Effects of Colloid Milling and Hot-Water Pretreatment on Physical Properties and Enzymatic Digestibility of Oak Wood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Colloid Milling (CM) Pretreatment
2.3. Hot Water (HW) Pretreatment
2.4. Enzymatic Digestibility Test
2.5. Composition Analysis of Untreated and Treated Oak Wood
2.6. Reaction Severity
2.7. Gel Filtration Chromatography (GFC) Analysis
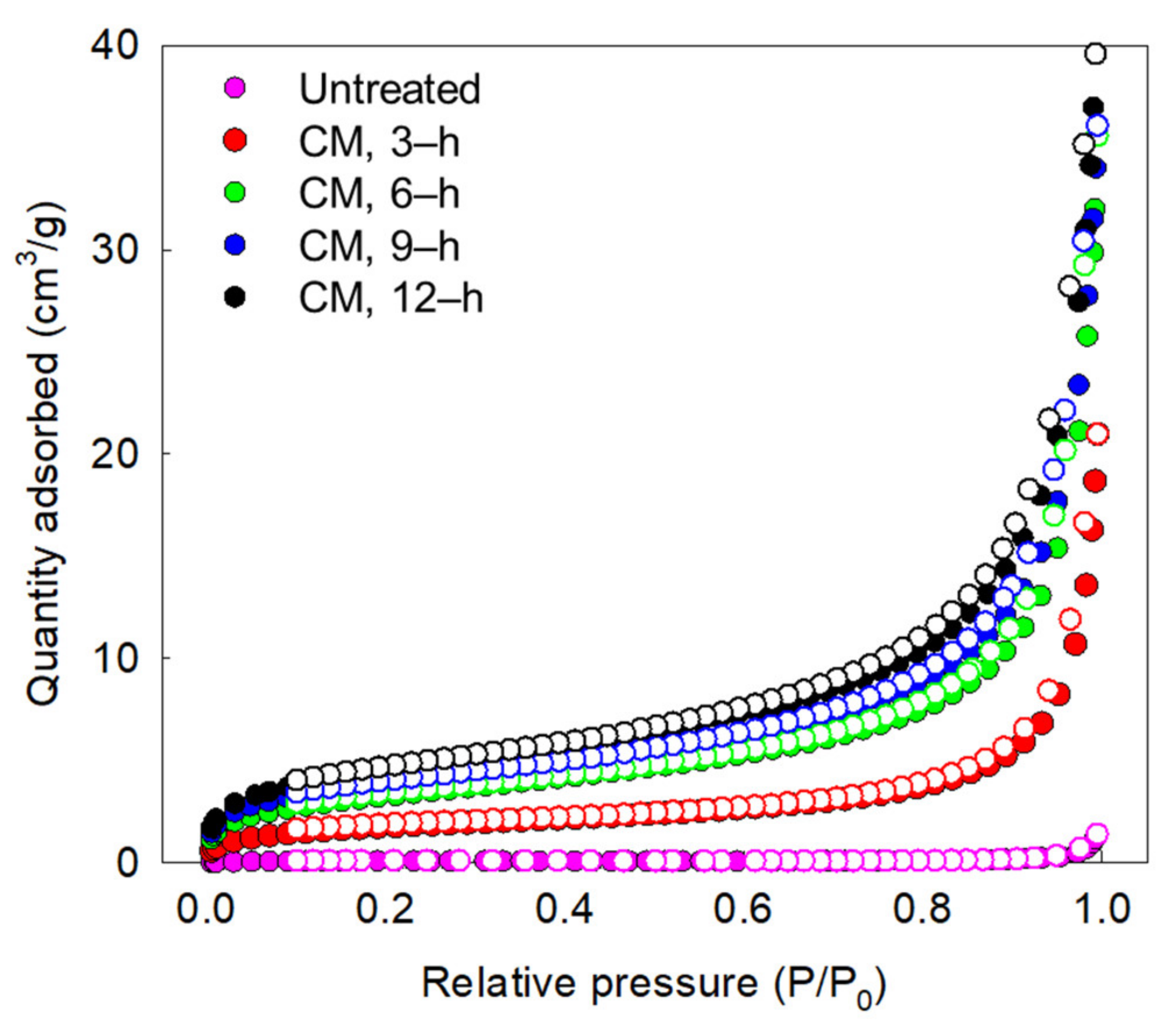
2.8. Physical Property Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
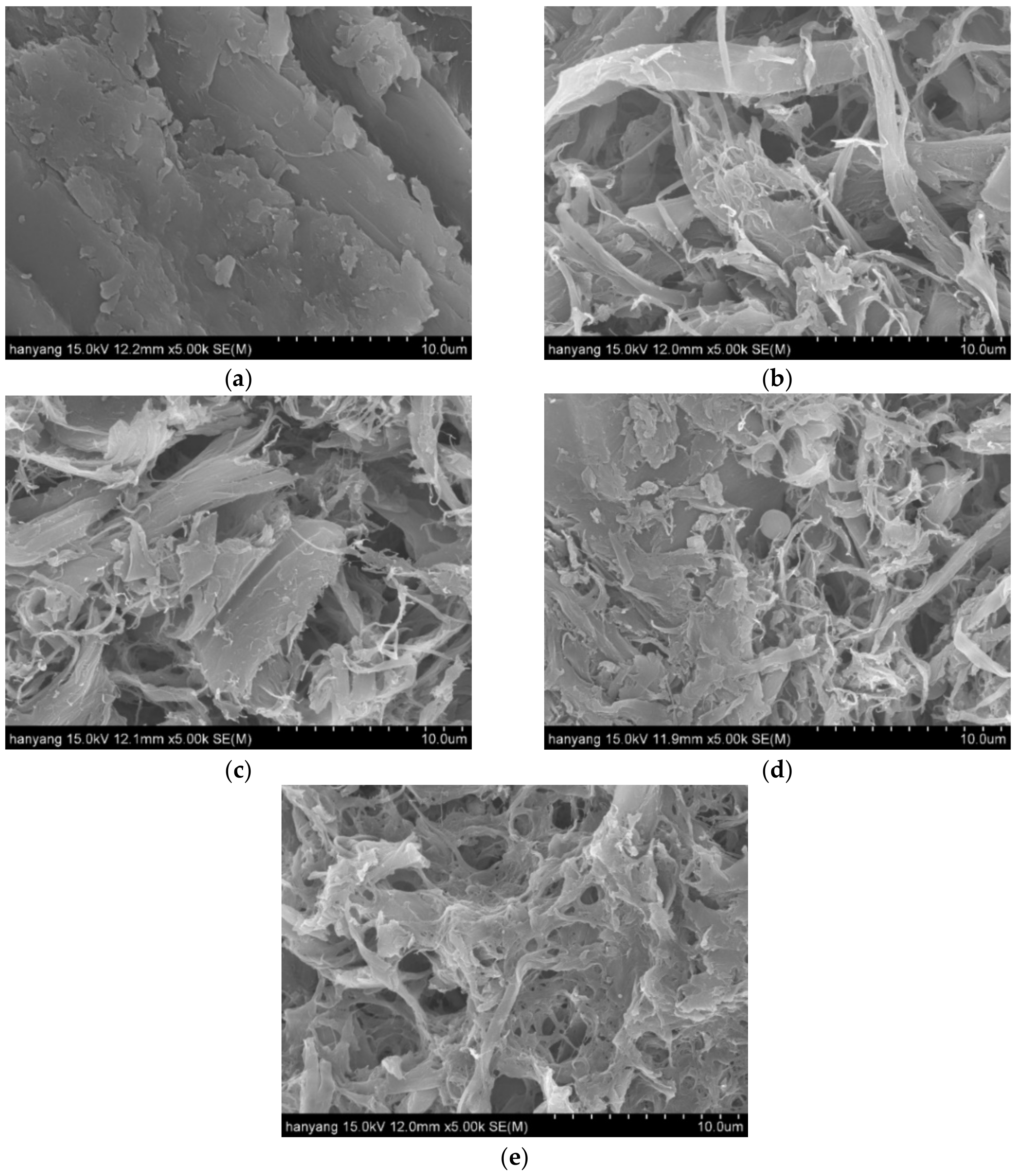
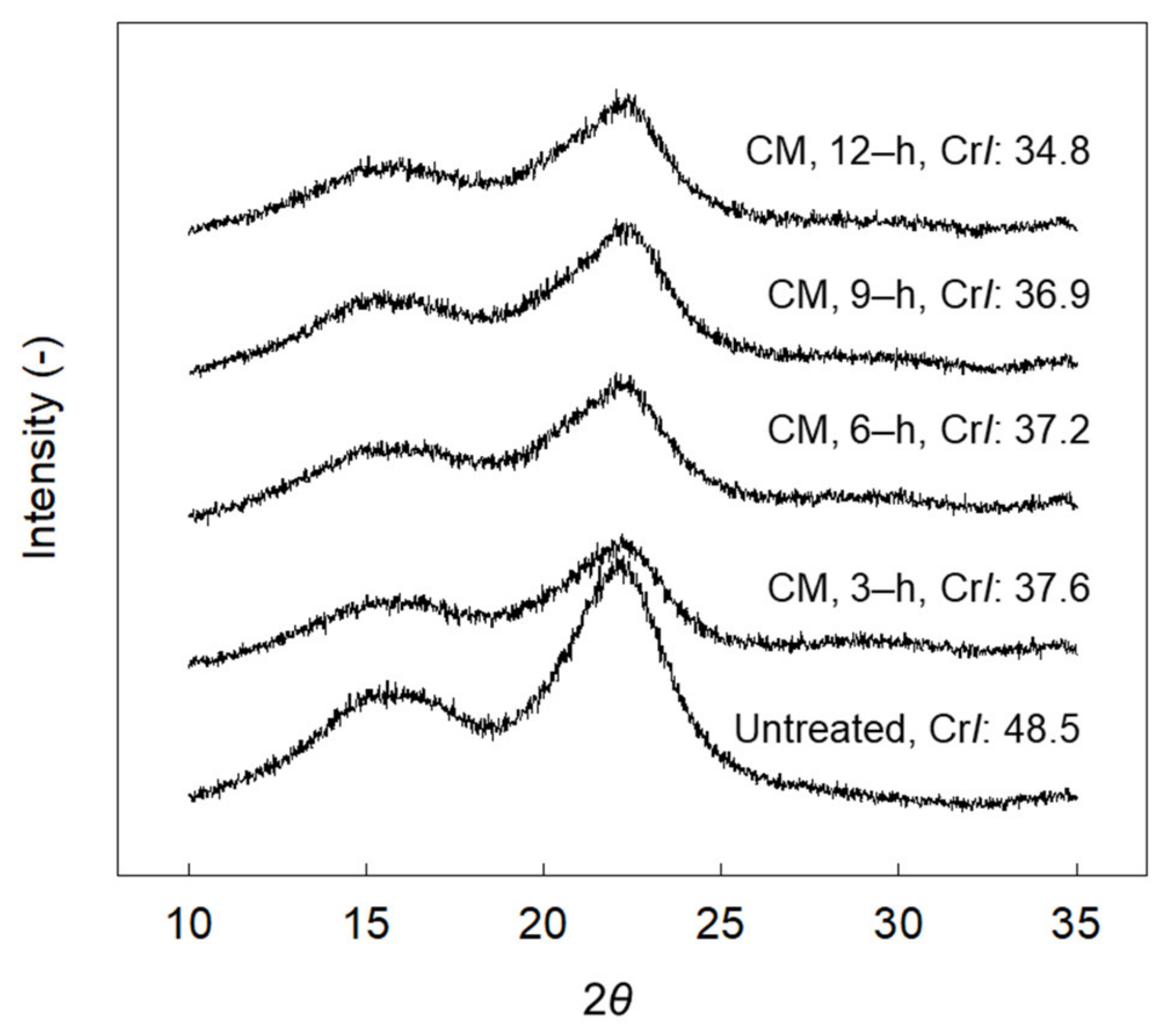
3.1. Colloid Milling (CM) Treatment: First-Step
3.2. Hot Water (HW) Treatment: Second-Step
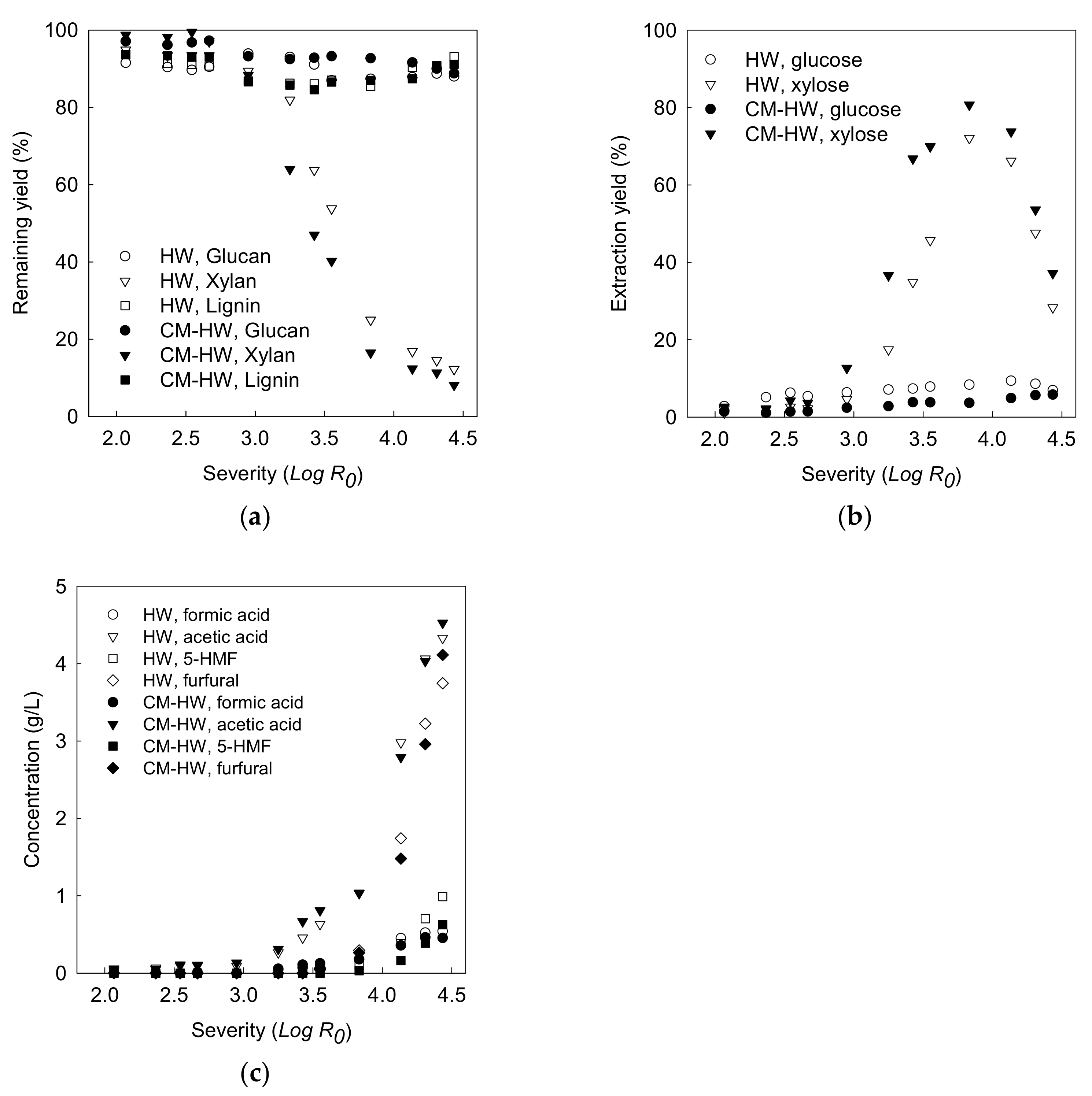
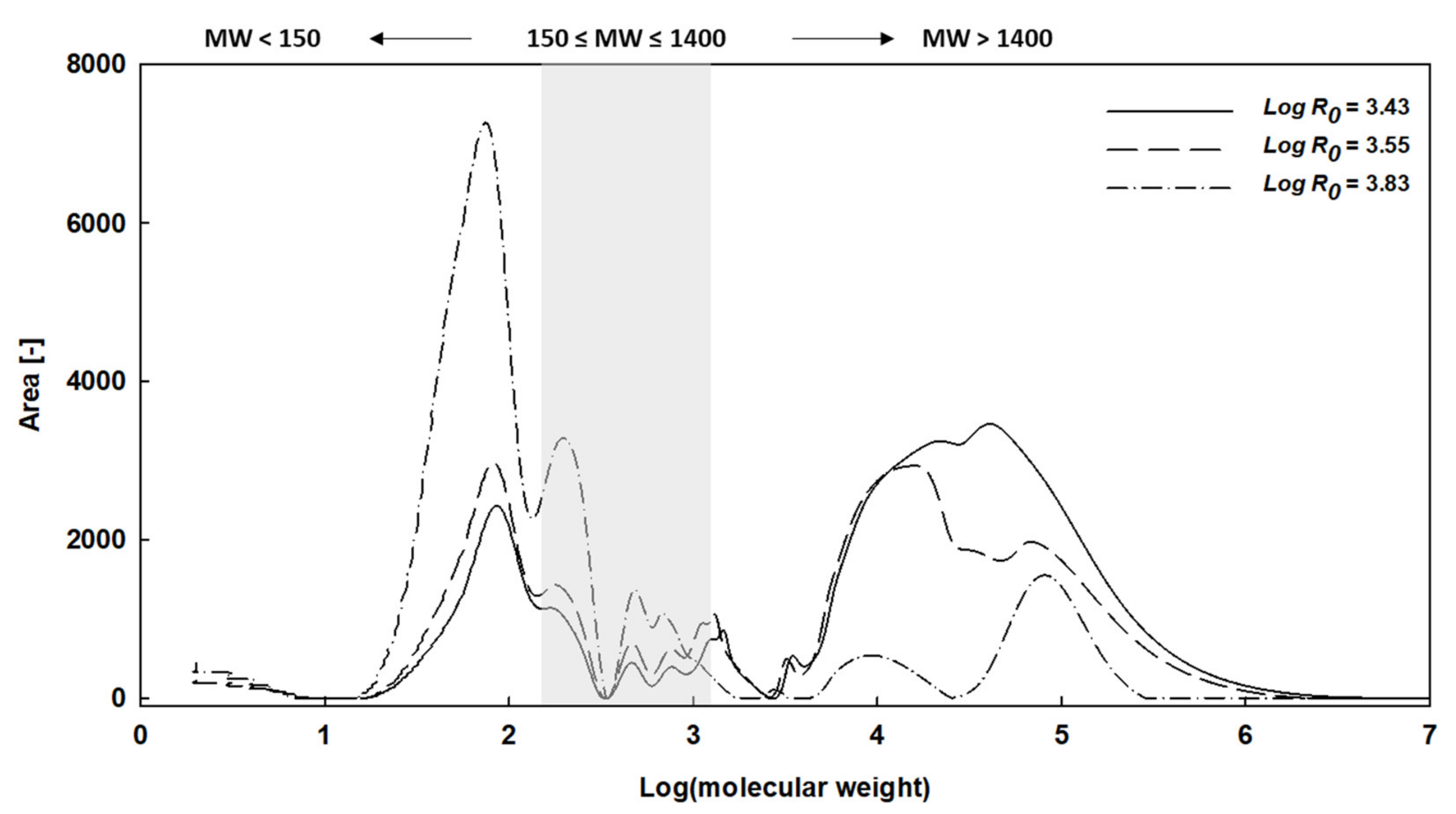
3.2.1. Effect of Reaction Severity on Xylan Recovery
3.2.2. Monosaccharide and Oligosaccharide in Liquid Hydrolysate
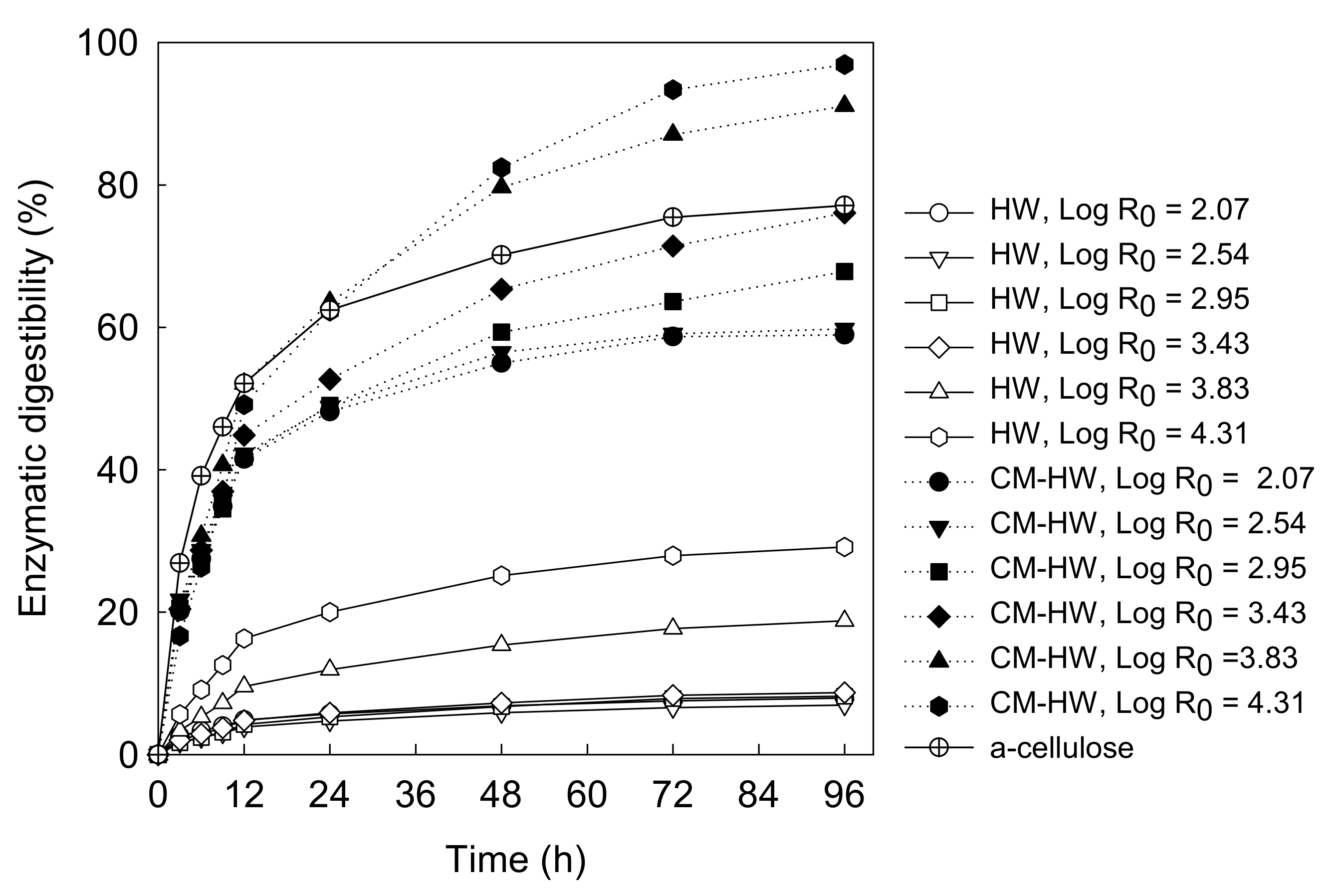
3.2.3. Enzymatic Digestibility Test of Untreated and Treated Oak Wood
3.2.4. Overall Mass Balance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yongzhuang, L.; Chen, W.; Xia, Q.; Guo, B.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Yu, H. Efficient cleavage of lignin–carbohydrate complexes and ultrafast extraction of lignin oligomers from wood biomass by microwave-assisted treatment with deep eutectic solvent. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, F.; Ragauskas, A. Pretreatment and lignocellulosic chemistry. Bioenergy Res. 2012, 5, 1043–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.P.; Kim, C.S. Lignin depolymerization and conversion: A review of thermochemical methods. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Chang, X.; Chen, D.; Xue, Y.; Liu, P.; Lin, H.; Han, S. A review on the pretreatment of lignocellulose for high-value chemicals. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 160, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabed, H.; Sahu, J.N.; Boyce, A.N.; Faruq, G. Fuel ethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass: An overview on feedstocks and technological approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 66, 751–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, T.H. Overview of technical barriers and implementation of cellulosic ethanol in the US. Energy 2014, 66, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, D.P.; Singla, A.; Negi, S. An overview of key pretreatment processes for biological conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.K.; Sharma, S. Recent updates on different methods of pretreatment of lignocellulosic feedstocks: A review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2017, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalheiro, F.; Duarte, L.C.; Gírio, F.; Moniz, P. Hydrothermal/liquid hot water pretreatment (autohydrolysis): A multipurpose process for biomass upgrading. In Biomass Fractionation Technologies for a Lignocellulosic Feedstock Based Biorefinery; Mussatto, S.I., Ed.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 315–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Woody biomass: Niche position as a source of sustainable renewable chemicals and energy and kinetics of hot-water extraction/hydrolysis. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalinski, T.; Ingram, T.; Brunner, G. Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass in water under elevated temperatures and pressures. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2008, 47, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Bhardwaj, N.; Agrawal, K.; Chaturvedi, V.; Verma, P. Current perspective on pretreatment technologies using lignocellulosic biomass: An emerging biorefinery concept. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 199, 106244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhuang, X.; Lv, S.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Tan, X. Liquid hot water pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse and its comparison with chemical pretreatment methods for the sugar recovery and structural changes. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Zhuang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, W.; Qi, W.; Wang, Q.; Tan, X. Step-change flow rate liquid hot water pretreatment of sweet sorghum bagasse for enhancement of total sugars recovery. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selig, M.J.; Viamajala, S.; Decker, S.R.; Tucker, M.P.; Himmel, M.E.; Vinzant, T.B. Deposition of lignin droplets produced during dilute acid pretreatment of maize stems retards enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hendrickson, R.; Mosier, N.S.; Ladisch, M.R. Liquid hot water pretreatment of cellulosic biomass. In Biofuels; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatma, S.; Hameed, A.; Noman, M.; Ahmed, T.; Shahid, M.; Tariq, M.; Tabassum, R. Lignocellulosic biomass: A sustainable bioenergy source for the future. Protein Pept. Lett. 2018, 25, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltanian, S.; Aghbashlo, M.; Almasi, F.; Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha, H.; Nizami, A.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Tabatabaei, M. A critical review of the effects of pretreatment methods on the exergetic aspects of lignocellulosic biofuels. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 212, 112792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, V.K.; Nguyen, D.D.; Dharmaraja, J.; Shobana, S.; Banu, J.R.; Saratale, R.G.; Kumar, G. A review on lignin structure, pretreatments, fermentation reactions and biorefinery potential. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hideno, A.; Inoue, H.; Tsukahara, K.; Fujimoto, S.; Minowa, T.; Inoue, S.; Sawayama, S. Wet disk milling pretreatment without sulfuric acid for enzymatic hydrolysis of rice straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2706–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, M.R.; Norrrahim, M.N.F.; Hirata, S.; Hassan, M.A. Hydrothermal and wet disk milling pretreatment for high conversion of biosugars from oil palm mesocarp fiber. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 181, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, Q.; Xiong, C.; Kuga, S.; Matsumoto, Y. Facile dissolution of wood pulp in aqueous NaOH/urea solution by ball milling pretreatment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 118, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, F. Preparation and characterization of starch nanocrystals combining ball milling with acid hydrolysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binod, P.; Satyanagalakshmi, K.; Sindhu, R.; Janu, K.U.; Sukumaran, R.K.; Pandey, A. Short duration microwave assisted pretreatment enhances the enzymatic saccharification and fermentable sugar yield from sugarcane bagasse. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigual, V.; Ovejero-Pérez, A.; Rivas, S.; Domínguez, J.C.; Alonso, M.V.; Oliet, M.; Rodriguez, F. Protic, aprotic, and choline-derived ionic liquids: Toward enhancing the accessibility of hardwood and softwood. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 8, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluiter, A.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Extractives in Biomass; NREL/TP-510-42619; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass; NREL/TP-510-42618; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sluiter, A.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Ash in Biomass; NREL/TP-510-42622; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Selig, M.; Weiss, N.; Ji, Y. Enzymatic Saccharification of Lignocellulosic Biomass; NREL/TP-510-42629; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D. Determination of Sugars, Byproducts, and Degradation Products in Liquid Fraction Process Samples; NREL/TP-510-42623; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Overend, R.P.; Chormet, E. Fractionation of lignocellulosics by steam-aqueous pretreatments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1987, 321, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tan, H. Study on crystal structures of enzyme-hydrolyzed cellulosic materials by X-ray diffraction. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2005, 36, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.; Bansal, P.; Lee, J.H.; Realff, M.J.; Bommarius, A.S. Cellulose crystallinity–a key predictor of the enzymatic hydrolysis rate. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 1571–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooshima, H.; Sakata, M.; Harano, Y. Adsorption of cellulase from Trichoderma viride on cellulose. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1983, 25, 3103–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Um, B.H.; Park, S.C. Effect of pretreatment reagent and hydrogen peroxide on enzymatic hydrolysis of oak in percolation process. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2001, 91, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayoubi, R.; Mehmood, N.; Husson, E.; Kouzayha, A.; Tabcheh, M.; Chaveriat, L.; Gosselin, I. Low temperature ionic liquid pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass to enhance bioethanol yield. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, M.; Karimi, K.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Pretreatment of spruce and oak by N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) for efficient conversion of their cellulose to ethanol. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4914–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reaction Conditions | Log R0 | |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | |
| 120 | 30 | 2.07 |
| 60 | 2.37 | |
| 90 | 2.54 | |
| 120 | 2.67 | |
| 150 | 30 | 2.95 |
| 60 | 3.25 | |
| 90 | 3.43 | |
| 120 | 3.55 | |
| 180 | 30 | 3.83 |
| 60 | 4.13 | |
| 90 | 4.31 | |
| 120 | 4.43 | |
| Samples | Milling Time | Surface Area | Pore Size | Pore Volume |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m2/g | nm | ×10−3cm3/g | ||
| Untreated | - | 0.3904 | 65.2820 | 2.0550 |
| CM-treated oak wood | 3 h | 6.5276 | 28.8735 | 30.9220 |
| 6 h | 11.9558 | 22.8739 | 52.5630 | |
| 9 h | 14.1727 | 20.3799 | 55.8180 | |
| 12 h | 16.4635 | 18.6886 | 57.8000 |
| Pretreatment | Enzymatic Hydrolysis | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method ( ) | Conditions ( ) | Conditions ( ) | Yield (%) | |
| Hot water | 170 °C, 60 min | 60 FPU 4, 72 h 5 | 76.5 | [35] |
| H2SO4 | 0.2 wt.%, 170 °C, 15 min | 60 FPU 4, 72 h 5 | 93.8 | [35] |
| Ammonia | 20 wt.%, 170 °C, 60 min | 60 FPU 4, 72 h 5 | 66.1 | [35] |
| H2O2 | 3.2 wt.%, 170 °C, 60 min | 60 FPU 4, 72 h 5 | 76.5 | [35] |
| [Emim][OAc] 1 | 98.0 wt.%, 45 °C, 40 min | 80 h (no information for enzyme loading) | 59.3 | [36] |
| [NMMO] 2 | 85.0 wt.%, 130 °C, 120 min | 15 FPU 4, 24 h 5 | 72.2 | [37] |
| CM-HW 3 | CM: 12 h, HW: 170 °C, 120 min | 15 FPU 4, 96 h 5 | 96.9 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.H.; Park, S.H.; Le, T.D.T.; Kim, T.H.; Oh, K.K. Effects of Colloid Milling and Hot-Water Pretreatment on Physical Properties and Enzymatic Digestibility of Oak Wood. Energies 2022, 15, 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15062210
Kim TH, Park SH, Le TDT, Kim TH, Oh KK. Effects of Colloid Milling and Hot-Water Pretreatment on Physical Properties and Enzymatic Digestibility of Oak Wood. Energies. 2022; 15(6):2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15062210
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tae Hoon, Seung Hyeon Park, Tin Diep Trung Le, Tae Hyun Kim, and Kyeong Keun Oh. 2022. "Effects of Colloid Milling and Hot-Water Pretreatment on Physical Properties and Enzymatic Digestibility of Oak Wood" Energies 15, no. 6: 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15062210
APA StyleKim, T. H., Park, S. H., Le, T. D. T., Kim, T. H., & Oh, K. K. (2022). Effects of Colloid Milling and Hot-Water Pretreatment on Physical Properties and Enzymatic Digestibility of Oak Wood. Energies, 15(6), 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15062210







