Optimal Tuning of Fractional Order Sliding Mode Controller for PMSM Speed Using Neural Network with Reinforcement Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- An RLNNA is proposed to obtain the optimal parameters, which is based on the FOSMC method for the speed controller of the PMSM.
- (2)
- An RLNNA-FOSMC is proposed in this paper. RLNNA can drive FOSMC to function with disturbances and reduce chattering without sacrificing robustness.
- (3)
- The effectiveness of the proposed control strategy is proved by the comparative simulations.
2. Analysis and Design of PMSM and FOSMC
2.1. Fundamentals of PMSM for Speed Control Application
2.2. Design of FOSMC
2.3. Stability Analysis Using FOSMC
3. Neural Network Algorithm with Reinforcement Learning (RLNNA)
3.1. Neural Network Algorithm (NNA)
3.1.1. Generating Initial Population
3.1.2. Update Weight Matrix
3.1.3. Bias Operator
3.1.4. Transfer Operator
3.2. Neural Network Algorithm with Reinforcement Learning (RLNNA)
3.2.1. Modification Factor with RL
3.2.2. Transfer Operator with Historical Population
3.2.3. Designed Feed-Back Operator
3.3. Performance Evaluation
4. Numerical Simulation
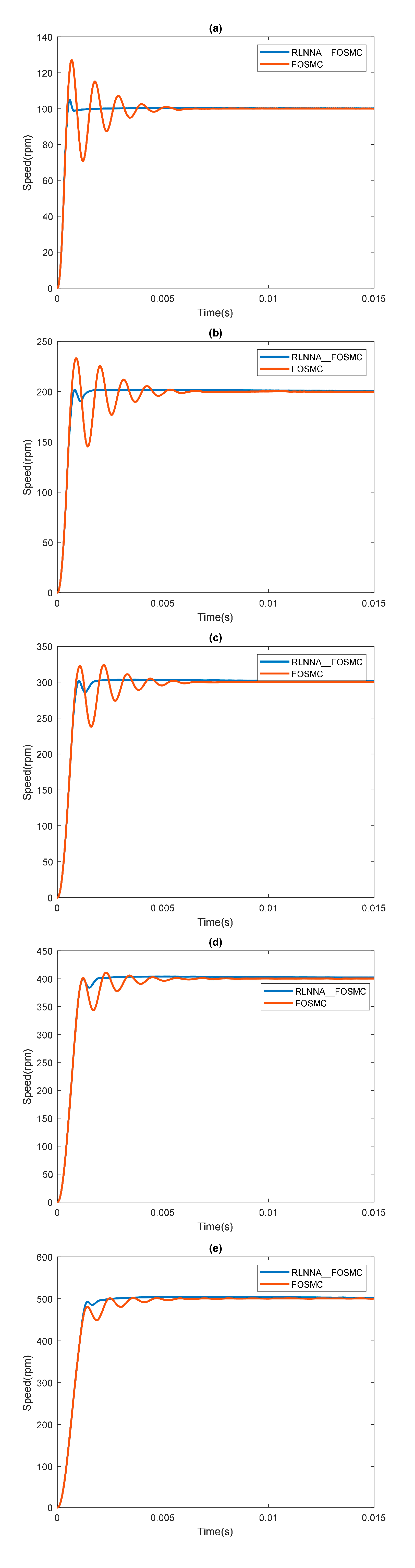
4.1. Case 1: One Step Speed Reference
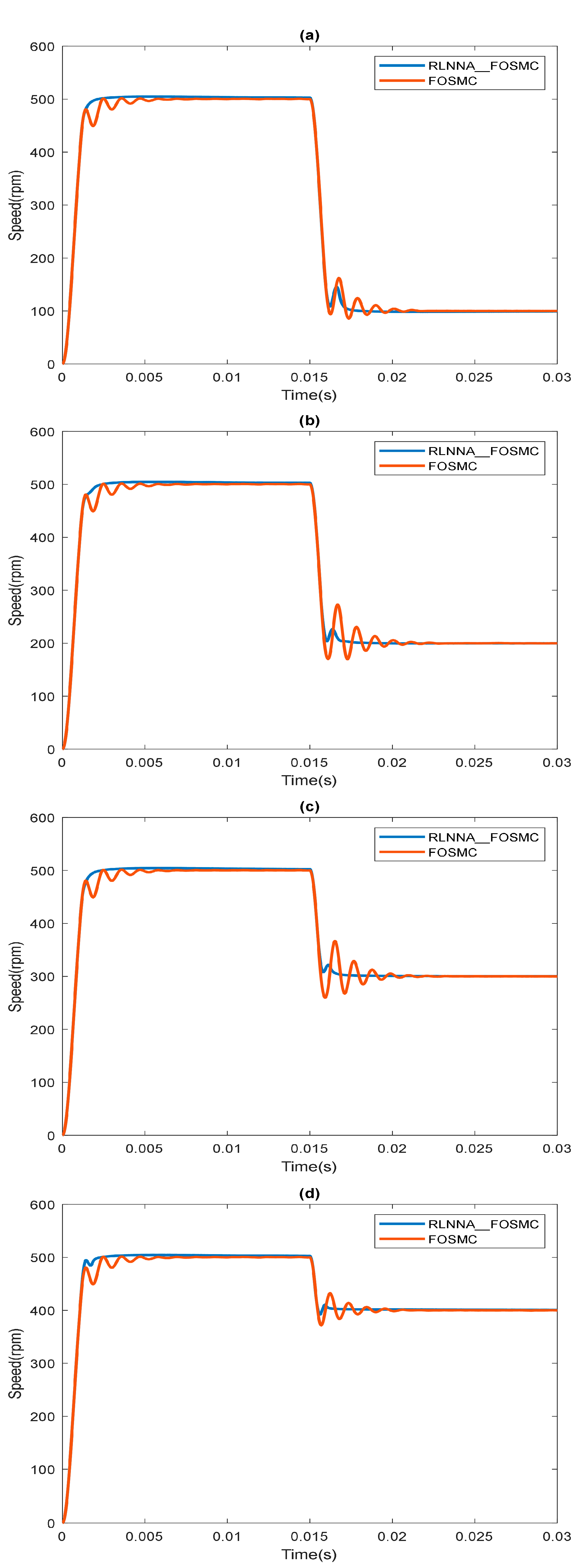
4.2. Case 2: Speed Drop
4.3. Case 3: Different Steps Reference
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Mu, C. Novel Composite Sliding Mode Control for PMSM Drive System Based on Disturbance Observer. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 0612905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, T.; Abdelkader, D.; Said, B.; Padmanaban, S.; Iqbal, A. Extended Kalman filter based sliding mode control of parallel-connected two five-phase PMSM drive system. Electronics 2018, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahraoui, Y.; Zaihidee, F.M.; Kermadi, M.; Mekhilef, S.; Mubin, M.; Tang, J.R.; Zaihidee, E.M. Fractional Order Sliding Mode Controller Based on Supervised Machine Learning Techniques for Speed Control of PMSM. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.T.; Pi, Y.G.; Luo, Y. Fractional order sliding-mode control based on parameters auto-tuning for velocity control of permanent magnet synchronous motor. ISA Trans. 2012, 51, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, S.; Lan, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, X. Continuous terminal sliding mode control with extended state observer for PMSM speed regulation system. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2017, 39, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaihidee, F.M.; Mekhilef, S.; Mubin, M. Robust speed control of pmsm using sliding mode control (smc)—A review. Energies 2019, 12, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, B.; Mao, D. Robust sliding mode control of PMSM based on a rapid nonlinear tracking differentiator and disturbance observer. Sensors 2018, 18, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saihi, L.; Boutera, A. Robust Sensorless Sliding Mode Control of PMSM with MRAS and Luenberger Extended Observer. In Proceedings of the 2016 8th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control ICMIC 2016, Algiers, Algeria, 15–17 November 2016; pp. 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Li, Y.; Jia, C. A novel direct torque control method based on asymmetric boundary layer sliding mode control for PMSM. Energies 2018, 11, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, K.; Zhang, Q. Robust current control-based generalized predictive control with sliding mode disturbance compensation for PMSM drives. ISA Trans. 2017, 71, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, W.; Mu, C.; Liu, Y. Improved deadbeat predictive current control combined sliding mode strategy for PMSM drive system. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, L. A Novel Discrete Compound Integral Terminal Sliding Mode Control with Disturbance Compensation for PMSM Speed System. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 27, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, L.; Ji, W. Improved Non-Singular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control with Disturbance Observer for PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 2753–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, G.; Lv, X. Model-Free Control Using Improved Smoothing Extended State Observer and Super-Twisting Nonlinear Sliding Mode Control for PMSM Drives. Energies 2021, 14, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Ni, S.; Xu, D.; Zhang, L.; Yan, X.-G. Disturbance-observer based prescribed-performance fuzzy sliding mode control for PMSM in electric vehicles. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 104, 104361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, B.; Wang, K.; Liang, J. Antidisturbance Sliding Mode-Based Deadbeat Direct Torque Control for PMSM Speed Regulation System. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 2705–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Ding, S.; Yu, X. Composite Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Control Design for PMSM Speed Regulation Problem Based on a Novel Disturbance Observer. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2591–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Yu, J.; Zhao, L. Combined Speed and Current Terminal Sliding Mode Control with Nonlinear Disturbance Observer for PMSM Drive. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 29594–29601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaihidee, F.M.; Mekhilef, S.; Mubin, M. Application of Fractional Order Sliding Mode Control for Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 101765–101774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, P.; Rajan, R.; Shanmugam, L.; Joo, Y.H. Adaptive fractional fuzzy integral sliding mode control for PMSM model. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 27, 1674–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Laghrouche, S.; N’Diaye, A.; Cirrincione, M. Hermite neural network-based second-order sliding-mode control of synchronous reluctance motor drive systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2021, 358, 400–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Li, S. Disturbance-Observer-Based Control and Related Methods—An Overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, W.H.; Li, S.; Guo, L.; Yan, Y. Disturbance/Uncertainty Estimation and Attenuation Techniques in PMSM Drives—A Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3273–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, H. Tuning of digital PID controllers using particle swarm optimization algorithm for a CAN-Based DC motor subject to stochastic delays. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5637–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Learning for Parameters Extraction of Photovoltaic Models. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, D.F.; Ragsdale, C.T.; Major, R.L. Combining a neural network with a genetic algorithm for process parameter optimization. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2000, 13, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadollah, A.; Sayyaadi, H.; Yadav, A. A dynamic metaheuristic optimization model inspired by biological nervous systems: Neural network algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2018, 71, 747–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arwa, E.O.; Folly, K.A. Reinforcement Learning Techniques for Optimal Power Control in Grid-Connected Microgrids: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 208992–209007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Hu, Z.; Gu, W.; Jiang, M.; Chen, M.; Hong, Q.; Booth, C. Combined heat and power system intelligent economic dispatch: A deep reinforcement learning approach. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 120, 106016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Viscous friction coefficient, | |
| The proportional coefficient for the current loop | 20 |
| The integral coefficient for the current loop | 100 |
| Speed (rpm) | Controller | ISE | IAE | ITAE | ITSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 2,274,941.12 | 23,737.00 | 87.92 | 316.72 |
| FOSMC [19] | 2,840,320.06 | 31,315.37 | 88.44 | 1027.89 | |
| 200 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 13,041,197.81 | 58,726.82 | 223.92 | 2795.94 |
| FOSMC [19] | 14,586,841.09 | 94,586.46 | 408.46 | 5163.30 | |
| 300 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 36,613,213.68 | 110,965.07 | 253.16 | 9876.56 |
| FOSMC [19] | 38,293,080.76 | 181,028.59 | 782.81 | 12,271.44 | |
| 400 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 76,973,812 | 193,110.9 | 312.10 | 24,084.45 |
| FOSMC [19] | 78,186,689.48 | 287,608.40 | 1076.129 | 25,081.94 | |
| 500 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 138,620,950.28 | 307,239.41 | 421.46547 | 49,550.83 |
| FOSMC [19] | 139,862,958.9 | 414,626.431 | 1317.05 | 50,222.20507 |
| Steep | Controller | ISE | IAE | ITAE | ITSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed (rmp) | Speed (rpm) | |||||
| 500 | 100 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 108 | 65,720.72574 | 5179.63287 | 106 |
| FOSMC [19] | 108 | 126,220.62648 | 5208.3477 | 106 | ||
| 200 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 108 | 161,145.4384 | 3335.614 | 105 | |
| FOSMC [19] | 108 | 232,818.2385 | 4122.318 | 105 | ||
| 300 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 108 | 228,359.0295 | 2282.5614 | 105 | |
| FOSMC [19] | 108 | 319,952.9358 | 2973.7440 | 105 | ||
| 400 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 108 | 280,244.0616 | 1459.20079 | 104 | |
| FOSMC [19] | 108 | 383,903.5256 | 1518.19764 | 104 | ||
| Steep | Controller | ISE | IAE | ITAE | ITSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed (rpm) | Speed (rpm) | Speed (rpm) | |||||
| 500 | 100 | 200 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 108 | 105 | 103 | 106 |
| FOSMC [19] | 108 | 105 | 103 | 106 | |||
| 200 | 300 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 108 | 105 | 103 | 105 | |
| FOSMC [19] | 108 | 105 | 103 | 105 | |||
| 300 | 400 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 108 | 105 | 103 | 105 | |
| FOSMC [19] | 108 | 105 | 103 | 105 | |||
| 400 | 500 | RLNNA_FOSMC | 108 | 105 | 103 | 104 | |
| FOSMC [19] | 108 | 105 | 103 | 104 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zahraoui, Y.; Zaihidee, F.M.; Kermadi, M.; Mekhilef, S.; Alhamrouni, I.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Stojcevski, A. Optimal Tuning of Fractional Order Sliding Mode Controller for PMSM Speed Using Neural Network with Reinforcement Learning. Energies 2023, 16, 4353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114353
Zahraoui Y, Zaihidee FM, Kermadi M, Mekhilef S, Alhamrouni I, Seyedmahmoudian M, Stojcevski A. Optimal Tuning of Fractional Order Sliding Mode Controller for PMSM Speed Using Neural Network with Reinforcement Learning. Energies. 2023; 16(11):4353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114353
Chicago/Turabian StyleZahraoui, Younes, Fardila M. Zaihidee, Mostefa Kermadi, Saad Mekhilef, Ibrahim Alhamrouni, Mehdi Seyedmahmoudian, and Alex Stojcevski. 2023. "Optimal Tuning of Fractional Order Sliding Mode Controller for PMSM Speed Using Neural Network with Reinforcement Learning" Energies 16, no. 11: 4353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114353
APA StyleZahraoui, Y., Zaihidee, F. M., Kermadi, M., Mekhilef, S., Alhamrouni, I., Seyedmahmoudian, M., & Stojcevski, A. (2023). Optimal Tuning of Fractional Order Sliding Mode Controller for PMSM Speed Using Neural Network with Reinforcement Learning. Energies, 16(11), 4353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114353











