Abstract
The microgrids operate in tie-up (TU) mode with the main grid normally, and operate in isolation (IN) mode without the main grid during faults. In a dynamic operational regime, protecting the microgrids is highly challenging. This article proposes a new microgrid protection scheme based on a state observer (SO) aided by a recurrent neural network (RNN). Initially, the particle filter (PF) serves as a SO to estimate the measured current/voltage signals from the corresponding bus. Then, a natural log of the difference between the estimated and measured current signal is taken to estimate the per-phase particle filter deviation (PFD). If the PFD of any single phase exceeds the preset threshold limit, the proposed scheme successfully detects and classifies the faults. Finally, the RNN is implemented on the SO-estimated voltage and current signals to retrieve the non-fundamental harmonic features, which are then utilized to compute RNN-based state observation energy (SOE). The directional attributes of the RNN-based SOE are employed for the localization of faults in a microgrid. The scheme is tested using Matlab® Simulink 2022b on an International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) microgrid test bed. The results indicate the efficacy of the proposed method in the TU and IN operation regimes on radial, loop, and meshed networks. Furthermore, the scheme can detect both high-impedance (HI) and low-impedance (LI) faults with 99.6% of accuracy.
1. Introduction
Microgrids offer multiple perks, including a cleaner environment, lower carbon emissions, better power quality, and an uninterruptible power supply. It is the mini version of the national grid with its renewable energy-based distributed generations (DGs), load, and distribution network, which are fully controlled and protected. A microgrid has three basic topological structures; radial, looped, and meshed. It has two operating regimes; in TU mode with a national grid and in IN mode without a national grid [].
1.1. Problem Statement and Prime Objective
The power flow is bidirectional in the TU mode and the fault current is very high due to national grid penetration, whereas the fault current in the IN mode is very low [,,]. In addition, renewable energy-based DGs are intermittent, which introduces nonlinear behavior in the microgrids. However, the conventional overcurrent protection strategies fail under such vibrant fault current characteristics, DGs intermittency, and bidirectional power flow [].
For that reason, the microgrid protection scheme needs special attention and presents significant research gaps to this day. Furthermore, the microgrids demand a protection scheme that works in both TU and IN modes across radial, loop, and meshed networks [,,]. As a consequence, the prime objective and target of this study are to devise a robust protection strategy that effectively protects the microgrid from HI and LI faults in radial, loop, and mashed scenarios. However, the strategy must be equipped to protect the microgrids in both TU and IN operational modes.
1.2. Literature Review
Several microgrid protection methods have been reported in the previous literature reviews, which counters the microgrid protection challenges in a larger aspect. A Kalman filter was utilized in [] to extract harmonic content from the current signal for the residual and total harmonic distortion indices calculation. Both of these indices were used for the detection and classification of almost all types of faults in microgrids, and the fault was localized through Kalman filter-based reactive power. The voltage sag, direction of active power flow, and magnitude of current during the fault were utilized to detect the LI faults in the low-voltage inverter-dominated microgrid []. The time–time (TT) transform was utilized to pre-process the current signal in [] to generate the TT matrix, and the TT-matrix z-score vector index was computed. Then, this index was compared with an unscended transform-based threshold value for the detection of faults. The envelope of the current was generated in [] from squaring and low pass filter methodology. Furthermore, the fault detected and classified from the variation in the current envelope was extracted using the auto-correlation function. The localization of the fault was conducted through the signature of reactive power. The accumulative sum and decision tree algorithm were implemented on voltage sag to differentiate between faults and other disturbances in the IN mode of the microgrid, and the faulty phase was also identified by this proposed strategy []. The wavelet transform-based protection scheme was proposed in [] for the loop configuration of the microgrid. The scheme used the tie-switch and protection coordination to generate a new index for the detection and classification of the loop-configuration microgrid. The auto cosine similarity index of each phase-sampled current was calculated in [] using a moveable window of one-fourth cycle length. The index magnitude detected the fault while its sign indicated the faulty feeder of the multi-DGs’ microgrid. The Hilbert transform-based superimposed reactive energy components were calculated in [] for the detection, classification, and localization of faults in microgrids. A micro phasors measurement unit-based protection strategy was suggested in [].
Some other intelligent protection schemes based on advanced signal-processing tools were proposed in the previous literature. In [], the detection and classification of data on different fault events was conducted through the machine learning algorithm during the TU and IN modes. Then, intelligent devices infrastructure was deployed locally for the protection of microgrids without any communication infrastructure. A convolution neural network (CNN) was suggested directly on the measured current in [] for the detection of fault events in the microgrids. No separate feature extraction was necessary for this scheme because the CNN in the scheme deployed convolution and pooling for the desired features. Another similar approach utilized the CNN technique from the deep learning algorithm for the detection, classification, and localization of different faults in photovoltaic-based microgrids []. Similarly, a CNN with the gorilla optimization technique was used in [] for detecting, classifying, and locating faults in the microgrids. This scheme utilized a spatio-temporal measurement data set for training purposes. The support vector machine classifiers were deployed on the RMS value of the voltage signal for fault detection and phase identification [], while the inter-harmonics injection was proposed for the localization of the faulty section in the microgrids. An interval type-two fuzzy logic system was also utilized for the protection of the microgrids []. Particle swarm optimization is also proposed for microgrid protection in []. The authors in [] proposed a protection scheme for microgrids using a deep-machine learning algorithm. The two-stage fuzzy logic system was also used for the detection, classification, and localization of faults in the microgrids [].
1.3. Limitations in Existing Schemes
The foregoing scheme attempted to solve several microgrid protection challenges in many aspects but still, a significant research gap remains, and some limitations of the existing research include: a large number of schemes do not protect the microgrid during HI faults []; noisy measurement conditions are not addressed in a significant portion of the papers [,]; huge data set training compulsion in few schemes with a very high computational burden [,,,,,,]; several schemes used high-cost devices such as phasors measurement units []; if any scheme covered all these aspects, it had a system-dependent threshold setting []; some schemes are not directly implemented on the nonlinear test systems of microgrids and they require separate linearization [].
In this scheme, the PF state estimator is implemented on the per-phase measured current and voltage signal of the corresponding node individually. After there, the PFD of the estimated current is calculated as a fault detection and classification index. After threshold comparison, if the PFD is greater than the threshold value, the fault is detected and the faulty phase is identified. Then, the directional properties of the RNN-assisted state observation energy are utilized for the fault section identification. The proposed scheme successfully detects, classifies, and locates the LI and HI faults in TU and IN mode under a radial, looped, and meshed topological structure.
1.4. Significant Contributions
The main contributions of the proposed scheme are listed here:
- Novel deployment of particle filters in microgrid protection schemes as a state observer with RNN support;
- First-time utilization of particle filters in the time and frequency domain for harmonics extraction;
- The scheme threshold value does not depend on the type of fault and microgrid system configuration;
- PF catering to the measurement noise autonomously is another feature of the proposed scheme [];
- The scheme is able to deal directly with nonlinear networks without any linearization due to PF capability [,];
- LI, as well as HI faults, are detected in the proposed scheme in both modes and different microgrid topologies;
- The proposed scheme provides backup protection in case of primary relay failure.
The rest of the research paper is structured as follows; Section 2 depicts the IEC test system. Section 3 describes the problem formulation and mathematical background. The proposed relay design is explained in Section 4. The communication-assisted SO-based decision unit is mentioned in Section 5. The results are illustrated in Section 6. Section 7 provides a comparison of the proposed scheme with similar previous work. Finally, the paper concludes with some future suggestions in Section 8.
2. IEC Microgrid TEST Bed
This section focuses on the utilized microgrid test system for fault data generation during different case studies. The microgrid test system utilized in the proposed SO-based scheme is the standard 13-bus IEC test bed. Six of the buses (B-n) are under consideration as depicted in Figure 1: PCC/B-1; B-2; B-3; B-4; B-5; B-6. There are four distributed generations: (1) three of them are inverter-based DGs (IBDGs); (2) one of them is a synchronous-based DG (SBDG). A total of five considered lines are labeled as Line 1 to Line 5. The test system is capable of providing three topological structures: (1) radial; (2) loop; and (3) meshed with the assistance of two circuit breakers (CBs) labeled as CB loop-1 and CB loop-2. The whole microgrid is connected to the main grid in TU mode by closing the main grid CB, and in IN mode by opening the main grid CB [].
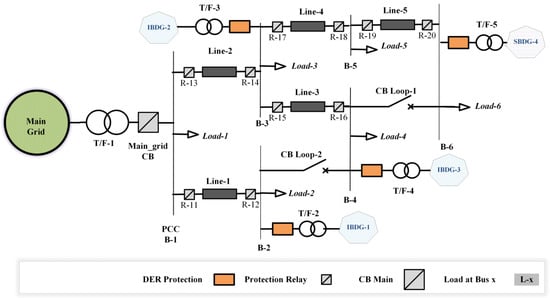
Figure 1.
Standard International Electro-Technical Commission test bed.
3. Mathematical Modeling
This section comprises the detailed mathematical conceptualization of the microgrid’s current and voltage signatures that are utilized for the computation of fault detection, classification, and localization indices. Then, the state–space model is elaborated on the microgrids’ voltage/current parameters for estimation. In addition, the PF and RNN theoretical background is also discussed. Furthermore, the computational procedure of PFD and RNN-assisted SOE are illustrated. Lastly, the threshold setting required for the successful operation of the relay during fault is described.
3.1. Per-Phase Microgrid Signals Formulation
The microgrids have non-linear, invariable, and bi-directional power flow characteristics. These dynamic characteristics of the microgrid badly affect its protection which depends on the measurement parameters such as voltage and current. However, the mathematical formulation of the microgrid voltages and current under a balanced microgrid grid code is as follows:
where is the measured voltage of the corresponding microgrid bus while the measured current signal is:
where:
The measured voltage at the nth sample;
Measured current at the nth sample;
The fundament frequency;
Measurement noise.
We only choose the measured current signal for the detection and phase identification of the fault through the PFD criterion. On the other hand, both voltage/current signals are used in the calculation of SOE for fault localization purposes.
3.2. State-Space Model
In order to avoid false tripping and blinding issues, we suggest a PF algorithm as a state-observation tool for the exact estimation of the voltage/current signals from the noisy measurements. The filtering problem entails predicting an unknown current state from a sequence of current and previous state-dependent measurements using a state–space model that describes state transition as well as the measurement/state. Therefore, the trigonometric derivative on Equations (1) and (2) is applied to find the state-space model, respectively, as follows:
and,
The simple form of these equations is as follows:
and,
where:
Measured single-phase voltage at the nth sample;
Measured single-phase current at the nth sample;
Measurement and any other arbitrary error.
Then, PF is implemented on these state–space Equations (5) and (6) for the exact state estimation of the measured voltage and current signal under noisy conditions.
3.3. Particle Filter as a State Observer
The particle filter has been frequently employed to handle non-linear or/and non-Gaussian filtering challenges. It is a sequential Monte-Carlo modeling technique that is based on significance sampling, which leverages discrete random measurements to approximate target probability distributions []. The detailed algorithm [] of PF is shown in the Appendix A. PF estimates the filtering distribution using an empirical measurement provided by a set of weighted samples also known as particles:
where:
A number of particles/samples;
Respective samples/particles and related weights at iε (1; );
Dirac delta mass located at .
3.4. Recurrent Neural Networks
Recurrent neural networks were invented in the 1980s and have recently evidenced state-of-the-art performance on a diverse variety of sequential data modeling tasks, including language modeling, speech recognition, image captioning, as well as music composition and fault diagnoses. A RNN is a deep-learning network structure that leverages data from the past to enhance the network’s efficiency on current and future signals. RNNs are distinguished by the presence of a hidden state and loops. The looping structure enables the network to hide previous knowledge and function on sequences. The recurrent layer of RNNs contains feedback loops. This allows them to retain information in memory for a longer period []. The findings demonstrate that the RNN is capable of performing well in one-step, long-term, or remaining useful life prediction tasks. The RNN-based approach is one of the most efficient ways for fault detection and fault location on microgrids due to its accuracy, durability, and speed. Therefore, RNN assistance is utilized to exact the non-fundamental features and calculate SOE in the proposed scheme []. The typical structure of a RNN was depicted in Figure 2a, while RNN workflow is mentioned in Figure 2b.
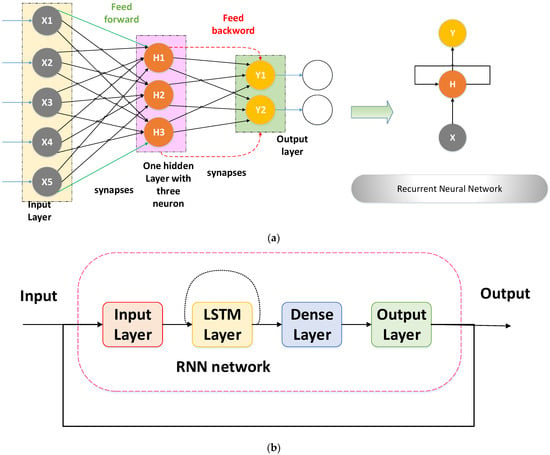
Figure 2.
(a) Standard infrastructure of typical RNN. (b) Workflow of RNN.
3.5. PFD and SOE Calculations
3.5.1. PFD
The timely and successful detection/classification of all kinds of faults is necessary for the safe operation of microgrids. Therefore, in this sub-section, the particle filter deviation is calculated as a fault detection/classification index.
PFD is computed in a two-stage process: (i) by taking the difference of the estimated current samples/particles from the measured signals; (ii) and then taking the natural logarithm of the calculated difference.
Then,
3.5.2. SOE
The exact fault localization is important in power systems for crew dispatch and the timely recovery of a power system outage. However, the fault localization mechanism plays an important role in this context. In the proposed scheme, the RNN structure employs three layers to extract the hidden feature maps from the input voltages and current estimated from the particle filter. Each layer convolves the input with several kernels to generate one-dimensional output feature maps. Initially, RNN is used to extract non-fundamental features from the SO-based estimated voltage and current. Then, the state observation energy is calculated through the vector multiplication of the estimated non-fundamental components of voltage and current in Equations (4) and (5):
After, the root mean square of the is calculated by just a multiplication factor of 0.7071:
3.6. SOE Directional Analysis
This sub-section elaborates on the mathematical concept used for directional analysis. The direction of the RNN-assisted SOE may be “+ive” or “−ive” at any node during fault events. The fault is regarded as a forward fault if the computed SOE is positive.
Additionally, it is regarded as reverse if the computed SOE is negative.
3.7. Predefined Threshold
In any robust scheme, threshold settings are crucial for the correct detection and localization of the faults. The scheme was tested under the worst fault and healthy conditions to discriminate between faulty and healthy states. Therefore, in order to avoid false tripping and relay blinding problems, the constant threshold value (R.threshold = 0.5) is chosen for . The proposed SO-based scheme is tested in these threshold settings in both TU and IN modes of operation under radial, loop, and meshed networks. The predefined threshold setting provides successful operational results under extreme and harsh system conditions.
4. Proposed SO-Based Relay
The comprehensive functioning procedure of the proposed scheme is discussed in this section. The comprehensive schematic diagram of the proposed SO-based microgrid protection scheme is illustrated in Figure 3. The proposed relay operation comprises four basic steps as follows:
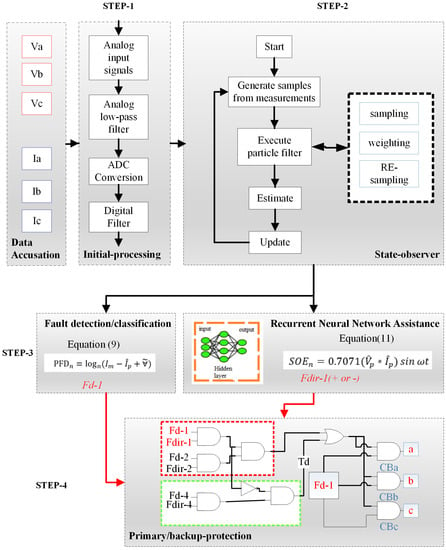
Figure 3.
Schematic demonstration of proposed state-observer-based protection scheme, where a, b, and c represented the phases.
4.1. Step 1
Initially, the voltage and current signals are acquired at the corresponding bus from the measurement devices. The measured signals from the corresponding bus contain measurements as well as some other arbitrary noises, and these signals are in analog form. However, the main purpose of this module is anti-aliasing and the analog-to-digital conversion of signals for accurate and precise decisions. Therefore, the measured three-phase voltage/current signals from the local measurements of the corresponding relay are pre-processed using a Butterworth filter for antialiasing purposes. Then, the 16-bit analog-to-digital converter having a sampling frequency of 3200 Hz is used to convert the continuous voltage and current signals into discrete ones. Then, these discrete signals are provided at the input of the state absorber/particle filter in the next step.
4.2. Step 2
The second and most crucial stage of the proposed microgrid protection scheme is the continuous state observation of the measured discrete current and voltage signals. A particle filter is the most suitable and state-of-the-art tool that is engaged in this step for the correct and precise estimation of the voltage/current signal from the noisy measured data set. The details flow chart of the state observer is depicted in Step 2 of Figure 3. Hence, the estimated current signal is further utilized in the calculations of fault detection and phase identification indices of the proposed method which is explained in detail in the next step.
4.3. Step 3
In the third step, the estimated current signals are utilized to compute the particle filter deviation from Equation (9). The particle filter deviation is the elementary index that is responsible for the timely detection and phase identification of occurring faults in the proposed scheme. If the PFD of any single phase is more than the R.threshold, the fault event is considered. There is no need for a separate fault classification unit in the proposed scheme because the PF is implemented per phase separately. An Fdet signal of the corresponding faulty phase is provided to the detection probe of the AND operators of the considered circuit breaker. However, the Fdir signal is also provided to the primary protection unit of the corresponding relay for zone identification purposes.
4.4. Step 4
The exact fault location is necessary for timely system recovery. Therefore, the fault section is identified on the base of the directional polarity behavior of state observation energy. Under the faulty condition, the SOE computed by any relay may be “+ive” or “−ive”. If the SOE is “+ive”, it is regarded as a forward fault, while the fault is considered as reverse if the SOE is “−ive”. In the case of a forward fault, an Ff decision signal is generated from the primary protection unit which energizes the directional probe of the AND operators of all phases of the considered circuit breakers. Contrariwise, if an FR decision signal is achieved, the backup protection unit is energized to deal with this situation.
5. Communication-Assisted Decision Unit
The microgrids had a dynamic model due to the bidirectional power flow, and different current characteristics. Therefore, many relays during the fault event exhibit forward faults at the same time. In order to build a more robust and accurate decision-making scheme, the final decision is based on the detection and direction signals simultaneously received and sent from three adjacent relays at the same time as depicted in the logic circuitry of the relay in Figure 4.
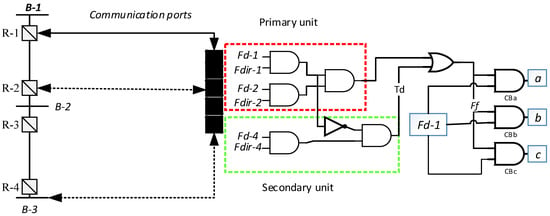
Figure 4.
Communication-assisted relay logic design, where a, b, and c represented the phases.
Relay-1 is the under-observation relay in Figure 4 used to understand the operation of the proposed algorithm. Relay-1 receives the fault detection and fault direction signals from relay-2: (1) if relay-2 has a forward fault like relay-1, then the primary protection unit operates and generates an Ff decision signal and energizes the directional probe of the AND-operators of all phases of the considered circuit breakers; (2) if relay-1 has forward faults but relay-2 has a reverse fault, the primary protection fails, and then relay-1 receives the signal from relay-4 to operate the secondary protection unit. Wireless communication is adopted to communicate these signals between the primary and secondary protection unit of the adjacent relays.
6. Results
This section provides a detailed analysis of different types of faults including HI faults, LI faults, and single-phase faults during different resistances. When the fault detection/classification module recognizes a fault in the microgrid, the RNN for fault section identification is engaged. The RNN structure was trained for fault localization to reduce the error between actual and estimated identifications. In order to generate fault data in this article, the IEC microgrid illustrated in Figure 1 was deployed in MATLAB/Simulink. Different types of line–line and line-to-ground faults are considered during different operational modes and topological structures of the microgrid as shown in Table 1. Some no-fault data generation is mentioned in Table 2. The proposed scheme provides successful results in all considered cases with a lesser detection time of less than half cycles.

Table 1.
Fault cases simulation conditions.

Table 2.
No-fault cases simulation conditions.
6.1. Backup Protection Case Study
In any communication base, microgrid protection scheme backup protection is crucial to protect the microgrid when primary protection fails. That is why here we will discuss the backup protection case study to examine the capability of the proposed scheme during primary unit failure. Figure 5 shows the case study when the primary protection fails and how the provided backup protection unit detects the fault event. In the mentioned scenario, the 3-phase fault hits at 0.1 s, which was not detected by the primary protection unit of the proposed scheme in the prescribed internal operation time due to any reason. After the failure of the primary protection unit, the relay backup protection unit waits for a predefined intentional time delay. Then, at the time instant of 0.4 s, the backup protection unit is activated, detects the fault, and restores the system to a normal state. Several other such scenarios are tested for the validation of the proposed scheme, but for the purpose of a better understanding and ease of the reader, only the most suitable is discussed here.
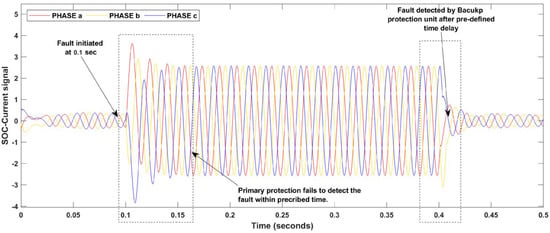
Figure 5.
Backup protection feature case study.
6.2. TU-Mode Case Study
The tie-up of microgrids with the main grid increases the current level and introduced bidirectional power flows. Conventional over-current relays fail to protect the microgrids in the TU mode of operation. Therefore, the efficiency of the presented scheme was also tested in the TU mode for both LI and HI faults.
6.2.1. LI-Fault at Line-2
The SO-current signal in Figure 6a depicts that a double line-to-ground fault with ZL = 0.1 Ω hits phase A and B at the time instant 0.2 s. Initially, the scheme needs to detect and classify the fault; therefore, the fault detection/classification index/PFD is operated successfully as depicted in Figure 6b. It is observed that the PFD of phases A and B is greater than in R.threshold, which suggests that the fault is precisely detected and classified by the presented scheme. Furthermore, the +ive direction of the RNN-assisted SOE in part (c) of Figure 6 indicates the presence of a forward fault in line 2. It is important to note that this fault hits the microgrid line 2 in the grid-tied mode, while the CB-loop-1 is opened and CB-loop-2 is closed at that time.
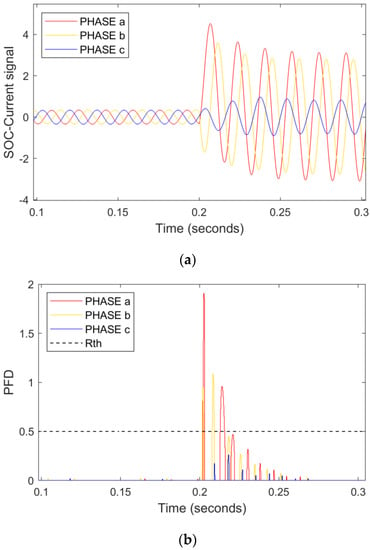
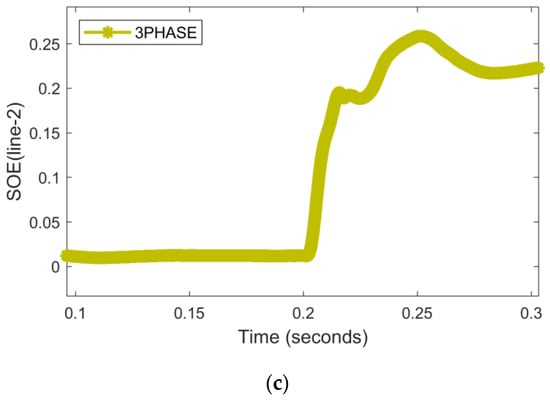
Figure 6.
An LI double line-to-ground fault with ZL = 0.1 Ω hits phase A and B in TU mode. (a) Current signals (b) PFD (c) RNN-assisted SOE.
6.2.2. HI-Fault at Line-4
High-impedance faults occur when a line drops on the ground over high-impedance things like dry ground, resistive soils, tree limbs, dry grass, and asphalt [,]. Therefore, these faults are difficult to detect in power systems due to very low fault current levels. An HI-fault with ZL = 50 Ω occurred at line 4 at the time instant 0.25 s as shown in Figure 7a–c. The PFD of phase A and C was raised above the pre-specified threshold value, and successfully detected/classified the HI-fault. The presence of positive RNN-assisted SOE indicates the presence of a forward fault in line 4. It is important to note that a high impedance fault hits the microgrid line 4 in the grid-tied mode, while the CB-loop-2 is opened and CB-loop-1 is closed at that time.
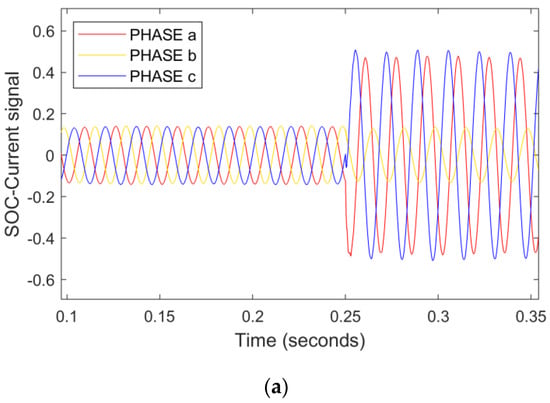
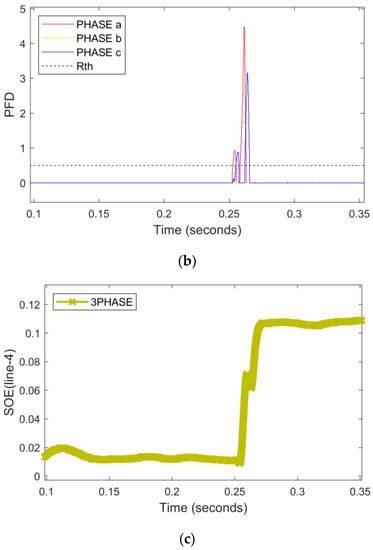
Figure 7.
An HI double line-to-ground fault with ZL = 50 Ω hits phase A and C in TU mode. (a) Current signals (b) PFD (c) RNN-assisted SOE.
In summary, it is observed from the above two case studies that the proposed SO-based and RNN-assisted scheme successfully detected, classified, and localized the different high-impedance and low-impedance faults in different topologies and different locations.
6.3. IN-Mode Case Study
The fault current during the islanded mode of the microgrids is reduced to a very low value. Therefore, the efficiency of the proposed scheme has also been validated during the IN mode for both LI and HI faults.
6.3.1. LI-Fault at Line-1
Here are three scenarios in one frame: (i)—the islanding mode; (ii)—low impedance; (iii)—the three-phase fault. Three-phase faults are less frequent but they are the most severe faults in the power system; therefore, the detection of these faults is necessary []. Consequently, a low impedance ABC-g fault hits line-1 at 0.14 s as depicted by the SO-current signal in Figure 8a. The variation in PFD of phase A, B, and C is greater than in R.threshold, which signifies that the 3-phase fault is successfully detected and classified by the presented scheme. Furthermore, the +ve direction of the RNN-assisted SOE in part (c) of Figure 8 implies the manifestation of a forward fault in line 1. It is important to note that this fault hits the microgrid line 1 in the islanded mode while the CB-loop-1 and CB-loop-2 are closed at that time. Moreover, the scheme has the capability to handle the most severe 3-phase faults in the microgrid.
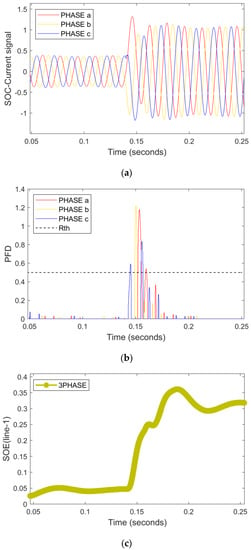
Figure 8.
An LI three-phase fault with ZL = 0.1 Ω in IN mode. (a) Current signals (b) PFD (c) RNN-assisted SOE.
6.3.2. HI-Fault at Line-3
At line-3, HI-faults with ZL = 80 Ω occurred when both loop-1 and loop-2 were open at a time of 0.11 s, as depicted in Figure 9a. The PFD of phase B and C are more than 0.5, which represents the timely detection/classification of the fault event. The illustration of the RNN-assisted +ive SOE in Figure 9c has shown the existence of a forward fault in line 3.
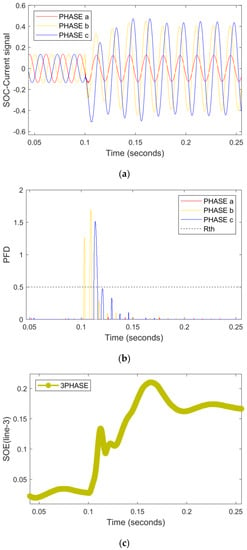
Figure 9.
An HI double line-to-ground fault with ZL = 80 Ω hits phase B and C in IN mode. (a) Current signals (b) PFD (c) RNN-assisted SOE.
In summary, it is observed from the above two case studies that the proposed SO-based and RNN-assisted scheme successfully detected, classified, and localized the different high-impedance and low-impedance faults in different topologies and different locations.
6.4. Single-Phase Tripping
In the electrical distribution network, single-phase faults are more frequent. The proposed state-observer-based scheme is capable to handle such kinds of faults and provide a single-phase tripping facility. Two cases of single-phase tripping during the TU and IN modes of operation are provided to test the scheme’s efficacy.
A single-phase B-g HI fault occurred in line-5 at t = 0.2 s during the TU operational mode as illustrated in Figure 10a–c. The PFD changes of phase A at 0.2 s are more than the 0.5 threshold value, while the ones of phases B and C are less than 0.5, indicating the presence of single-phase faults. The positive direction of RNN-assisted SOE depicts that the forward faults are present in line 5.
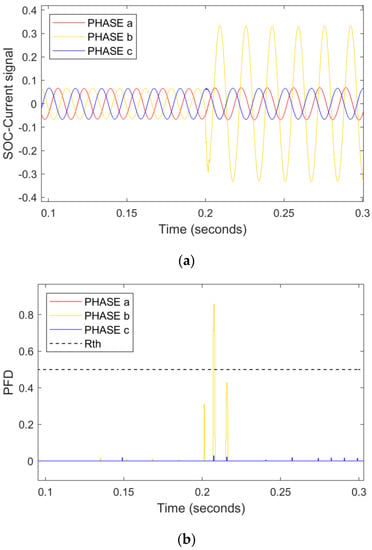
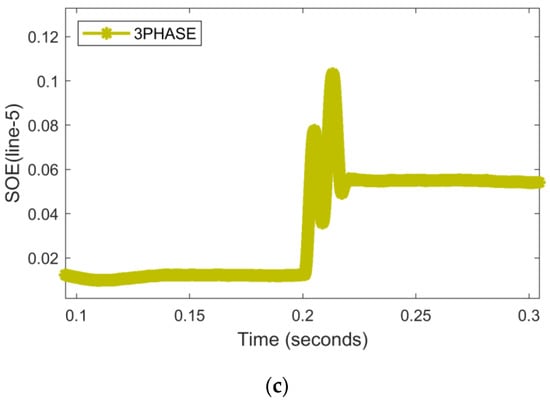
Figure 10.
An HI single-fault hits phase B ZL = 70 Ω in TU mode. (a) Current signals (b) PFD (c) RNN-assisted SOE.
Similarly, another A-g LI fault occurred in line 1 during islanded mode at 0.2 s, as shown by the SO-current signal in Figure 11a. The PFD at 0.2 s was raised from the pre-specified R.threshold; therefore, the technique correctly detects the single-phase problem. The positive direction of the RNN-assisted SOE represents that a forward fault is present at line 1.
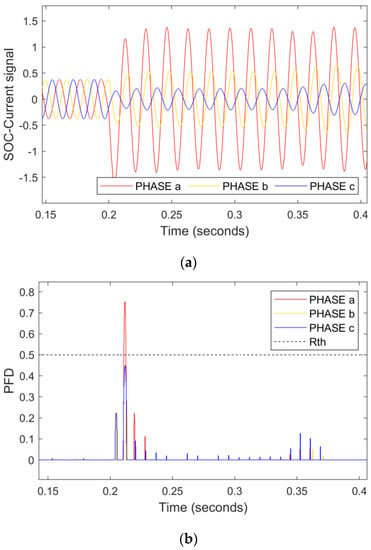
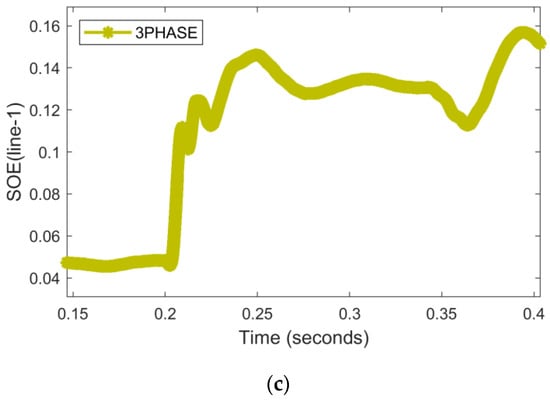
Figure 11.
An LI single-phase fault hits phase A in IN mode. (a) Current signals (b) PFD (c) RNN-assisted SOE.
7. Performance Comparison with Previous Schemes
Distinct from contemporaneous intelligent protection methods, the method strategy uses a RNN to directly train the faulty characteristics from the PF-estimated signals of current and voltage without the use of an external feature extractor. The proposed scheme is tested on various faults and no faults case studies, different fault locations, faults on different lines, different operational modes, different topologies, and different fault resistances. The overall results depict that the proposed strategy successfully works in such harsh system conditions without any false tripping and blinding issues. The presented SO-based scheme is compared with existing similar work for fair judgment on performance analysis, as depicted in Table 3. We chose signal processing and intelligent schemes such as: convolution neural network (CNN) [,], discrete transform (DT) with data mining approach [,], fuzzy logic (FL) [], and the support vector machine (SVM) [] for the fair judgment of scheme capabilities.

Table 3.
Performance analysis with other existing methods.
The proposed scheme exhibits a better performance as compared to some existing benchmark methods in the form of robustness, threshold independence, computational burden, noise consideration, etc.
The statistical performance analysis based on accuracy during the grid-tied and islanded mode of the established scheme is also achieved with all of the above-discussed benchmark methods. The analysis depicted in Figure 12 showed that the proposed scheme had a detection accuracy of 99.6% on average, which is better than most of the existing schemes. Moreover, it is also clear from Figure 13 that the training process percentage error is very low and RNN converges at only 20 epochs in both operational modes.
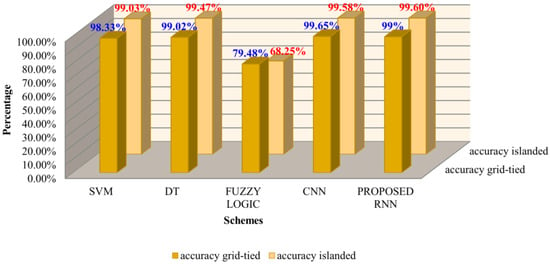
Figure 12.
Accuracy comparison of proposed scheme with existing benchmark.
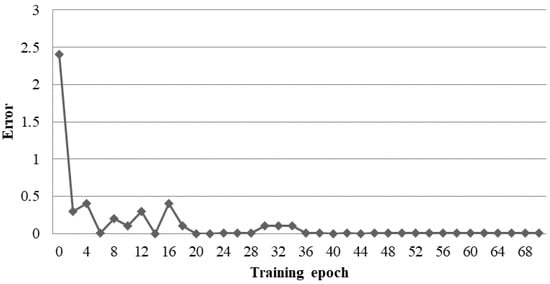
Figure 13.
Percentage error in training process of RNN converges.
8. Conclusions
Microgrids pose protection challenges due to different fault current characteristics under different operational regimes and bidirectional power flows. Therefore, the conventional over-current protection scheme fails to protect microgrids in such dynamic conditions. This paper proposed a microgrid protection strategy based on a PF and RNN hybrid algorithm. The particle filter is chosen as a state observer to calculate the particle filter deviation for detection and classification purposes, while the fault localization in this scheme is conducted by using the directional properties of RNN-assisted state observation energy. The scheme was tested on the IEC standard test bed using Matlab® Simulink 2022b. The scheme’s efficiency was also evaluated in radial as well as meshed cases in both the TU and IN operation modes. The results confirm the robustness of the suggested scheme deprived of any blinding and false tripping issues. In addition, the merit of the proposed scheme is the direct implementation of the nonlinear system without any linearization due to PF compatibilities. The scheme safely operates under noisy voltage and current measurement conditions. The RNN in the proposed scheme is well-suited for sequential statistical data. However, the scheme implementation on the imbalanced microgrid test system will also be left as future work.
Author Contributions
F.M.: writing/original draft preparation, conceptualization; H.H.K.: investigation, visualization; A.Z.: investigation, resources; M.U.A.: provided the proofreading of the manuscript; K.I.: supervision, proofreading. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
| Particle filter algorithm steps |
| Input: {xi k−1, wi k−1} Ns i = 1, zk Output: {xi k, wi k} Ns i = 1 wsum = 0 for i = 1, …, Ns do Step 1: propagate particle draw sample xi k ∼ q(xi k|xi k−1, zk) Step 2: update weight assign weight wi k Step 3: cumulative weight wsum = wsum + wi k End normalize weights for i = 1, …, Ns do wi k = wi k/wsum End Resample Ns particles with replacement for i = 1, …, Ns do wi k = 1/Ns End |
References
- Chandra, A.; Singh, G.K.; Pant, V. Protection Techniques for DC Microgrid—A Review. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 187, 106439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegunta, S.C.; Higginson, M.J.; Kenarangui, Y.E.; Li, G.T.; Zabel, D.W.; Tasdighi, M.; Shadman, A. AC Microgrid Protection System Design Challenges—A Practical Experience. Energies 2021, 14, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Dysko, A.; Hong, Q.; Tzelepis, D.; Booth, C.D. Transient Wavelet Energy-Based Protection Scheme for Inverter-Dominated Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 2533–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanpour, E.; Normandeau, M.; Joos, G.; Brissette, Y. A Protection System for Inverter Interfaced Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2022, 37, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeid, S.; Hu, Y.; Alasali, F.; El-Naily, N. Innovative Optimal Nonstandard Tripping Protection Scheme for Radial and Meshed Microgrid Systems. Energies 2022, 15, 4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, B.; Mishra, M.; Bansal, R.C.; Jena, R.K. AC Microgrid Protection—A Review: Current and Future Prospective. Appl. Energy 2020, 271, 115210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, M.W.; Arif, M.T.; Islam, S.N.; Haque, M.E. Microgrid Protection Challenges and Mitigation Approaches-A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 38895–38922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, F.; Imran, K.; Basit, S.; Bukhari, A.; Khalid, K. A Kalman Filter-Based Protection Strategy for Microgrids. IEEE Access 2017, 10, 73243–73256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Octávio, J.; Pereira, C.; Moreto, M. Protection Strategy for Fault Detection in Inverter-Dominated Low Voltage AC Microgrid. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 190, 106572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashteroodkhani, O.A.; Majidi, M.; Fadali, M.S.; Etezadi-Amoli, M.; Maali-Amiri, E. A Protection Scheme for Microgrids Using Time-Time Matrix z-Score Vector. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 110, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, S.; Jamali, S.Z.; Mehmood, K.K.; Bukhari, S.B.A.; Zaman, M.S.U.; Hussain, A.; Kim, C.H. Microgrid Protection Strategy Based on the Autocorrelation of Current Envelopes Using the Squaring and Low-Pass Filtering Method. Energies 2020, 13, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, S.; Farsa, A.R.; Jamali, S. Voltage-Based Protection of Microgrids Using Decision Tree Algorithms. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, e12274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switch, T.; Seo, H. New Protection Scheme Based on Coordination With. Energies 2019, 12, 4756. [Google Scholar]
- Mahfouz, M.M.A. A Protection Scheme for Multi-Distributed Smart Microgrid Based on Auto- Cosine Similarity of Feeders Current Patterns. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 186, 106405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, S.; Bukhari, A.; Saeed, M.; Zaman, U.; Haider, R.; Oh, Y.; Kim, C. Electrical Power and Energy Systems A Protection Scheme for Microgrid with Multiple Distributed Generations Using Superimposed Reactive Energy. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2017, 92, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbana, M.S.; Abbasy, N.; Meghed, A.; Shaker, N. MPMU-Based Smart Adaptive Protection Scheme for Microgrids. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2019, 7, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda, C.; Orozco-Henao, C.; Percybrooks, W.; Pulgarín-Rivera, J.D.; Montoya, O.D.; Gil-González, W.; Vélez, J.C. Intelligent Fault Detection System for Microgrids. Energies 2020, 13, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, S.B.A.; Kim, C.-H.; Mehmood, K.K.; Haider, R.; Saeed Uz Zaman, M. Convolutional Neural Network-Based Intelligent Protection Strategy for Microgrids. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2020, 14, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, M.; Koley, E.; Ghosh, S.; Mohanta, D.K.; Bansal, R.C. Spatio-Temporal Information Based Protection Scheme for PV Integrated Microgrid under Solar Irradiance Intermittency Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 116, 105576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatata, A.Y.; Essa, M.A.; Sedhom, B.E. Adaptive Protection Scheme for FREEDM Microgrid Based on Convolutional Neural Network and Gorilla Troops Optimization Technique. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 55583–55601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzesh, A.; Golsorkhi, M.S.; Savaghebi, M.; Baharizadeh, M. Support Vector Machine Based Fault Location Identification in Microgrids Using Interharmonic Injection. Energies 2021, 14, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, S.; Bukhari, A.; Haider, R.; Saeed, M.; Zaman, U.; Oh, Y.; Cho, G.; Kim, C. Electrical Power and Energy Systems An Interval Type-2 Fuzzy Logic Based Strategy for Microgrid Protection. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 98, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Huang, W.T.; Yao, K.C.; Chen, H.T.; Ma, C.C. Fault Location and Restoration of Microgrids via Particle Swarm Optimization. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z. A Novel Deep Learning–Based Fault Diagnosis Algorithm for Preventing Protection Malfunction. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 144, 108622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y. A Novel Particle Filter for Extended Target Tracking with Random Hypersurface Model. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 425, 127081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Hou, J. A New Adaptive Robust Unscented Kalman Filter for Improving the Accuracy of Target Tracking. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 77476–77489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, R.; Garnier, C.; Septier, F.; Klein, J. State Space Partitioning Based on Constrained Spectral Clustering for Block Particle Filtering. Signal Process. 2022, 201, 108727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Le Blond, S.; Wang, C. Artificial Neural Network Based Fault Detection and Fault Location in the DC Microgrid. Energy Procedia 2016, 103, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, O.I.; Jantan, A.; Omolara, A.E.; Dada, K.V.; Umar, A.M.; Linus, O.U.; Arshad, H.; Kazaure, A.A.; Gana, U.; Kiru, M.U. Comprehensive Review of Artificial Neural Network Applications to Pattern Recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 158820–158846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, A.; Ginn, H.L.; Mohammadpour, H.A. High Impedance Fault Detection: A Review. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 143, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, F.; Asif, M.; Khan, H.H.; Abbas, S.; Imran, K.; Hadier, U. High Impedance Faults Detection and Classification in Re- Newable Energy-Based Distribution Networks Using Time-Varying Kalman Filtering Technique. Eng. Proc. 2022, 20, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, Z. A Fault Diagnosis Algorithm for Microgrid Three-Phase Inverter Based on Trend Relationship of Adjacent Fold Lines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Li, X.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y. A New Convolutional Neural Network-Based Data-Driven Fault Diagnosis Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 5990–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Member, S.; Samantaray, S.R.; Member, S.; Zadeh, M.D. Data-Mining Model Based Intelligent Differential Microgrid Protection Scheme. IEEE Syst. J. 2017, 11, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).