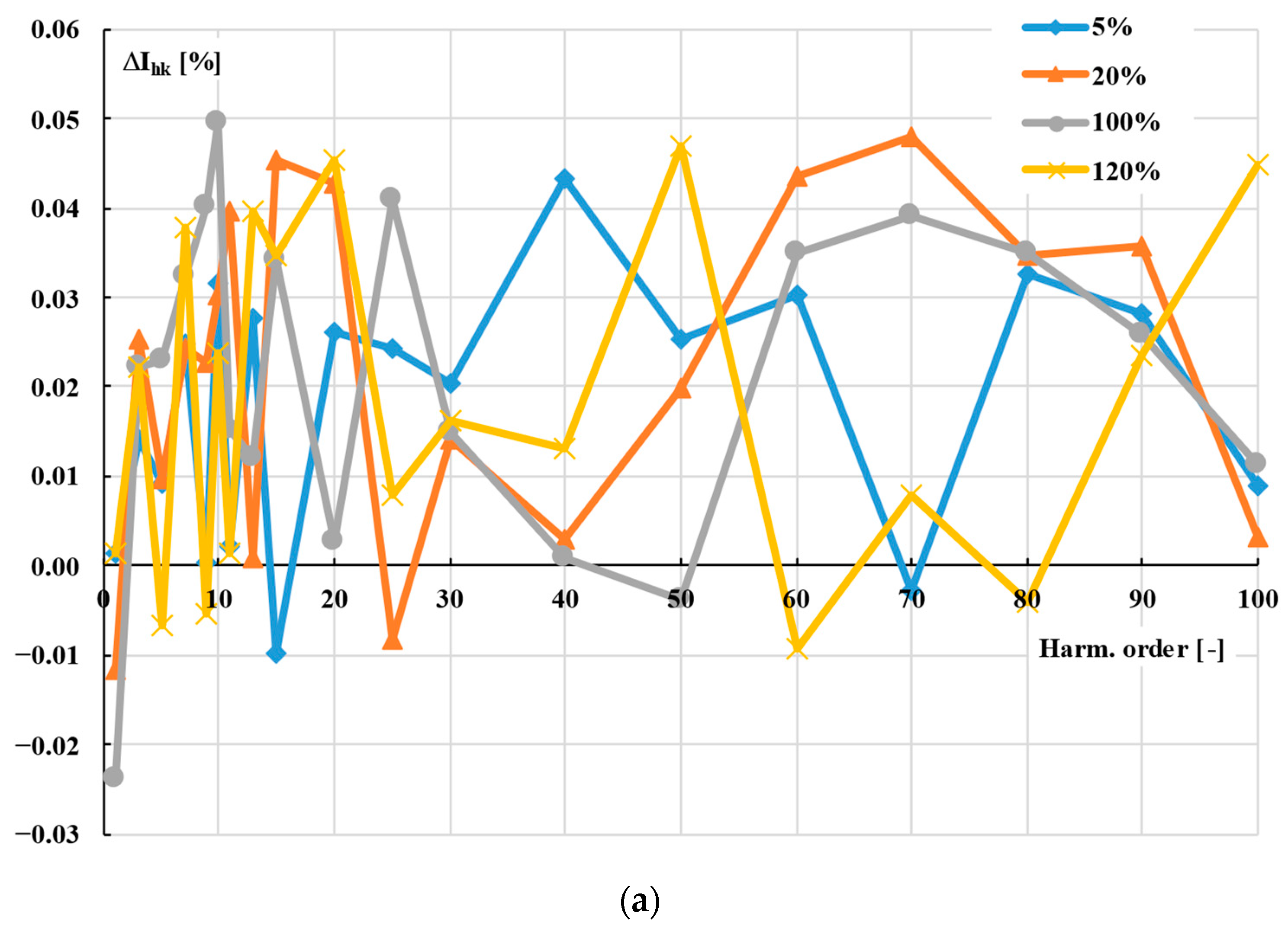
- I1hk—RMS value of the hk harmonic of the distorted primary current of DS;
- DS2hk—the RMS value of the hk harmonic of the distorted secondary current of DS;
- n—number of turns of the additional primary winding made by the 40 wires passed through the window of the transducer.
- φDS2hk—phase angle of the hk harmonic of the distorted secondary current of DS in relation to the reference voltage;
- φ1hk—phase angle of the hk harmonic of the distorted primary current of DS in relation to the reference voltage.
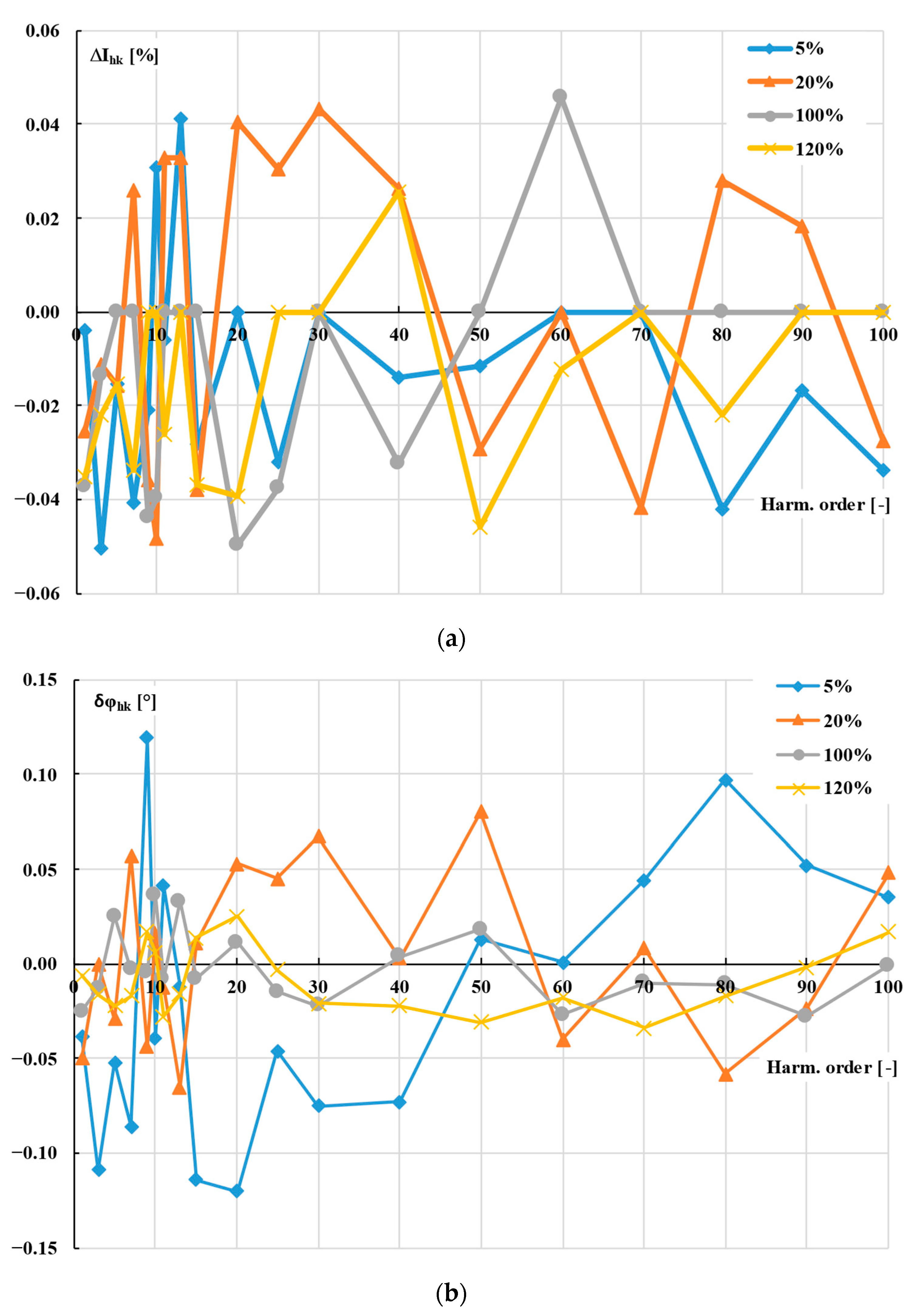
- ΔIhk—value of the current error for hk harmonic;
- δφhk—value of the phase displacement for hk harmonic.
- TCT—tested wideband reference inductive CT (the value of rated primary current is equal to 300 A RMS, the values of rated secondary currents from two secondary windings are equal to 5 A RMS and 1 A RMS);
- HCT—step-up current transformer [18].
- kTCT—rated value of current ratio of TCT (60 if secondary current is equal to 5 A or 300 if secondary current is equal to 1 A);
- ITCT2hk—RMS value of the hk harmonic of the distorted secondary current of TCT.
- φTCT2hk—phase angle of the hk harmonic of the distorted secondary current of TCT in relation to the reference voltage.
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEC 61869-1; Instrument Transformers-General Requirements; 2nd ed. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- IEC 61869-6; Instrument Transformers-Additional General Requirements for Low-Power Instrument Transformers. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Faifer, M.; Laurano, C.; Ottoboni, R.; Toscani, S.; Zanoni, M. Characterization of Voltage Instrument Transformers under Nonsinusoidal Conditions Based on the Best Linear Approximation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 2392–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faifer, M.; Ferrero, A.; Laurano, C.; Ottoboni, R.; Toscani, S.; Zanoni, M. An Innovative Approach to Express Uncertainty Introduced by Voltage Transformers. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 6696–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohns, E.; Fricke, S.; Pauling, F. An AC Power Amplifier for Testing Instrument Transformer Test Equipment. In Proceedings of the CPEM 2016-Conference on Precision Electromagnetic Measurements, Conference Digest, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristaldi, L.; Faifer, M.; Laurano, C.; Ottoboni, R.; Toscani, S.; Zanoni, M. A Low-Cost Generator for Testing and Calibrating Current Transformers. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 2792–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, M.; Stano, E. Review of Measuring Methods, Setups and Conditions for Evaluation of the Inductive Instrument Transformers Accuracy for Transformation of Distorted Waveforms. Energies 2023, 16, 4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, M.; Stano, E. Challenges of Accurate Measurement of Distorted Current and Voltage in the Power Grid by Conventional Instrument Transformers. Energies 2023, 16, 2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotti, G.; D’Avanzo, G.; Letizia, P.S.; Luiso, M. Measuring Harmonics with Inductive Voltage Transformers in Presence of Subharmonics. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faifer, M.; Laurano, C.; Ottoboni, R.; Toscani, S.; Zanoni, M. Harmonic Distortion Compensation in Voltage Transformers for Improved Power Quality Measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 3823–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, K.; Styblikova, R. Using Instrument Transformers in a Wider Frequency Range. In Proceedings of the Conference Record-IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Hangzhou, China, 10–12 May 2011; pp. 1207–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Crotti, G.; D’Avanzo, G.; Giordano, D.; Letizia, P.S.; Luiso, M. Extended SINDICOMP: Characterizing MV Voltage Transformers with Sine Waves. Energies 2021, 14, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faifer, M.; Laurano, C.; Ottoboni, R.; Toscani, S.; Zanoni, M.; Crotti, G.; Giordano, D.; Barbieri, L.; Gondola, M.; Mazza, P. Overcoming Frequency Response Measurements of Voltage Transformers: An Approach Based on Quasi-Sinusoidal Volterra Models. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 2800–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, P.; Laurano, C.; Muscas, C.; Pegoraro, P.A.; Toscani, S.; Zanoni, M. Harmonic Synchrophasors Measurement Algorithms with Embedded Compensation of Voltage Transformer Frequency Response. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 9001310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, M.; Stano, E. New Approach to Evaluate the Transformation Accuracy of Inductive CTs for Distorted Current. Energies 2023, 16, 3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, M.; Kaczmarek, P.; Stano, E. The Effect of the Load Power Factor of the Inductive CT’s Secondary Winding on Its Distorted Current’s Harmonics Transformation Accuracy. Energies 2022, 15, 6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataliotti, A.; Cosentino, V.; Crotti, G.; Giordano, D.; Modarres, M.; Di Cara, D.; Tinè, G.; Gallo, D.; Landi, C.; Luiso, M. Metrological Performances of Voltage and Current Instrument Transformers in Harmonics Measurements. In Proceedings of the I2MTC 2018-2018 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference: Discovering New Horizons in Instrumentation and Measurement, Proceedings, Houston, TX, USA, 14–17 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek, M.; Kaczmarek, P.; Stano, E. The Performance of the High-Current Transformer during Operation in the Wide Frequencies Range. Energies 2022, 15, 7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović-Grčić, D.; Filipović-Grčić, B.; Krajtner, D. Frequency Response and Harmonic Distortion Testing of Inductive Voltage Transformer Used for Power Quality Measurements. Procedia Eng. 2017, 202, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotti, G.; Chen, Y.; Çayci, H.; D’Avanzo, G.; Landi, C.; Letizia, P.S.; Luiso, M.; Mohns, E.; Muñoz, F.; Styblikova, R.; et al. How Instrument Transformers Influence Power Quality Measurements: A Proposal of Accuracy Verification Tests. Sensors 2022, 22, 5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.L.; Wan, R.S.; Guo, Y.; Chen, N.; Lee, W.J. A Redundancy Mechanism Design for Hall-Based Electronic Current Transformers. Energies 2017, 10, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Chen, R.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, W. Electronic Voltage and Current Transformers Testing Device. Sensors 2012, 12, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ma, J.; Huang, X.; Fang, Y. Predicting Iron Losses in Laminated Steel with given Non-Sinusoidalwaveforms of Flux Density. Energies 2015, 8, 13726–13740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniewska, E. Influence of the Selection of the Core Shape and Winding Arrangement on the Accuracy of Current Transformers with Through-Going Primary Cable. Energies 2021, 14, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, M.; Wolter, M. High-Frequency Current Transformer Design and Construction Guide. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yue, S.; Zhang, C. Loss Characteristics and Model Verification of Soft Magnetic Composites under Non-Sinusoidal Excitation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta, W.A.; Swieboda, C.; Leszczynski, J.S.; Soinski, M. Some Remarks on Metrological Properties and Production Technology of Current Transformers Made of Nanocrystalline Cores. Measurement 2017, 97, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniewska, E. Modern Methods of Construction Problem Solving in Designing Various Types of Instrument Transformers. Energies 2022, 15, 8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swieboda, C.; Walak, J.; Soinski, M.; Rygal, J.; Leszczynski, J.; Grybos, D. Nanocrystalline Oval Cut Cores for Current Instrument Transformer Prototypes. Measurement 2019, 136, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stano, E.; Kaczmarek, P.; Kaczmarek, M. Understanding the Frequency Characteristics of Current Error and Phase Displacement of the Corrected Inductive Current Transformer. Energies 2022, 15, 5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniewska, E.; Rajchert, R. Behaviour of Measuring Current Transformers with Cores Composed from Different Magnetic Materials at Non-Rated Loads and Overcurrents. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2019, 13, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingotti, A.; Peretto, L.; Bartolomei, L.; Cavaliere, D.; Tinarelli, R. Are Inductive Current Transformers Performance Really Affected by Actual Distorted Network Conditions? An Experimental Case Study. Sensors 2020, 20, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingotti, A.; Bartolomei, L.; Peretto, L.; Tinarelli, R. On the Long-Period Accuracy Behavior of Inductive and Low-Power Instrument Transformers. Sensors 2020, 20, 5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locci, N.; Muscas, C. Comparative Analysis between Active and Passive Current Transducers in Sinusoidal and Distorted Conditions. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2001, 50, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataliotti, A.; Di Cara, D.; Emanuel, A.E.; Nuccio, S. Current Transformers Effects on the Measurement of Harmonic Active Power in LV and MV Networks. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2011, 26, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballal, M.S.; Wath, M.G.; Suryawanshi, H.M. A Novel Approach for the Error Correction of Ct in the Presence of Harmonic Distortion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 4015–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghjoo, F.; Pak, M.H. Compensation of CT Distorted Secondary Current Waveform in Online Conditions. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 31, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, A.J.; Femine, A.D.; Gallo, D.; Langella, R.; Luiso, M. Compensation of Current Transformers’ Nonlinearities by Tensor Linearization. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 3841–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, D.; Landi, C.; Luiso, M. Real-Time Digital Compensation of Current Transformers over a Wide Frequency Range. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaczmarek, M.; Kaczmarek, P.; Stano, E. The Reference Wideband Inductive Current Transformer. Energies 2023, 16, 7307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16217307
Kaczmarek M, Kaczmarek P, Stano E. The Reference Wideband Inductive Current Transformer. Energies. 2023; 16(21):7307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16217307
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaczmarek, Michal, Piotr Kaczmarek, and Ernest Stano. 2023. "The Reference Wideband Inductive Current Transformer" Energies 16, no. 21: 7307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16217307
APA StyleKaczmarek, M., Kaczmarek, P., & Stano, E. (2023). The Reference Wideband Inductive Current Transformer. Energies, 16(21), 7307. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16217307







