Hourly Electricity Price Prediction for Electricity Market with High Proportion of Wind and Solar Power
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A time-sharing electricity price forecasting model is proposed in this paper based on SSA-DELM, considering the impact of wind and solar power on the price of electricity in the form of wind–load and solar–load ratios (wind–load ratio refers to the ratio of wind power to total load, and the same with solar power for solar–load ratio).
- In the scenario with a high coefficient of variation caused by the high frequency of low electricity prices, SSA-DELM has been shown to greatly improve the forecasting effect of the time-sharing electricity price.
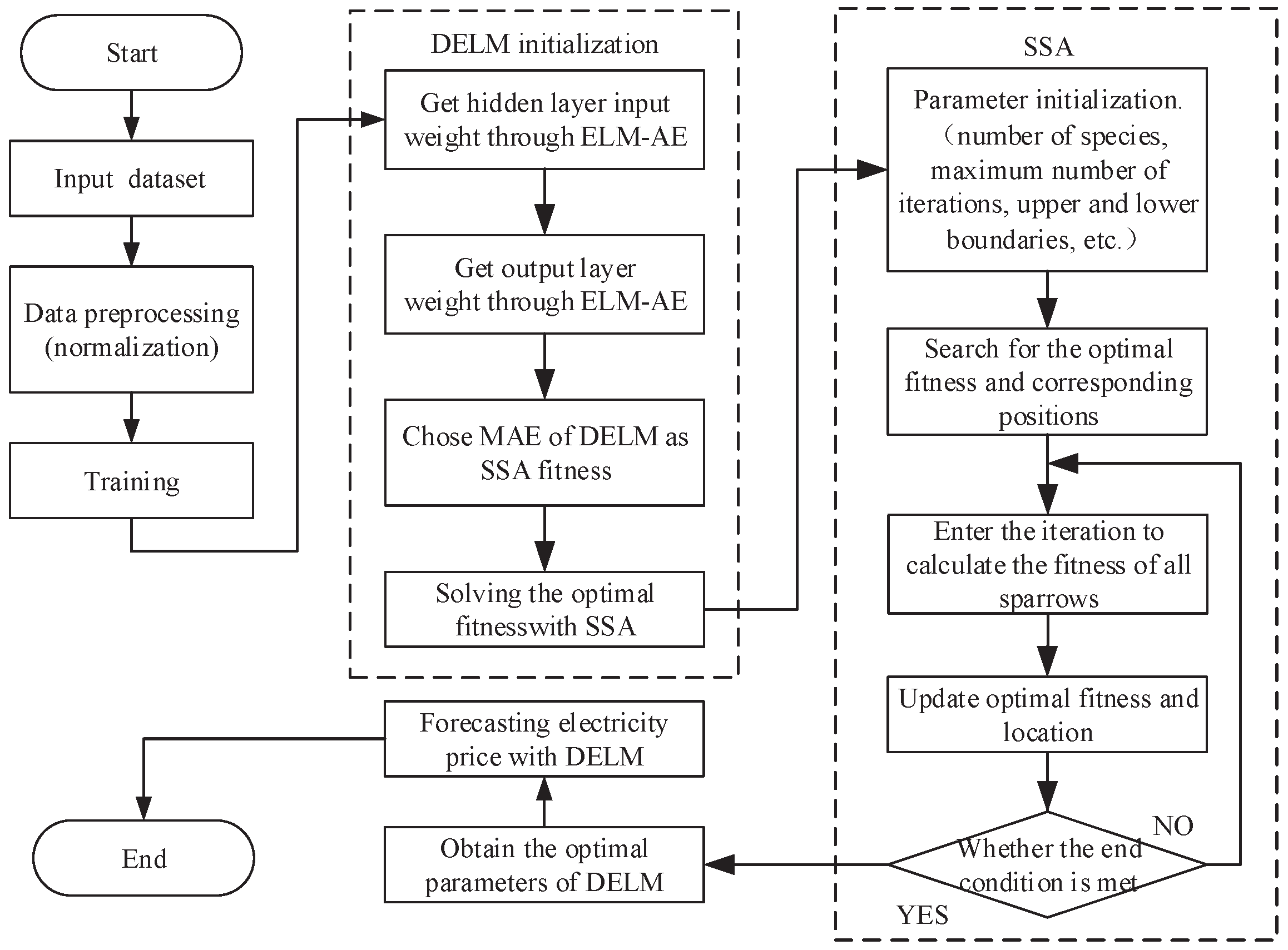
2. The Developed SSA-DELM
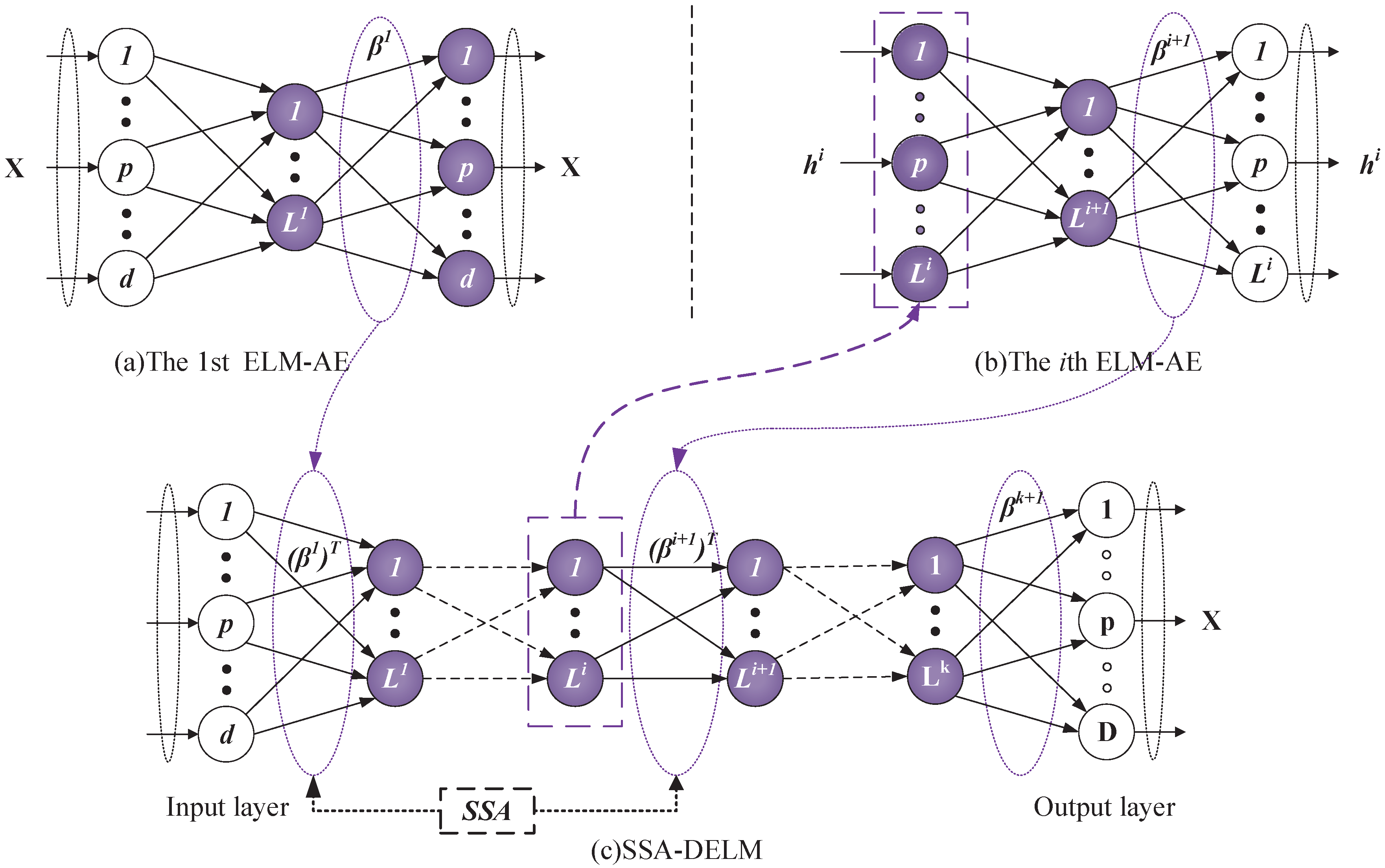
2.1. The Structure and Mathematical Expression of DELM
2.2. Mathematical Model of SSA Optimization Algorithm
- 1.
- Producers usually have a higher level of energy reserve, corresponding to higher fitness, to undertake the task of expanding the search scope and guiding the population to search and forage.
- 2.
- In order to obtain better fitness, the searchers follow the discoverers to look for food. At the same time, in order to improve their predation rate, some searchers will monitor the discoverers to compete for food.
- 3.
- When the whole population is in danger of being preyed on, the producer needs to guide all searchers into the safe area.
- 4.
- During the whole process, any sparrow can become a producer if it finds a better food source, and the proportion of producers in the sparrow population remains constant.
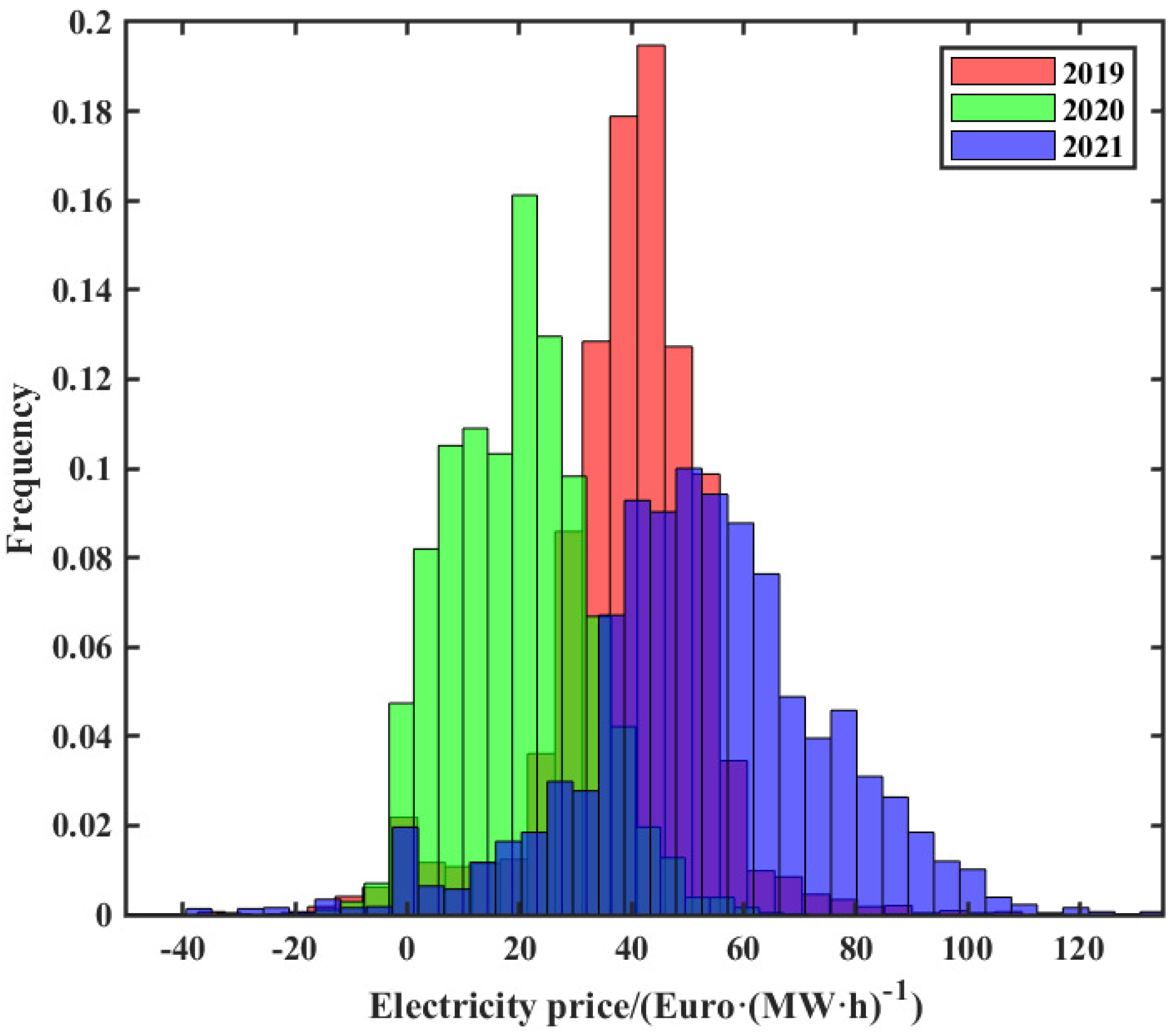
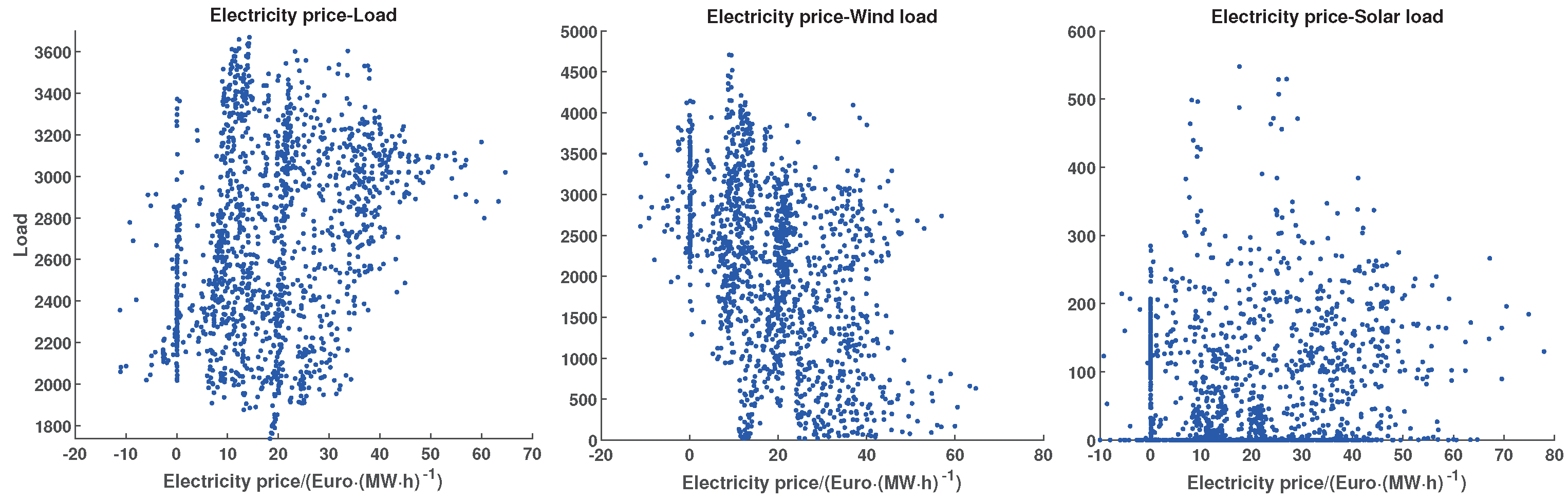
3. Analysis of Electricity Price
4. Electricity Price Model Design and Experiment Analysis
4.1. Design of Electricity Price Model
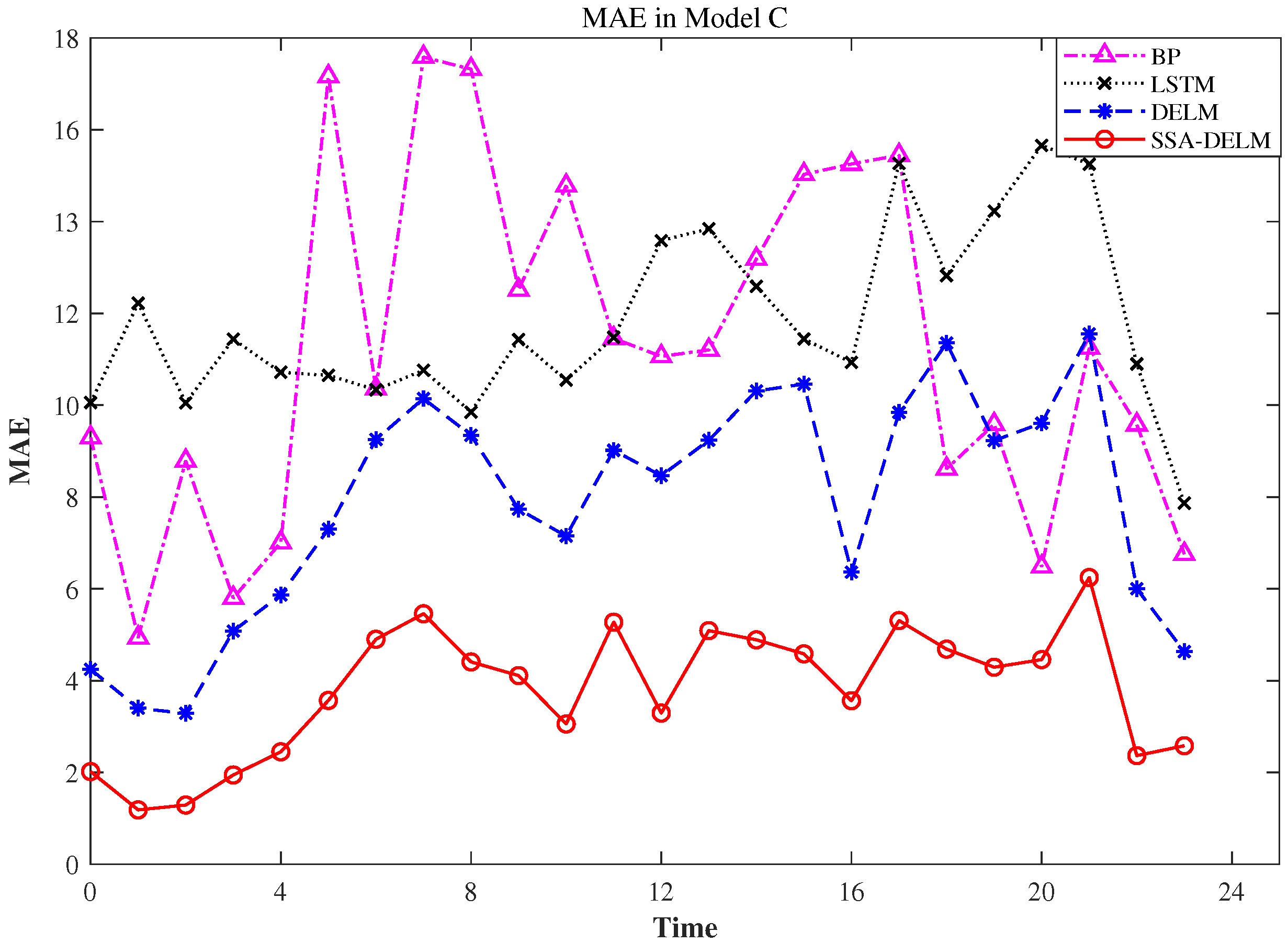
4.2. Analysis of the Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bunn, D.W. Forecasting loads and prices in competitive power markets. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Pandey, A.S.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Subramaniam, U.; Mekhilef, S.; Mihet-Popa, L. A Novel Hybrid Feature Selection Method for Day-Ahead Electricity Price Forecasting. Energies 2021, 14, 8455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, R.E. Modeling and forecasting electric daily peak loads using abductive networks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2006, 28, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.; Senjyu, T.; Urasaki, N.; Funabashi, T. A neural network based several-hour-ahead electric load forecasting using similar days approach. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2006, 28, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, R.; Shi, H.; Li, F.R. Deep learning for day-ahead electricity price forecasting. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziel, F.; Steinert, R. Probabilistic mid- and long-term electricity price forecasting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conejo, A.J.; Plazas, M.A.; Espinola, R.; Molina, A.B. Day-Ahead Electricity Price Forecasting Using the Wavelet Transform and ARIMA Models. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2005, 20, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbah, H.; El-hawary, M. Hourly Electricity Price Forecasting for the Next Month Using Multilayer Neural Network. IEEE Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2016, 39, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; He, D.; Harley, R.; Habetler, T.; Qu, G.N. A random forest method for real-time price forecasting in New York electricity market. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE PES General Meeting, Conference and Exposition, National Harbor, MD, USA, 30 October 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Weron, R. Electricity price forecasting:a review of the state-of-the-art with a look into the future. Int. J. Forecast. 2014, 30, 1030–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, S.K.; Saini, L.M.; Kumar, A. Electricity price forecasting in deregulated markets: A review and evaluation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2009, 31, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakaša, T.; Andročec, I.; Sprčić, P. Electricity price forecasting-ARIMA model approach. In Proceedings of the 2011 8th Intenational Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), Zagreb, Croatia, 25–27 May 2011; pp. 222–225. [Google Scholar]
- Pappas, S.S.; Ekonomou, L.; Karamousantas, D.C.; Chatzarakis, G.; Katsikas, S.; Liatsis, P. Electricity demand loads modeling using AutoRegressive Moving Average (ARMA) models. Energy 2008, 33, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, S.S.; Ekonomou, L.; Karampelas, P.; Karamousantas, D.C.; Katsikas, S.K.; Chatzarakis, G.E.; Skafidas, P.D. Electricity demand load forecasting of the Hellenic power system using an ARMA model. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2010, 80, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; Ljung, G.M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 129–174. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yin, B.D.; Ren, L.; Bian, X.F. Study of electricity short-term load forecast based on bp neural network. Electr. Meas. Instrum. 2011, 2, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.Y.; Wu, C.E. Short-Term Electricity Price Forecasting Based on Similar Day-Based Neural Network. Energies 2020, 13, 4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.H.; Huang, C.J. An Electricity Price Forecasting Model by Hybrid Structured Deep Neural Networks. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connor, J.T.; Martin, R.D.; Atlas, L.E. Recurrent neural networks and robust time series prediction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Instrum. 1994, 5, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gers, F.A.; Eck, D.; Schmidhuber, J. Applying LSTM to Time Series Predictable through Time-Window Approaches; Springer: London, UK, 2002; pp. 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.B. Electricity price prediction based on hybrid model of adam optimized LSTM neural network and wavelet transform. Energy 2019, 187, 115804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasun, L.L.C.; Zhou, H.; Huang, G.B.; Vong, C.M. Representational learning with ELMs for big data. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2013, 28, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiei, M.; Niknam, T.; Khooban, M.H. Probabilistic forecasting of hourly electricity price by generalization of ELM for usage in improved wavelet neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2016, 13, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryasin, O.Y.; Lukashov, A.I. A Python Application for Hourly Electricity Prices Forecasting Using Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Russian Automation Conference (RusAutoCon), Sochi, Russia, 29 September 2020; pp. 138–143. [Google Scholar]
- Hajirahimi, Z.; Khashei, M. Hybrid structures in time series modeling and forecasting: A review. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 86, 83–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Schell, K.R. Real-time electricity price forecasting of wind farms with deep neural network transfer learning and hybrid datasets. Appl. Energy 2021, 299, 117242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Siew, C.K. Extreme learning machine: A new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 July 2004; pp. 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Siew, C.K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y. Learning deep architectures for AI. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2009, 2, 1–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Reducing the Dimensionality of Data with Neural Networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, J.; Shen, B. A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: Sparrow search algorithm. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2020, 8, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prices and Load Statistics in Area DK1. Available online: https://ens.dk/en/our-services/statistics-data-key-figures-and-energy-maps/annual-and-monthly-statistics (accessed on 13 December 2021).
| Time | Mean | Variant Coefficient | Wind-and-Solar–Load Ratio | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
| 0:00 | 34.13 | 12.75 | 36.75 | 0.50 | 0.78 | 0.37 | - | 0.95 | 0.62 |
| 1:00 | 33.18 | 12.03 | 35.71 | 0.55 | 0.80 | 0.37 | - | 1.00 | 0.63 |
| 2:00 | 33.33 | 11.87 | 34.25 | 0.54 | 0.79 | 0.40 | - | 0.97 | 0.64 |
| 3:00 | 34.32 | 12.66 | 34.37 | 0.52 | 0.72 | 0.40 | - | 0.93 | 0.62 |
| 4:00 | 36.71 | 13.91 | 38.29 | 0.46 | 0.67 | 0.32 | - | 0.88 | 0.60 |
| 5:00 | 42.05 | 19.23 | 45.71 | 0.40 | 0.62 | 0.30 | - | 0.76 | 0.54 |
| 6:00 | 48.21 | 23.89 | 53.98 | 0.38 | 0.57 | 0.32 | - | 0.69 | 0.49 |
| 7:00 | 49.99 | 26.34 | 57.44 | 0.38 | 0.58 | 0.36 | - | 0.66 | 0.46 |
| 8:00 | 48.44 | 24.88 | 55.43 | 0.39 | 0.57 | 0.36 | - | 0.65 | 0.44 |
| 9:00 | 46.58 | 22.69 | 51.49 | 0.39 | 0.58 | 0.34 | - | 0.62 | 0.43 |
| 10:00 | 45.44 | 21.68 | 49.70 | 0.39 | 0.55 | 0.35 | - | 0.64 | 0.41 |
| 11:00 | 44.12 | 19.91 | 47.20 | 0.38 | 0.57 | 0.35 | - | 0.66 | 0.41 |
| 12:00 | 43.10 | 18.59 | 44.35 | 0.38 | 0.61 | 0.37 | - | 0.65 | 0.41 |
| 13:00 | 42.65 | 18.28 | 43.20 | 0.39 | 0.62 | 0.38 | - | 0.68 | 0.44 |
| 14:00 | 43.40 | 18.71 | 44.98 | 0.39 | 0.59 | 0.34 | - | 0.70 | 0.47 |
| 15:00 | 45.43 | 21.07 | 48.22 | 0.36 | 0.54 | 0.30 | - | 0.68 | 0.49 |
| 16:00 | 50.66 | 25.98 | 56.43 | 0.30 | 0.48 | 0.25 | - | 0.66 | 0.47 |
| 17:00 | 52.51 | 28.48 | 63.05 | 0.24 | 0.53 | 0.29 | - | 0.67 | 0.47 |
| 18:00 | 49.42 | 25.47 | 60.16 | 0.20 | 0.57 | 0.28 | - | 0.71 | 0.49 |
| 19:00 | 45.42 | 20.42 | 51.54 | 0.21 | 0.57 | 0.25 | - | 0.76 | 0.52 |
| 20:00 | 42.27 | 18.55 | 46.84 | 0.29 | 0.58 | 0.24 | - | 0.80 | 0.56 |
| 21:00 | 41.27 | 17.52 | 45.32 | 0.30 | 0.57 | 0.23 | - | 0.83 | 0.57 |
| 22:00 | 37.29 | 15.57 | 40.50 | 0.39 | 0.62 | 0.27 | - | 0.90 | 0.60 |
| 23:00 | 35.28 | 13.71 | 38.82 | 0.46 | 0.73 | 0.33 | - | 0.94 | 0.63 |
| Time | Mean Price/ Euro | Model A/ Euro | Model B/ Euro | Model C/ Euro | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | ||
| 00:00 | 12.08 | 6.7 | 7.8 | 5.9 | 8.1 | 7.3 | 8.3 |
| 01:00 | 11.68 | 8.7 | 10.3 | 6.2 | 6.9 | 6.1 | 7.7 |
| 02:00 | 11.39 | 8.5 | 9.3 | 6.2 | 7.6 | 6.8 | 8.4 |
| 03:00 | 12.26 | 5.6 | 7.4 | 6.8 | 9.0 | 6.9 | 8.0 |
| 04:00 | 13.21 | 5.8 | 7.7 | 6.8 | 8.2 | 7.4 | 8.7 |
| 05:00 | 17.86 | 13.1 | 15.2 | 8.1 | 11.8 | 9.1 | 12.2 |
| 06:00 | 22.45 | 10.0 | 12.3 | 5.3 | 7.1 | 5.7 | 7.5 |
| 07:00 | 25.44 | 3.5 | 3.9 | 9.3 | 11.0 | 7.7 | 10.0 |
| 08:00 | 24.70 | 9.7 | 12.1 | 13.2 | 15.6 | 11.3 | 15.1 |
| 09:00 | 22.85 | 13.0 | 15.1 | 13.4 | 17.6 | 12.3 | 18.2 |
| 10:00 | 21.62 | 12.6 | 17.1 | 17.1 | 21.5 | 16.2 | 21.5 |
| 11:00 | 20.32 | 16.7 | 24.9 | 15.7 | 22.7 | 17.3 | 21.2 |
| 12:00 | 19.38 | 14.7 | 24.3 | 15.7 | 22.5 | 17.0 | 22.7 |
| 13:00 | 19.21 | 16.4 | 23.8 | 16.7 | 23.1 | 15.6 | 22.3 |
| 14:00 | 19.38 | 13.9 | 16.6 | 12.4 | 16.8 | 14.0 | 17.6 |
| 15:00 | 21.06 | 8.8 | 11.7 | 9.6 | 12.5 | 10.9 | 13.6 |
| 16:00 | 24.83 | 6.8 | 8.3 | 8.4 | 9.7 | 7.3 | 9.9 |
| 17:00 | 26.24 | 11.3 | 13.7 | 9.6 | 11.9 | 9.3 | 11.0 |
| 18:00 | 22.30 | 7.7 | 10.2 | 7.0 | 8.7 | 7.6 | 9.5 |
| 19:00 | 18.91 | 6.1 | 8.9 | 5.5 | 6.4 | 5.7 | 6.9 |
| 20:00 | 17.69 | 6.6 | 8.7 | 6.6 | 7.6 | 5.1 | 6.4 |
| 21:00 | 16.97 | 6.5 | 9.4 | 6.1 | 8.0 | 6.2 | 7.9 |
| 22:00 | 14.79 | 5.4 | 7.0 | 3.4 | 4.8 | 5.3 | 5.8 |
| 23:00 | 12.37 | 5.5 | 6.9 | 5.2 | 6.1 | 5.1 | 6.0 |
| Mean | 18.71 | 9.3 | 12.2 | 9.2 | 11.9 | 9.3 | 11.9 |
| Algorithms | 2020 | 2021 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | |
| BP | 11.3 | 13.5 | 14.9 | 19.0 |
| LSTM | 11.8 | 13.8 | 11.1 | 14.4 |
| DELM | 7.9 | 9.4 | 16.3 | 20.4 |
| SSA-DELM | 3.8 | 4.7 | 9.3 | 11.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Tao, P.; Wu, X.; Yang, C.; Han, G.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Y. Hourly Electricity Price Prediction for Electricity Market with High Proportion of Wind and Solar Power. Energies 2022, 15, 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041345
Zhang Y, Tao P, Wu X, Yang C, Han G, Zhou H, Hu Y. Hourly Electricity Price Prediction for Electricity Market with High Proportion of Wind and Solar Power. Energies. 2022; 15(4):1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041345
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yangrui, Peng Tao, Xiangming Wu, Chenguang Yang, Guang Han, Hui Zhou, and Yinlong Hu. 2022. "Hourly Electricity Price Prediction for Electricity Market with High Proportion of Wind and Solar Power" Energies 15, no. 4: 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041345
APA StyleZhang, Y., Tao, P., Wu, X., Yang, C., Han, G., Zhou, H., & Hu, Y. (2022). Hourly Electricity Price Prediction for Electricity Market with High Proportion of Wind and Solar Power. Energies, 15(4), 1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041345






