A Numerical Study on Labyrinth Screw Pump (LSP) Performance under Viscous Fluid Flow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
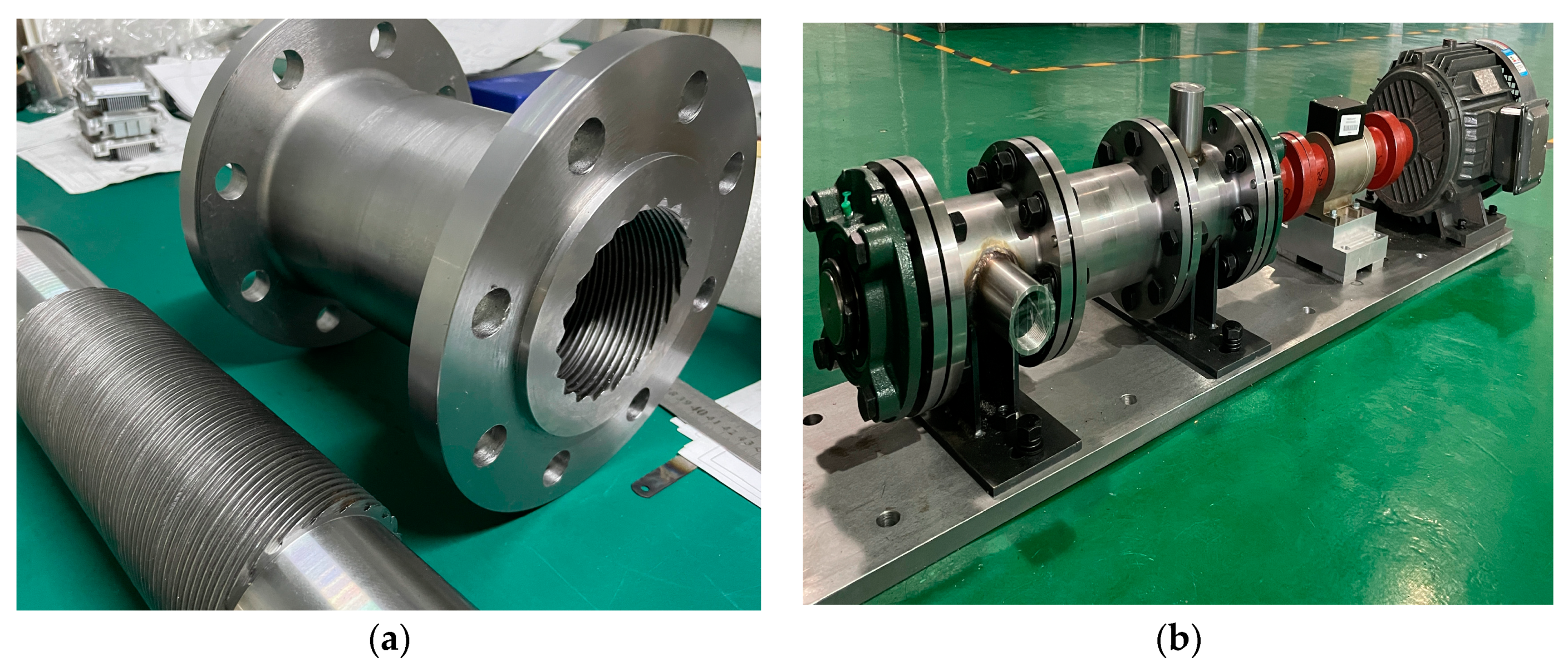
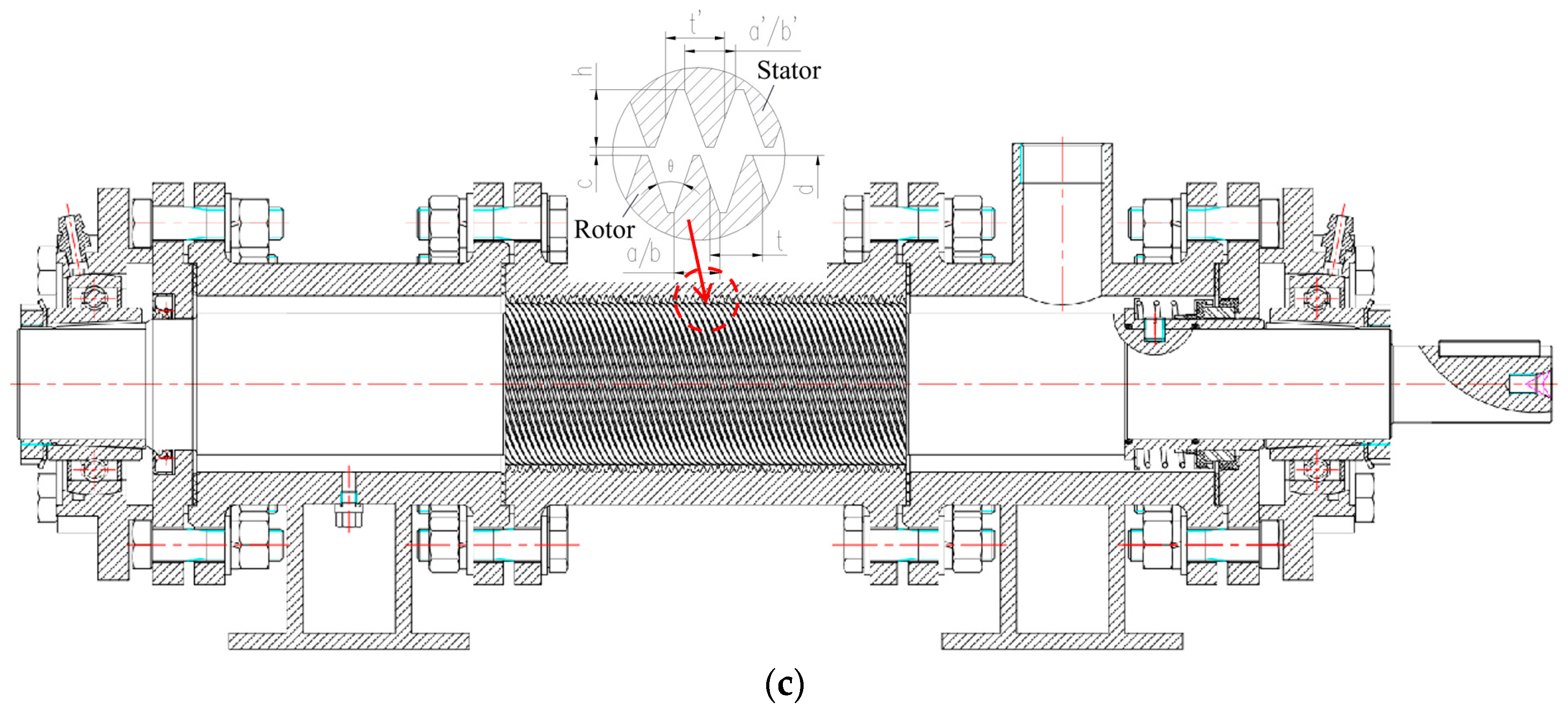
LSP Geometry and Prototype
2. Numerical Methodology
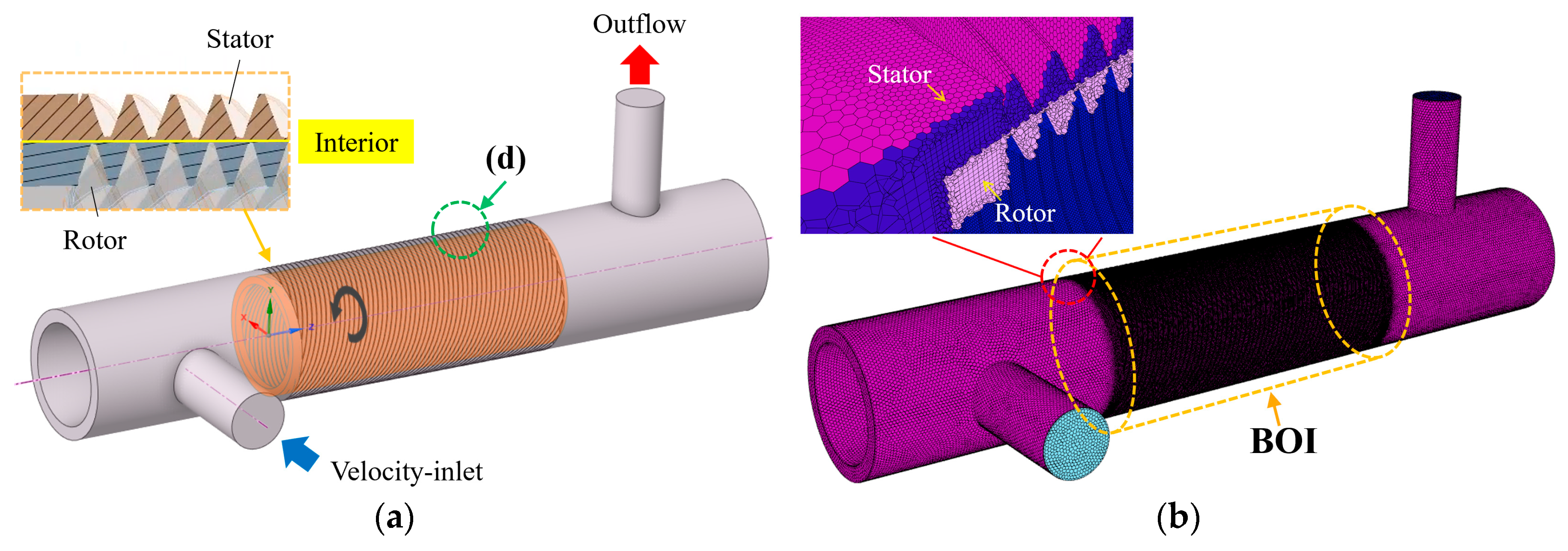
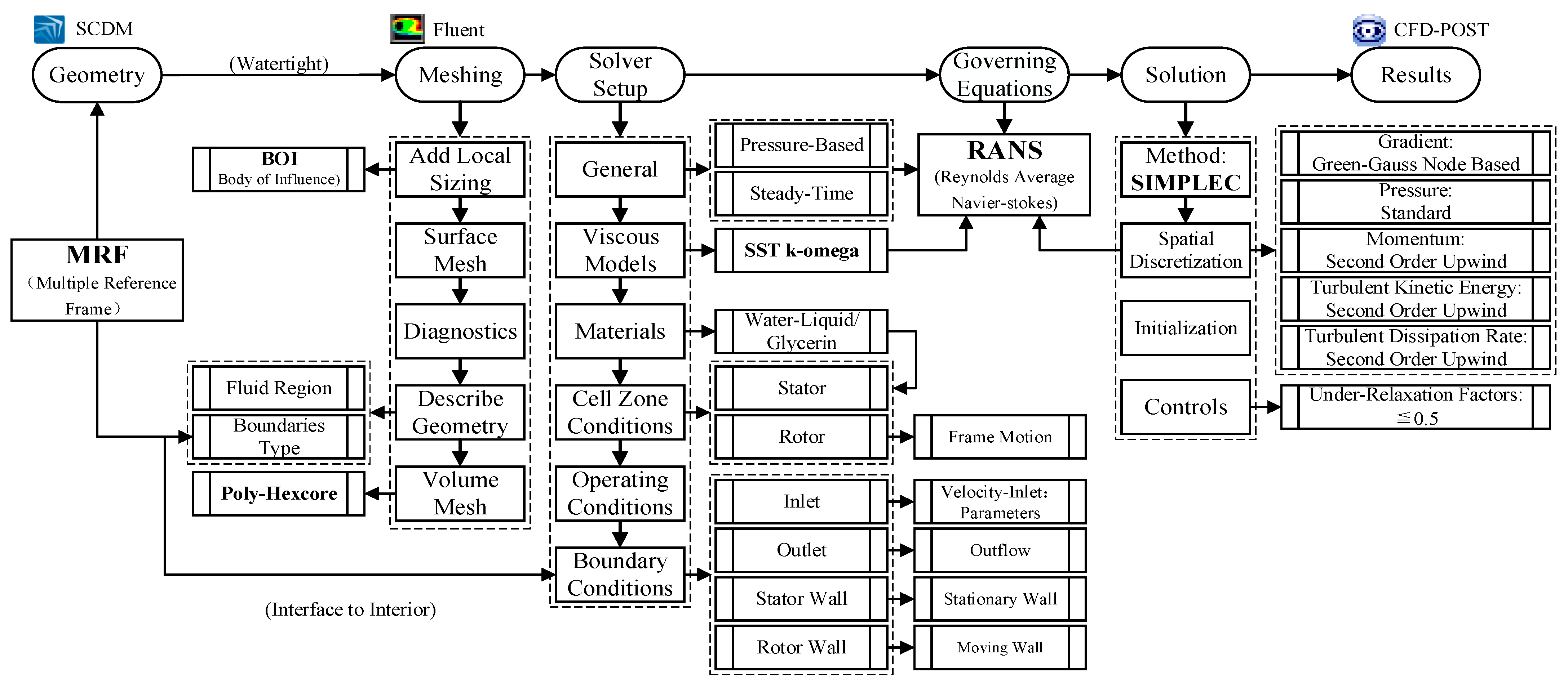
2.1. Mesh Generation
2.2. Mathematical Model
2.3. Numerical Scheme and Boundary Conditions
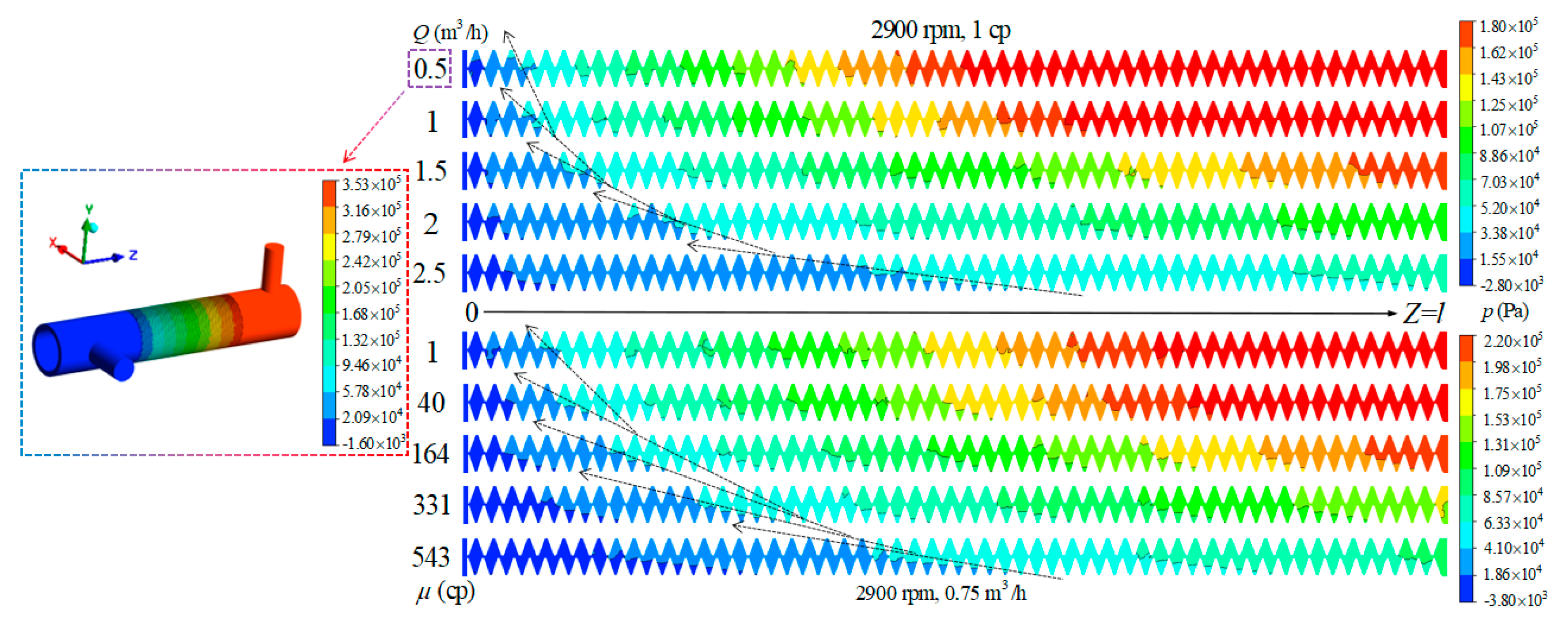
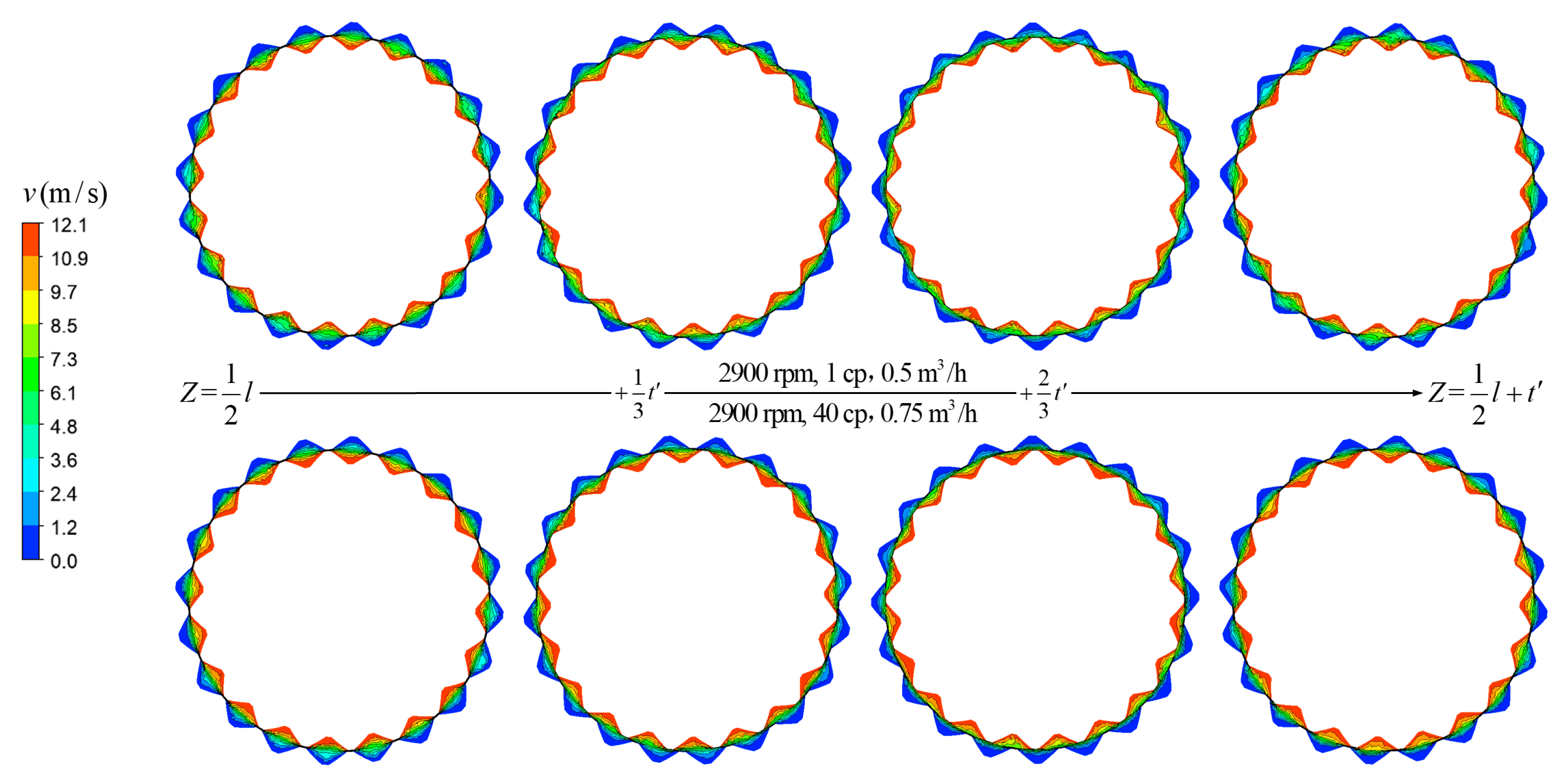
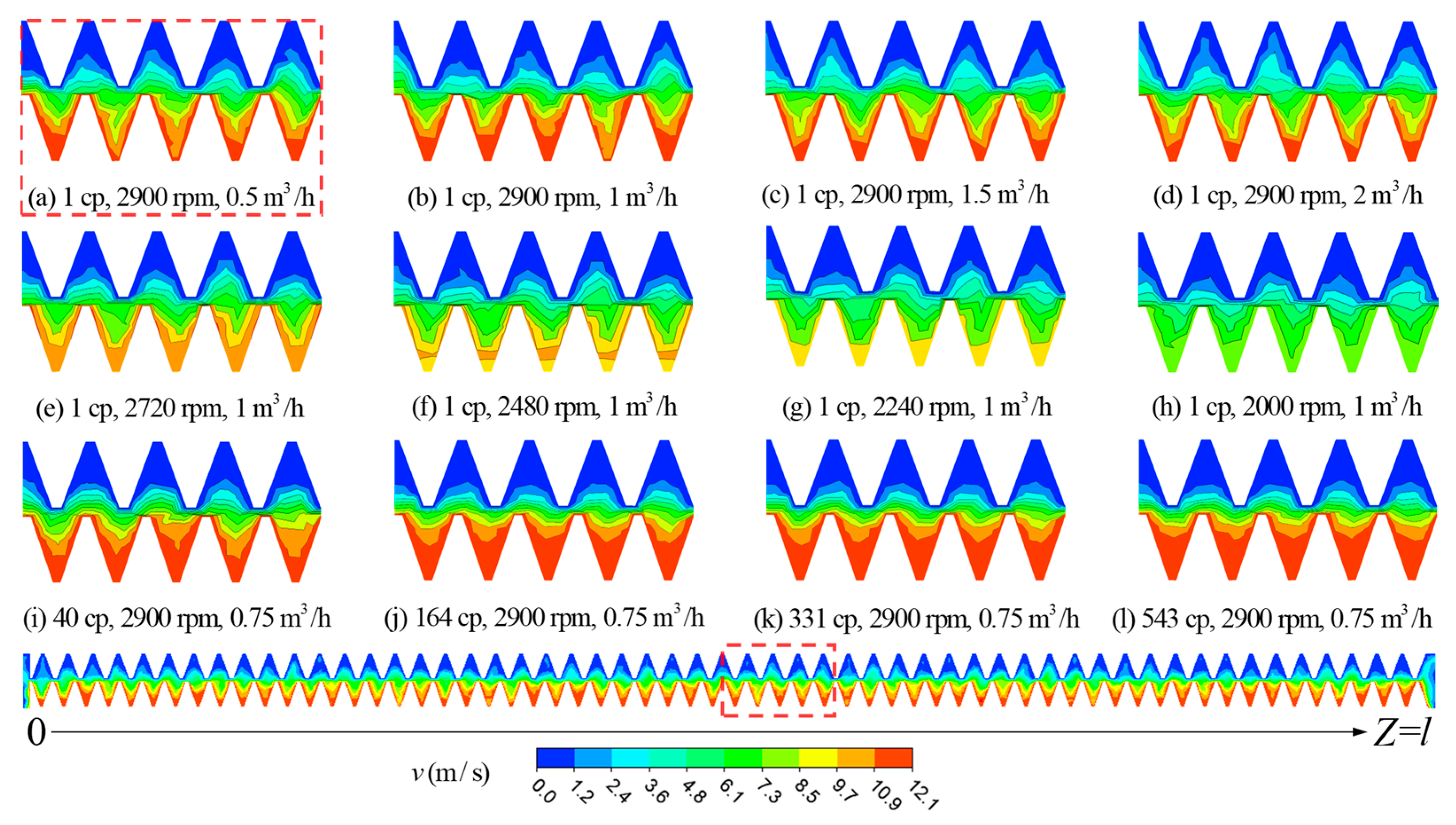
3. Results and Discussion
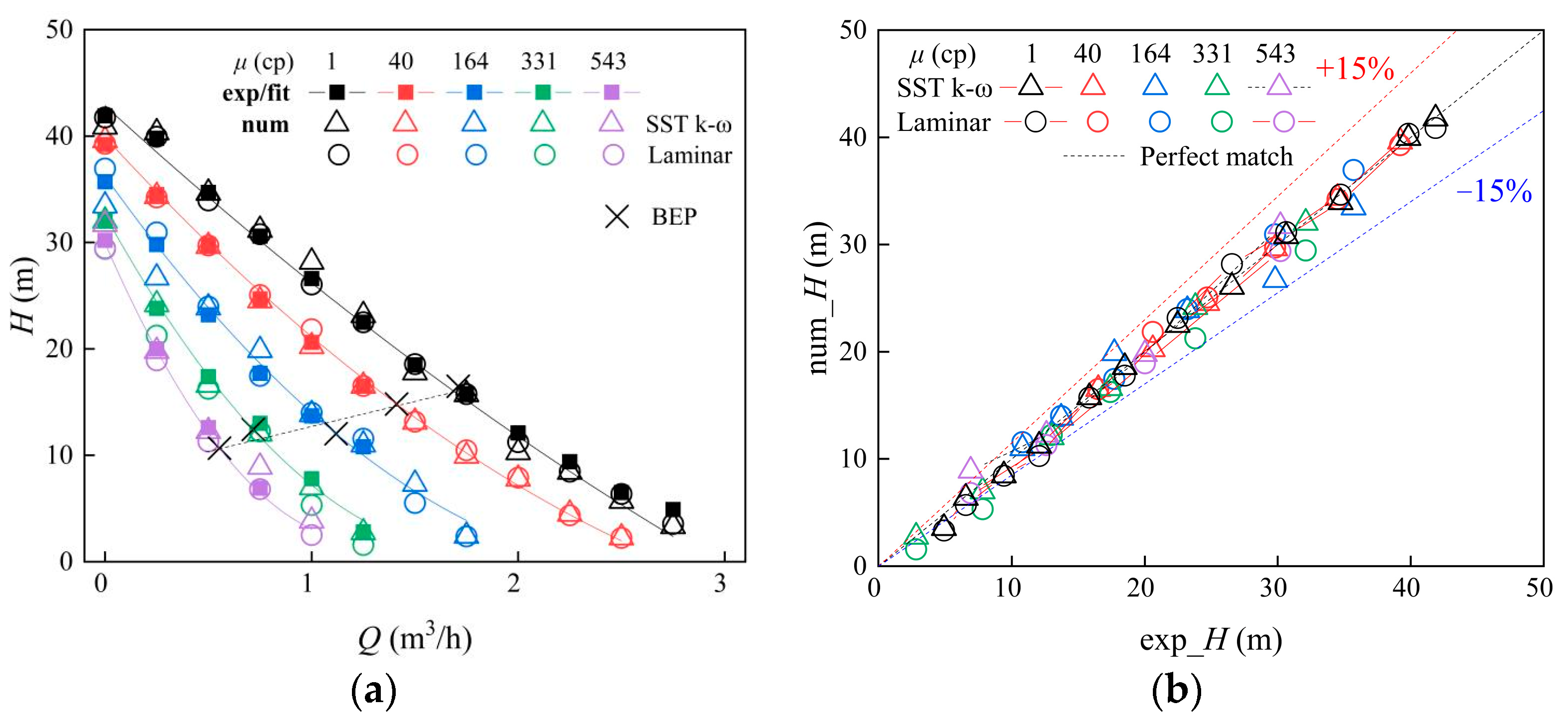
3.1. Turbulence Model Validation
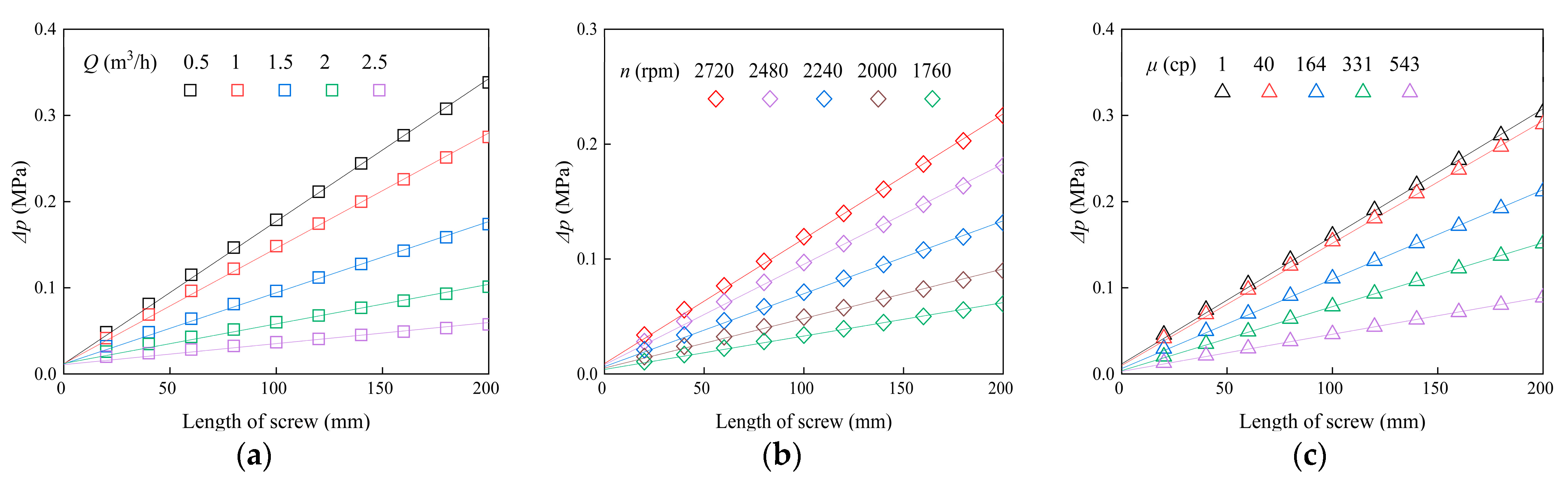
3.2. Comparison with Experimental Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| a | length of rotor thread crest, mm |
| a′ | length of stator thread crest, mm |
| b | length of rotor thread root, mm |
| b′ | length of stator thread root, mm |
| c | stator–rotor fitting clearance, mm |
| CQ | flow rate correction factor |
| CH | head correction factor |
| d | diameter of rotor, mm |
| g | gravitational acceleration, m2/s |
| h | groove depth, mm |
| H | head, mm |
| l | length of screw, mm |
| n | rotate speed, rpm |
| nr | rated rotate speed, rpm |
| p | pressure, Pa |
| Q | volumetric flow rate, m3/h |
| Qmax | maximum volumetric flow rate, m3/h |
| ReΩ | rotational Reynolds number |
| t | thread pitch of rotor, mm |
| t′ | thread pitch of stator, mm |
| v | velocity, m/s |
| z | number of screw twist |
| Greek symbols | |
| α | Angle of thread profile, deg |
| η | hydraulic efficiency, % |
| θ | Angle of thread, deg |
| μ | dynamic viscosity, cp |
| ν | kinematic viscosity, m2/s |
| ρ | density, kg/m3 |
| Φ | flow coefficient |
| Ψ | specific head |
| ωs | specific speed |
| Ω | angular speed, rad/s |
| Subscripts | |
| conv | conversion value |
| exp | experiment value |
| fit | fitted curve |
| num | numerical simulation |
| i | inlet |
| o | outlet |
| n | normalized |
| w | value tested for water |
References
- Zhu, J.; Banjar, H.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, H.-Q. CFD simulation and experimental study of oil viscosity effect on multi-stage electrical submersible pump (ESP) performance. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 146, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhu, J.; Rutter, R.; Zhang, H.-Q. A Numerical Study on Erosion Model Selection and Effect of Pump Type and Sand Characters in Electrical Submersible Pumps by Sandy Flow. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2019, 141, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte Verde, W.; Kindermann, E.; Biazussi, J.L.; Estevam, V.; Foresti, B.P.; Bannwart, A.C. Experimental Investiga-tion of the Effects of Fluid Viscosity on Electrical Submersible Pumps Performance. SPE Prod. Oper. 2022, 38, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, H.; Cao, G.; Zhang, J.; Peng, J.; Banjar, H.; Zhang, H.-Q. A New Mechanistic Model To Predict Boosting Pressure of Electrical Submersible Pumps Under High-Viscosity Fluid Flow with Validations by Experimental Data. SPE J. 2019, 25, 744–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhu, J.; Rutter, R.; Zhang, H.Q. Experimental Study on Deteriorated Performance, Vibration, and Geome-try Changes of an Electrical Submersible Pump Under Sand Water Flow Condition. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2021, 143, 082104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.-Q. Experiments and mechanistic modeling of viscosity effect on a multistage ESP performance under viscous fluid flow. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2021, 235, 1976–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, C.; Biazussi, J.L.; Verde, W.M.; Estevam, V.; Bannwart, A.C.; Tavares, A.; Santos, M.P.d.L.; Rocha, P.S.D.M.V. Experimental Study on the Performance of Electrical Submersible Pump Operating with Ultraviscous Oil. SPE J. 2022, 27, 2470–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Om, I.L.; Han, U.C.; Ryo, S.I.; Kim, C.Y.; Sol, Y.N. A New Analytical Approach to Calculate a Slippage inside a Pro-gressing Cavity Pump with a Metallic Stator Using a Middle Streamline and a Structural Periodicity. SPE J. 2022, 27, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelik, L.; Brennan, J. Progressing Cavity Pumps, Downhole Pumps, and Mudmotors; Gulf Publishing Company: Houston, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Berton, M.; Allain, O.; Goulay, C.; Lemetayer, P. Complex fluid flow and mechanical modeling of metal progressing cavity pumps PCP’s. In Proceedings of the SPE Heavy Oil Conference and Exhibition, Kuwait City, Kuwait, 12–14 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ramde, S.; Beauquin, J.; Bellett, D.; Duret-Thual, C.; Olivier, G.; Pierchon, A. Innovative solutions in pcp technologies, run life improvement with experimental and numerical works. In Proceedings of the SPE Artificial Lift Conference & Exhibition-North America, Huston, TX, USA, 7 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Shu, M.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Y. Flow Field Numerical Simulation and Performance Analysis of Progressing Cavity Pump. SPE Prod. Oper. 2021, 36, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubiev, A.I. The Development of a Three-stage Screw-Type Labyrinth Seal. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Fluid Sealing, Weinheim, Germany, May 1969; pp. 348–350. [Google Scholar]
- Golubev, A.I.; Pjatigorskaja, E.I. Determination of optimal parameters of labyrinth-screw seals and pump. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Fluid Sealing, BHR Group Conference Series, Brugge, Belgium, 30 November–1 December 2020; pp. 473–481. [Google Scholar]
- Golubev, A.I.; Pyatigorskaya, E.I. Efficiency Coefficients of a Labyrinth Pump. Chem. Pet. Eng. 2005, 41, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, K. Modeling of Pumping Performance of Labyrinth Screw Pump (LSP) by 2D Reynolds Stress Equations. J. Fluids Eng. 2009, 131, 085001–0850015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrenko, P.; Lebedev, A. Labyrinth screw pump theory. Motrol Motoryz. Energetyka Rol. 2014, 16, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Andrenko, P.; Rogovyi, A.; Hrechka, I.; Khovanskyi, S.; Svynarenko, M. Characteristics improvement of labyrinth screw pump using design modification in screw. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1741, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Ban, Z.; Qin, B.; Liu, H.; Dai, M. Theoretical Leakage Equations Towards Liquid-Phase Flow in the Straight-Through Labyrinth Seal. J. Tribol. 2021, 144, 031802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.; Jiang, S. Theoretical and experimental research towards laby-rinth sealing mechanism of liquid nitrogen in the cryogenic spindle. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 167, 108502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, S.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, D. Experimental and Modeling Investigation on Gas-Liquid Two-Phase Flow in Horizontal Gas Wells. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2022, 145, 013102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Upchurch, E.R.; Ozbayoglu, E.M.; Baldino, S.; Zheng, D.; Wang, J. Gas Migration Model for Non-Newtonian Fluids Under Shut-In Well Conditions. In Proceedings of the SPE/IADC Middle East Drilling Technology Conference and Exhibition, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 23–25 May 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesana, N.R.; Throneberry, J.M.; McLaury, B.S.; Shirazi, S.A.; Rybicki, E.F. Effect of particle size and liquid vis-cosity on erosion in annular and slug flow. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2014, 136, 012901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoff, H. Incompressible flow in a labyrinth seal. J. Fluid Mech. 1980, 100, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraji, M.; Joseph, S.P.; Nirmal, N. Optimization of Labyrinth Seal for Screw Compressor. In Proceedings of the ASME/JSME 2007 Thermal Engineering Heat Transfer Summer Conference, Vancouver, Canada, 8–12 July 2007; pp. 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asok, S.P.; Sankaranarayanasamy, K.; Sundararajan, T.; Vaidyanathan, G.; Kumar, K.U. Pressure drop and cavita-tion investigations on static helical-grooved square, triangular and curved cavity liquid labyrinth seals. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2011, 241, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.; Untaroiu, A.; Wood, H.G.; Weaver, B.K.; Morgan, N.; Jin, H. Response surface mapping of performance for helical groove seals with incompressible flow. In Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 49842. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, C.; Wood, H.G. Developing an optimal helix angle as a function of pressure for helical Groove seals. In Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 58042, p. V01AT05A020. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, C.; Wood, H. Evaluating Configurations of Double Surface Helical Groove Seals Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. In Turbo Expo: Power for Land, Sea, and Air; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 51012, p. V02CT42A053. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, C.; Wood, H. Second stage optimization of helical groove seals using computational fluid dynamics to evaluate the dependency of optimized design on preswirl. In Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 51579, p. V003T12A028. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Wang, K. CFD numerical simulation and experimental study of effects of screw-sleeve fitting clearance upon triangular thread labyrinth screw pump (LSP) performance. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2010, 3, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Zhang, Y.C. Numerical Simulation of Labyrinth Screw Pump with Separated Structure by Fluent. In Applied Mechanics and Materials; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Bach, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 455, pp. 242–247. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Jang, H.; Kwak, H.; Moon, Y.; Kim, C. Leakage analysis of helical grooved pump seal using CFD. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 4183–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Zhu, H.; Hu, B. Performance Research and Structure Optimization of Labyrinth Screw Pump. Micromachines 2021, 12, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Cao, G.; Zhu, H.; Zhong, R.; Zhu, H. Study on the Labyrinth Screw Pump for Heavy Oil Production. In Proceedings of the SPE Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference and Exhibition, Adelaide, Australia, 17–19 October 2022. [Google Scholar]


| Description | Values |
|---|---|
| Groove depth (h, mm) | 3.5 |
| Angle of thread (θ, deg) | 40 |
| Angle of thread profile (α, deg) | 15 |
| Number of thread (z) | 20 |
| Length of thread crest of stator/rotor (a′/a, mm) | 0.5/0.4 |
| Length of thread root of stator/rotor (b′/b, mm) | 3.1/2.8 |
| Thread pitch of stator/rotor (t′/t, mm) | 3.6/3.2 |
| Length of screw (l, mm) | 200 |
| Stator–rotor clearance (c, mm) | 0.5 |
| Case | Ci | pi (kg/m3) | μi (cp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 97.1% | 1253.4 | 780 |
| 2 | 95.2% | 1248.4 | 543 |
| 3 | 94.2% | 1245.8 | 454 |
| 4 | 92.4% | 1241.0 | 331 |
| 5 | 90.0% | 1234.7 | 219 |
| 6 | 87.5% | 1228.2 | 164 |
| 7 | 85.0% | 1221.6 | 109 |
| 8 | 75.8% | 1197.4 | 40 |
| 9 | 69.3% | 1180.3 | 21 |
| 10 | 0% (Water) | 998.2 | 1 |
| Grid Number | 1,088,856 | 1,495,643 | 1,620,869 | 1,883,255 | 2,125,254 | 2,534,559 | 2,611,752 | 2,664,602 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H (m) | 29.54 | 26.90 | 26.37 | 26.43 | 29.26 | 25.40 | 26.06 | 26.06 |
| error | 11.24% | 1.329% | −0.702% | −0.456% | 10.19% | −4.344% | −1.852% | −1.854% |
| Parameters | Testing Condition |
|---|---|
| Speed (Figure 4) | 1760, 2000, 2240, 2480, 2720, 2900 rpm |
| Flow rates | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75, 2, 2.25, 2.5, 2.75 m3/h |
| Viscosity | 1, 40, 164, 331, 543 cP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, W.; Zeng, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, H. A Numerical Study on Labyrinth Screw Pump (LSP) Performance under Viscous Fluid Flow. Energies 2023, 16, 5997. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165997
Ke W, Zeng H, Wang Z, Yu H, Liu Y, Zheng D, Zhu J, Zhu H. A Numerical Study on Labyrinth Screw Pump (LSP) Performance under Viscous Fluid Flow. Energies. 2023; 16(16):5997. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165997
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Wenqi, Hao Zeng, Zhuoyu Wang, Hong Yu, Yaxin Liu, Danzhu Zheng, Jianjun Zhu, and Haiwen Zhu. 2023. "A Numerical Study on Labyrinth Screw Pump (LSP) Performance under Viscous Fluid Flow" Energies 16, no. 16: 5997. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165997
APA StyleKe, W., Zeng, H., Wang, Z., Yu, H., Liu, Y., Zheng, D., Zhu, J., & Zhu, H. (2023). A Numerical Study on Labyrinth Screw Pump (LSP) Performance under Viscous Fluid Flow. Energies, 16(16), 5997. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165997








